Synthesis of Novel Nilotinib Analogues and Biological Evaluation of Their Antiplatelet Activity and Functionality towards Cancer Cell Proliferation In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
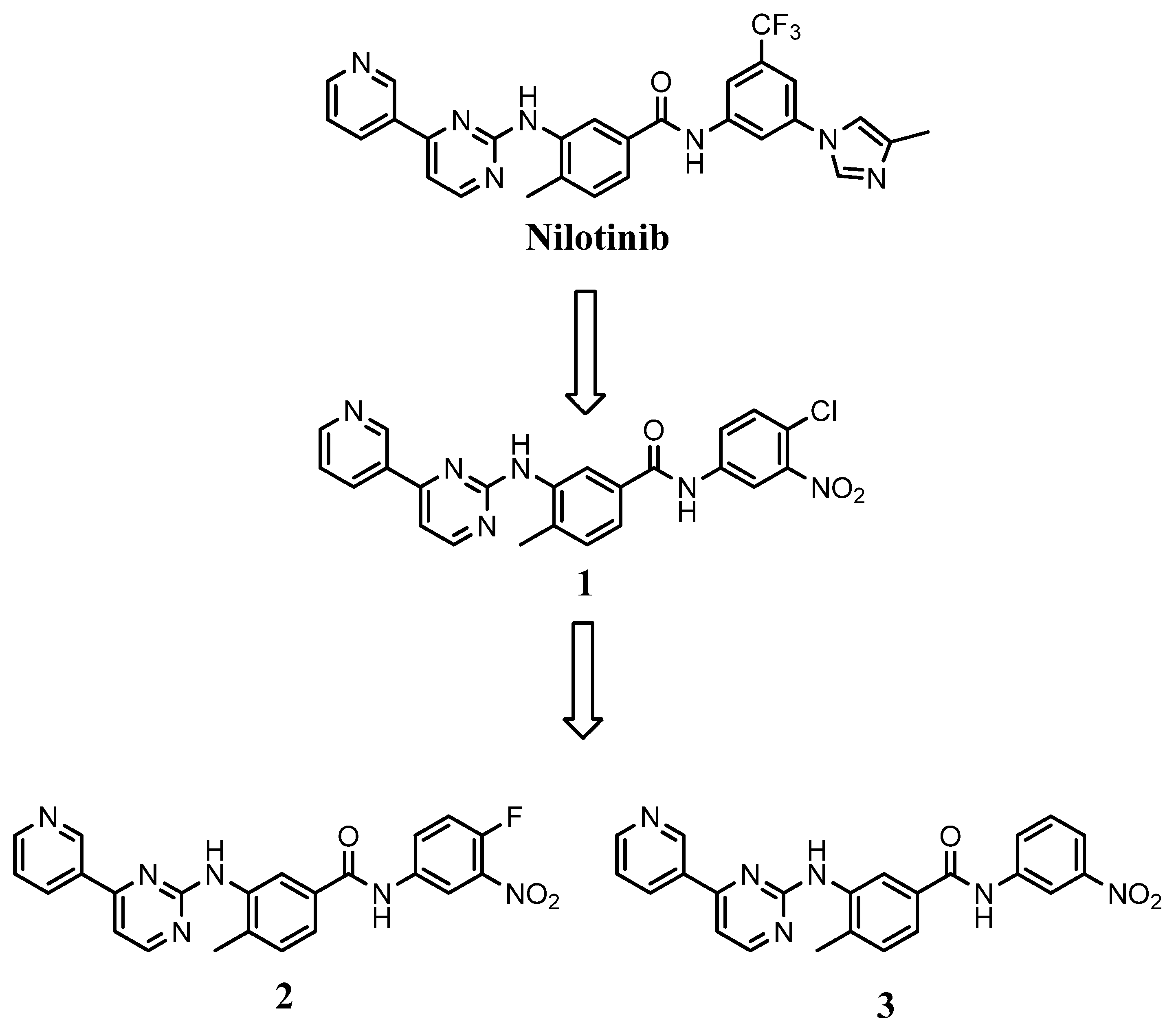
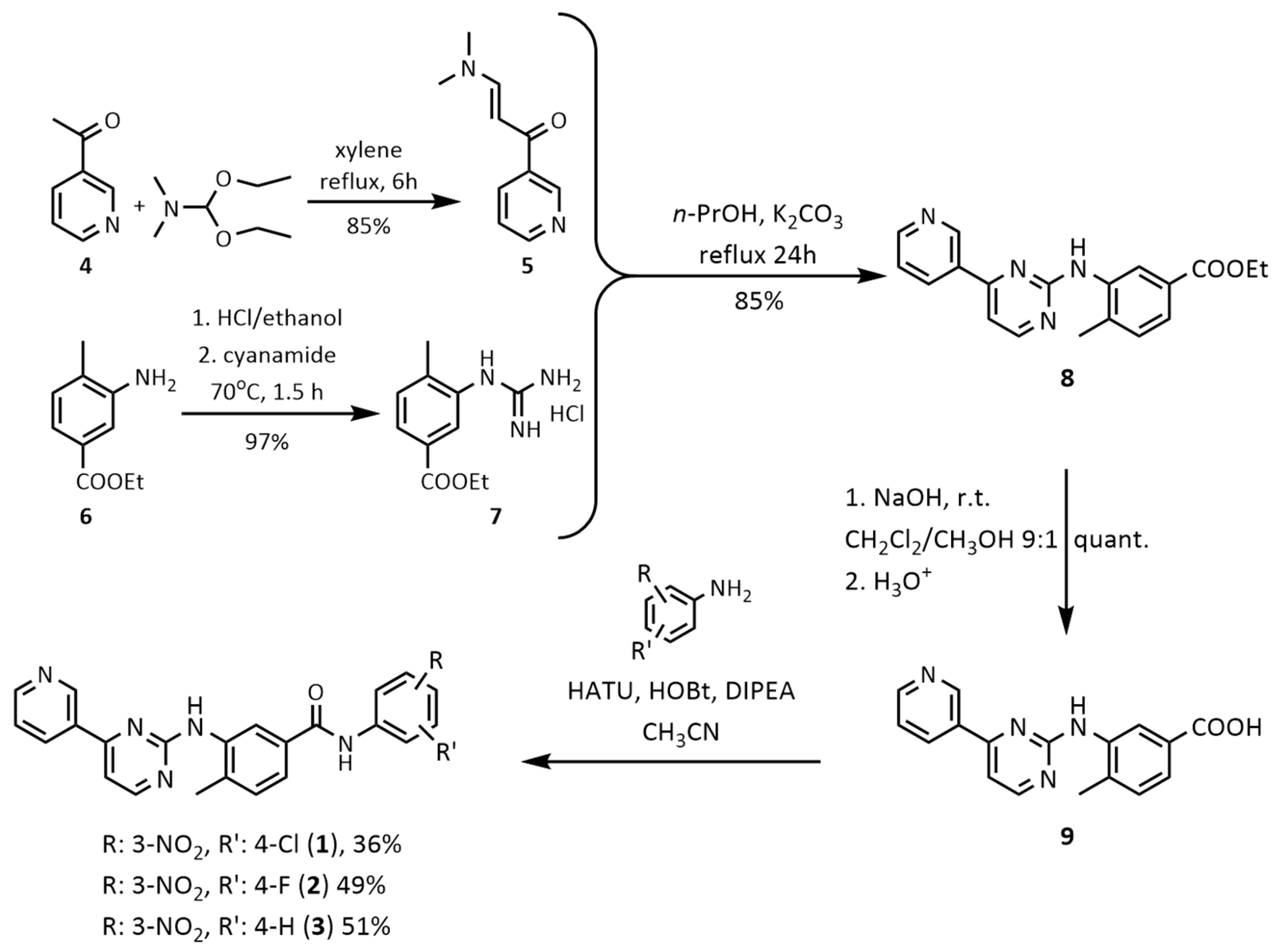
2.1. Chemistry
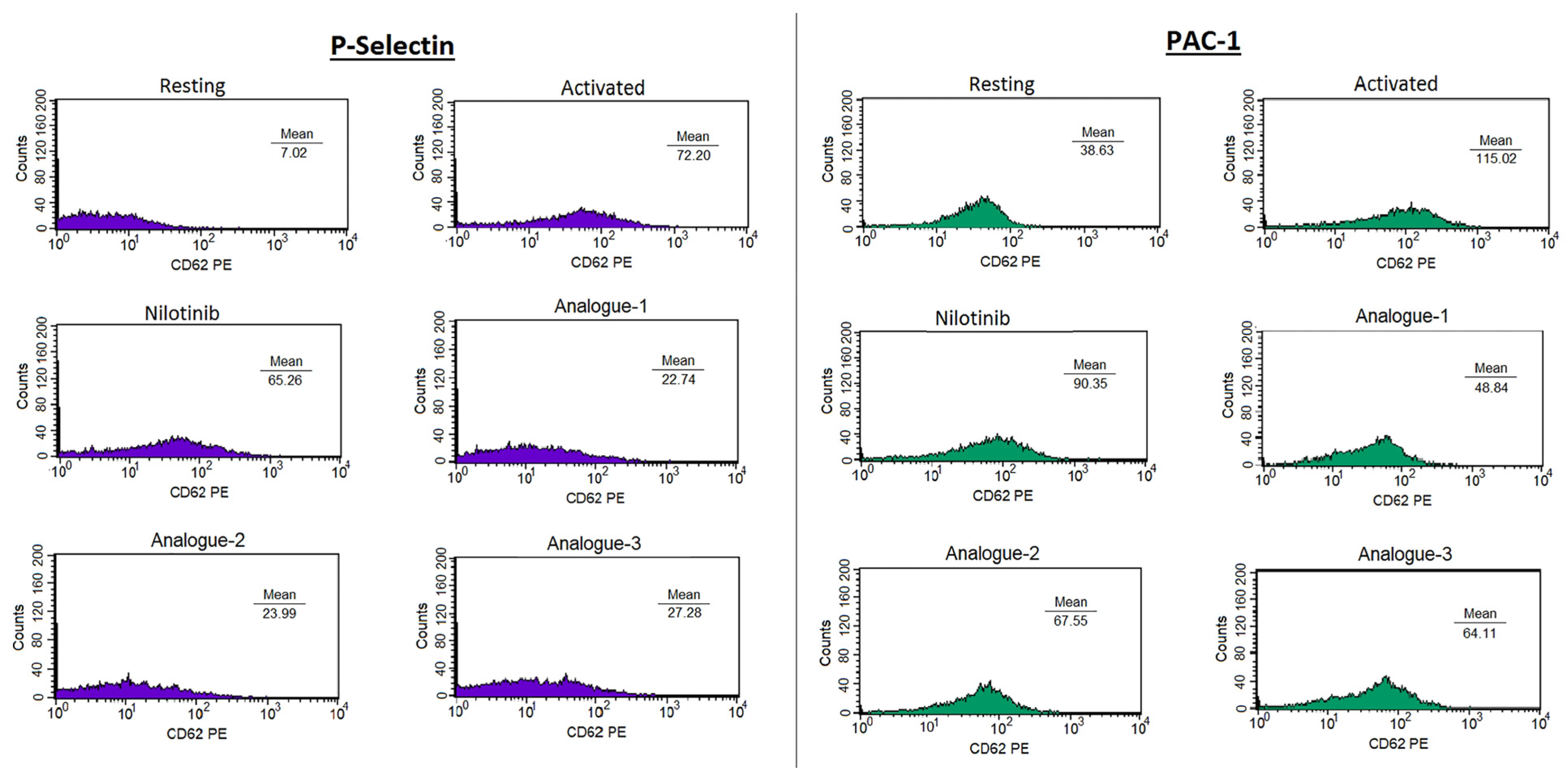
2.2. Platelet Aggregation Assay—Light Transmittance Aggregometry and Flow Cytometry
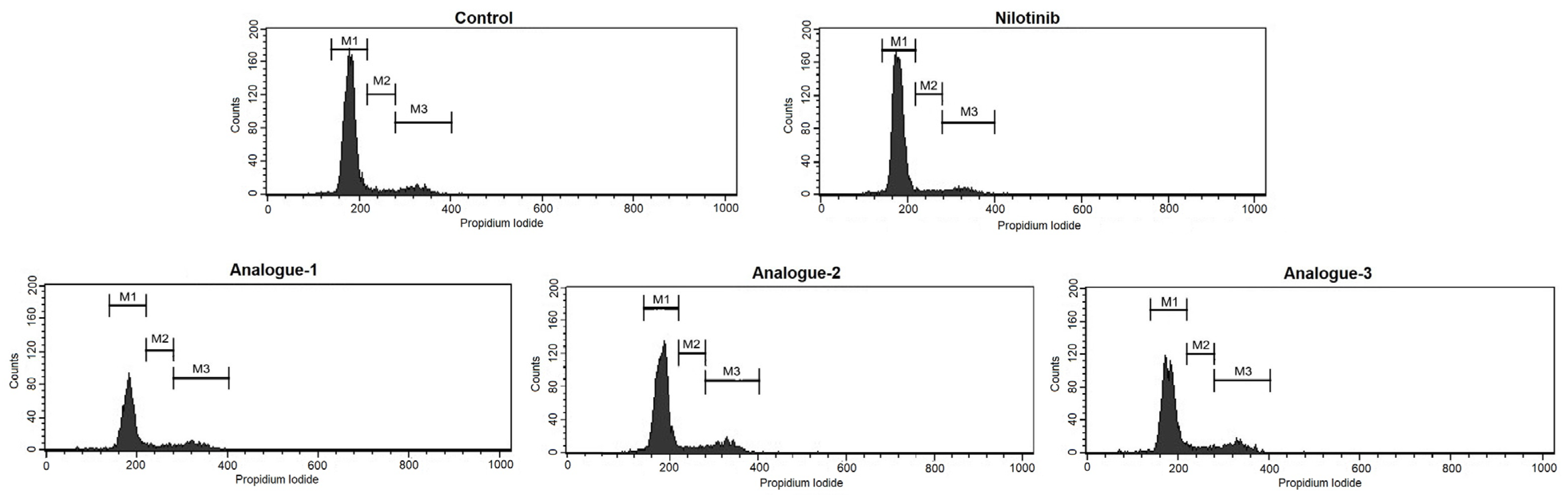
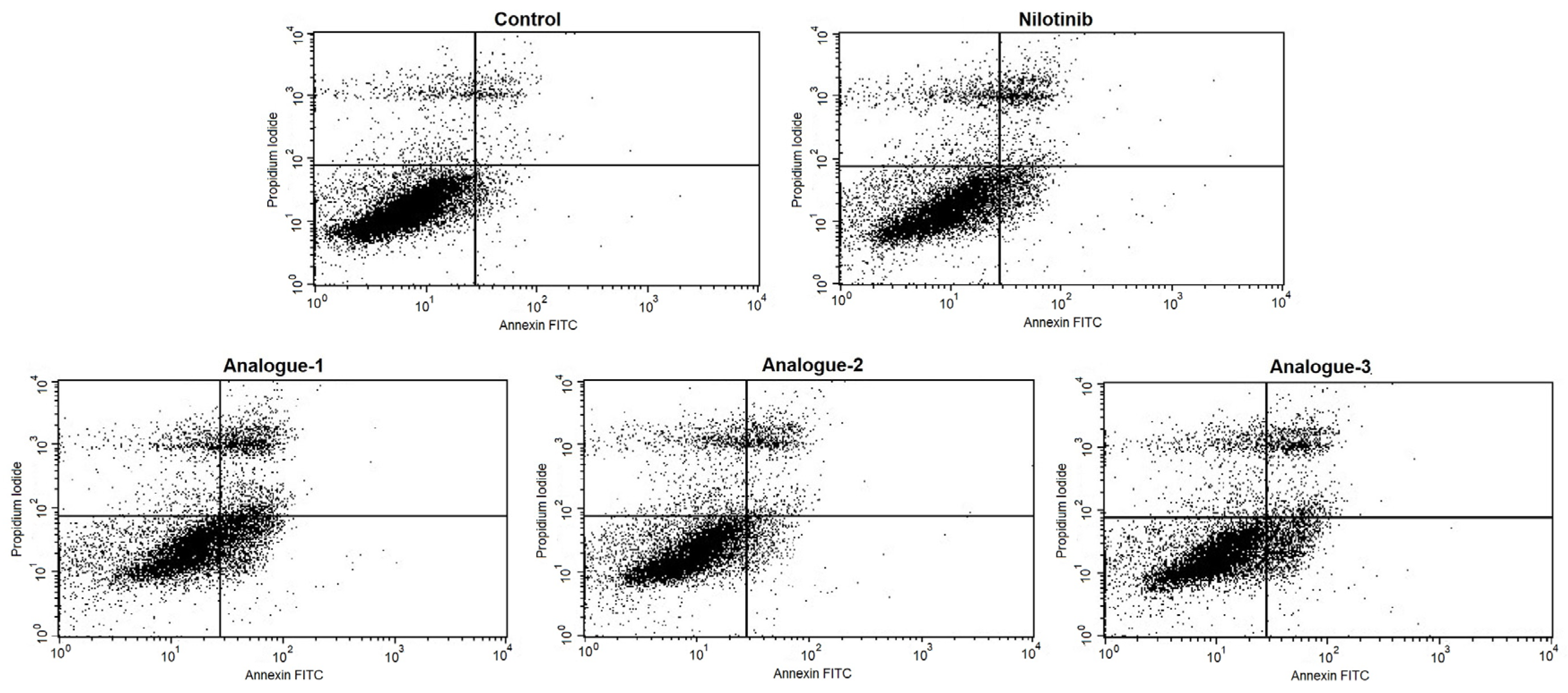
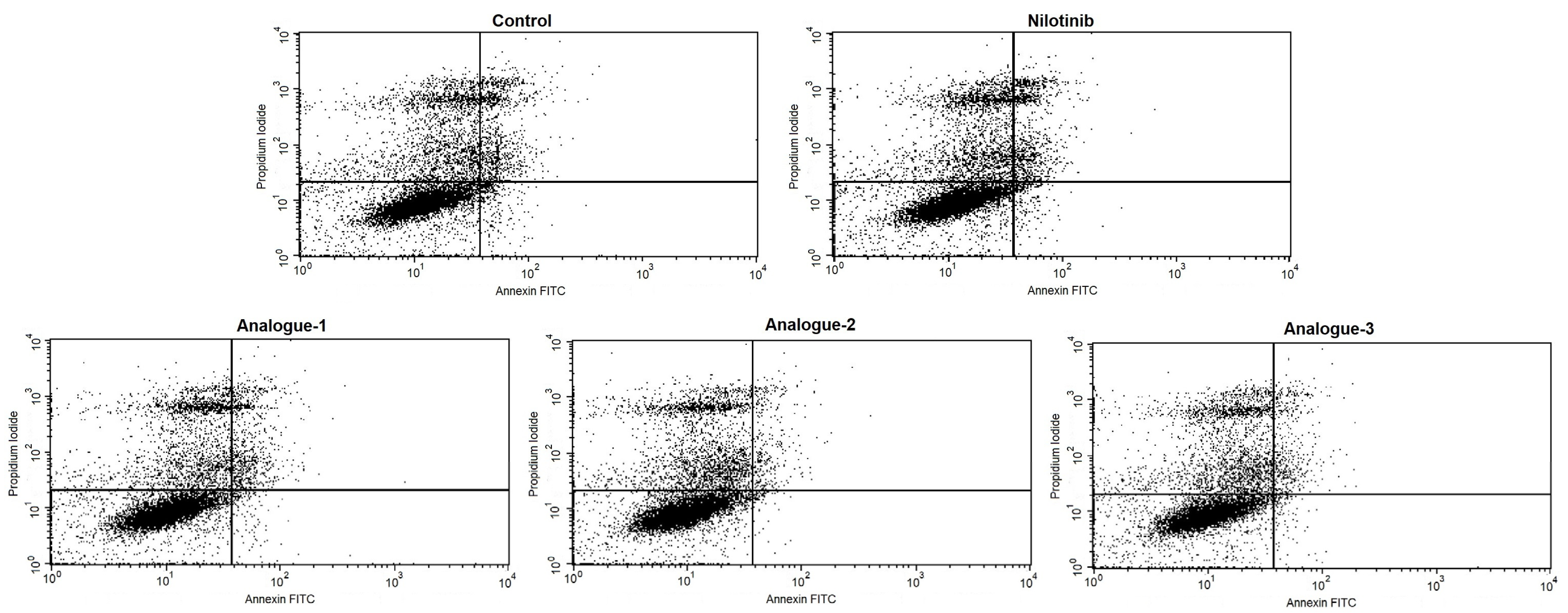
2.3. Cell Cycle Distribution and Apoptosis Assay by Flow Cytometry
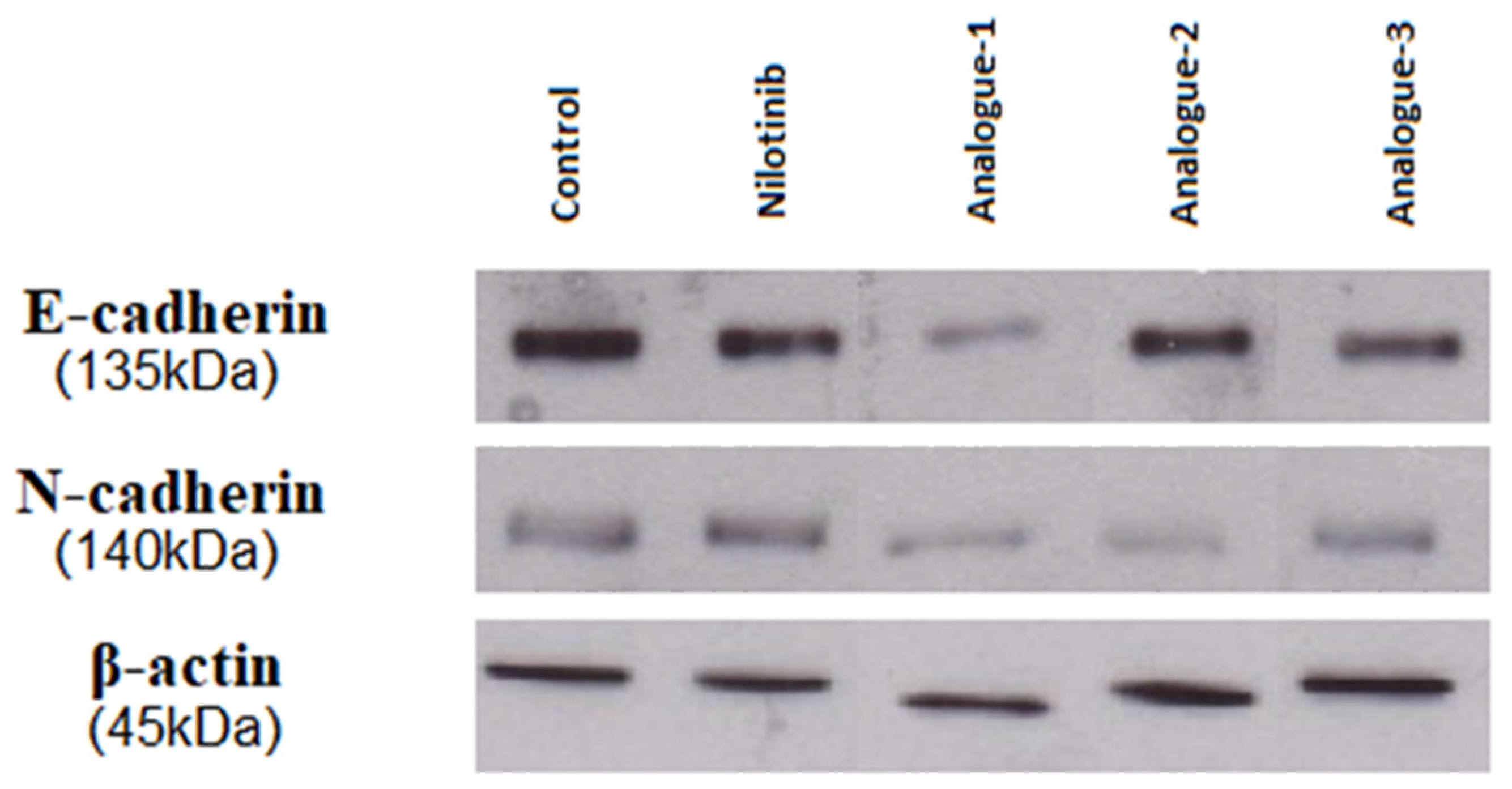
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
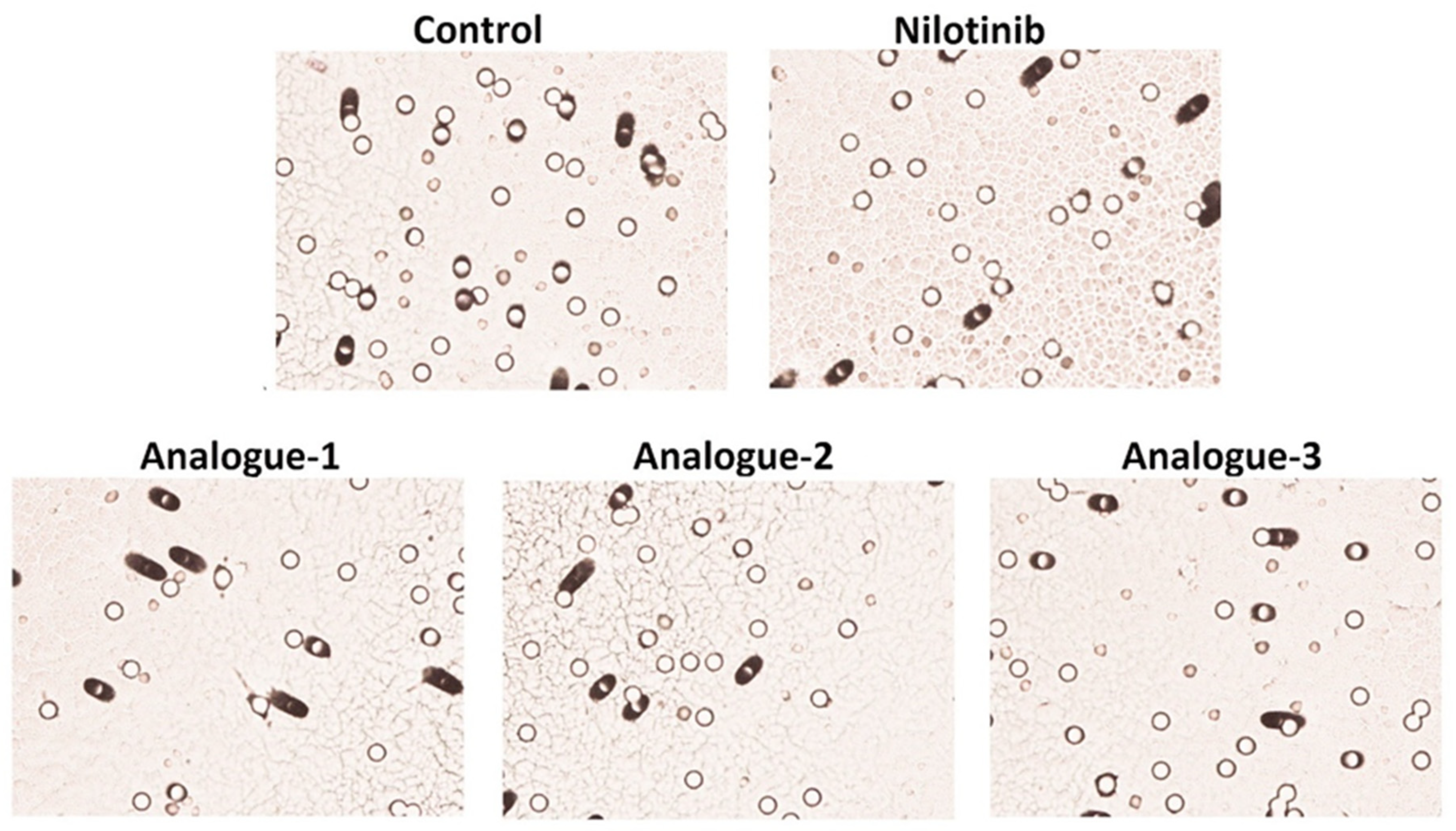
2.5. Migration Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Synthesis of the Final Compounds 1–3
3.2.1. 4-Methyl-N-(4-fluoro-3-nitrophenyl)-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl) amino] Benzamide (2)
3.2.2. Synthesis of 4-Methyl-N-(3-nitrophenyl)-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl) amino] Benzamide (3)
3.3. Biology
3.4. Platelet Aggregation Assay—Light Transmittance Aggregometry and Flow Cytometry
3.5. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.6. Cell Cycle Distribution and Apoptosis Assay by Flow Cytometry
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
3.8. Migration Assay
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feitelson, M.A.; Arzumanyan, A.; Kulathinal, R.J.; Blain, S.W.; Holcombe, R.F.; Mahajna, J.; Marino, M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Nawroth, R.; Sanchez-Garcia, I.; et al. Sustained Proliferation in Cancer: Mechanisms and Novel Therapeutic Targets. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S25–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Malvezzi, M.; Santucci, C.; Boffetta, P.; Collatuzzo, G.; Levi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E. European Cancer Mortality Predictions for the Year 2023 with Focus on Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmartello, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Bertuccio, P.; Boffetta, P.; Levi, F.; Negri, E.; Malvezzi, M. European Cancer Mortality Predictions for the Year 2022 with Focus on Ovarian Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carioli, G.; Malvezzi, M.; Bertuccio, P.; Boffetta, P.; Levi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E. European Cancer Mortality Predictions for the Year 2021 with Focus on Pancreatic and Female Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossari, F.; Minutolo, F.; Orciuolo, E. Past, Present, and Future of Bcr-Abl Inhibitors: From Chemical Development to Clinical Efficacy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaehler, M.; Osteresch, P.; Künstner, A.; Vieth, S.J.; Esser, D.; Möller, M.; Busch, H.; Vater, I.; Spielmann, M.; Cascorbi, I.; et al. Clonal Evolution in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistance: Lessons from in Vitro-Models. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1200897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, M.; Mauro, M.; Aftandilian, C.; Sakamoto, K.M.; Hijiya, N. Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Children and Young Adults. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2022, 17, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Lei, X.; Tang, G.; Cao, X.; Peng, J. Recent Advances in Bcr-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Overriding T315I Mutation. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 97, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: 2020 Update on Diagnosis, Therapy and Monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 691–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Cortes, J. Molecular Biology of Bcr-Abl1-Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, J.; Sasaki, K.; Issa, G.C.; Lipton, J.H.; Radich, J.P.; Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.M. Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in 2023—Common Ground and Common Sense. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.-Y.; Zhou, L.-Y. Research Advance of BCR-ABL Mutation and the Efficacy of Second and Third Generation TKI in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia—Review. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2023, 31, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Cortes, J. Use of Second- and Third-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: An Evolving Treatment Paradigm. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015, 15, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratacap, M.P.; Martin, V.; Valéra, M.C.; Allart, S.; Garcia, C.; Sié, P.; Recher, C.; Payrastre, B. The New Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitor and Anticancer Drug Dasatinib Reversibly Affects Platelet Activation in Vitro and in Vivo. Blood 2009, 114, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, M. Dasatinib: A Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 2289–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpaz, M.; Shah, N.P.; Kantarjian, H.; Donato, N.; Nicoll, J.; Paquette, R.; Cortes, J.; O’Brien, S.; Nicaise, C.; Bleickardt, E.; et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-Resistant Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglio, G.; Kim, D.-W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.; Etienne, G.; Lobo, C.; Pasquini, R.; Clark, R.E.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.P.; et al. Nilotinib versus Imatinib for Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazarika, M.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Q.; Lee, S.L.; Ramchandani, R.; Garnett, C.; Orr, M.S.; Sridhara, R.; Booth, B.; Leighton, J.K.; et al. Tasigna for Chronic and Accelerated Phase Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Resistant to or Intolerant of Imatinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5325–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeRemer, D.L.; Ustun, C.; Natarajan, K.; Jarkowski, A.; Sweeney, R.P. Nilotinib: A New Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Pharmacotherapy 2008, 28, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Jabbour, E.; Deininger, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Apperley, J.; Cortes, J.; Chuah, C.; DeAngelo, D.J.; DiPersio, J.; Hochhaus, A.; et al. Ponatinib after Failure of Second-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Resistant Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, J.H.; Chuah, C.; Guerci-bresler, A.; Rosti, G.; Simpson, D.; Assouline, S.; Etienne, G.; Nicolini, F.E.; Coutre, P.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Ponatinib versus Imatinib for Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia: An International, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamroe, C.L.; Comeau, J.M. Ponatinib: A New Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Ann. Pharmacother. 2013, 47, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Ponatinib: A Review of Its Use in Adults with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia or Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Drugs 2014, 74, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, N.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhu, H.; Du, X.; et al. Olverembatinib (HQP1351), a Well-Tolerated and Effective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for Patients with T315I-Mutated Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Results of an Open-Label, Multicenter Phase 1/2 Trial. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Olverembatinib: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Hassan, S.; Eşkazan, A.E. Novel BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzoug-Larabi, M.; Spasojevic, C.; Eymard, M.; Hugonin, C.; Auclair, C.; Karam, M. Protein Kinase C Inhibitor Gö6976 but Not Gö6983 Induces the Reversion of E- to N-Cadherin Switch and Metastatic Phenotype in Melanoma: Identification of the Role of Protein Kinase D1. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Ng, A.S.; Cai, S.; Li, Q.; Yang, L.; Kerr, D. Novel Therapeutic Strategies: Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, e358–e368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastushenko, I.; Blanpain, C. EMT Transition States during Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Kang, Y. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.S.; Kang, H.E.; Kim, N.H.; Yook, J.I. Therapeutic Implications of Cancer Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT). Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurzu, S. Epithelial-Mesenchymal, Mesenchymal-Epithelial, and Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Malignant Tumors: An Update. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurzu, S.; Kobori, L.; Fodor, D.; Jung, I. Epithelial Mesenchymal and Endothelial Mesenchymal Transitions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2962580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, Y.I.; Schecterson, L.; Gumbiner, B.M. Roles for E-Cadherin Cell Surface Regulation in Cancer. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New Insights into the Mechanisms of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Implications for Cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolijn, K.; Verhoef, E.I.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H. Morphological and Immunohistochemical Identification of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Clinical Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24488–24498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Acedo, A.-L.; Langiu, M.; Crescence, L.; Mège, D.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions Modulate Cancer-Associated Thrombosis Risk in Different Cancer Types. Cancers 2022, 14, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, S.; Pasi, J. Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Cancer-Associated Thrombosis. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes-Ferreira, M.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Würdinger, T. Circulating Platelets as Liquid Biopsy Sources for Cancer Detection. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1727–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roweth, H.G.; Battinelli, E.M. Lessons to Learn from Tumor-Educated Platelets. Blood 2021, 137, 3174–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantureux, L.; Mège, D.; Crescence, L.; Carminita, E.; Robert, S.; Cointe, S.; Brouilly, N.; Ezzedine, W.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; et al. The Interaction of Platelets with Colorectal Cancer Cells Inhibits Tumor Growth but Promotes Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilli, M.; Iannaccone, G.; La Vecchia, G.; Cappannoli, L.; Scacciavillani, R.; Minotti, G.; Massetti, M.; Crea, F.; Aspromonte, N. Platelets: The Point of Interconnection among Cancer, Inflammation and Cardiovascular Diseases. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catani, M.V.; Savini, I.; Tullio, V.; Gasperi, V. The “Janus Face” of Platelets in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Harris, J.; Ware, J. Platelets: Linking Hemostasis and Cancer. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2362–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Acedo, A.L.; Mège, D.; Crescence, L.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Platelets, Thrombo-Inflammation, and Cancer: Collaborating With the Enemy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezouar, S.; Darbousset, R.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Inhibition of Platelet Activation Prevents the P-selectin and Integrin-dependent Accumulation of Cancer Cell Microparticles and Reduces Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremeskel, S.; LeVatte, T.; Liwski, R.S.; Johnston, B.; Bezuhly, M. The Reversible P2Y12 Inhibitor Ticagrelor Inhibits Metastasis and Improves Survival in Mouse Models of Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Wilson, M.; Price, J.F.; Belch, J.F.; Meade, T.W.; Mehta, Z. Effect of Daily Aspirin on Risk of Cancer Metastasis: A Study of Incident Cancers during Randomised Controlled Trials. Lancet 2012, 379, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liao, F.; Song, Q.; Yao, Y. Tumor-Educated Platelets Facilitate Thrombus Formation Through Migration. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 857865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakeas, V.; Kotsopoulos, J.; Brooks, J.D.; Cheung, M.C.; Rosella, L.; Lipscombe, L.; Akbari, M.R.; Austin, P.C.; Narod, S.A. Platelet Count and Survival after Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chapelain, O.; Ho-Tin-Noé, B. Intratumoral Platelets: Harmful or Incidental Bystanders of the Tumor Microenvironment? Cancers 2022, 14, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrkhany, S.; Kuijpers, M.J.E.; oude Egbrink, M.G.A.; Griffioen, A.W. Platelets as Messengers of Early-Stage Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, G.C.; Francis, C.W. Cancer-Associated Thrombosis. Hematology 2013, 2013, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haguet, H.; Douxfils, J.; Chatelain, C.; Graux, C.; Mullier, F.; Dogné, J.-M. BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Which Mechanism(s) May Explain the Risk of Thrombosis? TH Open 2018, 02, e68–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 Recommendations for Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.-W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.; Etienne, G.; Boquimpani, C.; Pasquini, R.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes with Frontline Nilotinib versus Imatinib in Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase: ENESTnd 10-Year Analysis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Rosti, G.; Cross, N.C.P.; Steegmann, J.L.; le Coutre, P.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Petrov, L.; Masszi, T.; Hellmann, A.; Griskevicius, L.; et al. Frontline Nilotinib in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase: Results from the European ENEST1st Study. Leukemia 2016, 30, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Saglio, G.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.-W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.D.; Etienne, G.; Dorlhiac-Llacer, P.E.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-Term Benefits and Risks of Frontline Nilotinib vs Imatinib for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase: 5-Year Update of the Randomized ENESTnd Trial. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazi, D.; Ntemou, N.; Brentas, A.; Alivertis, D.; Skobridis, K.; Tselepis, A.D. Molecular Requirements for the Expression of Antiplatelet Effects by Synthetic Structural Optimized Analogues of the Anticancer Drugs Imatinib and Nilotinib. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 4225–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankwa, S.; Dols, M.-M.; Wei, L.; Glennon, E.K.K.; Kain, H.S.; Kaushansky, A.; Smith, J.D. Exploiting Polypharmacology to Dissect Host Kinases and Kinase Inhibitors That Modulate Endothelial Barrier Integrity. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 1679–1692.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, C.; Carbone, D.; Cascioferro, S.M.; Parrino, B.; Diana, P. Multi or Single-Kinase Inhibitors to Counteract Drug Resistance in Cancer: What Is New? Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skobridis, K.; Kinigopoulou, M.; Theodorou, V.; Giannousi, E.; Russell, A.; Chauhan, R.; Sala, R.; Brownlow, N.; Kiriakidis, S.; Domin, J.; et al. Novel Imatinib Derivatives with Altered Specificity between Bcr–Abl and FMS, KIT, and PDGF Receptors. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosma, A.; Pantazi, D.; Voulgari, P.; Ntemou, N.; Brentas, A.; Alivertis, D.; Siskos, M.G.; Tselepis, A.D.; Skobridis, K. Expressing Enhanced Inhibitory Effects toward Arachidonic Acid Induced Platelet Activation: Design, Synthesis, DFT Calculations and in Vitro Evaluation of Imatinib Analogues. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202200405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinigopoulou, M.; Filippidou, M.; Gogou, M.; Giannousi, A.; Fouka, P.; Ntemou, N.; Alivertis, D.; Georgis, C.; Brentas, A.; Polychronidou, V.; et al. An Optimized Approach in the Synthesis of Imatinib Intermediates and Analogues. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61458–61467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, V.; Skobridis, K.; Tzakos, A.G.; Ragoussis, V. A Simple Method for the Alkaline Hydrolysis of Esters. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 8230–8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, V.; Alagiannis, M.; Ntemou, N.; Brentas, A.; Voulgari, P.; Polychronidou, V.; Gogou, M.; Giannelos, M.; Skobridis, K. Mild Alkaline Hydrolysis of Hindered Esters in Non-Aqueous Solution. Arkivoc 2018, 2018, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantzi, K.I.; Dimitriou, A.A.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Tselepis, A.D. The Platelet Hyporesponsiveness to Clopidogrel in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients Treated with 75 Mg/Day Clopidogrel May Be Overcome within 1 Month of Treatment. Platelets 2012, 23, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsios, J.V.; Papathanasiou, A.I.; Rodis, F.I.; Elisaf, M.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Tselepis, A.D. Atorvastatin Does Not Affect the Antiplatelet Potency of Clopidogrel When It Is Administered Concomitantly for 5 Weeks in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes. Circulation 2004, 109, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tselepis, A.D.; Tsoumani, M.E.; Kalantzi, K.I.; Dimitriou, A.A.; Tellis, C.C.; Goudevenos, I.A. Influence of High-density Lipoprotein and Paraoxonase-1 on Platelet Reactivity in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes Receiving Clopidogrel Therapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzumanian, V.A.; Kiseleva, O.I.; Poverennaya, E.V. The Curious Case of the HepG2 Cell Line: 40 Years of Expertise. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, M.T.; Tolosa, L.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Culture and Functional Characterization of Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Protoc. Vitr. Hepatocyte Res. 2015, 1250, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, G.A.; Vartholomatos, G.; Goussia, A.; Batistatou, A.; Tsamis, K.; Voulgaris, S.; Kyritsis, A.P. Fast Cell Cycle Analysis for Intraoperative Characterization of Brain Tumor Margins and Malignancy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fezza, M.; Moussa, M.; Aoun, R.; Haber, R.; Hilal, G. DKK1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Inflammation, Migration and Invasion: Implication of TGF-Β1. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Zhou, M.; Huang, D.; Wasan, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, L.; Huang, H.; Ma, S.; Shen, M.; Ruan, S. Resveratrol Inhibits the Invasion and Metastasis of Colon Cancer through Reversal of Epithelial- Mesenchymal Transition via the AKT/GSK-3β/Snail Signaling Pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, M. Role of Platelets and Platelet Receptors in Cancer Metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantureux, L.; Crescence, L.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Effects of Platelets on Cancer Progression. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164, S40–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Inoue, K. Platelets and Cancer: Pathology and Drug Targets. Platelets 2018, 29, 771–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haemmerle, M.; Stone, R.L.; Menter, D.G.; Afshar-Kharghan, V.; Sood, A.K. The Platelet Lifeline to Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 965–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
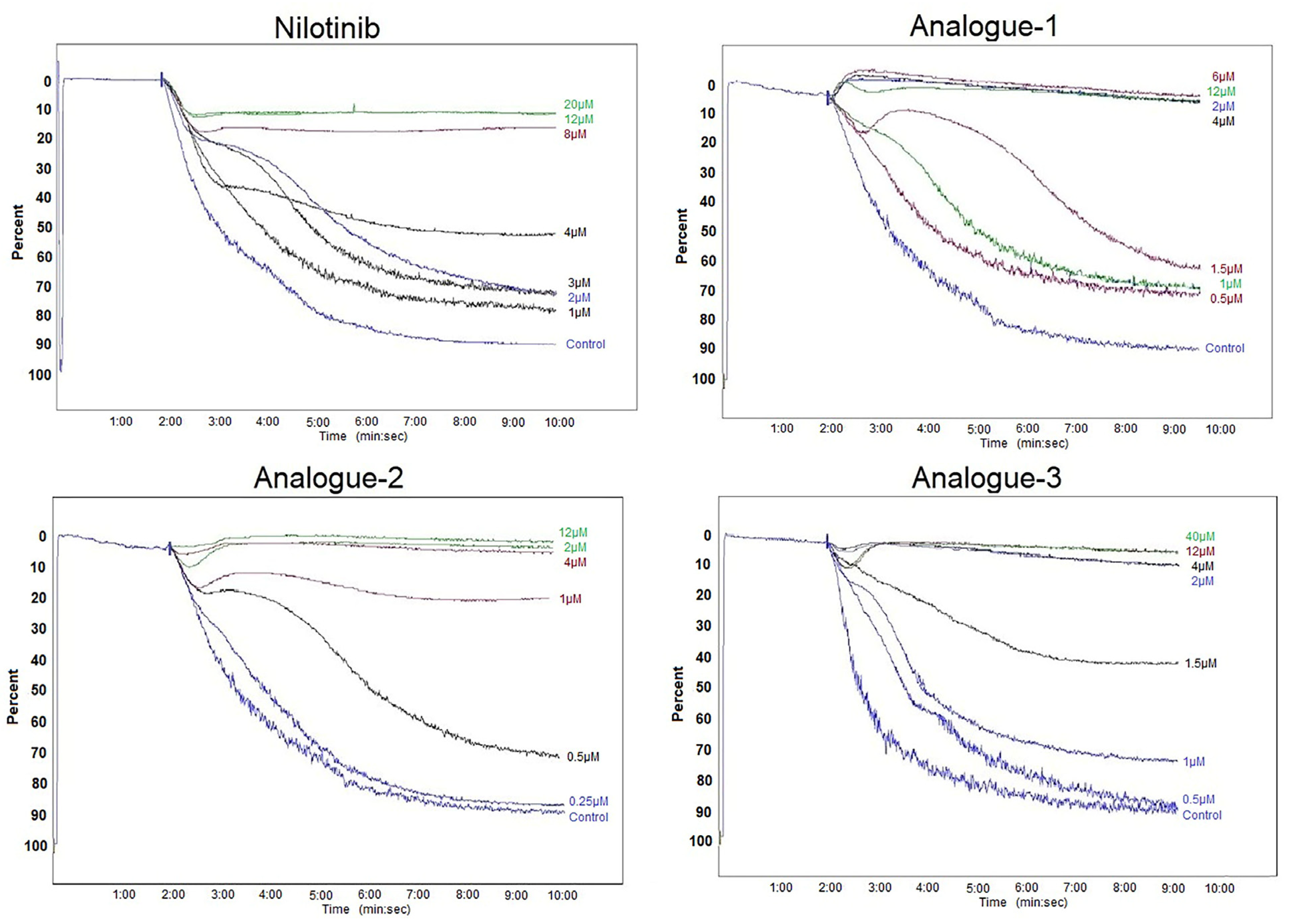
| Compounds | IC50 Values (μM) | Threshold Concentration (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| Nilotinib | 3.94 ± 2.09 | 10.00 ± 2.83 |
| Analogue-1 | 1.42 ± 0.43 * | 2.50 ± 1.32 * |
| Analogue-2 | 0.94 ± 0.66 * | 6.00 ± 5.29 |
| Analogue-3 | 1.50 ± 1.08 * | 2.87 ± 1.31 * |
| Compounds | % Inhibition P-Selectin | % Inhibition PAC-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Nilotinib | 36.49 ± 22.80 | 37.20 ± 29.29 |
| Analogue-1 | 81.94 ± 11.55 * | 74.82 ± 11.18 * |
| Analogue-2 | 72.98 ± 27.57 | 67.15 ± 26.86 |
| Analogue-3 | 66.38 ± 17.45 | 62.95 ± 27.14 |
| % Gated Cells | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Cycle Phases | Control | Nilotinib | Analogue-1 | Analogue-2 | Analogue-3 |
| M1(G0/G1) | 85.14 ± 2.84 | 87.37 ± 2.17 | 78.35 ± 3.51 * | 81.59 ± 1.19 * | 79.96 ± 4.53 * |
| M2(S) | 4.62 ± 1.01 | 3.91 ± 0.86 | 6.39 ± 1.03 | 5.62 ± 0.27 | 5.38 ± 1.19 |
| M3(G2/M) | 9.84 ± 1.92 | 8.20 ± 1.51 | 13.26 ± 2.20 * | 12.25 ± 0.85 * | 13.84 ± 3.03 * |
| % Gated Cells | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cells | Control | Nilotinib | Analogue-1 | Analogue-2 | Analogue-3 |
| Alive cells (LL) | 85.98 ± 3.37 | 72.09 ± 8.77 * | 64.97 ± 8.55 * | 81.33 ± 3.35 | 77.30 ± 4.96 * |
| Positive PI cells (UL) | 8.23 ± 4.39 | 11.27 ± 2.01 | 10.23 ± 2.77 | 9.48 ± 2.80 | 9.33 ± 3.17 |
| Positive Annexin-V cells (LR) | 1.73 ± 1.00 | 6.96 ± 4.15 | 12.41 ± 6.91 * | 2.95 ± 2.05 | 5.89 ± 4.96 |
| Positive PI/Positive Annexin-V cells (UR) | 4.06 ± 0.96 | 9.68 ± 4.79 | 12.40 ± 4.49 | 6.25 ± 2.82 | 7.48 ± 3.10 |
| % Gated Cells | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cells | Control | Nilotinib | Analogue-1 | Analogue-2 | Analogue-3 |
| Alive cells (LL) | 71.82 ± 4.75 | 76.64 ± 6.75 | 69.61 ± 8.21 | 71.52 ± 8.63 | 77.51 ± 5.66 |
| Positive PI cells (UL) | 8.31 ± 8.10 | 8.42 ± 7.61 | 7.64 ± 7.54 | 8.87 ± 9.85 | 8.82 ± 8.84 |
| Positive Annexin-V cells (LR) | 10.83 ± 5.68 | 6.63 ± 4.58 | 9.65 ± 4.58 | 8.18 ± 4.48 | 5.66 ± 2.91 |
| Positive PI/Positive Annexin-V cells (UR) | 9.03 ± 3.88 | 8.32 ± 3.57 | 13.11 ± 8.64 | 11.25 ± 10.30 | 8.01 ± 4.86 |
| Samples | E-Cadherin (% Band) | N-Cadherin (% Band) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 25.01 | 20.74 |
| Nilotinib | 15.32 | 20.56 |
| Analogue-1 | 4.32 | 10.75 |
| Analogue-2 | 18.74 | 7.21 |
| Analogue-3 | 12.06 | 14.07 |
| Samples | Number of Migrated HepG2 Cells | % Inhibition of Cell Migration |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 826 ± 173.95 | |
| Nilotinib | 695 ± 65.05 | 15.24 ± 7.85 |
| Analogue-1 | 610 ± 106.07 * | 25.98 ± 2.22 * |
| Analogue-2 | 682 ± 136.47 * | 17.37 ± 0.66 * |
| Analogue-3 | 616 ± 129.40 * | 25.42 ± 0.15 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pechlivani, L.; Ntemou, N.; Pantazi, D.; Alivertis, D.; Skobridis, K.; Tselepis, A.D. Synthesis of Novel Nilotinib Analogues and Biological Evaluation of Their Antiplatelet Activity and Functionality towards Cancer Cell Proliferation In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030349
Pechlivani L, Ntemou N, Pantazi D, Alivertis D, Skobridis K, Tselepis AD. Synthesis of Novel Nilotinib Analogues and Biological Evaluation of Their Antiplatelet Activity and Functionality towards Cancer Cell Proliferation In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(3):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030349
Chicago/Turabian StylePechlivani, Louisa, Nikoleta Ntemou, Despoina Pantazi, Dimitrios Alivertis, Konstantinos Skobridis, and Alexandros D. Tselepis. 2024. "Synthesis of Novel Nilotinib Analogues and Biological Evaluation of Their Antiplatelet Activity and Functionality towards Cancer Cell Proliferation In Vitro" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 3: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030349
APA StylePechlivani, L., Ntemou, N., Pantazi, D., Alivertis, D., Skobridis, K., & Tselepis, A. D. (2024). Synthesis of Novel Nilotinib Analogues and Biological Evaluation of Their Antiplatelet Activity and Functionality towards Cancer Cell Proliferation In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals, 17(3), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17030349









