Identification of Ureidocoumarin-Based Selective Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors via Drug Repurposing Approach, Biological Evaluation, and In Silico Studies
Abstract
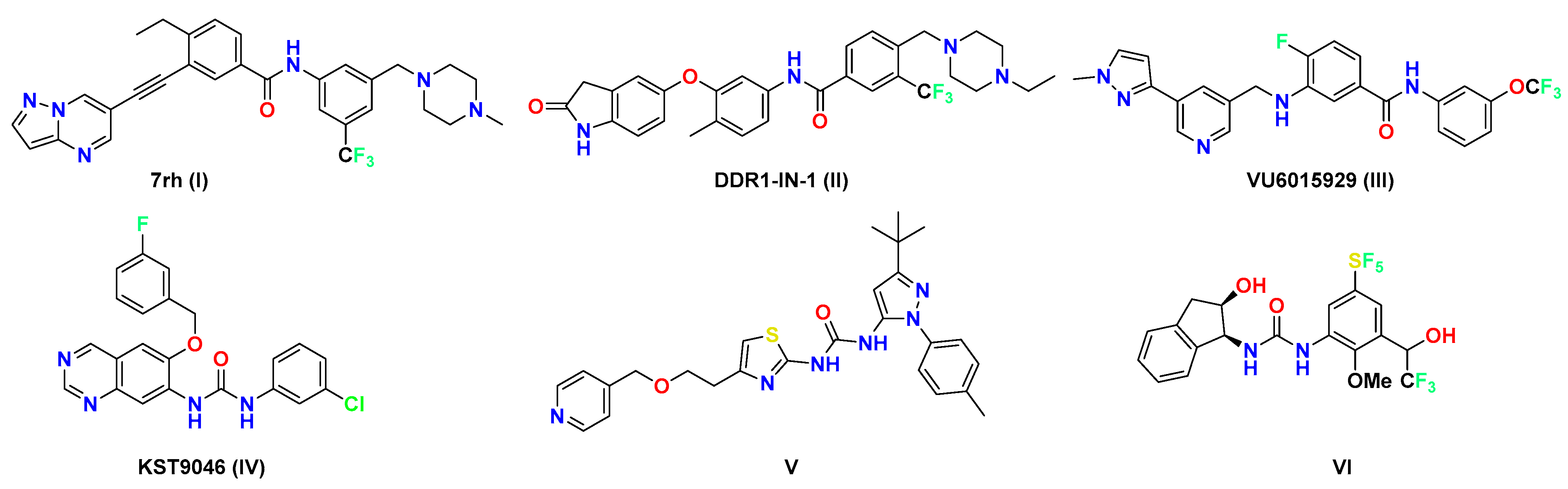
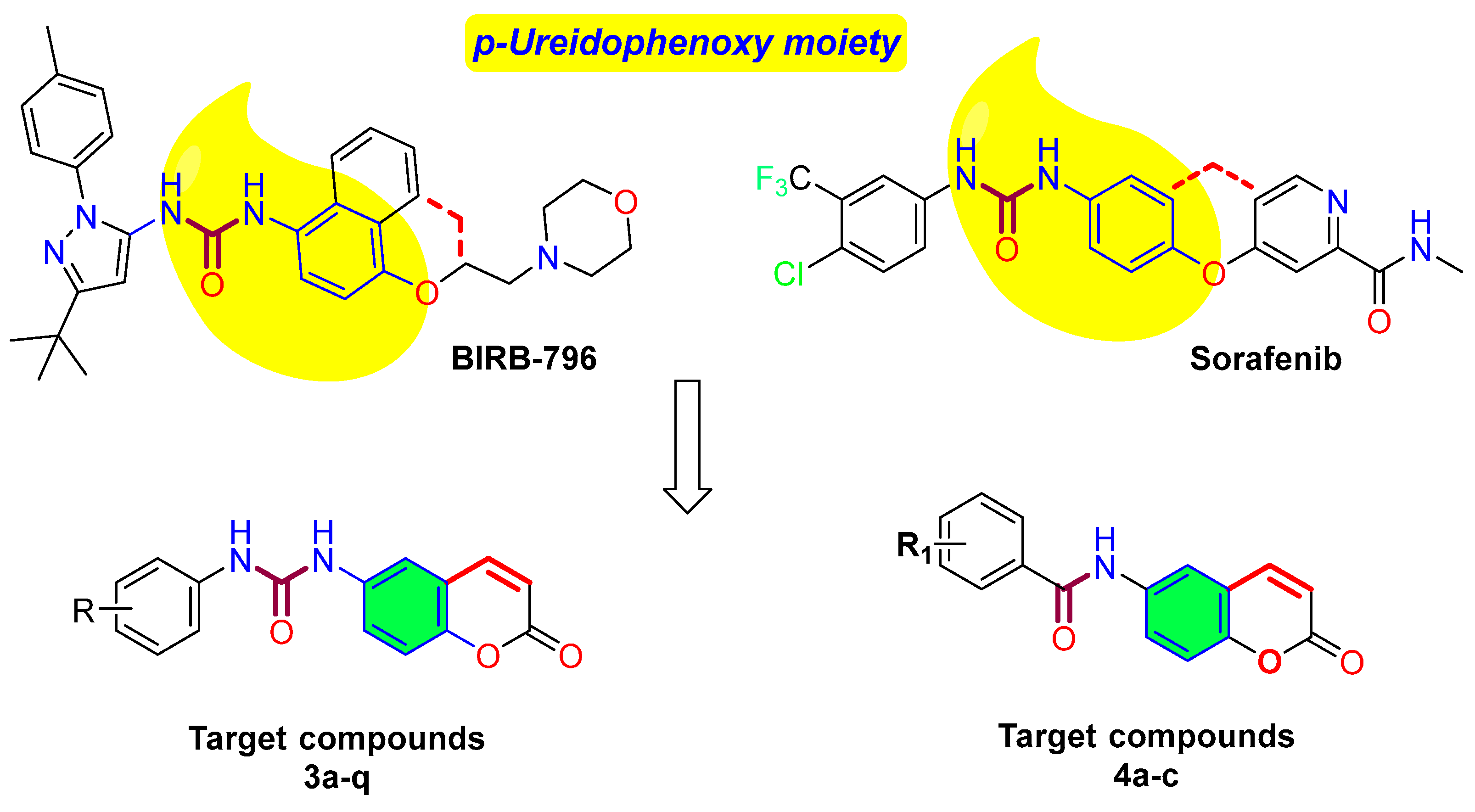
1. Introduction
2. Results
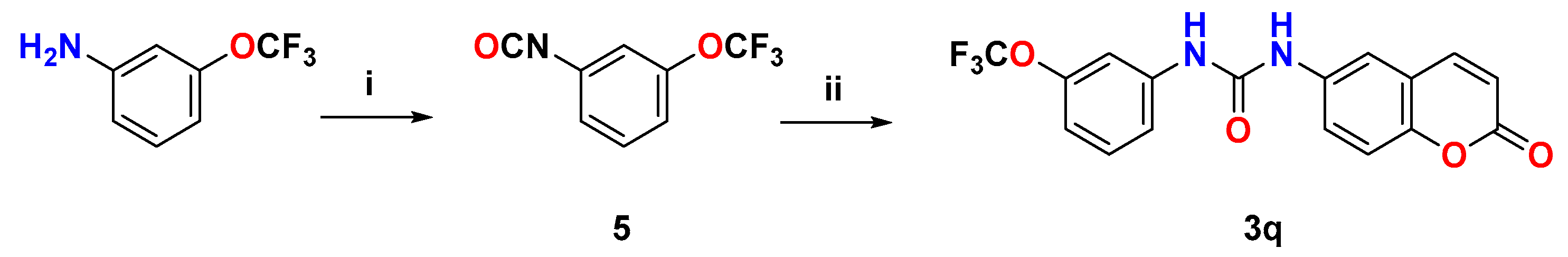
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. In Vitro Biochemical DDR1/2 Kinase Inhibitory Activities
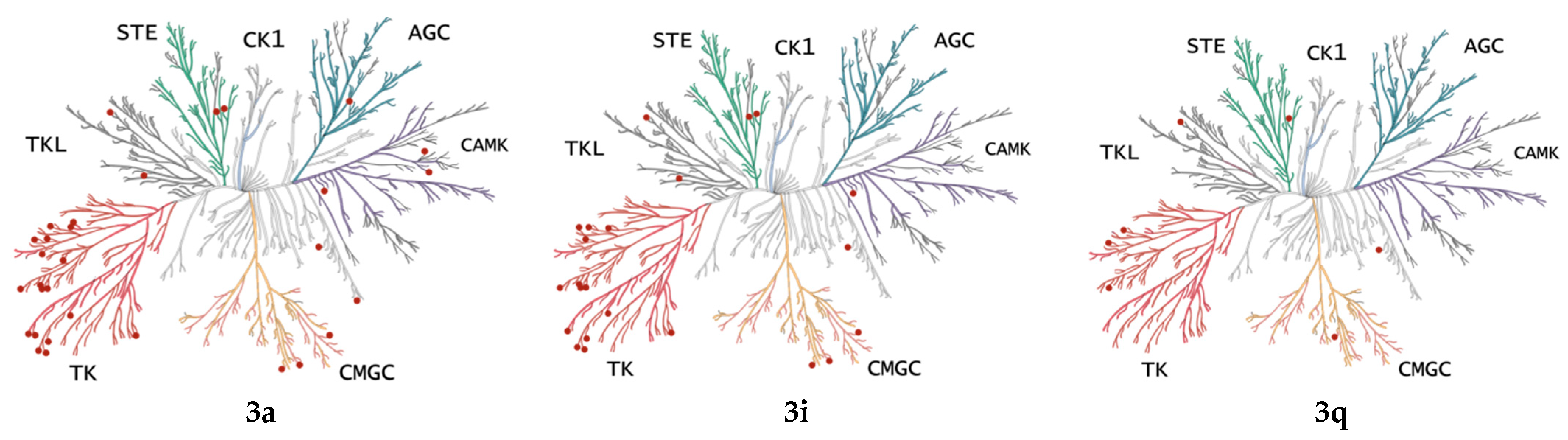
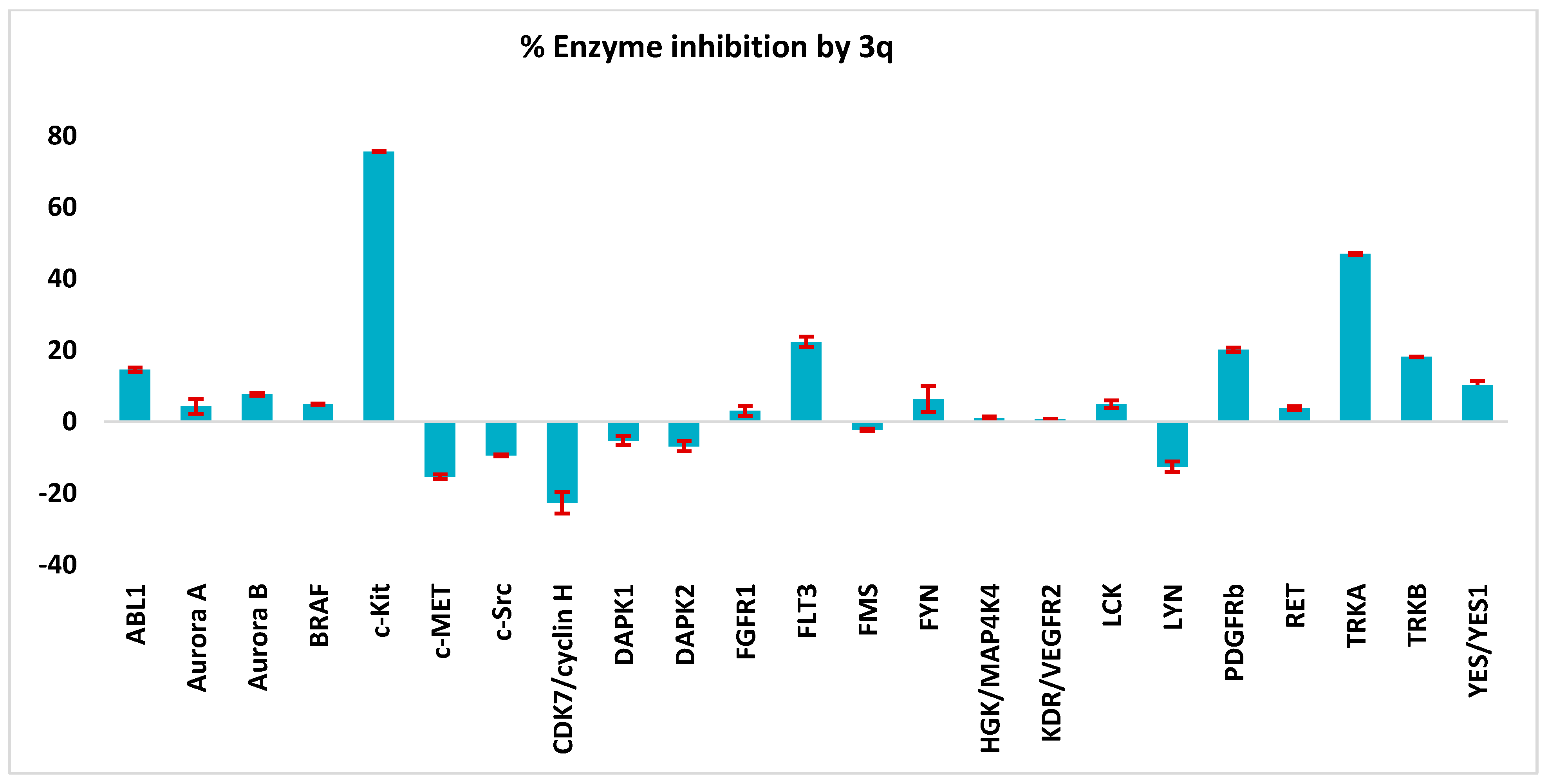
2.3. Kinase Profile of Representative Compounds
2.3.1. Prediction of Kinase Targets by KinScreen
2.3.2. Biochemical Kinase Profile
2.4. In Vitro Cell-Based Antiproliferative Activities
2.5. In Silico ADMET Prediction
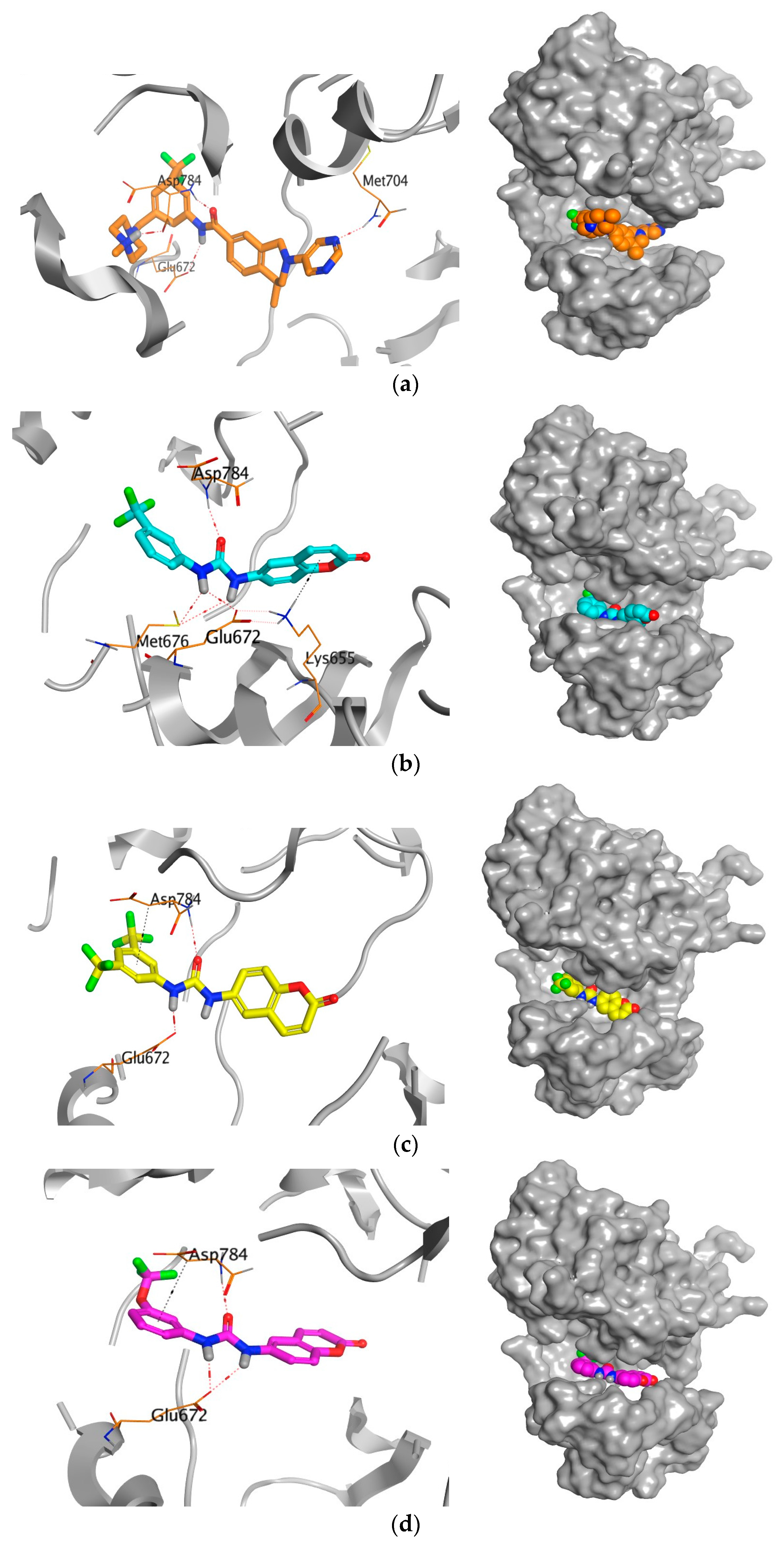
2.6. Molecular Docking Studies
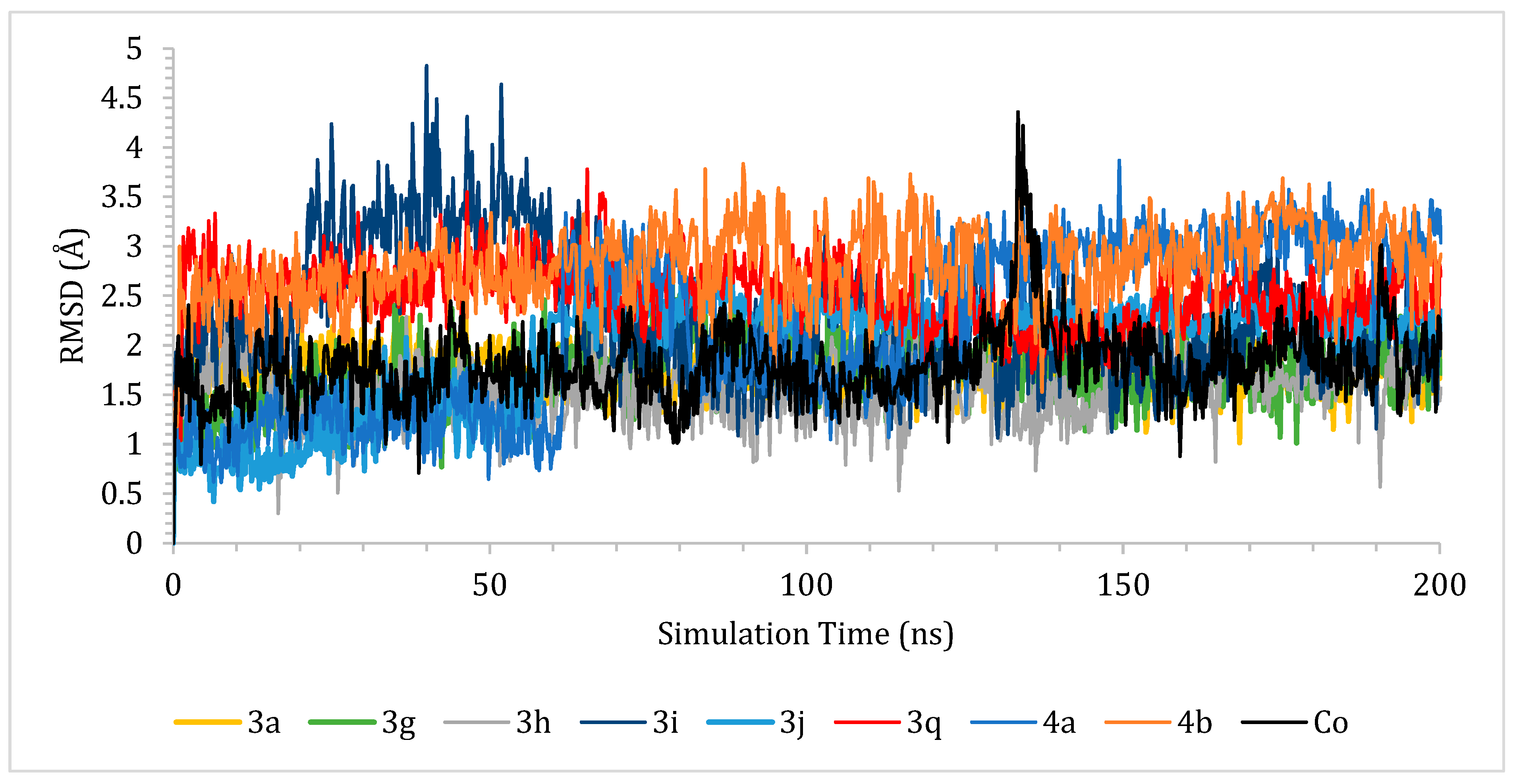
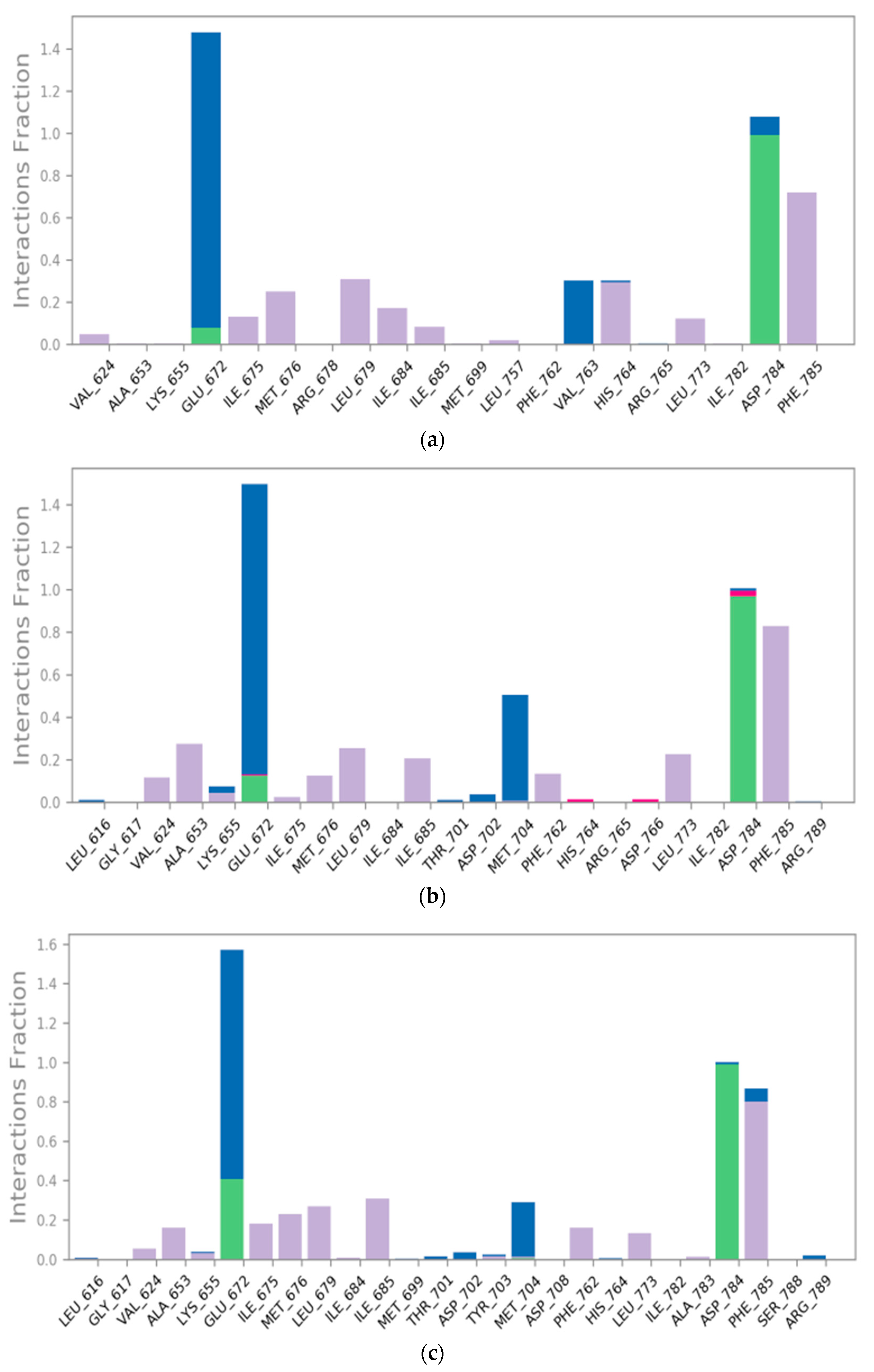
2.7. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
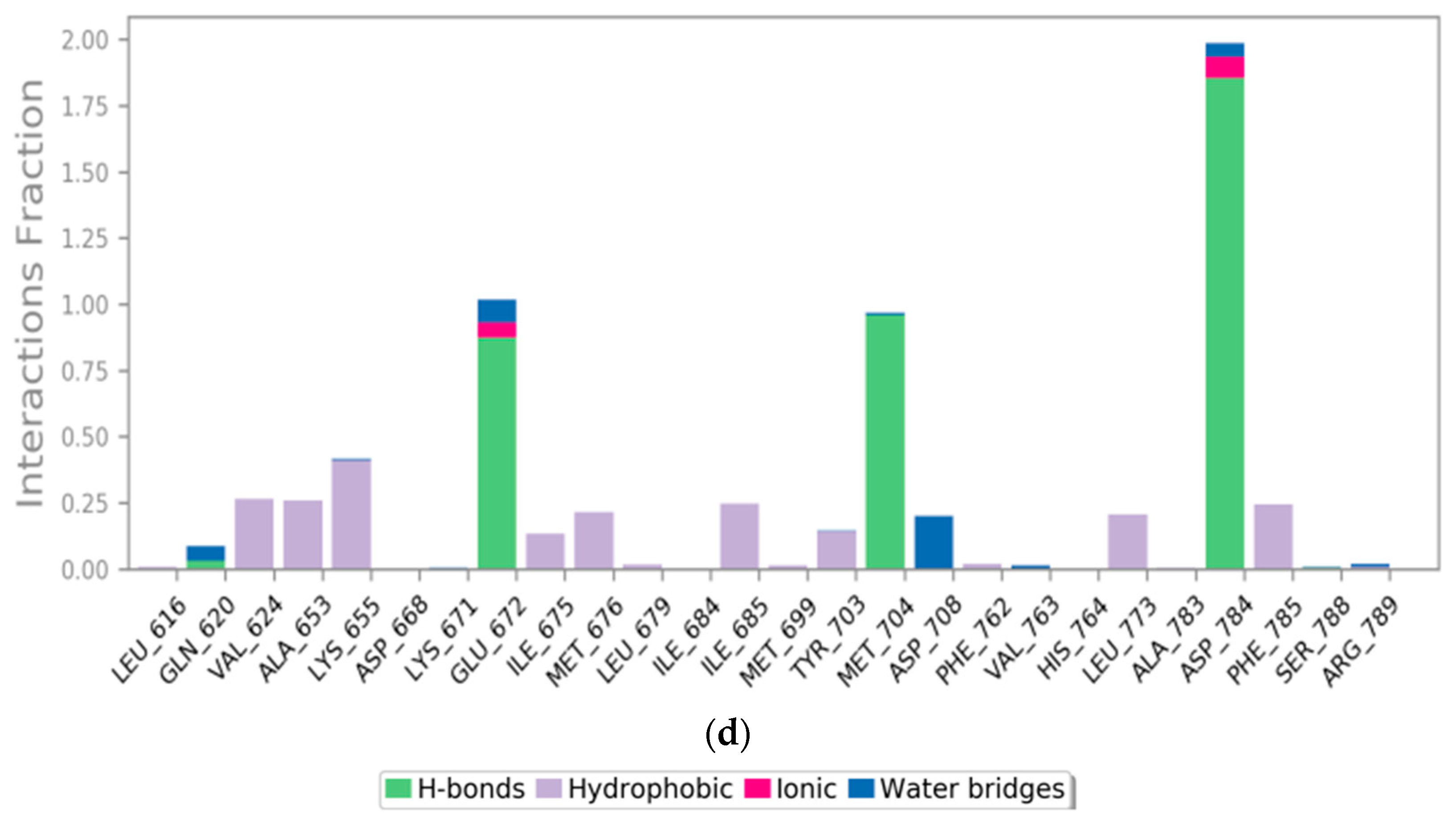
2.7.1. RMSD Analysis
2.7.2. Histogram and Heat Map Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 6-Ureidocoumarins 3a–p and 6-Amidocoumarins 4a–c
3.1.2. Synthesis of 1-(2-Oxo-2H-chromen-6-yl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)urea (3q)
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. In Vitro Kinase Assay
3.2.2. Cell-Based Anticancer Evaluation
3.3. In Silico Studies
3.3.1. KinScreen Prediction
3.3.2. ADMET Prediction
3.3.3. Molecular Docking Study
3.3.4. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, H.-L.; Sohail, A.; Valiathan, R.R.; Wasinski, B.D.; Kumarasiri, M.; Mahasenan, K.V.; Bernardo, M.M.; Tokmina-Roszyk, D.; Fields, G.B.; Mobashery, S. Shedding of discoidin domain receptor 1 by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12114–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiathan, R.R.; Marco, M.; Leitinger, B.; Kleer, C.G.; Fridman, R. Discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases: New players in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Ren, X.; Ding, K. Small Molecule Discoidin Domain Receptor Kinase Inhibitors and Potential Medical Applications: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, H.N.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, B.T.; Moon, W.S. Overexpression of discoidin domain receptor 1 increases the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in association with matrix metalloproteinase. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, D.; Teramoto, A. Enhancement of pituitary adenoma cell invasion and adhesion is mediated by discoidin domain receptor-1. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2007, 82, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Lu, Q.; Nada, H.; Woo, J.; Quan, G.; Lee, K. The journey of DDR1 and DDR2 kinase inhibitors as rising stars in the fight against cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matada, G.S.P.; Das, A.; Dhiwar, P.S.; Ghara, A. DDR1 and DDR2: A review on signaling pathway and small molecule inhibitors as an anticancer agent. Med. Chem. Res. 2021, 30, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, T.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ohba, M.; Ohmori, T. Receptor tyrosine kinase-targeted cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bilal, M.; Raza, A.; Khan, M.I.; Mehmood, S.; Hayat, U.; Hassan, S.T.; Iqbal, H.M. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their unique therapeutic potentialities to combat cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Ko, Y.T. Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in glioblastoma. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2020, 43, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, D.; Yokota, K.; Gouda, M.; Narumi, Y.; Ohmoto, H.; Nishiwaki, E.; Akita, K.; Kirii, Y. Activity-based kinase profiling of approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Genes Cells 2013, 18, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.I.; Hunt, J.P.; Herrgard, S.; Ciceri, P.; Wodicka, L.M.; Pallares, G.; Hocker, M.; Treiber, D.K.; Zarrinkar, P.P. Comprehensive analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.; Waters, B.; Spiegel, K.; Alnadaf, T.; Manley, P.W.; Buchdunger, E.; Walker, C.; Jarai, G. Inhibition of collagen-induced discoidin domain receptor 1 and 2 activation by imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 599, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantscheff, M.; Eberhard, D.; Abraham, Y.; Bastuck, S.; Boesche, M.; Hobson, S.; Mathieson, T.; Perrin, J.; Raida, M.; Rau, C. Quantitative chemical proteomics reveals mechanisms of action of clinical ABL kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, U.; Rix, L.R.; Terker, A.; Fernbach, N.; Hantschel, O.; Planyavsky, M.; Breitwieser, F.; Herrmann, H.; Colinge, J.; Bennett, K. A comprehensive target selectivity survey of the BCR-ABL kinase inhibitor INNO-406 by kinase profiling and chemical proteomics in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 2010, 24, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Wen, D.; Long, H.; Luo, J.; Feng, Y. Identification of GZD824 as an orally bioavailable inhibitor that targets phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated breakpoint cluster region–abelson (Bcr-Abl) kinase and overcomes clinically acquired mutation-induced resistance against imatinib. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.J.; Hebron, M.; Missner, A.A.; Wang, R.; Gao, X.; Kurd-Misto, B.T.; Liu, X.; Moussa, C.E.-H. Multikinase Abl/DDR/Src inhibition produces optimal effects for tyrosine kinase inhibition in neurodegeneration. Drugs R&D 2019, 19, 149–166. [Google Scholar]
- El-Damasy, A.K.; Cho, N.C.; Nam, G.; Pae, A.N.; Keum, G. Discovery of a Nanomolar Multikinase Inhibitor (KST016366): A New Benzothiazole Derivative with Remarkable Broad-Spectrum Antiproliferative Activity. Chemmedchem 2016, 11, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.S.; Duan, L.; Luo, J.F.; Zhang, L.W.; Lu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, Z.C.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.M.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of 3-(2-(Pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidin-6-yl)-ethynyl)benzamides as Novel Selective and Orally Bioavailable Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3281–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Tan, L.; Weisberg, E.L.; Liu, F.Y.; Canning, P.; Choi, H.G.; Ezell, S.A.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Discovery of a Potent and Selective DDR1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2145–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, D.E.; Borza, C.M.; Blobaum, A.L.; Pozzi, A.; Lindsley, C.W. Discovery of VU6015929: A Selective Discoidin Domain Receptor 1/2 (DDR1/2) Inhibitor to Explore the Role of DDR1 in Antifibrotic Therapy. Acs Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, A.; Park, J.E.; Cho, N.C.; Sim, T.; Pae, A.N.; Roh, E.J. Discovery of a broad spectrum antiproliferative agent with selectivity for DDR1 kinase: Cell line-based assay, kinase panel, molecular docking, and toxicity studies. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richters, A.; Nguyen, H.D.; Phan, T.; Simard, J.R.; Grutter, C.; Engel, J.; Rauh, D. Identification of Type II and III DDR2 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4252–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, H.; Okimura, K.; Udagawa, S.; Kaino, M.; Meguro, H.; Sekiya, Y. Preparation of N-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl)-N’-[3-(pentafluorosulfanyl)phenyl]urea Derivatives as Inhibitors of Discoidin Domain Receptor Kinase 1 (DDR1). World patent WO 2017038870, 9 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Masuda, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Okimura, K.; Udagawa, S.; Kaino, M.; Meguro, H.; et al. Preparation of Urea Derivatives for Inhibiting Discoidin Domain Receptor 1. World patent WO 2017038873 A1, 9 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nishio, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Kubota, Y.; Tsutsui, H.; Masuda, T.; Okimura, K.; Udagawa, S.; Kaino, M.; Meguro, H.; Sekiya, Y. Preparation of Urea Derivatives for Inhibiting Discoidin Domain Receptor 1. World patent WO 2017038871, 9 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.W.; Berdini, V.; Buck, I.M.; Carr, M.E.; Cleasby, A.; Coyle, J.E.; Curry, J.E.; Day, J.E.; Day, P.J.; Hearn, K. Fragment-based discovery of potent and selective DDR1/2 inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, T.I.; Bauman, J.E.; Bologa, C.G.; Buranda, T.; Chigaev, A.; Edwards, B.S.; Jarvik, J.W.; Gresham, H.D.; Haynes, M.K.; Hjelle, B.; et al. 2011. Drug repurposing from an academic perspective. Drug Discov. Today Ther. Strateg. 2011, 8, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Damasy, A.K.; Kim, H.J.; Nocentini, A.; Seo, S.H.; Eldehna, W.M.; Bang, E.-K.; Supuran, C.T.; Keum, G. Discovery of new 6-ureido/amidocoumarins as highly potent and selective inhibitors for the tumour-relevant carbonic anhydrases IX and XII. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2154603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Niizuma, S.; Hara, S.; Kawada, H.; Hada, K.; Shimada, H.; Tanaka, H.; Nakanishi, Y. Preparation of benzamide derivatives as discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) inhibitors. World patent WO2013161851, 31 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, B.; Ritter, M.; Benz, J.; Kocer, B.; Sarie, J.C.; Hochstrasser, R.; Rudolph, M.G.; Kadono, S.; Matsuura, T.; Murata, T.; et al. Novel potent and highly selective DDR1 inhibitors from integrated lead finding. Med. Chem. Res. 2023, 32, 1400–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, E.H.; Yang, J.; Pan, X.; Liao, X.; Yang, X.S. Polyphosphoric acid-promoted synthesis of coumarins lacking substituents at positions 3 and 4. Synth. Commun. 2020, 50, 3080–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thacker, P.S.; Srikanth, D.; Angeli, A.; Singh, P.; Chinchilli, K.K.; Arifuddin, M.; Supuran, C.T. Coumarin-Thiourea Hybrids Show Potent Carbonic Anhydrase IX and XIII Inhibitory Action. Chemmedchem 2021, 16, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angapelly, S.; Ramya, P.V.S.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Arifuddin, M. Sulfocoumarin-, Coumarin-, 4-Sulfamoylphenyl-Bearing Indazole-3-carboxamide Hybrids: Synthesis and Selective Inhibition of Tumor-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase Isozymes IX and XII. Chemmedchem 2017, 12, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.way2drug.com/KinScreen/ (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Pires, D.E.V.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaction Biology Corporation. Available online: http://www.reactionbiology.com/webapps/site/Kinase_Assay_Protocol.aspx (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Lee, J.H.; El-Damasy, A.K.; Seo, S.H.; Gadhe, C.G.; Pae, A.N.; Jeong, N.; Hong, S.S.; Keum, G. Novel 5,6-disubstituted pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as broad spectrum antiproliferative agents: Synthesis, cell based assays, kinase profile and molecular docking study. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5596–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DTP Human Tumor Cell Line Screen Process. Available online: https://dtp.cancer.gov/discovery_development/nci-60/methodology.htm (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Schrödinger Release 2022-1: Maestro; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving force field accuracy on challenging regimes of chemical space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Release, S. 3: Desmond molecular dynamics system, DE Shaw research, New York, NY, 2017. In Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Abel, R.; Zhu, K.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Friesner, R.A. The VSGB 2.0 model: A next generation energy model for high resolution protein structure modeling. Proteins 2011, 79, 2794–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.; Wu, C.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neria, E.; Fischer, S.; Karplus, M. Simulation of activation free energies in molecular systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 105, 1902–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual, D.U. Desmond2. 2. 2009. Available online: https://www.cines.fr/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/des22_user_manual.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Martyna, G.J.; Klein, M.L.; Tuckerman, M. Nosé–Hoover chains: The canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



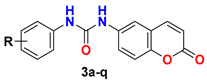 | 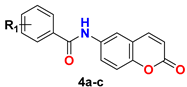 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | R | % Inhibition at 10 μM (SEM) | |
| DDR1 | DDR2 | ||
| 3a | 3-CF3 | 92.65 (0.50) | 83.63 (0.34) |
| 3b | 4-CF3 | 24.49 (1.29) | 11.67 (4.48) |
| 3c | 4-F | 25.60 (0.68) | 15.95 (6.69) |
| 3d | 4-Br | 23.05 (2.12) | 7.53 (1.95) |
| 3e | 4-n-Butyl | 15.36 (0.34) | 3.07 (1.41) |
| 3f | 4-Butoxy | 10.55 (0.77) | 5.52 (2.69) |
| 3g | 4-Cl-3-CF3 | 48.96 (0.82) | 39.26 (9.89) |
| 3h | 3-Cl-4-F | 57.20 (2.30) | 27.47 (0.23) |
| 3i | 3,5-CF3 | 77.06 (0.55) | 67.34 ± (1.41) |
| 3j | 3,5-Cl | 48.53 (1.17) | 23.33 (1.49) |
| 3k | 3,5-CH3 | 33.76 (0.59) | 17.29 (1.97) |
| 3l | 2,4-Cl | 19.04 (1.39) | 17.13 (1.07) |
| 3m | 2,4-F | 5.83 (3.72) | 0.78 (5.17) |
| 3n | 4-Cl-2-CH3 | 10.70 (1.13) | 8.02 (3.85) |
| 3o | 2-Cl-6-CH3 | 15.69 (5.59) | −1.40 (5.19) |
| 3p | 2,6-Br-4-F | 15.02 (0.38) | 17.06 (0.40) |
| 3q | 3-OCF3 | 87.37 (1.05) | 70.07 (0.32) |
| 4a | 4-Cl-3-CF3 | 5.82 (2.16) | 3.77 (3.71) |
| 4b | 3,5-CF3 | 12.64 (0.26) | 6.06 (7.72) |
| 4c | 3,5-F | 22.37 (0.75) | 17.01 (1.89) |
| Compound No. | (IC50, μM) (SEM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DDR1 | DDR2 | SI b | |
| 3a | 0.321 (0.174) | 2.39 (0.344) | 7.5 |
| 3g | 2.90 (0.077) | >10 | >3.4 |
| 3h | 1.66 (0.082) | >10 | >6.0 |
| 3i | 1.53 (0.450) | 19.0 (10.9) | 12.4 |
| 3j | 2.52 (0.454) | >10 | >4.0 |
| 3q | 0.191 (0.018) | 5.08 (0.181) | 26.6 |
| Staurosporine | 0.005 (0.000) | 0.0009 (0.000) | 0.18 |
| DDR1-IN-1 | 0.0747 (0.005) | 0.0597 (0.004) | 0.8 |
| VU6015929 | 0.0684 (0.002) | 0.00155 (0.000) | 0.02 |
| Compound No. | Confidence | Name | UniProt ID | ChEMBL ID | Prediction Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3a | 0.66 | Dual specificity MAPK kinase 7 | O14733 | CHEMBL3530 | 0.69 |
| 0.56 | MAP kinase p38 gamma | P53778 | CHEMBL4674 | 0.71 | |
| 0.51 | Serine/threonine protein kinase RAF | P04049 | CHEMBL1906 | 0.88 | |
| 0.46 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | P29323 | CHEMBL3290 | 0.77 | |
| 0.42 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Q16832 | CHEMBL5122 | 0.84 | |
| 3i | 0.59 | Dual specificity MAPK kinase 7 | O14733 | CHEMBL3530 | 0.69 |
| 0.53 | MAP kinase p38 gamma | P53778 | CHEMBL4674 | 0.71 | |
| 0.51 | Serine/threonine protein kinase RAF | P04049 | CHEMBL1906 | 0.88 | |
| 0.47 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | P29323 | CHEMBL3290 | 0.77 | |
| 0.45 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Q16832 | CHEMBL5122 | 0.84 | |
| 3q | 0.48 | Serine/threonine protein kinase RAF | P04049 | CHEMBL1906 | 0.88 |
| 0.37 | Nerve growth factor receptor TrkA | P04629 | CHEMBL2815 | 0.78 | |
| 0.34 | Serine/threonine protein kinase NLK | Q9UBE8 | CHEMBL5364 | 0.78 | |
| 0.33 | PDGFR receptor alpha | P16234 | CHEMBL2007 | 0.84 | |
| 0.29 | Dual specificity MAPK kinase 7 | O14733 | CHEMBL3530 | 0.69 |
| Compound | CLoP a | MR a | % Growth inhibition at 10 µM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K562 b | HCT116 c | A549 d | NCI-H23 d | NCI-H460 d | MCF-7 e | T47D e | |||
| 3a | 4.12 | 84.77 | 33.24 | 20.87 | 10.39 | 13.21 | 15.85 | 29.24 | 24.61 |
| 3g | 4.65 | 89.37 | 80.85 | 84.3 | 60.15 | 95.15 | 81.9 | 88.07 | 91.27 |
| 3h | 4.08 | 83.27 | 32.24 | 14.12 | 15.14 | 14.34 | 20.64 | 25.37 | 24.63 |
| 3i | 5.03 | 91.27 | 86.27 | 97.91 | 84.76 | 100.22 | 93.64 | 96.19 | 95.2 |
| 3j | 4.65 | 87.47 | 84.58 | 98.64 | 83.76 | 106.33 | 98.83 | 94.52 | 96.46 |
| 3q | 4.23 | 87.11 | 67.08 | 66.33 | 45.65 | 56.64 | 69.93 | 57.03 | 69.44 |
| Compound | GI50, µM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K562 a | HCT116 b | A549 c | NCI-H23 c | NCI-H460 c | MCF-7 d | T47D d | |
| 3i e | 0.55 | 0.732 | 1.59 | 0.94 | 0.69 | 1.94 | 1.34 |
| 3j | 2.34 | 2.31 | 2.90 | 2.67 | 2.27 | 2.28 | 1.93 |
| DDR1-IN-1 f | NT h | 8.7 | >10 | NT h | NT h | NT h | >10 |
| 7rh g | 0.038 | 1.13 | 2.74 | 2.08 | 2.98 | 2.15 | 1.88 |
| Properties | ADMET Properties and Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3i | 3q | ||
| Absorption | Water Solubility | −5.095 | −4.457 |
| CaCO2 permeability | 0.715 | 0.721 | |
| Intestinal absorption (human) | 87.169 | 88.852 | |
| Skin permeability | −2.786 | −2.812 | |
| P-glycoprotein substrate | Yes | Yes | |
| P-glycoprotein I inhibitor | No | No | |
| P-glycoprotein II inhibitor | Yes | Yes | |
| Distribution | VDss (human) | −0.471 | −0.640 |
| Fraction unbound (human) | 0.115 | 0.151 | |
| BBB permeability | −0.833 | −0.643 | |
| CNS permeability | −1.561 | −1.933 | |
| Metabolism | CYP2D6 substrate | No | No |
| CYP3A4 substrate | Yes | Yes | |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor | Yes | Yes | |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor | Yes | Yes | |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor | Yes | Yes | |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor | No | No | |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | No | Yes | |
| Excretion | Total clearance | 0.083 | 0.106 |
| Renal OCT2 substrate | No | No | |
| Toxicity | AMES toxicity | No | No |
| Max. tolerated dose (human) | 0.346 | 0.464 | |
| hERG I inhibitor | No | No | |
| hERG II inhibitor | Yes | Yes | |
| Oral rat acute toxicity (LD50) | 2.480 | 2.539 | |
| Oral rat chronic toxicity (LOAEL) | 1.073 | 1.167 | |
| Hepatotoxicity | Yes | Yes | |
| Skin sensitization | No | No | |
| T. Pyriformis toxicity | 0.975 | 0.901 | |
| Minnow toxicity | 0.445 | 0.553 | |
| Complex | ΔG Binding | Coulomb | Covalent | H-bond | Lipo | Bind Packing | Solv_GB | VdW | St. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3a | −59.46 | −12.82 | 0.31 | −0.55 | −19.61 | −1.94 | 22.80 | −47.65 | 3.79 |
| 3i | −67.76 | −14.25 | 1.08 | −0.54 | −20.35 | −1.84 | 21.35 | −53.20 | 4.44 |
| 3q | −63.68 | −12.63 | 1.14 | −0.87 | −19.66 | −1.59 | 20.39 | −50.45 | 4.68 |
| Co | −79.82 | −27.70 | 2.61 | −2.22 | −27.51 | −0.56 | 40.97 | −65.40 | 5.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Damasy, A.K.; Kim, H.J.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A.; Alnajjar, R.; Khalifa, M.M.; Bang, E.-K.; Keum, G. Identification of Ureidocoumarin-Based Selective Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors via Drug Repurposing Approach, Biological Evaluation, and In Silico Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040427
El-Damasy AK, Kim HJ, Al-Karmalawy AA, Alnajjar R, Khalifa MM, Bang E-K, Keum G. Identification of Ureidocoumarin-Based Selective Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors via Drug Repurposing Approach, Biological Evaluation, and In Silico Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(4):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040427
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Damasy, Ashraf K., Hyun Ji Kim, Ahmed A. Al-Karmalawy, Radwan Alnajjar, Mohamed M. Khalifa, Eun-Kyoung Bang, and Gyochang Keum. 2024. "Identification of Ureidocoumarin-Based Selective Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors via Drug Repurposing Approach, Biological Evaluation, and In Silico Studies" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 4: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040427
APA StyleEl-Damasy, A. K., Kim, H. J., Al-Karmalawy, A. A., Alnajjar, R., Khalifa, M. M., Bang, E.-K., & Keum, G. (2024). Identification of Ureidocoumarin-Based Selective Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) Inhibitors via Drug Repurposing Approach, Biological Evaluation, and In Silico Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 17(4), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17040427








