Identification of Antagonistic Action of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1 by Computational Target Prediction Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
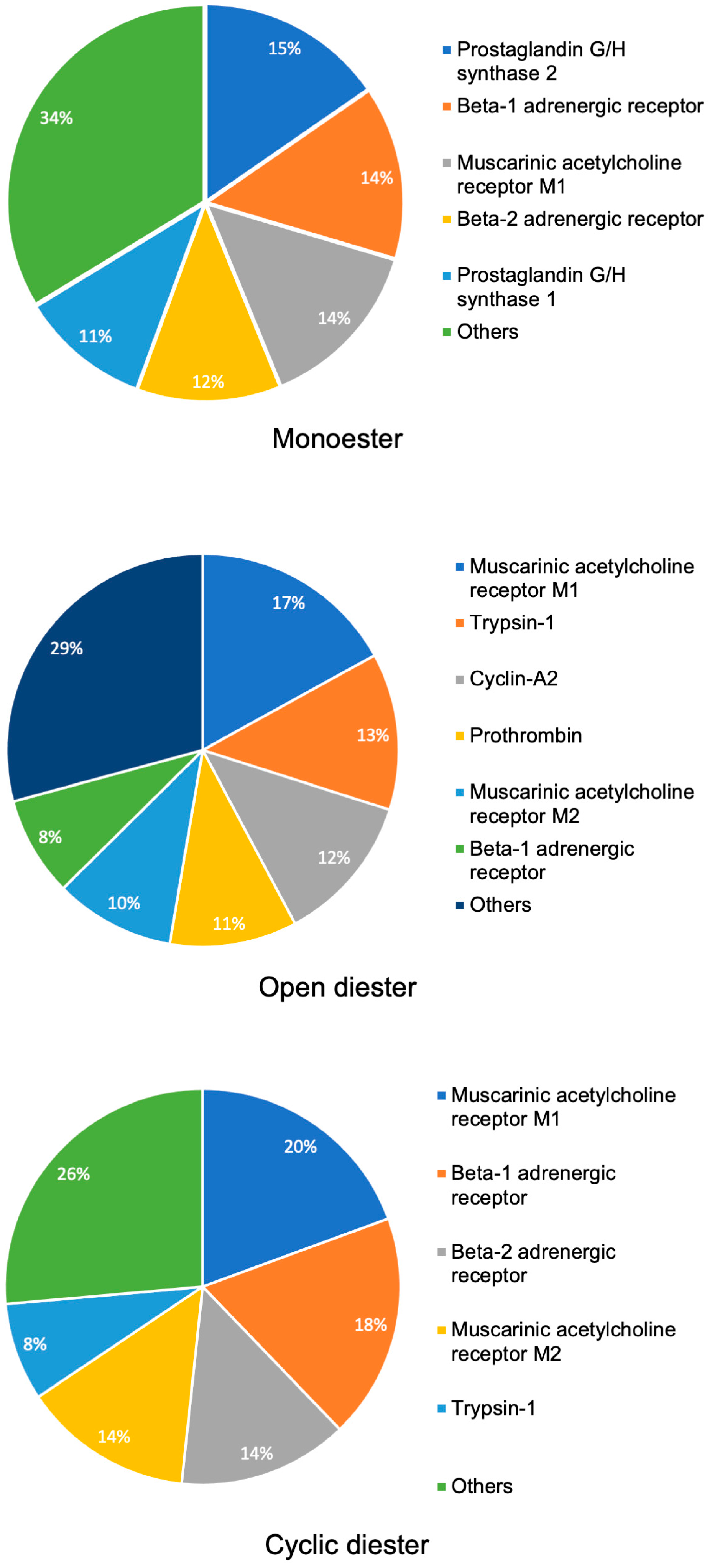
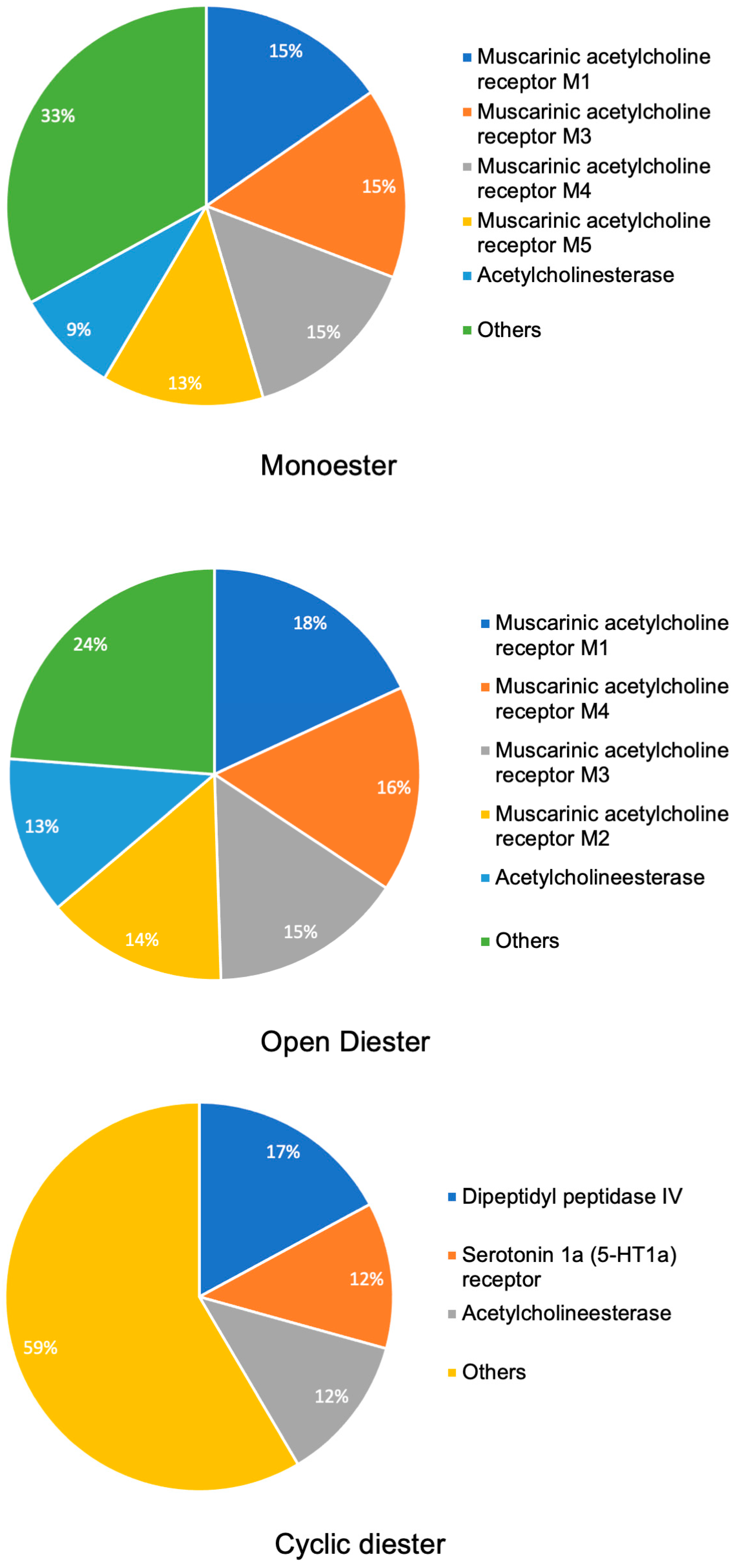
2.1. Target Prediction Analysis
2.2. Molecular Docking
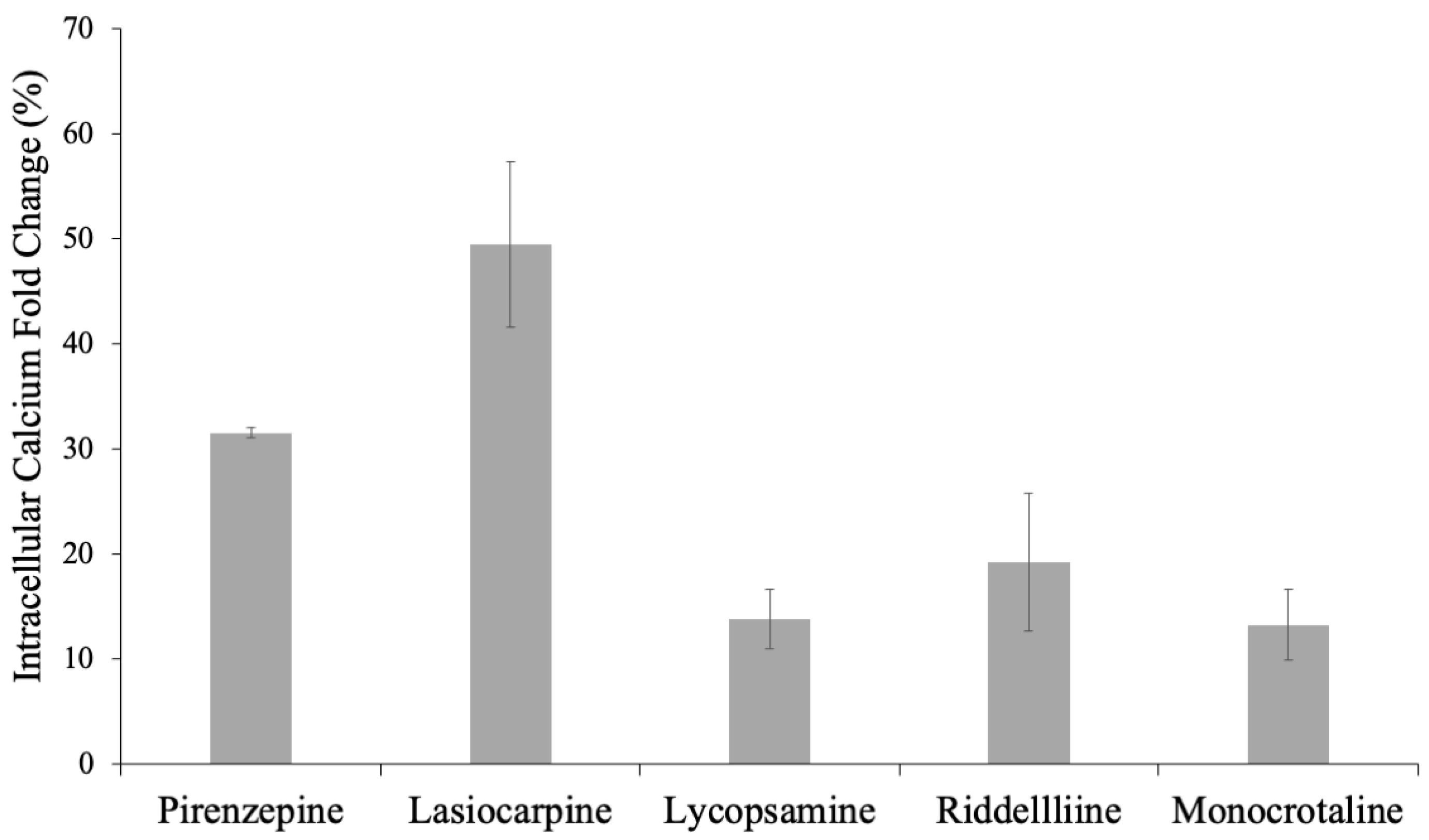
2.3. Determination of Agonistic or Antagonistic Functions by a Calcium Efflux Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
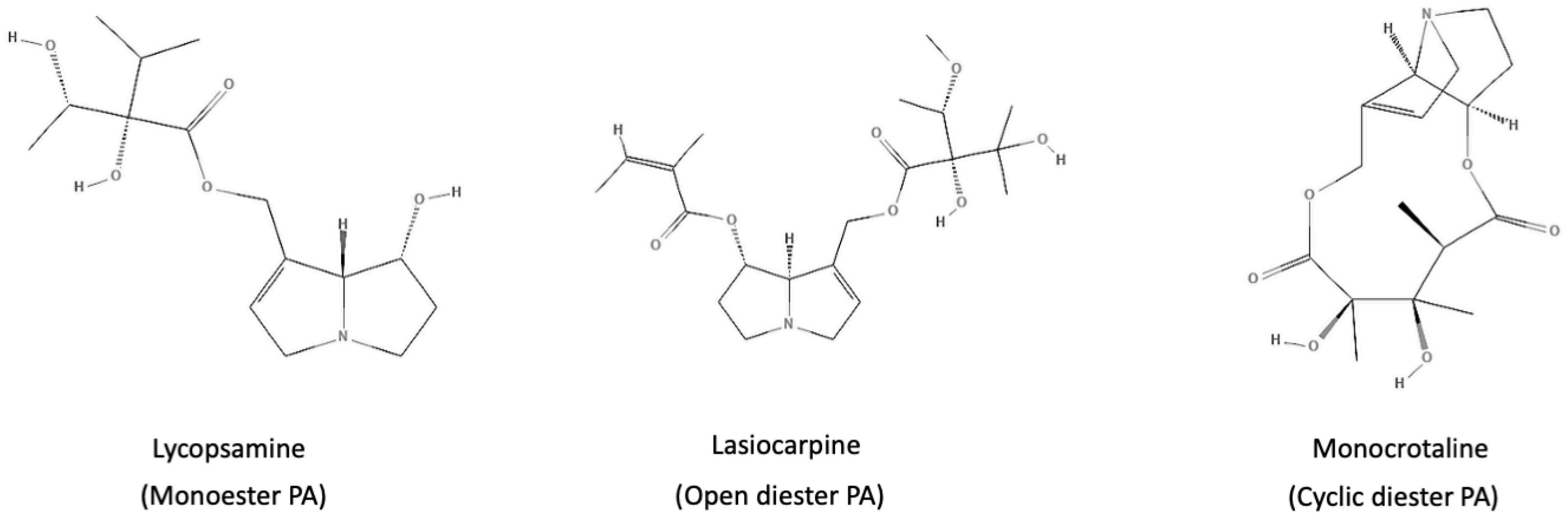
4.1. Collection of Chemical Structures and Classification of PAs
4.2. Target Prediction with ChemMapper
4.3. Target Prediction Using SwissTargetPrediction
4.4. Analysis of Target Prediction
4.5. Molecular Docking
4.6. Determination of Agonistic/Antagonistic Activity by Calcium Efflux Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Bodi, D.; Ronczka, S.; Gottschalk, C.; Behr, N.; Skibba, A.; Wagner, M.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M.; Preiss-Weigert, A.; These, A. Determination of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in tea, herbal drugs and honey. Food Addit. Contam.—Part. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2014, 31, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, M.; Meins, J.; Diemert, S.; Zagermann-Muncke, P.; Goebel, R.; Schrenk, D.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M.; Abdel-Tawab, M. Detection of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in German licensed herbal medicinal teas. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Toxic phytochemicals and their potential risks for human cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrenk, D.; Gao, L.; Lin, G.; Mahony, C.; Mulder, P.P.; Peijnenburg, A.; Pfuhler, S.; Rietjens, I.M.; Rutz, L.; Steinhoff, B.; et al. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in food and phytomedicine: Occurrence, exposure, toxicity, mechanisms, and risk assessment—A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.P.; Xia, Q.; Lin, G.; Chou, M.W. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids—Genotoxicity, Metabolism Enzymes, Metabolic Activation, and Mechanisms. Drug Metab. Rev. 2004, 36, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, T. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids between plants and insects: A new chapter of an old story. Chemoecology 1994, 5–6, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, T. Chemical ecology of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Planta 1999, 207, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, S.; Köhler, N.; Rozhon, W. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids: Biosynthesis, biological activities and occurrence in crop plants. Molecules 2019, 24, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, C.; Ronczka, S.; Preiß-Weigert, A.; Ostertag, J.; Klaffke, H.; Schafft, H.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in natural and experimental grass silages and implications for feed safety. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 207, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, J.; Waizenegger, J.; Braeuning, A.; Hessel-Pras, S. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids induce cell death in human heparg cells in a structure-dependent manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BfR, Opinion No. 018/2013 of 5 July 2013. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Herbal Teas and Teas. 2013, pp. 1–29. Available online: https://www.bfr.bund.de/cm/349/pyrrolizidine-alkaloids-in-herbal-teas-and-teas.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Mädge, I.; Cramer, L.; Rahaus, I.; Jerz, G.; Winterhalter, P.; Beuerle, T. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids in herbal teas for infants, pregnant or lactating women. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM); Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; et al. Risks for human health related to the presence of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in honey, tea, herbal infusions and food supplements. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, M.G.; Cohen, L.; Opris, M.; Nanau, R.M.; Jeong, H. Hepatotoxicity of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 18, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Naß, J.; Knorz, C.; Klauck, S.M.; Küpper, J.-H.; Efferth, T. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids cause cell cycle and DNA damage repair defects as analyzed by transcriptomics in cytochrome P450 3A4-overexpressing HepG2 clone 9 cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, 38, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.A.; Molyneux, R.J.; Colegate, S.M. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids: Potential Role in the Etiology of Cancers, Pulmonary Hypertension, Congenital Anomalies, and Liver Disease. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxtable, R.J.; Yan, C.C.; Wild, S.; Maxwell, S.; Cooper, R. Physicochemical and metabolic basis for the differing neurotoxicity of the pyrrolizidine alkaloids, trichodesmine and monocrotaline. Neurochem. Res. 1996, 21, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, D.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. Shaping the interaction landscape of bioactive molecules. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 3073–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Cai, C.; Liu, X.; Ku, X.; Jiang, H.; Gao, D.; Li, H. ChemMapper: A versatile web server for exploring pharmacology and chemical structure association based on molecular 3D similarity method. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1827–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gfeller, D.; Grosdidier, A.; Wirth, M.; Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: A web server for target prediction of bioactive small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwomoh, L.; Tejeda, G.S.; Tobin, A.B. Targeting the M1 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuronal Signal. 2022, 6, NS20210004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raies, A.B.; Bajic, V.B. In silico toxicology: Computational methods for the prediction of chemical toxicity. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2016, 6, 147–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.S.; Gupta, R.; Liguori, M.J.; Hu, M.; Huang, X.; Mantena, S.R.; Mittelstadt, S.W.; Blomme, E.A.G.; Van Vleet, T.R. Novel Computational Approach to Predict Off-Target Interactions for Small Molecules. Front. Big Data 2019, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerich, J.; Ecker, G.F. In silico toxicology: From structure–activity relationships towards deep learning and adverse outcome pathways. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2020, 10, e1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JECFA (Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives). Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants: Aflatoxins; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lohse, J.C.; Paredes, E.; González, C.M.; Koene, M.; Mageed, M. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid toxicosis and hepatic encephalopathy in horses in Easter Island, Chile. Austral J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 50, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitanga, B.P.S.; Nascimento, R.P.; Silva, V.D.A.; Costa, S.L. The role of astrocytes in metabolism and neurotoxicity of the pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline, the main toxin of Crotalaria retusa. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Berg, A.; Huang, Q.; Yang, L.J.; Hamdoun, S.; Klinger, A.; Greten, H.J.; Fleischer, E.; Berg, T.; Wong, V.K.; et al. MCC1019, a selective inhibitor of the Polo-box domain of Polo-like kinase 1 as novel, potent anticancer candidate. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckers, M.; Paul, N.W.; Efferth, T. Bisphenolic compounds alter gene expression in MCF-7 cells through interaction with estrogen receptor α. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 399, 115030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wess, J.; Eglen, R.M.; Gautam, D. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: Mutant mice provide new insights for drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A. M1 Muscarinic Agonists Target Major Hallmarks of Alzheimers Disease—An Update. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2007, 4, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannard, K. The acute treatment of nerve agent exposure. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 249, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RamaRao, G.; Bhattacharya, B.K. Multiple signal transduction pathways alterations during nerve agent toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Peijnenburg, A.; de Haan, L.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M. Prediction of in vivo genotoxicity of lasiocarpine and riddelliine in rat liver using a combined in vitro-physiologically based kinetic modelling-facilitated reverse dosimetry approach. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BfR Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung SN 030/2016. Aktualisierte Risikobewertung zu Gehalten an 1,2-ungesättigten Pyrrolizidinal-kaloiden (PA) in Lebensmitteln. BFR—Bundesinstitut Für Risikobewertung 2020, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wong, S.E.; Lightstone, F.C. Message passing interface and multithreading hybrid for parallel molecular docking of large databases on petascale high performance computing machines. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
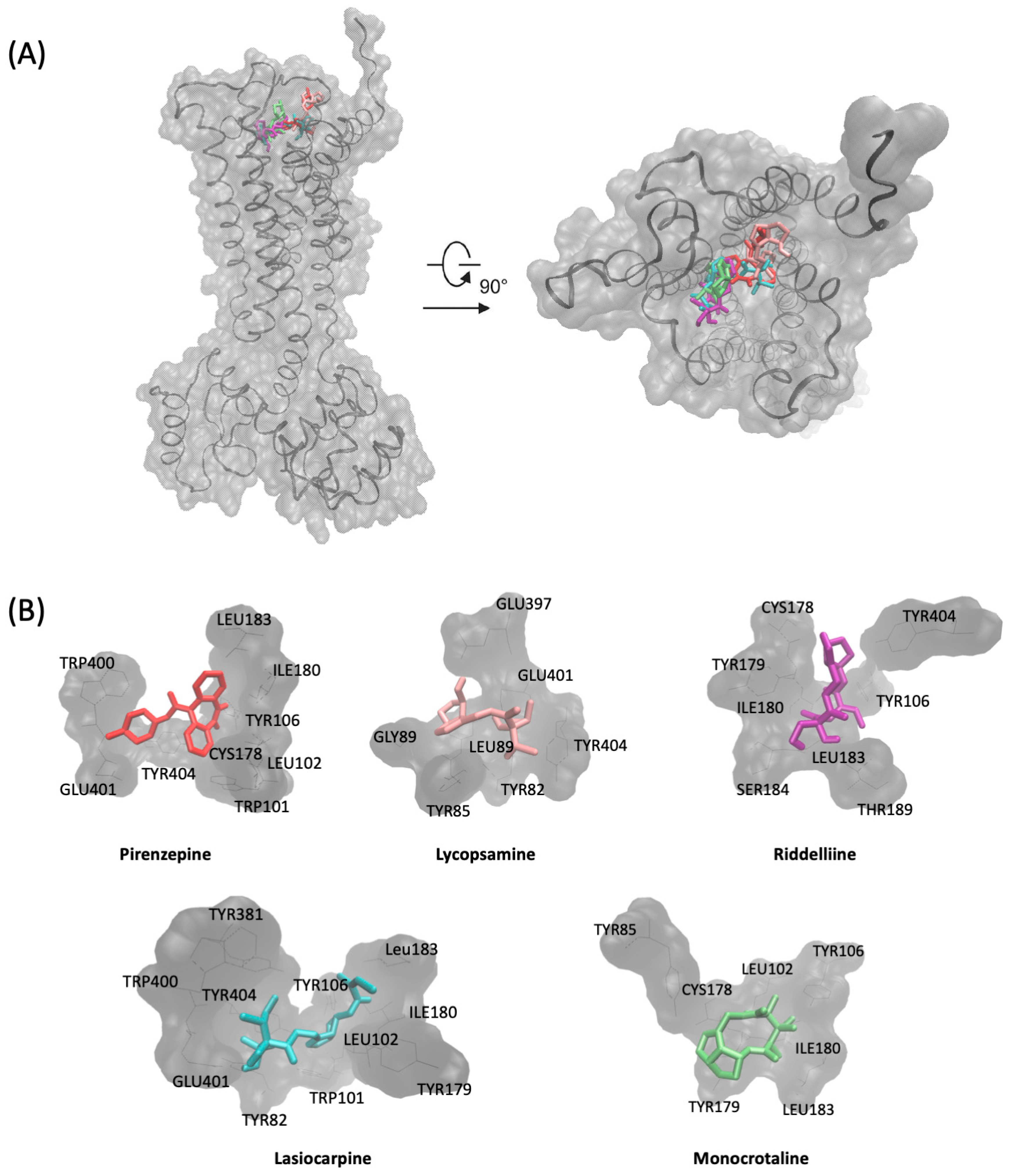
| Compound | Mean Binding Energy–VinaLC (kcal/mol) | pKi/nM | Amino Acids Involved in Interactions | Amino Acids Involved in H-Bonds |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pirenzepine | −7.42 (±0.32) | 2.74 × 103 (±0.09 × 103) | Trp101, Leu102, Tyr106, Cys178, Leu183, Trp400, Glu401, Tyr404 | |
| Heliotrine | −5.31 (±0.34) | 36.27 × 103 (±7.08 × 103) | Tyr82, Tyr85, Cys98, Trp101, Tyr106, Cys178, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Tyr381, Tyr404 | Tyr106, Cys178, Ile180 |
| Rinderine | −5.62 (±0.12) | 39.69 × 103 (±7.08 × 103) | Leu102, Tyr106, Cys178, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Thr189, Tyr381, Tyr404 | Ile180 (2), Tyr381 |
| Lycopsamine | −5.71 (±0.13) | 4.44 × 106) (±0.68 × 106) | Tyr82, Tyr85, Leu86, Gly89, Glu397, Glu401, Tyr404 | Tyr82, Glu397, Glu401 |
| Echimidine | −6.04 (±0.29) | 21.61 × 103 (±8.21 × 103) | Tyr82, Tyr85, Tyr106, Cys178, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Thr189, Trp400, Glu401, Tyr404 | Thr189, Glu401 |
| Lasiocarpine | −6.19 (±0.23) | 8.91 × 103 (±1.53 × 103) | Tyr82, Trp101, Leu102, Tyr106, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Tyr381, Trp400, Glu401, Tyr404 | Ile180, Glu401 |
| Echiumine | −6.06 (±0.19) | 16.99 × 103 (±2.51 × 103) | Tyr82, Tyr85, Tyr106, Cys178, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Thr189, Trp400, Glu401, Tyr404 | Tyr106 |
| Riddelliine | −7.17 (±0.42) | 4.67 × 103 (±0.04 × 103) | Tyr106, Cys178, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Ser184, Thr189, Tyr404 | Ile180, Leu183 |
| Senecionine | −7.36 (±0.42) | 8.44 × 103 (±0.0) | Trp101, Leu102, Tyr106, Cys178, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Thr189, Tyr404 | Tyr404 |
| Monocrotaline | −6.96 (±0.3) | 1.55 × 106 (±0.0) | Tyr85, Leu102, Tyr106, Cys178, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183 | Tyr106 |
| Casuarine | −5.06 (±0.18) | 9.84 × 106 (±0.66 × 106) | Tyr85, Leu86, Gly89, Gln177, Glu397, Glu401 | Leu86, Gln177, Glu397(2), Glu401 |
| Tussilagine | −5.16 (±0.7) | 3.67 × 106 (±0.04 × 106) | Tyr106, Tyr179, Ile180, Leu183, Thr189 | Ile180 |
| Crotanecine | −4.57 (±0.15) | 13.20 × 106 (±0.26 × 106) | Tyr85, Leu86, Gly89, Glu397, Glu401 | Glu397(2), Glu401 |
| Otonecine | −4.74 (±0.16) | 10.20 × 106 (±0.06 × 106) | Tyr82, Tyr85, Gln177, Cys178, Glu501, Tyr404 | Tyr85, Gln177, Glu501 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdalfattah, S.; Knorz, C.; Ayoobi, A.; Omer, E.A.; Rosellini, M.; Riedl, M.; Meesters, C.; Efferth, T. Identification of Antagonistic Action of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1 by Computational Target Prediction Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010080
Abdalfattah S, Knorz C, Ayoobi A, Omer EA, Rosellini M, Riedl M, Meesters C, Efferth T. Identification of Antagonistic Action of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1 by Computational Target Prediction Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(1):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010080
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdalfattah, Sara, Caroline Knorz, Akhtar Ayoobi, Ejlal A. Omer, Matteo Rosellini, Max Riedl, Christian Meesters, and Thomas Efferth. 2024. "Identification of Antagonistic Action of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1 by Computational Target Prediction Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 1: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010080
APA StyleAbdalfattah, S., Knorz, C., Ayoobi, A., Omer, E. A., Rosellini, M., Riedl, M., Meesters, C., & Efferth, T. (2024). Identification of Antagonistic Action of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids in Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor M1 by Computational Target Prediction Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 17(1), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17010080








