Neuroprotective Effects of Tryptanthrin-6-Oxime in a Rat Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BBB Permeability for TRYP-Ox (In Silico)
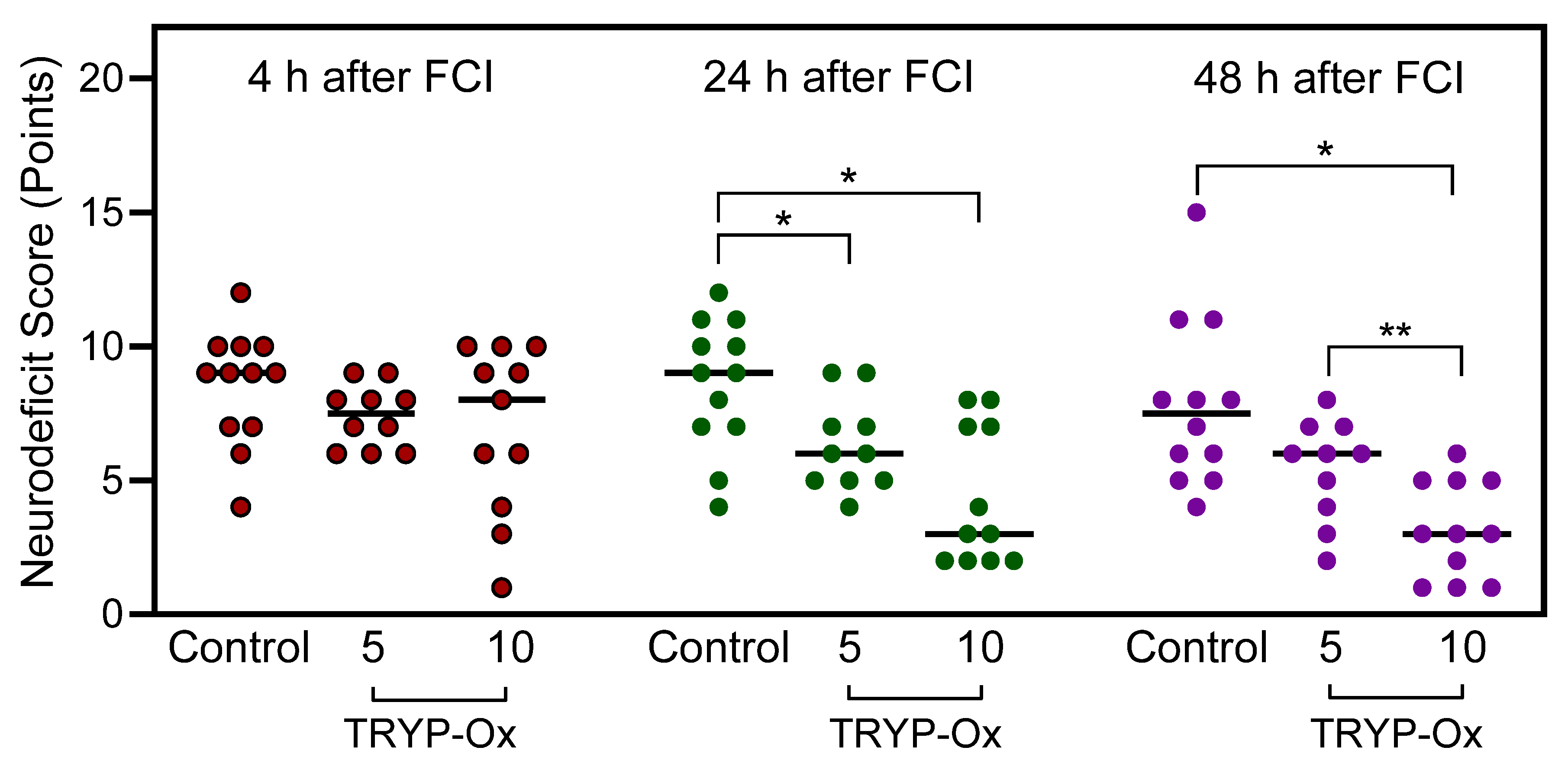
2.2. Effects of TRYP-Ox on Neurological Status
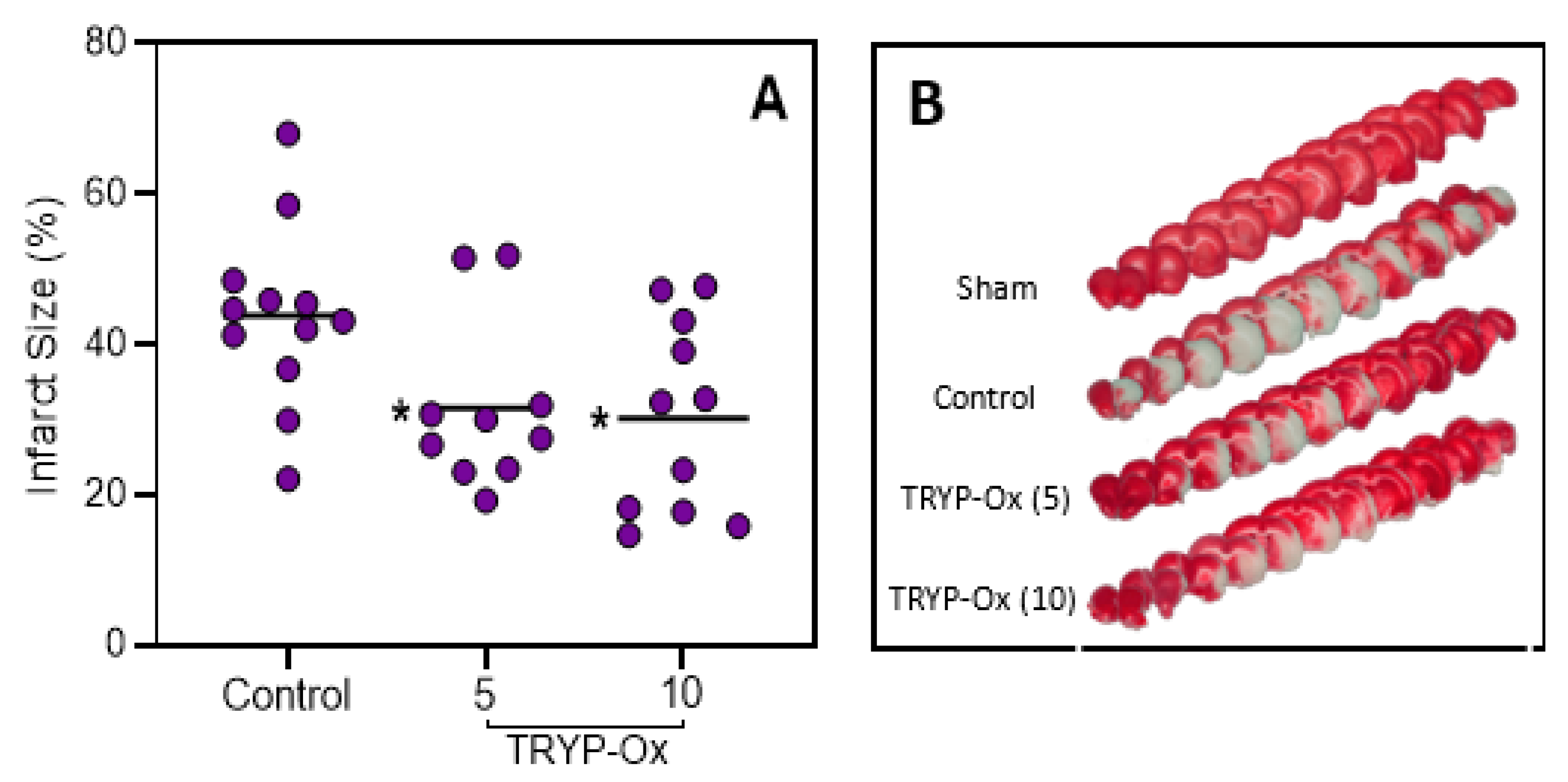
2.3. Effects of TRYP-Ox on Infarct Size
2.4. Effects of TRYP-Ox on Brain Edema
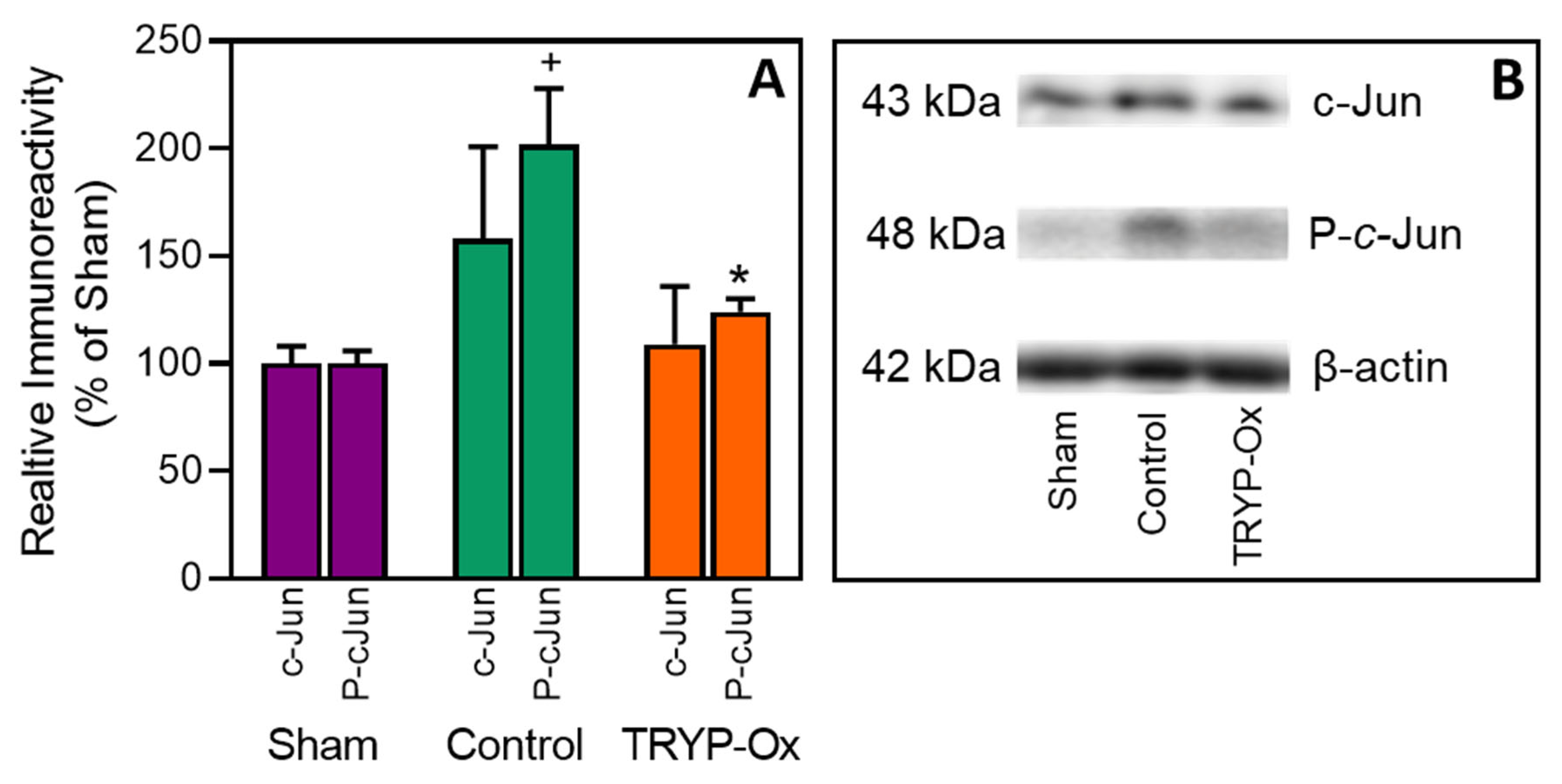
2.5. Effect of TRYP-Ox on JNK Activity
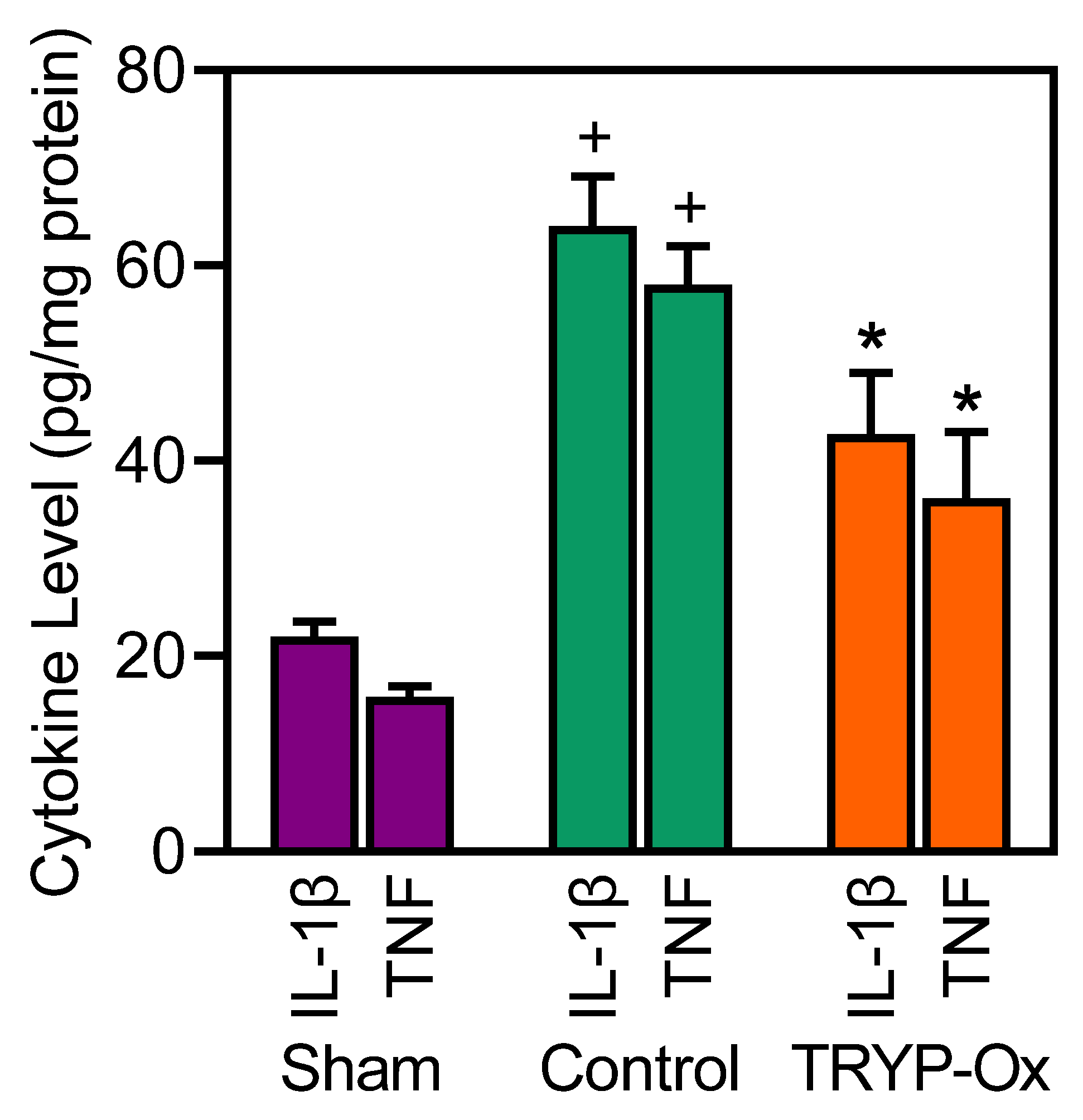
2.6. Effects of TRYP-Ox on the Levels of Cytokines in the Cortex
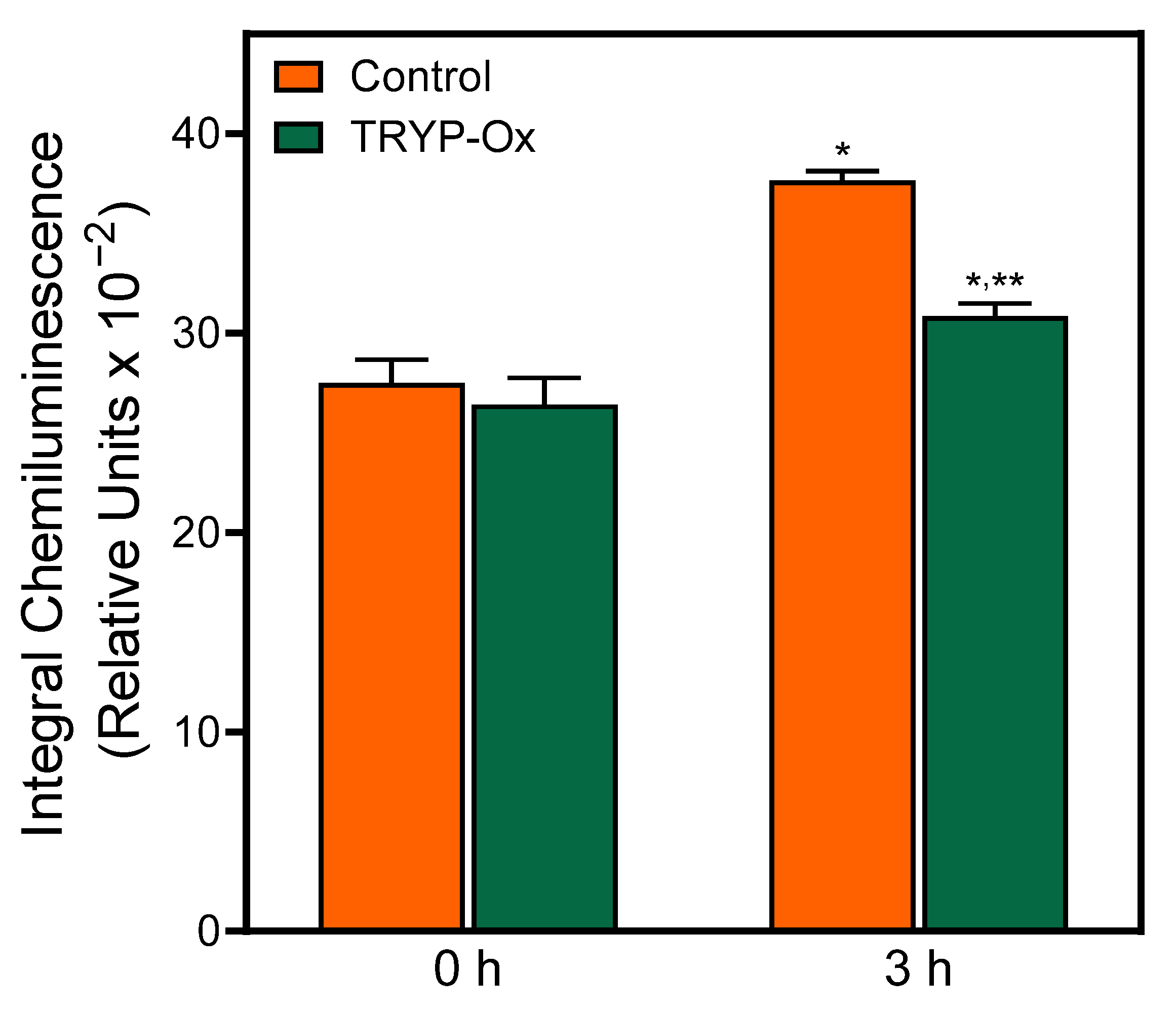
2.7. Antioxidant Effect of TRYP-Ox
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemicals, Drugs, and Kits
4.3. Compounds and Doses
4.4. Molecular Modeling
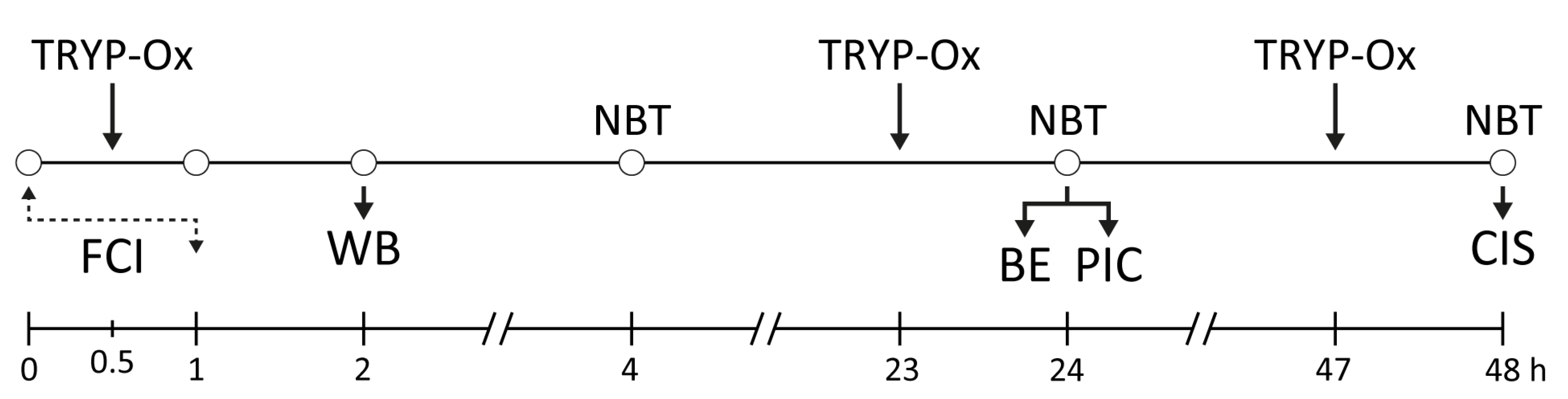
4.5. Experimental In Vivo Protocols
4.6. Experimental Ex Vivo Protocol
4.7. Transient FCI Model
4.8. Neurological Deficit Evaluation
4.9. Cerebral Infarct Size Assessment
4.10. Brain Edema Measurement
4.11. Analysis of IL-1β and TNF Levels in Brain
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Luengo-Fernandez, R.; Paul, N.L.; Gray, A.M.; Pendlebury, S.T.; Bull, L.M.; Welch, S.J.; Cuthbertson, F.C.; Rothwell, P.M.; Oxford Vascular, S. Population-based study of disability and institutionalization after transient ischemic attack and stroke: 10-year results of the Oxford Vascular Study. Stroke 2013, 44, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, E146–E603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanese, L.; Tarsia, J.; Fisher, M. Acute Ischemic Stroke Therapy Overview. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriakose, D.; Xiao, Z.C. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Stroke: Present Status and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Q.Z.; Zhang, S.T.; Lei, P. Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 259–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, M.; Gerner, S.T.; Bähr, M.; Doeppner, T.R. Neuroprotective Strategies for Ischemic Stroke-Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 54334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, A.A.; Couch, Y.; Hadley, G.; Buchan, A.M. Neuroprotection in stroke: The importance of collaboration and reproducibility. Brain 2017, 140, 2079–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.N.; Wang, L.P.; Sun, L.Y.; Dong, J.H. Neuroprotective effect of magnesium supplementation on cerebral ischemic diseases. Life Sci. 2021, 272, 119257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, E.; Chen, F.; Xiao, J.B.; Wang, M.F. Neuroprotective phytochemicals in experimental ischemic stroke: Mechanisms and potential clinical applications. Oxidative Med. Cell. Long. 2021, 2021, 6687386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyden, P.; Buchan, A.; Boltze, J.; Fisher, M.; Consortium, S.X. Top priorities for cerebroprotective studies-a paradigm shift report from STAIR XI. Stroke 2021, 52, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogalewski, A.; Schneider, A.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Schabitz, W.R. Toward a multimodal neuroprotective treatment of stroke. Stroke 2006, 37, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M. New approaches to neuroprotective drug development. Stroke 2011, 42, S24–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secades, J.J.; Alvarez-Sabin, J.; Castillo, J.; Diez-Tejedor, E.; Martinez-Vila, E.; Rios, J.; Oudovenko, N. Citicoline for acute ischemic stroke: A systematic review and formal meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trials. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1984–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, A.; Lo, E.H.; Renu, A.; van Leyen, K.; Lyden, P.D. The future of neuroprotection in stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajah, G.B.; Ding, Y. Experimental neuroprotection in ischemic stroke: A concise review. Neurosurg. Focus. 2017, 42, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Sakai, K.; Sasaki, C.; Zhang, W.R.; Warita, H.; Abe, K. c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and JNK interacting protein response in rat brain after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 284, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, E.A.; Bamford, M. Role of mitogen- and stress-activated kinases in ischemic injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2002, 22, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Friguls, B.; Dalfo, E.; Planas, A.M. Early modifications in the expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/ERK), stress-activated kinases SAPK/JNK and p38, and their phosphorylated substrates following focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 105, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsello, T.; Clarke, P.G.; Hirt, L.; Vercelli, A.; Repici, M.; Schorderet, D.F.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Bonny, C. A peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase protects against excitotoxicity and cerebral ischemia. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1180–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, G.X.; Pei, D.S.; Guan, Q.H.; Zhang, G.Y. Activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 3 is mediated by the GluR6 center dot PSD-95 center dot MLK3 signaling module following cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2005, 1061, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atochin, D.N.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Seledtsov, V.I.; Swanson, H.; Quinn, M.T.; Huang, P.L. A novel dual NO-donating oxime and c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 618, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.M.; Badruddeen; Mujahid, M.; Akhtar, J.; Khan, M.I.; Ahmad, U. An overview of stroke: Mechanism in vivo experimental models thereof, and neuroprotective agents. Curr. Protein Pept. Sc. 2020, 21, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Han, Z.P.; Zhao, H.P.; Luo, Y.M. MAPK: A Key Player in the development and progression of stroke. CNS Neurol. Disord-Dr. 2020, 19, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, S.; Hiver, A.; Szyndralewiez, C.; Gaillard, P.; Gotteland, J.P.; Vitte, P.A. AS601245 (1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl(2-{[2-(3-pyridinyl)ethyl]amino}-4 pyrimidinyl) acetonitrile): A c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase inhibitor with neuroprotective properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Signore, A.P.; Yin, W.; Cao, G.; Yin, X.M.; Sun, F.; Luo, Y.; Graham, S.H.; Chen, J. Neuroprotection against focal ischemic brain injury by inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and attenuation of the mitochondrial apoptosis-signaling pathway. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2005, 25, 694–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.H.; Pei, D.S.; Liu, X.M.; Wang, X.T.; Xu, T.L.; Zhang, G.Y. Neuroprotection against ischemic brain injury by SP600125 via suppressing the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of apoptosis. Brain Res. 2006, 1092, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedova, M.; Anfinogenova, Y.; Atochina-Vasserman, E.N.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Atochin, D.N. c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) in myocardial and cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeldt, S.C.H.; Laufer, S.; Goettert, M.I. A Highly selective in vitro JNK3 inhibitor, FMU200, restores mitochondrial membrane potential and reduces oxidative stress and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Aliev, O.I.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Smol’yakova, V.I.; Osipenko, A.N.; Plotnikov, M.B.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Plotnikov, E.V.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of the lithium salt of a novel JNK inhibitor in an animal model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 92119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, M.B.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Smolyakova, V.I.; Aliev, O.I.; Trofimova, E.S.; Sherstoboev, E.Y.; Osipenko, A.N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Anfinogenova, Y.J.; Schepetkin, I.A.; et al. neuroprotective effects of a novel inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Cells 2020, 9, 81860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, M.B.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Aliev, O.I.; Smol’iakova, V.I.; Fomina, T.I.; Osipenko, A.N.; Rydchenko, V.S.; Anfinogenova, Y.J.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Schepetkin, I.A.; et al. Protective effects of a new c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor in the model of global cerebral ischemia in rats. Molecules 2019, 24, 91722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouns, R.; De Deyn, P.P. The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamorro, A.; Dirnagl, U.; Urra, X.; Planas, A.M. Neuroprotection in acute stroke: Targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; He, Y.; Chen, S.; Qi, S.; Shen, J. Therapeutic targets of oxidative/nitrosative stress and neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke: Applications for natural product efficacy with omics and systemic biology. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anrather, J.; Iadecola, C. Inflammation and Stroke: An Overview. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 335, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Manjal, S.K.; Rawal, R.K.; Kumar, K. Recent synthetic and medicinal perspectives of tryptanthrin. Bioorgan Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 4533–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpotina, L.N.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Hammaker, D.; Kuhs, A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Quinn, M.T. Therapeutic effects of tryptanthrin and tryptanthrin-6-oxime in models of rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahne, E.A.; Eigenmann, D.E.; Sampath, C.; Butterweck, V.; Culot, M.; Cecchelli, R.; Gosselet, F.; Walter, F.R.; Deli, M.A.; Smiesko, M.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and in vitro blood-brain barrier screening of the plant-derived alkaloid tryptanthrin. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Potapov, A.S.; Kovrizhina, A.R.; Matveevskaya, V.V.; Belyanin, M.L.; Atochin, D.N.; Zanoza, S.O.; Gaidarzhy, N.M.; Lyakhov, S.A.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular modeling of 11H-indeno[1,2-b]quinoxalin-11-one derivatives and tryptanthrin-6-oxime as c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenderhauf, C.; Hammann, F.; Huwyler, J. Computational Prediction of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Using Decision Tree Induction. Molecules 2012, 17, 10429–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissi, E.A.; Caceres, T.; Videla, L.A. Visible chemiluminescence from rat brain homogenates undergoing autoxidation. I. Effect of additives and products accumulation. J. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1986, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamo, A.M.; Llesuy, S.F.; Pasquini, J.M.; Boveris, A. Brain chemiluminescence and oxidative stress in hyperthyroid rats. Biochem. J. 1989, 263, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Kogure, K.; Sugioka, K.; Nakano, M. Importance of two iron-reducing systems in lipid peroxidation of rat brain: Implications for oxygen toxicity in the central nervous system. Biochem. Int. 1987, 14, 741–749. [Google Scholar]
- Azorin, I.; Bella, M.C.; Iborra, F.J.; Fornas, E.; Renau-Piqueras, J. Effect of tert-butyl hydroperoxide addition on spontaneous chemiluminescence in brain. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontella, F.U.; Gassen, E.; Pulrolnik, V.; Wannmacher, C.M.; Klein, A.B.; Wajner, M.; Dutra-Filho, C.S. Stimulation of lipid peroxidation in vitro in rat brain by the metabolites accumulating in maple syrup urine disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 2002, 17, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgaravatti, A.M.; Magnusson, A.S.; Oliveira, A.S.; Mescka, C.P.; Zanin, F.; Sgarbi, M.B.; Pederzolli, C.D.; Wyse, A.T.; Wannmacher, C.M.; Wajner, M.; et al. Effects of 1,4-butanediol administration on oxidative stress in rat brain: Study of the neurotoxicity of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in vivo. Metab. Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.Y.; Schulien, A.J.; Molyneaux, B.J.; Aizenman, E. Lessons from recent advances in ischemic stroke management and targeting Kv2.1 for neuroprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roleira, F.M.F.; Siquet, C.; Orru, E.; Garrido, E.M.; Garrido, J.; Milhazes, N.; Podda, G.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Reis, S.; Carvalho, R.A.; et al. Lipophilic phenolic antioxidants: Correlation between antioxidant profile, partition coefficients and redox properties. Bioorgan Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5816–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.; Dave, K.M.; Stetler, R.A.; Manickam, D.S. Targeting the blood-brain barrier for the delivery of stroke therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Wu, C.J.; Dornbos, D.; Li, S.J.; Song, H.Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Ding, Y.C.; Ji, X.M. Multiphase adjuvant neuroprotection: A novel paradigm for improving acute ischemic stroke outcomes. Brain Circ. 2020, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senda, D.M.; Franzin, S.; Mori, M.A.; de Oliveira, R.M.W.; Milani, H. Acute, post-ischemic sensorimotor deficits correlate positively with infarct size but fail to predict its occurrence and magnitude after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 216, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.S.; Sayeed, I.; Cale, H.A.; Morrison, K.C.; Boatright, J.H.; Pardue, M.T.; Stein, D.G. Severity of middle cerebral artery occlusion determines retinal deficits in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 254, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreihofer, D.A.; Do, K.D.; Schreihofer, A.M. High-soy diet decreases infarct size after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in female rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Reg. 2005, 289, R103–R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, F.; Allix, M.; Plotkine, M.; Boulu, R.G. Neurological and Behavioral Outcomes of Focal Cerebral-Ischemia in Rats. Stroke 1992, 23, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reglodi, D.; Tamas, A.; Lengvari, I. Examination of sensorimotor performance following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 59, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Xue, X.J.; Zhao, J.; Qian, C.X.; Guo, Z.J.; Ito, Y.; Sun, W.J. Diosgenin attenuates the brain injury induced by transient focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Steroids 2016, 113, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legos, J.J.; Erhardt, J.A.; White, R.F.; Lenhard, S.C.; Chandra, S.; Parsons, A.A.; Tuma, R.F.; Barone, F.C. SB 239063, a novel p38 inhibitor, attenuates early neuronal injury following ischemia. Brain Res 2001, 892, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyko, M.; Ohayon, S.; Goldsmith, T.; Novack, L.; Novack, V.; Perry, Z.H.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Gruenbaum, S.E.; Steiner, O.; Shapira, Y.; et al. Morphological and neuro-behavioral parallels in the rat model of stroke. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 223, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, C.Y.; Burke, R.E. Targeting the JNK signaling pathway for stroke and Parkinson’s diseases therapy. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2005, 4, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.L.; Manhas, N.; Raghubir, R. Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 54, 34–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brecht, S.; Kirchhof, R.; Chromik, A.; Willesen, M.; Nicolaus, T.; Raivich, G.; Wessig, J.; Waetzig, V.; Goetz, M.; Claussen, M.; et al. Specific pathophysiological functions of JNK isoforms in the brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Barrett, T.; Whitmarsh, A.J.; Cavanagh, J.; Sluss, H.K.; Derijard, B.; Davis, R.J. Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2760–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Nishina, H. Diverse roles of JNK and MKK pathways in the brain. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 459265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, C.Y.; Whitmarsh, A.J.; Yang, D.D.; Liao, G.H.; Schloemer, A.J.; Dong, C.; Bao, J.; Banasiak, K.J.; Haddad, G.G.; Flavell, R.A.; et al. A critical role of neural-specific JNK3 for ischemic apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15184–15189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Hanks, T.S.; Kochetkova, I.; Pascual, D.W.; Jutila, M.A.; Quinn, M.T. Identification and characterization of a novel class of c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 81, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhang, G.Y. The neuroprotective effects of K252a through inhibiting MLK3/MKK7/JNK3 signaling pathway on ischemic brain injury in rat hippocampal CA1 region. Neuroscience 2005, 131, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carboni, S.; Boschert, U.; Gaillard, P.; Gotteland, J.P.; Gillon, J.Y.; Vitte, P.A. AS601245, a c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor, reduces axon/dendrite damage and cognitive deficits after global cerebral ischaemia in gerbils. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenitsky, V.P.; Delgado, M.; Nadolny, L.; Sahasrabudhe, K.; Ayala, L.; Clareen, S.S.; Hilgraf, R.; Albers, R.; Kois, A.; Hughes, K.; et al. Aminopurine based JNK inhibitors for the prevention of ischemia reperfusion injury. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehringer, M.; Muth, F.; Koch, P.; Laufer, S.A. c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors: A patent review (2010–2014). Expert. Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.; Gehringer, M.; Laufer, S.A. Inhibitors of c-Jun N-terminal kinases: An update. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 72–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginet, V.; Puyal, J.; Magnin, G.; Clarke, P.G.H.; Truttmann, A.C. Limited role of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway in a neonatal rat model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Sarmah, D.; Mounica, L.; Kaur, H.; Kesharwani, R.; Verma, G.; Veeresh, P.; Kotian, V.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; et al. Cell death pathways in ischemic stroke and targeted pharmacotherapy. Trans. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 1185–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Chen, W.W.; Zhou, Y.M.; Tian, Y.T.; Liao, F. Xanthotoxol Exerts Neuroprotective Effects Via Suppression of the inflammatory response in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 33, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammouda, M.B.; Ford, A.E.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.Y. The JNK signaling pathway in inflammatory skin disorders and cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raivich, G.; Behrens, A. Role of the AP-1 transcription factor c-Jun in developing, adult and injured brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 78, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, D.; Buendia, I.; Lanquetin, A.; Glavan, M.; Vivien, D.; Rubio, M. Filling the gaps on stroke research: Focus on inflammation and immunity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeter, M.; Kury, P.; Jander, S. Inflammatory gene expression in focal cortical brain ischemia: Differences between rats and mice. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 117, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Liu, M.Z.; Chen, M.Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, T.T.; Jiang, Y.X.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.H. Natural medicine in neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: Challenges and prospective. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 216, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaill, I.; Plotkine, M.; Lerouet, D. Antioxidant strategies in the treatment of stroke. Free Radic. Bio Med. 2005, 39, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Shuaib, A. Neuroprotective effects of free radical scavengers in stroke. Drug Aging 2007, 24, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilgun-Sherki, Y.; Melamed, E.; Offen, D. Oxidative stress induced-neurodegenerative diseases: The need for antioxidants that penetrate the blood brain barrier. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.R.; Ashwood, T. Free radical trapping as a therapeutic approach to neuroprotection in stroke: Experimental and clinical studies with NXY-059 and free radical scavengers. CNS Neurol. Disord-Dr. 2005, 4, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, M.; Endo, A.; Yatsushige, H.; Fushimi, K.; Otomo, Y. Clinical effects of early edaravone use in acute ischemic stroke patients treated by endovascular reperfusion therapy. Stroke 2019, 50, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slemmer, J.E.; Shacka, J.J.; Sweeney, M.I.; Weber, J.T. Antioxidants and free radical scavengers for the treatment of stroke, traumatic brain injury and aging. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gu, J.; Wu, P.F.; Wang, F.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, Y.J.; Wu, W.N.; Dong, L.D.; Chen, J.G. Protection by tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside against cerebral ischemia: Involvement of JNK, SIRT1, and NF-kappa B pathways and inhibition of intracellular ROS/RNS generation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.; Han, L.; Ambrogini, E.; Weinstein, R.S.; Manolagas, S.C. Glucocorticoids and tumor necrosis factor α increase oxidative stress and suppress wnt protein signaling in osteoblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44326–44335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waetzig, V.; Herdegen, T. A single c-Jun N-terminal kinase isoform (JNK3-p54) is an effector in both neuronal differentiation and cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Tian, H.; Li, H.C.; Zhang, G.Y. Antioxidant N-acetylcysteine inhibits the activation of JNK3 mediated by the GluR6-PSD95-MLK3 signaling module during cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 408, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Hao, L.Y.; Guan, Q.H.; Gu, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.Y. Neuroprotection of ethanol against ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury through decreasing c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 (JNK3) activation by enhancing GABA release. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 1125–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.M.; Prasanna, P.; Seshua, K.V.A.; Renuka, B.; Rao, C.V.L.; Kumar, G.S.; Narasimhulu, C.P.; Babu, P.A.; Puranik, R.C.; Subramanyam, D.; et al. Novel indolo[2,1-b]quinazoline analogues as cytostatic agents: Synthesis, biological evaluation and structure-activity relationship. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 2303–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.; Feuerstein, G.; Howells, D.W.; Hurn, P.D.; Kent, T.A.; Savitz, S.I.; Lo, E.H.; Grp, S. Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable preclinical recommendations. Stroke 2009, 40, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic. Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Crippen, G.M. Atomic physicochemical parameters for 3-dimensional-structure-directed quantitative structure-activity-relationships. 2. Modeling dispersive and hydrophobic interactions. J. Chem. Inf. Comp. Sci. 1987, 27, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertl, P.; Rohde, B.; Selzer, P. Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment-based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral-artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Alfieri, A.; Allan, S.M.; Carswell, H.V.; Deuchar, G.A.; Farr, T.D.; Flecknell, P.; Gallagher, L.; Gibson, C.L.; Haley, M.J.; et al. The IMPROVE guidelines (ischaemia models: Procedural refinements of in vivo experiments). J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2017, 37, 3488–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, D.; Lu, M.; Chopp, M. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, B.; Brint, S.; Tanabe, J.; Jacewicz, M.; Wang, X.J.; Pulsinelli, W. Temporal thresholds for neocortical infarction in rats subjected to reversible focal cerebral-ischemia. Stroke 1991, 22, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuts, R.; Frank, D.; Gruenbaum, B.F.; Grinshpun, J.; Melamed, I.; Knyazer, B.; Tarabrin, O.; Zvenigorodsky, V.; Shelef, I.; Zlotnik, A.; et al. A novel method for assessing cerebral edema, infarcted zone and blood-brain barrier breakdown in a single post-stroke rodent brain. Front. Neurosci-Switz. 2019, 13, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Schallert, T.; Keep, R.F.; Wu, J.; Hoff, J.T.; Xi, G. Behavioral tests after intracerebral hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke 2002, 33, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Brain water content. A misunderstood measurement? Transl. Stroke Res. 2012, 3, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Brain Hemisphere | Sham-Operated | FCI Control | TRYP-Ox | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left Hemisphere | Total | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 4.4 ± 0.1 * | 3.9 ± 0.1 *+ |
| Supraventricular part | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 0.1 * | 4.1 ± 0.1 *+ | |
| Subventricular part | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 * | 3.6 ± 0.1 * | |
| Right Hemisphere | Total | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 3.5 ± 0.1 |
| Supraventricular part | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | |
| Subventricular part | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 3.4 ± 0.1 * | 3.4 ± 0.1 * | |
| Cerebellum | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 3.4 ± 0.04 | 3.4 ± 0.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plotnikov, M.B.; Chernysheva, G.A.; Smol’yakova, V.I.; Aliev, O.I.; Anishchenko, A.M.; Ulyakhina, O.A.; Trofimova, E.S.; Ligacheva, A.A.; Anfinogenova, N.D.; Osipenko, A.N.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Tryptanthrin-6-Oxime in a Rat Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081057
Plotnikov MB, Chernysheva GA, Smol’yakova VI, Aliev OI, Anishchenko AM, Ulyakhina OA, Trofimova ES, Ligacheva AA, Anfinogenova ND, Osipenko AN, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Tryptanthrin-6-Oxime in a Rat Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081057
Chicago/Turabian StylePlotnikov, Mark B., Galina A. Chernysheva, Vera I. Smol’yakova, Oleg I. Aliev, Anna M. Anishchenko, Olga A. Ulyakhina, Eugene S. Trofimova, Anastasia A. Ligacheva, Nina D. Anfinogenova, Anton N. Osipenko, and et al. 2023. "Neuroprotective Effects of Tryptanthrin-6-Oxime in a Rat Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081057
APA StylePlotnikov, M. B., Chernysheva, G. A., Smol’yakova, V. I., Aliev, O. I., Anishchenko, A. M., Ulyakhina, O. A., Trofimova, E. S., Ligacheva, A. A., Anfinogenova, N. D., Osipenko, A. N., Kovrizhina, A. R., Khlebnikov, A. I., Schepetkin, I. A., Drozd, A. G., Plotnikov, E. V., Atochin, D. N., & Quinn, M. T. (2023). Neuroprotective Effects of Tryptanthrin-6-Oxime in a Rat Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081057












