Repurposing Synthetic Congeners of a Natural Product Aurone Unveils a Lead Antitumor Agent Inhibiting Folded P-Loop Conformation of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Rational of Profiling a Focused Library of Sulfuretin-Congeners as Anticancer Agents
2.2. Profiling of Sulfuretin and Its Congeners for Antiproliferative Activities
2.2.1. Blood Cancers
2.2.2. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
2.2.3. Colorectal Cancer
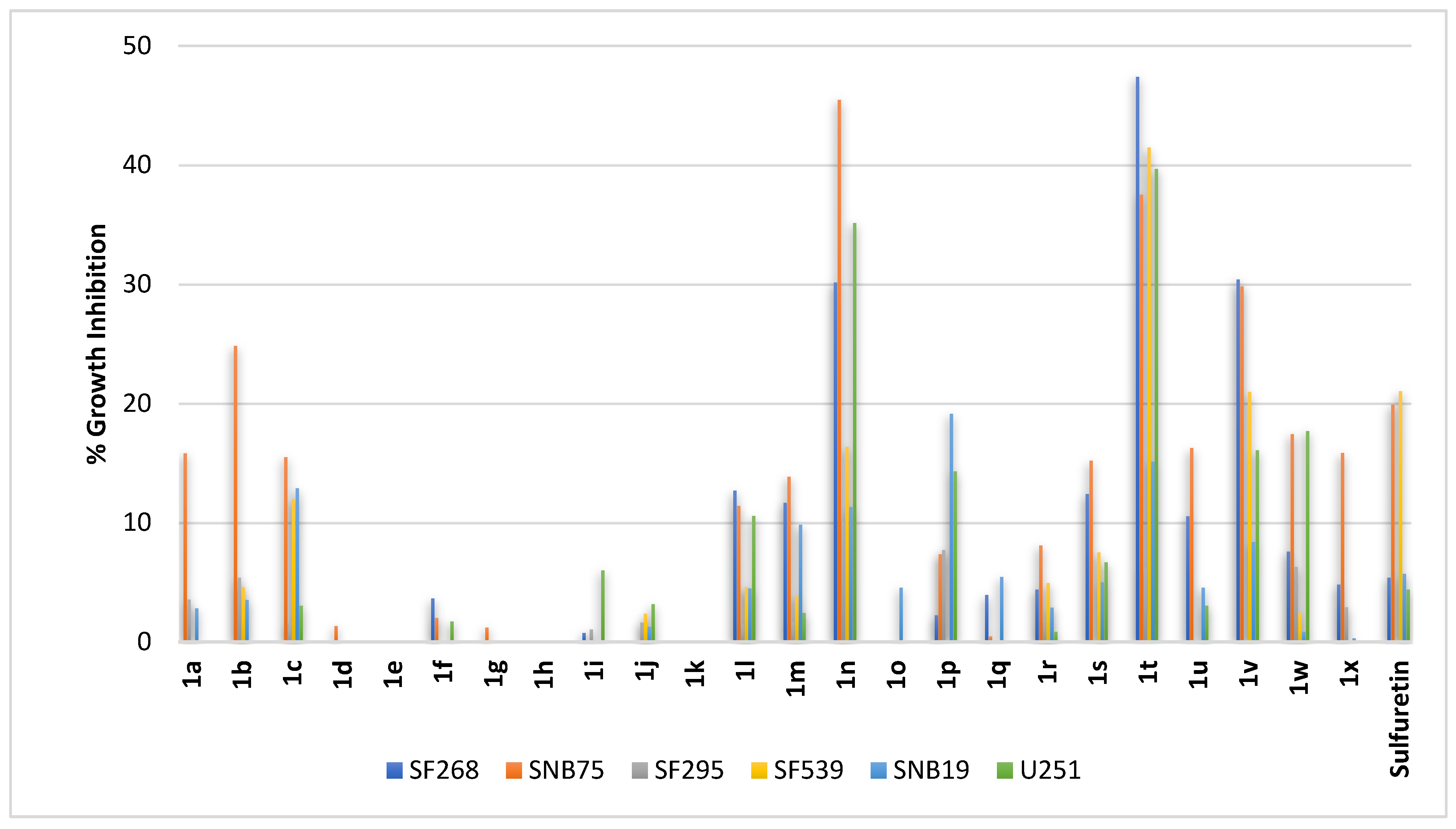
2.2.4. Brain Cancer
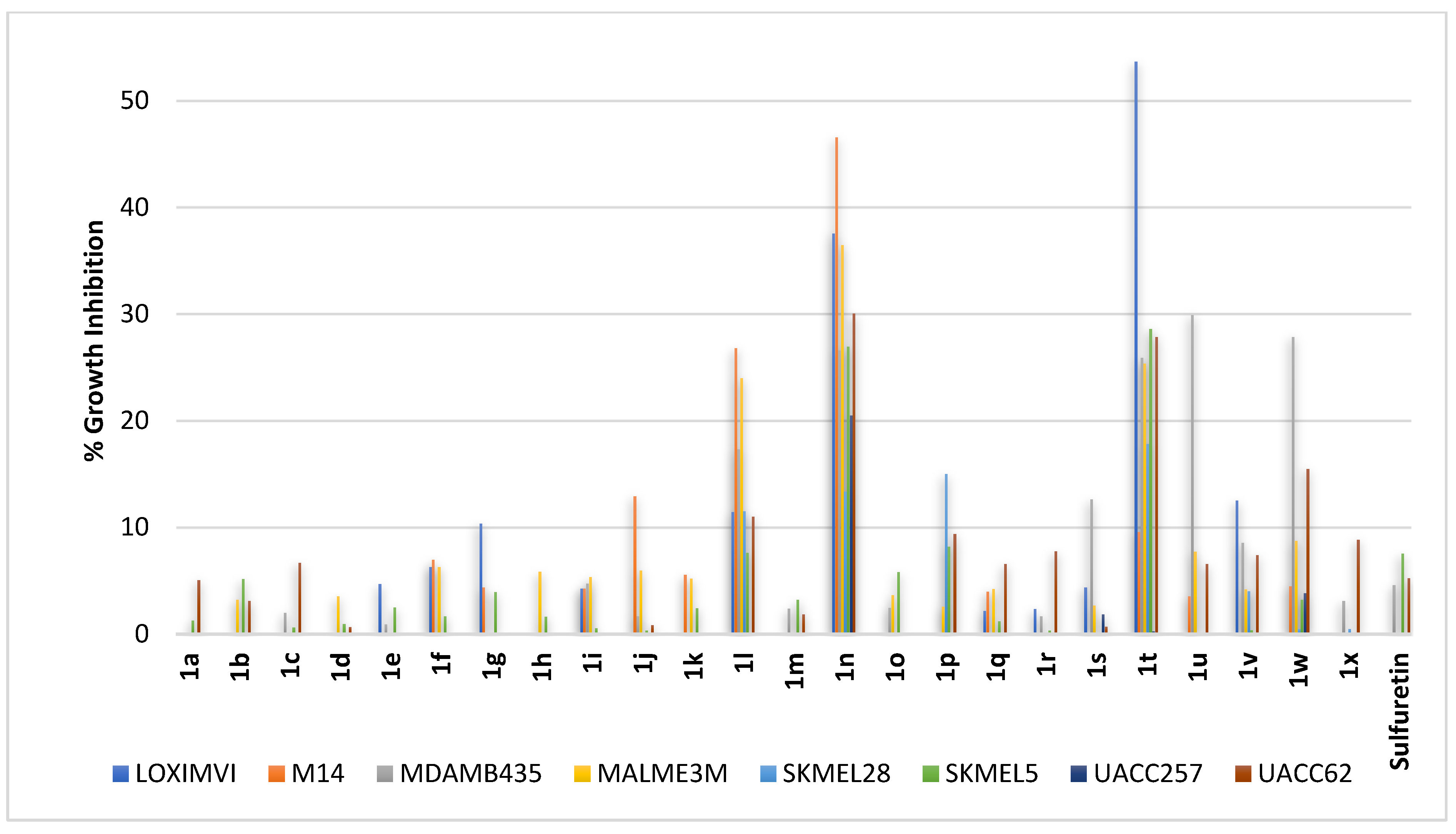
2.2.5. Skin Cancer
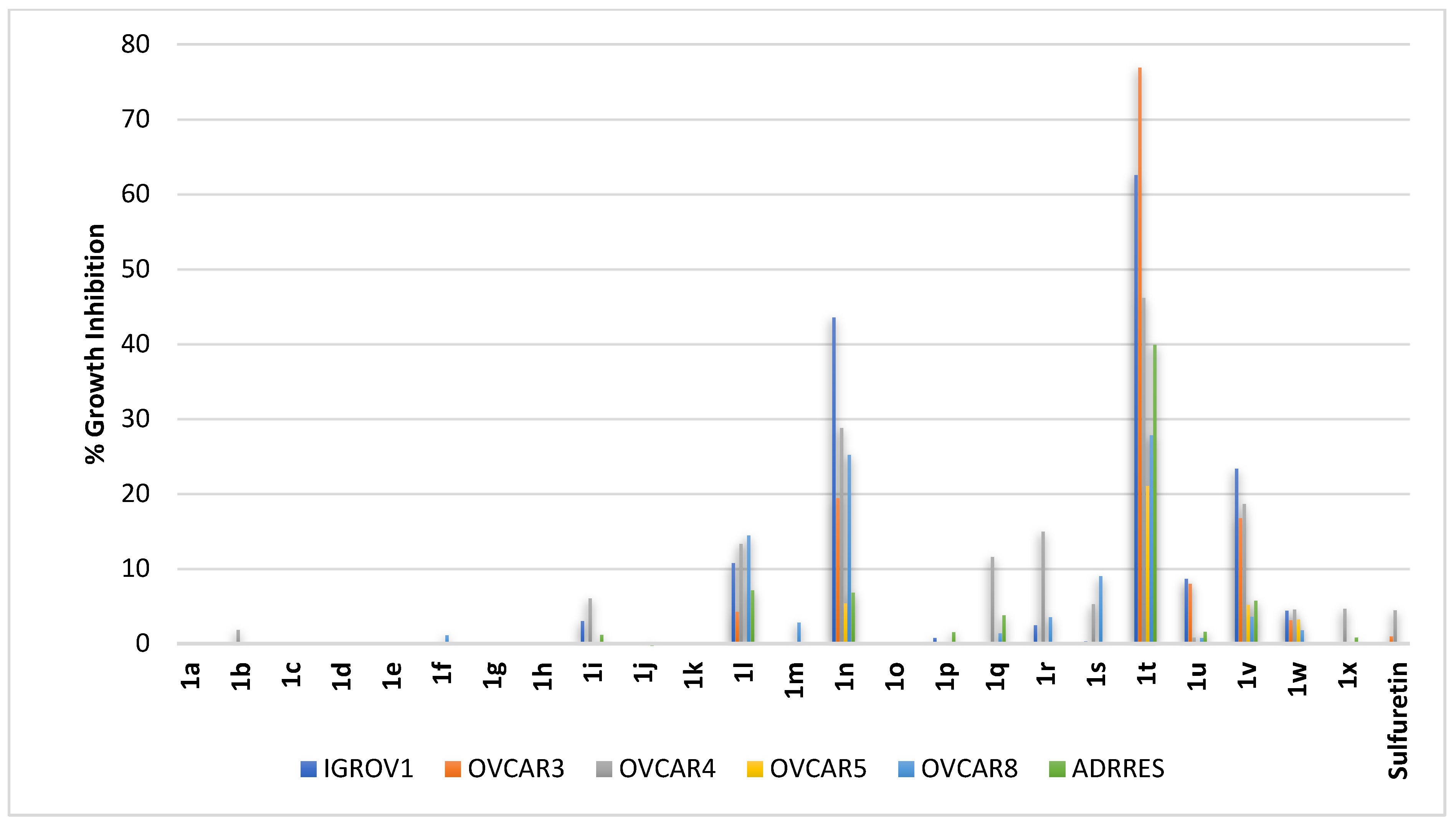
2.2.6. Ovarian Cancer
2.2.7. Renal Cancer
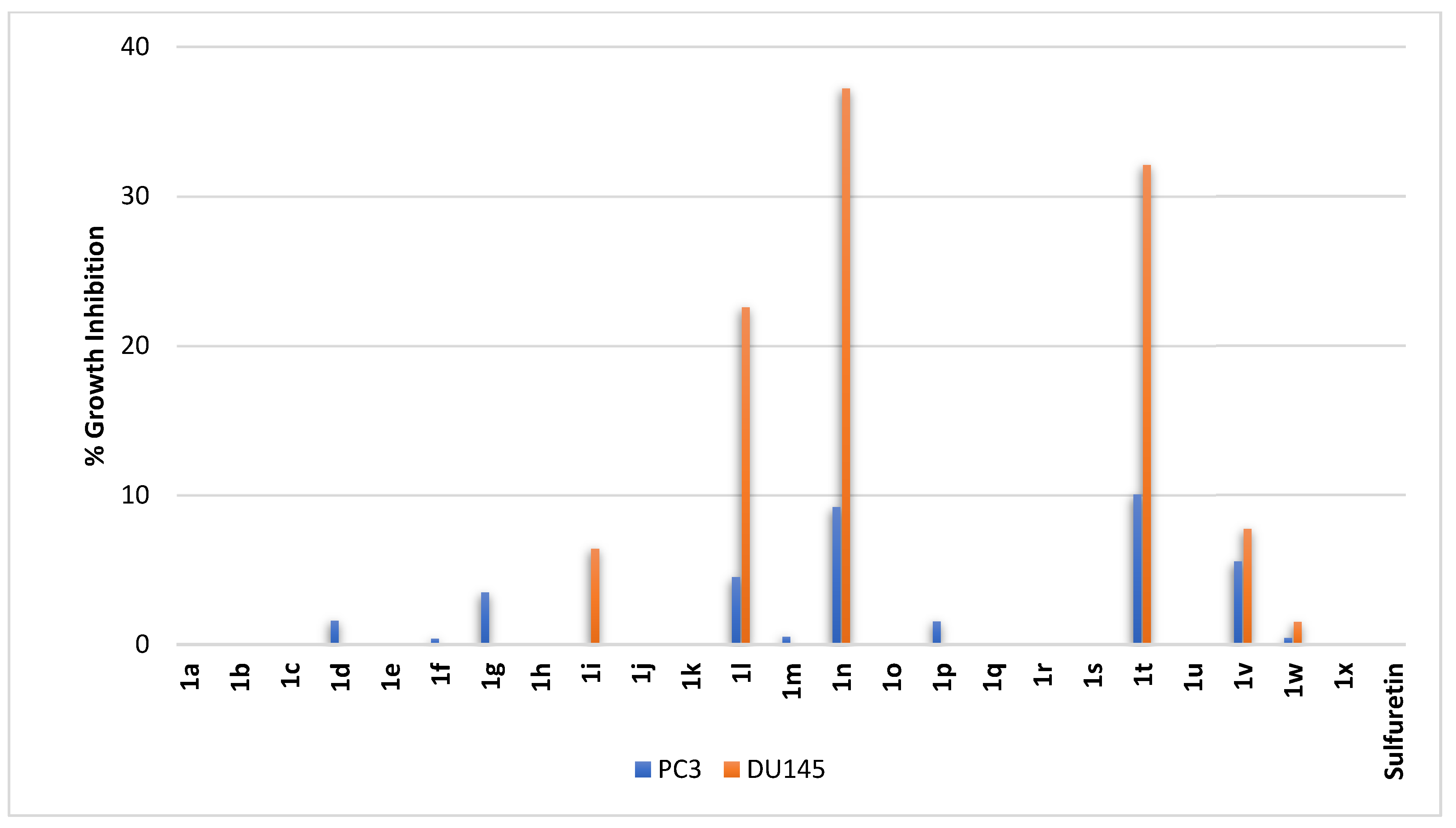
2.2.8. Prostate Cancer
2.2.9. Breast Cancer
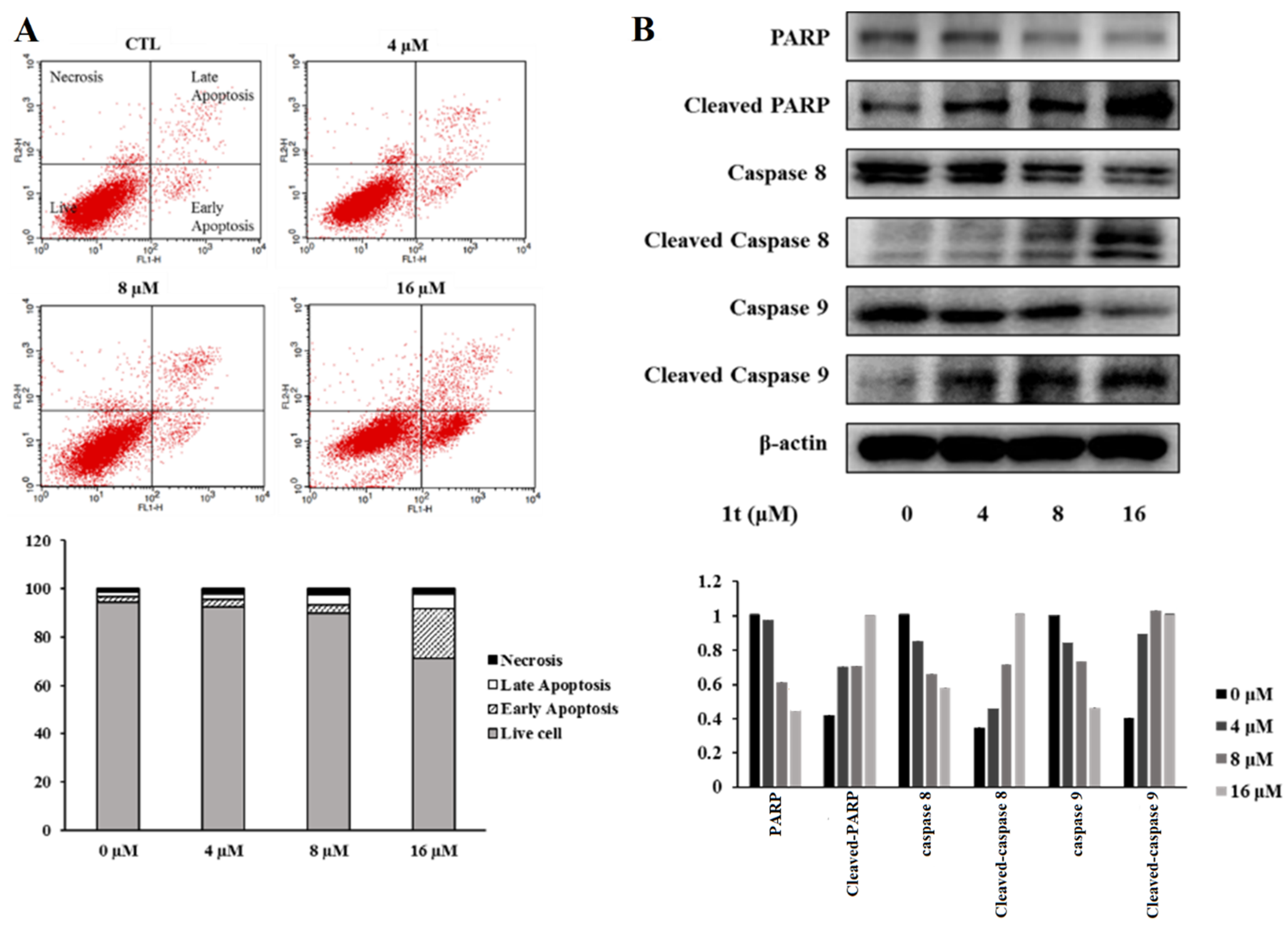
2.3. Compound 1t Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells
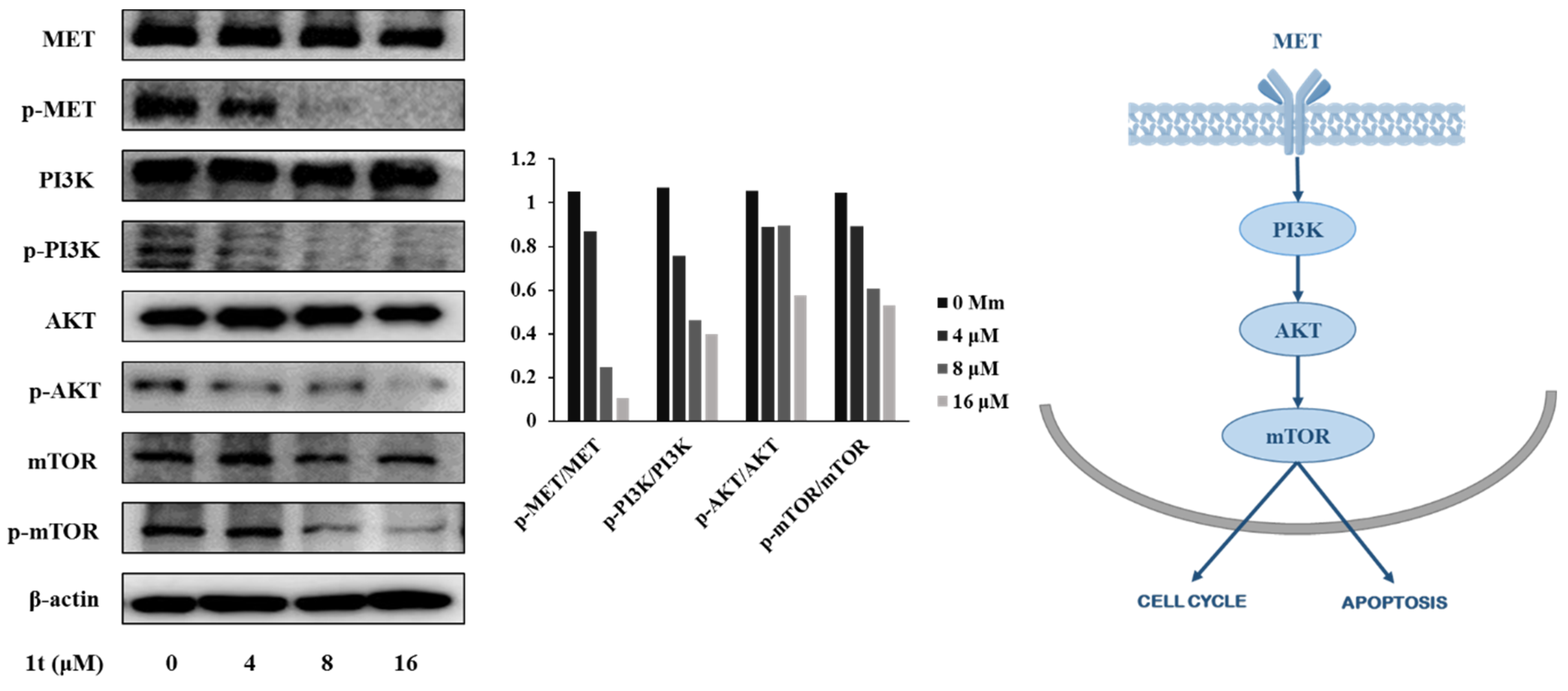
2.4. Compound 1t Inhibits Activation of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase and Downregulates Its Downstream in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells
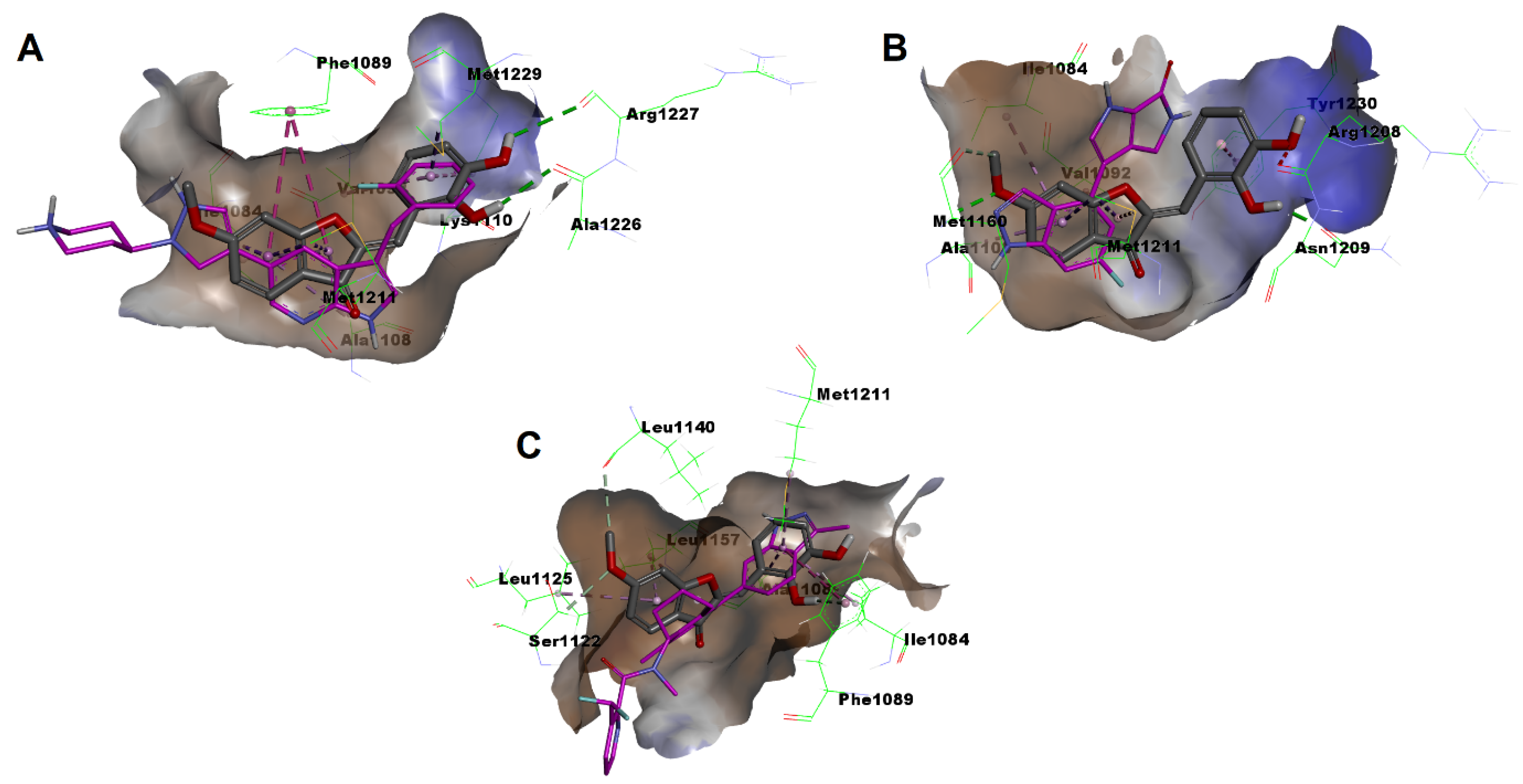
2.5. In Silico Docking Simulation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Biological Evaluations
3.2.1. In Vitro Profiling against Human Cancer Cells Panels
3.2.2. In Vitro Evaluation of Antiproliferative Mechanisms
3.3. In Silico Simulation Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, M.M.; Hassan, A.H.E.; Lee, K.W.; Cho, M.C.; Yang, J.S.; Song, J.; Min, K.H.; Hong, J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, Y.S. Design, synthesis and cytotoxicity of chimeric erlotinib-alkylphospholipid hybrids. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, H. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence and death for 29 cancer groups in 2019 and trends analysis of the global cancer burden, 1990–2019. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, G.R.; Leong, D.P.; Rangarajan, S.; Lanas, F.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Gupta, R.; Diaz, R.; Avezum, A.; Oliveira, G.B.F.; Wielgosz, A.; et al. Variations in common diseases, hospital admissions, and deaths in middle-aged adults in 21 countries from five continents (PURE): A prospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Kim, Y.H. Cancer prevention from the perspective of global cancer burden patterns. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, Y.A.; Aanei, C. Revisiting the hallmarks of cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1016–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, A.K.; Hassan, A.H.E.; Chung, K.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Gil, H.-S.; Lee, K.-T.; Roh, E.J. Diarylurea derivatives comprising 2,4-diarylpyrimidines: Discovery of novel potential anticancer agents via combined failed-ligands repurposing and molecular hybridization approaches. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 103, 104121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikarasu, P.; Surajambika, R.R.; Ramalakshmi, N. Chalcones and Flavones as Multifunctional Anticancer Agents—A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2022, 18, 84–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Lee, M.-G.; Won, M.; Koo, S.; Arambula, J.F.; Sessler, J.L.; Chi, S.-G.; Kim, J.S. Targeting Heterogeneous Tumors Using a Multifunctional Molecular Prodrug. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15611–15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atashrazm, F.; Lowenthal, R.M.; Woods, G.M.; Holloway, A.F.; Dickinson, J.L. Fucoidan and cancer: A multifunctional molecule with anti-tumor potential. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2327–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, M.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Conjugated polymers as multifunctional biomedical platforms: Anticancer activity and apoptosis imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6942–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kuljaca, S.; Tee, A.; Marshall, G.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Multifunctional anticancer agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2006, 32, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, A.; Hammock, B.D.; Serhan, C.N.; Panigrahy, D. Carcinogenesis: Failure of resolution of inflammation? Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 218, 107670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Baby, D.; Rajguru, J.P.; Patil, P.B.; Thakkannavar, S.S.; Pujari, V.B. Inflammation and cancer. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M. Inflammation and cancer. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2018, 23, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhoff, G.; Molls, M.; Radons, J. Chronic Inflammation in Cancer Development. Front. Immunol. 2012, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.; Dugourd, A.; Memon, D.; Petursson, B.; Petsalaki, E.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Beltrao, P. Pan-Cancer landscape of protein activities identifies drivers of signalling dysregulation and patient survival. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2023, 19, e10631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; He, D.N.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhu, X.; Wen, X.L.; Li, X.H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, Z.Z. Oncogenic signaling pathway dysregulation landscape reveals the role of pathways at multiple omics levels in pan-cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 916400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonski, K.P.; Pirkl, M.; Ćevid, D.; Bühlmann, P.; Beerenwinkel, N. Identifying cancer pathway dysregulations using differential causal effects. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Singh, J.K.; Wunnava, A.; Al-Obeed, O.; Abdulla, M.; Srivastava, S.K. Emerging trends in colorectal cancer: Dysregulated signaling pathways Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koveitypour, Z.; Panahi, F.; Vakilian, M.; Peymani, M.; Seyed Forootan, F.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H.; Ghaedi, K. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Paul, A.M.; Rameshwar, P.; Pillai, M.R. Epigenetic Dysregulation at the Crossroad of Women’s Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Peng, Y.; Gao, A.; Du, C.; Herman, J.G. Epigenetic heterogeneity in cancer. Biomark. Res. 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Spezia, M.; Huang, S.; Yuan, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ji, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, B.; Luo, W.; et al. Breast cancer development and progression: Risk factors, cancer stem cells, signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, R.; Brugge, J.S. Signal transduction in cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a006098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvé, S.; Ladroue, C.; Laine, E.; Mahtouk, K.; Guégan, J.; Gad, S.; Le Jeune, H.; Le Gentil, M.; Nuel, G.; Kim, W.Y.; et al. Genetic evidence of a precisely tuned dysregulation in the hypoxia signaling pathway during oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6554–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, A.; Vaux, D.L. Cell Death in the Origin and Treatment of Cancer. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Hiramoto, A.; Kim, H.-S.; Wataya, Y. Anticancer Strategy Targeting Cell Death Regulators: Switching the Mechanism of Anticancer Floxuridine-Induced Cell Death from Necrosis to Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.; Lai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Lin, X.; Cao, S. Apoptotic Pathway as the Therapeutic Target for Anticancer Traditional Chinese Medicines. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R. Recent advances in understanding the cell death pathways activated by anticancer therapy. Cancer 2005, 103, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B. A New Golden Age of Natural Products Drug Discovery. Cell 2015, 163, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.H.E.; Park, H.R.; Yoon, Y.M.; Kim, H.I.; Yoo, S.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, Y.S. Antiproliferative 3-deoxysphingomyelin analogs: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking of pyrrolidine-based 3-deoxysphingomyelin analogs as anticancer agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.M.; Hassan, A.H.E.; Lee, Y.S. An expeditious entry to rare tetrahydroimidazo[1,5-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidin-7(8H)-ones: A single-step gateway synthesis of glochidine congeners. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 130760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Chung, K.-S.; Shin, J.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Gil, H.-S.; Lee, H.-H.; Choi, E.; Choi, J.-H.; Hassan, A.H.E.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. The Anti-Proliferative Activity of the Hybrid TMS-TMF-4f Compound Against Human Cervical Cancer Involves Apoptosis Mediated by STAT3 Inactivation. Cancers 2019, 11, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-W.; Chung, K.-S.; Seo, J.-H.; Yim, S.-V.; Park, H.-J.; Choi, J.-H.; Lee, K.-T. Sulfuretin from heartwood of Rhus verniciflua triggers apoptosis through activation of Fas, Caspase-8, and the mitochondrial death pathway in HL-60 human leukemia cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-M.; Noh, E.-M.; Kwon, K.-B.; Kim, J.-S.; You, Y.-O.; Hwang, J.-K.; Hwang, B.-M.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.-J.; Jung, S.-H.; et al. Suppression of TPA-induced tumor cell invasion by sulfuretin via inhibition of NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.-S.; Park, Y.M.; Choi, J.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Shin, M.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, K.-T. Sulfuretin isolated from heartwood of Rhus verniciflua inhibits LPS-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, and pro-inflammatory cytokines expression via the down-regulation of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.Y.; Shin, M.C.; Shin, J.-S.; Lee, K.-T.; Lee, Y.S. Synthesis of aurones and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide and PGE2 productions in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4520–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, M.; Rosenberg, D.W. Multifaceted roles of PGE2 in inflammation and cancer. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, D.C.; Abe, T.; Hill, W.D.; Studdard, A.M.; Carothers, J.; Masuya, M.; Fleming, P.A.; Drake, C.J.; Ogawa, M. Hematopoietic origin of microglial and perivascular cells in brain. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 186, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglitis, M.A.; Mezey, E. Hematopoietic cells differentiate into both microglia and macroglia in the brains of adult mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4080–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, H.-w.; Derrick, D.S.; Rao, S.; Van Gaest, A.; Cheng, L.; Podolak, J.; Lawson, S.; Xue, C.; Garg, D.; White, R.; et al. Cabozantinib and dasatinib synergize to induce tumor regression in non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusolino, L.; Comoglio, P.M. Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: Cell signalling for invasive growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graupera, M.; Potente, M. Regulation of angiogenesis by PI3K signaling networks. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, W.; Tang, X.; Chen, J.; Mou, H.; Chen, Q.Y. Curcumin inhibited HGF-induced EMT and angiogenesis through regulating c-Met dependent PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in lung cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2016, 3, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.L.; Zhang, P.M.; Jiang, M.; Yu, S.W.; Wang, L. Myricetin induces apoptosis and autophagy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling in human colon cancer cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.M.; Gulhati, P.; Rampy, B.A.; Han, Y.; Rychahou, P.G.; Doan, H.Q.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M. Novel expression patterns of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway components in colorectal cancer. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2010, 210, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Xu, X.Y. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells: From basic research to clinical application. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, C.R.W.; Rai, B.K.; Munchhof, M.J.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Buckbinder, L. Understanding the Impact of the P-loop Conformation on Kinase Selectivity. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collie, G.W.; Michaelides, I.N.; Embrey, K.; Stubbs, C.J.; Börjesson, U.; Dale, I.L.; Snijder, A.; Barlind, L.; Song, K.; Khurana, P.; et al. Structural Basis for Targeting the Folded P-Loop Conformation of c-MET. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collie, G.W.; Barlind, L.; Bazzaz, S.; Börjesson, U.; Dale, I.L.; Disch, J.S.; Habeshian, S.; Jetson, R.; Khurana, P.; Madin, A.; et al. Discovery of a selective c-MET inhibitor with a novel binding mode. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 75, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.D.; Kaufman, M.D.; Lu, W.-P.; Gupta, A.; Leary, C.B.; Wise, S.C.; Rutkoski, T.J.; Ahn, Y.M.; Al-Ani, G.; Bulfer, S.L.; et al. Ripretinib (DCC-2618) Is a Switch Control Kinase Inhibitor of a Broad Spectrum of Oncogenic and Drug-Resistant KIT and PDGFRA Variants. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 738–751.e739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.H.E.; Phan, T.N.; Choi, Y.; Moon, S.; No, J.H.; Lee, Y.S. Design, Rational Repurposing, Synthesis, In Vitro Evaluation, Homology Modeling and In Silico Study of Sulfuretin Analogs as Potential Antileishmanial Hit Compounds. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.H.E.; Kim, H.J.; Gee, M.S.; Park, J.-H.; Jeon, H.R.; Lee, C.J.; Choi, Y.; Moon, S.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.K.; et al. Positional scanning of natural product hispidol’s ring-B: Discovery of highly selective human monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor analogues downregulating neuroinflammation for management of neurodegenerative diseases. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, W.S.; Jin, M.; Yu, J.; Kim, W.K.; Song, J.; Chung, H.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, S.K. A novel selenonucleoside suppresses tumor growth by targeting Skp2 degradation in paclitaxel-resistant prostate cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 158, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.; Hong, J.-Y.; Bae, S.Y.; Kang, S.S.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.K. Antitumor Activity of Americanin A Isolated from the Seeds of Phytolacca americana by Regulating the ATM/ATR Signaling Pathway and the Skp2–p27 Axis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
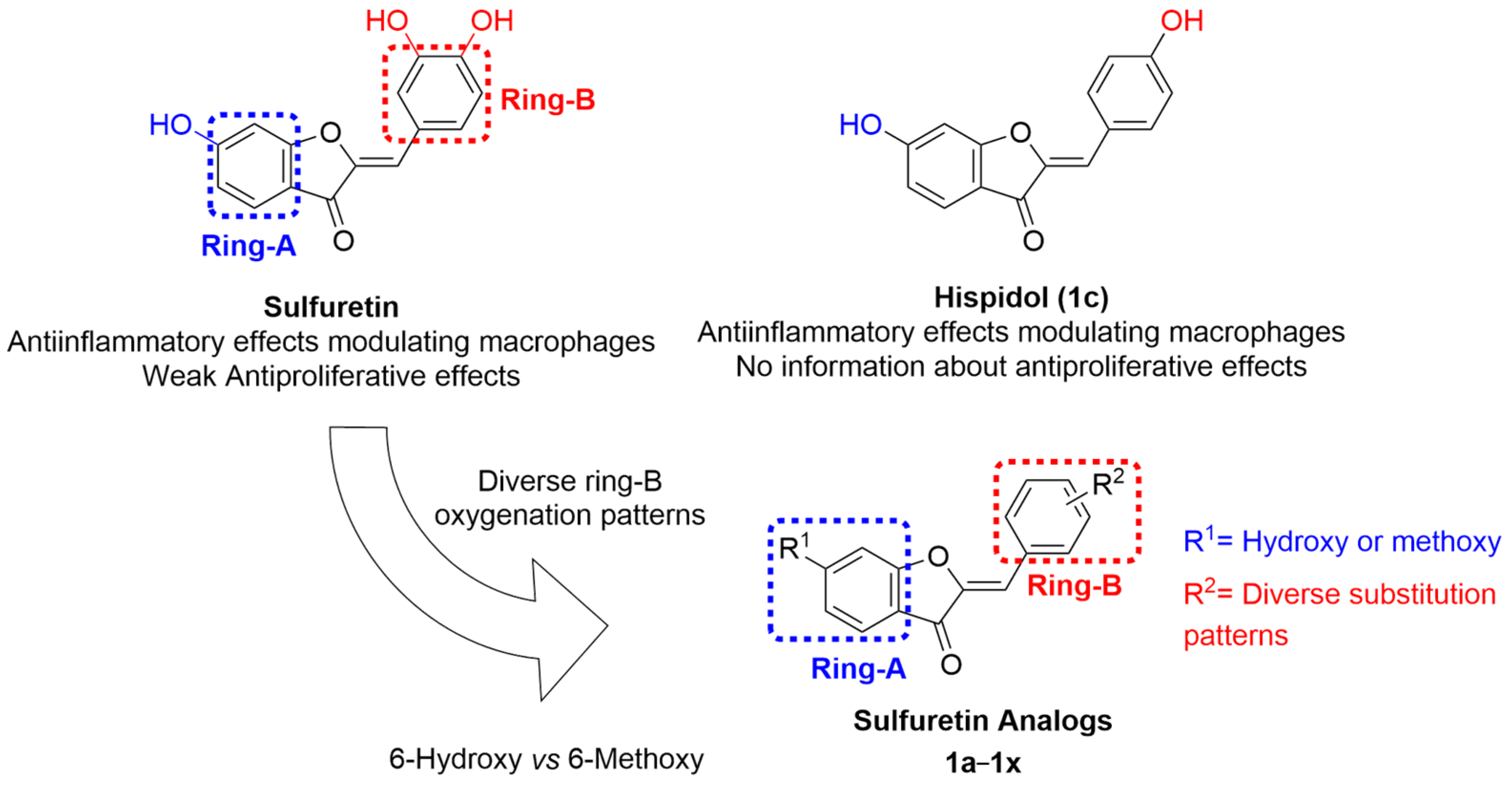
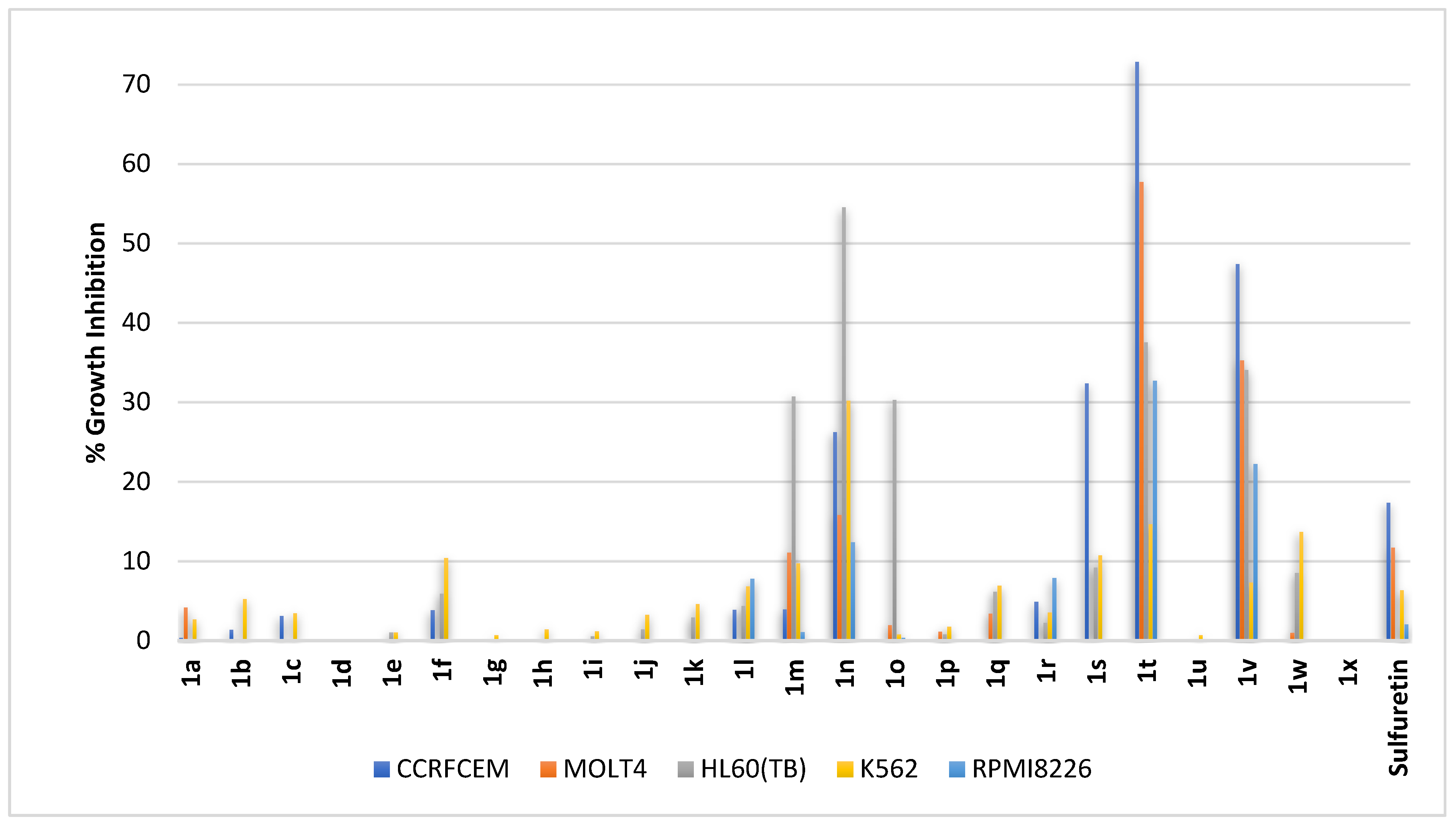
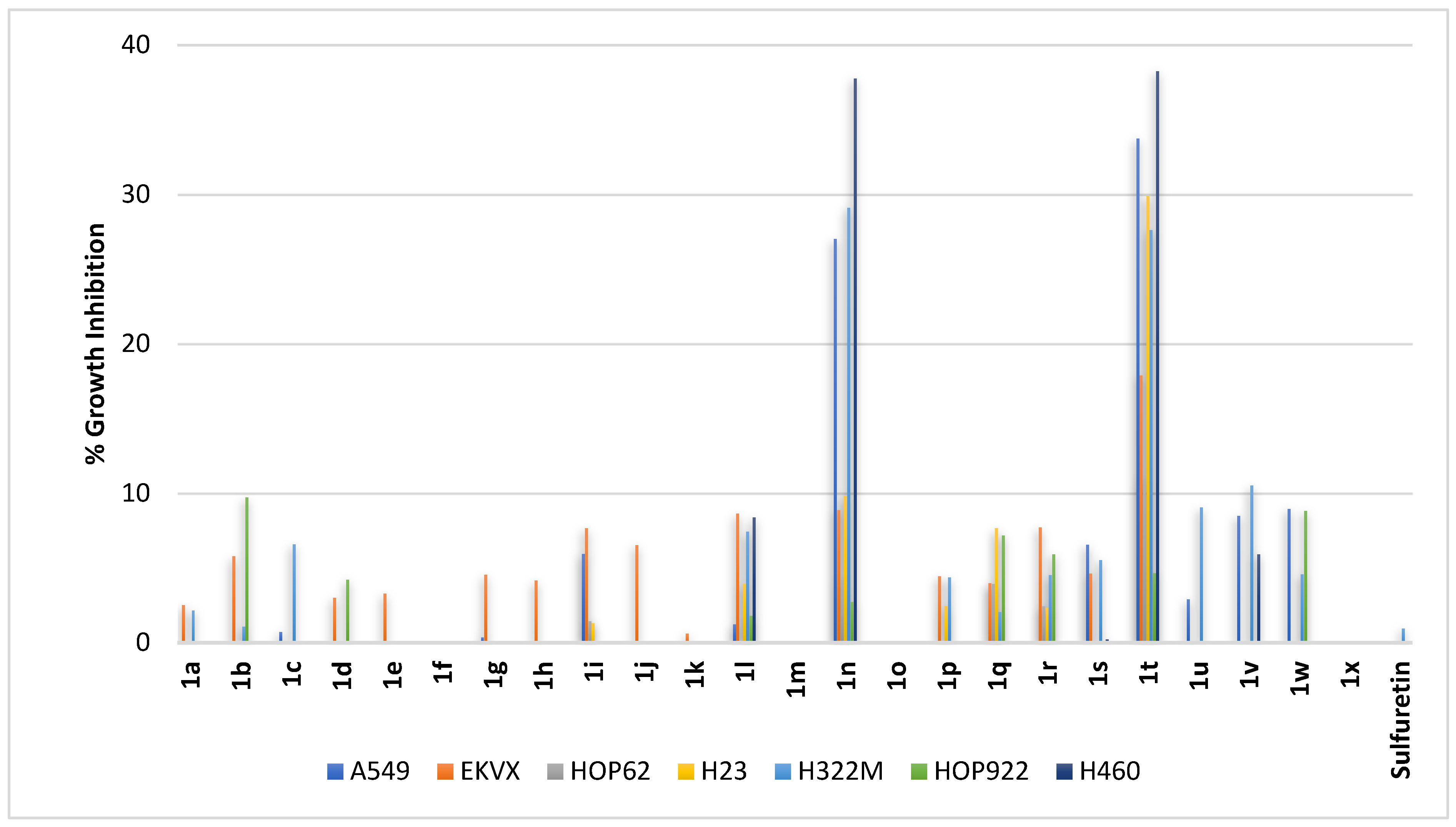
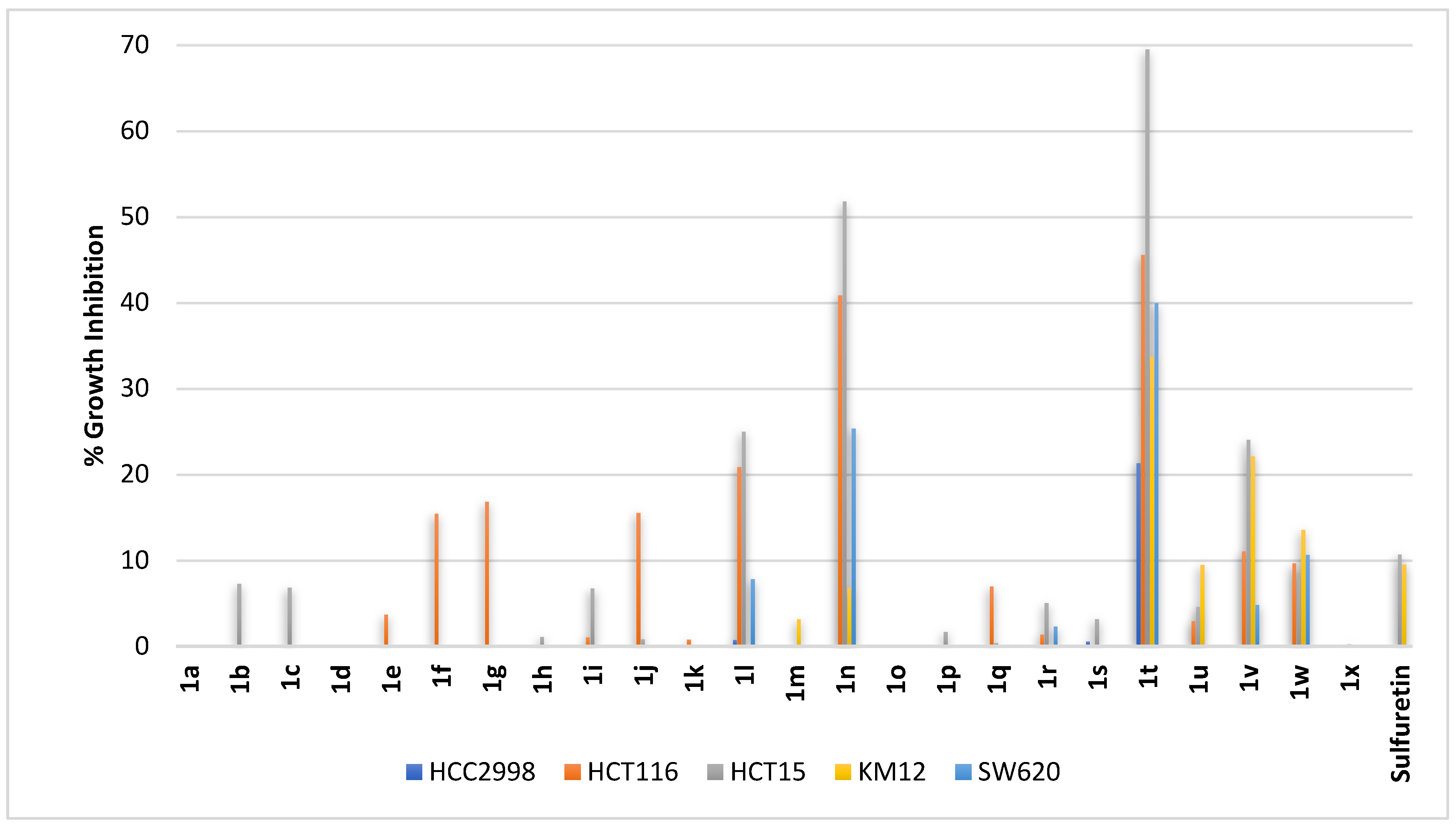



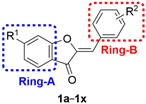 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comp. | R1 | R2 | PGE2 IC50 (µM) | Comp. | R1 | R2 | PGE2 IC50 (µM) |
| 1a | 6-Hydroxy | 2′-Hydroxy | 1.80 | 1n | 6-Hydroxy | 3′,5′-Dimethoxy | 1.67 |
| 1b | 6-Hydroxy | 3′-Hydroxy | 9.30 | 1o | 6-Hydroxy | 2′,3′,4′-Trimethoxy | NR |
| 1c | 6-Hydroxy | 4′-Hydroxy | 1.06 | 1p | 6-Hydroxy | 4′-Methoxymethoxy | NR |
| 1d | 6-Hydroxy | 2′,4′-Dihydroxy | 18.62 | 1q | 6-Methoxy | 2′-Hydroxy | 2.22 |
| 1e | 6-Hydroxy | 2′,5′-Dihydroxy | NR 1 | 1r | 6-Methoxy | 3′-Hydroxy | 13.15 |
| 1f | 6-Hydroxy | 3′,5′-Dihydroxy | NR | 1s | 6-Methoxy | 4′-Hydroxy | 35.82 |
| 1g | 6-Hydroxy | 3′,4′,5′-Trihydroxy | 37.62 | 1t | 6-Methoxy | 2′,3′-Dihydroxy | NR |
| 1h | 6-Hydroxy | 2′-Methoxy | 18.10 | 1u | 6-Methoxy | 2′,4′-Dihydroxy | 8.80 |
| 1i | 6-Hydroxy | 3′-Methoxy | 3.79 | 1v | 6-Methoxy | 3′,4′-Dihydroxy | 4.90 |
| 1j | 6-Hydroxy | 4′-Methoxy | 2.00 | 1w | 6-Methoxy | 2′-Methoxy | 59.50 |
| 1k | 6-Hydroxy | 2′,3′-Dimethoxy | NR | 1x | 6-Methoxy | 3′-Methoxy | 2.50 |
| 1l | 6-Hydroxy | 2′,5′-Dimethoxy | NR | Sulfuretin | 6-Hydroxy | 3′,4′-Dihydroxy | 5.90 |
| 1m | 6-Hydroxy | 3′,4′-Dimethoxy | 2.90 | ||||
| Compound | Cell Line 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | HCT116 | MDAMB231 | |
| IC50 (μM) 2 | IC50 (μM) 2 | IC50 (μM) 2 | |
| 1t | 19.7 | 8.68 | >50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, A.H.E.; Wang, C.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Jeon, H.R.; Choi, Y.; Moon, S.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, S.B.; Mahmoud, K.; et al. Repurposing Synthetic Congeners of a Natural Product Aurone Unveils a Lead Antitumor Agent Inhibiting Folded P-Loop Conformation of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111597
Hassan AHE, Wang CY, Lee CJ, Jeon HR, Choi Y, Moon S, Lee CH, Kim YJ, Cho SB, Mahmoud K, et al. Repurposing Synthetic Congeners of a Natural Product Aurone Unveils a Lead Antitumor Agent Inhibiting Folded P-Loop Conformation of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(11):1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111597
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Ahmed H. E., Cai Yi Wang, Cheol Jung Lee, Hye Rim Jeon, Yeonwoo Choi, Suyeon Moon, Chae Hyeon Lee, Yeon Ju Kim, Soo Bin Cho, Kazem Mahmoud, and et al. 2023. "Repurposing Synthetic Congeners of a Natural Product Aurone Unveils a Lead Antitumor Agent Inhibiting Folded P-Loop Conformation of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 11: 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111597
APA StyleHassan, A. H. E., Wang, C. Y., Lee, C. J., Jeon, H. R., Choi, Y., Moon, S., Lee, C. H., Kim, Y. J., Cho, S. B., Mahmoud, K., El-Sayed, S. M., Lee, S. K., & Lee, Y. S. (2023). Repurposing Synthetic Congeners of a Natural Product Aurone Unveils a Lead Antitumor Agent Inhibiting Folded P-Loop Conformation of MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Pharmaceuticals, 16(11), 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16111597









