Unraveling the Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Bioactive Compounds Involved in the Modulation of Ischemic Stroke by Network Pharmacology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
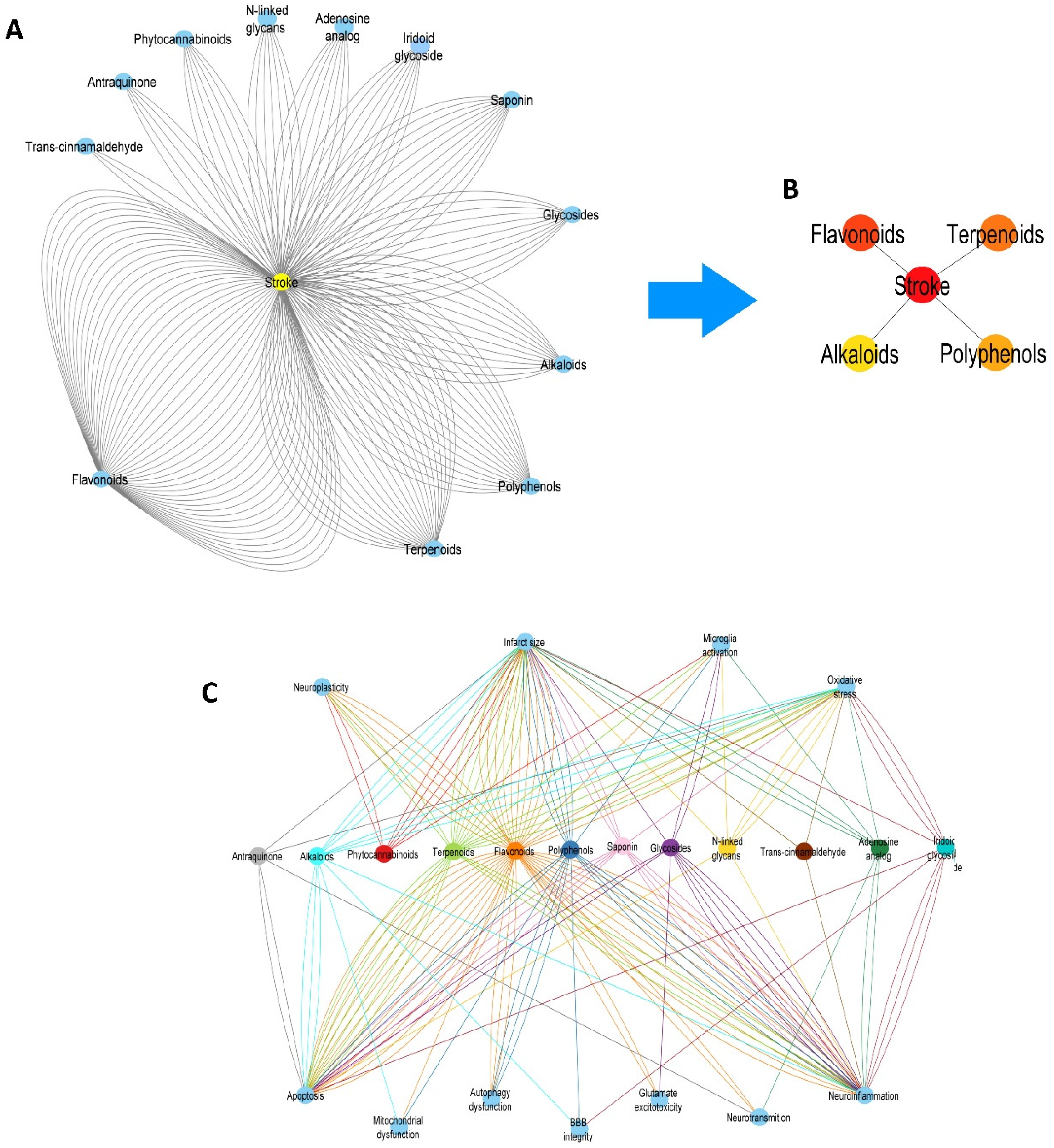
2.1. Twelve Chemical Classes of NBCs Target the Principal Pathological Processes Elicited by IS, but Only Flavonoids and Terpenoids Are the Most Studied
2.2. Network of NBCs and the Most Common Pathological Pathways Associated with IS
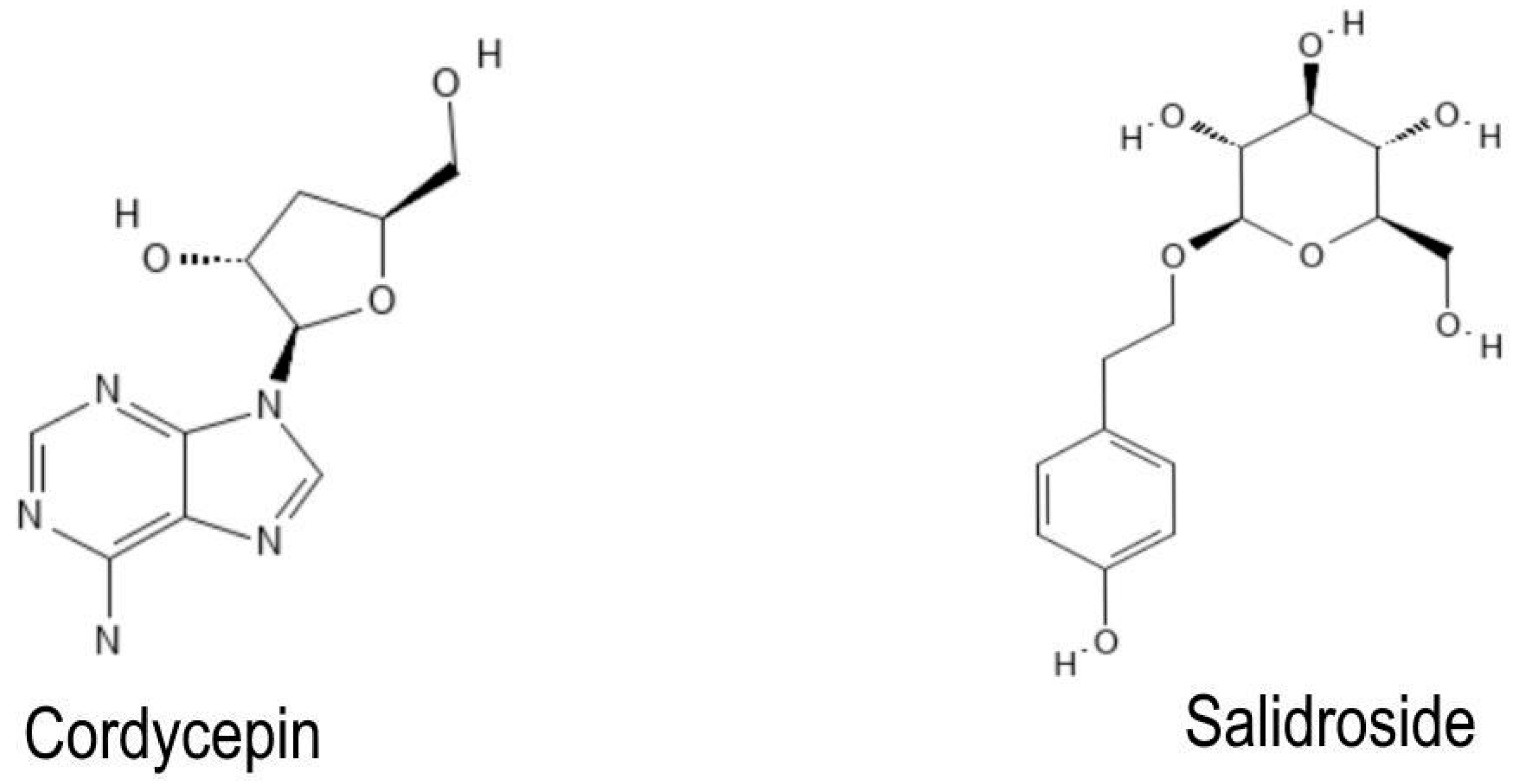
2.3. Chemoinformatic Analysis of the NBCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
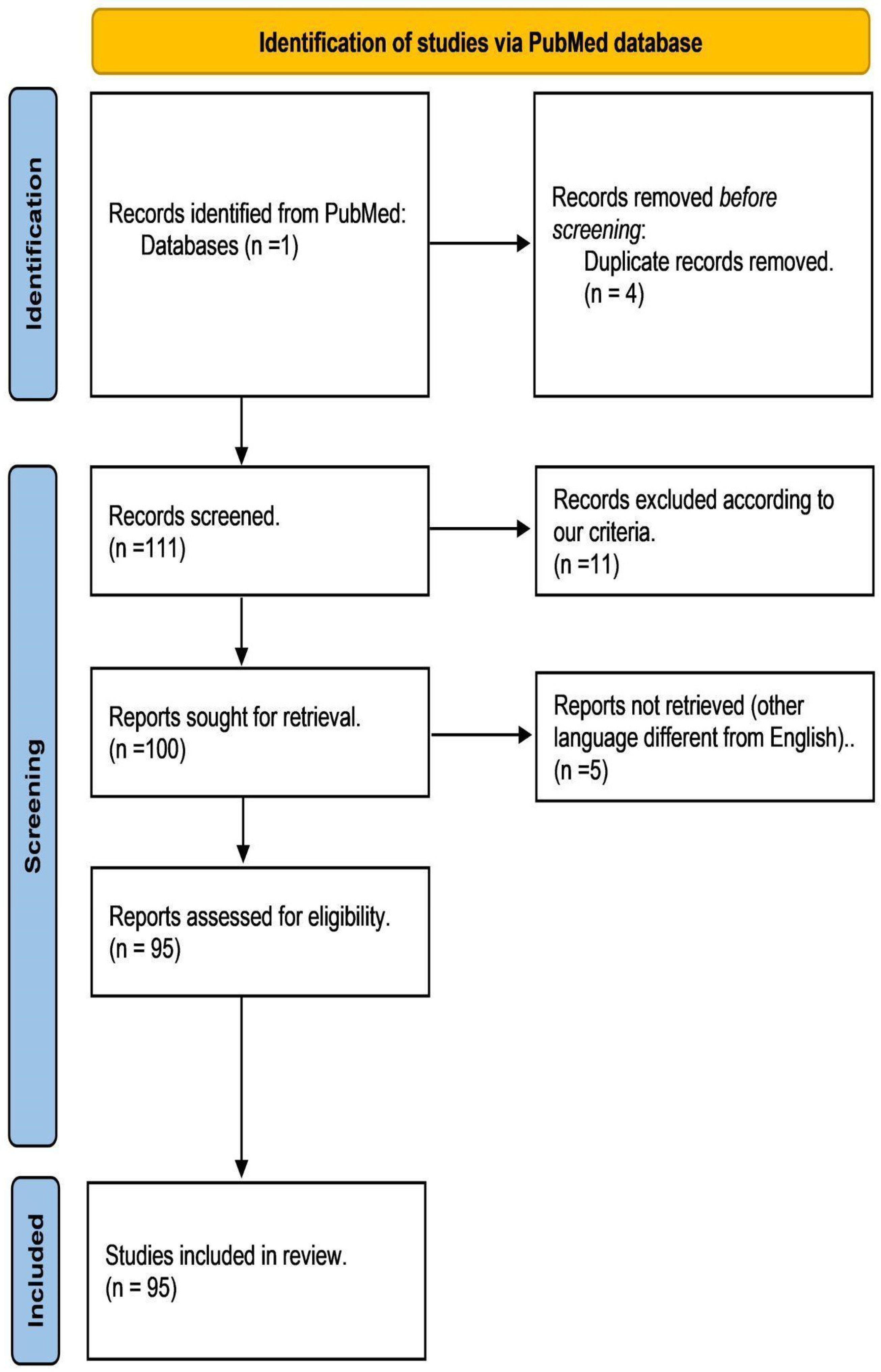
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Network Pharmacology Analysis
4.3. Cheminformatic Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC Stroke Facts. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/stroke/facts.htm (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Saini, V.; Guada, L.; Yavagal, D.R. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology 2021, 97, S6–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; De Silva, D.A.; Macleod, M.R.; Coutts, S.B.; Schwamm, L.H.; Davis, S.M.; Donnan, G.A. Ischaemic Stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herpich, F.; Rincon, F. Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Carroll, C.B.; Aguilar, M.I. Management of Postthrombolysis Hemorrhagic and Orolingual Angioedema Complications. Neurohospitalist 2015, 5, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurd, M.D.; Goel, I.; Sakai, Y.; Teramura, Y. Current Status of Ischemic Stroke Treatment: From Thrombolysis to Potential Regenerative Medicine. Regen. Ther. 2021, 18, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C. In Silico Screening of Natural Products Isolated from Mexican Herbal Medicines against COVID-19. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, J.B. The Role of Natural Products in Modern Drug Discovery. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2019, 91 (Suppl. S3), e20190105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Bioactive Compounds: Technological Advancements; Sinha, R.P.; Häder, h.c.D.-P. (Eds.) Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9780128206553. [Google Scholar]
- Sytar, O.; Smetanska, I. Special Issue “Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources (2020, 2021)”. Molecules 2022, 27, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sairazi, N.S.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S. Natural Products and Their Bioactive Compounds: Neuroprotective Potentials against Neurodegenerative Diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 6565396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Steinberg, G.K. Novel Stroke Therapeutics: Unraveling Stroke Pathophysiology and Its Impact on Clinical Treatments. Neuron 2015, 87, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putteeraj, M.; Lim, W.L.; Teoh, S.L.; Yahaya, M.F. Flavonoids and Its Neuroprotective Effects on Brain Ischemia and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1710–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Li, H.; Lu, D.; Yuan, J.; Ma, R.; Li, J.; Ren, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Neuroprotective Effect for Cerebral Ischemia by Natural Products: A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 607412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Y.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Deng, C.; Liu, X. Neuroprotective Effect of Glycosides in Buyang Huanwu Decoction on Pyroptosis Following Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 242, 112051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B. Polyphenols and Neuroprotection against Ischemia and Neurodegeneration. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1222–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.-H. Therapeutic Angiogenesis after Ischemic Stroke: Chinese Medicines, Bone Marrow Stromal Cells (BMSCs) and Their Combinational Treatment. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismailoglu, U.B.; Saracoglu, I.; Harput, U.S.; Sahin-Erdemli, I. Effects of Phenylpropanoid and Iridoid Glycosides on Free Radical-Induced Impairment of Endothelium-Dependent Relaxation in Rat Aortic Rings. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, F.; Tahir Ul Qamar, M.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Albutti, A.; Alwashmi, A.S.S.; Aljasir, M.A. Network Pharmacology Approach for Medicinal Plants: Review and Assessment. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network Pharmacology: The next Paradigm in Drug Discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhong, P. A Network Pharmacology to Explore the Mechanism of in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6611018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Chen, X.; Mei, Z.; Liu, X.; Feng, Z.; Liao, J.; Deng, Y.; Ge, J. An Integrated Analysis of Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Reveal the Mechanism of Chinese Medicine Formula Naotaifang in Treating Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 3783–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.J.; Ma, S.; Wang, M.; Yao, M.; Li, R.; Li, W.W.; Zhao, X.; Hu, D.; et al. Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification to Explore the Mechanism of Sanhua Decoction in the Treatment of Ischaemic Stroke. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.-P.; Wan, Q. Therapeutic Targets of Neuroprotection and Neurorestoration in Ischemic Stroke: Applications for Natural Compounds from Medicinal Herbs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 148, 112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanas, F.; Seron, P. Facing the Stroke Burden Worldwide. Lancet Glob Health 2021, 9, e235–e236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Norrving, B.; Mensah, G.A. Global Burden of Stroke. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Xu, H.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Shao, A.; Lou, M. Natural Compounds for SIRT1-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Stroke: A Potential Therapeutic Target in the Future. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1949718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Yin, F.-T.; Zhou, X.-H.; Zhang, A.-H.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.-L.; Wang, X.-J. The Signaling Pathways and Targets of Natural Compounds from Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treating Ischemic Stroke. Molecules 2022, 27, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Câmara, J.S.; Albuquerque, B.R.; Aguiar, J.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Granato, D.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Food Bioactive Compounds and Emerging Techniques for Their Extraction: Polyphenols as a Case Study. Foods 2021, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucá, M.M.; Cysne Filho, F.M.S.; de Almeida, J.C.; Mesquita, D.d.S.; Barriga, J.R.d.M.; Dias, K.C.F.; Barbosa, T.M.; Vasconcelos, L.C.; Leal, L.K.A.M.; Ribeiro, J.E.; et al. Flavonoids: Biological Activities and Therapeutic Potential. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ferdinando, M.; Brunetti, C.; Fini, A.; Tattini, M. Flavonoids as Antioxidants in Plants Under Abiotic Stresses. In Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 159–179. ISBN 9781461406334. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, S.; Al-Taweel, A. Terpenes and Terpenoids; BoD—Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9781789847765. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X. Advances in Pharmacological Activities of Terpenoids. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X2090355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Smith, M.; Khatoon, T. Biological Activity of The Terpenoids and Their Derivatives. Fortschr. Arzneimittelforsch. 1963, 5, 279–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boonkaew, T.; Camper, N.D. Biological Activities of Ginkgo Extracts. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Wong, Y.Y. The Bioavailability of Ginkgolides in Ginkgo Biloba Extracts. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hartogh, D.J.; Gabriel, A.; Tsiani, E. Antidiabetic Properties of Curcumin II: Evidence from In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2019, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Antidotal or Protective Effects of Curcuma Longa (turmeric) and Its Active Ingredient, Curcumin, against Natural and Chemical Toxicities: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman, A.M.; Lushchak, O.V.; Zayachkivska, A.; Koliada, A. Curcumin. In Anti-Aging Pharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 153–176. ISBN 9780128236796. [Google Scholar]
- Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Bordoloi, D.; Padmavathi, G.; Monisha, J.; Roy, N.K.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, the Golden Nutraceutical: Multitargeting for Multiple Chronic Diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1325–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urošević, M.; Nikolić, L.; Gajić, I.; Nikolić, V.; Dinić, A.; Miljković, V. Curcumin: Biological Activities and Modern Pharmaceutical Forms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.M.; Salama, M.M.; Salem, M.A. Bioactive Lead Compounds and Molecular Targets for the Treatment of Heart Diseases. In Phytochemicals as Lead Compounds for New Drug Discovery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 67–94. ISBN 9780128178904. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability Enhancement of Baicalin: A Review. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 44, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Guan, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, Z.; Ishfaq, M. An Overview of Pharmacological Activities of Baicalin and Its Aglycone Baicalein: New Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Signaling Pathways. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Ren, X.; Yu, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhu, C.; Sun, H.; Kong, Q.; Fu, X.; Mou, H. Fucose-Containing Bacterial Exopolysaccharides: Sources, Biological Activities, and Food Applications. Food Chem. X 2022, 13, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-B.; Choi, J.-H.; Chang, Y.K.; Mun, S. Production of High-Purity Fucose from the Seaweed of Undaria Pinnatifida through Acid-Hydrolysis and Simulated-Moving Bed Purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H.; Jagerovic, N. An Overview on Medicinal Chemistry of Synthetic and Natural Derivatives of Cannabidiol. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinney, W.A.; McDonnell, M.E.; Zhong, H.M.; Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Ling, W.; Qian, T.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Z.; Petkanas, D.; et al. Discovery of KLS-13019, a Cannabidiol-Derived Neuroprotective Agent, with Improved Potency, Safety, and Permeability. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Shan, A. Biological Function of Resveratrol and Its Application in Animal Production: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Lin, H.-S.; Ho, P.C.; Ng, K.-Y. The Impact of Aqueous Solubility and Dose on the Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Resveratrol. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2593–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-X.; Heredia, A.; Song, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, B.; Davis, C.; Redfield, R. Resveratrol Glucuronides as the Metabolites of Resveratrol in Humans: Characterization, Synthesis, and Anti-HIV Activity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J. Pharmacological Effects of Icariin. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 179–203. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.-Y.; Ding, D.-N.; Wang, Y.-R.; Liu, S.-X.; Peng, C.; Shen, F.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Li, C.; Tang, L.-P.; Han, F.-J. Icariin as a Potential Anticancer Agent: A Review of Its Biological Effects on Various Cancers. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1216363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sun, X.; Wu, M. Icariin, an Up-and-Coming Bioactive Compound Against Neurological Diseases: Network Pharmacology-Based Study and Literature Review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 3619–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, R.; Rácz, C.P.; Dulf, F.V. Bioavailability Improvement Strategies for Icariin and Its Derivates: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.S.; Bice, C.; Putnam, W.C.; Leff, R.; Kulikova, A.; Nakamura, A.; Ivleva, E.I.; Van Enkevort, E.; Holmes, T.; Miingi, N. Human Safety and Pharmacokinetics Study of Orally Administered Icariin: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X1985678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.A.; Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Patel, M.; Awadelkareem, A.M.; Snoussi, M.; Ashraf, M.S.; Adnan, M.; Hadi, S. Cordycepin for Health and Wellbeing: A Potent Bioactive Metabolite of an Entomopathogenic Medicinal Fungus and Its Nutraceutical and Therapeutic Potential. Molecules 2020, 25, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Lee, R.J.; Wang, D.; Teng, L. Cordycepin, a Natural Antineoplastic Agent, Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via Caspase-Dependent Pathways. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Kasim, V. Therapeutic Potential and Molecular Mechanisms of Salidroside in Ischemic Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 974775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venketasubramanian, N.; Kumar, R.; Soertidewi, L.; Abu Bakar, A.; Laik, C.; Gan, R. The NeuroAiD Safe Treatment (NeST) Registry: A Protocol. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e009866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Vázquez, O.S.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; Ramírez-Aldana, R.; Torre, P.G.-D.; Rivero-Segura, N.A. Structural and Pharmacological Network Analysis of miRNAs Involved in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, H.-H.; Ho, C.-W.; Ko, M.-T.; Lin, C.-Y. cytoHubba: Identifying Hub Objects and Sub-Networks from Complex Interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. S4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.D.A. Elementary Pharmacoinformatics; Pharmamed Press: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 9789385433665. [Google Scholar]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An Open-Source Program for Chemistry Aware Data Visualization and Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead- and Drug-like Compounds: The Rule-of-Five Revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Arellano, J.I.; Gómez-Verjan, J.C.; Rojano-Vilchis, N.A.; Mendoza-Cruz, M.; Jiménez-Estrada, M.; López-Valdés, H.E.; Martínez-Coria, H.; Gutiérrez-Juárez, R.; González-Espinosa, C.; Reyes-Chilpa, R.; et al. Chemoinformatic Analysis of Selected Cacalolides from (A. Gray) H. Rob. & Brettell and (Kunth) Cass. and Their Effects on FcεRI-Dependent Degranulation in Mast Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram-Ralph, E.; Amare, M. Factors Affecting Drug Absorption and Distribution. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 24, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Baicalin | Cannabidiol | Cordycepin | Curcumin | Fucose | Ginkgolide A | Ginkgolide B | Ginkgolide C | Ginkgolide K | Icariin | Resveratrol | Salidroside | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical Properties | Log P | 1.051 | 6.158 | −2.195 | 1.945 | −0.994 | 1.176 | 0.146 | −1.095 | 0.914 | 1.092 | 2.048 | −1.071 |
| Log S | −2.724 | −4.493 | −2.724 | −3.622 | −0.256 | −2.526 | −2.127 | −1.728 | −2.277 | −4.133 | −2.864 | −1.016 | |
| TPSA | 183.21 | 40.46 | 116.03 | 93.06 | 90.15 | 128.59 | 148.82 | 169.05 | 128.59 | 234.29 | 60.69 | 119.61 | |
| MW | 446.08 | 314.46 | 251.1 | 368.38 | 164.16 | 408.4 | 424.4 | 440.13 | 406.38 | 676.24 | 228.24 | 300.3 | |
| nRB | 4 | 6 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 5 | |
| HBD | 6 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 5 | |
| HBA | 11 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 15 | 3 | 7 | |
| Pharmacokinetic Properties | GI absorption | Low | High | High | High | High | High | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | High |
| BBB permeable | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | |
| P-gp substrate | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| CYP1A2 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | |
| CYP2D6 Inhibitor | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | |
| Log Kp (Skin permeation) | −8.23 | −3.59 | −8.27 | −6.28 | −8.79 | −8.37 | −9.16 | −9.95 | −9.95 | −9.25 | −5.47 | −8.88 | |
| Medicinal Chemistry Properties | Lipinski violations | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Ghose violations | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | |
| Veber violations | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bioavailability Score | 0.11 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.17 | 0.55 | 0.55 | |
| Lead-likeness violations | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |
| Synthetic accessibility | 5.09 | 4.05 | 3.67 | 2.97 | 4.05 | 6.28 | 6.38 | 6.48 | 6.48 | 7.24 | 2.02 | 4.26 | |
| Toxicoinformatic Properties | Mutagenic | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | high | high | none |
| Tumorigenic | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | |
| Irritant | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | |
| Reproductive effects | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | none | high | high | none |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; Zepeda-Arzate, E.A.; Santiago-de-la-Cruz, J.A.; Estrella-Parra, E.A.; Rivero-Segura, N.A. Unraveling the Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Bioactive Compounds Involved in the Modulation of Ischemic Stroke by Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101376
Gomez-Verjan JC, Zepeda-Arzate EA, Santiago-de-la-Cruz JA, Estrella-Parra EA, Rivero-Segura NA. Unraveling the Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Bioactive Compounds Involved in the Modulation of Ischemic Stroke by Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(10):1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101376
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez-Verjan, Juan Carlos, Emmanuel Alejandro Zepeda-Arzate, José Alberto Santiago-de-la-Cruz, Edgar Antonio Estrella-Parra, and Nadia Alejandra Rivero-Segura. 2023. "Unraveling the Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Bioactive Compounds Involved in the Modulation of Ischemic Stroke by Network Pharmacology" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 10: 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101376
APA StyleGomez-Verjan, J. C., Zepeda-Arzate, E. A., Santiago-de-la-Cruz, J. A., Estrella-Parra, E. A., & Rivero-Segura, N. A. (2023). Unraveling the Neuroprotective Effect of Natural Bioactive Compounds Involved in the Modulation of Ischemic Stroke by Network Pharmacology. Pharmaceuticals, 16(10), 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16101376










