Cu and Zn Interactions with Peptides Revealed by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
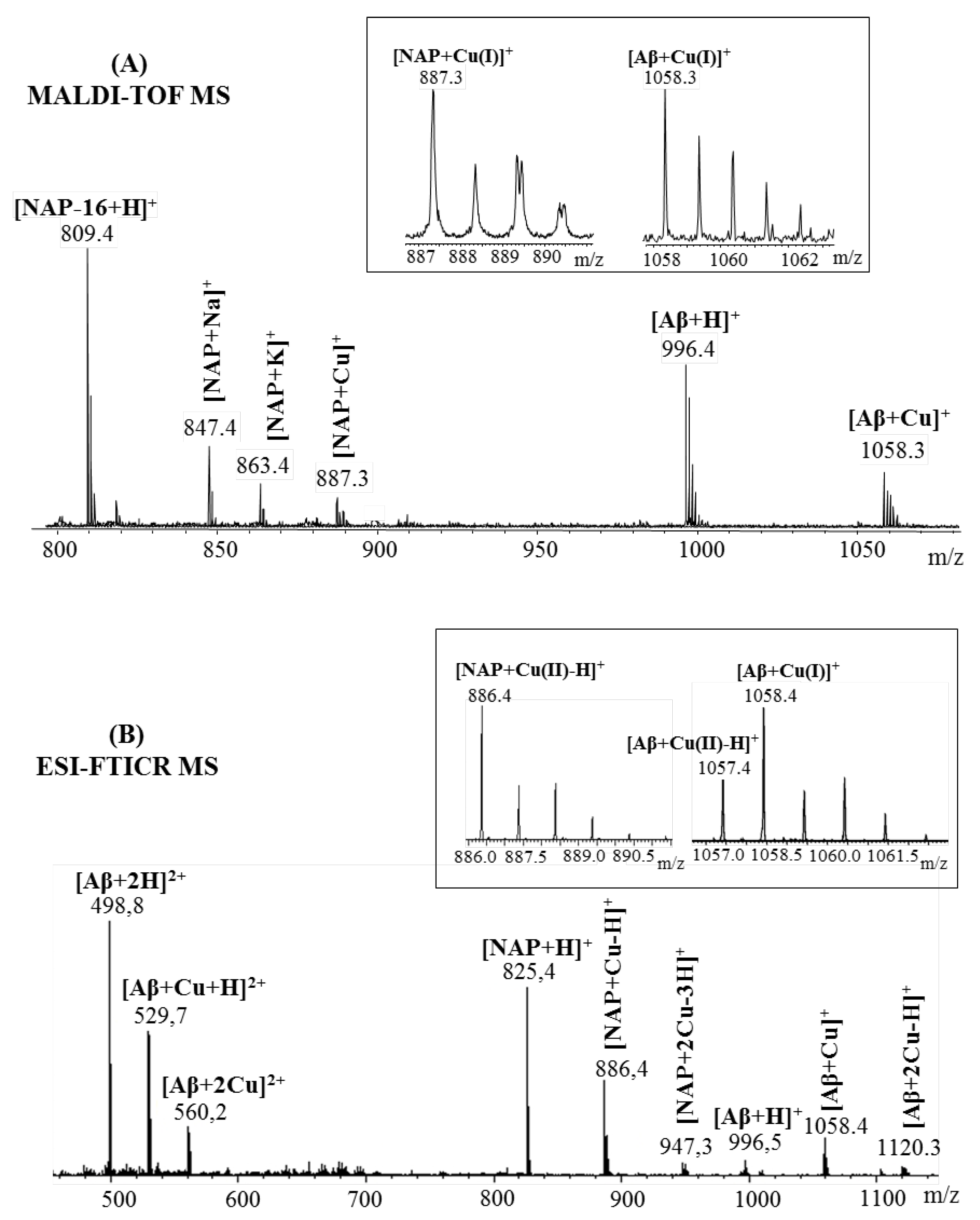
2.1. Mass Spectrometric Analysis
2.2. Peptides Affinity toward Metal Ions: Competition Study
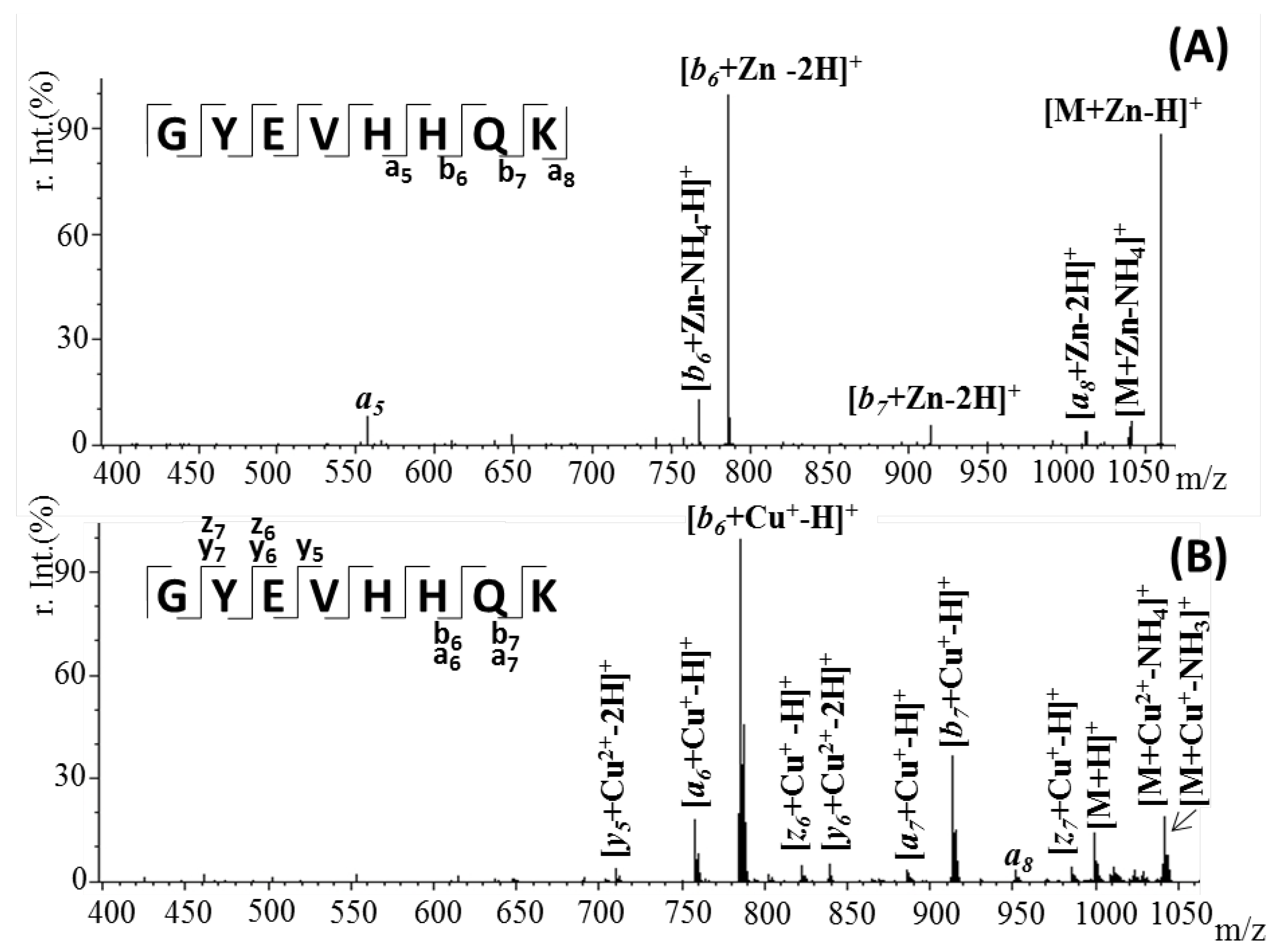
2.3. Confirmation of Metal Ion Binding by Tandem Mass Spectrometry
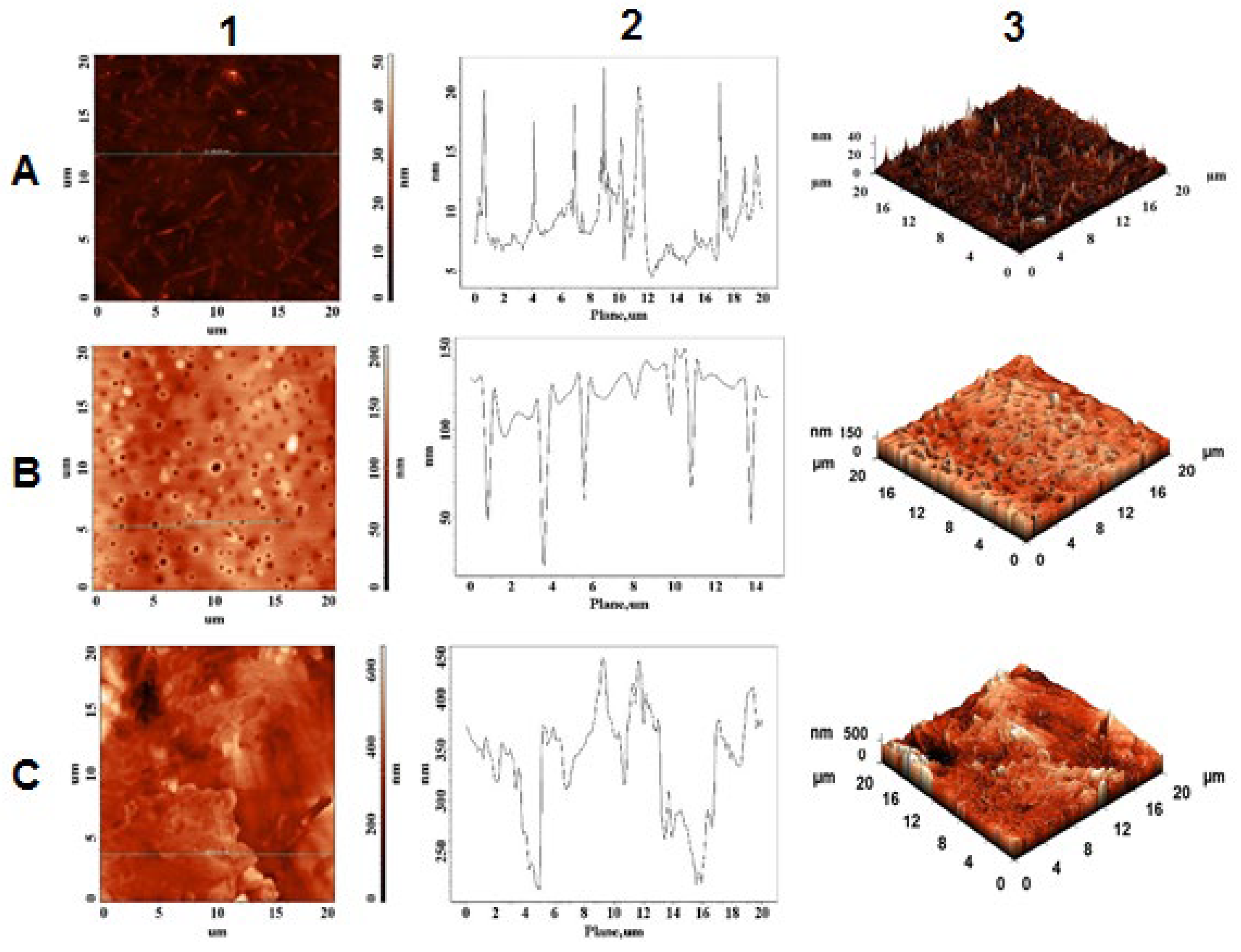
2.4. Morphological and Topographical Characterization/Atomic Force Microscopy Investigation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Peptide Synthesis
4.3. Mass Spectrometry and Peptide Complex Formation
4.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunbar, R.C.; Polfer, N.C.; Berden, G.; Oomens, J. Metal Ion Binding to Peptides: Oxygen or Nitrogen Sites? Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 330–332, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitta, R.K.; Gross, M.L. Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry Reveal Self-Association and Metal-Ion Binding of Hydrophobic Peptides: A Study of the Gramicidin Dimer. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, D.D.; Schug, K.A. A Review on the Interrogation of Peptide–Metal Interactions Using Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 686, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampà, M.; Sgobba, E. Insight to functional conformation and noncovalent interactions of protein-protein assembly using MALDI mass spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Fan, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Li, N.; Guo, M. Advances in MS based strategies for probing ligand-target interactions: Focus on soft ionization mass spectrometric techniques. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, E.; Zenobi, R.; Vetter, S. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectra Reflect Solution-Phase Zinc Finger Peptide Complexation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertz, S.H.; Cope, S.; Dorton, D.; Murphy, M.; Ogle, C.A. Organocuprate Cross-Coupling: The Central Role of the Copper(III) Intermediate and the Importance of the Copper(I) Precursor. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 7212–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohani, N.; Hurrell, R.; Kelishadi, R.; Schulin, R. Zinc and Its Importance for Human Health: An Integrative Review. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013, 18, 144–157. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, K.H.; Wuehler, S.E.; Peerson, J.M. The Importance of Zinc in Human Nutrition and Estimation of the Global Prevalence of Zinc Deficiency. Food Nutr. Bull. 2001, 22, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselbalch, S.G.; Madsen, K.; Svarer, C.; Pinborg, L.H.; Holm, S.; Paulson, O.B.; Waldemar, G.; Knudsen, G.M. Reduced 5-HT2A Receptor Binding in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, H.; Luczkowski, M.; Remelli, M.; Valensin, D. Copper, Zinc and Iron in Neurodegenerative Diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Prion Diseases). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatta, P.; Drago, D.; Bolognin, S.; Sensi, S.L. Alzheimer’s Disease, Metal Ions and Metal Homeostatic Therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Fernandez-Lima, F.A.; Perez, L.M.; Russell, D.H. A New Copper Containing MALDI Matrix That Yields High Abundances of [Peptide + Cu] + Ions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudent, M.; Girault, H.H. On-Line Electrogeneration of Copper-Peptide Complexes in Microspray Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 19, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bluhm, B.K.; Shields, S.J.; Bayse, C.A.; Hall, M.B.; Russell, D.H. Determination of Copper Binding Sites in Peptides Containing Basic Residues: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Study. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 204, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupaescu, A.V.; Jureschi, M.; Ciobanu, C.I.; Ion, L.; Zbancioc, G.; Petre, B.A.; Drochioiu, G. FTIR and MS Evidence for Heavy Metal Binding to Anti-Amyloidal NAP-Like Peptides. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murariu, M.; Habasescu, L.; Ciobanu, C.-I.; Gradinaru, R.V.; Pui, A.; Drochioiu, G.; Mangalagiu, I. Interaction of Amyloid Aβ(9–16) Peptide Fragment with Metal Ions: CD, FT-IR, and Fluorescence Spectroscopic Studies. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, H. Zn(II) Chelating with Peptides Found in Sesame Protein Hydrolysates: Identification of the Binding Sites of Complexes. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Anedda, R. NMR Studies of Zinc Binding in a Multi-Histidinic Peptide Fragment. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 1282–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Drogaris, P.; Bern, M. Identification of Tandem Mass Spectra of Mixtures of Isomeric Peptides. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3270–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupaescu, A.-V.; Ciobanu, C.-I.; Humelnicu, I.; Petre, B.A.; Murariu, M.; Drochioiu, G. Design and Synthesis of New Anti-Amyloid NAP-Based/like Peptides. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2019, 64, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, A.T.; Raja, A. Biochemistry, Histidine. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, B.B.; Kinter, M. Effects of the Position of Internal Histidine Residues on the Collision-Induced Fragmentation of Triply Protonated Tryptic Peptides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 12, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Frankevich, V.; Knochenmuss, R.; Friess, S.D.; Zenobi, R. Reduction of Cu(II) in Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 14, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Prudent, M.; Qiao, L.; Mendez, M.A.; Girault, H.H. Copper(i) and Copper(Ii) Binding to β-Amyloid 16 (Aβ16) Studied by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Metallomics 2010, 2, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roepstorff, P.; Fohlman, J. Proposal for a common nomenclature for sequence ions in mass spectra of peptides. Biomed. Mass Spectrom. 1984, 11, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suckau, D.; Resemann, A.; Schuerenberg, M.; Hufnagel, P.; Franzen, J.; Holle, A. A novel MALDI LIFT-TOF/TOF mass spectrometer for proteomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzaskowski, B.; Adamowicz, L.; Deymier, P.A. A Theoretical Study of Zinc(II) Interactions with Amino Acid Models and Peptide Fragments. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 13, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, P.; Zerrouk, N.; Martens, T.; Charlot, M.-F.; Girerd, J.J.; Chaumeil, J.C.; Tomas, A. Copper Complexation by Amino Acid: L-Glutamine–Copper(II)– L-Histidine Ternary System. J. Trace Microprobe Tech. 2003, 21, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, C.S.; Jureschi, M.; Drochioiu, G. Aluminium binding to modified amyloid-β peptides: Implications for alzheimer’s disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.; Homburg, S.V.; Ehrmann, A. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) on Biopolymers and Hydrogels for Biotechnological Applications—Possibilities and Limits. Polymers 2022, 14, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habasescu, L.; Jureschi, M.; Petre, B.-A.; Mihai, M.; Gradinaru, R.-V.; Murariu, M.; Drochioiu, G. Histidine-Lacked Aβ(1–16) Peptides: PH-Dependent Conformational Changes in Metal Ion Binding. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 2529–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drochioiu, G.; Manea, M.; Dragusanu, M.; Murariu, M.; Dragan, E.S.; Petre, B.A.; Mezo, G.; Przybylski, M. Interaction of β-Amyloid(1–40) Peptide with Pairs of Metal Ions: An Electrospray Ion Trap Mass Spectrometric Model Study. Biophys. Chem. 2009, 144, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hane, F.; Tran, G.; Attwood, S.J.; Leonenko, Z. Cu2+ affects amyloid-β (1–42) aggregation by increasing peptide-peptide binding forces. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österlund, N.; Wärmländer, S.K.T.S.; Gräslund, A. Cell-Penetrating Peptides with Unexpected Anti-Amyloid Properties. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupaescu, A.-V.; Iavorschi, M.; Covasa, M. The Use of Bioactive Compounds in Hyperglycemia- and Amyloid Fibrils-Induced Toxicity in Type 2 Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, A.; Khavinson, V.; Linkova, N.; Petukhov, M. Neuroepigenetic Mechanisms of Action of Ultrashort Peptides in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernick, D.; Zhong, R.; Li, L. The Role of HDL and HDL Mimetic Peptides as Potential Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanasu, C. Peptides-Based Therapy and Diagnosis. Strategies for Non-Invasive Therapies in Cancer. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, X.; Xiao, W.; Lam, K.S. Tumor-Targeting Peptides from Combinatorial Libraries. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic Peptides: Current Applications and Future Directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jureschi, M.; Humelnicu, I.; Petre, B.A.; Ciobanu, C.I.; Murariu, M.; Drochioiu, G. Solid Phase Synthesis of Four Analogs of Amyloid-β(9–16) Peptide: MS and FT-IR Characterization. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2019, 64, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
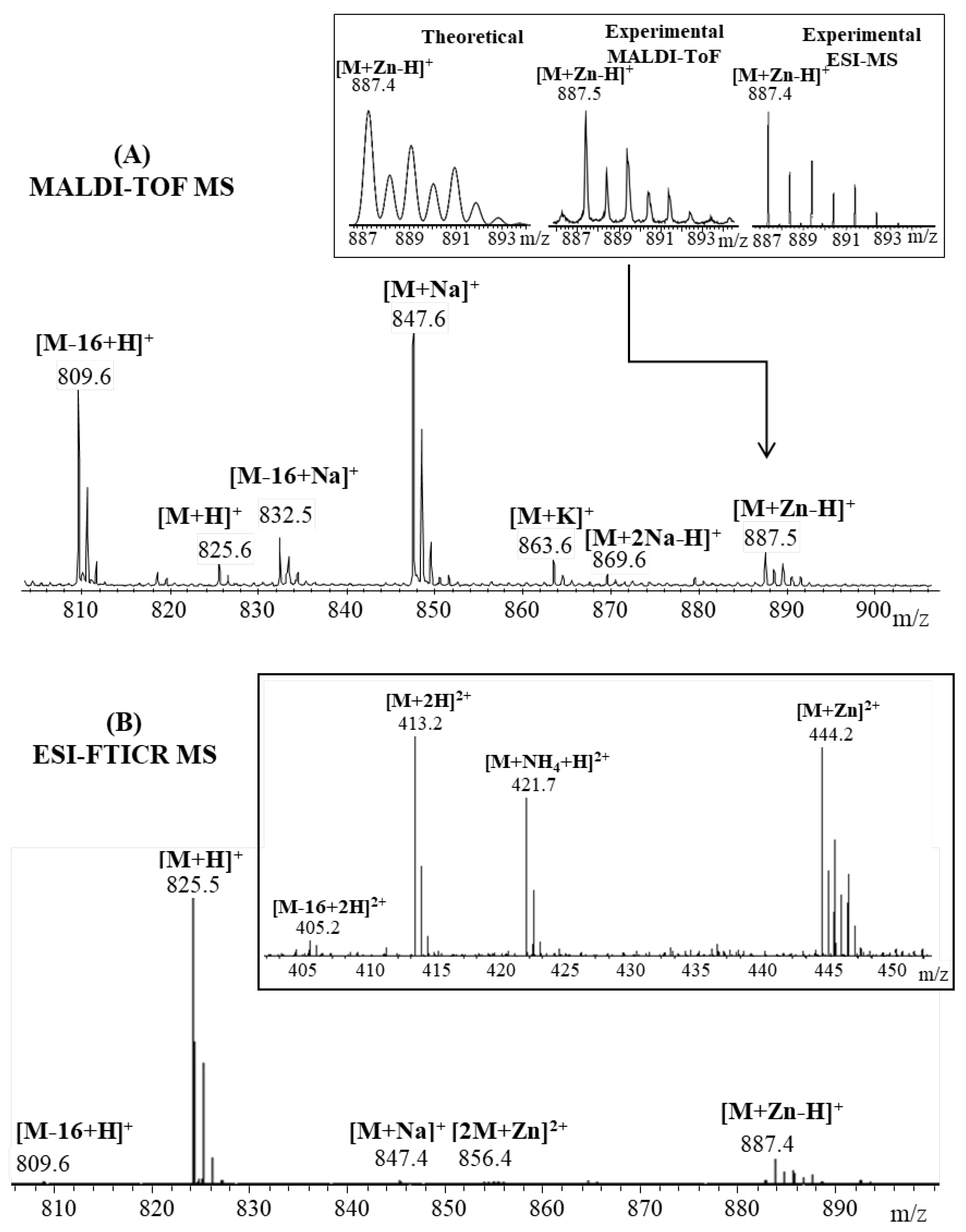
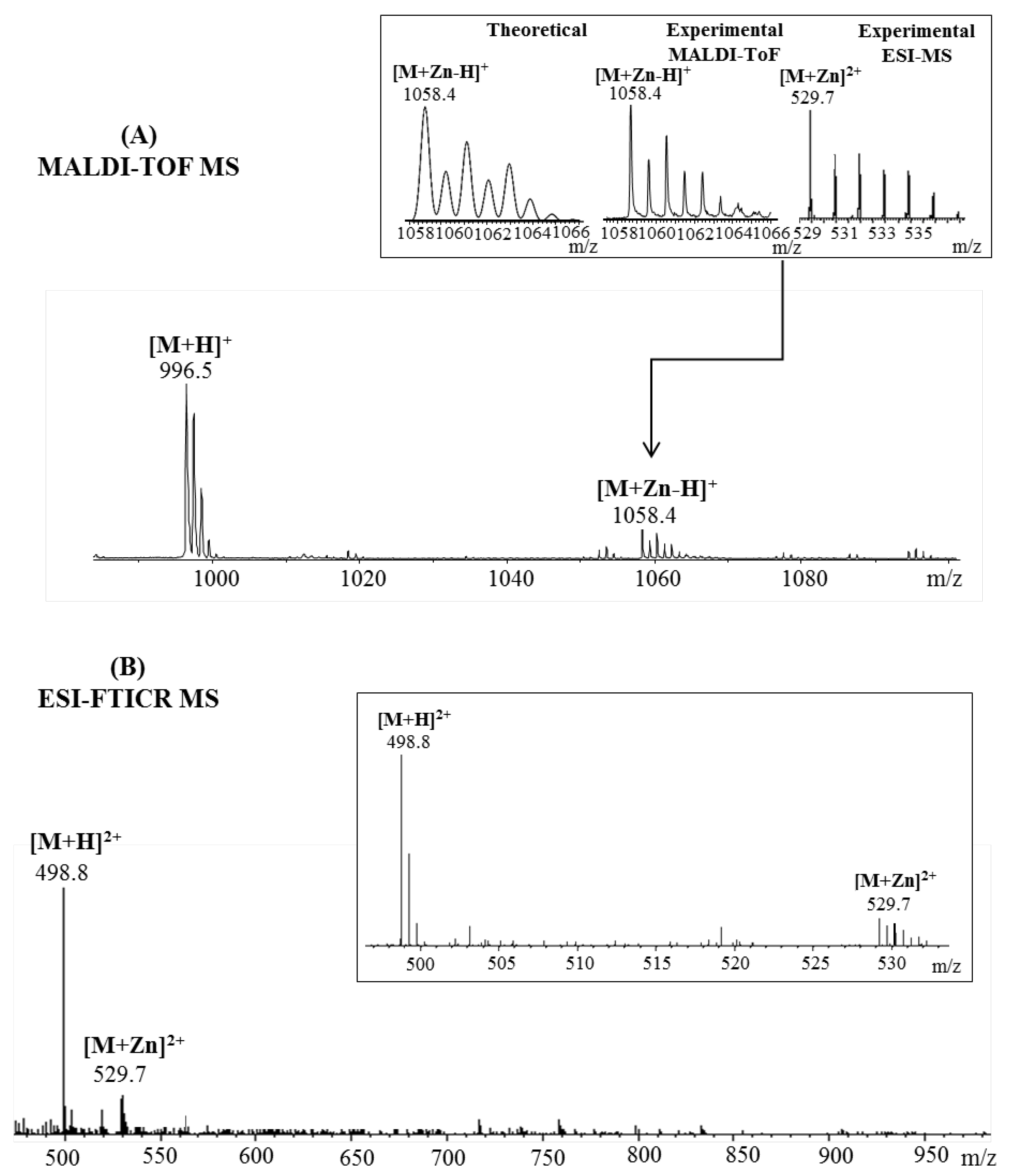
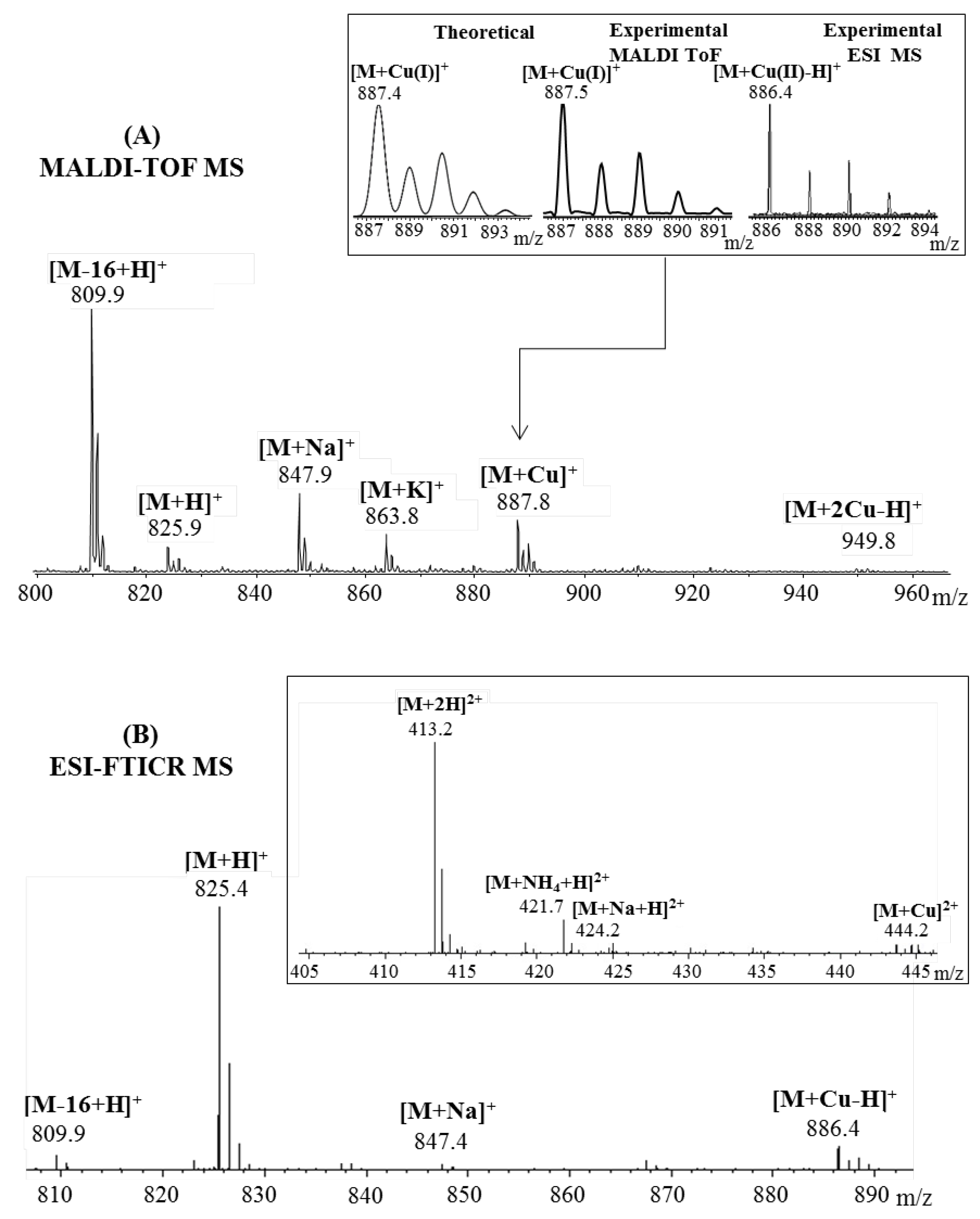
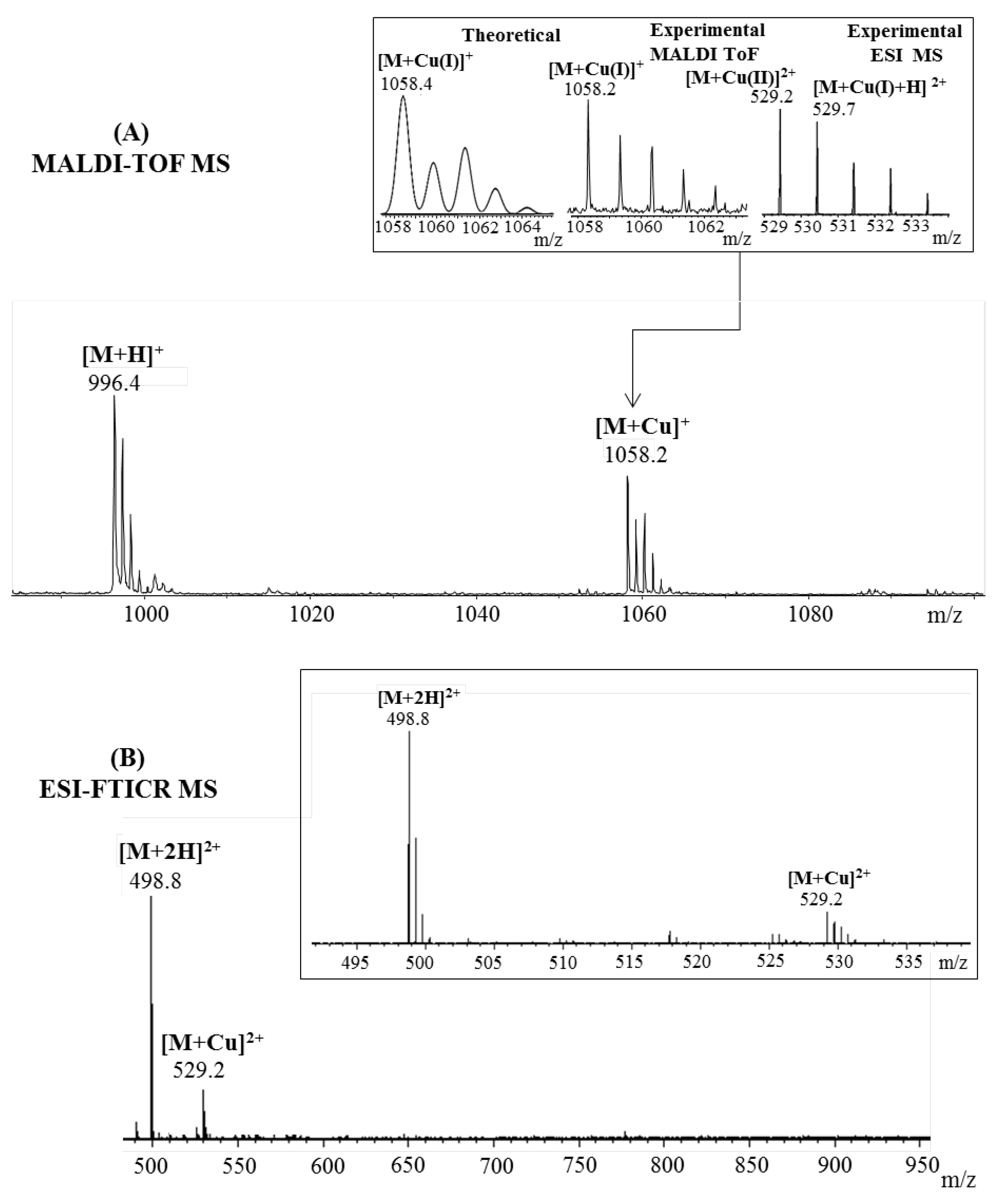

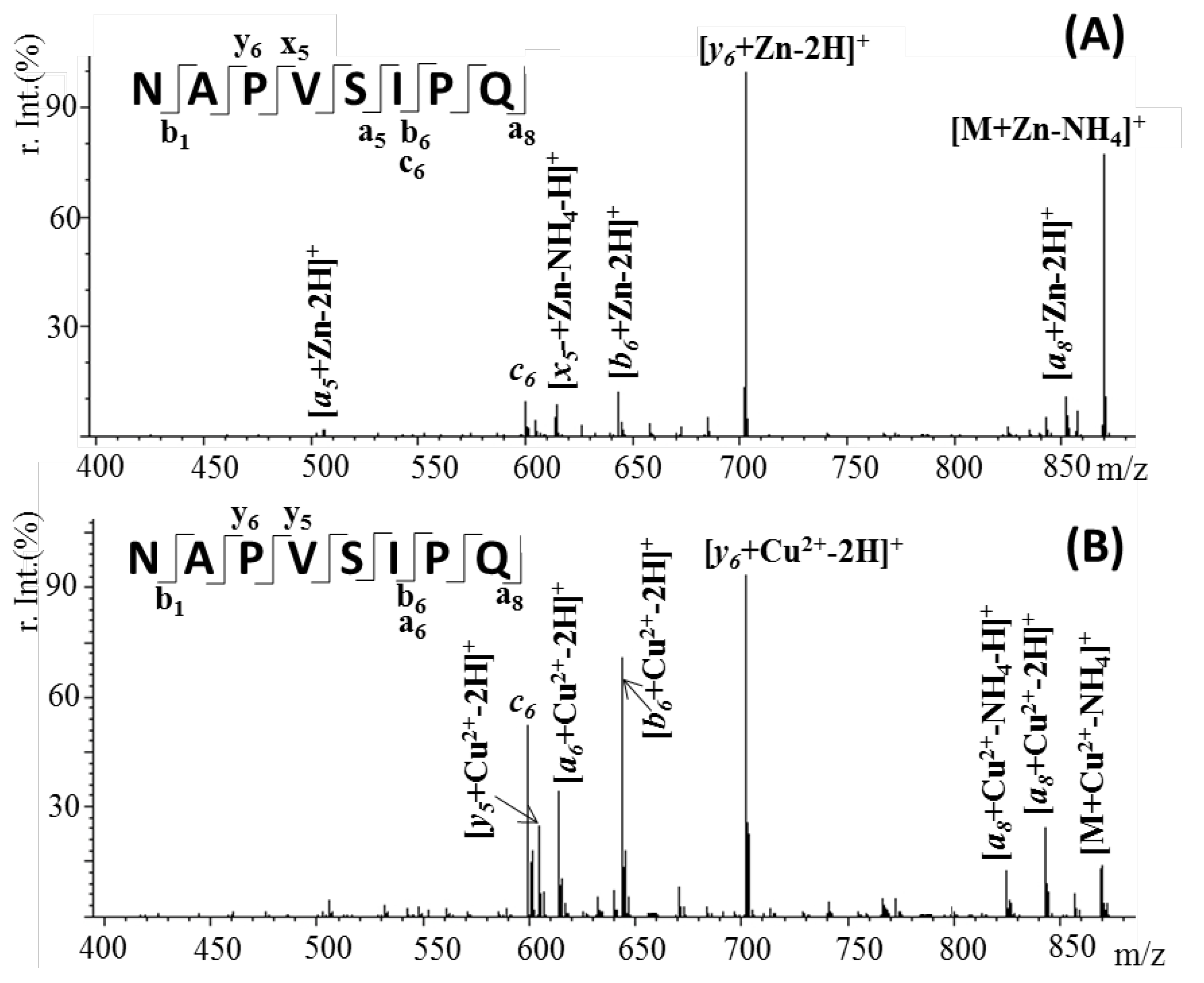


| Fragmented Ion | Sequence | Predicted (m/z) | Observed (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [M+ Zn-H]+ | [M + Zn-NH4]+ | 871.1988 | 871.2012 |
| [a8 + Zn-2H]+ | 842.4358 | 842.4398 | |
| [y6 + Zn-2H]+ | 703.3127 | 703.3145 | |
| [b6 + Zn-2H]+ | 645.2395 | 645.2457 | |
| [x5 + Zn-NH4-H]+ | 615.4617 | 615.4673 | |
| c6 | 599.3511 | 599.3515 | |
| [a5 + Zn-2H]+ | 504.3096 | 504.3138 | |
| [M+ Cu-H]+ | [M + Cu2+-NH4]+ | 869.3648 | 869.3651 |
| [a8 + Cu2+-2H]+ | 840.4818 | 840.4827 | |
| [a8 + Cu2+-NH4-H]+ | 823.4428 | 823.443 | |
| [y6 + Cu2+-2H]+ | 701.3787 | 701.3782 | |
| [b6 + Cu2+-2H]+ | 643.2024 | 643.1998 | |
| [a6 + Cu2+-2H]+ | 615.1836 | 615.1843 | |
| [y5 + Cu2+-2H]+ | 604.1872 | 604.1902 | |
| c6 | 599.3511 | 599.3524 |
| Fragmented Ion | Sequence | Predicted (m/z) | Observed (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [M + Zn-H]+ | [M + Zn-H]+ | 1060.3988 | 1060.4022 |
| [M + Zn-NH4]+ | 1043.4514 | 1043.4437 | |
| [a8 + Zn-2H]+ | 1014.2408 | 1014.2487 | |
| [b7 + Zn-2H]+ | 914.3472 | 914.3408 | |
| [b6 + Zn-2H]+ | 786.2281 | 786.2245 | |
| [b6 + Zn-NH4-H]+ | 769.2502 | 769.2429 | |
| a5 | 558.2040 | 558.1998 | |
| [M + Cu-H]+ | [M + Cu+-NH3]+ | 1043.3867 | 1043.3816 |
| [M + Cu2+-NH4]+ | 1042.3859 | 1042.3842 | |
| [z7 + Cu+-H]+ | 985.4288 | 985.4268 | |
| a8 | 951.4534 | 951.4452 | |
| [b7 + Cu+-H]+ | 913.3502 | 913.3427 | |
| [a7 + Cu+-H]+ | 885.2957 | 885.2904 | |
| [y6 + Cu2+-2H]+ | 838.3398 | 838.3342 | |
| [z6 + Cu+-H]+ | 822.3448 | 822.3403 | |
| [b6 + Cu+-H]+ | 785.2418 | 785.2442 | |
| [a6 + Cu+-H]+ | 757.2336 | 757.2369 | |
| [y5 + Cu2+-2H]+ | 709.3309 | 709.3378 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iavorschi, M.; Lupăescu, A.-V.; Darie-Ion, L.; Indeykina, M.; Hitruc, G.E.; Petre, B.A. Cu and Zn Interactions with Peptides Revealed by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091096
Iavorschi M, Lupăescu A-V, Darie-Ion L, Indeykina M, Hitruc GE, Petre BA. Cu and Zn Interactions with Peptides Revealed by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(9):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091096
Chicago/Turabian StyleIavorschi, Monica, Ancuța-Veronica Lupăescu, Laura Darie-Ion, Maria Indeykina, Gabriela Elena Hitruc, and Brîndușa Alina Petre. 2022. "Cu and Zn Interactions with Peptides Revealed by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 9: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091096
APA StyleIavorschi, M., Lupăescu, A.-V., Darie-Ion, L., Indeykina, M., Hitruc, G. E., & Petre, B. A. (2022). Cu and Zn Interactions with Peptides Revealed by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091096







