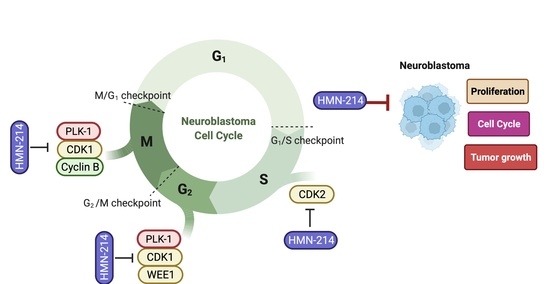
Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 by HMN-214 Blocks Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PLK1 Expression Strongly Correlates with Poor NB Survival
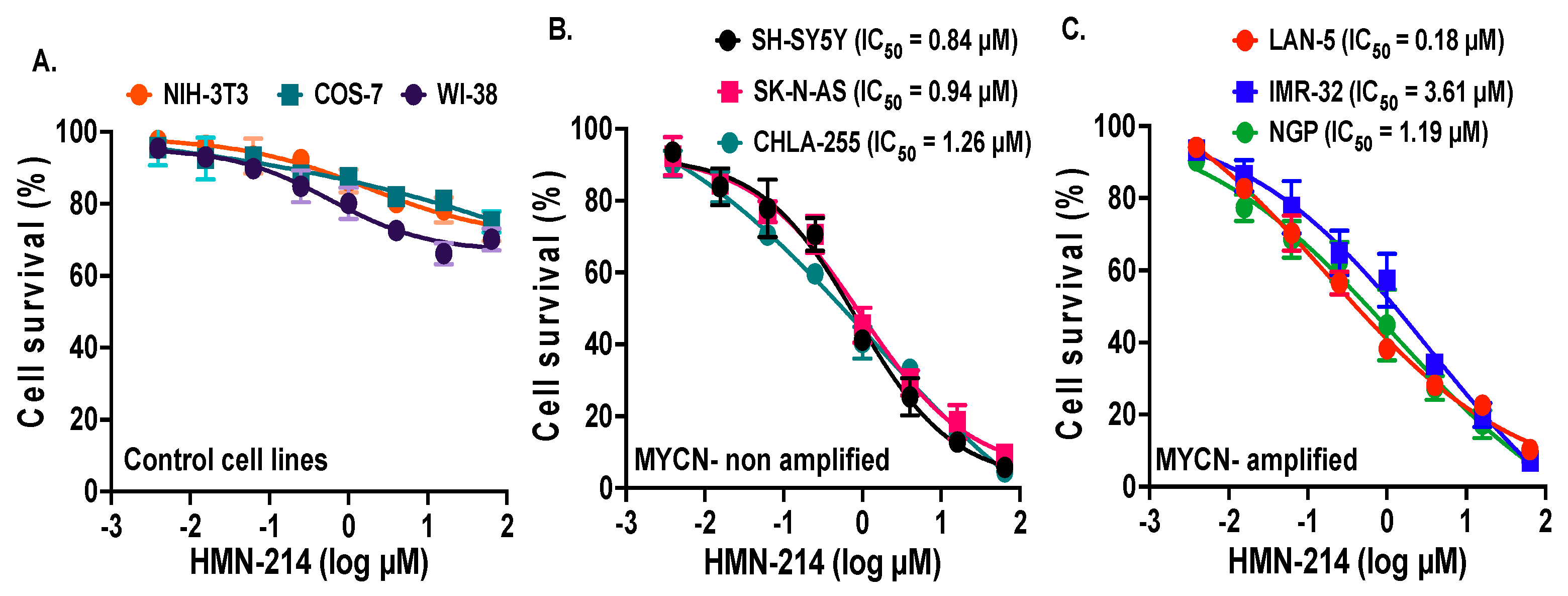
2.2. HMN-214 Inhibits NB Cell Proliferation and Colony Formation
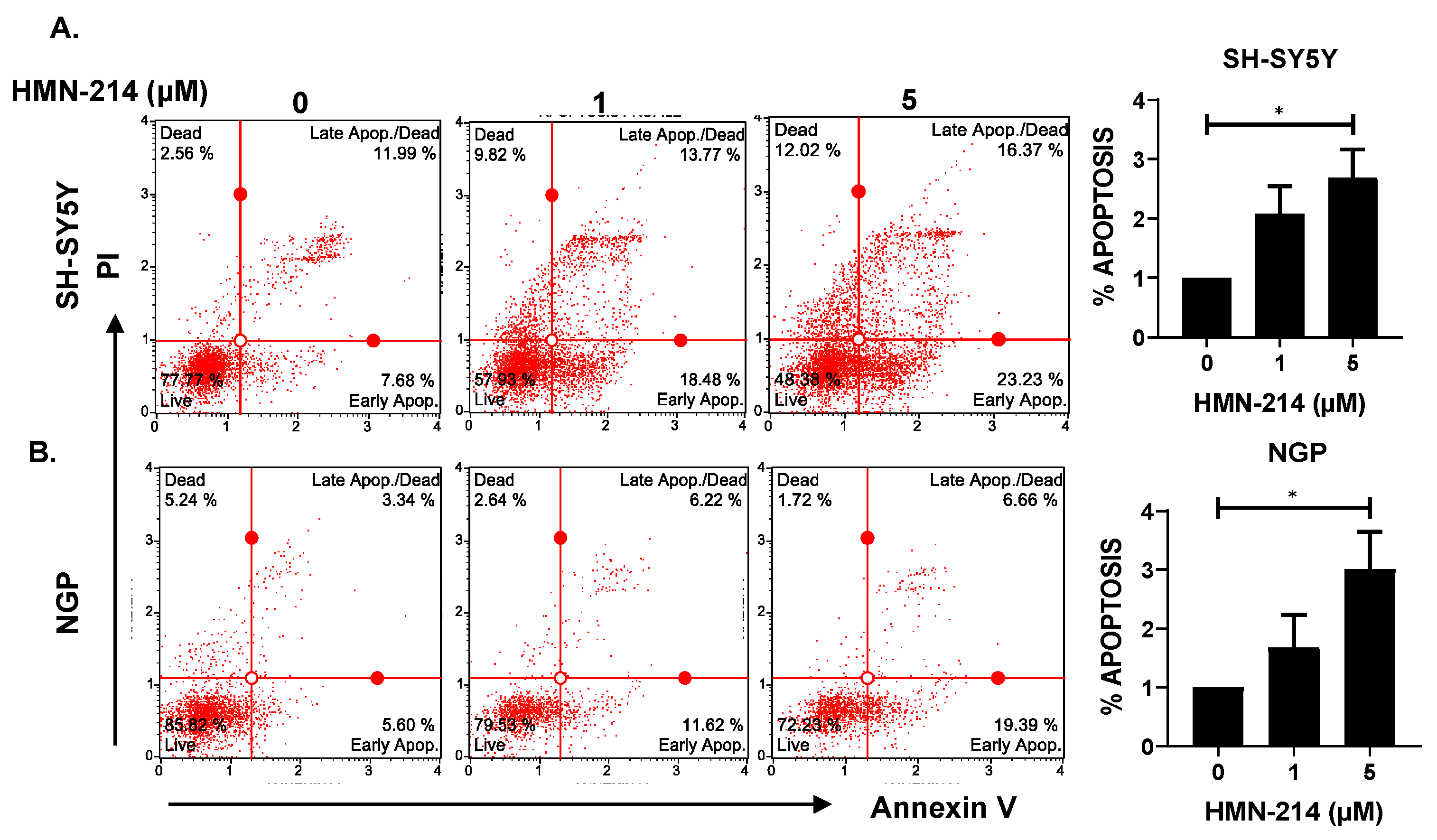
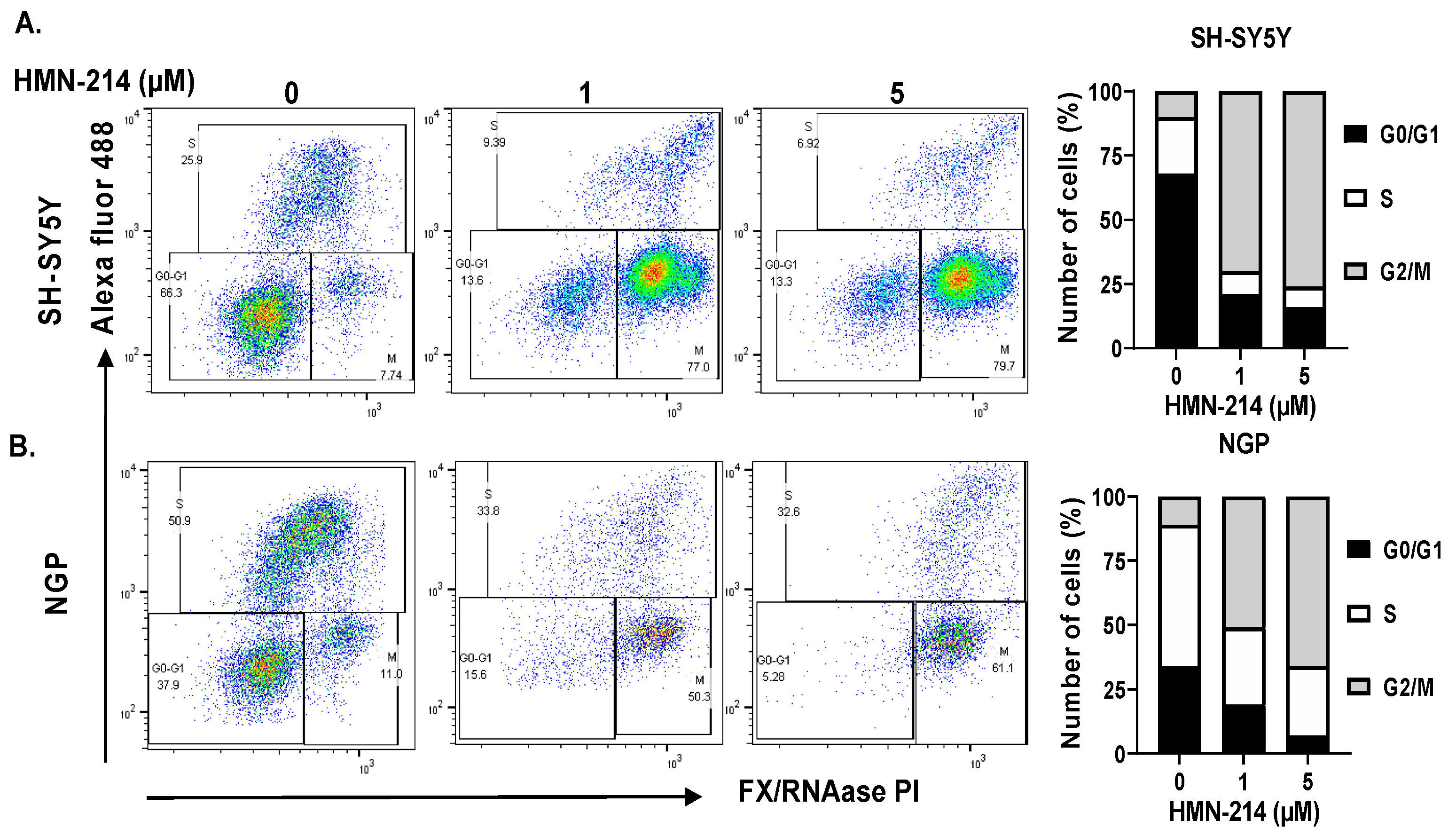
2.3. HMN-214 Induces Apoptosis and Blocks Cell Cycle Progression in NB
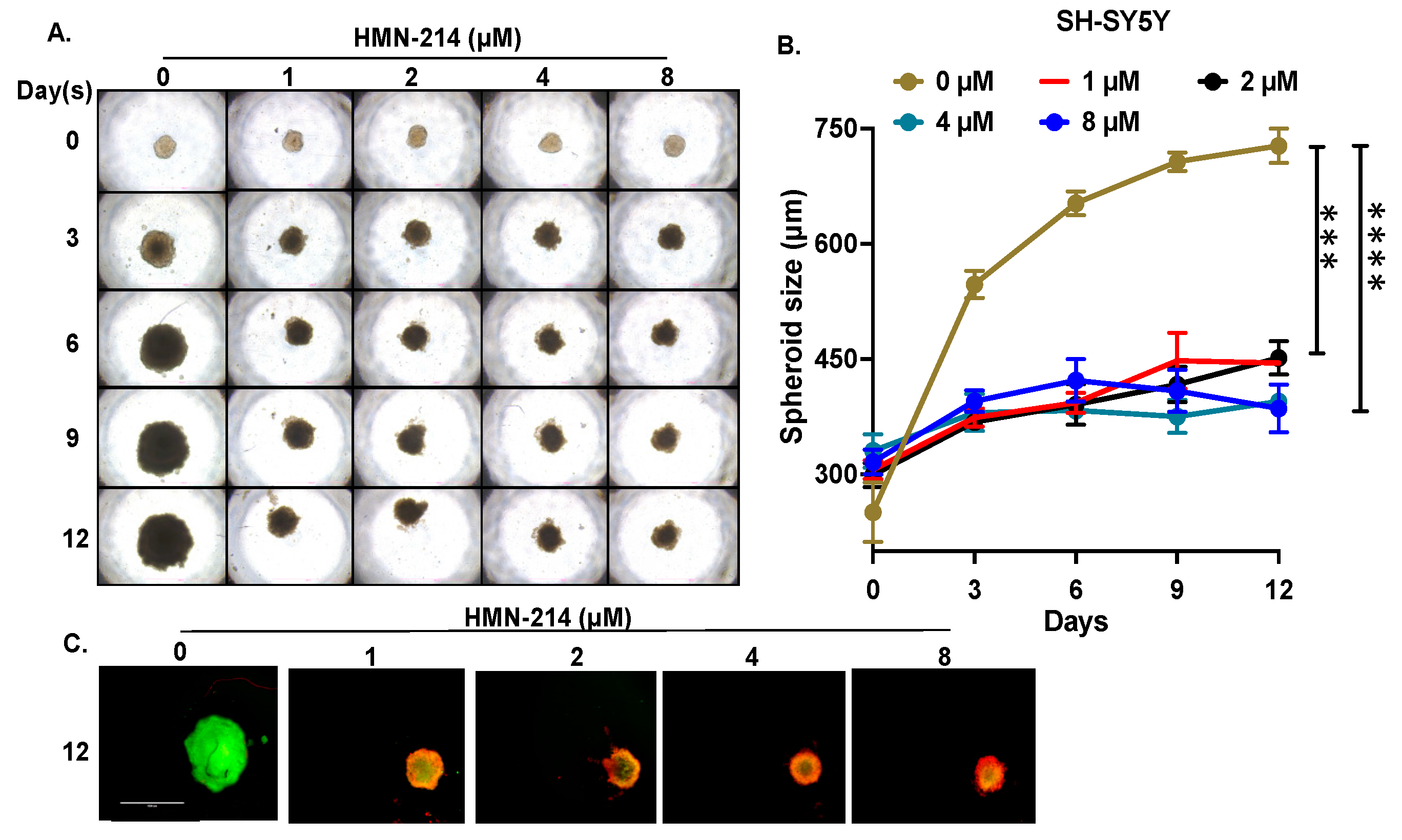
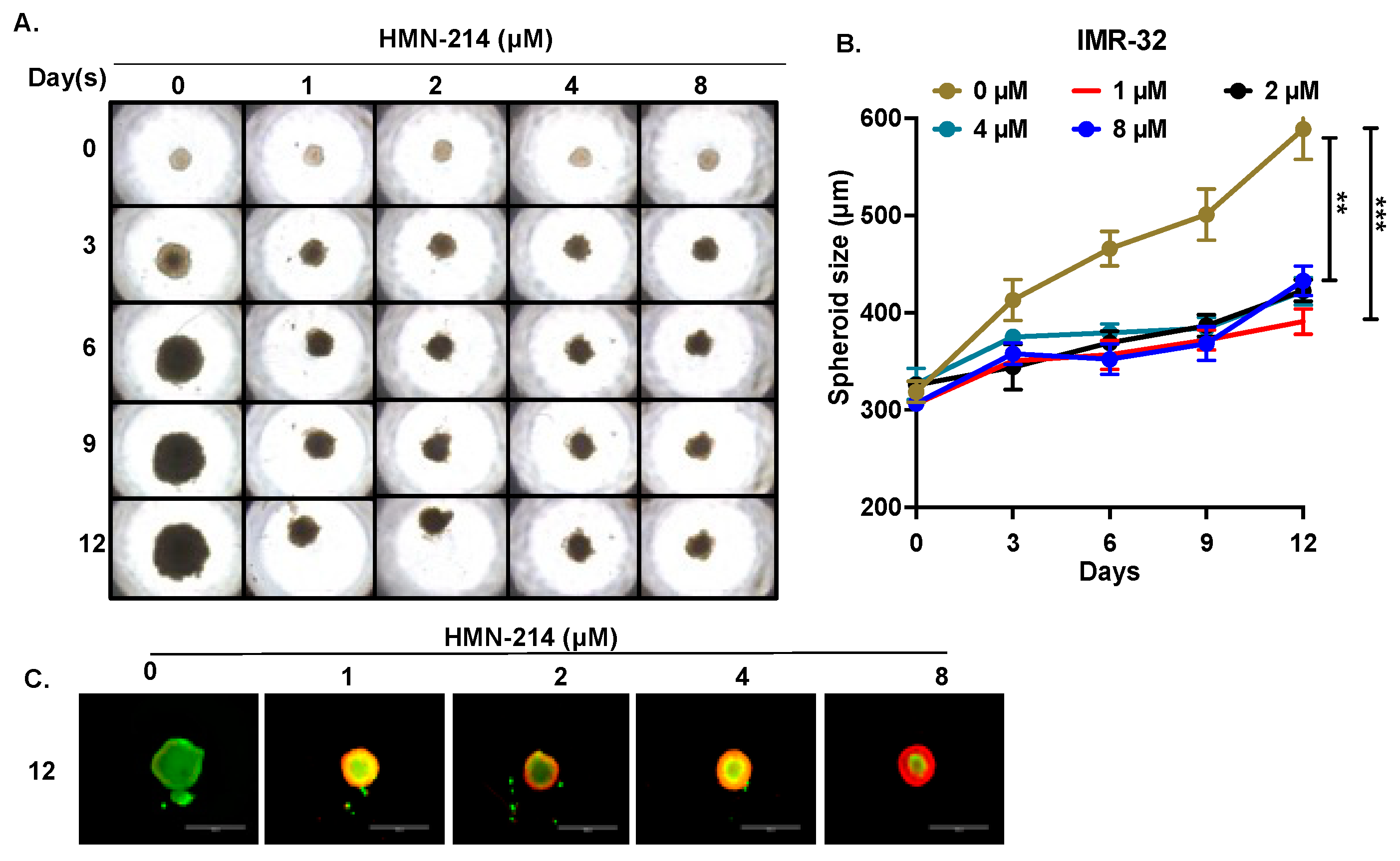
2.4. HMN-214 Inhibits NB Spheroid Tumor Growth
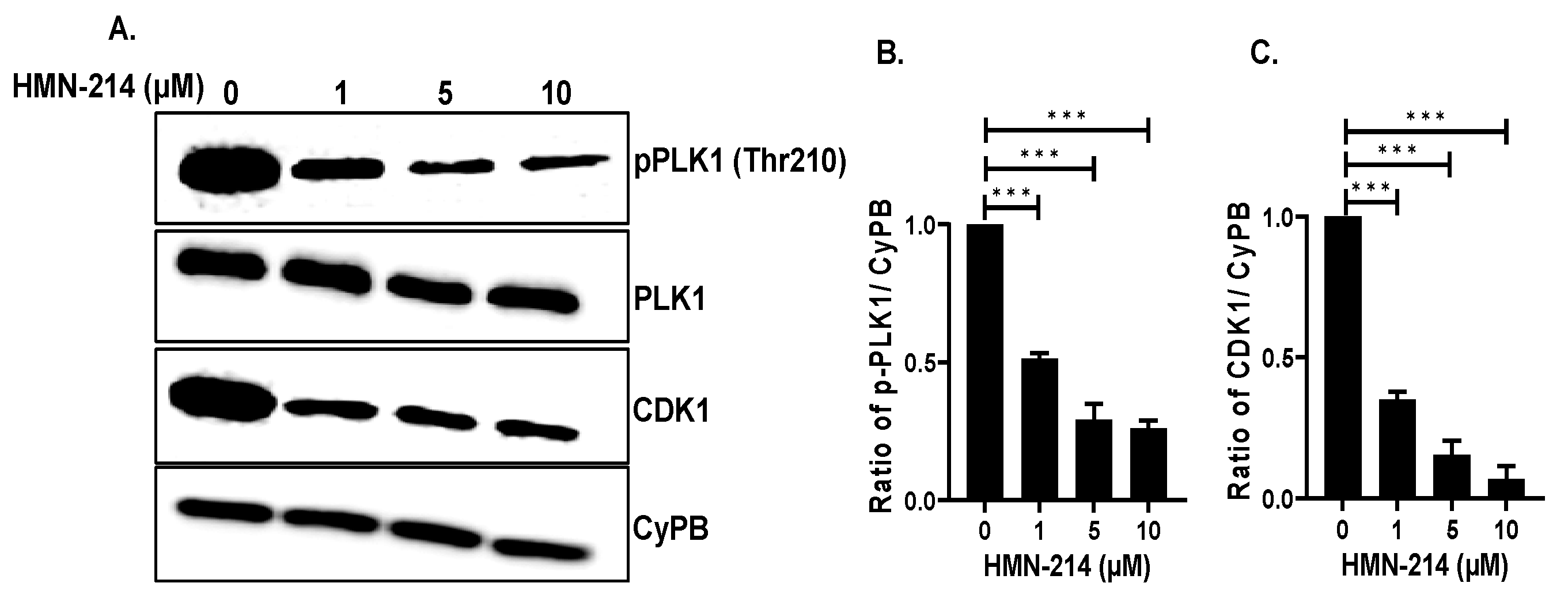
2.5. HMN-214 Inhibits PLK1 Pathway and Cell Cycle Signaling Cascade
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture, Reagents and Patient Dataset
4.2. Cell Viability and Colonogenic Assay
4.3. Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Assay
4.4. 3D Spheroid Tumor Assay
4.5. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
5. Statistical Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Twist, C.J.; Schmidt, M.L.; Naranjo, A.; London, W.B.; Tenney, S.C.; Marachelian, A.; Shimada, H.; Collins, M.H.; Esiashvili, N.; Adkins, E.S.; et al. Maintaining Outstanding Outcomes Using Response- and Biology-Based Therapy for Intermediate-Risk Neuroblastoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group Study ANBL0531. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3243–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, C.H.; Beierle, A.M.; Hutchins, S.C.; Marayati, R.; Bownes, L.V.; Stewart, J.E.; Markert, H.R.; Erwin, M.H.; Aye, J.M.; Yoon, K.J.; et al. Targeting High-Risk Neuroblastoma Patient-Derived Xenografts with Oncolytic Virotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.; Foster, J. High-Risk Neuroblastoma Treatment Review. Children 2018, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyai, L.; Trexler, M.; Kerekes, K.; Csuka, O.; Patthy, L. Use of signals of positive and negative selection to distinguish cancer genes and passenger genes. eLife 2021, 10, e59629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kressin, M.; Fietz, D.; Becker, S.; Strebhardt, K. Modelling the Functions of Polo-Like Kinases in Mice and Their Applications as Cancer Targets with a Special Focus on Ovarian Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, M.; Sanhaji, M.; Pietsch, L.; Béquignon, I.; Herbrand, A.K.; Süß, E.; Gande, S.L.; Caspar, B.; Kudlinzki, D.; Saxena, K.; et al. Modulation of the Allosteric Communication between the Polo-Box Domain and the Catalytic Domain in Plk1 by Small Compounds. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X. PLK1, A Potential Target for Cancer Therapy. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.Y.; Hwang, H.I.; Jang, Y.J. Polo-like kinase-1 in DNA damage response. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kim, J. PLK-1 Targeted Inhibitors and Their Potential against Tumorigenesis. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 705745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, G.; Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Kim, J. Regulatory functional territory of PLK-1 and their substrates beyond mitosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37942–37962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gatz, S.A.; Aladowicz, E.; Casanova, M.; Chisholm, J.C.; Kearns, P.R.; Fulda, S.; Geoerger, B.; Schäfer, B.W.; Shipley, J.M. A Perspective on Polo-Like Kinase-1 Inhibition for the Treatment of Rhabdomyosarcomas. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, R.; Li, M.; Xia, S. Identification and assessment of PLK1/2/3/4 in lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma: Evidence from methylation profile. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6652–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.-H.; Yeh, H.-N.; Huang, C.-T.; Wang, W.-H.; Hsu, W.-M.; Huang, H.-C.; Juan, H.-F. BI-2536 Promotes Neuroblastoma Cell Death via Minichromosome Maintenance Complex Components 2 and 10. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaglani, S.; Gonzalez-Kozlova, E.; Lundon, D.J.; Tewari, A.K.; Dogra, N.; Kyprianou, N. Exosomes as A Next-Generation Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tool in Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollur, S.; Prasad, S.; Pradeep, S.; Veerapur, R.; Patil, S.; Amachawadi, R.G.; S, R.P.; Lamraoui, G.; Al-Kheraif, A.; Elgorban, A.; et al. Luteolin-Fabricated ZnO Nanostructures Showed PLK-1 Mediated Anti-Breast Cancer Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liang, S.; Saliakoura, M.; Yang, H.; Vassella, E.; Konstantinidou, G.; Tschan, M.; Hegedüs, B.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Y.; et al. Synergistic effects of FGFR1 and PLK1 inhibitors target a metabolic liability in KRAS-mutant cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoffski, P. Polo-like kinase (PLK) inhibitors in preclinical and early clinical development in oncology. Oncologist 2009, 14, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.D.; Elmer, J.J.; Eaton, S.; Gonzalez-Malerva, L.; LaBaer, J.; Rege, K. Kinome-level screening identifies inhibition of polo-like kinase-1 (PLK1) as a target for enhancing non-viral transgene expression. J. Control. Release 2015, 204, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, D.V.; Martens-de Kemp, S.R.; Buijze, M.; Stigter-van Walsum, M.; Bloemena, E.; Dietrich, R.; Leemans, C.R.; van Beusechem, V.W.; Braakhuis, B.J.; Brakenhoff, R.H. Targeting PLK1 as a novel chemopreventive approach to eradicate preneoplastic mucosal changes in the head and neck. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97928–97940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, M.; Honmura, T.; Watanabe, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nogawa, M.; Nishimura, I.; Katoh, F.; Matsuda, M.; Hidaka, H. In vivo antitumor activity of a novel sulfonamide, HMN-214, against human tumor xenografts in mice and the spectrum of cytotoxicity of its active metabolite, HMN-176. Investig. New Drugs 2003, 21, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, L.L.; Taylor, C.; Pilkington, D.L.; Cohen, J.L.; von Hoff, D.D. A phase I pharmacokinetic study of HMN-214, a novel oral stilbene derivative with polo-like kinase-1-interacting properties, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5182–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Ohshima, N.; Ikenoya, M.; Komori, K.; Katoh, F.; Hidaka, H. HMN-176, an active metabolite of the synthetic antitumor agent HMN-214, restores chemosensitivity to multidrug-resistant cells by targeting the transcription factor NF-Y. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6942–6947. [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio, M.A.; Mikhailov, A.; Rieder, C.L.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Palazzo, R.E. The small organic compound HMN-176 delays satisfaction of the spindle assembly checkpoint by inhibiting centrosome-dependent microtubule nucleation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Gundrum, L.; Cerna, C.; Gomez, L.; Izbicka, E. Investigation of HMN-176 anticancer activity in human tumor specimens in vitro and the effects of HMN-176 on differential gene expression. Investig. New Drugs 2005, 23, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovejero, S.; Bueno, A.; Sacristan, M.P. Working on Genomic Stability: From the S-Phase to Mitosis. Genes 2020, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akopyan, K.; Cascales, H.S.; Hukasova, E.; Saurin, A.; Müllers, E.; Jaiswal, H.; Hollman, D.A.; Kops, G.; Medema, R.; Lindqvist, A. Assessing kinetics from fixed cells reveals activation of the mitotic entry network at the S/G2 transition. Mol. Cell. 2014, 53, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, B.; Hegarat, N.; Akopyan, K.; Sala-Gaston, J.; Bartek, J.; Hochegger, H.; Lindqvist, A. DNA Replication Determines Timing of Mitosis by Restricting CDK1 and PLK1 Activation. Mol. Cell. 2018, 71, 117–128.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, H.; Benada, J.; Müllers, E.; Akopyan, K.; Burdova, K.; Koolmeister, T.; Helleday, T.; Medema, R.H.; Macurek, L.; Lindqvist, A. ATM/Wip1 activities at chromatin control Plk1 re-activation to determine G2 checkpoint duration. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2161–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, T.; Li, F.; Sun, L.; Wei, H.; Zhenye, Y.; et al. Polo-like kinase 1 coordinates biosynthesis during cell cycle progression by directly activating pentose phosphate pathway. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmucker, S.; Sumara, I. Molecular dynamics of PLK1 during mitosis. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 1, e954507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, H. Current clinical trials with polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors in solid tumors. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, S.K.; Eng, C. Up-and-Coming Experimental Drug Options for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 12, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; Park, J.E.; Bang, J.K.; Lee, E. Recent Advances and New Strategies in Targeting Plk1 for Anticancer Therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinshtein, N.; Datti, A.; Fujitani, M.; Uehling, D.; Prakesch, M.; Isaac, M.; Irwin, M.S.; Wrana, J.L.; Al-Awar, R.; Kaplan, D.R. Small molecule kinase inhibitor screen identifies polo-like kinase 1 as a target for neuroblastoma tumor-initiating cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carcer Diez, G.; Venkateswaran, S.V.; Salgueiro, L.; El Bakkali, A.; Somogyi, K.; Rowald, K.; Montañés, P.; Sanclemente, M.; Escobar, B.; de Martino, A.; et al. Plk1 overexpression induces chromosomal instability and suppresses tumor development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, T.L.; Zhong, W.; Setaluri, V.; Spiegelman, V.S.; Ahmad, N. Targeted depletion of Polo-like kinase (Plk) 1 through lentiviral shRNA or a small-molecule inhibitor causes mitotic catastrophe and induction of apoptosis in human melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussey, K.J.; Bapat, A.; Linnehan, C.; Wandoloski, M.; Dastrup, E.; Rogers, E.; Gonzales, P.; Demeure, M.J. Targeting polo-like kinase 1, a regulator of p53, in the treatment of adrenocortical carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.; Golubeva, V.; Rix, L.L.R.; Berndt, N.; Luo, Y.; Ward, G.A.; Gray, J.E.; Schonbrunn, E.; Lawrence, H.R.; Monteiro, A.N.; et al. Dual Targeting of WEE1 and PLK1 by AZD1775 Elicits Single Agent Cellular Anticancer Activity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Bi, C.; Zhao, X.; Lwin, T.; Wang, C.; Yuan, J.; Silva, A.S.; Shah, B.D.; Fang, B.; Li, T.; et al. PLK1 stabilizes a MYC-dependent kinase network in aggressive B cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5517–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, F.; Weiss, J.G.; Lindner, S.E.; Lohmüller, M.; Herzog, S.; Spiegl, S.F.; Menke, P.; Geley, S.; Labi, V.; Villunger, A. Checkpoint kinase 1 is essential for normal B cell development and lymphomagenesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, R.; Agarwal, S. Dual Targeting of PI3K and HDAC by CUDC-907 Inhibits Pediatric Neuroblastoma Growth. Cancers 2022, 14, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, R.; Rouse, D.C.; Yu, Y.; Kabir, A.S.; Muth, A.; Yang, J.; Lipton, J.M.; Agarwal, S. BX-795 inhibits neuroblastoma growth and enhances sensitivity towards chemotherapy. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 15, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| PLK1 | AAGAGATCCCGGAGGTCCTA | TCATTCAGGAAAAGGTTGCC |
| WEE1 | TGGAGATCAATGGCATGAAA | AGTGCCATTGCTGAAGGTCT |
| CDK1 | CATGGATTCTTCACTTGTTAAGGT | TCCACTTCTGGCCACACTTC |
| CDK2 | TGGACACGCTGCTGGATG | AATGGCAGAAAGCTAGGCCC |
| c-Myc | TACACTAACATCCCACGCTCTG | CGCATCCTTGTCCTGTGAGT |
| CCBN1 | AAGAGCTTTAAACTTTGGTCTGGG | CTTTGTAAGTCCTTGATTTACCATG |
| CHEK1 | GACTGGGACTTGGTGCAAAC | TGCCATGAGTTGATGGAAGA |
| CHEK2 | TGAGAACCTTATGTGGAACCCC | ACAGCACGGTTATACCCAGC |
| MDM2 | GCAGTGAATCTACAGGGACGC | ATCCTGATCCAACCAATCACC |
| GAPDH | CACCATCTTCCAGGAGCGAG | TGATGACCCTTTTGGCTCCC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chilamakuri, R.; Rouse, D.C.; Agarwal, S. Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 by HMN-214 Blocks Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050523
Chilamakuri R, Rouse DC, Agarwal S. Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 by HMN-214 Blocks Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(5):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050523
Chicago/Turabian StyleChilamakuri, Rameswari, Danielle Crystal Rouse, and Saurabh Agarwal. 2022. "Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 by HMN-214 Blocks Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 5: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050523
APA StyleChilamakuri, R., Rouse, D. C., & Agarwal, S. (2022). Inhibition of Polo-like Kinase 1 by HMN-214 Blocks Cell Cycle Progression and Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth. Pharmaceuticals, 15(5), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15050523