Carbon Dots for Killing Microorganisms: An Update since 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Antimicrobial CDs
2.1. Nitrogen-Doped CDs
2.1.1. Nitrogen-Doped CDs Derived from Biomass
2.1.2. Nitrogen-Doped CDs Derived from Nitrogen-Containing Compounds
2.2. Metal-Containing CDs
2.3. CDs Derived from Antibacterial Compounds (Including Antibiotics)
2.4. Photoresponsive CDs
2.4.1. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
2.4.2. Photothermal Therapy (PTT)
3. Applications of Antimicrobial CDs in Medical and Industry Fields
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoseinnejad, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Katouzian, I. Inorganic and metal nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity in food packaging applications. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghunath, A.; Perumal, E. Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: A promise for the future. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Lin, Z.; Wang, T.; Yao, Z.; Qin, M.; Zheng, S.; Lu, W. Where does the toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles come from: The nanoparticles, the ions, or a combination of both? J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soenen, S.J.; Parak, W.J.; Rejman, J.; Manshian, B. (Intra)cellular stability of inorganic nanoparticles: Effects on cytotoxicity, particle functionality, and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2109–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon dots: A new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Lu, S.; Yang, B. Carbon-dot-enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Song, H.; Qu, X.; Chang, J.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Carbon dots as a new class of nanomedicines: Opportunities and challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 442, 214010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lu, S. The light of carbon dots: From mechanism to applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Lan, M. Recent advances and prospects of carbon dots in phototherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ðorđević, L.; Arcudi, F.; Cacioppo, M.; Prato, M. A multifunctional chemical toolbox to engineer carbon dots for biomedical and energy applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 112–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, P.; Zhang, H.; Duan, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Carbon dots as a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of cancer related anemia. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhenadhayalan, N.; Lin, K.C.; Saleh, T.A. Recent advances in functionalized carbon dots toward the design of efficient materials for sensing and catalysis applications. Small 2020, 16, 1905767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.W.; Bao, Y.W.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.G. Carbon quantum dots with intrinsic mitochondrial targeting ability for mitochondria-based theranostics. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10948–10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, T.; Gooding, J.J.; Liu, J. Review of carbon and graphene quantum dots for sensing. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Jia, C.; Wu, F.G. Carbon dots for intracellular sensing. Small Struct. 2022, 3, 2200033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Bao, Y.W.; Wu, F.G. Carbon dots for sensing and killing microorganisms. C 2019, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Tao, S.; Yue, D.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, W.; Yang, B. Recent advances in energy conversion applications of carbon dots: From optoelectronic devices to electrocatalysis. Small 2020, 16, 2001295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Sun, Y.P. Design and fabrication of carbon dots for energy conversion and storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2315–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, G.A.M.; Martindale, B.C.M.; Reisner, E. Carbon dots as photosensitisers for solar-driven catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6111–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Gomes, V.G.; Dehghani, A.; Ardekani, S.M. Engineering carbon quantum dots for photomediated theranostics. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.H.; Gao, G.; Chen, X.; Jia, H.R.; Li, Y.H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, F.G. Carbon dot-based platform for simultaneous bacterial distinguishment and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32170–32181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.H.; Cheng, X.; Bao, Y.W.; Hua, X.W.; Gao, G.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.W.; Zhu, Y.X.; Wu, F.G. Multifunctional quaternized carbon dots with enhanced biofilm penetration and eradication efficiencies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5104–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Sun, L.; Xue, S.; Qu, D.; An, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Recent advances of carbon dots as new antimicrobial agents. SmartMat 2022, 3, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.G. Carbon dots as drug delivery vehicles for antimicrobial applications: A minireview. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202200003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Jabari, E.; Jabbari, E. Functionalized carbon-based nanomaterials and quantum dots with antibacterial activity: A review. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahshahanipour, M.; Rezaei, B.; Ensafi, A.A.; Etemadifar, Z. An ancient plant for the synthesis of a novel carbon dot and its applications as an antibacterial agent and probe for sensing of an anti-cancer drug. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boobalan, T.; Sethupathi, M.; Sengottuvelan, N.; Kumar, P.; Balaji, P.; Gulyás, B.; Padmanabhan, P.; Selvan, S.T.; Arun, A. Mushroom-derived carbon dots for toxic metal ion detection and as antibacterial and anticancer agents. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 5910–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. N-doped carbon dots derived from leaves with low toxicity via damaging cytomembrane for broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, P.; Lakshmanan, A.; Priya, S.S.; Geetha, P.; Rameshkumar, P.; Kannan, K.; Hegde, T.A.; Vinitha, G. Fluorescent carbon quantum dots from Ananas comosus waste peels: A promising material for NLO behaviour, antibacterial, and antioxidant activities. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 124, 108397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Quan, T.; Yang, L.; Deng, L.; Kang, X.; Gao, M.; Xia, Z.; Li, X.; Gao, D. N,Cl-codoped carbon dots from Impatiens balsamina L. stems and a deep eutectic solvent and their applications for Gram-positive bacteria identification, antibacterial activity, cell imaging, and ClO− sensing. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 29022–29036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, M.T.; Yanalak, G.; Aksoy, I.; Aslan, E.; Patır, I.H. Green carbon dots (GCDs) for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and antibacterial applications. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 7317–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Maruthapandi, M.; Das, P.; Luong, J.H.T.; Gedanken, A. Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots with antibacterial activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskalen, H.; Çeşme, M.; Kerli, S.; Özğan, Ş. Green synthesis of water-soluble fluorescent carbon dots from rosemary leaves: Applications in food storage capacity, fingerprint detection, and antibacterial activity. J. Chem. Res. 2021, 45, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiyan, S.; Arumugam, L.; Srirengan, S.P.; Pitchan, R.; Sevugan, P.; Kannan, K.; Pitchan, G.; Hegde, T.A.; Gandhirajan, V. Biocompatible carbon quantum dots derived from sugarcane industrial wastes for effective nonlinear optical behavior and antimicrobial activity applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30363–30372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, W.; Chen, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Cu2+-doped carbon dots as fluorescence probe for specific recognition of Cr(VI) and its antimicrobial activity. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Maruthapandi, M.; Saravanan, A.; Natan, M.; Jacobi, G.; Banin, E.; Gedanken, A. Carbon dots for heavy-metal sensing, pH-sensitive cargo delivery, and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 11777–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y. One-pot synthesis of Forsythia@carbon quantum dots with natural anti-wood rot fungus activity. Mater. Des. 2021, 206, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
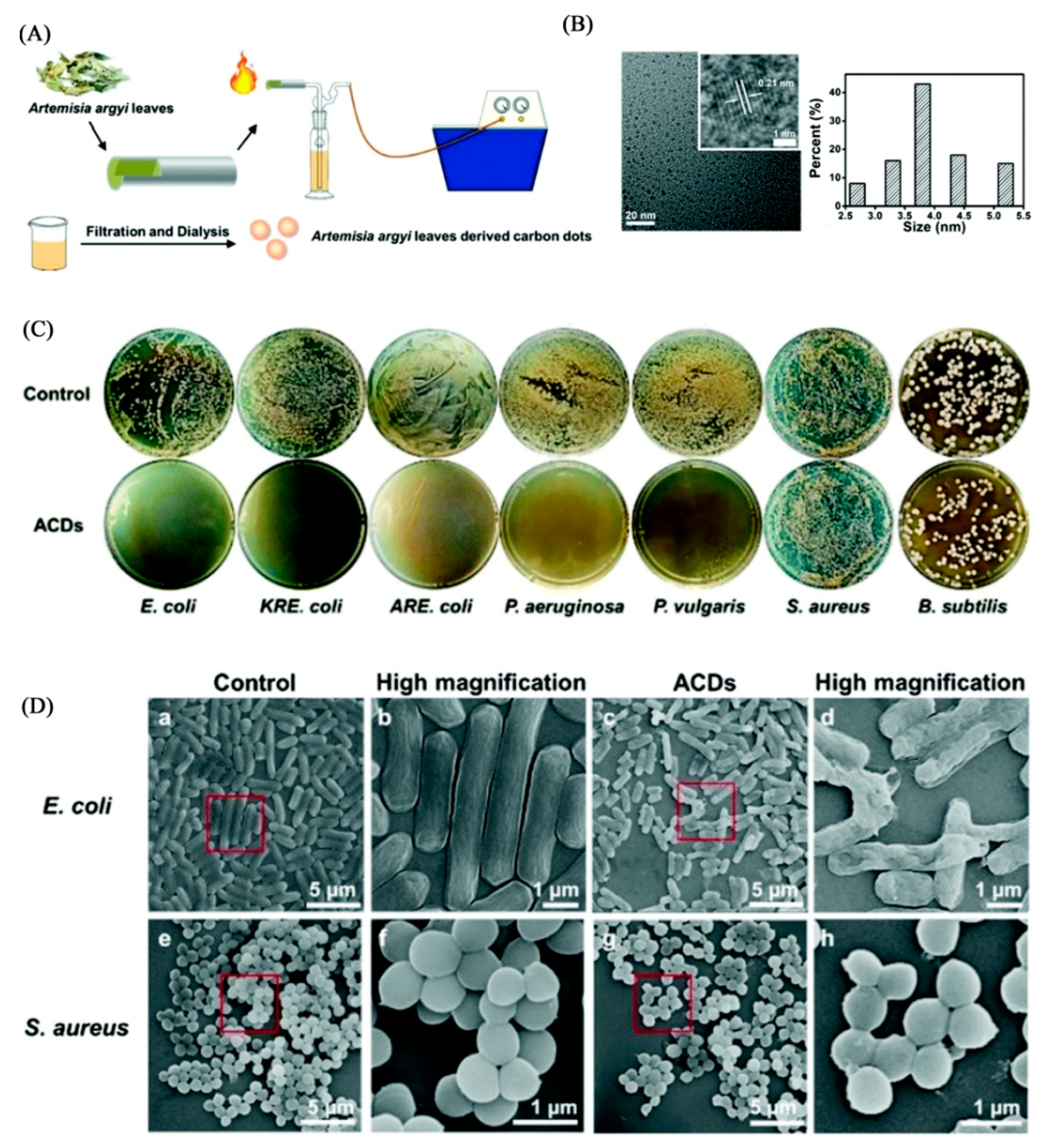
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, B.; Shao, M.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Selective inactivation of Gram-negative bacteria by carbon dots derived from natural biomass: Artemisia argyi leaves. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
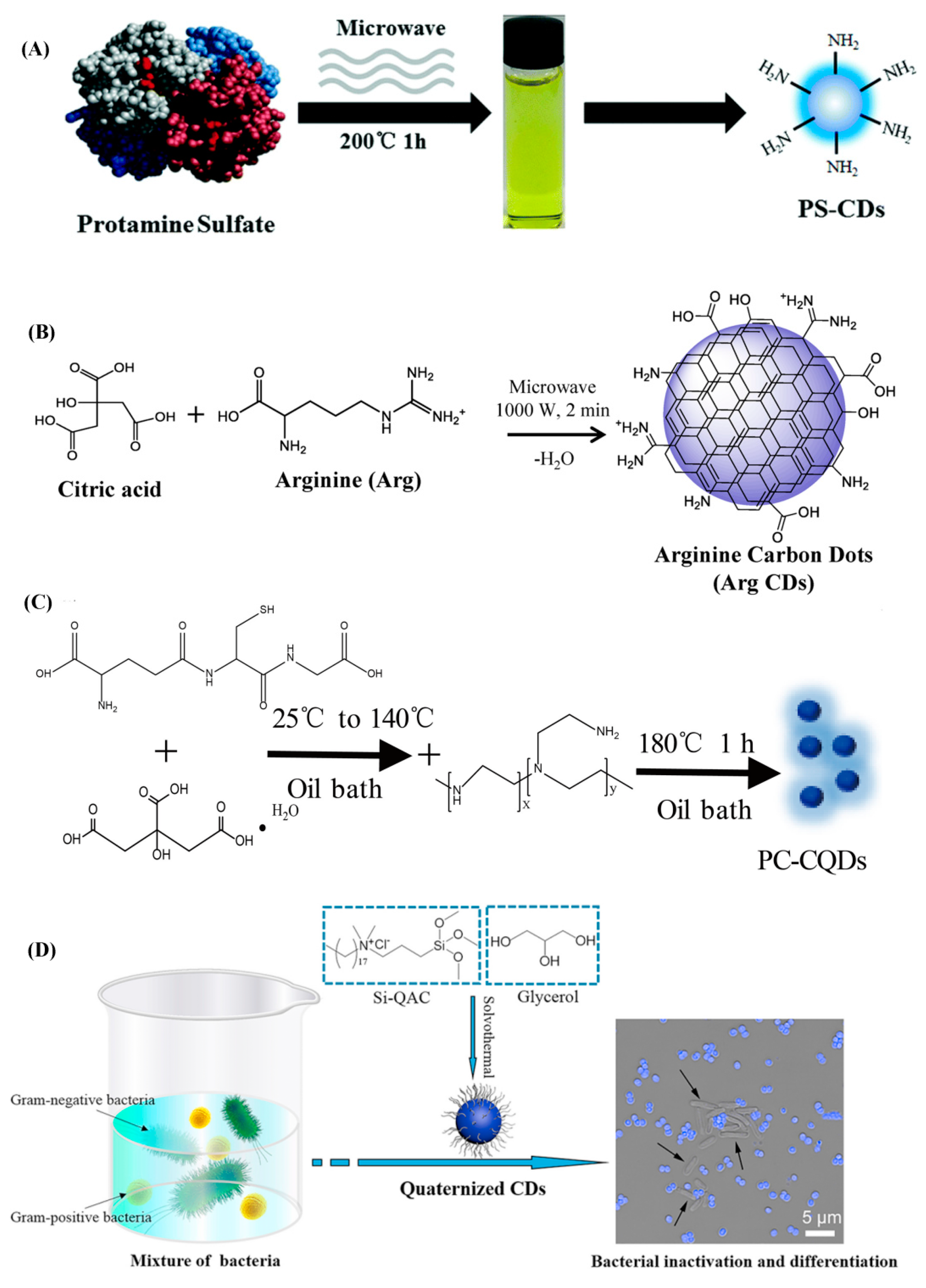
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Xiao, X. Facile one-pot synthesis of multifunctional protamine sulfate-derived carbon dots for antibacterial applications and fluorescence imaging of bacteria. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suner, S.S.; Sahiner, M.; Ayyala, R.S.; Bhethanabotle, V.R.; Sahiner, N. Nitrogen-doped arginine carbon dots and its metal nanoparticle composites as antibacterial agent. C 2020, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Devkota, A.; Yadegari, Z.; Dumenyo, K.; Taheri, A. Antibacterial properties of citric acid/β-alanine carbon dots against Gram-negative bacteria. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.W.; Kang, D.H. Effect of amino acid-derived nitrogen and/or sulfur doping on the visible-light-driven antimicrobial activity of carbon quantum dots: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suner, S.S.; Sahiner, M.; Ayyala, R.S.; Bhethanabotla, V.R.; Sahiner, N. Versatile Fluorescent carbon dots from citric acid and cysteine with antimicrobial, anti-biofilm, antioxidant, and AChE enzyme inhibition capabilities. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagic, M.; Kociova, S.; Smerkova, K.; Michalkova, H.; Setka, M.; Svec, P.; Pribyl, J.; Masilko, J.; Balkova, R.; Heger, Z.; et al. One-pot synthesis of natural amine-modified biocompatible carbon quantum dots with antibacterial activity. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2020, 580, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Huang, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, S.; Lin, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, A.; Miao, C.; Lin, X.; et al. Antibacterial activity of positively charged carbon quantum dots without detectable resistance for wound healing with mixed bacteria infection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 111971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Li, P.; Fang, F.; Shi, W.; Glowacki, J.; Pan, D.; Shen, L. Antibacterial and osteogenic carbon quantum dots for regeneration of bone defects infected with multidrug-resistant bacteria. Carbon 2021, 184, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gao, G.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.H.; Chen, X.; Wu, F.G. One-step synthesis of carbon dots with bacterial contact-enhanced fluorescence emission: Fast Gram-type identification and selective Gram-positive bacterial inactivation. Carbon 2019, 146, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Gu, J.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Han, H. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for preventing biofilm formation and eradicating drug-resistant bacteria infection. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4739–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Tang, W.; Cao, W.; Zhou, J.; Gong, X.; Xing, X. Surface chemistry-dependent antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 16744–16757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, X. Rapid and low-temperature synthesis of N, P co-doped yellow emitting carbon dots and their applications as antibacterial agent and detection probe to Sudan Red I. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, L. One-step synthesis of blue-green luminescent carbon dots by a low-temperature rapid method and their high-performance antibacterial effect and bacterial imaging. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 155101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Yu, M.; Lu, H.; Xing, X. Antibacterial carbon dots derived from polyethylene glycol/polyethyleneimine with potent anti-friction performance as water-based lubrication additives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e50620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Wu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, L.; Weng, S.; Lin, X. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as an antimicrobial agent against Staphylococcus for the treatment of infected wounds. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 179, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.R.; Bhati, A.; Saini, D.; Gunture; Chauhan, N.; Khare, P.; Sonkar, S.K. Antibacterial nitrogen-doped carbon dots as a reversible “fluorescent nanoswitch” and fluorescent ink. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, G.; Lei, J.; Liu, M.; Jin, Y.; Li, B. One-step and one-precursor hydrothermal synthesis of carbon dots with superior antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7095–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Maruthapandi, M.; Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Margel, S.; Luong, J.H.T.; Gedanken, A. Applications of N-doped carbon dots as antimicrobial agents, antibiotic carriers, and selective fluorescent probes for nitro explosives. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Wu, F.; Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Song, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Shen, J. Genipin cross-linked carbon dots for antimicrobial, bioimaging and bacterial discrimination. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 190, 110930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, M.; Ke, X.; Gong, X.; Li, Z.; Xing, X. Cytocompatible amphipathic carbon quantum dots as potent membrane-active antibacterial agents with low drug resistance and effective inhibition of biofilm formation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 3290–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, X.; Li, J. Preparation of two types of silver-doped fluorescent carbon dots and determination of their antibacterial properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 214, 111306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Lu, M.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Chen, F.; Xiong, X.; Yin, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhou, D. Ultrasmall Fe-doped carbon dots nanozymes for photoenhanced antibacterial therapy and wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 12, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.; Wei, X.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Z. Copper doped carbon dots for addressing bacterial biofilm formation, wound infection, and tooth staining. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9479–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; He, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Jin, J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Jiang, B.; Liu, Y. Mechanistic studies on the antibacterial behavior of Ag nanoparticles decorated with carbon dots having different oxidation degrees. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, S.; Thakur, A.; Sharma, A.; Pooja, D.; Minhas, A.P. Bactericidal activity of Cannabis sativa phytochemicals from leaf extract and their derived carbon dots and Ag@carbon dots. Mater. Lett. 2020, 262, 127122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cheng, F.; Yao, Y.; Yi, X.; Wei, B.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; He, J. Facile synthesis of a carbon dots and silver nanoparticles (CDs/AgNPs) composite for antibacterial application. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18417–18422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradlou, O.; Rabiei, Z.; Delavari, N. Antibacterial effects of carbon quantum dots@hematite nanostructures deposited on titanium against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. J. Potoch. Photobio. A 2019, 379, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elkodous, M.; EI-Sayyad, G.S.; Youssry, S.M.; Nada, H.G.; Gobara, M.; Elsayed, M.A.; EI-Khawaga, A.M.; Kawamura, G.; Tan, W.K.; EI-Batal, A.I.; et al. Carbon-dot-loaded CoxNi1−xFe2O4; x = 0.9/SiO2/TiO2 nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial potential: An engineered nanocomposite for wastewater treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Yao, J.; Shi, W. Synthesis of carbon dot-ZnO-based nanomaterials for antibacterial application. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 4496–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, W.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, W.; Fakhri, A.; Gupta, V.K. Preparation of carbon dots-hematite quantum dots-loaded hydroxypropyl cellulose-chitosan nanocomposites for drug delivery, sunlight catalytic and antimicrobial application. J. Potoch. Photobio. B 2021, 219, 112201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemera, D.J.; Etefa, H.F.; Kumar, V.; Dejene, F.B. Hybridization of nickel oxide nanoparticles with carbon dots and its application for antibacterial activities. Luminescence 2022, 37, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Li, H.; Niu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Fan, H.; Wang, K. Carbon quantum dots modified Ag2S/CS nanocomposite as effective antibacterial agents. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 220, 111456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Qin, K.; Liu, F.; Zheng, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Wei, Y. Carbon dots derived from kanamycin sulfate with antibacterial activity and selectivity for Cr6+ detection. Analyst 2021, 146, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shu, W.; Lei, B.; Zhang, H. Antibacterial activity and synergetic mechanism of carbon dots against Gram-positive and -negative bacteria. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 6937–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
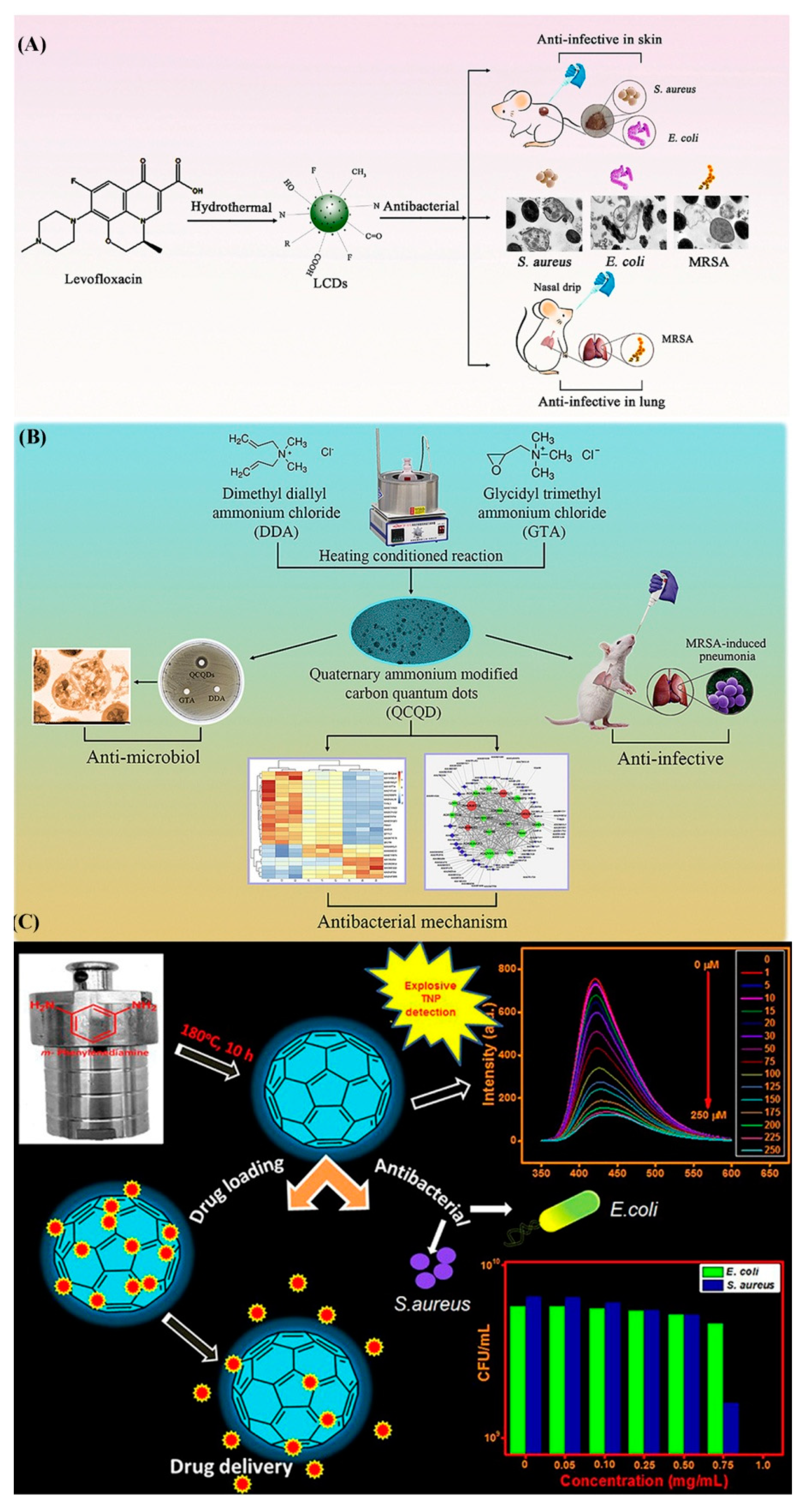
- Wu, L.N.; Yang, Y.J.; Huang, L.X.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.R.; Lin, L.Q.; Lei, Y.; Liu, A.L. Levofloxacin-based carbon dots to enhance antibacterial activities and combat antibiotic resistance. Carbon 2022, 186, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Weng, S.; Ruan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lin, L.; Lin, X. Quaternary ammonium carbon quantum dots as an antimicrobial agent against Gram-positive bacteria for the treatment of MRSA-infected pneumonia in mice. Carbon 2020, 163, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.; Zhou, N.; Shen, J.; Meng, N. A multifunctional carbon dot-based nanoplatform for bioimaging and quaternary ammonium salt/photothermal synergistic antibacterial therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Gu, H.; Ran, B.; Liu, W.; Sun, W.; Wang, D.; Du, J.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Accelerated antibacterial red-carbon dots with photodynamic therapy against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. China Mater. 2022, 65, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lin, F.; Sun, W.; Wu, F.G.; Yang, H.; Lv, R.; Zhu, Y.X.; Jia, H.R.; Wang, C.; Gao, G.; et al. Self-assembled rose bengal-exopolysaccharide nanoparticles for improved photodynamic inactivation of bacteria by enhancing singlet oxygen generation directly in the solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16715–16722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Bao, Y.W.; Wu, F.G. Improving the phototherapeutic efficiencies of molecular and nanoscale materials by targeting mitochondria. Molecules 2018, 23, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCroy, G.E.; Yang, S.T.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Shiral Fernando, K.A.; Bunker, C.E.; Hu, Y.; Luo, P.G.; Sun, Y.P. Functionalized carbon nanoparticles: Syntheses and applications in optical bioimaging and energy conversion. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 320–321, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Viswanath, B.; Reddy, A.S.; Yoon, M. Fungus-derived photoluminescent carbon nanodots for ultrasensitive detection of Hg2+ ions and photoinduced bactericidal activity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.Z.; Milenkovic, M.M.; Dakic, I.R.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.M.; Milosavljevic, M.S.; Budimir, M.D.; Paunovic, V.G.; Dramicanin, M.D.; Markovic, Z.M.; Trajkovic, V.S. Photodynamic antibacterial effect of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4428–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanković, N.K.; Bodik, M.; Šiffalovič, P.; Kotlar, M.; Mičušik, M.; Špitalsky, Z.; Danko, M.; Milivojević, D.D.; Kleinova, A.; Kubat, P.; et al. Antibacterial and antibiofouling properties of light triggered fluorescent hydrophobic carbon quantum dots Langmuir–Blodgett thin films. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4154–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Nishanthi, S.T.; Purohit, B.; Shanavas, A.; Kailasam, K. Metal-free visible light photocatalytic carbon nitride quantum dots as efficient antibacterial agents: An insight study. Carbon 2019, 152, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, W.; Lv, P.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Narh, C.; Cao, X.; Ghiladi, R.A.; et al. Carbon quantum dots: A bright future as photosensitizers for in vitro antibacterial photodynamic inactivation. J. Potoch. Photobio. B 2020, 206, 111864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Hua, K.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y. Iodine-doped carbon dots with inherent peroxidase catalytic activity for photocatalytic antibacterial and wound disinfection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Yu, W. Zinc-doped carbon dots as effective blue-light-activated antibacterial agent. Nano 2021, 16, 2150031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, F.; Lu, J.E.; Mecado, R.; Rojas-Andrade, M.D.; Ning, S.; Azhar, Z.; Sandhu, J.; Cazares, R.; Saltikov, C.; Chen, S. Antibacterial activity of nitrogen-doped carbon dots enhanced by atomic aispersion of copper. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11629–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tian, H.; Yu, L.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Preparation of terbium doped carbon dots and their antibacterial capacity against Escherichia coli. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2020, 32, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
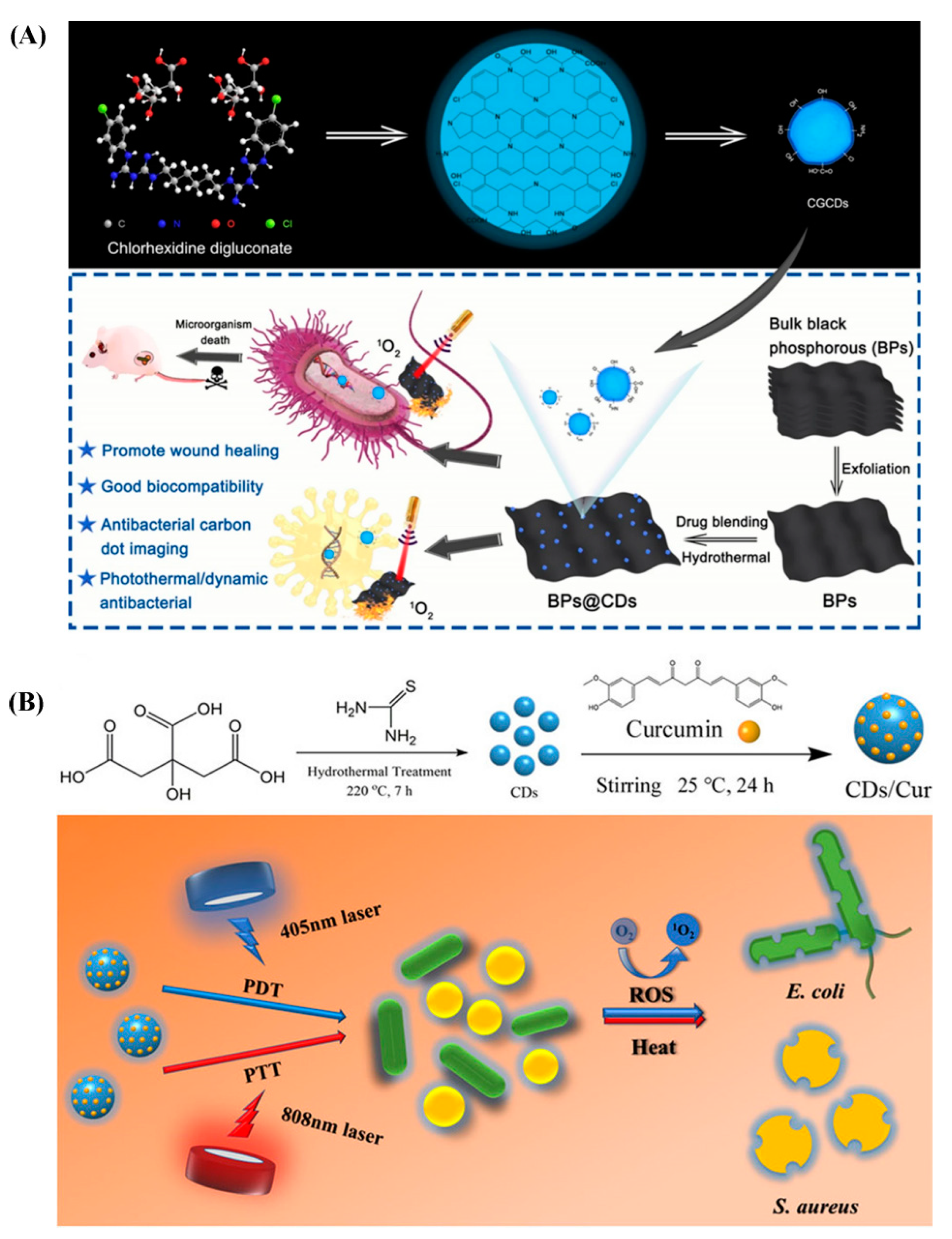
- Yan, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Su, R.; Li, P.; Su, W. Fluorescent carbon dot-curcumin nanocomposites for remarkable antibacterial activity with synergistic photodynamic and photothermal abilities. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 6703–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, B.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chu, X.; Ge, M.; Zhou, N.; Shen, J. Wound healing acceleration by antibacterial biodegradable black phosphorus nanosheets loaded with cationic carbon dots. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 6411–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kuang, W.; Shi, L.; Ye, X.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X.; Shi, Q.; Tan, S. Carbon quantum dot-decorated TiO2 for fast and sustainable antibacterial properties under visible-light. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Su, K.; Tan, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yeung, K.W.K. Near-infrared light photocatalysis and photothermy of carbon quantum dots and Au nanoparticles loaded titania nanotube array. Mater. Des. 2019, 177, 107845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Zhong, Q.; Ye, X.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Tan, S.; Shi, Q. Antibacterial nanorods made of carbon quantum dots-ZnO under visible light irradiation. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 2019, 19, 3982–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhao, P.; Lyu, B.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ma, J. Carbon quantum dots decorated on ZnO nanoparticles: An efficient visible-light responsive antibacterial agents. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, Z.M.; Kováčová, M.; Humpolíček, P.; Budimir, M.D.; Vajd’ák, J.; Kubát, P.; Mičušík, M.; Švajdlenková, H.; Danko, M.; Capáková, Z.; et al. Antibacterial photodynamic activity of carbon quantum dots/polydimethylsiloxane nanocomposites against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 26, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčová, M.; Bodík, M.; Mičušík, M.; Humpolíček, P.; Šiffalovič, P.; Špitalský, Z. Increasing the effectivity of the antimicrobial surface of carbon quantum dots-based nanocomposite by atmospheric pressure plasma. Clin. Plasma Med. 2020, 19–20, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Kováčová, M.; Humpolíček, P.; Vajd’ák, J.; Bodík, M.; Špitalský, Z. Antibacterial photodynamic activity of hydrophobic carbon quantum dots and polycaprolactone based nanocomposite processed via both electrospinning and solvent casting method. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 35, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budimir, M.; Marković, Z.; Vajdak, J.; Jovanović, S.; Kubat, P.; Humpoliček, P.; Mičušik, M.; Danko, M.; Barras, A.; Milivojevič, D.; et al. Enhanced visible light-triggered antibacterial activity of carbon quantum dots/polyurethane nanocomposites by gamma rays induced pre-treatment. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 185, 109499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkahla, H.; Boudjemaa, R.; Caosi, V.; Pineau, D.; Curcio, A.; Lomas, J.S.; Decorse, P.; Chevillot-Biraud, A.; Azaïs, T.; Wilhelm, C.; et al. Carbon dots, a powerful non-toxic support for bioimaging by fluorescence nanoscopy and eradication of bacteria by photothermia. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Ni, H.; Yang, Y.; Shan, C.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y. Smart nanoprobe based on two-photon sensitized terbium-carbon dots for dual-mode fluorescence thermometer and antibacterial. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Su, H.; Sun, G.; Ni, Y.; Sun, W. Antibacterial carbon dots/iron oxychloride nanoplatform for chemodynamic and photothermal therapy. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 45, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, A.; Haddad, Y.; Milosavljevic, V.; Michalkova, H. Guran, R.; Bhowmick, S.; Moulick, A. Peptide-carbon quantum dots conjugate, derived from human retinoic acid receptor responder protein 2, against antibiotic-resistant Gram positive and Gram negative pathogenic bacteria. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Lv, K.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Ma, D. Fluorescent carbon dots with a high nitric oxide payload for effective antibacterial activity and bacterial imaging. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 6486–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
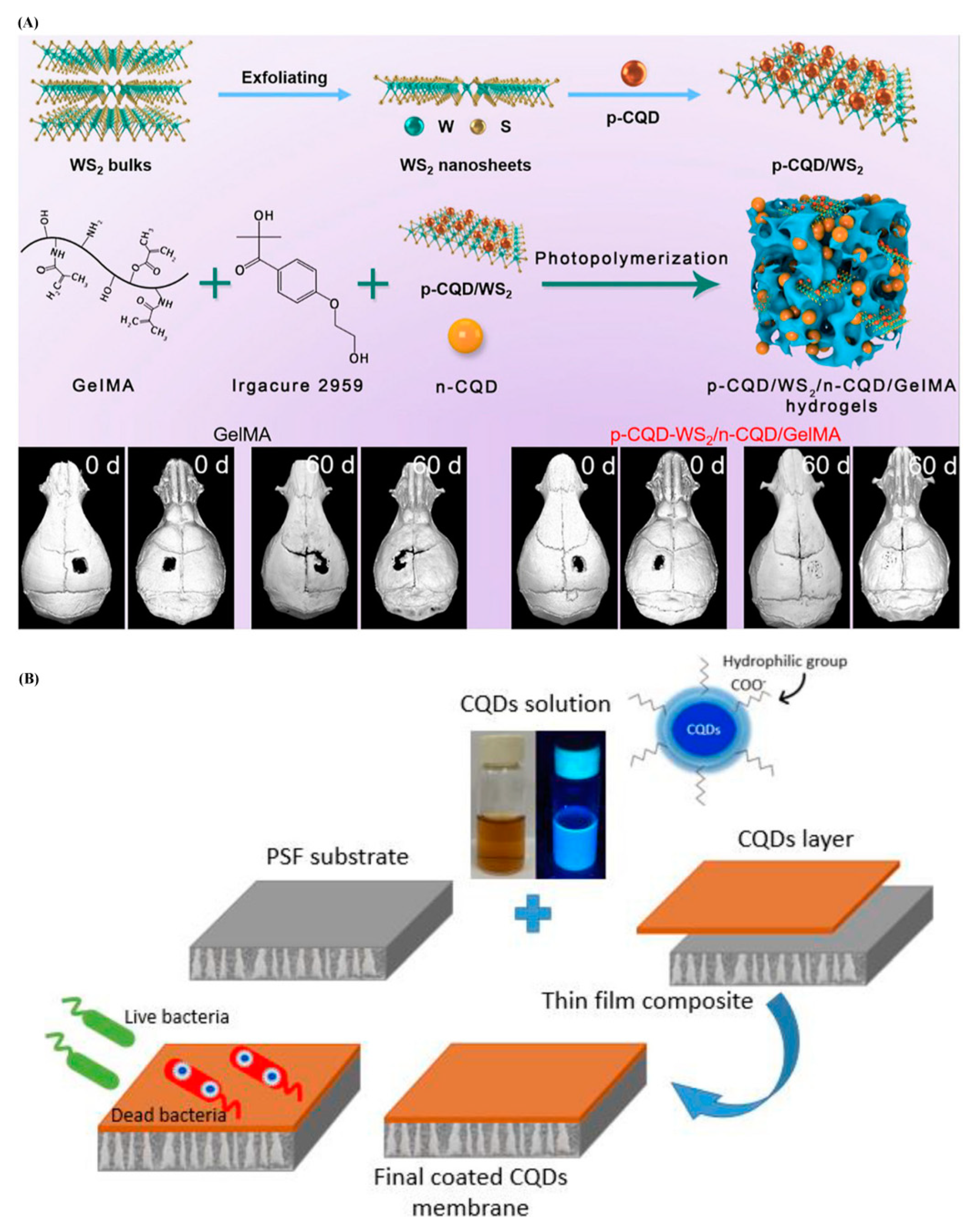
- Mahat, N.A.; Shamsudin, S.A.; Jullok, N.; Ma’Radzi, A.H. Carbon quantum dots embedded polysulfone membranes for antibacterial performance in the process of forward osmosis. Desalination 2020, 493, 114618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulivand, H.; Shahbazi, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Rahmandoost, M. Novel antifouling and antibacterial polyethersulfone membrane prepared by embedding nitrogen-doped carbon dots for efficient salt and dye rejection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousheh, S.A.; Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Molaei, R. Preparation of antimicrobial/ultraviolet protective bacterial nanocellulose film with carbon dots synthesized from lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 216–225. [Google Scholar]
- Riahi, Z.; Rhim, J.W.; Bagheri, R.; Pircheraghi, G.; Lotfali, E. Carboxymethyl cellulose-based functional film integrated with chitosan-based carbon quantum dots for active food packaging applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 166, 106794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Raw Materials | Preparation Method | Size * (nm) | Charge (mV) | QY (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lawsonia inermis (Henna) | Hydrothermal treatment | 3–7 | −39 | 28.7 | [27] |
| Oyster mushroom | Hydrothermal treatment | 8 | – | – | [28] |
| Osmanthus leaves | Hydrothermal treatment | 4–9 | −20 | – | [29] |
| Tea leaves | Hydrothermal treatment | 3–7 | −20 | – | [29] |
| Ananas comosus waste peels | Hydrothermal treatment | 2.4 ± 0.5 | – | 10.65 | [30] |
| Impatiens balsamina L. stems | Hydrothermal treatment | 2–4.5 | 22.47 | 54 | [31] |
| Aloe vera leaves | Hydrothermal treatment | 10–20 | – | – | [32] |
| Medicinal turmeric leaves | Hydrothermal treatment | 1.5–4.0 | −7 | – | [33] |
| Rosemary leaves | Hydrothermal treatment | 16.1 ± 4.6 | – | – | [34] |
| Sugarcane bagasse pulp | Hydrothermal treatment | 1.7 ± 0.2 | – | 17.98 | [35] |
| Waste tea extract | Hydrothermal treatment | 0.85 | – | 3.26 | [36] |
| Waste jute caddies | Hydrothermal treatment | 6.05 | – | 14.5 | [37] |
| Forsythia | Microwave treatment | 2.6 | – | – | [38] |
| Artemisia argyi leaves | Smoking simulation method | 2–5 | – | – | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon Dots for Killing Microorganisms: An Update since 2019. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101236
Lin F, Wang Z, Wu F-G. Carbon Dots for Killing Microorganisms: An Update since 2019. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(10):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101236
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Fengming, Zihao Wang, and Fu-Gen Wu. 2022. "Carbon Dots for Killing Microorganisms: An Update since 2019" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 10: 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101236
APA StyleLin, F., Wang, Z., & Wu, F.-G. (2022). Carbon Dots for Killing Microorganisms: An Update since 2019. Pharmaceuticals, 15(10), 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15101236