Transcranial Focal Electrical Stimulation Modifies Biogenic Amines’ Alterations Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine in Rat Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TFS Did Not Alter the Tissue Content of Biogenic Amines
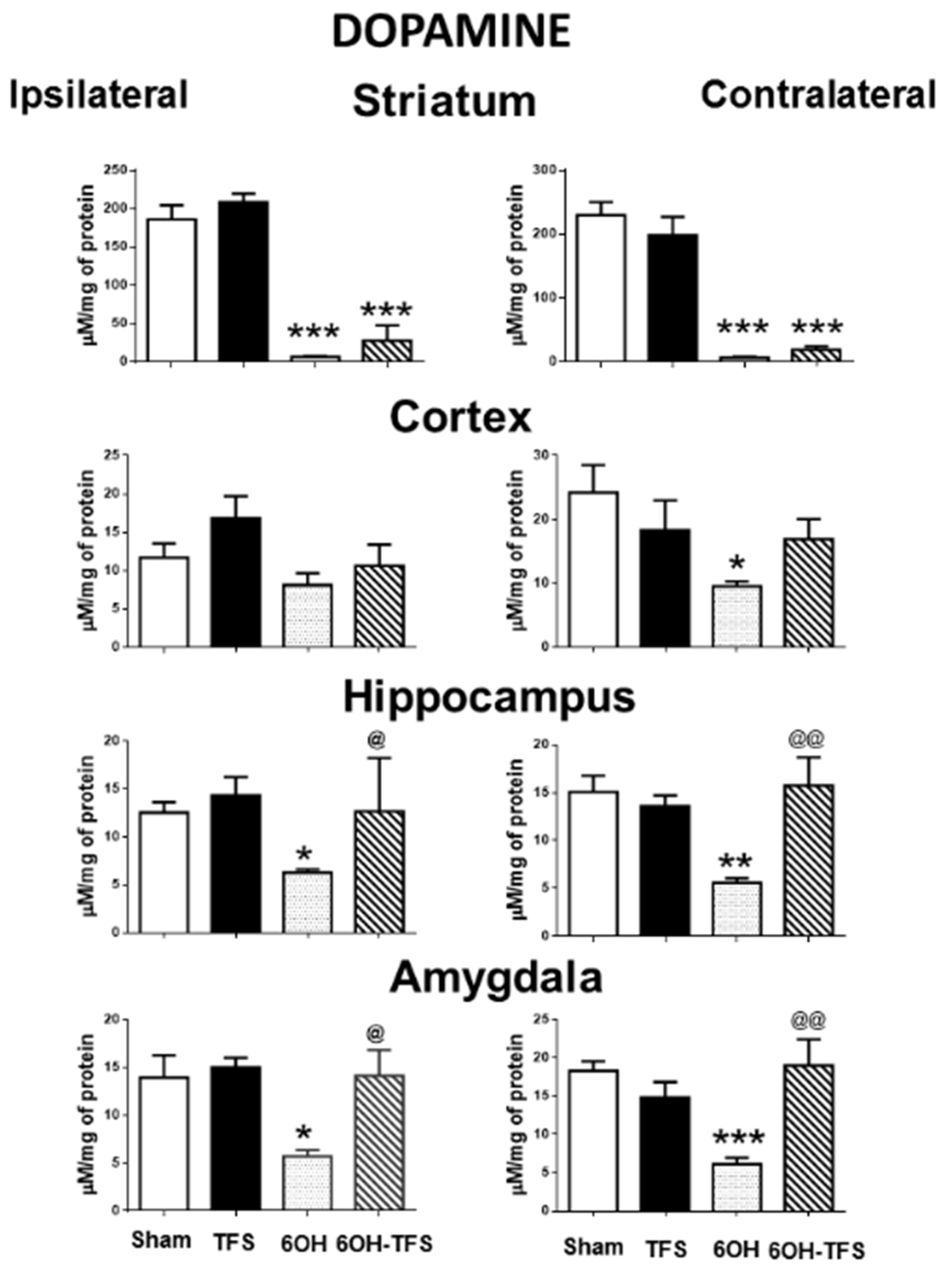
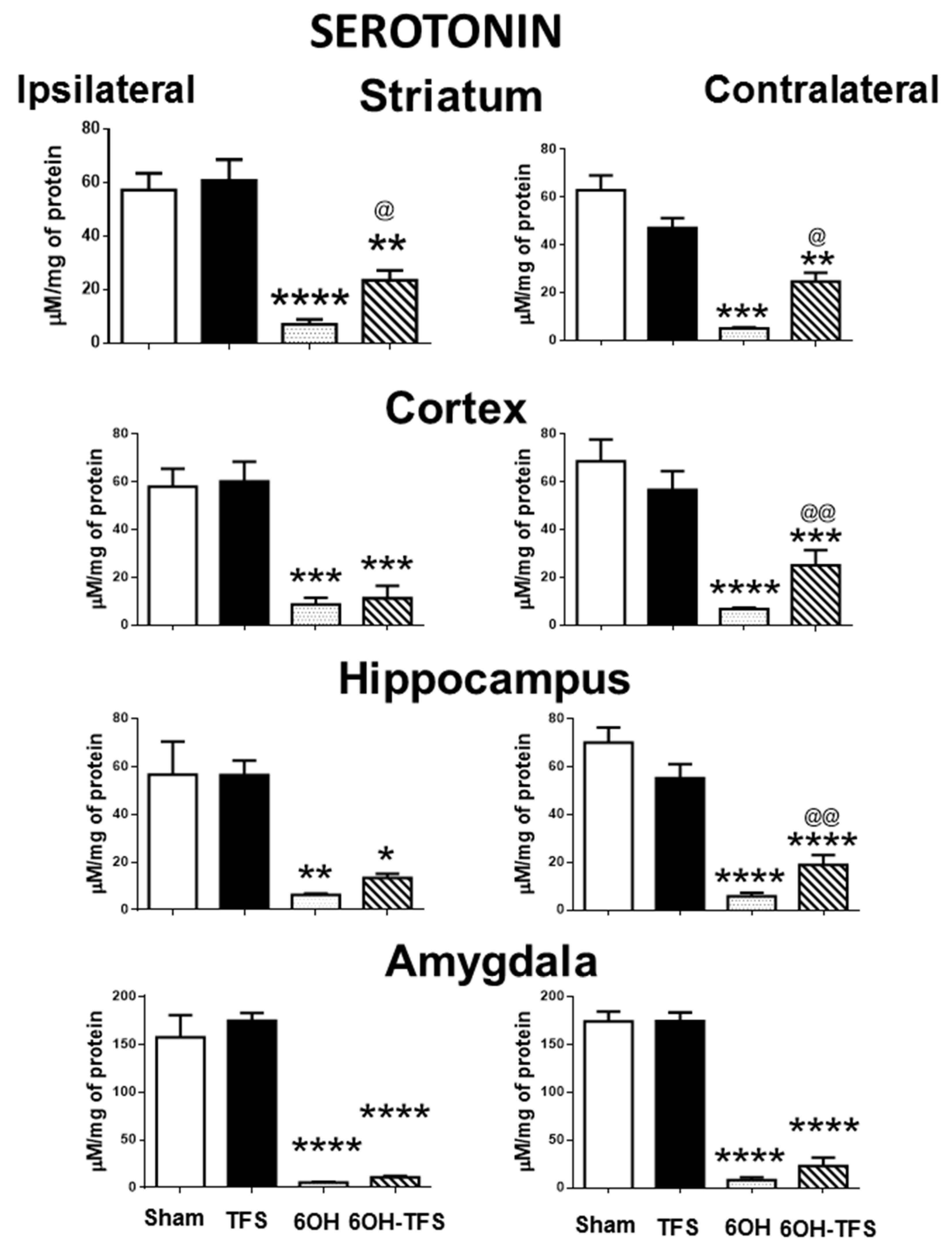
2.2. Intrastriatal Administration of 6-OHDA Modifies the Brain Tissue Content of Biogenic Amines
2.3. TFS Modifies the Changes in the Tissue Content of Biogenic Amines Induced by the Intrastriatal Administration of 6-OHDA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Surgery and Intrastriatal Injection of 6-OHDA
4.3. Experimental Groups
4.4. Evaluation of Tissue Content of Biogenic Amines by Chromatography
4.5. Statistical Analysis and Sample Size
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, C.A.; Kouzani, A.; Lee, K.H.; Ross, E.K. Neurostimulation Devices for the Treatment of Neurologic Disorders. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1427–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcarra, J.A.; Situ-Kcomt, M.; Artusi, C.A.; Duker, A.P.; Lopiano, L.; Okun, M.S.; Espay, A.J.; Merola, A. Subthalamic deep brain stimulation and levodopa in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of combined effects. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Xu, J. Deep brain stimulation for refractory temporal lobe epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis with an emphasis on alleviation of seizure frequency outcome. Childs. Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.T.H.; Rowell, D.; Connelly, L.B. Cost-Effectiveness of Deep Brain Stimulation With Movement Disorders: A Systematic Review. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, M.; Konomura, K.; Shiroiwa, T. Cost-Minimization Analysis of Deep-Brain Stimulation Using National Database of Japanese Health Insurance Claims. Neuromodulation 2018, 21, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besio, W.G.; Koka, K.; Cole, A.J. Effects of non-invasive transcutaneous electrical stimulation via concentric ring electrodes on pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besio, W.G.; Gale, K.N.; Medvedev, A.V. Possible therapeutic effects of transcutaneous electrical stimulation via concentric ring electrodes. Epilepsia 2010, 51 (Suppl. 3), 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besio, W.G.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Medvedev, A.V.; Koka, K. Transcutaneous focal electrical stimulation via concentric ring electrodes reduces synchrony induced by pentylenetetrazole in beta and gamma bands in rats. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2011, 21, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeyev, O.; Luna-Munguía, H.; Rogel-Salazar, G.; Liu, X.; Besio, W.G. Non-invasive transcranial focal stimulation via tripolar concentric ring electrodes lessens behavioral seizure activity of recurrent pentylenetetrazole administrations in rats. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 21, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besio, W.; Cuellar-Herrera, M.; Luna-Munguia, H.; Orozco-Suárez, S.; Rocha, L. Effects of transcranial focal electrical stimulation alone and associated with a sub-effective dose of diazepam on pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus and subsequent neuronal damage in rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 28, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pérez, D.; Castañeda-Cabral, J.L.; Orozco-Suárez, S.; Sotelo, J.; Besio, W.; Rocha, L. Noninvasive transcranial focal stimulation affects the convulsive seizure-induced P-glycoprotein expression and function in rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 115, 107659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Gómez, C.E.; Alcántara-González, D.; Luna-Munguía, H.; Bañuelos-Cabrera, I.; Magdaleno-Madrigal, V.; Fernández-Mas, R.; Besio, W.; Rocha, L. Transcranial focal electrical stimulation reduces the convulsive expression and amino acid release in the hippocampus during pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 49, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandini, F.; Armentero, M.-T. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perfeito, R.; Cunha-Oliveira, T.; Rego, A.C. Reprint of: Revisiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease-resemblance to the effect of amphetamine drugs of abuse. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.-T.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Gao, G.-D.; Wang, X.-L. 6-OHDA induced calcium influx through N-type calcium channel alters membrane properties via PKA pathway in substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 575, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Baltazar, D.; Zavala-Flores, L.M.; Villanueva-Olivo, A. The 6-hydroxydopamine model and parkinsonian pathophysiology: Novel findings in an older model. Neurologia 2017, 32, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Tilson, H.A.; Nanry, K.P.; Hudson, P.M.; Hong, J.S.; Stachowiak, M.K. Increased dopamine release from striata of rats after unilateral nigrostriatal bundle damage. Brain Res. 1988, 461, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskow Jaunarajs, K.L.; George, J.A.; Bishop, C. L-DOPA-induced dysregulation of extrastriatal dopamine and serotonin and affective symptoms in a bilateral rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2012, 218, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, P.; Noras, L.; Jochem, J.; Szkilnik, R.; Brus, H.; Körossy, E.; Drab, J.; Kostrzewa, R.M.; Brus, R. Histaminergic activity in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 15, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F.-X.; Hu, D.-N.; Luo, J.-H. Involvement of brain endogenous histamine in the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N.; Huang, Z.-L.; Mikuni, N.; Miura, Y.; Urade, Y.; Hashimoto, N. Deep brain stimulation of the posterior hypothalamus activates the histaminergic system to exert antiepileptic effect in rat pentylenetetrazol model. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 205, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, T.M.; Cheng, J.J.; Eskandar, E.N. Mechanisms of deep brain stimulation. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 115, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gui, X.-H.; Xue, Z.-F.; Huang, L.-P.; Fang, R.-M.; Ke, X.-H.; Li, L.; Fang, Y.-Q. Dynamic of neurochemical alterations in striatum, hippocampus and cortex after the 6-OHDA mesostriatal lesion. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branchi, I.; D’Andrea, I.; Armida, M.; Carnevale, D.; Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; Pèzzola, A.; Potenza, R.L.; Morgese, M.G.; Cassano, T.; Minghetti, L.; et al. Striatal 6-OHDA lesion in mice: Investigating early neurochemical changes underlying Parkinson’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, R.M.; Barbiero, J.; Gradowski, R.W.; Bochen, S.; Lima, M.M.S.; Da Cunha, C.; Andreatini, R.; Vital, M.A.B.F. Induction of depressive-like behavior by intranigral 6-OHDA is directly correlated with deficits in striatal dopamine and hippocampal serotonin. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 259, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantic, I.; Cumic, J.; Skodric, S.R.; Dugalic, S.; Brodski, C. Oxidopamine and oxidative stress: Recent advances in experimental physiology and pharmacology. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2021, 336, 109380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varešlija, D.; Tipton, K.F.; Davey, G.P.; McDonald, A.G. 6-Hydroxydopamine: A far from simple neurotoxin. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, R.; Jochem, J.; Nowak, P.; Adwent, M.; Boroń, D.; Brus, H.; Kostrzewa, R.M. Effect of pre- and postnatal manganese exposure on brain histamine content in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, J.O.; Anichtchik, O.V.; Eriksson, K.S.; Kaslin, J.; Tuomisto, L.; Kalimo, H.; Röyttä, M.; Panula, P. Increased brain histamine levels in Parkinson’s disease but not in multiple system atrophy. J. Neurochem. 2002, 81, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anichtchik, O.V.; Rinne, J.O.; Kalimo, H.; Panula, P. An altered histaminergic innervation of the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 163, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizuete, M.L.; Merino, M.; Venero, J.L.; Santiago, M.; Cano, J.; Machado, A. Histamine infusion induces a selective dopaminergic neuronal death along with an inflammatory reaction in rat substantia nigra. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.-J.; Huang, Y.-T.; Huang, Y.-Z.; Kuo, C.-W.; Peng, C.-W.; Rotenberg, A.; Juan, C.-H.; Pei, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, K.-Y.; et al. Early transcranial direct current stimulation treatment exerts neuroprotective effects on 6-OHDA-induced Parkinsonism in rats. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Jiang, H.; Jia, W.; Sun, P.; Xie, J. High frequency stimulation of subthalamic nucleus results in behavioral recovery by increasing striatal dopamine release in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 263, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Q.; Ding, J.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, K. Reduced plasma serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid levels in Parkinson’s disease are associated with nonmotor symptoms. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocabicak, E.; Jahanshahi, A.; Schonfeld, L.; Hescham, S.-A.; Temel, Y.; Tan, S. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Rat Subthalamic Nucleus Induced Inhibition of Median Raphe Serotonergic and Dopaminergic Neurotransmission. Turk. Neurosurg. 2015, 25, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiani, E.; Delaville, C.; Benazzouz, A. The combined depletion of monoamines alters the effectiveness of subthalamic deep brain stimulation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 82, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.K.H.; Hartung, H.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Temel, Y.; Sharp, T. A combined in vivo neurochemical and electrophysiological analysis of the effect of high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus on 5-HT transmission. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 233, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navailles, S.; De Deurwaerdère, P. Contribution of serotonergic transmission to the motor and cognitive effects of high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or levodopa in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasi, G.; Lanotte, M.; Albert, U.; Zibetti, M.; Castelli, L.; Maina, G.; Lopiano, L. Transient acute depressive state induced by subthalamic region stimulation. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 273, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.-X.; Li, G.-Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xi, K.; Li, H.-Z.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhu, J.-N. Regularizing firing patterns of rat subthalamic neurons ameliorates parkinsonian motor deficits. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 5413–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panula, P.; Pirvola, U.; Auvinen, S.; Airaksinen, M.S. Histamine-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat brain. Neuroscience 1989, 28, 585–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Natteru, P.A.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Saeed, D.; Zahoor, H.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.S.; Zaheer, A. Neuroinflammation Induces Neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Valle-Dorado, M.G.; Santana-Gómez, C.E.; Orozco-Suárez, S.A.; Rocha, L. The mast cell stabilizer sodium cromoglycate reduces histamine release and status epilepticus-induced neuronal damage in the rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2015, 92, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Togashi, H.; Yoshioka, M.; Mano, Y. Effects of acute repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on dopamine release in the rat dorsolateral striatum. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 217, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Mansouri, M.; Ghalami, J.; Mokhtari, Z.; Roghani, M. Sesamin imparts neuroprotection against intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity by inhibition of astroglial activation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlán, D.; Molnár-Perl, I. New aspects of the simultaneous analysis of amino acids and amines as their o-phthaldialdehyde derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography. Analysis of wine, beer and vinegar. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 987, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sañuda-Peña, M.C.; Harvey-White, J.D.; Kalra, S.; Cohen, S.A. Determination of submicromolar concentrations of neurotransmitter amino acids by fluorescence detection using a modification of the 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate method for amino acid analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 828, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, N.J. The Bradford method for protein quantitation. Methods Mol. Biol. 1994, 32, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgoewer, A.; Mayer, B. Sample size estimation for pilot animal experiments by using a Markov Chain Monte Carlo approach. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2017, 45, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santana-Gómez, C.E.; Pérez-Pérez, D.; Fonseca-Barriendos, D.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Besio, W.; Rocha, L. Transcranial Focal Electrical Stimulation Modifies Biogenic Amines’ Alterations Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine in Rat Brain. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080706
Santana-Gómez CE, Pérez-Pérez D, Fonseca-Barriendos D, Arias-Carrión O, Besio W, Rocha L. Transcranial Focal Electrical Stimulation Modifies Biogenic Amines’ Alterations Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine in Rat Brain. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(8):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080706
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantana-Gómez, Cesar Emmanuel, Daniel Pérez-Pérez, Daniel Fonseca-Barriendos, Oscar Arias-Carrión, Walter Besio, and Luisa Rocha. 2021. "Transcranial Focal Electrical Stimulation Modifies Biogenic Amines’ Alterations Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine in Rat Brain" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 8: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080706
APA StyleSantana-Gómez, C. E., Pérez-Pérez, D., Fonseca-Barriendos, D., Arias-Carrión, O., Besio, W., & Rocha, L. (2021). Transcranial Focal Electrical Stimulation Modifies Biogenic Amines’ Alterations Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine in Rat Brain. Pharmaceuticals, 14(8), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080706






