Celecoxib Decrease Seizures Susceptibility in a Rat Model of Inflammation by Inhibiting HMGB1 Translocation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
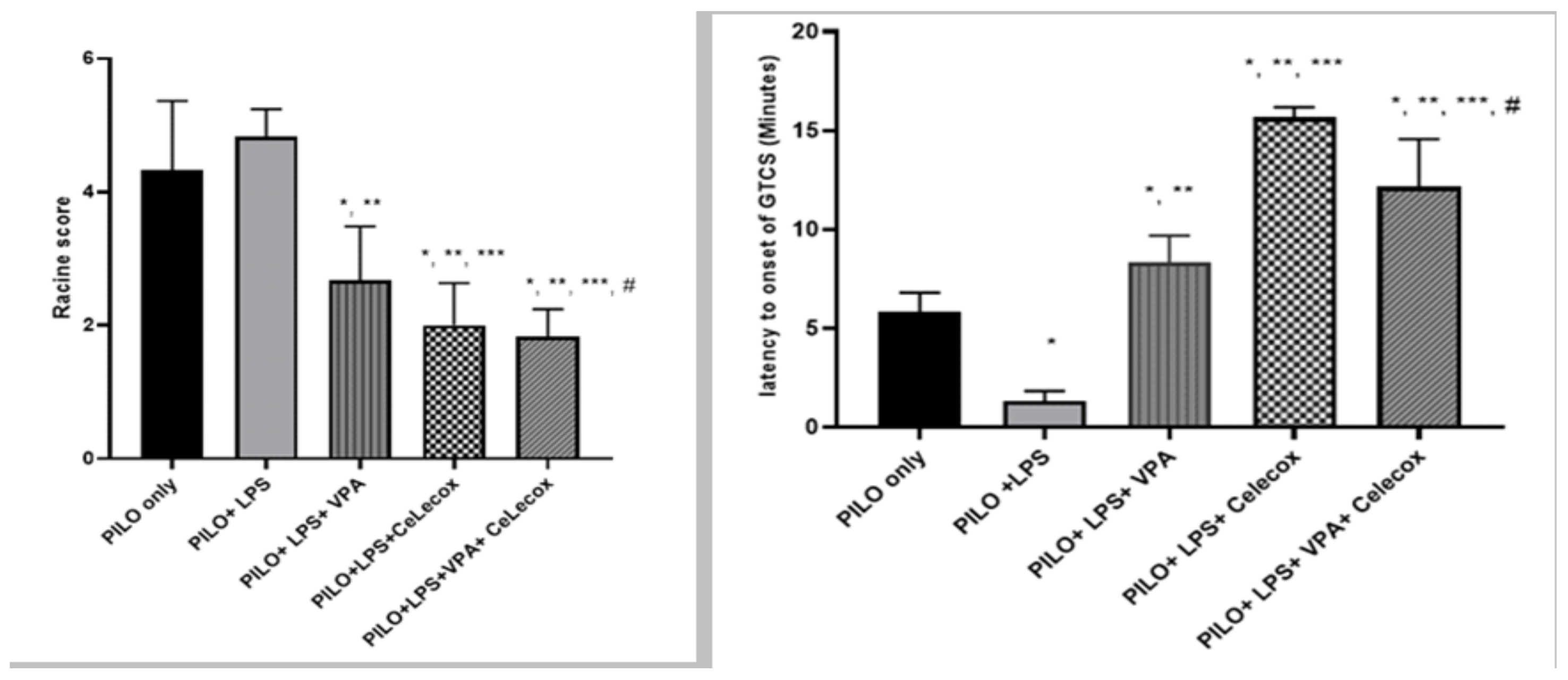
2.1. Effects of Tested Drugs on Racine Score and Latency to Onset of Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure (GTCS)
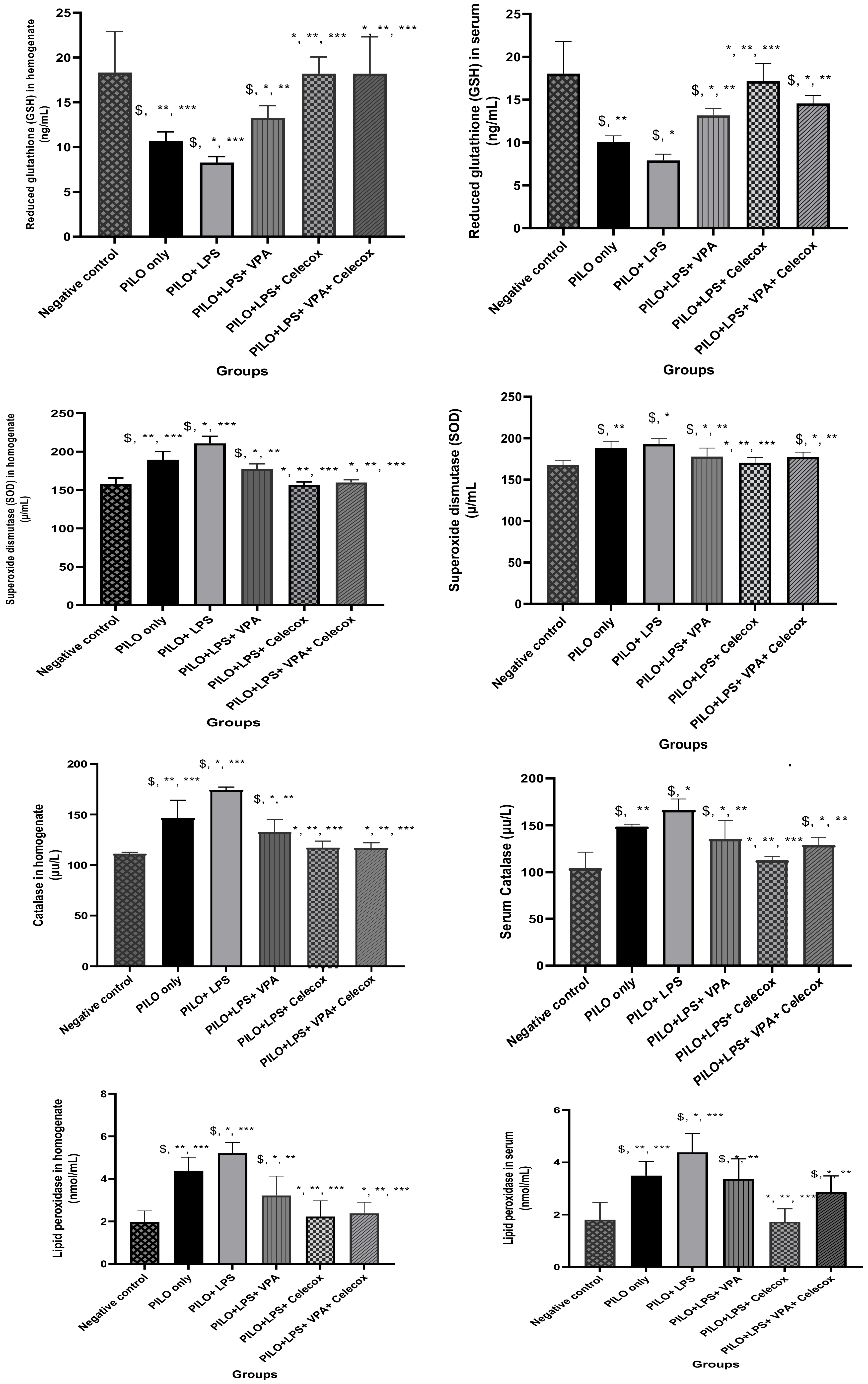
2.2. Oxidative Stress Markers
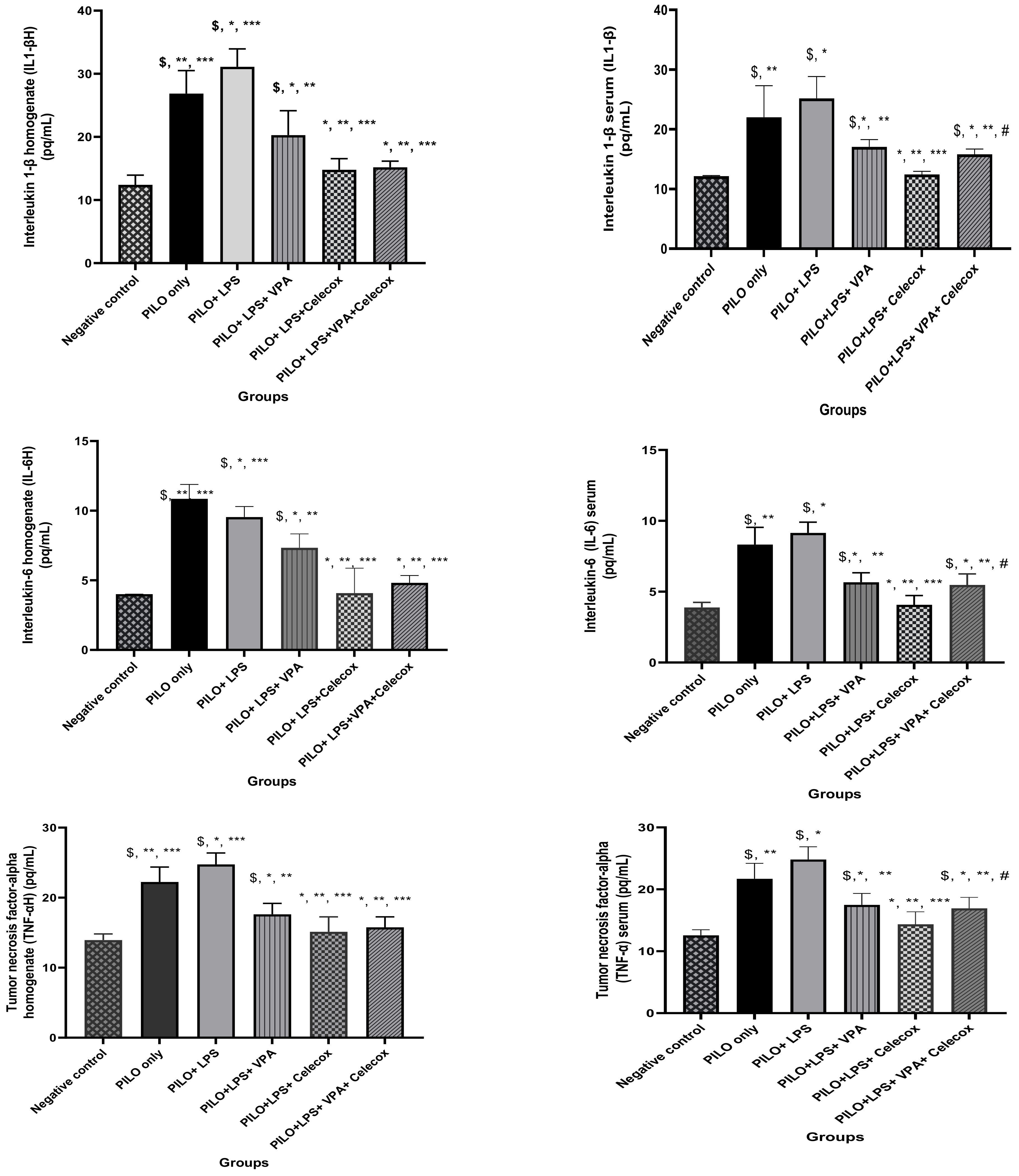
2.3. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
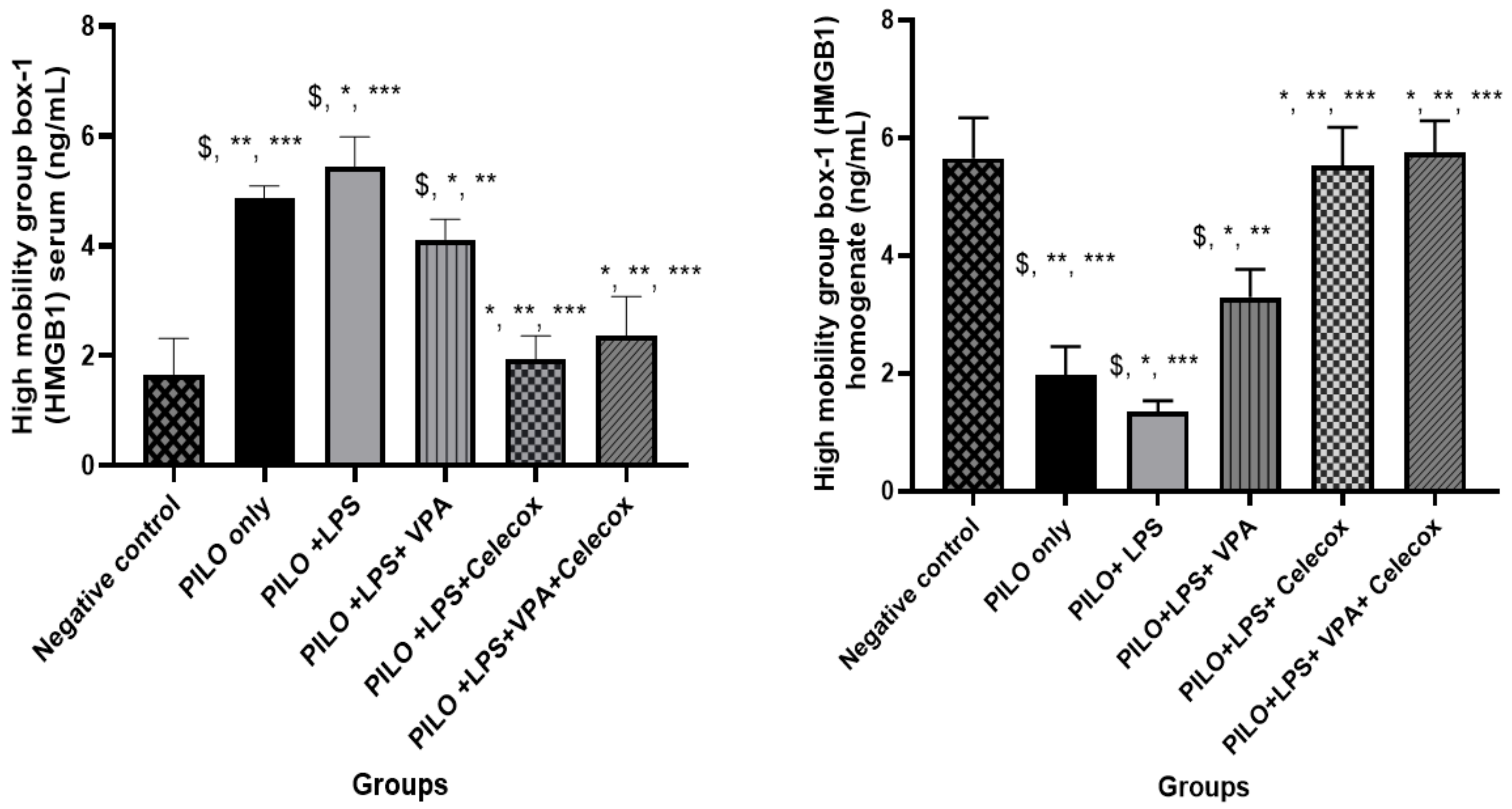
2.4. Dynamic Changes of High Mobility Group Box-1 (HMGB1)
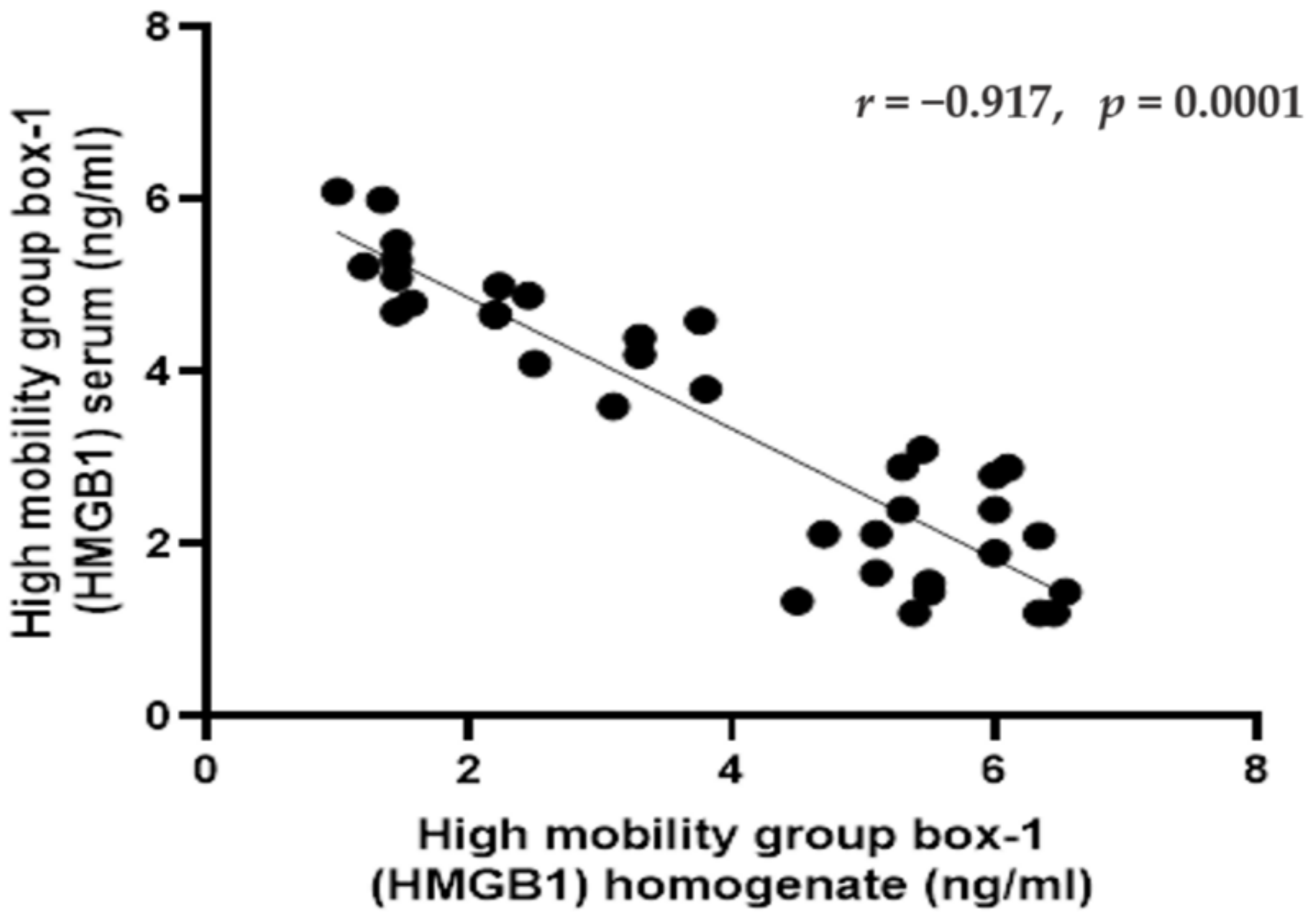
2.5. Correlations between HMGB1 in Serum and Homogenate in Rats of Different Groups
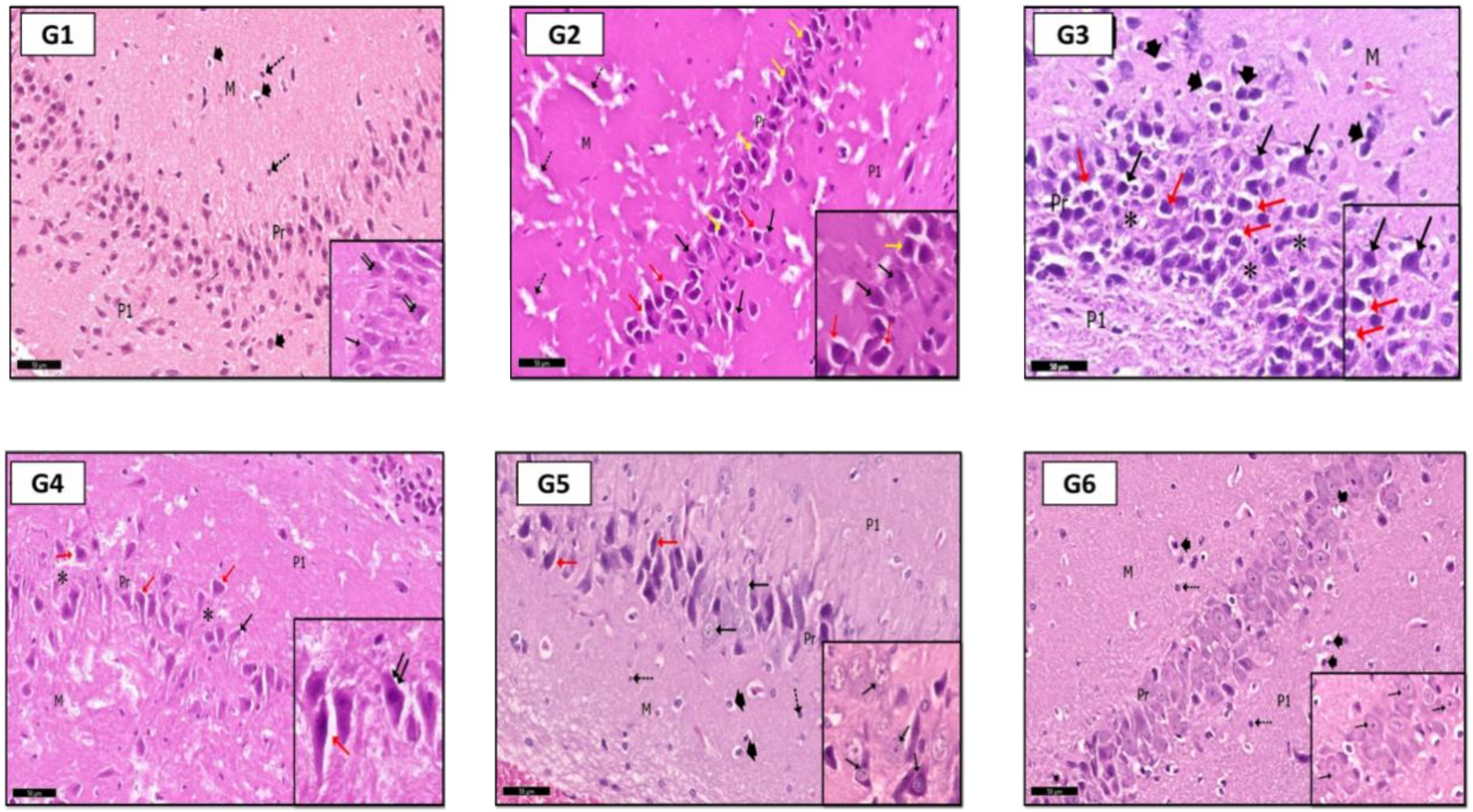
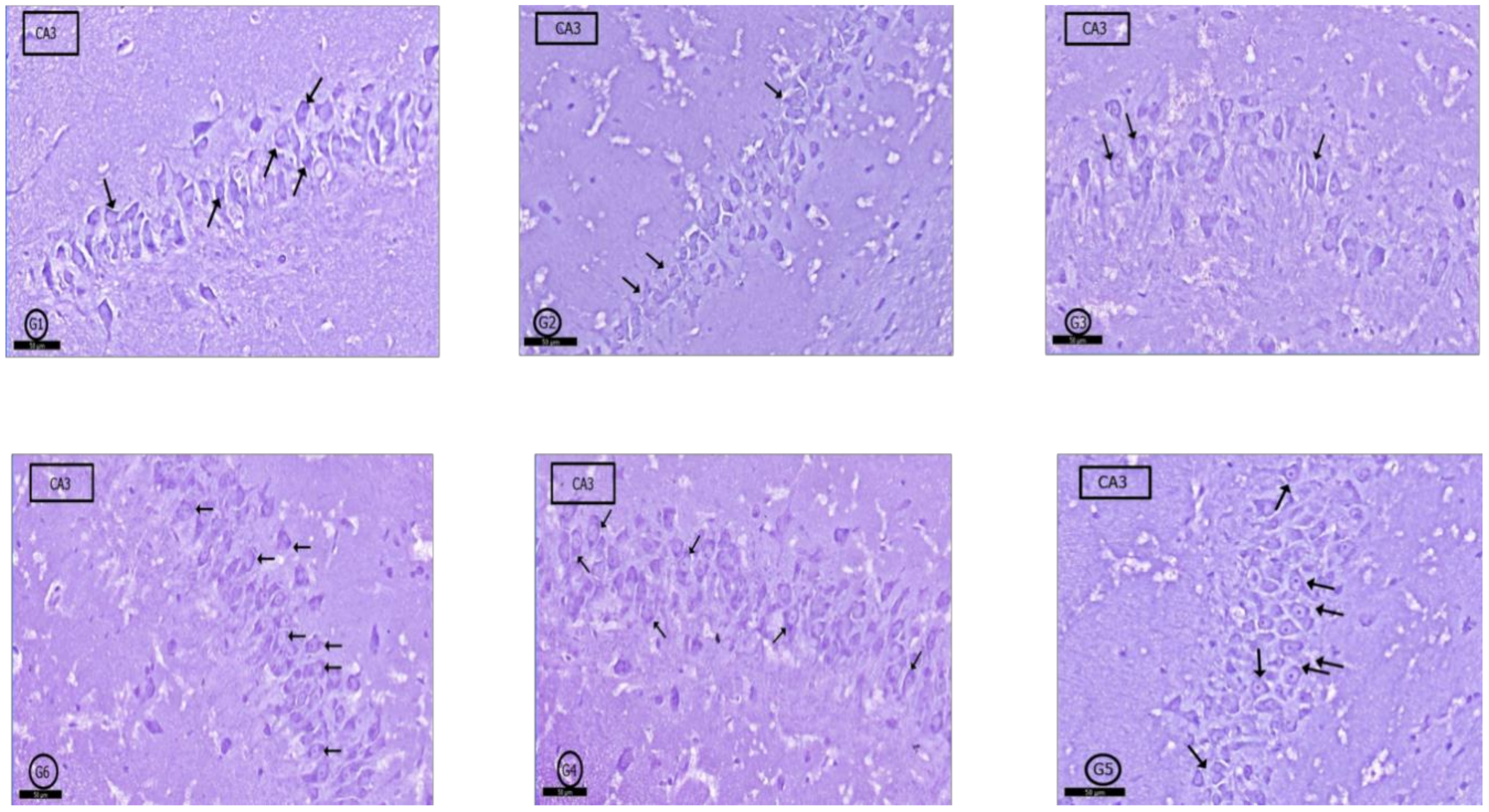
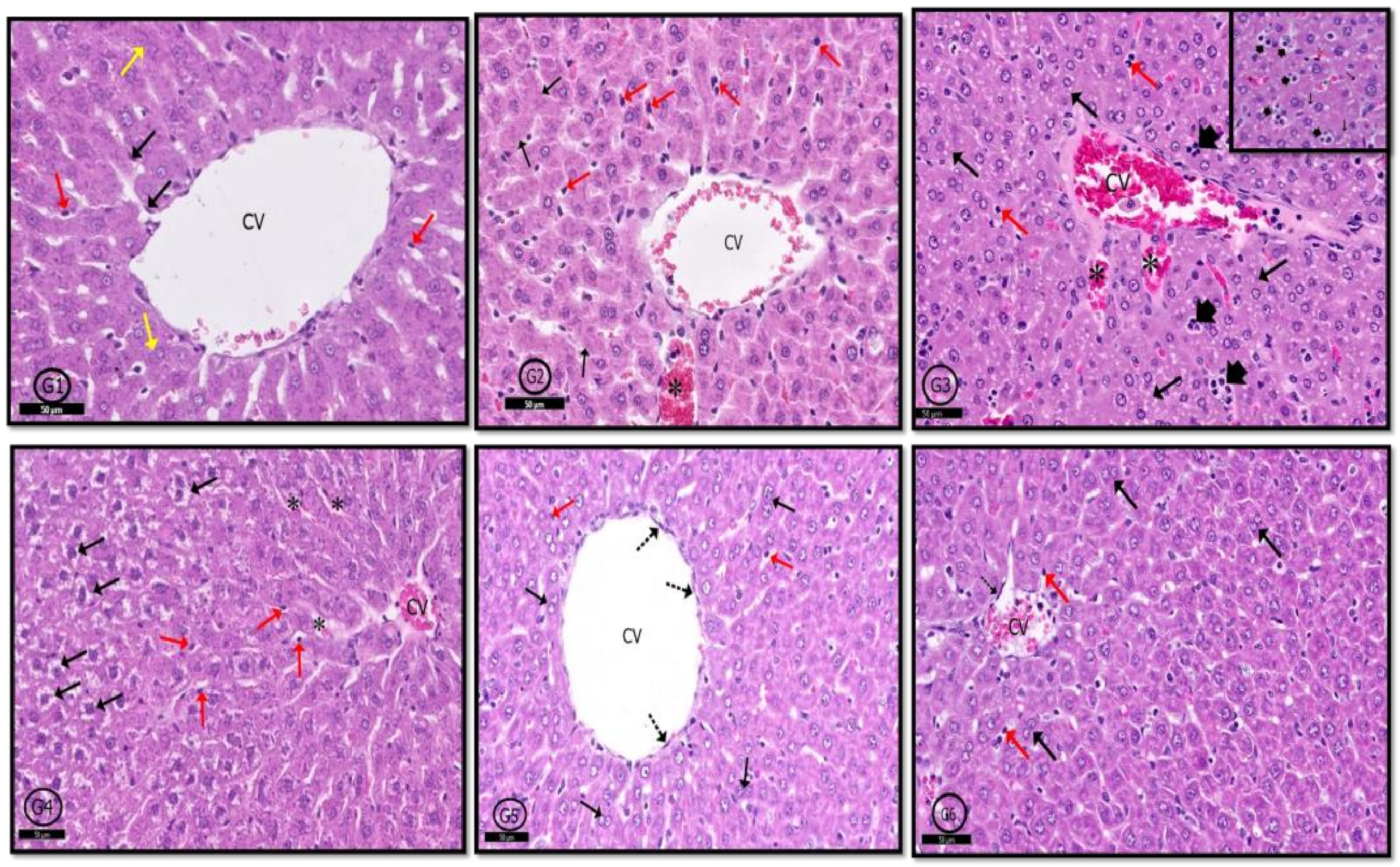
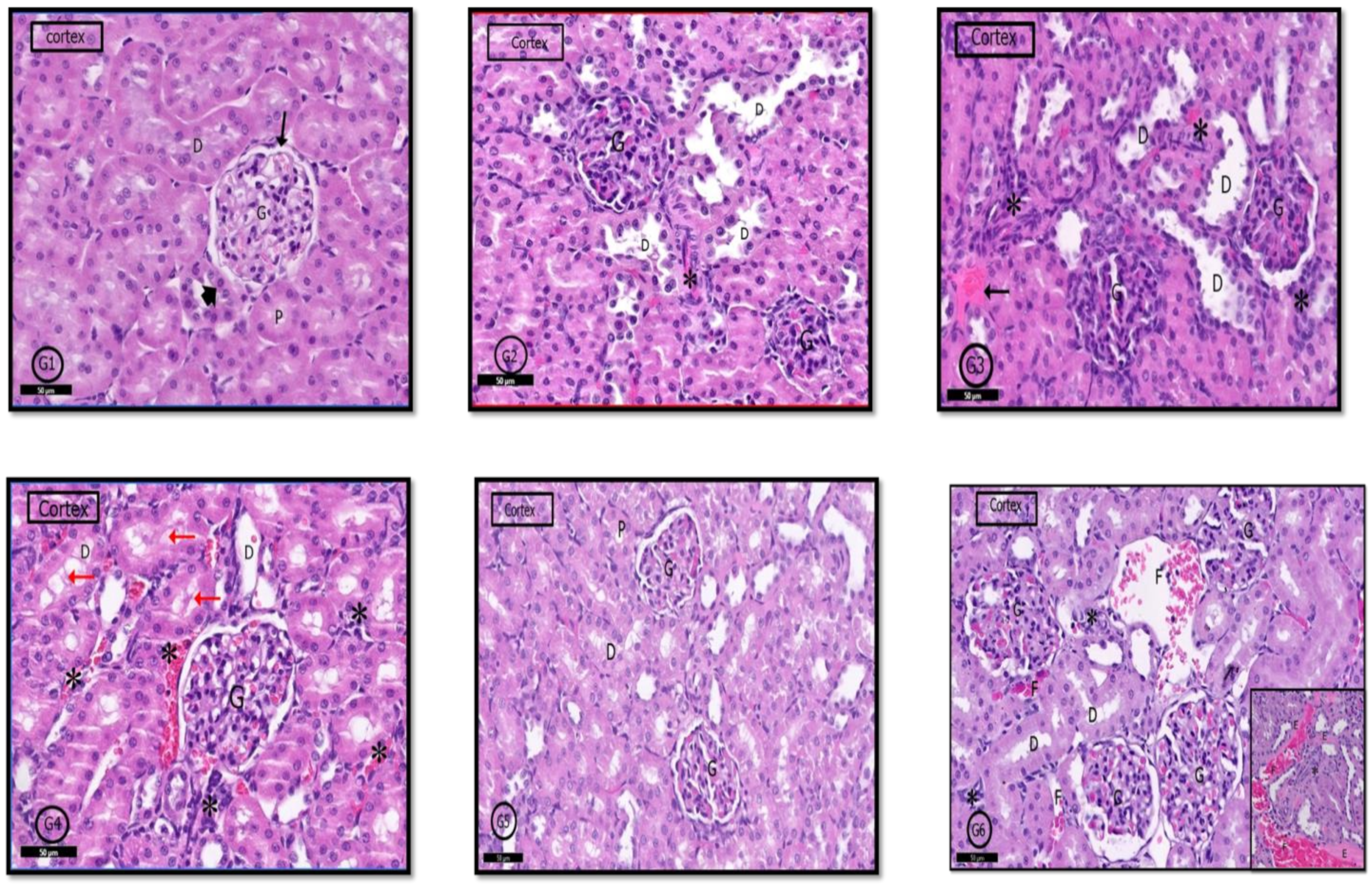
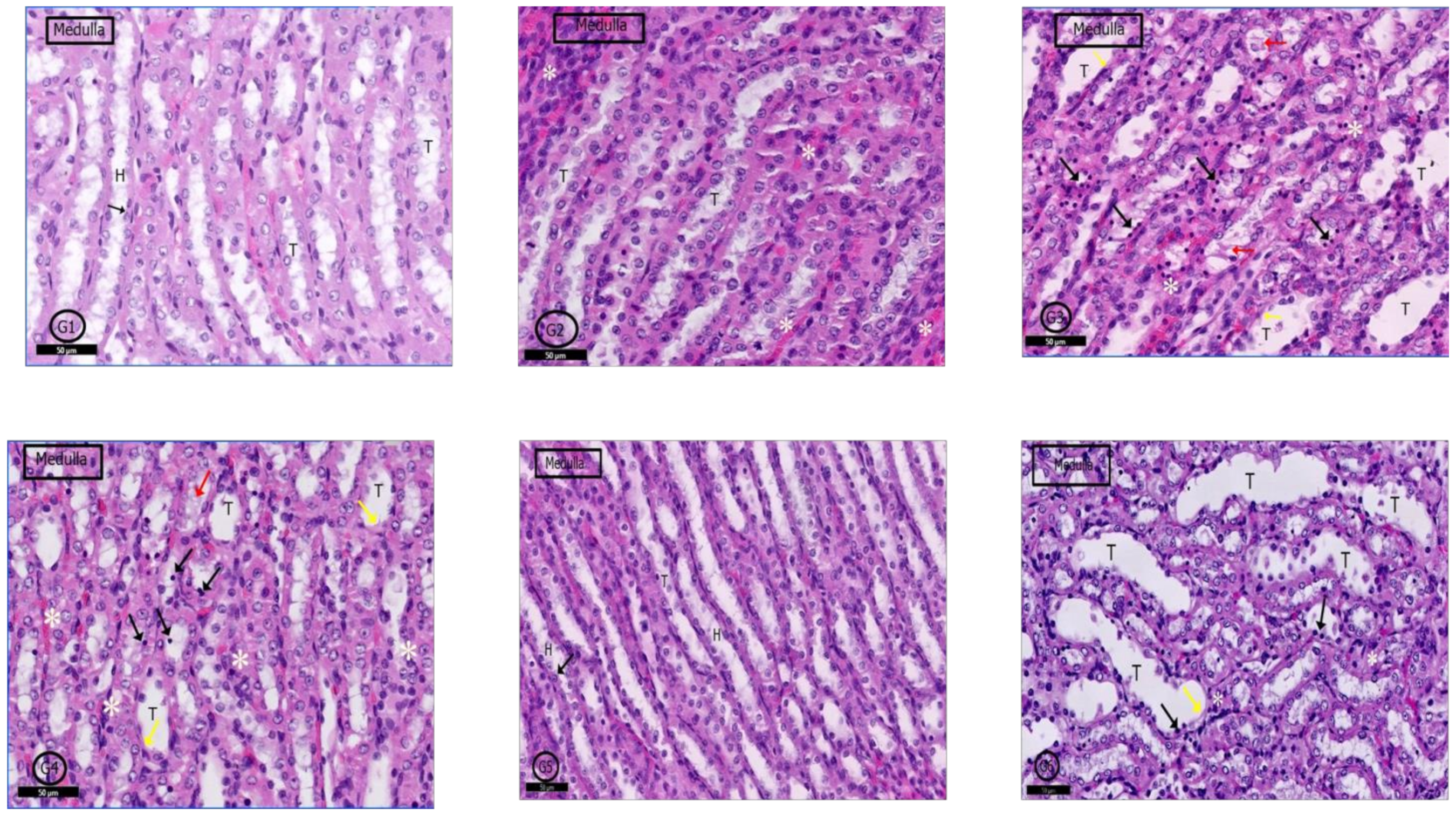
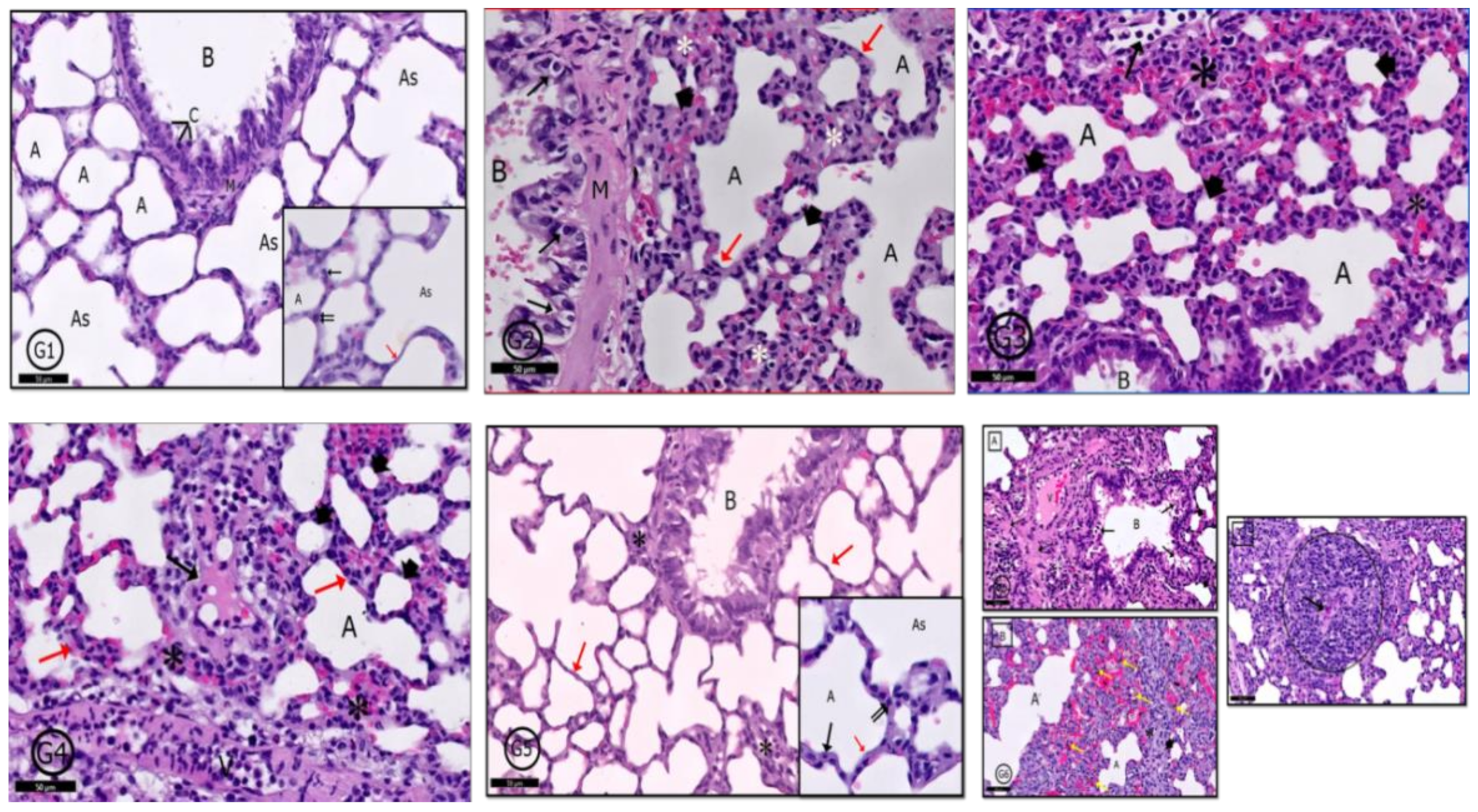
2.6. Histological Results
2.6.1. Hippocampus
2.6.2. Liver
2.6.3. Renal Cortex
2.6.4. Renal Medulla
2.6.5. Lung
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Chemicals
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Induction of Experimental Epilepsy
4.2.2. Experimental Design
4.2.3. Evaluation of Epilepsy
4.3. Biochemical Measurements
4.3.1. Samples Collection
4.3.2. Brain Homogenate Preparation
4.3.3. Biochemical Parameters in Hippocampal Homogenate and Serum
4.3.4. Histopathological Examination
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andres-Mach, M.; Zagaja, M.; Haratym-Maj, A.; Rola, R.; Maj, M.; Haratym, J.; Dudra-Jastrzębska, M.; Łuszczki, J.J. A long-term treatment with arachidonyl-2′-chloroethylamide combined with valproate increases neurogenesis in a mouse pilocarpine model of Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarati, A.M.; Lewis, M.L.; Pittman, Q.J. Neurobehavioral comorbidities of epilepsy: Role of inflammation. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Musto, A.E. The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy. J. Neuronflamm. 2018, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, Y.N.; Shaikh, M.; Chakraborti, A.; Kumari, Y.; Aledo-Serrano, Á.; Aleksovska, K.; Alvim, M.K.M.; Othman, I. HMGB1: A common biomarker and potential target for TBI, neuroinflammation, epilepsy, and cognitive dysfunction. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronica, E.; Bauer, S.; Bozzi, Y.; Caleo, M.; Dingledine, R.; Gorter, J.A.; Henshall, D.C.; Kaufer, D.; Koh, S.; Löscher, W. Neuroinflammatory targets and treatments for epilepsy validated in experimental models. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Sosa, M.; Orozco-Suárez, S.; Vega-García, A.; Caballero-Chacón, S.; Feria-Romero, I.A. Immunomodulatory effect of Celecoxib on HMGB1/TLR4 pathway in a recurrent seizures model in immature rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2018, 170, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska-Adamu, J.; Dmowska, M.; Cybulska, R.; Krawczyk, A.; Pawlikowska-Pawlęga, B. Investigations of hippocampal astrocytes in lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned rats in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2011, 49, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ho, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, C.-W.J.; Chao, Y.-M.; Chang, A.Y.; Chan, J.Y. Peripheral inflammation increases seizure susceptibility via the induction of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in the hippocampus. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, C.D.; Buijs, R.M.; Sitges, M. The anti-seizure drugs vinpocetine and carbamazepine, but not valproic acid, reduce inflammatory IL-1β and TNF-α expression in rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, L. The effects of antiepileptic drug valproic acid on apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in epileptic rats. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 28, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirhadi, K. Anticonvulsant effect of celecoxib in mice induced by PTZ. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2012, 11, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, C.; Kukal, S.; Dahiya, U.R.; Kukreti, R. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors: Future therapeutic strategies for epilepsy management. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Armenta, M.; Nava-Ruíz, C.; Juárez-Rebollar, D.; Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Yescas Gómez, P. Oxidative stress associated with neuronal apoptosis in experimental models of epilepsy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, G. Mitochondrial damage in hippocampal neurons of rats with epileptic protein expression of Fas and caspase-3. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaa, F.; El-Shamy, K.A.; El-Shaikh, K.A.; El-Kassaby, M. Efficacy of fish liver oil and propolis as neuroprotective agents in pilocarpine epileptic rats treated with valproate. Pathophysiology 2011, 18, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamse, S.; Sadr, S.S.; Roghani, M.; Hasanzadeh, G.; Mohammadian, M. Rosmarinic acid exerts a neuroprotective effect in the kainate rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy: Underlying mechanisms. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katyal, J.; Kumar, H.; Gupta, Y.K. Anticonvulsant activity of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor etoricoxib in pentylenetetrazole-kindled rats is associated with memory impairment. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 44, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, P.-S.; Ma, L.; Niu, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhou, R.; Yu, J.-Q. Anticonvulsant effect of Swertiamarin against Pilocarpine-induced seizures in adult male mice. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyu, F.; Dikmen, M. Inflammatory aspects of epileptogenesis: Contribution of molecular inflammatory mechanisms. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2017, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Yu, D.; Yoon, J.; Park, J. Valproic acid attenuates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines lipopolysaccharide-treated canine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (in vitro) and in a canine endotoxemia model (in vivo). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 166, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.B.; McLaughlin, L.D.; Ebenezer, P.J.; Nair, A.R.; Francis, J. Valproic acid effects in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in an animal model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 268, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.-A.; Jung, K.-Y.; Park, B.; Kim, T.-J.; Jun, J.-S.; Kim, K.T.; Yang, T.-W.; Lee, S.-T.; Jung, K.-H.; Chu, K. Impact of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, on cortical excitability and electrophysiological properties of the brain in healthy volunteers: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temp, F.R.; Marafiga, J.R.; Milanesi, L.H.; Duarte, T.; Rambo, L.M.; Pillat, M.M.; Mello, C.F. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors differentially attenuate pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures and increase of pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 810, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.-W.; Kaizaki, A.; Tien, L.-T.; Pang, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Numazawa, S.; Bhatt, A.; Cai, Z. Celecoxib attenuates systemic lipopolysaccharide-induced brain inflammation and white matter injury in the neonatal rats. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagib, M.M.; Tadros, M.G.; Abd Al-khalek, H.A.; Rahmo, R.M.; Sabri, N.A.; Khalifa, A.E.; Masoud, S.I. Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotective effect of adjuvant therapy with phenytoin in pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures: Impact on Sirt1/NRF2 signaling pathways. Neurotoxicology 2018, 68, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiasalari, Z.; Roghani, M.; Khalili, M.; Rahmati, B.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T. Antiepileptogenic effect of curcumin on kainate-induced model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Liu, K.; Wake, H.; Teshigawara, K.; Yoshino, T.; Takahashi, H.; Mori, S.; Nishibori, M. Therapeutic effects of anti-HMGB1 monoclonal antibody on pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroso, M.; Balosso, S.; Ravizza, T.; Liu, J.; Bianchi, M.; Vezzani, A. Interleukin-1 type 1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signalling in epilepsy: The importance of IL-1beta and high-mobility group box 1. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 270, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousson, E.; Keshta, A.T.; Hussein, Y.; Fekry, R.M.; Abo-Ghaneima, W.K. Renal protective effect of ginkgo biloba and l-carnitine extracts against pentylenetetrazol induced toxicity, oxidative stress, injury and proliferation alternation in epileptic rats. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.D.; Crother, T.R.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Jupelli, M.; Chen, S.; Dagvadorj, J.; Arditi, M.; Shimada, K. The NLRP3 inflammasome is required for the development of hypoxemia in LPS/mechanical ventilation acute lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mowafy, A.M.; Katary, M.M.; Pye, C.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Elmarakby, A.A. Novel molecular triggers underlie valproate-induced liver injury and its alleviation by the omega-3 fatty acid DHA: Role of inflammation and apoptosis. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidaurre, J.; Gedela, S.; Yarosz, S. Antiepileptic drugs and liver disease. Pediatric Neurol. 2017, 77, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trankle, C.; Abbate, A. PCSK9 Inhibition in Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Novel Opportunity. Transl. Med. 2016, 6, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.E.; Hassoun, H.T. Inflammatory mechanisms of organ crosstalk during ischemic acute kidney injury. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Abreu, K.L.S.; da Silva Junior, G.B.; Muniz, T.D.; Barreto, A.G.C.; Lima, R.S.A.; Holanda, M.A.; Pereira, E.D.B.; Libório, A.B.; de Francesco Daher, E. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with lung disease: Kidney-lung crosstalk. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiva 2013, 25, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Jhun, B.W.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, K.; Choi, H.Y. A case of drug-induced interstitial pneumonitis caused by valproic acid for the treatment of seizure disorders. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2014, 77, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Z.-P.; Yang, K.; Xu, G.-N.; Zhu, L.; Hou, L.-N.; Zhang, W.-H.; Chen, H.-Z.; Cui, Y.-Y. Role of M3 mAChR in in vivo and in vitro models of LPS-induced inflammatory response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalonga, E.C.; Silva, F.M.; Noronha, I.L. Valproic acid prevents renal dysfunction and inflammation in the ischemia-reperfusion injury model. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mock, C.M.; Schwetschenau, K.H. Levocarnitine for valproic-acid-induced hyperammonemic encephalopathy. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2012, 69, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, R. Celecoxib protects hyperoxia-induced lung injury via NF-κB and AQP1. Front. Pediatrics 2019, 7, 228. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, G.S.; Yi, C.-O.; Cho, Y.J.; Jeon, B.T.; Nizamudtinova, I.T.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, Y.-M.; Huh, J.W.; Lee, J.-H. Anti-inflammatory effects of celecoxib in rat lungs with smoke-induced emphysema. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L184–L191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, H.; Gezici, A.; Ozturk, H. The effect of celecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, on liver ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in rats. Hepatol. Res. 2006, 34, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewal, R.K.; Modi, M.; Saikia, U.N.; Chakrabarti, A.; Medhi, B. Increase in seizure susceptibility in sepsis like condition explained by spiking cytokines and altered adhesion molecules level with impaired blood brain barrier integrity in experimental model of rats treated with lipopolysaccharides. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 135, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borham, L.E.; Mahfoz, A.M.; Ibrahim, I.A.; Shahzad, N.; Alrefai, A.A.; Labib, A.A.; Sef, B.B.; Alshareef, A.; Khan, M.; Milibary, A. The effect of some immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory drugs on Li-pilocarpine-induced epileptic disorders in Wistar rats. Brain Res. 2016, 1648, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsaegh, H.; Eweis, H.; Kamel, F.; Alrafiah, A. Celecoxib Decrease Seizures Susceptibility in a Rat Model of Inflammation by Inhibiting HMGB1 Translocation. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040380
Alsaegh H, Eweis H, Kamel F, Alrafiah A. Celecoxib Decrease Seizures Susceptibility in a Rat Model of Inflammation by Inhibiting HMGB1 Translocation. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(4):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040380
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsaegh, Hadeel, Hala Eweis, Fatemah Kamel, and Aziza Alrafiah. 2021. "Celecoxib Decrease Seizures Susceptibility in a Rat Model of Inflammation by Inhibiting HMGB1 Translocation" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 4: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040380
APA StyleAlsaegh, H., Eweis, H., Kamel, F., & Alrafiah, A. (2021). Celecoxib Decrease Seizures Susceptibility in a Rat Model of Inflammation by Inhibiting HMGB1 Translocation. Pharmaceuticals, 14(4), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14040380





