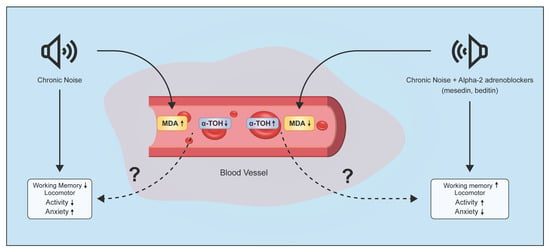
Alpha2-Adrenoblockers Regulate Development of Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Behaviour of Rats under Chronic Acoustic Stress Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Biochemical Findings
2.1.1. Changes of MDA Level in Plasma and EM under Chronic Acoustic Stress Conditions and Use of α2-Adrenoblockers
2.1.2. Changes of α-T in Plasma and EM under Chronic Acoustic Stress Conditions and Use of α2-Adrenoblockers
2.2. Behavioural Findings
2.2.1. Quantification of Arm Entries in Y-Maze
2.2.2. Spontaneous Alternations
2.2.3. Total Mobile Episodes
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Purification of Erythrocyte Membrane
4.3. Determination of MDA
4.4. Determination of α-T Content in Blood Plasma and EM
4.5. Y-Maze
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidman, M.; Standring, R. Noise and quality of life. Int. J. Envrion. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3730–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogden, J.D. Detrimental health effects of noise pollution. J. Med. Soc. 2006, 71, 847–851. [Google Scholar]
- Daiber, A.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Oelze, M.; Hahad, O.; Li, H.; Schulz, R.; Steven, S.; Münzel, T. Oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to traffic noise-induced vascular and cerebral dysfunction via uncoupling of nitric oxide synthases. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Colombo, R.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A. Biomarkers of oxidative damage in human disease. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterbauer, H.; Schaur, R.J.; Zollner, H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 11, 81–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefania, S.; Vincent, J.; Luigia, T.; Karl-Heinz, K. Severe Life Stress and Oxidative Stress in the Brain:From Animal Models to Human Pathology. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinina, E.E. Oxygine Metabolism Products in the Functional Activity of Cells (Life and Death, Creation and Destruction). Physiological and Clinical-Biochemical Aspects; Medical Press: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2006. (In Russia) [Google Scholar]
- Urso, M.L.; Clarkson, P.M. Oxidative stress, exercise, and antioxidant supplementation. Toxicology 2003, 189, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M. The definition and measurement of antioxidants in biological systems. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 18, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dündar, Y.; Aslan, R. Antioxidative stress. East. J. Med. 2000, 5, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Melkonyan, M.M.; Shirinyan, E.A.; Hynanyan, L.S.; Manukyan, A.L.; Minasyan, A.A.; Hakobyan, N.R.; Yavroyan, J.V. The effects of selective alpha-adrenoblocker beditin on the intensity of lipid peroxidation and membrane phosphoinositides content in acoustic stress conditions. New Armen. Med. J. 2010, 4, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rahal, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, V.; Yadav, B.; Tiwari, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Dhama, K. Oxidative stress, prooxidants, and antioxidants: The interplay. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 761264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirinyan, E.; Harutyunyan, S. Mesedin—A new anti-hypoxic property possessing peripheral post-synaptic α2-Adrenoblocker. Med. Sci. Educ. 2015, 18, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Westman, J.C.; Walters, J. Noise and stress: A comprehensive approach. Envrion. Health Perspect. 1981, 41, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kloet, E.R. Hormones, brain and stress. Endocr. Regul. 2003, 37, 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Arnsten, F.T.; Goldman-Rakic, P.S. Noise stress impairs prefrontal cognitive function in monkeys. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Schmauss, C. Strain-Specific Cognitive Deficits in Adult Mice Exposed to Early Life Stress. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 125, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessica, C.J.; Katy, S.; Alexander, R.G.; Victor, M.L.; Jeremy, S.B.; Gokhan, O.; Pengcheng, Z.; Samantha, K.O.; Matthew, A.W. Anxiety Cells in a Hippocampal-Hypothalamic Circuit. Neuron 2018, 97, 670–683. [Google Scholar]
- Cleal, M.; Fontana, B.D.; Ranson, D.C.; McBride, S.D.; Swinny, J.D.; Redhead, E.S.; Parker, M.O. The Free-movement pattern Y-maze: A cross-species measure of working memory and executive function. Behav. Res. 2021, 53, 536–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manukyan, A.L.; Grigoryan, A.S.; Hunanyan, L.S.; Harutyunyan, H.A.; Manukyan, M.V.; Mkrtchyan, V.S.; Melkonyan, M.M. Alfa2-adrenoblockers attenuate the elevated plasma cholesterol, anxiety levels and restore impaired spatial memory of rats under the chronic noise exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babisch, W. Stress hormones in the research on cardiovascular effects of noise. Noise Health 2003, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Manikandan, S.; Padma, M.K.; Srikumar, R.; Jeya, P.N.; Muthuvel, A.; Sheela, D.R. Effect of chronic noise stress on spatial memory of rats in relation to neuronal dendritic alteration and free radical-imbalance in hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 399, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, D.; Bielefeld, E.C.; Harris, K.C.; Hu, B.H. The role of oxidative stress in noise-induced hearing loss. Ear Hear. 2006, 27, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Ralli, M.; Sergi, B.; Parrilla, C.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G. Protective properties of antioxidant drugs in noise-induced hearing loss in the guinea pig. Audiol. Med. 2006, 6, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Zhou, T.; Pannell, B.K.; Ziegler, A.; Best, T.M. Biological and physiological role of reactive oxygen species—The good, the bad and the ugly. Acta Physiol. 2015, 214, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marreiro, D.D.; Cruz, K.J.; Morais, J.B.; Beserra, J.B.; Severo, J.S.; de Oliveira, A.R.S. Zinc and oxidative stress: Current mechanisms. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, T.; Ziegler, A.C.; Dimitrion, P.; Zuo, L. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases: From molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2525967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricordi, C.; Garcia-Contreras, M.; Farnetti, S. Diet and inflammation: Possible effects on immunity, chronic diseases, andlifespan. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2015, 34, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrag, M.; Mueller, C.; Zabel, M.; Croffon, A.; Kirsch, W.M.; Ghribi, O.; Squitti, R.; Perry, G. Oxidative stress in blood in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Rasheed, O.F.; Farid, Y.Y.; Al-Nasiri, U.S. Coenzyme Q10 and oxidative stress markers in seminal plasma of Iraqi patients with male infertility. Saudi Med. J. 2010, 31, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panin, L.E.; Mokrushnikov, P.V.; Kunitsyn, V.G.; Zaitsev, B.N.; Zaitsev, B.N. Interaction Mechanism of Cortisol and Catecholamines with Structural Components of Erythrocyte Membrane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 9462–9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrushnikov, P.V.; Panin, L.E. The action of stress hormones on the structure and function of erythrocyte membrane. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2015, 34, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunitsyn, V.G.; Panin, L.E. Mechanism of Erythrocyte Deformation under the Action of Stress Hormones. Int. J. Biophys. 2013, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Delmas-Beauvieux, M.C.; Peuchant, E.; Richard-Harston, S.; Decamps, A.; Reignier, B.; Emeriau, J.P.; Rainfray, M. Antioxidant defenses and oxidative stress markers in erythrocytes and plasma from normally nourished elderly Alzheimer patients. Age Ageing 2001, 30, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajanov, M.; Chavushyan, V.; Matinyan, S.; Danielyan, M.; Yenkoyan, K. Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology-triggered oxidative stress, alterations in monoamines levels, and structural damage of locus coeruleus neurons are partially recovered by a mix of proteoglycans of embryonic genesis. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 131, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Liew, W.P.; Sulaiman Rahman., H. Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress: A Mutual Interplay in Age-Related Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Diez, C.; Miguel, V.; Mennerich, D.; Kietzmann, T.; Sánchez-Pérez, P.; Cadenas, S.; Lamas, S. Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podda, M.; Grundmann-Kollmann, M. Low molecular weight antioxidants and their role in skin ageing. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2001, 26, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, M.F.; Hoffmeister, C.; Tonello, R.; de Oliveira Ferreira, A.P.; Ferreira, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of vitamin E on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Inflammation 2015, 38, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A. Molecular mechanism of alpha-tocopherol action. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.; Harrainne, T.; Wassall, S.R.; Stilwell, W.; Katsaras, J. The location and behavior of alpha-tocopherol in membranes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkonian, M.M. The changes of the Erythrocyte Membranes Lipids Fatty Acids composition under the acoustic stress Conditions and a-tocopherolacetate Application. Med. Sci. Armen. 1993, 33, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Traber, M.G.; Atkinson, J. Vitamin E, antioxidant and nothing more. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukyan, A.L.; Grigoryan, A.S.; Hunanyan, L.S.; Harutyunyan, H.A.; Manukyan, M.V.; Melkonyan, M.M. Adrenergic alpha-2 receptor antagonists cease augmented oxidation of plasma proteins and anxiety of rats caused by chronic noise exposure. Noise Health 2020, 22, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukyan, A. Alfa-2 adrenoblokers decrease elevated carbonylation of erythrocytes’ membranes proteins and regulate behavioral changes induced by noise action. Life Sci. 2020, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleva, V.; Robert, D.K. Antioxidant-Induced Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2091–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moret, C.; Briley, M. The importance of norepinephrine in depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2011, 7, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ruslán, Á.D.; Annia, G. Adrenaline and Noradrenaline: Protectors against Oxidative Stress or Molecular Targets? J. Phys. Chem. 2015, 119, 3479–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, S.Z. α2—Adrenoceptors in the treatment of major neuropsychiatric disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 38, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kable, J.W.; Murrin, L.C.; Bylund, D.B. In vivo gene modification elucidates subtype-specific functions of alpha (2)-adrenergic receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. 2000, 293, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Frankenhaeuser, M. Psychoneuroendocrine approaches to the study of emotion as related to stress on coping. In Nebraska Symposium on Motivation; Howe, H.E., Dienstbier, R.A., Eds.; University of Nebraska Press: Lincoln, NE, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, E. Hippocampus: Cognitive Processes and Neural Representations that Underlie Declarative Memory. Neuron 2004, 44, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannenholz, L.; Jimenez, J.C.; Kheirbek, M.A. Local and regional heterogeneity underlying hippocampal modulation of cognition and mood. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfitt, G.M.; Nguyen, R.; Bang, J.Y.; Aqrabawi, A.J.; Tran, M.M.; Seo, D.; Richards, B.A.; Kim, J.C. Bidirectional control of anxiety-related behaviors in mice: Role of inputs arising from the ventral hippocampus to the lateral septum and medial prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 1715–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, D.C.; Singer, J.E. Urban Stress: Experiments on Noise and Social Stressors; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Bücheler, M.M.; Hadamek, K.; Hein, L. Two α2-adrenergic receptor subtypes, α2A and α2C, inhibit transmitter release in the brain of gene-targeted mice. Neuroscience 2002, 109, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, I.-H.; Shih, J.-H.; Jhao, Y.-T.; Chen, H.-C.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chen, C.-F.F.; Huang, Y.-S.; Shiue, C.-Y.; Ma, K.-H. Regulation of noise-induced loss of serotonin transporters with resveratrol in a rat model using 4-[18F]-ADAM/small-animal positron emission tomography. Molecules 2019, 24, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, R.; Sheela, D.R.; James, S.; Manohar, S. Noise-stress-induced brain neurotransmitter changes and the effect of ocimum sanctum (Linn) treatment in albinorats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 98, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, M.G.; Vasina, V.; Raschi, E.; Crema, F.; De Ponti, F. The β3-adrenoceptor as a therapeutic target: Current perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2009, 59, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigeuz Manzanares, P.A.; Isoardi, N.A.; Carrer, H.F.; Malina, V.A. Previous stress facilitates fear memory, attenuates GABAergic inhibition, and increases synaptic plasticity in the rat basolateral amigdala. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8725–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emily, P.; Nafisa, J. Assessing Spatial Working Memory Using the Spontaneous Alternation Y-maze Test in Aged Male Mice. Bio Protoc. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkonyan, M.M.; Hunanyan, L.; Lourhmati, A.; Layer, N.; Beer-Hammer, S.; Yenkoyan, K.; Schwab, M.; Danielyan, L. Neuroprotective, neurogenic, and amyloid beta reducing effect of a novel alpha 2-Adrenoblocker, mesedin, on astroglia and neuronal progenitors upon hypoxia and glutamate exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkonyan, M.M.; Melik-Agaeva, E.; Mchitaryan, V.G. The intensity of lipid peroxidation processes and the activity of enzymes depending on sex under stress. Med. Sci. Armen. 1986, 26, 322–328. (In Russia) [Google Scholar]
- Yenkoyan, K.; Fereshetyan, K.; Matinyan, S.; Chavushyan, V.; Aghajanov., M. The role of monoamines in the development of Alzheimer’s disease and neuroprotective effect of a proline rich polypeptide. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.Q.; Qin, Z.Q. Influence of combined traffic noise on the ability of learning and memory. Noise Health 2018, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Low, T.Y.; Seow, T.K.; Chung, M.C. Separation of human erythrocyte membrane associated proteins with one-dimensional and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis followed by identification with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2002, 2, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterbauer, H.; Cheeseman, K.H. Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: Malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzym. 1990, 186, 407–421. [Google Scholar]
- Duggan, D.D. Spectrofluorometric determination of tocopherols. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1954, 84, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.N. The value of spontaneous alternation behavior (SAB) as a test of retention in pharmacological investigations of memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, R.; Page, D.T.; Merzlyak, I.; Kim, C.; Tecott, L.H.; Janak, P.H.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Sur, M. Reduced conditioned fear response in mice that lack Dlx1 and show subtype-specific loss of interneurons. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2009, 1, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melkonyan, M.; Manukyan, A.; Hunanyan, L.; Grigoryan, A.; Harutyunyan, H.; Sukiasyan, L.; Danielyan, L.; Yenkoyan, K. Alpha2-Adrenoblockers Regulate Development of Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Behaviour of Rats under Chronic Acoustic Stress Conditions. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060529
Melkonyan M, Manukyan A, Hunanyan L, Grigoryan A, Harutyunyan H, Sukiasyan L, Danielyan L, Yenkoyan K. Alpha2-Adrenoblockers Regulate Development of Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Behaviour of Rats under Chronic Acoustic Stress Conditions. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(6):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060529
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelkonyan, Magdalina, Ashkhen Manukyan, Lilit Hunanyan, Artem Grigoryan, Hayk Harutyunyan, Lilit Sukiasyan, Lusine Danielyan, and Konstantin Yenkoyan. 2021. "Alpha2-Adrenoblockers Regulate Development of Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Behaviour of Rats under Chronic Acoustic Stress Conditions" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 6: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060529
APA StyleMelkonyan, M., Manukyan, A., Hunanyan, L., Grigoryan, A., Harutyunyan, H., Sukiasyan, L., Danielyan, L., & Yenkoyan, K. (2021). Alpha2-Adrenoblockers Regulate Development of Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Behaviour of Rats under Chronic Acoustic Stress Conditions. Pharmaceuticals, 14(6), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060529