Synthesis of Novel Fluorinated Xanthine Derivatives with High Adenosine A2B Receptor Binding Affinity
Abstract
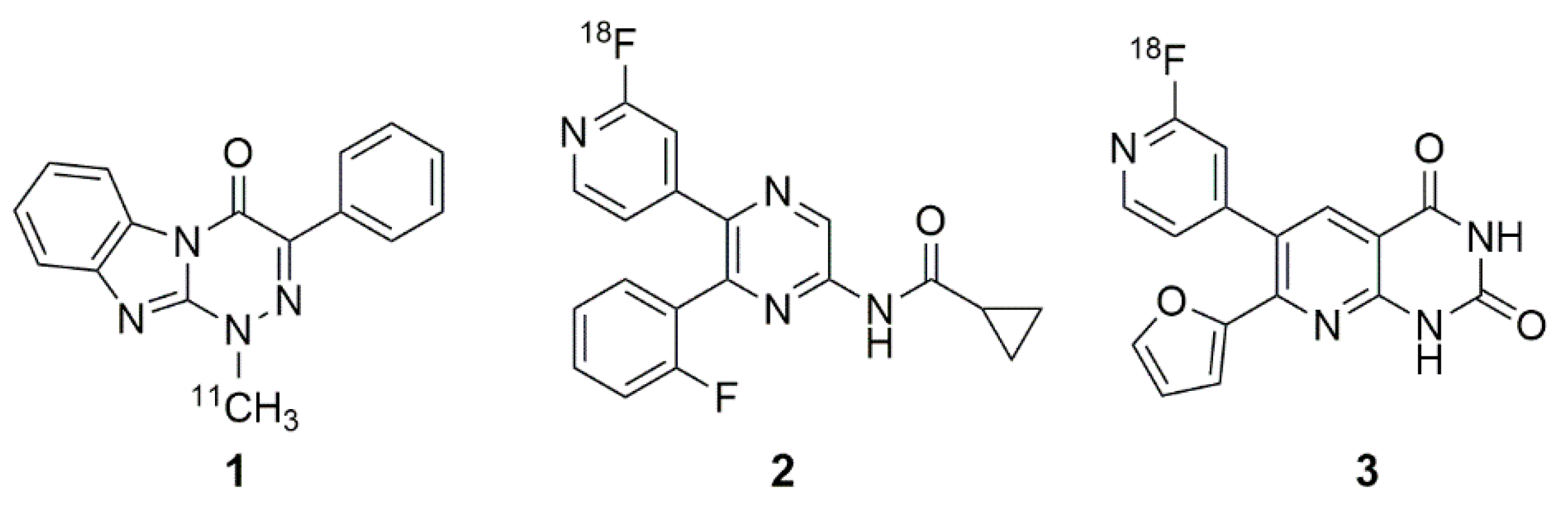
1. Introduction
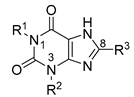 | R1 | R2 | R3 | Ki (human A2B) ± SEM in nM |
| PSB-603 (X = –Cl) PSB-1901 (X = –Br) | –propyl | –H | 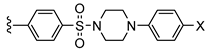 | 0.553 ± 0.103 [13] a 0.0835 ± 0.0033 [23] a |
| MRS-1754 | –propyl | –propyl | 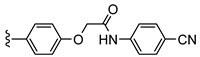 | 1.97 ± 0.31 [19] b |
| CVT-6975 | –methyl | –methyl | 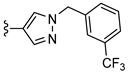 | 1.0 [20] c |
2. Results and Discussion
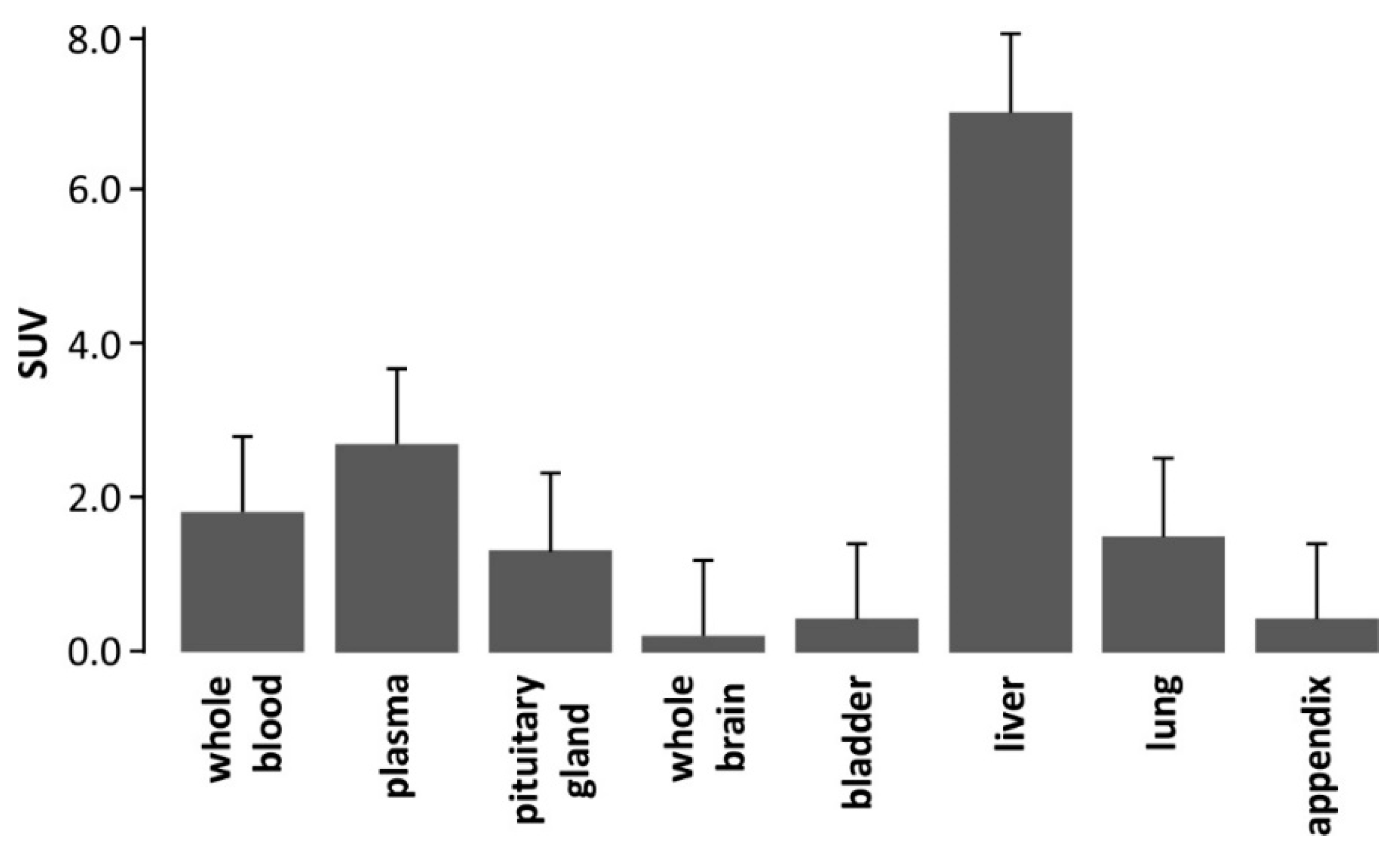
2.1. Organ Distribution of [3H]PSB-603 in Mice
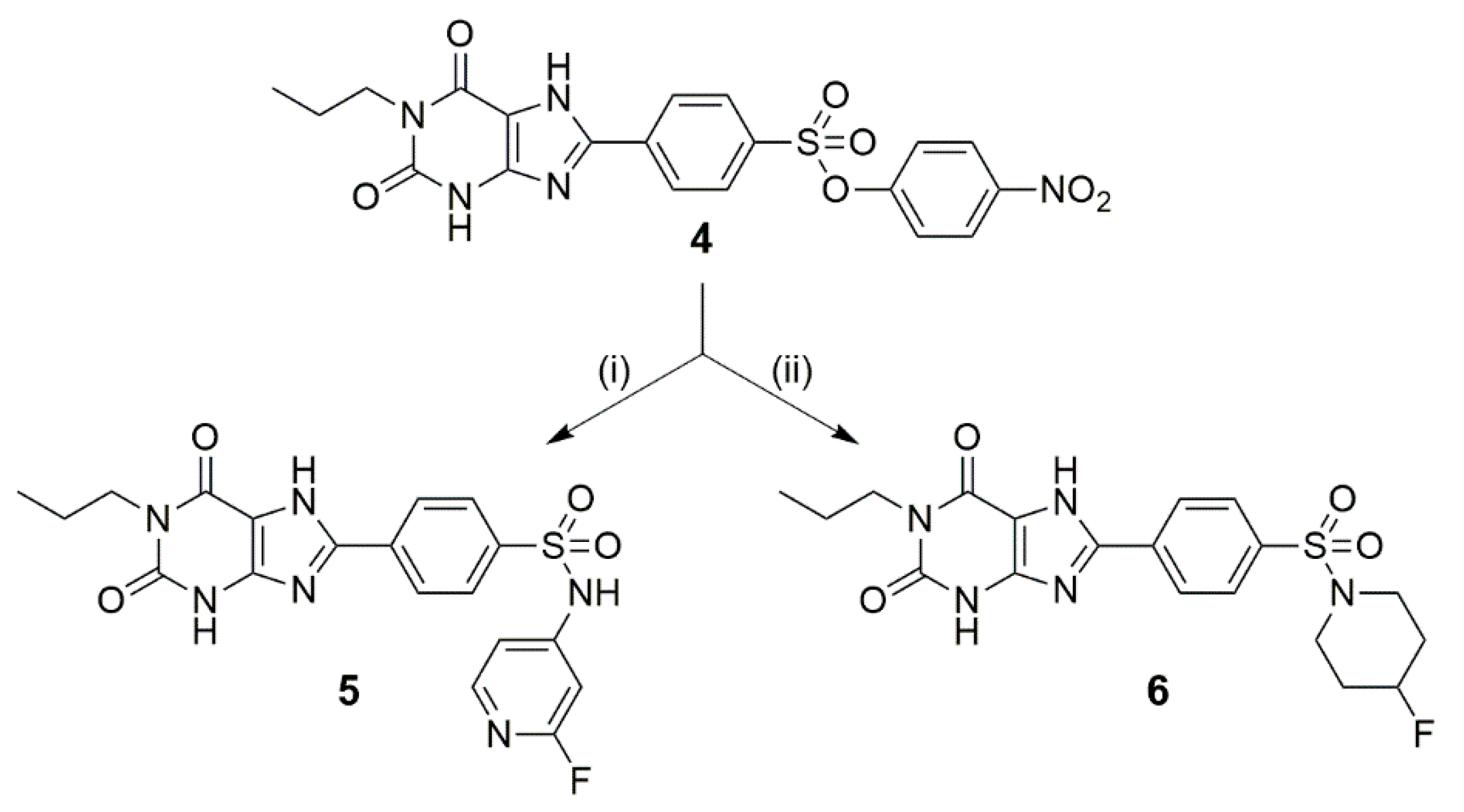
2.2. Synthesis of 5 and 6
2.3. Affinity towards Adenosine Receptor Subtypes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Organ Distribution Studies of [3H]PSB-603 in Mice
3.2. Chemistry
3.2.1. General Methods and Materials
3.2.2. Syntheses
4-(2,6-Dioxo-1-propyl-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purin-8-yl)-N-(2-fluoropyridin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide (5)
8-(4-((4-Fluoropiperidin-1-yl)sulfonyl)phenyl)-1-propyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione (6)
3.3. In Vitro Binding Assays: Determination of Ki Values
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feoktistov, I.; Biaggioni, I. Adenosine A2B receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1997, 49, 381–402. [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Abbracchio, M.P.; Burnstock, G.; Daly, J.W.; Harden, T.K.; Jacobson, K.A.; Leff, P.; Williams, M. Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1994, 46, 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Jzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Klotz, K.-N.; Linden, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 527–552. [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Jzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Linden, J.; Müller, C.E. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors—An update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredholm, B.B.; Irenius, E.; Kull, B.; Schulte, G. Comparison of the potency of adenosine as an agonist at human adenosine receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 61, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, C.; Sara, S.; Abdul Muttaleb Yousef, J.; Ghadir, K.; Nikhil, A. Therapeutic Potentials of A2B Adenosine Receptor Ligands: Current Status and Perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2741–2771. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.-G.; Jacobson, K.A. A2B Adenosine Receptor and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Baqi, Y.; Hinz, S.; Namasivayam, V. Medicinal Chemistry of A2B Adenosine Receptors. In The Adenosine Receptors; Borea, P.A., Varani, K., Gessi, S., Merighi, S., Vincenzi, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 34, pp. 137–168. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchio, E.A.; White, P.J.; May, L.T. The adenosine A2B G protein-coupled receptor: Recent advances and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 198, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarapynbiang, M.; Bijayashree, M.; Utpal, C.D.; Pratap, C.A. Recent Progress of Adenosine Receptor Modulators in the Development of Anticancer Chemotherapeutic Agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2842–2858. [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi, M.H.; Raoofi Mohseni, S.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Anvari, E.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2032–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Jacobson, K.A. Recent developments in adenosine receptor ligands and their potential as novel drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1290–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrmann, T.; Hinz, S.; Bertarelli, D.C.G.; Li, W.; Florin, N.C.; Scheiff, A.B.; Müller, C.E. 1-Alkyl-8-(piperazine-1-sulfonyl)phenylxanthines: Development and characterization of adenosine A2B receptor antagonists and a new radioligand with subnanomolar affinity and subtype specificity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3994–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Kitabatake, K.; Abe, R.; Tsukimoto, M. Involvement of A2B Receptor in DNA Damage Response and Radiosensitizing Effect of A2B Receptor Antagonists on Mouse B16 Melanoma. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabatake, K.; Yoshida, E.; Kaji, T.; Tsukimoto, M. Involvement of adenosine A2B receptor in radiation-induced translocation of epidermal growth factor receptor and DNA damage response leading to radioresistance in human lung cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, D.; Giacomelli, C.; Taliani, S.; Barresi, E.; Robello, M.; Daniele, S.; Bartoli, A.; Burchielli, S.; Pardini, S.; Salvadori, P.A.; et al. Toward PET imaging of A2B adenosine receptors: A carbon-11 labeled triazinobenzimidazole tracer: Synthesis and imaging of a new A2B PET tracer. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2016, 43, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, M.; Hinz, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Namasivayam, V.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Teodoro, R.; Toussaint, M.; Kranz, M.; Juhl, C.; Steinbach, J.; et al. Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of a fluorine-18 labeled pyrazine based radioligand for PET imaging of the adenosine A2B receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4650–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, M.; Moldovan, R.-P.; Hinz, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Gündel, D.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Toussaint, M.; Teodoro, R.; Juhl, C.; Steinbach, J.; et al. Development of a Radiofluorinated Adenosine A2B Receptor Antagonist as Potential Ligand for PET Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Ji, X.-d.; Melman, N.; Linden, J.; Jacobson, K.A. Anilide derivatives of an 8-phenylxanthine carboxylic congener are highly potent and selective antagonists at human A2B adenosine receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, R.V.; Elzein, E.; Perry, T.; Li, X.; Palle, V.; Varkhedkar, V.; Gimbel, A.; Maa, T.; Zeng, D.; Zablocki, J. Novel 1,3-disubstituted 8-(1-benzyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl) xanthines: High affinity and selective A2B adenosine receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3682–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Preti, D.; Bovero, A.; Romagnoli, R.; Fruttarolo, F.; Zaid, N.A.; Moorman, A.R.; Varani, K.; Gessi, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new 8-heterocyclic xanthine derivatives as highly potent and selective human A2B adenosine receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortore, G.; Martinelli, A. A2B receptor ligands: Past, present and future trends. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Seel, C.J.; Temirak, A.; Namasivayam, V.; Arridu, A.; Schabikowski, J.; Baqi, Y.; Hinz, S.; Hockemeyer, J.; Müller, C.E. A2B Adenosine Receptor Antagonists with Picomolar Potency. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4032–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, P.; van den Hoff, J.; Steinbach, J. Development of 18F-labeled radiotracers for neuroreceptor imaging with positron emission tomography. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 777–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pike, W.V. Considerations in the development of reversibly binding PET radioligands for brain imaging. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1818–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, B.; Liu, J.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Teodoro, R.; Ludwig, F.-A.; Chezal, J.-M.; Moreau, E.; Brust, P.; Maisonial-Besset, A. Targeting cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) in brain: Toward the development of a PET radioligand labeled with fluorine-18. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 86, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Waterbeemd, H.; Camenisch, G.; Folkers, G.; Chretien, J.R.; Raevsky, O.A. Estimation of blood-brain barrier crossing of drugs using molecular size and shape, and H-bonding descriptors. J. Drug Target 1998, 6, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS drug design: Balancing physicochemical properties for optimal brain exposure. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2584–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, R.N. Determination of lipophilicity and its use as a predictor of blood-brain barrier penetration of molecular imaging agents. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2003, 5, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, D.; Scanlon, M.; Ham, J. Adenosine signalling pathways in the pituitary gland: One ligand, multiple receptors. J. Endochrinol. 2003, 177, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dixon, A.K.; Gubitz, A.K.; Sirinathsinghji, D.J.S.; Richardson, P.J.; Freeman, T.C. Tissue distribution of adenosine receptor mRNAs in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 118, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E. Synthesis of 3-substituted 6-aminouracils. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 6539–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Sandoval-Ramírez, J. A new versatile synthesis of xanthines with variable substituents in the 1-, 3-, 7- and 8-positions. Synthesis 1995, 1995, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E. General synthesis and properties of 1-monosubstituted xanthines. Synthesis 1993, 1993, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Müller, C.E. Preparation, properties, reactions and adenosine receptor affinities of sulfophenylxanthine nitrophenyl esters: toward the development of sulfonic acid prodrugs with peroral bioavailability. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, M.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Moldovan, R.; Sekhar, K.V.G.C.; Brust, P.; Wenzel, B. Do spiroindolines have the potential to replace vesamicol as lead compound for the development of radioligands targeting the vesicular acetylcholine transporter? Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5107–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Bertarelli, D.C.G.; Hayallah, A.M.; Meyer, H.; Klotz, K.-N.; Müller, C.E. A new synthesis of sulfonamides by aminolysis of p-nitrophenylsulfonates yielding potent and selective adenosine A2B receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4384–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaya, N.; Ishiyama, T.; Muto, R.; Watanabe, T.; Ochiai, Y. Pyrazole Derivatives. EP1762568A1, 14 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alnouri, M.; Jepards, S.; Casari, A.; Schiedel, A.; Hinz, S.; Müller, C. Selectivity is species-dependent: Characterization of standard agonists and antagonists at human, rat, and mouse adenosine receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2015, 11, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, K.-N.; Lohse, M.J.; Schwabe, U.; Cristalli, G.; Vittori, S.; Grifantini, M. 2-Chloro-N6-[3H]cyclopentyladenosine ([3HCCPA) —A high affinity agonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1989, 340, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Maurinsh, J.; Sauer, R. Binding of [3H]MSX-2 (3-(3-hydroxypropyl)-7-methyl-8-(m-methoxystyryl)-1-propargylxanthine) to rat striatal membranes—A new, selective antagonist radioligand for A2A adenosine receptors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 10, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; Diekmann, M.; Thorand, M.; Ozola, V. [3H]8-Ethyl-4-methyl-2-phenyl-(8R)-4,5,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[2,1-i]-purin-5-one ([3H]PSB-11), a Novel High-Affinity Antagonist Radioligand for Human A3 Adenosine Receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compd. | 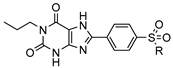 | Ki in nM (or % Inhibition of Radioligand Binding at a Concentration of 1 µM) a |
Selectivity Ratio Ki(Ax)/Ki(A2B) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | A2B | A2A | A1 | A3 | A2A/A2B | A1/A2B | A3/A2B | |
| 5 | 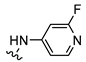 | 9.97 ± 0.86 | 375 ± 53 | 255 ± 32 | ~1000 (45 ± 3%) | 38 | 25 | 100 |
| 6 | 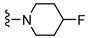 | 12.3 ± 3.6 | 158 ± 28 | ~1000 (44 ± 1%) | >1000 (38 ± 2%) | 13 | 81 | >81 |
| PSB-603 |  | 0.55 ± 0.10 b | >10,000 (7 ± 14%) b | >10,000 (10 ± 3%) b | >10,000 (10 ± 15%) b | >18,000 | >18,000 | >18,000 |
| 7 | 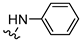 | 31.4 ± 0.9 b,c | 23 ± 13 b,d | 1.8 ± 1.0 b,d | >1000 (48%) b | 0.7 | 0.06 | >32 |
| 8 | 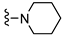 | 19.7 ± 4.7 b | 714 ± 122 b,d | 91.1 ± 25.0 b,d | 140 ± 20 b | 35 | 4 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lindemann, M.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Hinz, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Teodoro, R.; Juhl, C.; Steinbach, J.; Brust, P.; Müller, C.E.; Wenzel, B. Synthesis of Novel Fluorinated Xanthine Derivatives with High Adenosine A2B Receptor Binding Affinity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050485
Lindemann M, Dukic-Stefanovic S, Hinz S, Deuther-Conrad W, Teodoro R, Juhl C, Steinbach J, Brust P, Müller CE, Wenzel B. Synthesis of Novel Fluorinated Xanthine Derivatives with High Adenosine A2B Receptor Binding Affinity. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050485
Chicago/Turabian StyleLindemann, Marcel, Sladjana Dukic-Stefanovic, Sonja Hinz, Winnie Deuther-Conrad, Rodrigo Teodoro, Cathleen Juhl, Jörg Steinbach, Peter Brust, Christa E. Müller, and Barbara Wenzel. 2021. "Synthesis of Novel Fluorinated Xanthine Derivatives with High Adenosine A2B Receptor Binding Affinity" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050485
APA StyleLindemann, M., Dukic-Stefanovic, S., Hinz, S., Deuther-Conrad, W., Teodoro, R., Juhl, C., Steinbach, J., Brust, P., Müller, C. E., & Wenzel, B. (2021). Synthesis of Novel Fluorinated Xanthine Derivatives with High Adenosine A2B Receptor Binding Affinity. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050485








