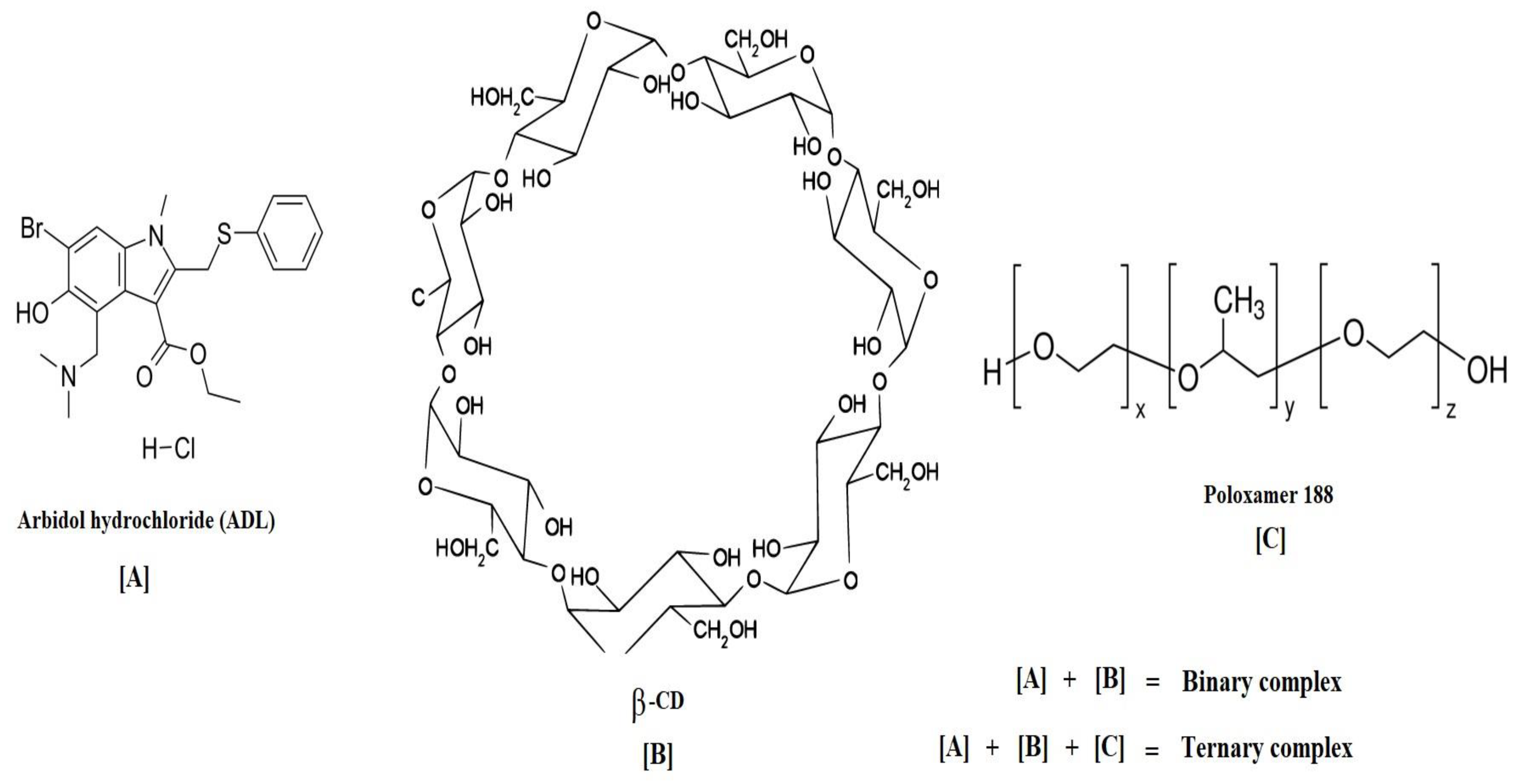
Improving the Solubilization and Bioavailability of Arbidol Hydrochloride by the Preparation of Binary and Ternary β-Cyclodextrin Complexes with Poloxamer 188
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Phase Solubility Studies for ADL in Binary and Ternary Systems
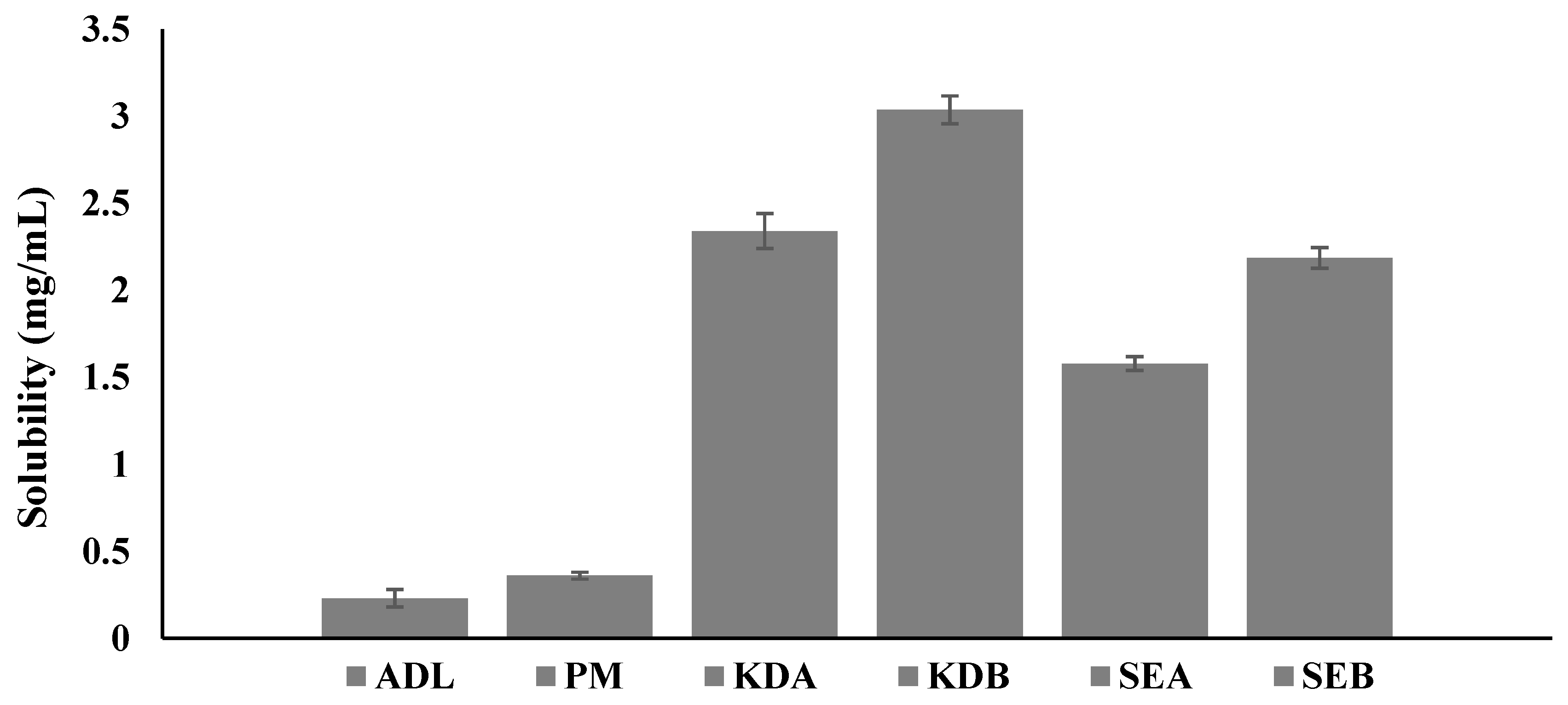
2.2. Aqueous Solubility Determination of the Solid Complexes
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
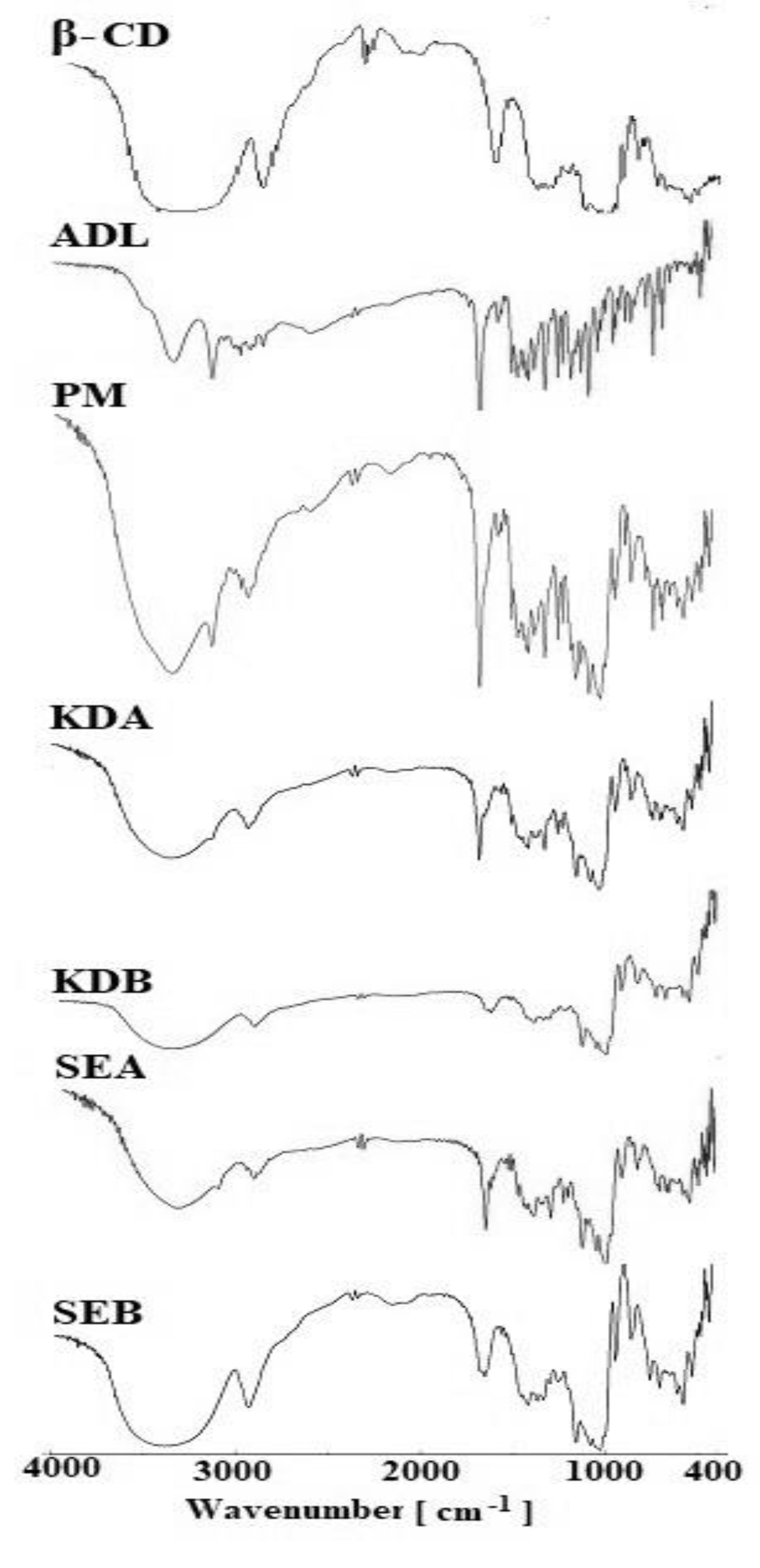
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
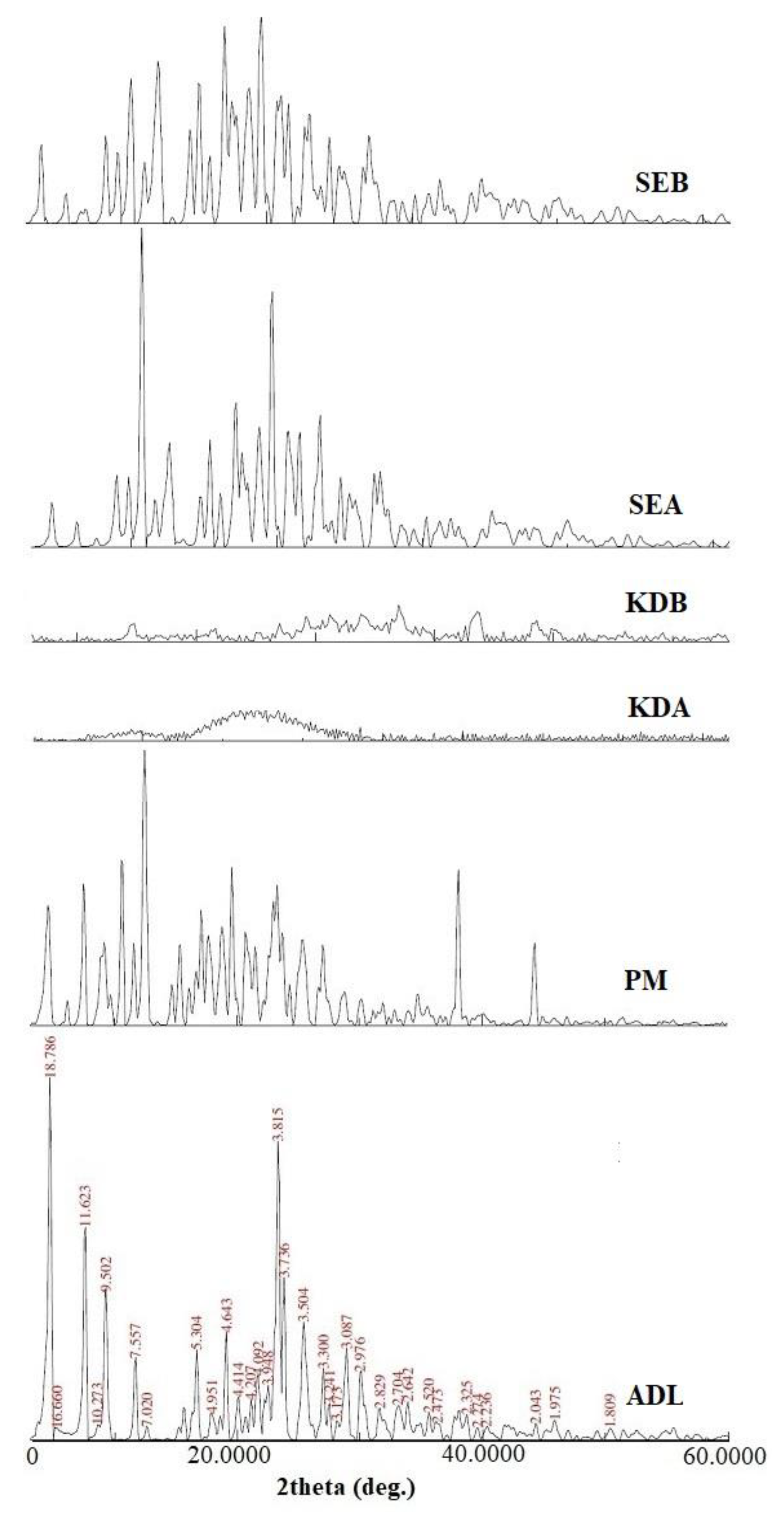
2.5. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) Studies
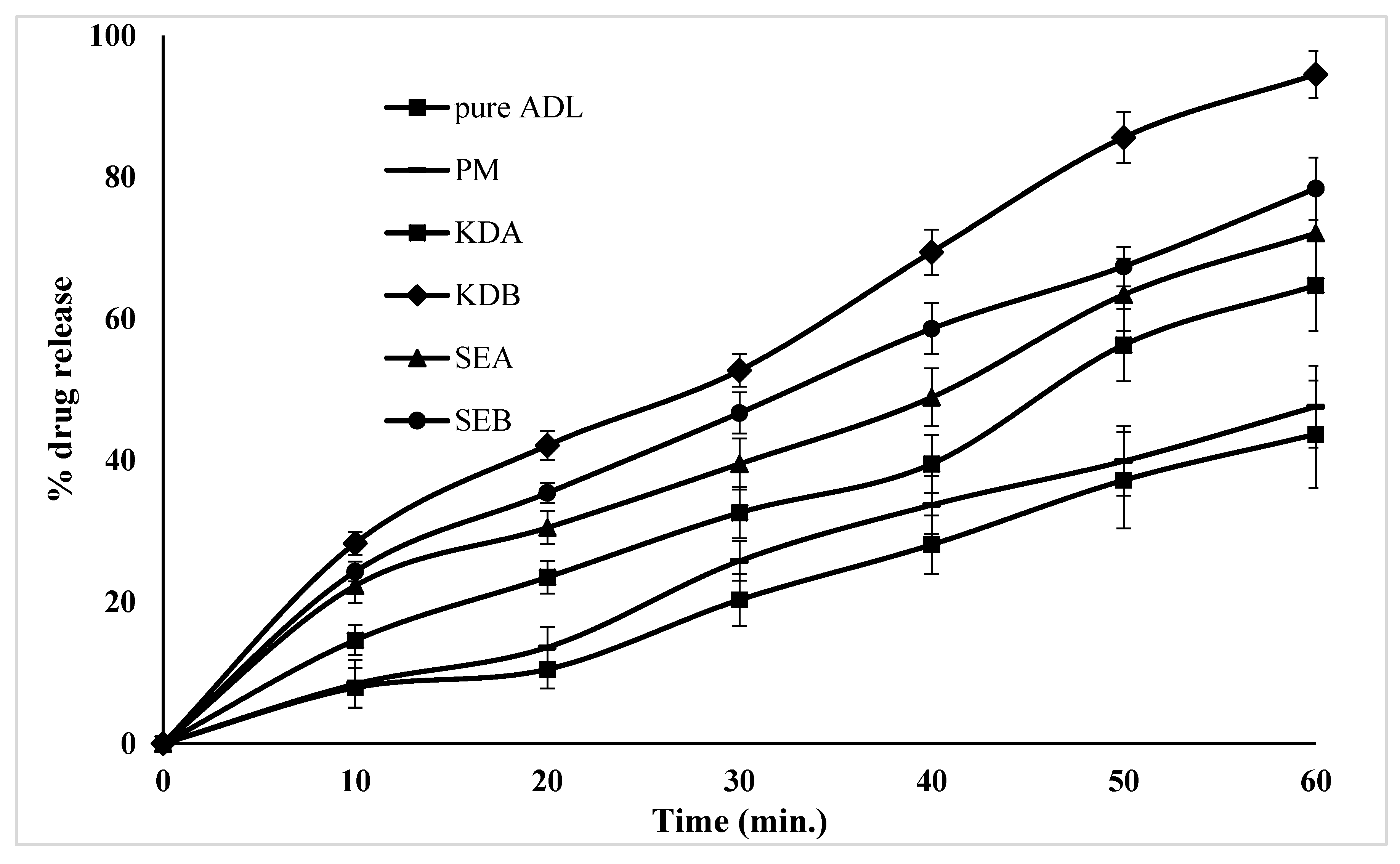
2.6. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
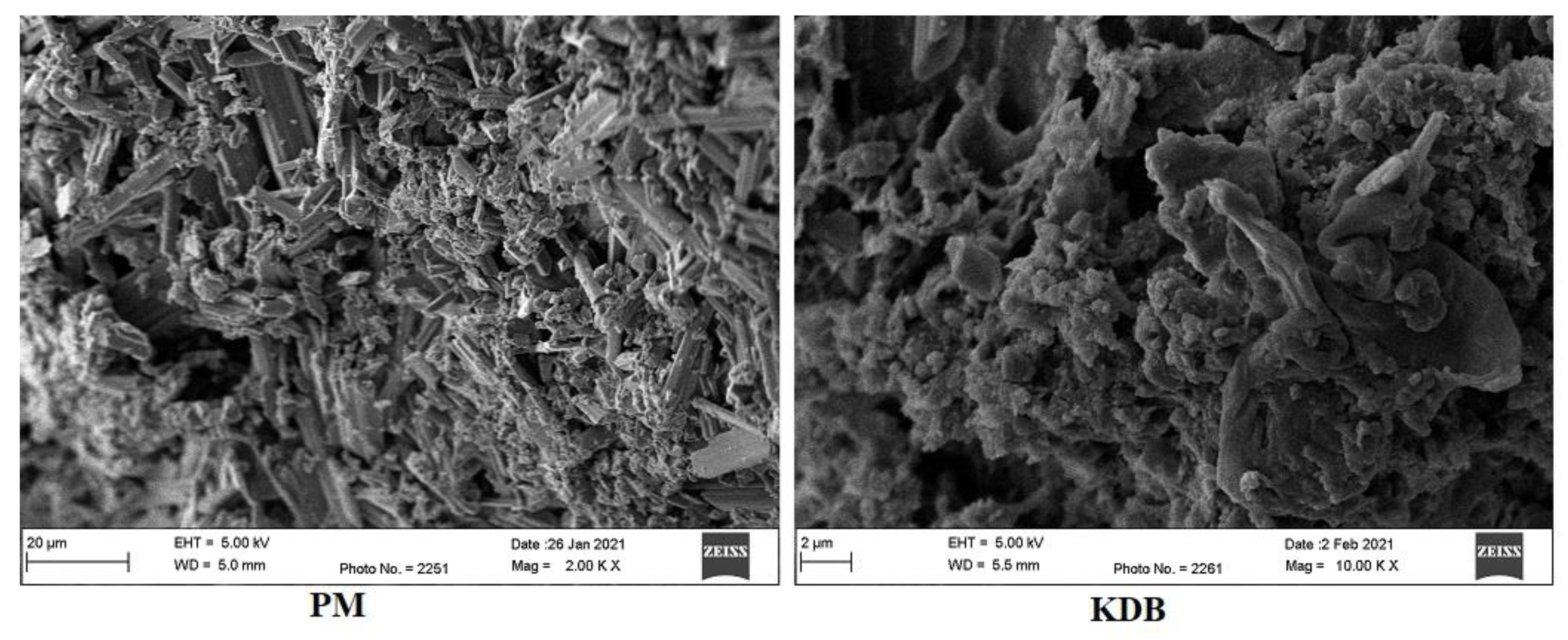
2.7. Morphology
2.8. D and 2D 1HNMR Studies
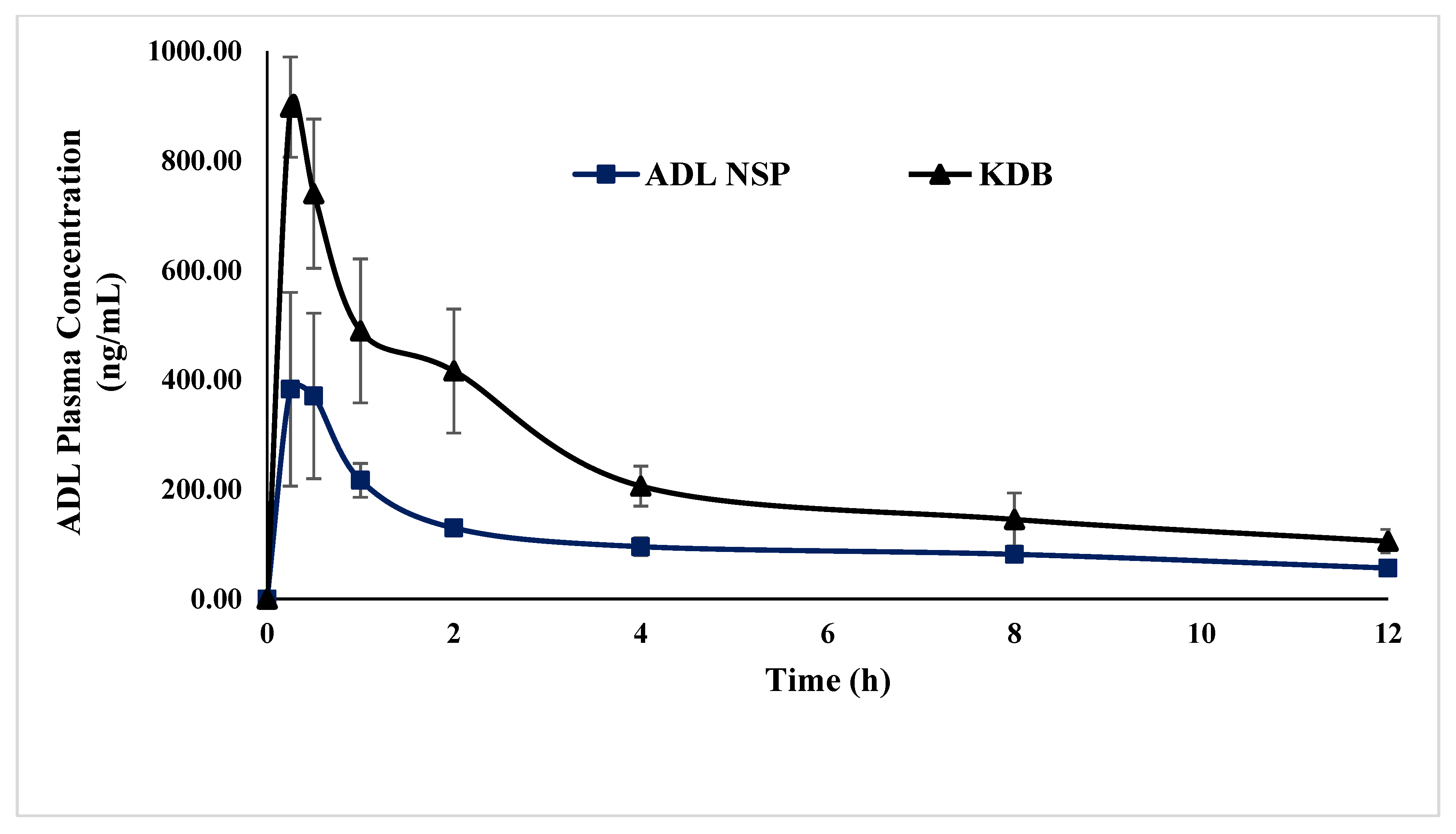
2.9. Pharmacokinetic Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Phase Solubility Studies for ADL in Binary and Ternary Systems
3.3. Preparation of the Complexes
3.3.1. Preparation of the Physical Mixture (PM)
3.3.2. Preparation of the Complexes by the Kneading (KD) Method
3.3.3. Preparation of the Complexes by the Solvent Evaporation (SE) Method
3.4. Characterization of the Complexes
3.4.1. Aqueous Solubility Determination of the Solid Complexes
3.4.2. DSC Studies
3.4.3. FTIR Studies
3.4.4. PXRD Studies
3.5. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
3.6. Morphology
3.7. 1D and 2D 1HNMR Studies
3.8. Bioanalytical Method Conditions
3.9. Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, M.J.; Burtseva, E.I.; Ellery, P.J.; Marsh, G.A.; Lew, A.M.; Slepushkin, A.N.; Crowe, S.M.; Tannock, G.A. Antiviral activity of arbidol, a broad-spectrum drug for use against respiratory viruses, varies according to test conditions. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriskin, Y.S.; Leneva, I.A.; Pécheur, E.I.; Polyak, S.J. Arbidol: A broad-spectrum antiviral compound that blocks viral fusion. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.J.; Sasadeusz, J.J.; Tannock, G.A. Antiviral chemotherapeutic agents against respiratory viruses: Where are we now and what’s in the pipeline? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2004, 10, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, K.; Chen, R.; Guo, Q.; Lu, J.; Wu, X.; He, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. Clinical features and efficacy of antiviral drug, Arbidol in 220 nonemergency COVID-19 patients from East-West-Lake Shelter Hospital in Wuhan: A retrospective case series. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojomi, M.; Yassin, Z.; Keyvani, H.; Makiani, M.J.; Roham, M.; Laali, A.; Dehghan, N.; Navaei, M.; Ranjbar, M. Effect of Arbidol (Umifenovir) on COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leneva, I.A.; Fediakina, I.T.; Gus’kova, T.A.; Glushkov, R.G. Sensitivity of various influenza virus strains to arbidol. Influence of arbidol combination with different antiviral drugs on reproduction of influenza virus A. Ter. Arkh. 2005, 77, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Liu, S.; Cheng, K. Potential treatment methods targeting 2019-nCoV infection. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 205, 112687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Full Prescribing Information: Arbidol (umifenovir) film-coated tablets 50 and 100 mg: Corrections and Additions. State Register of Medicines. Open joint-stock company “Pharmstandard-Tomskchempharm Prospekt Lenina, Tomsk, Tomsk Region, 634009”. (In Russian)
- Liu, X.; Huang, Y.W.; Li, J.; Li, X.B.; Bi, K.S.; Chen, X.H. Determination of arbidol in human plasma by LC-ESI-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eropkin, M.Y.; Solovskii, M.V.; Smirnova, M.Y.; Bryazzhikova, T.S.; Gudkova, T.M.; Konovalova, N.I. Synthesis and biological activity of water-soluble polymer complexes of arbidol. Pharm. Chem. J. 2009, 43, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, S.M.; Sunada, H.; Wang, Q.F. Improvement of dissolution rate of arbidol hydrochloride from solid dispersion prepared with PEG system by fusion method. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Chi, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T. The delivery of arbidol by salt engineering: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and pharmacokinetics. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm 2017, 43, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surov, A.O.; Manin, A.N.; Churakov, A.V.; Perlovich, G.L. New Solid Forms of the Antiviral Drug Arbidol: Crystal Structures, Thermodynamic Stability, and Solubility. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4154–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, N.; Ghosh, B.; Roy, D.; Bhaumik, B.; Roy, M.N. Exploring the Inclusion Complex of a Drug (Umbelliferone) with α-Cyclodextrin Optimized by Molecular Docking and Increasing Bioavailability with Minimizing the Doses in Human Body. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30243–30251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Worku, Z.A.; Van den Mooter, G. Oral formulation strategies to improve solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 1361–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldum, H.S.; Larsen, K.L.; Madsen, F. Cyclodextrin controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs from hydrogels. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, R.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, J.; Khar, R.K. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: An updated review. Aaps Pharmscitech. 2005, 6, E329–E357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodratti, A.M.; Alexandridis, P. Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Villa, C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.; Magalhães, M.; Veiga, F.; Figueiras, A. Poloxamers, poloxamines and polymeric micelles: Definition, structure and therapeutic applications in cancer. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K.A. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–212. [Google Scholar]
- Anwer, M.K.; Jamil, S.; Ansari, M.J.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Ali, B.E.; Ganaie, M.A.; Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Shakeel, F. Water soluble binary and ternary complexes of diosmin with β-cyclodextrin: Spectroscopic characterization, release studies and anti-oxidant activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 199, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghareeb, M.M.; Abdulrasool, A.A.; Hussein, A.A.; Noordin, M.I. Kneading technique for preparation of binary solid dispersion of meloxicam with poloxamer 188. Aaps Pharmscitech. 2009, 10, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Sandström, C.; Zhang, H.; Tan, T. NMR Study on the Inclusion Complexes of β-Cyclodextrin with Isoflavones. Molecules 2016, 21, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowrirajan, C.; Yousuf, S.; Israel, V.E. Binding of Coumarin 334 with β-Cyclodextrin and with C-Hexylpyrogallol[4]arene: Opposite Fluorescence Behavior. J. Spectrosc. 2013, 2013, 408506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessine, F.B.; Calderini, A.; Alexandrino, G.L. Review: Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes Probed by NMR Techniques; Open access book chapter; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Wang, S.; Yao, W.F.; Wu, H.Z.; Meng, S.N.; Wei, M.J. Pharmacokinetic properties and bioequivalence of two formulations of arbidol: An open-label, single-dose, randomized-sequence, two-period crossover study in healthy Chinese male volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2009, 31, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Kuang, C.; Zhang, X. Preparation and evaluation of taste masked oral suspension of arbidol hydrochloride. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, M.K.; Mohammad, M.; Khalil, N.Y.; Imam, F.; Ansari, M.J.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Shakeel, F.; Iqbal, M. Solubility, thermodynamics and molecular interaction studies of delafloxacin in environmental friendly ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, M.K.; Ahmed, M.M.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alshahrani, S.; Fatima, F.; Ansari, M.N.; Rehman, N.U.; Al-Shdefat, R.I. Eluxadoline Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Improved Colon Targeting in Rat Model of Ulcerative Colitis. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwer, M.K.; Iqbal, M.; Muharram, M.M.; Mohammad, M.; Ezzeldin, E.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alalaiwe, A.; Imam, F. Development of Lipomer Nanoparticles for the Enhancement of Drug Release, Anti-microbial Activity and Bioavailability of Delafloxacin. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwer, M.K.; Mohammad, M.; Ezzeldin, E.; Fatima, F.; Alalaiwe, A.; Iqbal, M. Preparation of sustained release apremilast-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: In vitro characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Ezzeldin, E.; Herqash, R.N.; Anwer, M.K.; Azam, F. Development and validation of a novel UPLC-MS/MS method for quantification of delafloxacin in plasma and aqueous humour for pharmacokinetic analyses. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1138, 121961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
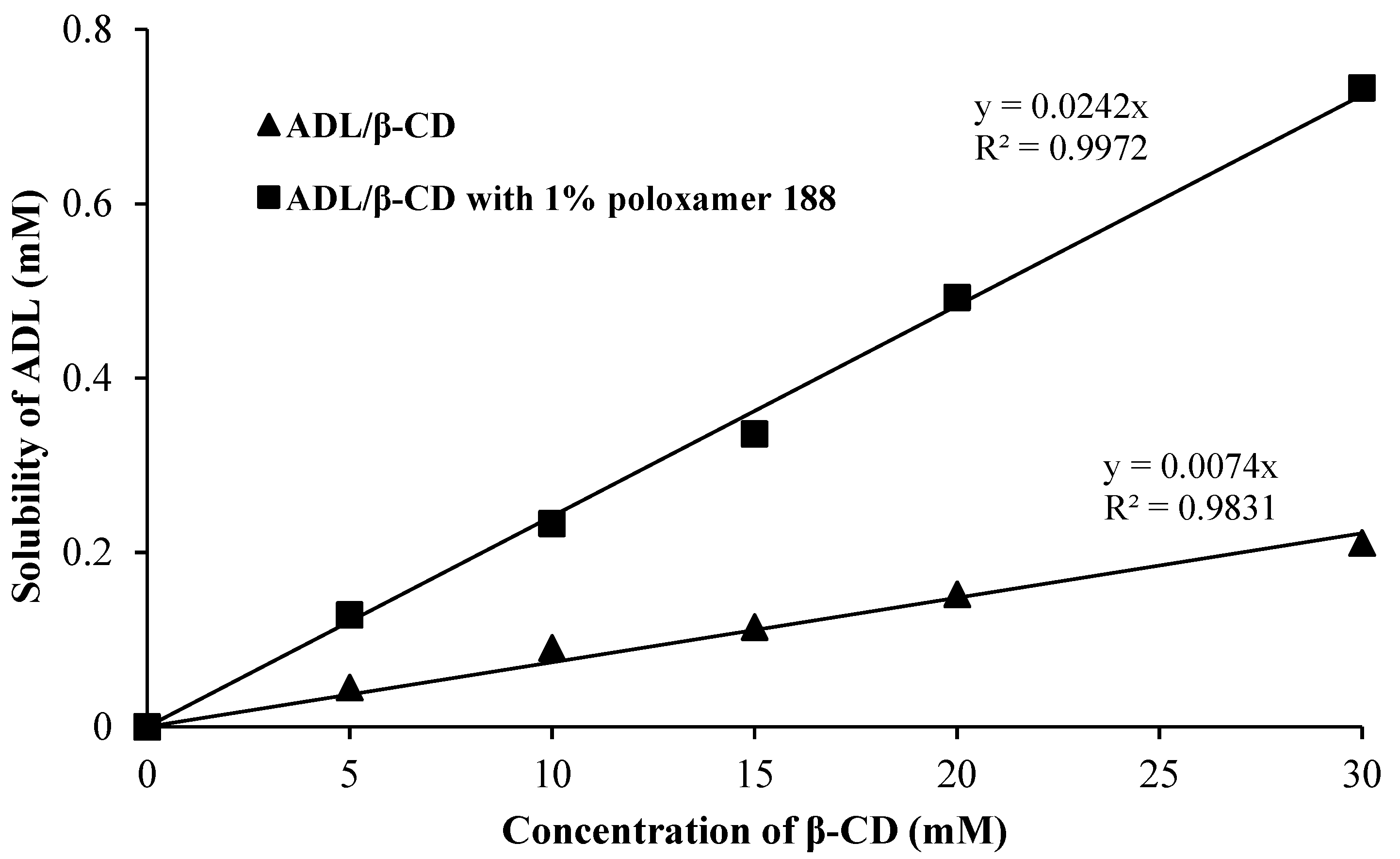



| Complexes | Stability Constant (Ks) | Complexation Efficiency (CE) |
|---|---|---|
| Arbidol/β-CD | 550 M−1 | 0.0064 |
| Arbidol/β-CD with 1% Poloxamer 188 | 2134 M−1 | 0.0250 |
| Parameters | ADL NSP (n = 6) | (KDB) (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax(ng/mL) | 387 ± 171 | 897 ± 92 * |
| Tmax(h) | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| AUC0-T(ng.h/mL) | 1317 ± 127 | 2858 ± 674 ** |
| AUC0-∞ (ng.h/mL) | 1838 ± 31 | 3745 ± 1105 ** |
| Kel(h) | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.02 |
| T1/2 (h) | 6.57 ± 1.79 | 6.04 ± 1.74 |
| MRT (h) | 9.35 ± 2.09 | 7.96 ± 1.82 |
| Relative Bioavailability (%) | 100 | 217 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwer, M.K.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Ansari, M.N.; Ezzeldin, E.; Khalil, N.Y.; Ali, R. Improving the Solubilization and Bioavailability of Arbidol Hydrochloride by the Preparation of Binary and Ternary β-Cyclodextrin Complexes with Poloxamer 188. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050411
Anwer MK, Iqbal M, Ahmed MM, Aldawsari MF, Ansari MN, Ezzeldin E, Khalil NY, Ali R. Improving the Solubilization and Bioavailability of Arbidol Hydrochloride by the Preparation of Binary and Ternary β-Cyclodextrin Complexes with Poloxamer 188. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050411
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwer, Md. Khalid, Muzaffar Iqbal, Mohammad Muqtader Ahmed, Mohammed F. Aldawsari, Mohd Nazam Ansari, Essam Ezzeldin, Nasr Y. Khalil, and Raisuddin Ali. 2021. "Improving the Solubilization and Bioavailability of Arbidol Hydrochloride by the Preparation of Binary and Ternary β-Cyclodextrin Complexes with Poloxamer 188" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050411
APA StyleAnwer, M. K., Iqbal, M., Ahmed, M. M., Aldawsari, M. F., Ansari, M. N., Ezzeldin, E., Khalil, N. Y., & Ali, R. (2021). Improving the Solubilization and Bioavailability of Arbidol Hydrochloride by the Preparation of Binary and Ternary β-Cyclodextrin Complexes with Poloxamer 188. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050411









