Intramuscular Evaluation of Chimeric Locked Nucleic Acid/2′OMethyl-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides for Targeted Exon 23 Skipping in Mdx Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
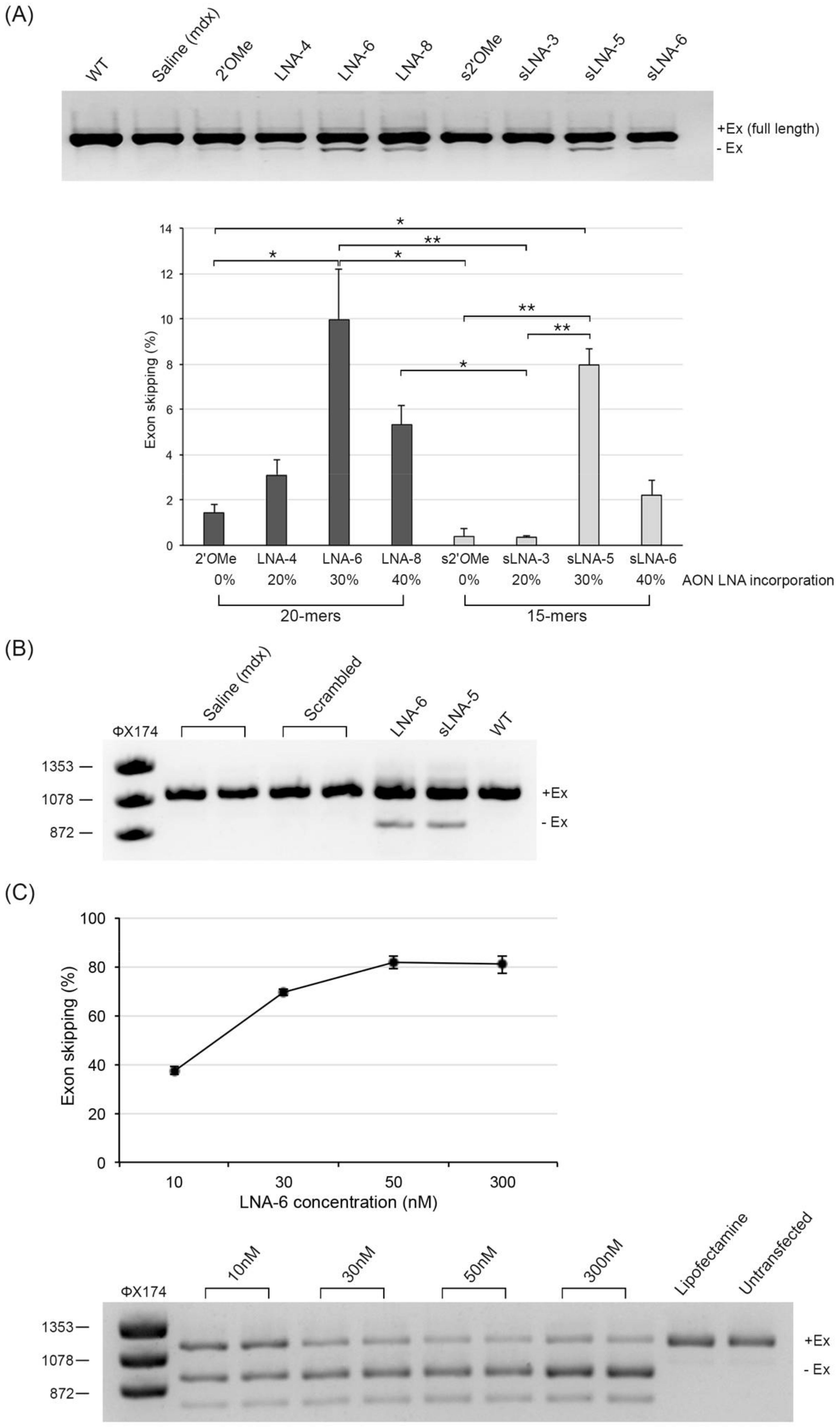
2.1. Evaluation of Exon Skipping Efficiency of Chimeric LNA/2′OMe AONs after Intramuscular Delivery in Mdx Mice
2.2. Evaluation of Dystrophin Restoration after Intramuscular Delivery of Chimeric LNA/2′OMe AONs in Mdx Mice
2.2.1. Immunofluorescence: Number of Dystrophin Positive Fibres in Muscle Section
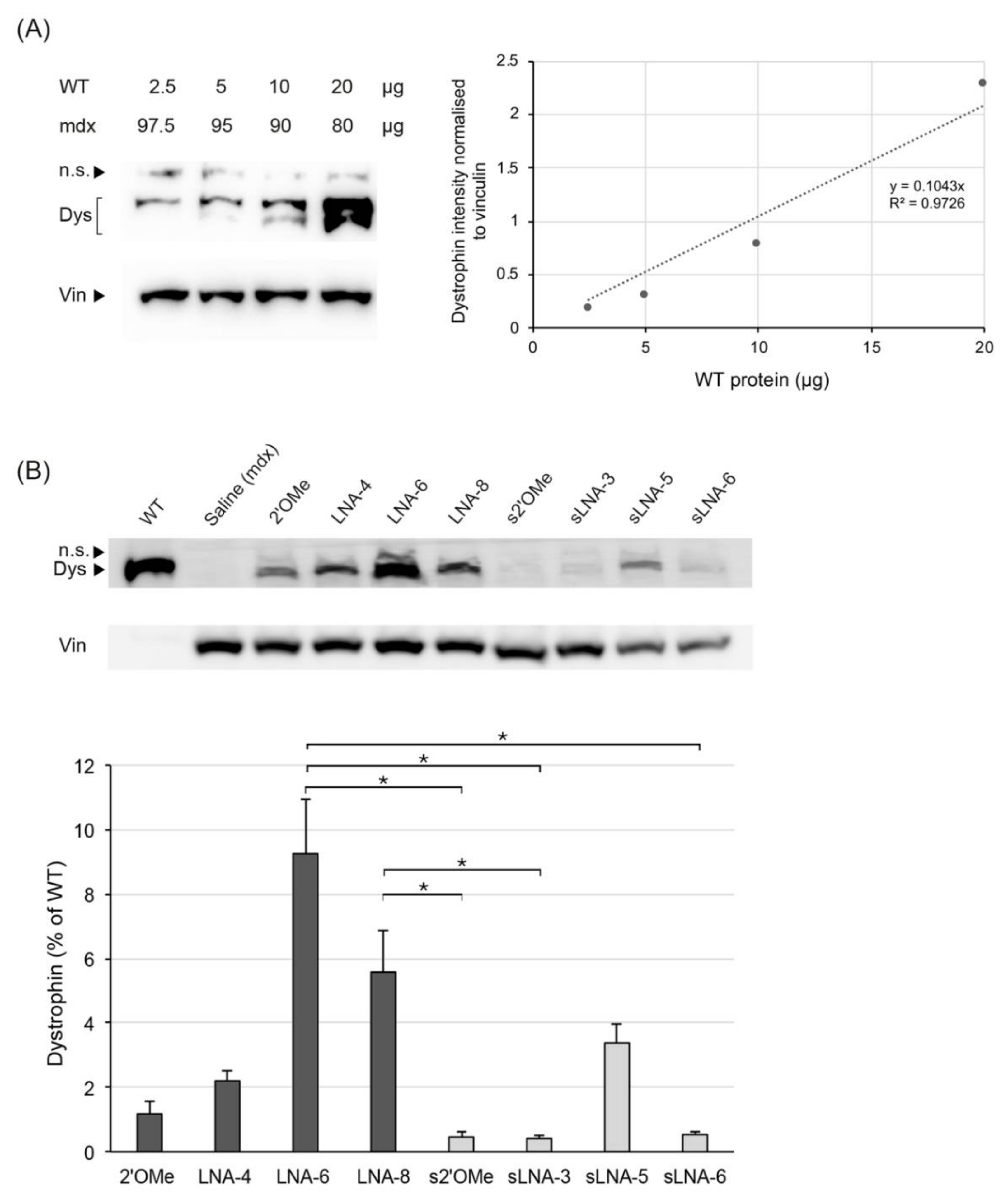
2.2.2. Mass Spectrometry Quantification of Dystrophin
2.2.3. Western Blot Quantification of Dystrophin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antisense Oligonucleotides
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.3. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
4.4. Isolation of Primary Mdx Myoblasts and Transfection
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muntoni, F.; Torelli, S.; Ferlini, A. Dystrophin and mutations: One gene, several proteins, multiple phenotypes. Lancet. Neurol. 2003, 2, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, M.; Hoffman, E.P.; Bertelson, C.J.; Monaco, A.P.; Feener, C.; Kunkel, L.M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell 1987, 50, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helderman-van den Enden, A.T.J.M.; Straathof, C.S.; Aartsma-Rus, A.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Verbist, B.M.; Bakker, E.; Verschuuren, J.J.; Ginjaar, H.B. Becker muscular dystrophy patients with deletions around exon 51; a promising outlook for exon skipping therapy in Duchenne patients. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2010, 20, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, C.J.; Honeyman, K.; Cheng, A.J.; Ly, T.; Lloyd, F.; Fletcher, S.; Morgan, J.E.; Partridge, T.A.; Wilton, S.D. Antisense-induced exon skipping and synthesis of dystrophin in the mdx mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Janson, A.A.; Kaman, W.E.; Bremmer-Bout, M.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Baas, F.; van Ommen, G.J.; van Deutekom, J.C. Therapeutic antisense-induced exon skipping in cultured muscle cells from six different DMD patients. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Bremmer-Bout, M.; Janson, A.A.; den Dunnen, J.T.; van Ommen, G.J.; van Deutekom, J.C. Targeted exon skipping as a potential gene correction therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2002, 12 (Suppl. 1), S71–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; van Ommen, G.J. Antisense-mediated exon skipping: A versatile tool with therapeutic and research applications. Rna 2007, 13, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokota, T.; Duddy, W.; Partridge, T. Optimizing exon skipping therapies for DMD. Acta Myol. 2007, 26, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Amantana, A.; Iversen, P.L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of phosphorodiamidate morpholino antisense oligomers. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, J.; Lou, F.; Rabinowitz, A.; Yin, H.; Rosenfeld, J.; Wilton, S.D.; Partridge, T.A.; Lu, Q.L. Systemic delivery of morpholino oligonucleotide restores dystrophin expression bodywide and improves dystrophic pathology. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, S.; Honeyman, K.; Fall, A.M.; Harding, P.L.; Johnsen, R.D.; Steinhaus, J.P.; Moulton, H.M.; Iversen, P.L.; Wilton, S.D. Morpholino oligomer-mediated exon skipping averts the onset of dystrophic pathology in the mdx mouse. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2007, 15, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendell, J.R.; Goemans, N.; Lowes, L.P.; Alfano, L.N.; Berry, K.; Shao, J.; Kaye, E.M.; Mercuri, E.; Eteplirsen Study, G.; Telethon Foundation, D.M.D.I.N. Longitudinal effect of eteplirsen versus historical control on ambulation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charleston, J.S.; Schnell, F.J.; Dworzak, J.; Donoghue, C.; Lewis, S.; Chen, L.; Young, G.D.; Milici, A.J.; Voss, J.; DeAlwis, U.; et al. Eteplirsen treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: Exon skipping and dystrophin production. Neurology 2018, 90, e2146–e2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.A. Eteplirsen Approved for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: The FDA Faces a Difficult Choice. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2016, 24, 1884–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Krieg, A.M. FDA Approves Eteplirsen for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: The Next Chapter in the Eteplirsen Saga. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Arechavala-Gomeza, V. Why dystrophin quantification is key in the eteplirsen saga. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Eliopoulos, H.; Han, L.; Kinane, T.B.; Lowes, L.P.; Mendell, J.R.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Henricson, E.K.; McDonald, C.M.; Eteplirsen, I.; et al. Eteplirsen Treatment Attenuates Respiratory Decline in Ambulatory and Non-Ambulatory Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 6, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfano, L.N.; Charleston, J.S.; Connolly, A.M.; Cripe, L.; Donoghue, C.; Dracker, R.; Dworzak, J.; Eliopoulos, H.; Frank, D.E.; Lewis, S.; et al. Long-term treatment with eteplirsen in nonambulatory patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Medicine 2019, 98, e15858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, M. Casimersen: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.R.; Kuntz, N.L.; Koenig, E.; East, L.; Upadhyay, S.; Han, B.; Shieh, P.B. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of casimersen in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy amenable to exon 45 skipping: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-titration trial. Muscle Nerve 2021, 64, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntoni, F.; Frank, D.; Sardone, V.; Morgan, J.; Schnell, F.; Charleston, J.; Desjardins, C.; Phadke, R.; Sewry, C.; Popplewell, L.; et al. Golodirsen Induces Exon Skipping Leading to Sarcolemmal Dystrophin Expression in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patients With Mutations Amenable to Exon 53 Skipping (S22.001). Neurology 2018, 90, S22.001. [Google Scholar]
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02310906, Phase I/II study of SRP- 4053 in DMD Patients. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02310906 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02500381, Study of SRP-4045 and SRP- 4053 in DMD Patients (ESSENCE). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02500381 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Komaki, H.; Nagata, T.; Saito, T.; Masuda, S.; Takeshita, E.; Sasaki, M.; Tachimori, H.; Nakamura, H.; Aoki, Y.; Takeda, S. Systemic administration of the antisense oligonucleotide NS-065/NCNP-01 for skipping of exon 53 in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhillon, S. Viltolarsen: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goemans, N.M.; Tulinius, M.; van den Akker, J.T.; Burm, B.E.; Ekhart, P.F.; Heuvelmans, N.; Holling, T.; Janson, A.A.; Platenburg, G.J.; Sipkens, J.A.; et al. Systemic administration of PRO051 in Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goemans, N.; Mercuri, E.; Belousova, E.; Komaki, H.; Dubrovsky, A.; McDonald, C.M.; Kraus, J.E.; Lourbakos, A.; Lin, Z.; Campion, G.; et al. A randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trial of an antisense oligonucleotide, drisapersen, in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2018, 28, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voit, T.; Topaloglu, H.; Straub, V.; Muntoni, F.; Deconinck, N.; Campion, G.; De Kimpe, S.J.; Eagle, M.; Guglieri, M.; Hood, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of drisapersen for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DEMAND II): An exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. Neurol. 2014, 13, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.M.; Wong, B.; Flanigan, K.M.; Wilson, R.; de Kimpe, S.; Lourbakos, A.; Lin, Z.; Campion, G.; the Demand V study group. Placebo-controlled Phase 2 Trial of Drisapersen for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, S. Antisense oligonucleotides: Towards clinical trials. Trends Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; Kang, S.H.; Gryaznov, S.M.; DeDionisio, L.; Heidenreich, O.; Sullivan, S.; Xu, X.; Nerenberg, M.I. Effect of phosphorothioate modification of oligodeoxynucleotides on specific protein binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 26801–26805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, D.A.; Valdez, B.C.; Henning, D.; Greenberg, S.; Busch, H. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides bind in a non sequence-specific manner to the nucleolar protein C23/nucleolin. FEBS Lett. 1995, 366, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.; Liang, X.H.; Crooke, S.T. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides can displace NEAT1 RNA and form nuclear paraspeckle-like structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8648–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.H.; Sun, H.; Shen, W.; Crooke, S.T. Identification and characterization of intracellular proteins that bind oligonucleotides with phosphorothioate linkages. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 2927–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.H.; Shen, W.; Sun, H.; Kinberger, G.A.; Prakash, T.P.; Nichols, J.G.; Crooke, S.T. Hsp90 protein interacts with phosphorothioate oligonucleotides containing hydrophobic 2′-modifications and enhances antisense activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3892–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.; De Hoyos, C.L.; Migawa, M.T.; Vickers, T.A.; Sun, H.; Low, A.; Bell, T.A., 3rd; Rahdar, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hart, C.E.; et al. Chemical modification of PS-ASO therapeutics reduces cellular protein-binding and improves the therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyenvalle, A.; Griffith, G.; Babbs, A.; El Andaloussi, S.; Ezzat, K.; Avril, A.; Dugovic, B.; Chaussenot, R.; Ferry, A.; Voit, T.; et al. Functional correction in mouse models of muscular dystrophy using exon-skipping tricyclo-DNA oligomers. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relizani, K.; Griffith, G.; Echevarria, L.; Zarrouki, F.; Facchinetti, P.; Vaillend, C.; Leumann, C.; Garcia, L.; Goyenvalle, A. Efficacy and Safety Profile of Tricyclo-DNA Antisense Oligonucleotides in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mouse Model. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshkin, A.A.; Singh, S.K.; Nielsen, P.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Meldgaard, M.; Olsen, C.E.; Wengel, J. LNA (Locked Nucleic Acids): Synthesis of the adenine, cytosine, guanine, 5-methylcytosine, thymine and uracil bicyclonucleoside monomers, oligomerisation, and unprecedented nucleic acid recognition. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 3607–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleavey, G.F.; Damha, M.J. Designing chemically modified oligonucleotides for targeted gene silencing. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aartsma-Rus, A.; Kaman, W.E.; Bremmer-Bout, M.; Janson, A.A.; den Dunnen, J.T.; van Ommen, G.J.; van Deutekom, J.C. Comparative analysis of antisense oligonucleotide analogs for targeted DMD exon 46 skipping in muscle cells. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimo, T.; Tachibana, K.; Saito, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tomita, E.; Waki, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Doi, T.; Inoue, T.; Kawakami, J.; et al. Design and evaluation of locked nucleic acid-based splice-switching oligonucleotides in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8174–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pires, V.B.; Simoes, R.; Mamchaoui, K.; Carvalho, C.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Short (16-mer) locked nucleic acid splice-switching oligonucleotides restore dystrophin production in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy myotubes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, B.T.; Adams, A.M.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D.; Veedu, R.N. Rational Design of Short Locked Nucleic Acid-Modified 2′-O-Methyl Antisense Oligonucleotides for Efficient Exon-Skipping In Vitro. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christou, M.; Wengel, J.; Sokratous, K.; Kyriacou, K.; Nikolaou, G.; Phylactou, L.A.; Mastroyiannopoulos, N.P. Systemic Evaluation of Chimeric LNA/2′-O-Methyl Steric Blockers for Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Therapy. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemskerk, H.A.; de Winter, C.L.; de Kimpe, S.J.; van Kuik-Romeijn, P.; Heuvelmans, N.; Platenburg, G.J.; van Ommen, G.J.; van Deutekom, J.C.; Aartsma-Rus, A. In vivo comparison of 2′-O-methyl phosphorothioate and morpholino antisense oligonucleotides for Duchenne muscular dystrophy exon skipping. J. Gene Med. 2009, 11, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.J.; Honeyman, K.; McClorey, G.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D. Improved antisense oligonucleotide induced exon skipping in the mdx mouse model of muscular dystrophy. J. Gene Med. 2002, 4, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitali, P.; Heemskerk, H.; Vossen, R.H.; Ferlini, A.; den Dunnen, J.T.; t Hoen, P.A.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Accurate quantification of dystrophin mRNA and exon skipping levels in duchenne muscular dystrophy. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2010, 90, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, F.J.; Fletcher, S.; Johnsen, R.S.; Wilton, S.D. Challenges of Interpreting Dystrophin Content by Western Blot. US Neurol. 2019, 15, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, D.; Yasuda, S.; Li, S.; Chamberlain, J.S.; Metzger, J.M. Emergent dilated cardiomyopathy caused by targeted repair of dystrophic skeletal muscle. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2008, 16, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malerba, A.; Boldrin, L.; Dickson, G. Long-term systemic administration of unconjugated morpholino oligomers for therapeutic expression of dystrophin by exon skipping in skeletal muscle: Implications for cardiac muscle integrity. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011, 21, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jearawiriyapaisarn, N.; Moulton, H.M.; Sazani, P.; Kole, R.; Willis, M.S. Long-term improvement in mdx cardiomyopathy after therapy with peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 85, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betts, C.; Saleh, A.F.; Arzumanov, A.A.; Hammond, S.M.; Godfrey, C.; Coursindel, T.; Gait, M.J.; Wood, M.J. Pip6-PMO, A New Generation of Peptide-oligonucleotide Conjugates With Improved Cardiac Exon Skipping Activity for DMD Treatment. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gait, M.J.; Arzumanov, A.A.; McClorey, G.; Godfrey, C.; Betts, C.; Hammond, S.; Wood, M.J.A. Cell-Penetrating Peptide Conjugates of Steric Blocking Oligonucleotides as Therapeutics for Neuromuscular Diseases from a Historical Perspective to Current Prospects of Treatment. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2019, 29, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenblatt, J.D.; Lunt, A.I.; Parry, D.J.; Partridge, T.A. Culturing satellite cells from living single muscle fiber explants. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 1995, 31, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alelyunas, Y.W.; Wrona, M.D.; Mortishire-Smith, R.J.; Tomczyk, N.; Rainville, P.D. Quantitation by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Using Target Enhancement and Tof-MRM to Achieve Femtogram-level On-column Sensitivity for Quantitation of Drugs in Human Plasma. Available online: https://www.waters.com/webassets/cms/library/docs/720005182en.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- MacLean, B.; Tomazela, D.M.; Shulman, N.; Chambers, M.; Finney, G.L.; Frewen, B.; Kern, R.; Tabb, D.L.; Liebler, D.C.; MacCoss, M.J. Skyline: An open source document editor for creating and analyzing targeted proteomics experiments. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| AON ID | Sequence (5′ → 3′) and Modifications | Length | % LNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2′OMe | mG* mG* mC* mC* mA* mA* mA* mC* mC* mU* mC* mG* mG* mC* mU* mU* mA* mC* mC* mU | 20mer | 0 |
| LNA-4 | mG* G* mC* mC* mA* mA* A* mC* mC* mU* mC* G* mG* mC* mU* mU* A* mC* mC* mU | 20mer | 20 |
| LNA-6 | mG* G* mC* mC* A* mA* mA* C* mC* mU* mC* G* mG* mC* mU* T* mA* mC* C* mU | 20mer | 30 |
| LNA-8 | mG* G* mC* mC* A* mA* A* mC* C* mU* mC* G* mG* C* mU* T* mA* mC* C* mU | 20mer | 40 |
| s2′OMe | mA* mA* mC* mC* mU* mC* mG* mG* mC* mU* mU* mA* mC* mC* mU | 15mer | 0 |
| sLNA-3 | mA* mA* mC* C* mU* mC* mG* G* mC* mU* mU* A* mC* mC* mU | 15mer | 20 |
| sLNA-5 | mA* A* mC* mC* T* mC* mG* G* mC* mU* T* mA* mC* C* mU | 15mer | 33 |
| sLNA-6 | A* mA* mC* C* mU* C* mG* mG* C* mU* T* mA* mC* C* mU | 15mer | 40 |
| CAG-scrambled | C* mA* mG* C* mA* mG* C* mA* mG* C* mA* mG* C* mA* mG* C* mA* mG | 18mer | 33 |
| bold = LNA, m = 2′OMe, * = PS linkages | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgiadou, M.; Christou, M.; Sokratous, K.; Wengel, J.; Michailidou, K.; Kyriacou, K.; Koutsoulidou, A.; Mastroyiannopoulos, N.P.; Phylactou, L.A. Intramuscular Evaluation of Chimeric Locked Nucleic Acid/2′OMethyl-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides for Targeted Exon 23 Skipping in Mdx Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111113
Georgiadou M, Christou M, Sokratous K, Wengel J, Michailidou K, Kyriacou K, Koutsoulidou A, Mastroyiannopoulos NP, Phylactou LA. Intramuscular Evaluation of Chimeric Locked Nucleic Acid/2′OMethyl-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides for Targeted Exon 23 Skipping in Mdx Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(11):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111113
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgiadou, Michaella, Melina Christou, Kleitos Sokratous, Jesper Wengel, Kyriaki Michailidou, Kyriacos Kyriacou, Andrie Koutsoulidou, Nikolaos P. Mastroyiannopoulos, and Leonidas A. Phylactou. 2021. "Intramuscular Evaluation of Chimeric Locked Nucleic Acid/2′OMethyl-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides for Targeted Exon 23 Skipping in Mdx Mice" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 11: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111113
APA StyleGeorgiadou, M., Christou, M., Sokratous, K., Wengel, J., Michailidou, K., Kyriacou, K., Koutsoulidou, A., Mastroyiannopoulos, N. P., & Phylactou, L. A. (2021). Intramuscular Evaluation of Chimeric Locked Nucleic Acid/2′OMethyl-Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides for Targeted Exon 23 Skipping in Mdx Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 14(11), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111113







