Atorvastatin Increases the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs ARSR and CHROME in Hypercholesterolemic Patients: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics
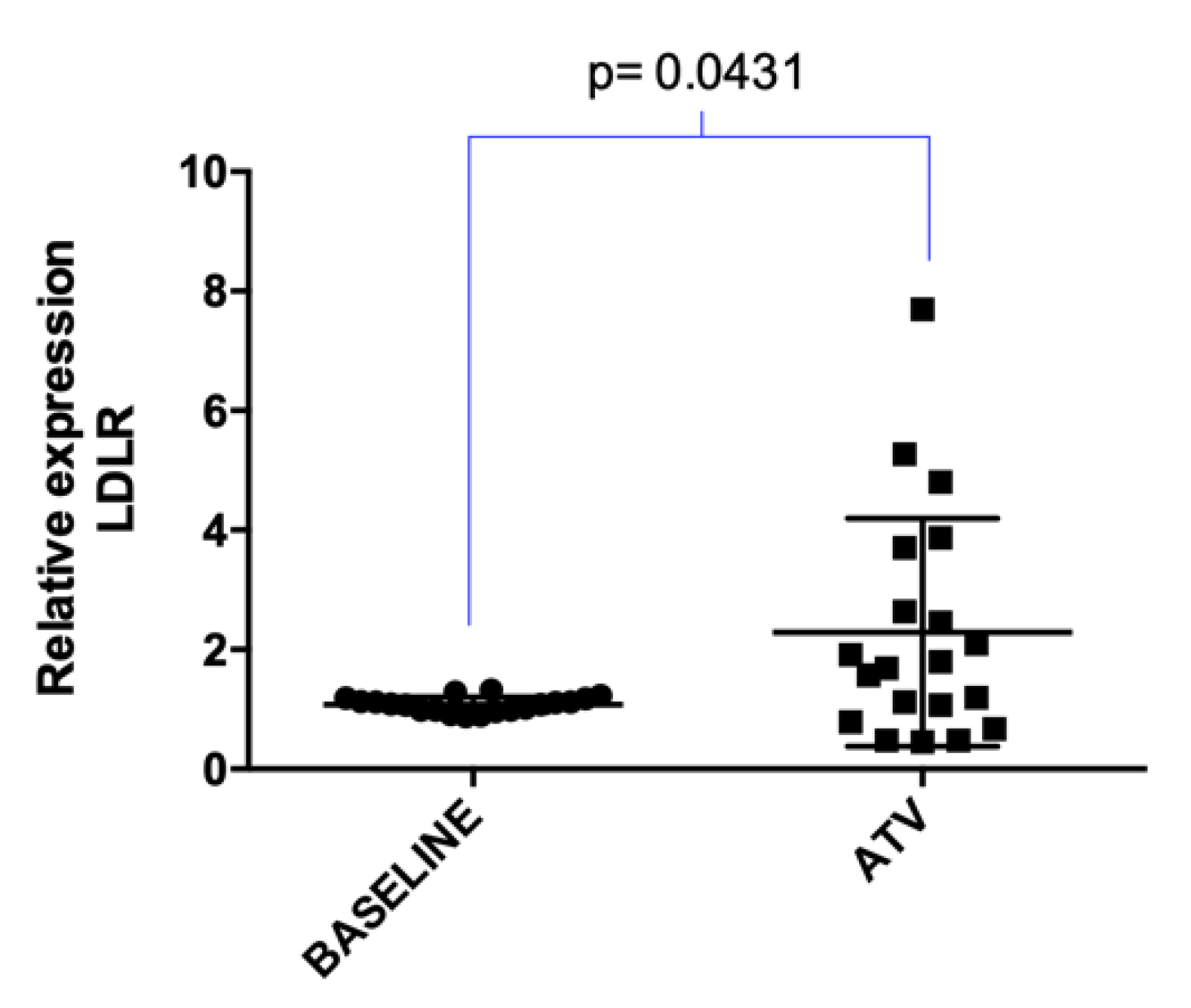
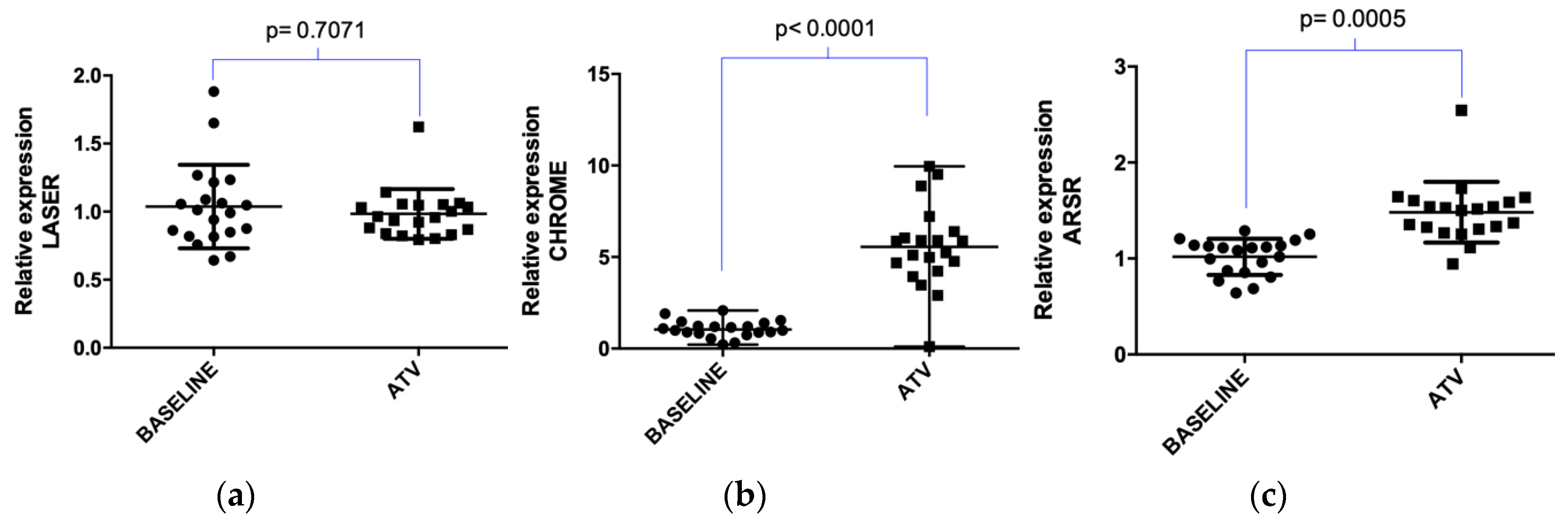
2.2. Atorvastatin Effect on LDLR Gene and lncRNAs Expression in Hypercholesterolemic Patients Following Statin Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Individual’s Selection and Treatment Protocol
4.2. Biochemical Analysis
4.3. Molecular Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, U.; Kishore, J.; Garg, A.; Anand, T.; Chakraborty, M.; Lali, P. Dyslipidemia and associated risk factors in a resettlement colony of Delhi. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2013, 7, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozman, D.; Monostory, K. Perspectives of the non-statin hypolipidemic agents. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 127, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, W.P.; Anderson, K.; Wilson, P.W.; Levy, D. Lipids and risk of coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Ann. Epidemiol. 1992, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.J.; Elosua, R. Cardiovascular risk factors. Insights from Framingham Heart Study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2008, 61, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.D.; Allen, I.E.; Connelly, J.E.; Korenblat, B.M.; Smith, M.E.; Bishop, D.; Luo, D. Clinical outcomes in statin treatment trials: A meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRosa, J.C.; He, J.; Vupputuri, S. Effect of statins on risk of coronary disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA 1999, 282, 2340–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, M. Chemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of statins: An update. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 19, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansette, P.M.; Jaoen, M.; Pons, C. HMG-CoA reductase activity in human liver microsomes: Comparative inhibition by statins. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2000, 52, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.A.; Lin, F.; Hulley, S.B.; Blanche, P.J.; Waters, D.; Shiboski, S.; Rotter, J.I.; Nickerson, D.A.; Yang, H.; Saad, M.; et al. Phenotypic predictors of response to simvastatin therapy among African-Americans and Caucasians: The Cholesterol and Pharmacogenetics (CAP) Study. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajinami, K.; Takekoshi, N.; Brousseau, M.E.; Schaefer, E.J. Pharmacogenetics of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: Exploring the potential for genotype-based individualization of coronary heart disease management. Atherosclerosis 2004, 177, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, A.; Alvear, M.; Cuevas, A.; Saavedra, N.; Zambrano, T.; Salazar, L.A. Identification of pharmacogenetic predictors of lipid-lowering response to atorvastatin in Chilean subjects with hypercholesterolemia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos, J.; Zambrano, T.; Rosales, A.; Salazar, L.A. Influence of SREBP-2 and SCAP gene polymorphisms on lipid-lowering response to atorvastatin in a cohort of Chilean subjects with Amerindian background. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajinami, K.; Akao, H.; Polisecki, E.; Schaefer, E.J. Pharmacogenomics of statin responsiveness. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 65K–70K, discussion 34K–35K. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, G.; Langmann, T. Pharmacogenomics of cholesterol-lowering therapy. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2006, 44, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, Z. Resistance and intolerance to statins. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, T.; Saavedra, K.; Salazar, L.A. Chapter 31 - Pharmacoepigenetics of Statins. In Translational Epigenetics, Pharmacoepigenetics; Cacabelos, R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; Volume 10, pp. 817–825. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chiu, D.K.; Wang, T.; Deng, Y. Advances in long noncoding RNAs: Identification, structure prediction and function annotation. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2016, 15, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, L.Y.; Cheng, X.S. Novel Approaches for the Treatment of Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Current Status and Future Challenges. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, E.J.; van Solingen, C.; Scacalossi, K.R.; Ouimet, M.; Afonso, M.S.; Prins, J.; Koelwyn, G.J.; Sharma, M.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Carpenter, S.; et al. The long noncoding RNA CHROME regulates cholesterol homeostasis in primates. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, S.; Cai, D.; Bian, D.; Wang, F. Long noncoding RNA lncARSR promotes hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis via modulating Akt/SREBP-2/HMGCR pathway. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Solingen, C.; Scacalossi, K.R.; Moore, K.J. Long noncoding RNAs in lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2018, 29, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli, A.; Martelli, F.; Farsetti, A.; Gaetano, C. The Dark That Matters: Long Non-coding RNAs as Master Regulators of Cellular Metabolism in Non-communicable Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, N. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance by increasing nuclear SREBP-1c protein stability. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S.; Shin, D.J.; Tran, M.; Wang, L. Long noncoding RNA H19 interacts with polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 to reprogram hepatic lipid homeostasis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1768–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Silencing of H19 inhibits the adipogenesis and inflammation response in ox-LDL-treated Raw264.7 cells by up-regulating miR-130b. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 93, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cheng, M.; Niu, Y.; Chi, X.; Liu, X.; Fan, J.; Fan, H.; Chang, Y.; Yang, W. Identification of a novel human long non-coding RNA that regulates hepatic lipid metabolism by inhibiting SREBP-1c. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, P.; Kadakkuzha, B.M.; Faghihi, M.A.; Magistri, M.; Zeier, Z.; Khorkova, O.; Coito, C.; Hsiao, J.; Lawrence, M.; Wahlestedt, C. Regulation of the apolipoprotein gene cluster by a long noncoding RNA. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Li, X.; Xie, L.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Jia, L.; Dong, X.; Ren, X.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C.; et al. A long non-coding RNA, APOA4-AS, regulates APOA4 expression depending on HuR in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6423–6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, X. Long non-coding RNAs expression profile in HepG2 cells reveals the potential role of long non-coding RNAs in the cholesterol metabolism. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Yan, J.; Ren, J.; Zhong, B.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yi, J.; Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. A novel long noncoding RNA Lnc-HC binds hnRNPA2B1 to regulate expressions of Cyp7a1 and Abca1 in hepatocytic cholesterol metabolism. Hepatology 2016, 64, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Song, T.; Cai, X.; Sun, B.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates abnormal lipid metabolism in hepatoma cells through an miR-9-mediated RXRA signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ruan, X.; Yang, L.; Kiesewetter, K.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, H.; Chen, Y.; Gucek, M.; Zhu, J.; Cao, H. A liver-enriched long non-coding RNA, lncLSTR, regulates systemic lipid metabolism in mice. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.W.; Zhao, J.Y.; Li, S.F.; Huang, J.L.; Qiu, Y.R.; Ma, X.; Wu, S.G.; Chen, Z.P.; Hu, Y.R.; Yang, J.Y.; et al. RP5-833A20.1/miR-382-5p/NFIA-dependent signal transduction pathway contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and inflammatory reaction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.P.; Hu, Y.R.; Zhao, J.Y.; Li, S.F.; Qiu, Y.R.; Lu, J.B.; Wang, Y.C.; et al. A lincRNA-DYNLRB2-2/GPR119/GLP-1R/ABCA1-dependent signal transduction pathway is essential for the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, T.; Jones, M.; Thomas, B.J.; Wu, X.; Gilliland, T.; Qian, K.; Eskin, A.; Casero, D.; Zhang, Z.; Sandhu, J.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis by a long noncoding RNA. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchel, K.; Theusch, E.; Cubitt, C.; Dose, A.C.; Stevens, K.; Naidoo, D.; Medina, M.W. RP1-13D10.2 Is a Novel Modulator of Statin-Induced Changes in Cholesterol. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2016, 9, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Luo, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; et al. Regulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis by a Novel Long Non-coding RNA LASER. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisegang, M.S.; Bibli, S.I.; Gunther, S.; Pfluger-Muller, B.; Oo, J.A.; Hoper, C.; Seredinski, S.; Yekelchyk, M.; Schmitz-Rixen, T.; Schurmann, C.; et al. Pleiotropic effects of laminar flow and statins depend on the Kruppel-like factor-induced lncRNA MANTIS. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2523–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilde, T.J.; van Wissen, S.; Wollersheim, H.; Trip, M.D.; Kastelein, J.J.; Stalenhoef, A.F. Effect of aggressive versus conventional lipid lowering on atherosclerosis progression in familial hypercholesterolaemia (ASAP): A prospective, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2001, 357, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.H.; Ose, L.; Frohlich, J.; Scott, R.S.; Dujovne, C.A.; Escobar, I.D.; Bertolami, M.C.; Cihon, F.; Maccubbin, D.L.; Mercuri, M. Differential effects of simvastatin and atorvastatin on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and apolipoprotein A-I are consistent across hypercholesterolemic patient subgroups. Clin. Cardiol. 2003, 26, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mazza, F.; Stefanutti, C.; Di Giacomo, S.; Vivenzio, A.; Fraone, N.; Mazzarella, B.; Bucci, A. Effects of low-dose atorvastatin and rosuvastatin on plasma lipid profiles: A long-term, randomized, open-label study in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2008, 8, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocathikorn, A.; Taylor, R.R.; Mamotte, C.D. Atorvastatin increases expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor mRNA in human circulating mononuclear cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Merz, C.N.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Clark, L.T.; Hunninghake, D.B.; Pasternak, R.C.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Stone, N.J.; Coordinating Committee of the National Cholesterol Education Program. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.wma.net/what-we-do/medical-ethics/declaration-of-helsinki/ (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Jaramillo, P.C.; Munoz, M.A.; Lanas, M.C.; Lanas, Z.F.; Salazar, L.A. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase G894T gene polymorphism in Chilean subjects with coronary artery disease and controls. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 371, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iempridee, T.; Wiwithaphon, S.; Piboonprai, K.; Pratedrat, P.; Khumkhrong, P.; Japrung, D.; Temisak, S.; Laiwejpithaya, S.; Chaopotong, P.; Dharakul, T. Identification of reference genes for circulating long noncoding RNA analysis in serum of cervical cancer patients. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Gui, Y.Z.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, X.B.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.P. MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, enhances LDL uptake in HepG2 cells in vitro by regulating LDLR and PCSK9 expression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | n = 20 |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 47.30 ± 11.35 |
| Men/Women (n) | (6/14) |
| Glycemia (mg/dL) | 95.94 ± 6.94 |
| AST/GOT (UI/L) | 23.73 ± 5.32 |
| ALT/GPT (UI/L) | 30.25 ± 7.14 |
| CK (UI/L) | 110.18 ± 25.99 |
| Uremia (mg/dL) | 30.88 ± 6.31 |
| Ureic Nitrogen (mg/dL) | 13.31 ± 3.18 |
| Blood Creatinin (mg/dL) | 1.08 ± 0.16 |
| Hemoglobin (Hb) (g/dL) | 13.83 ± 1.15 |
| Hematocrit (Hto.) (%) | 41.25 ± 3.04 |
| Leucocytes (×103/μL) | 6.68 ± 1.89 |
| Platelets (×103/μL) | 243.56 ± 44.06 |
| Total Bilirubin (TB) (mg/dL) | 0.52 ± 0.14 |
| Direct Bilirubin (DB) (mg/dL) | 0.13 ± 0.04 |
| Indirect Bilirubin (IB) (mg/dL) | 0.37 ± 0.14 |
| Lipids | Baseline (mg/dL) | Post-Treatment (mg/dL) | Change (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 239.35 ± 28.28 | 158.15 ± 33.41 *** | 34.13 ± 10.71 | <0.0001 |
| HDL-C | 44.45 ± 10.09 | 41.20 ± 9.48 | 6.42 ± 14.92 | 0.3005 |
| LDL-C | 164.62 ± 26.32 | 91.37 ± 28.28 *** | 44.61 ± 14.02 | <0.0001 |
| VLDL-C | 30.78 ± 13.04 | 24.19 ± 11.23 | 15.04 ± 36.78 | 0.0948 |
| TG | 150.40 ± 66.23 | 121.65 ± 55.40 | 10.96 ± 37.89 | 0.1447 |
| TC/HDL-C | 5.55 ± 0.95 | 3.92 ± 0.80 *** | 28.43 ± 13.33 | <0.0001 |
| Name | Forward Primer (5’-3’) | Reverse Primer (5’-3’) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| LASER | AAGGTGCCACAGATGCTCAA | GGGAGGTATCCCGGAGAAGT | [37] |
| ARSR | TTTGAAATGCTCTTTGAGGGAT | TGCAGGTTGTCTGAAGTTGGA | [20] |
| CHROME | GCAGGAGCTTGAATTTCAGT | TGTACTGAGTGGGCATTTAT | [19] |
| U6 | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACATATAC | GGAACGCTTCACGAATTTGC | [48] |
| LDLR | CTGAAATCGCCGTGTTACTG | GCCAATCCCTTGTGACATCT | [49] |
| RPL27 | TCCGGACGCAAAGCTGTCATC | GGTCAATTCCAGCCACCAGAGCAT | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paez, I.; Prado, Y.; Ubilla, C.G.; Zambrano, T.; Salazar, L.A. Atorvastatin Increases the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs ARSR and CHROME in Hypercholesterolemic Patients: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110382
Paez I, Prado Y, Ubilla CG, Zambrano T, Salazar LA. Atorvastatin Increases the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs ARSR and CHROME in Hypercholesterolemic Patients: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(11):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110382
Chicago/Turabian StylePaez, Isis, Yalena Prado, Carmen G. Ubilla, Tomás Zambrano, and Luis A. Salazar. 2020. "Atorvastatin Increases the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs ARSR and CHROME in Hypercholesterolemic Patients: A Pilot Study" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 11: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110382
APA StylePaez, I., Prado, Y., Ubilla, C. G., Zambrano, T., & Salazar, L. A. (2020). Atorvastatin Increases the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs ARSR and CHROME in Hypercholesterolemic Patients: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceuticals, 13(11), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110382






