Characterization of iRGD-Ligand Modified Arginine-Histidine-Rich Peptides for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Delivery to αvβ3 Integrin-Expressing Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
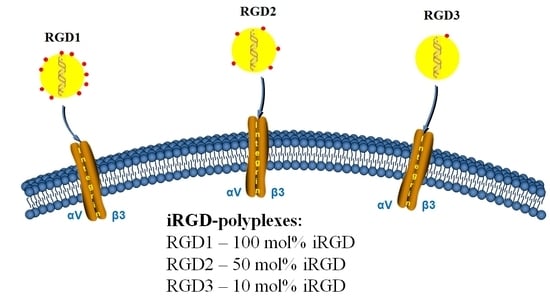
2.1. Design of the Carriers
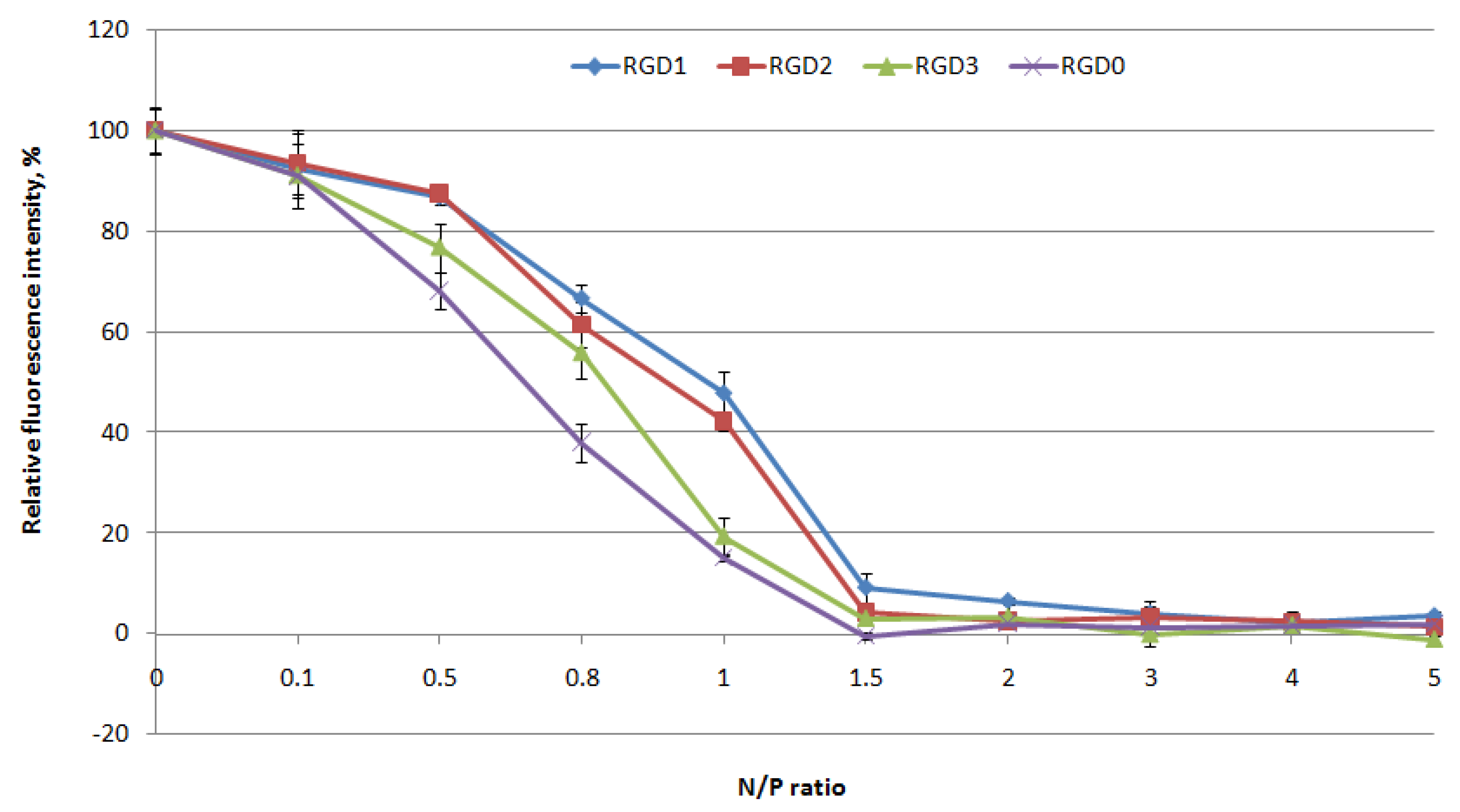
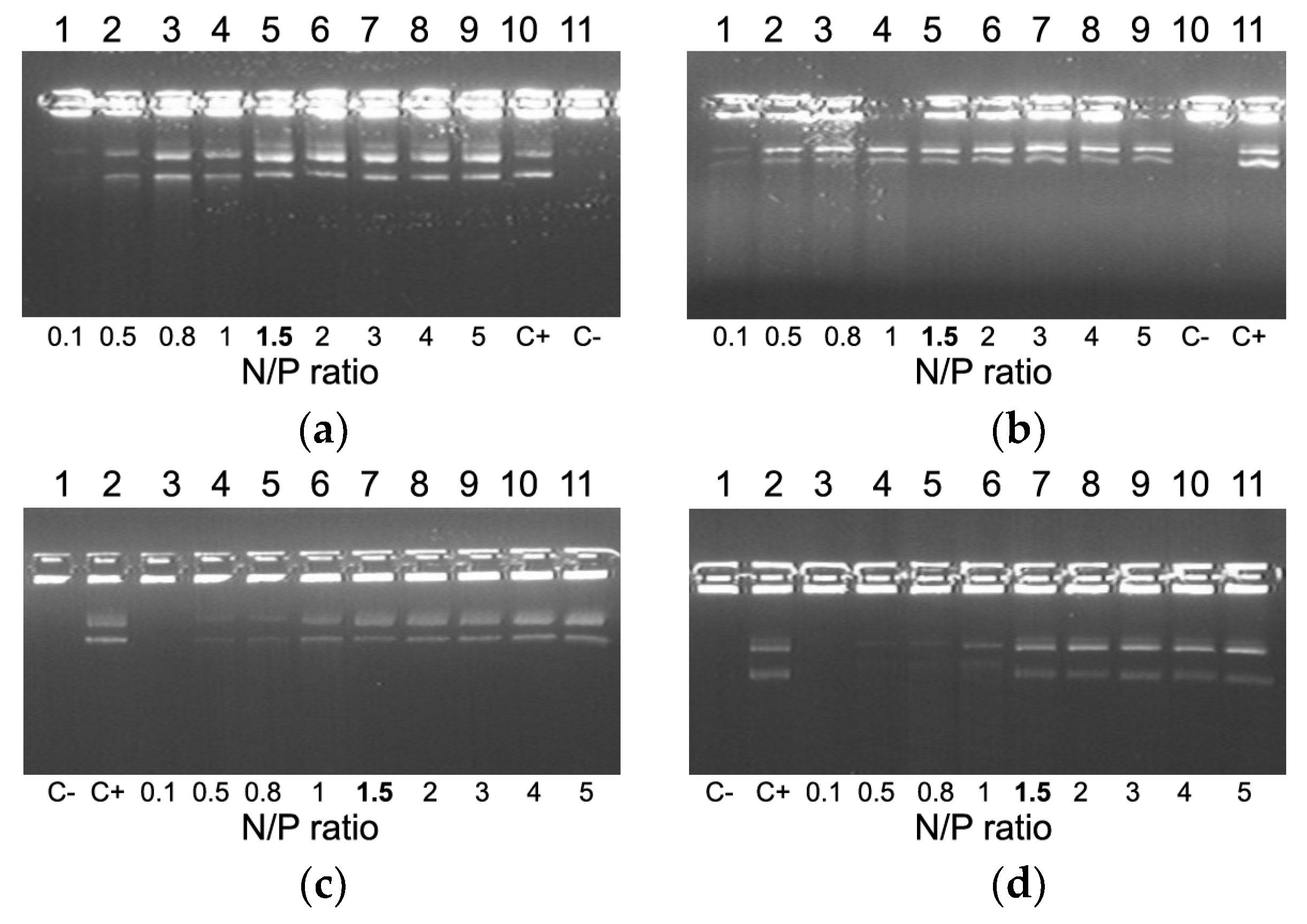
2.2. Evaluation of NA-Binding and NA-Protective Properties of the Carriers
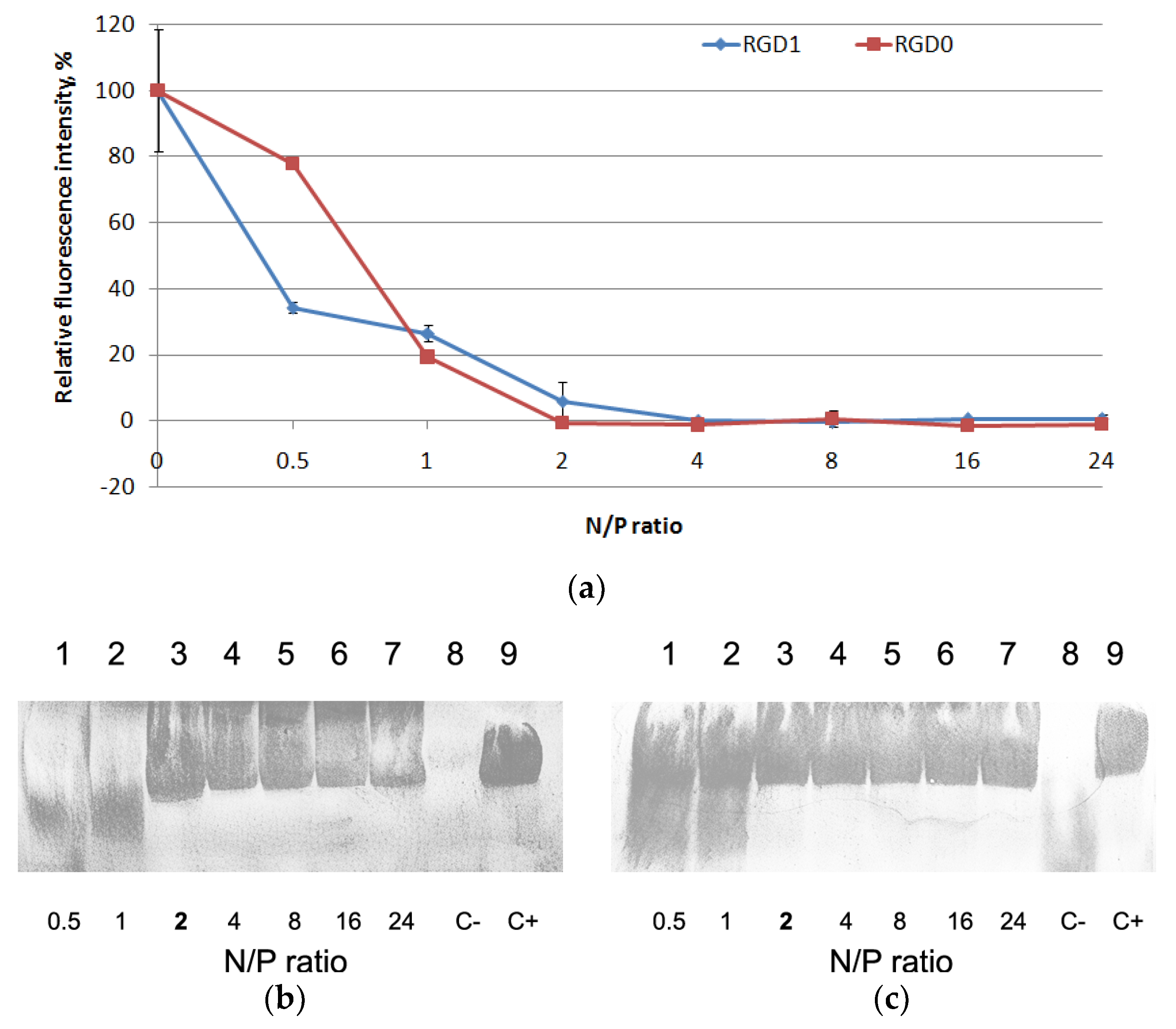
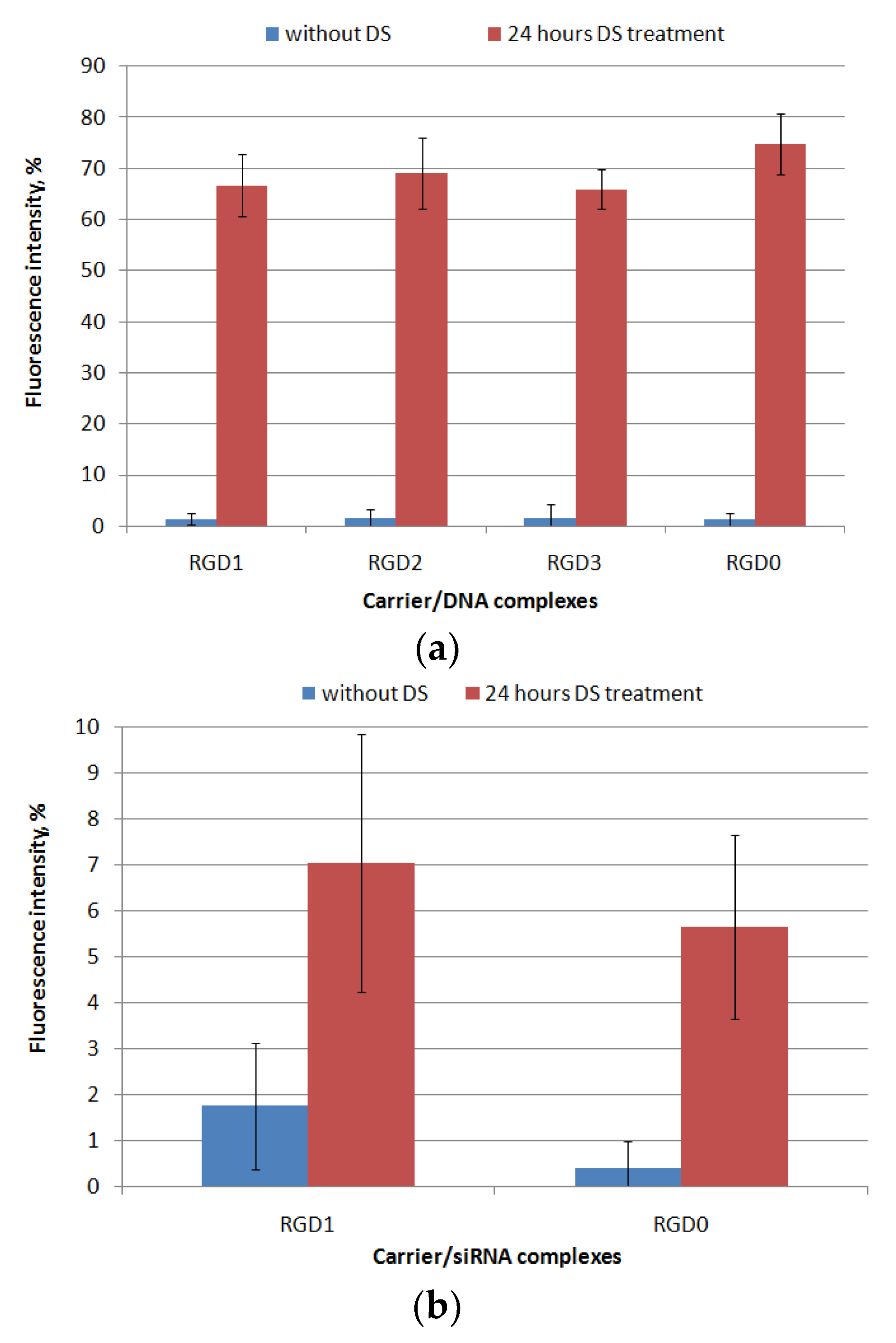
2.3. Relaxation of NA/Peptide Complexes by Polyanions
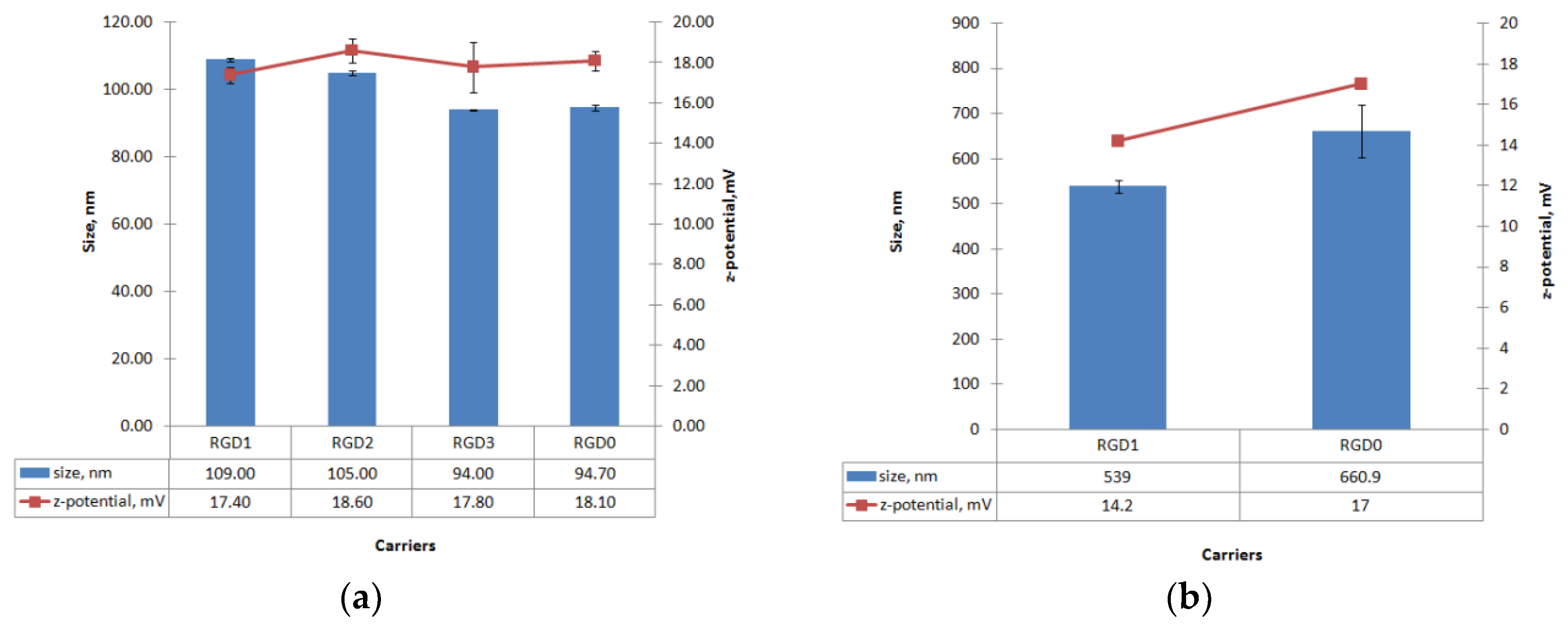
2.4. Measurement of Size and Zeta-Potential of Peptide/NA Complexes
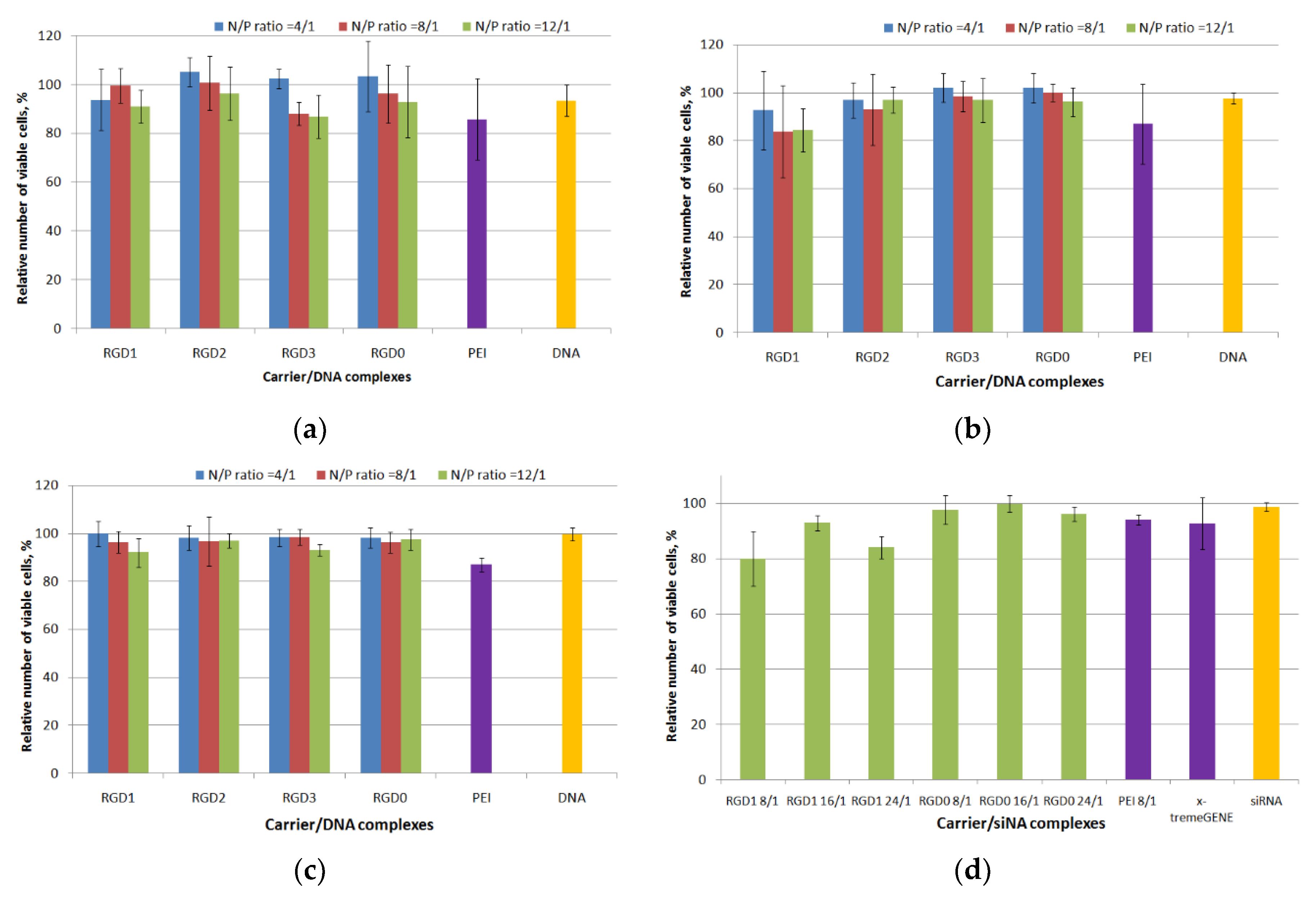
2.5. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Peptide/NA Complexes
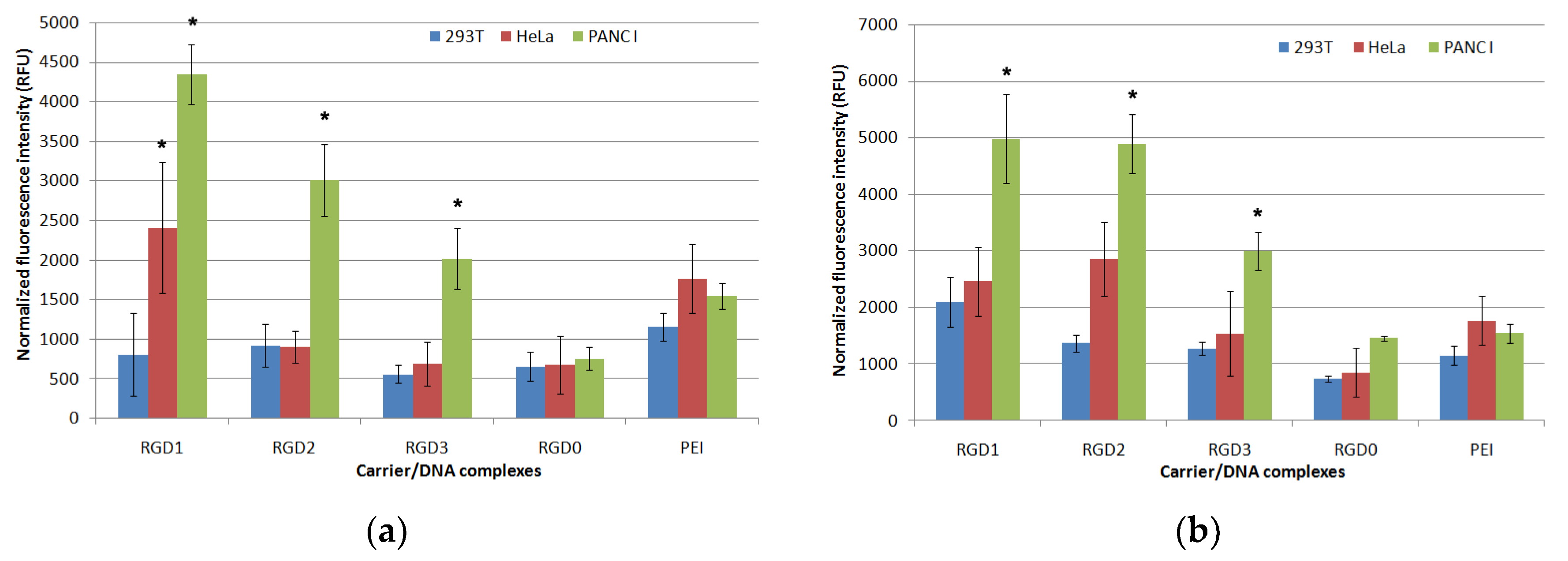
2.6. Cellular Uptake of Peptide/DNA Polyplexes
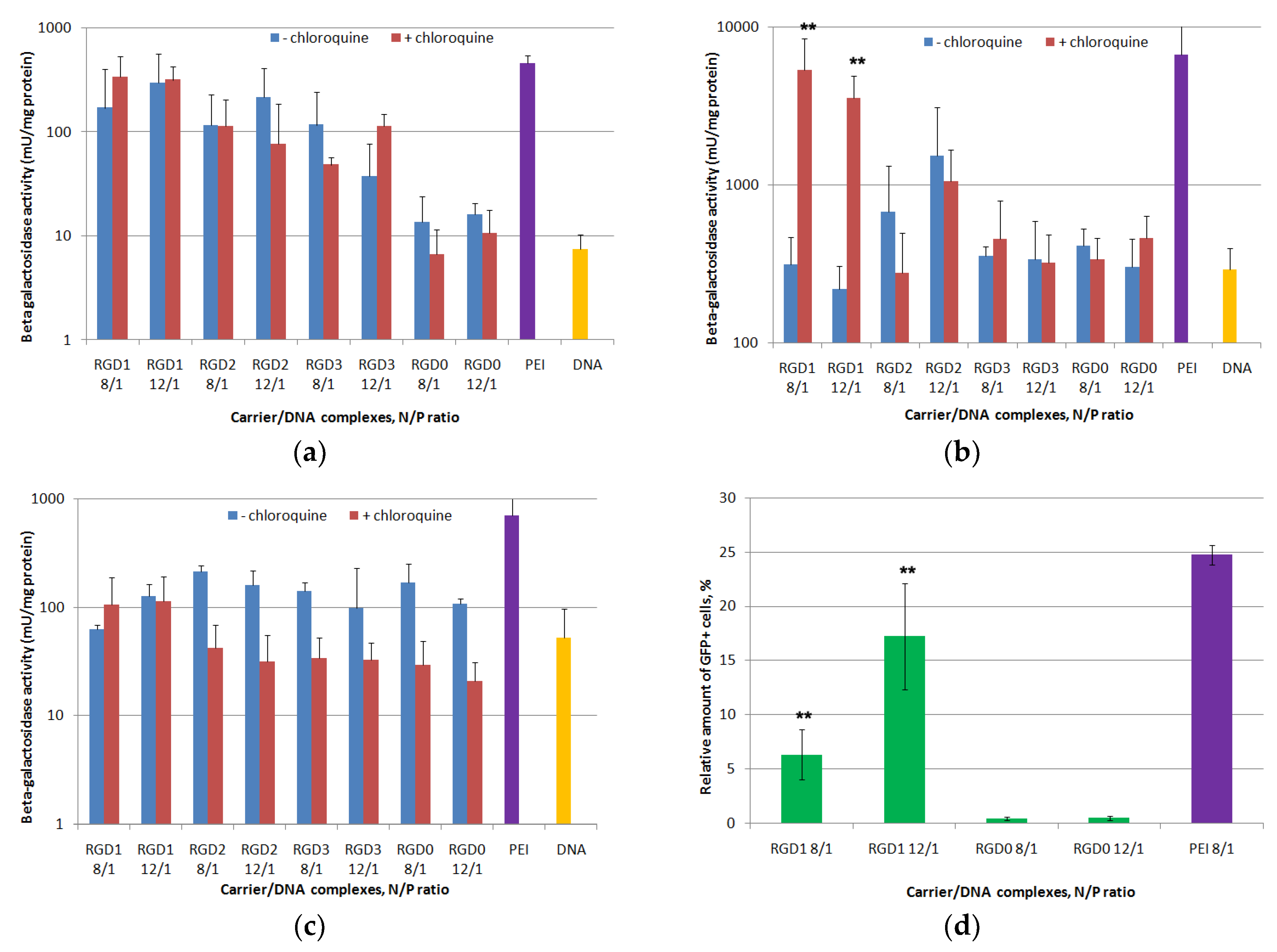
2.7. In Vitro Transfection Studies of DNA-Polyplexes
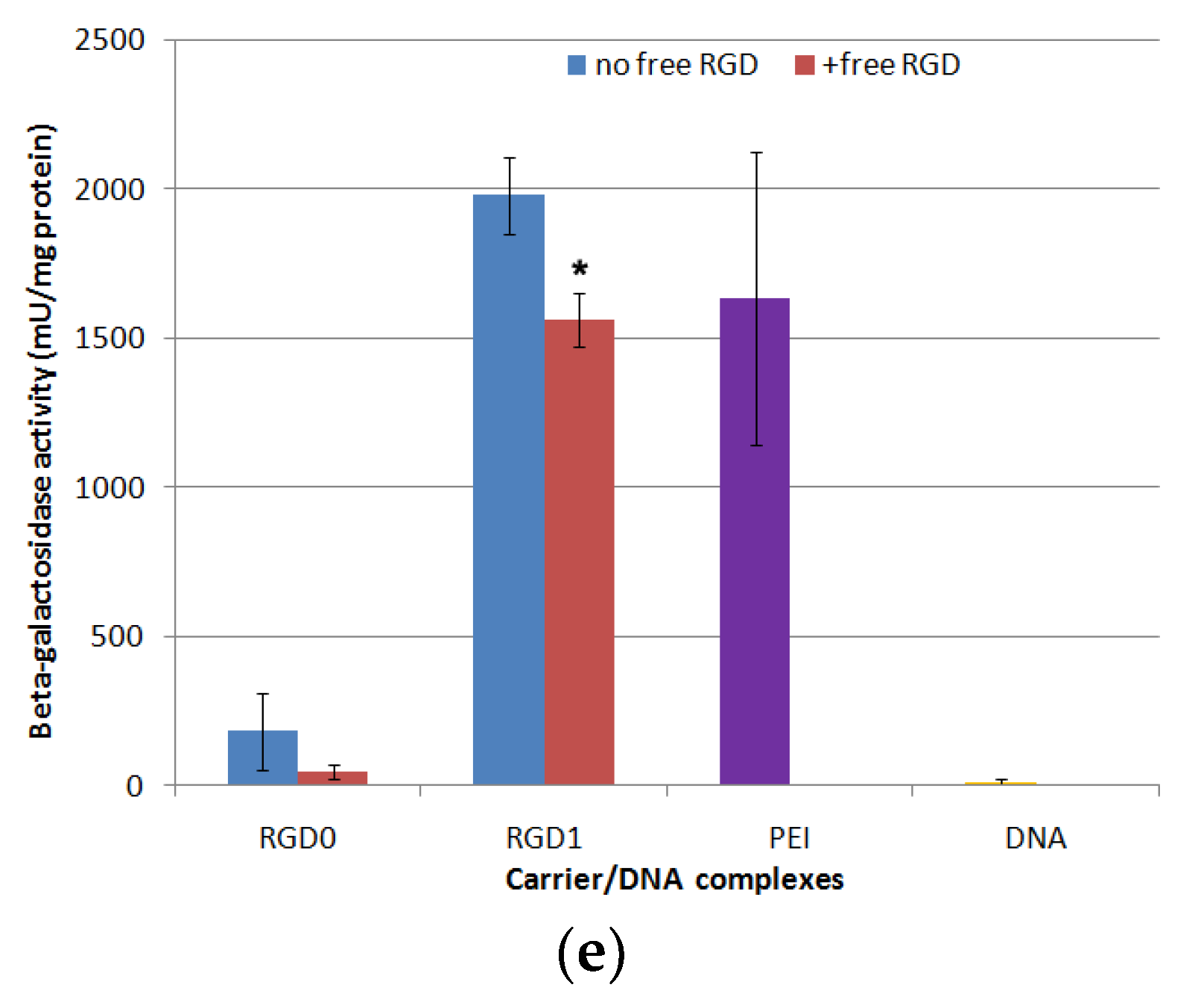
2.8. Proliferative Activity of Cancer Cells after Suicidal Gene Delivery
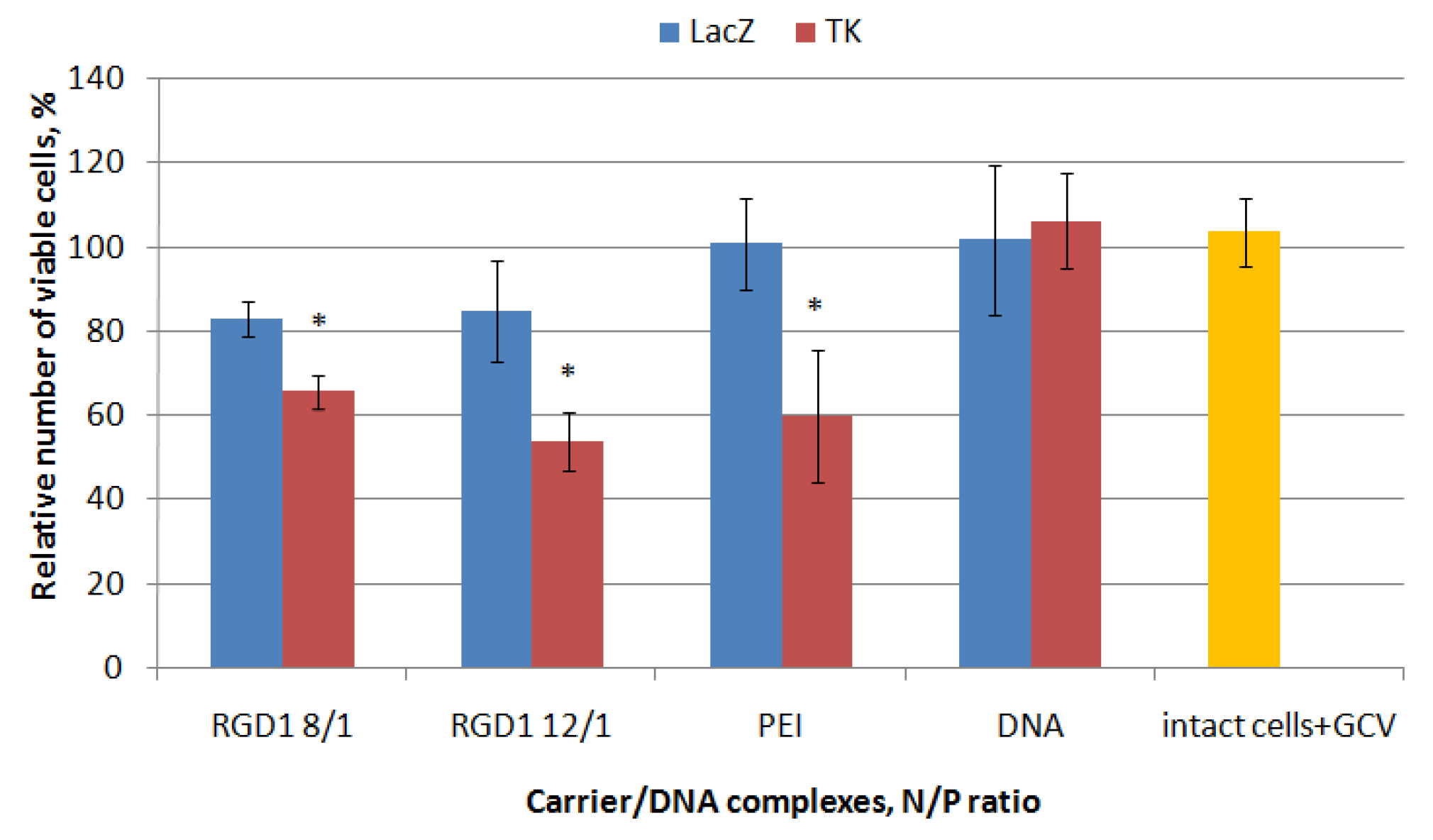
2.9. In Vitro GFP and VEGFA Gene Expression Silencing by Carrier/siRNA Complexes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Lines
3.2. Peptide Synthesis
3.3. Plasmids and siRNAs
3.4. Preparation of DNA- and RNA-Complexes
3.5. DNA- and RNA-Binding Assays
3.6. DNase I and RNase A Protection Assays
3.7. Measurement of Size and Z-Potential of Peptide/DNA and Peptide/RNA Complexes
3.8. Relaxation of DNA- and RNA-Complexes by Dextran-Sulfate
3.9. Expression of αvβ3 Integrins in Cell Lines
3.10. Gene Transfer
3.11. Cellular Uptake of Peptide/DNA Complexes
3.12. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.13. Analysis of Proliferative Activity of PANC-1 Cells after Suicidal Gene Therapy
3.14. siRNA Transfer to MDA-MB-231 Cells and GFP Fluorescence Detection
3.15. siRNA Transfer to EA.hy926 Cells and Quantitative RT-PCR
3.16. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ginn, S.L.; Amaya, A.K.; Alexander, I.E.; Edelstein, M.; Abedi, M.R. Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide to 2017: An update. J. Gene Med. 2018, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belitsky, G.A.; Kirsanov, K.I.; Lesovaya, E.A.; Yakubovskaya, M.G. Prevention of therapy-related malignances in cancer survivors. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2114–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahle, J.; Walther, W. Vectors and strategies for nonviral cancer gene therapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Kang, G.; Wang, T.; Huang, H.E. Tumor angiogenesis and anti - angiogenic gene therapy for cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, C.E.; High, K.A.; Joung, J.K.; Kohn, D.B.; Ozawa, K.; Sadelain, M. Gene therapy comes of age. Science 2018, 359, eaan4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, A.; Kiselev, A. Peptide modules for overcoming barriers of nucleic acids transport to cells. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A. Non-Viral Vectors for Gene Delivery. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. -Asia 2018, 9, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.E.; Zahid, M. Cell Penetrating Peptides, Novel Vectors for Gene Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futaki, S. Membrane-permeable arginine-rich peptides and the translocation mechanisms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midoux, P.; Monsigny, M. Efficient gene transfer by histidylated polylysine/pDNA complexes. Bioconjug. Chem. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amreddy, N.; Babu, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Ahmed, R.; Mehta, M.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Based Cancer Drug and Gene Delivery. In Advances in Cancer Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 115–170. [Google Scholar]
- Caswell, P.T.; Vadrevu, S.; Norman, J.C. Integrins: Masters and slaves of endocytic transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Rofstad, E.K. Integrins as therapeutic targets in the organ-specific metastasis of human malignant melanoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoslahti, E. Tumor penetrating peptides for improved drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temming, K.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Molema, G.; Kok, R.J. RGD-based strategies for selective delivery of therapeutics and imaging agents to the tumour vasculature. Drug Resist. Updates 2005, 8, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S. RGD peptide-based non-viral gene delivery vectors targeting integrin α v β 3 for cancer therapy. J. Drug Target 2019, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Hosaka, S.; Kawa, S.; Kiyosawa, K. Potential tumor-targeting peptide vector of histidylated oligolysine conjugated to a tumor-homing RGD motif. Cancer Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teesalu, T.; Sugahara, K.N.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Ruoslahti, E. C-end rule peptides mediate neuropilin-1-dependent cell, vascular, and tissue penetration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16157–16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.H.; Hao, L.; Muzumdar, M.D.; Raghavan, S.; Kwon, E.J.; Pulver, E.M.; Hsu, F.; Aguirre, A.J.; Wolpin, B.M.; Hahn, W.C.; et al. iRGD-guided Tumor-penetrating Nanocomplexes for Therapeutic siRNA Delivery to Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorge, J.D.; Pang, A.; Fujita, D.J. Delivery of gene targeting siRNAs to breast cancer cells using a multifunctional peptide complex that promotes both targeted delivery and endosomal release. PLoS ONE 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Huang, M.; Guo, W.W.; Huang, Q.; zhen Zhang, L.; Jiang, G. Nano-based delivery of RNAi in cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Hwang, H.S.; Shim, M.S.; Cho, Y.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, H.C. Controlling complexation/decomplexation and sizes of polymer-based electrostatic pDNA polyplexes is one of the key factors in effective transfection. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisakar, D.; Vij, M.; Pandey, T.; Natarajan, P.; Sharma, R.; Mishra, S.; Ganguli, M. Deciphering the Role of Chondroitin Sulfate in Increasing the Transfection Efficiency of Amphipathic Peptide-Based Nanocomplexes. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Shubina, A.; Sokolov, D.; Selkov, S.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. CXCR4-targeted modular peptide carriers for efficient anti-VEGF siRNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejman, J.; Oberle, V.; Zuhorn, I.S.; Hoekstra, D. Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Anchordoquy, T. Drug Delivery Trends in Clinical Trials and Translational Medicine: Challenges and Opportunities in the Delivery of Nucleic Acid-Based Therapeutics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, A.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Haas, T.A. Differences in integrin expression and signaling within human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.A.; Nam, K.; Kim, S.W. Tumor targeting RGD conjugated bio-reducible polymer for VEGF siRNA expressing plasmid delivery. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7543–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, X.; Min, J.; Le, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Dogan, A.A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, J.; et al. Nanoparticle delivery systems for DNA/RNA and their potential applications in nanomedicine. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2507–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Ramu, S.; Markland, F. Anti-Angiogenesis and RGD-Containing Snake Venom Disintegrins. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 2860–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouton, C.W.; Seymour, L.W. Key issues in non-viral gene delivery1PII of original article: S0169-409X(98)00048-9. The article was originally published in Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 34 (1998) 3–19.1. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, N.; Ponti, F.; Mantovani, D.; Candiani, G. Non-Viral in vitro Gene Delivery: It is Now Time to Set the Bar! Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wonder, E.; Simón-Gracia, L.; Scodeller, P.; Majzoub, R.N.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Ewert, K.K.; Teesalu, T.; Safinya, C.R. Competition of charge-mediated and specific binding by peptide-tagged cationic liposome–DNA nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2018, 166, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guryanov, I.A.; Vlasov, G.P.; Lesina, E.A.; Kiselev, A.V.; Baranov, V.S.; Avdeeva, E.V.; Vorob’ev, V.I. Cationic oligopeptides modified with lipophilic fragments: Use for DNA delivery to cells. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2005, 31, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheis, R.; Kichler, A.; Wallner, G.; Kursa, M.; Ogris, M.; Felzmann, T.; Buchberger, M.; Wagner, E. Coupling of cell-binding ligands to polyethylenimine for targeted gene delivery. Gene Ther. 1997, 4, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Bogacheva, M.; Shubina, A.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Development of a receptor-targeted gene delivery system using CXCR4 ligand-conjugated cross-linking peptides. J. Gene Med. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouanet, M.; Lebrin, M.; Gross, F.; Bournet, B.; Cordelier, P.; Buscail, L. Gene therapy for pancreatic cancer: Specificity, issues and hopes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J. Animal Models for Studying Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer. In Animal Models for the Study of Human Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 997–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Stojanović, N.; Dekanić, A.; Paradžik, M.; Majhen, D.; Ferenčak, K.; Ruščić, J.; Bardak, I.; Supina, C.; Tomicic, M.T.; Osmak, M.; et al. Differential Effects of Integrin α v Knockdown and Cilengitide on Sensitization of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Melanoma Cells to Microtubule Poisons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 1334–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H. iRGD: A Promising Peptide for Cancer Imaging and a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Various Cancers. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagaya, H.; Oba, M.; Miura, Y.; Koyama, H.; Ishii, T.; Shimada, T.; Takato, T.; Kataoka, K.; Miyata, T. Impact of polyplex micelles installed with cyclic RGD peptide as ligand on gene delivery to vascular lesions. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.A.; Maretina, M.A.; Kiselev, A.V. VEGFA Gene Silencing in CXCR4-Expressing Cells via siRNA Delivery by Means of Targeted Peptide Carrier. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1974, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, A.; Petrosyan, M.; Maretina, M.; Balashova, N.; Polyanskih, L.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Anti-angiogenic treatment of endometriosis via anti-VEGFA siRNA delivery by means of peptide-based carrier in a rat subcutaneous model. Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, N.K.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Hong, H.K.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.B.; Woo, S.J.; Park, K.H.; Kim, H. Therapeutic effects of a novel siRNA-based anti-VEGF (siVEGF) nanoball for the treatment of choroidal neovascularization. Nanoscale 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorova, A.A.; Shtykalova, S.V.; Maretina, M.A.; Sokolov, D.I.; Selkov, S.A.; Baranov, V.S.; Kiselev, A.V. Synergistic Anti-Angiogenic Effects Using Peptide-Based Combinatorial Delivery of siRNAs Targeting VEGFA, VEGFR1, and Endoglin Genes. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slita, A.; Egorova, A.; Casals, E.; Kiselev, A.; Rosenholm, J.M. Characterization of modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles as vectors for siRNA delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselev, A.V.; Il’ina, P.L.; Egorova, A.A.; Baranov, A.N.; Guryanov, I.A.; Bayanova, N.V.; Tarasenko, I.I.; Lesina, E.A.; Vlasov, G.P.; Baranov, V.S. Lysine dendrimers as vectors for delivery of genetic constructs to eukaryotic cells. Russ. J. Genet. 2007, 43, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beidler, J.L.; Hilliard, P.R.; Rill, R.L. Ultrasensitive staining of nucleic acids with silver. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.A.; Shtykalova, S.V.; Maretina, M.A.; Selyutin, A.V.; Shved, N.Y.; Krylova, N.V.; Ilina, A.V.; Pyankov, I.A.; Freund, S.A.; Selkov, S.A.; et al. Cys-flanked cationic peptides for cell delivery of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene for suicide gene therapy of uterine leiomyoma. Mol. Biol. 2020, 54, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Composition (mol%) |
|---|---|
| RGD0 | RRRRRRRRRHHHH (100 mol%) |
| RGD1 | RRRRRRRRRHHHH-CRGDRGPDC (100 mol%) |__________| |
| RGD2 | RRRRRRRRRHHHH (50 mol%) RRRRRRRRRHHHH-CRGDRGPDC (50 mol%) |__________| |
| RGD3 | RRRRRRRRRHHHH (90 mol%) RRRRRRRRRHHHH-CRGDRGPDC (10 mol%) |__________| |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egorova, A.; Selutin, A.; Maretina, M.; Selkov, S.; Baranov, V.; Kiselev, A. Characterization of iRGD-Ligand Modified Arginine-Histidine-Rich Peptides for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Delivery to αvβ3 Integrin-Expressing Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100300
Egorova A, Selutin A, Maretina M, Selkov S, Baranov V, Kiselev A. Characterization of iRGD-Ligand Modified Arginine-Histidine-Rich Peptides for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Delivery to αvβ3 Integrin-Expressing Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(10):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100300
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgorova, Anna, Alexander Selutin, Marianna Maretina, Sergei Selkov, Vladislav Baranov, and Anton Kiselev. 2020. "Characterization of iRGD-Ligand Modified Arginine-Histidine-Rich Peptides for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Delivery to αvβ3 Integrin-Expressing Cancer Cells" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 10: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100300
APA StyleEgorova, A., Selutin, A., Maretina, M., Selkov, S., Baranov, V., & Kiselev, A. (2020). Characterization of iRGD-Ligand Modified Arginine-Histidine-Rich Peptides for Nucleic Acid Therapeutics Delivery to αvβ3 Integrin-Expressing Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 13(10), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100300