A Decade of Antifungal Leads from Natural Products: 2010–2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Pipeline of Antifungal Natural Product Leads
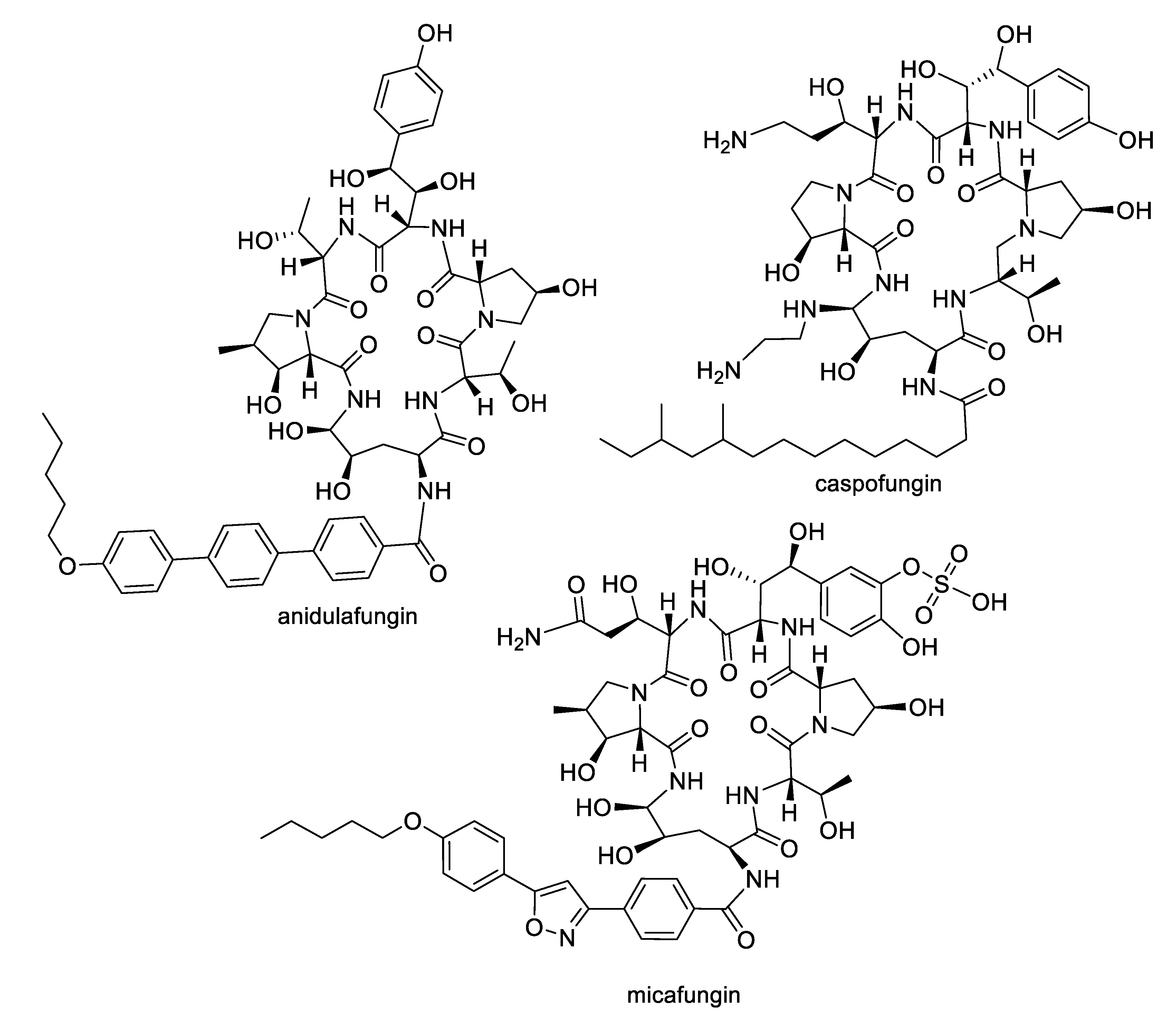
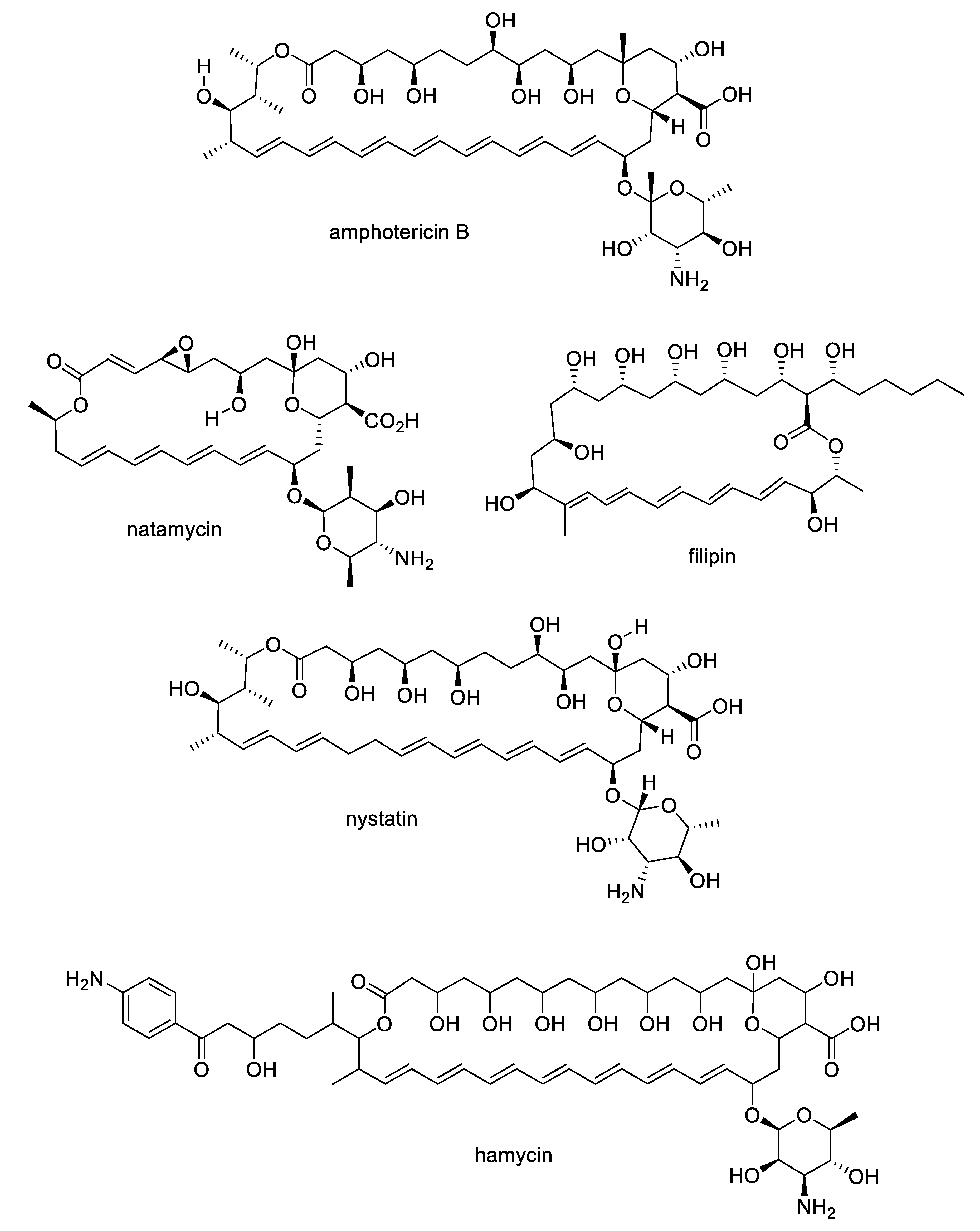
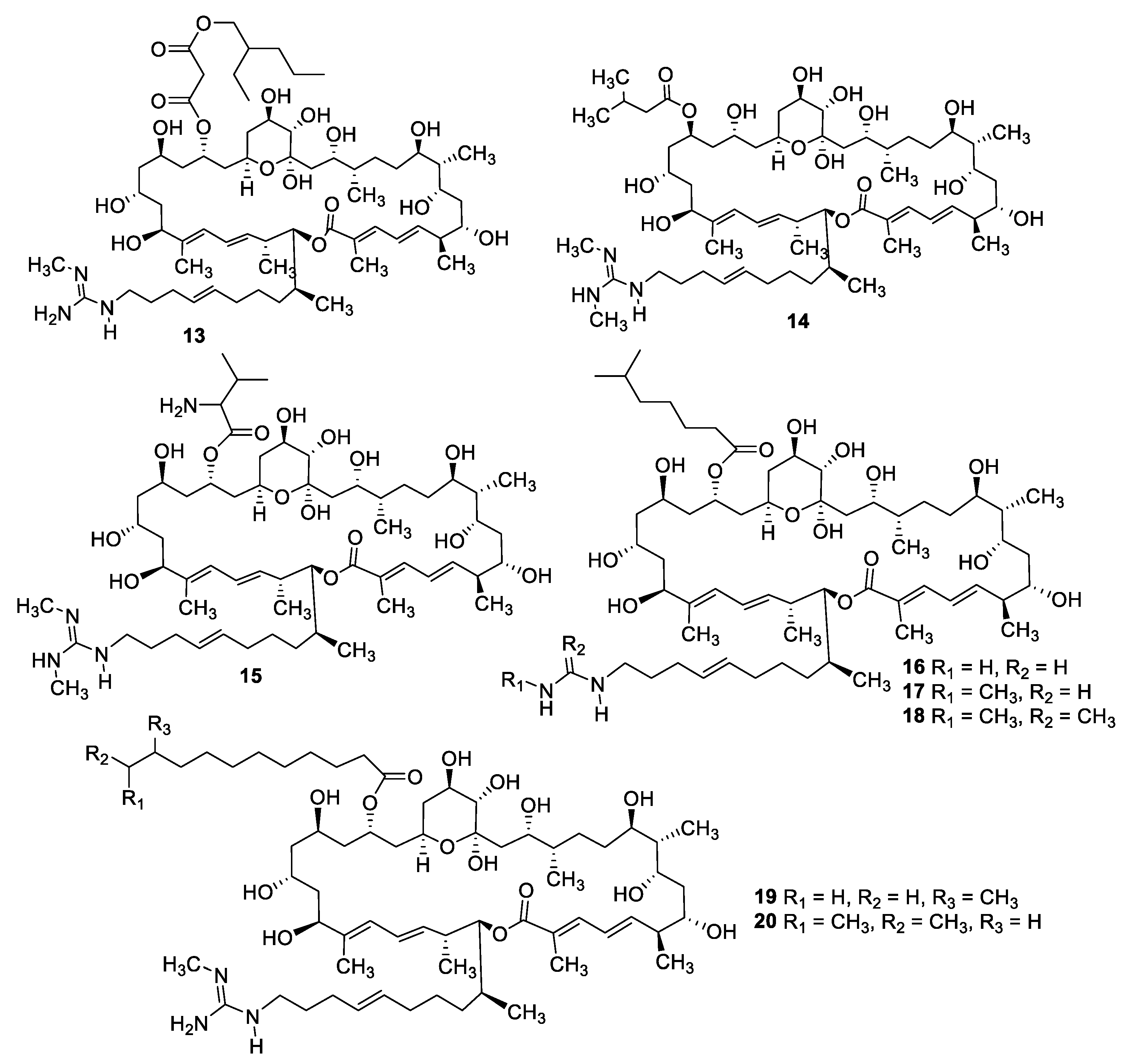
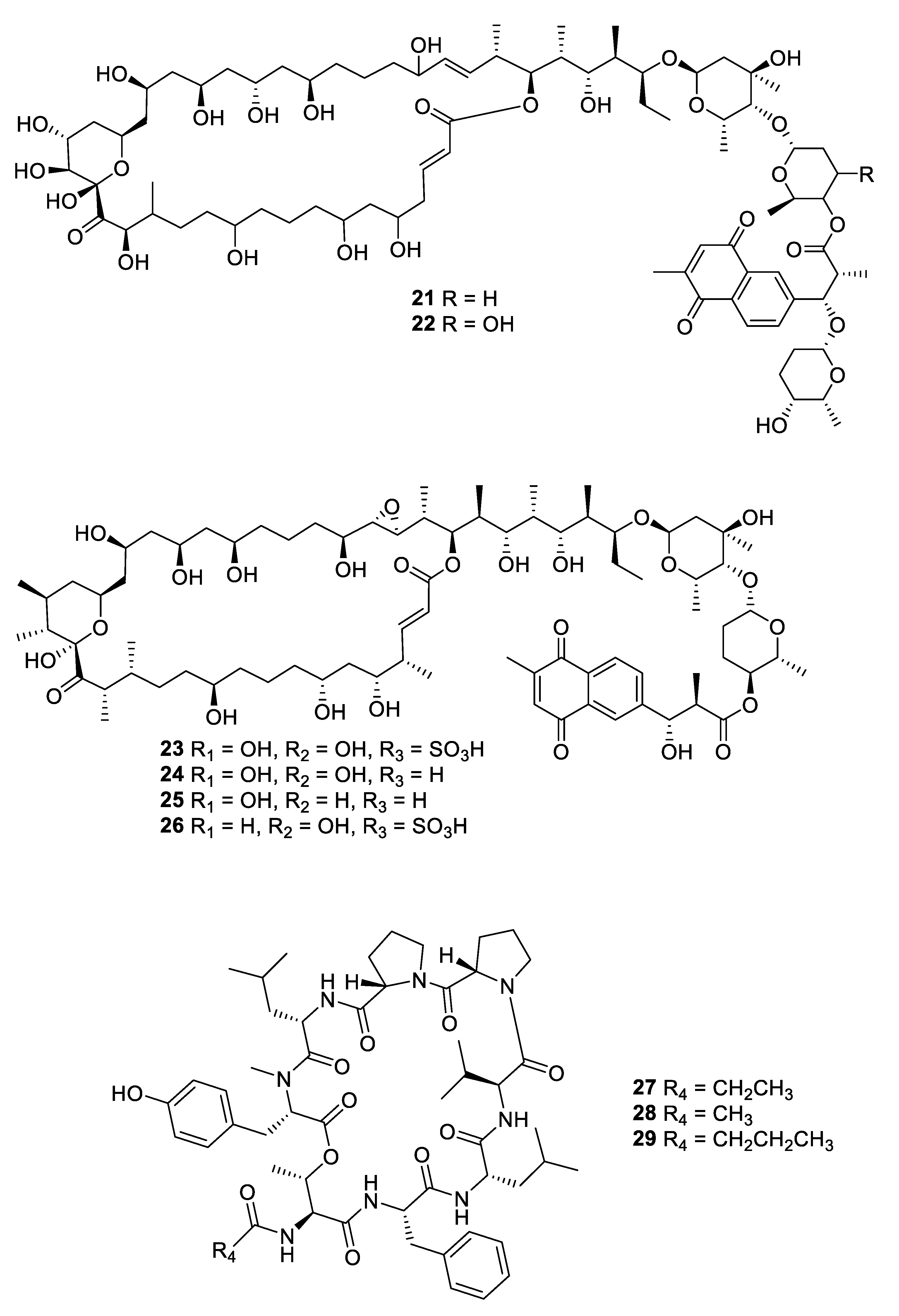
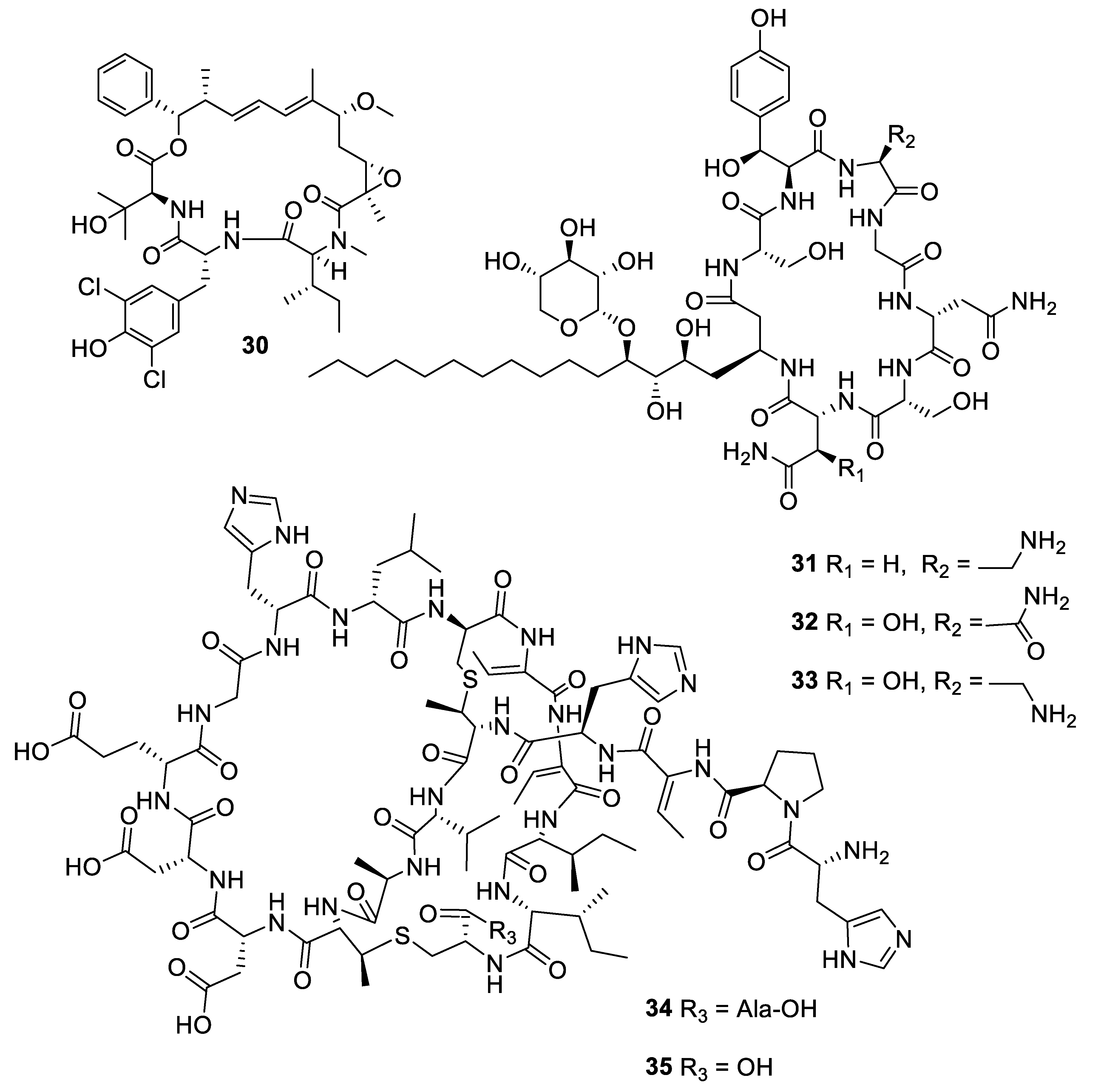
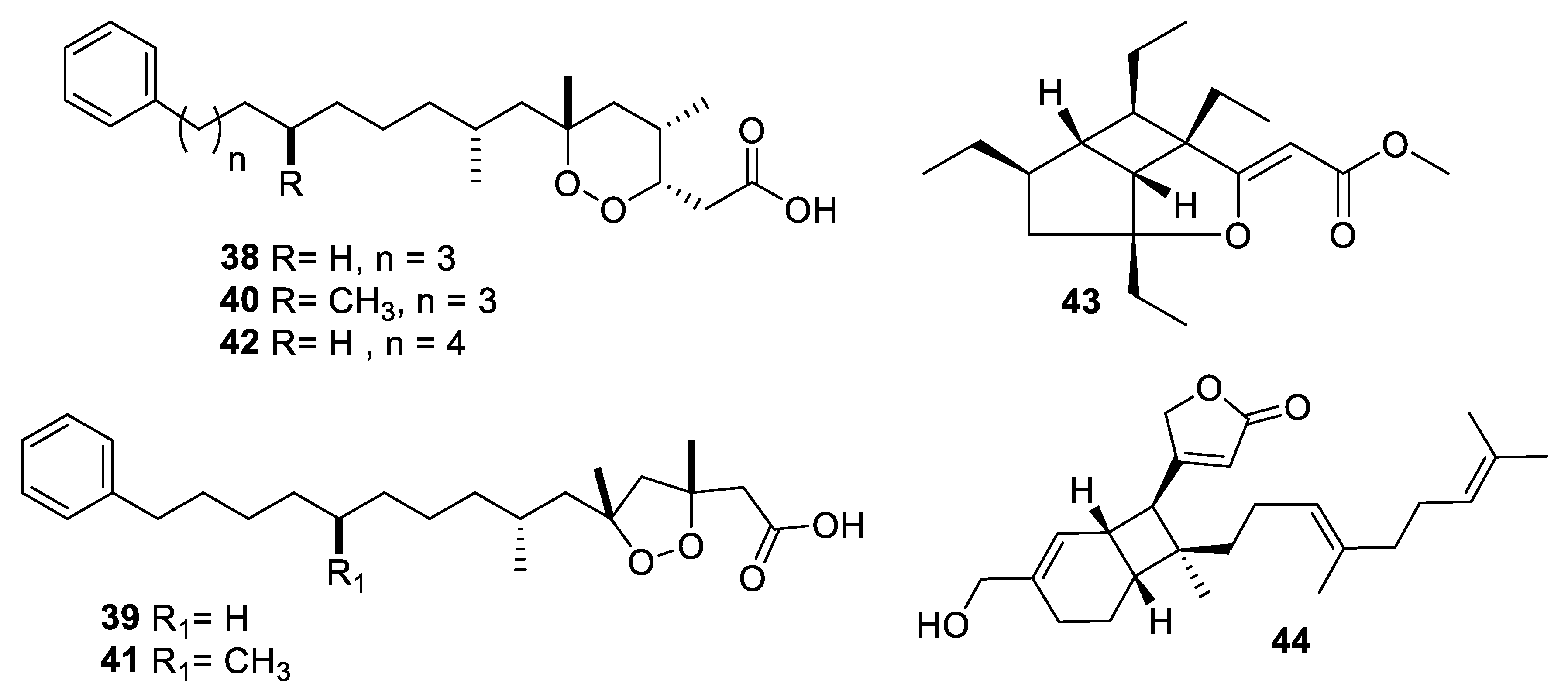
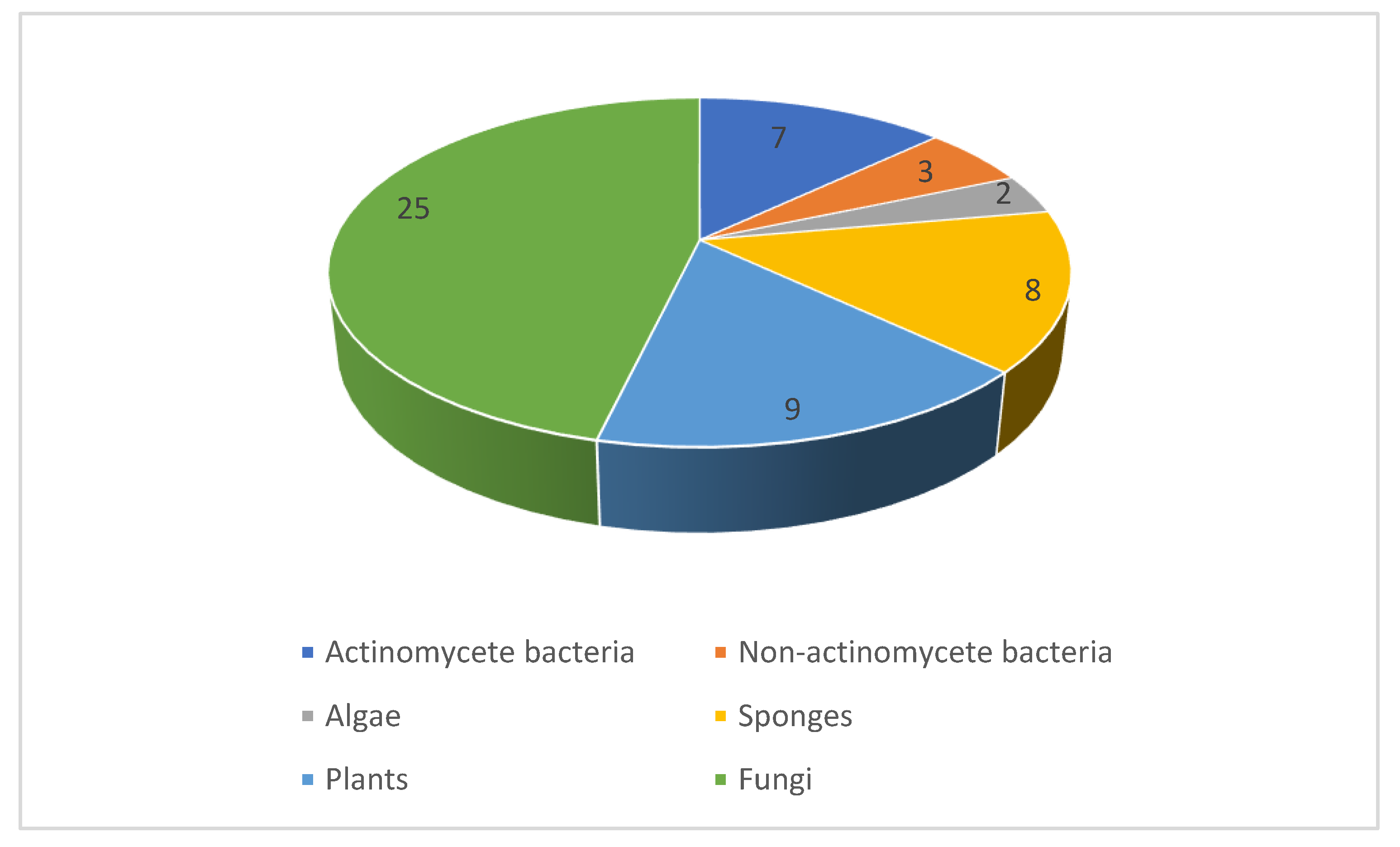
2.1. Natural Product Antifungal Leads from Bacteria and Algae
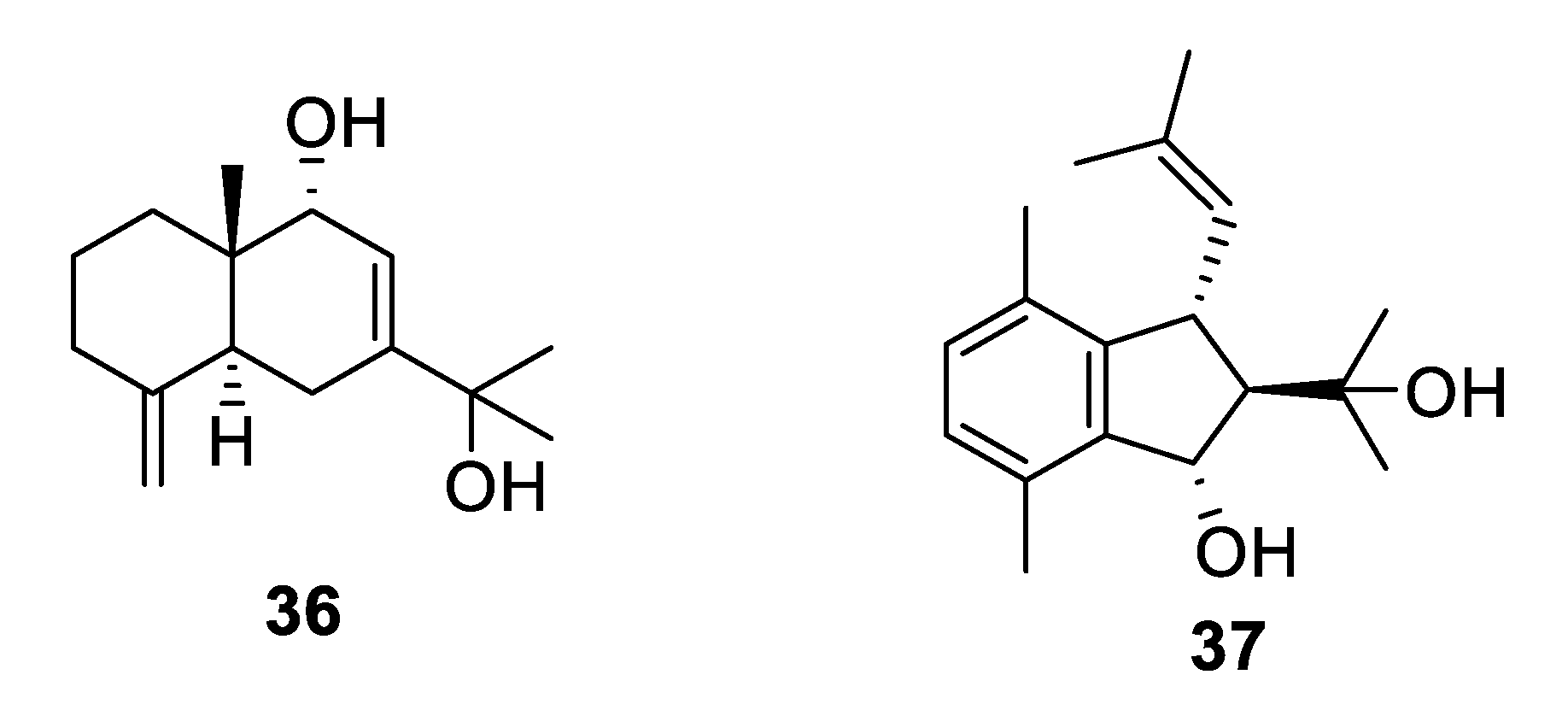
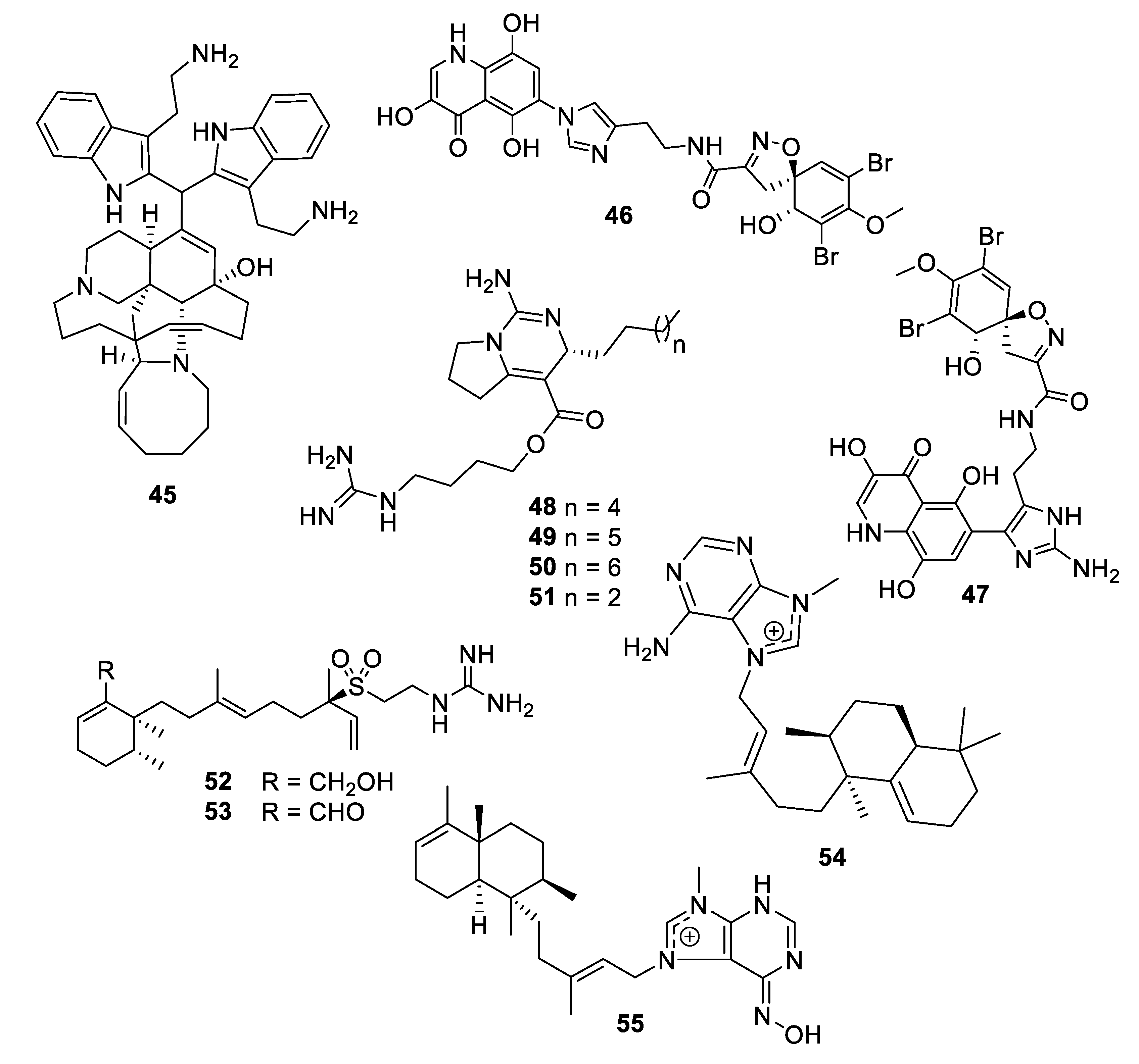
2.2. Natural Product Antifungal Leads from Sponges
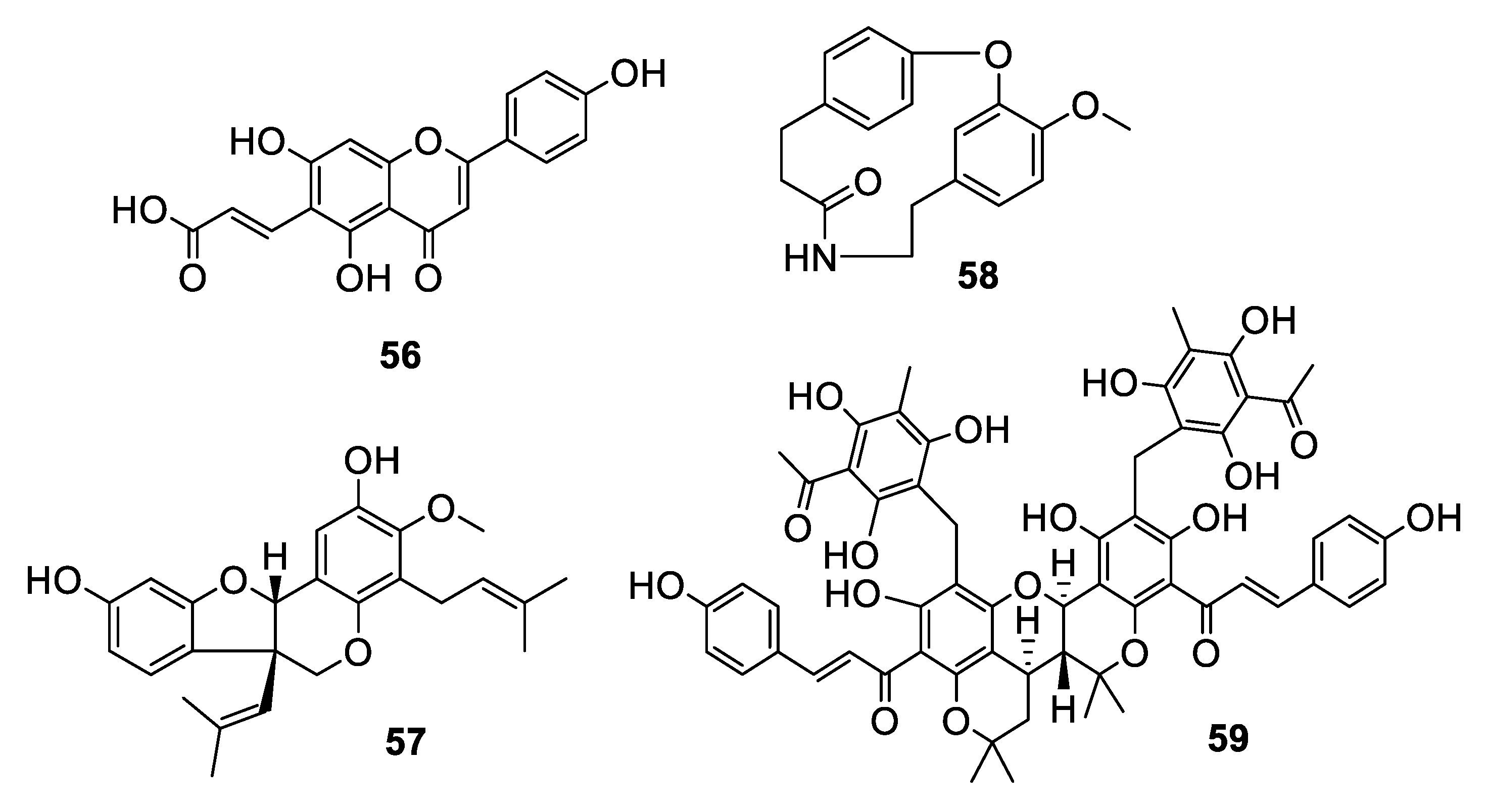
2.3. Natural Product Antifungal Leads from Plants
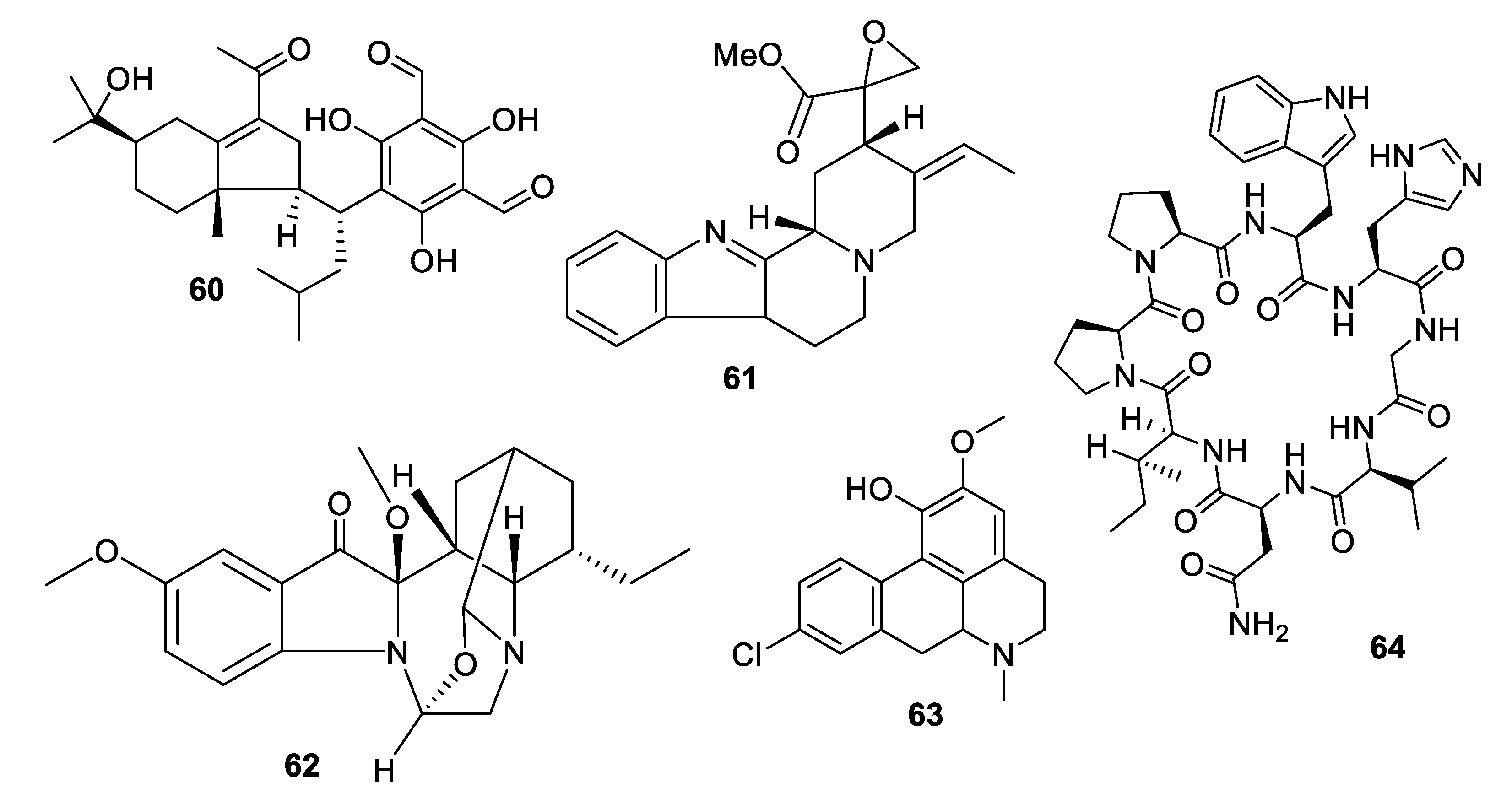
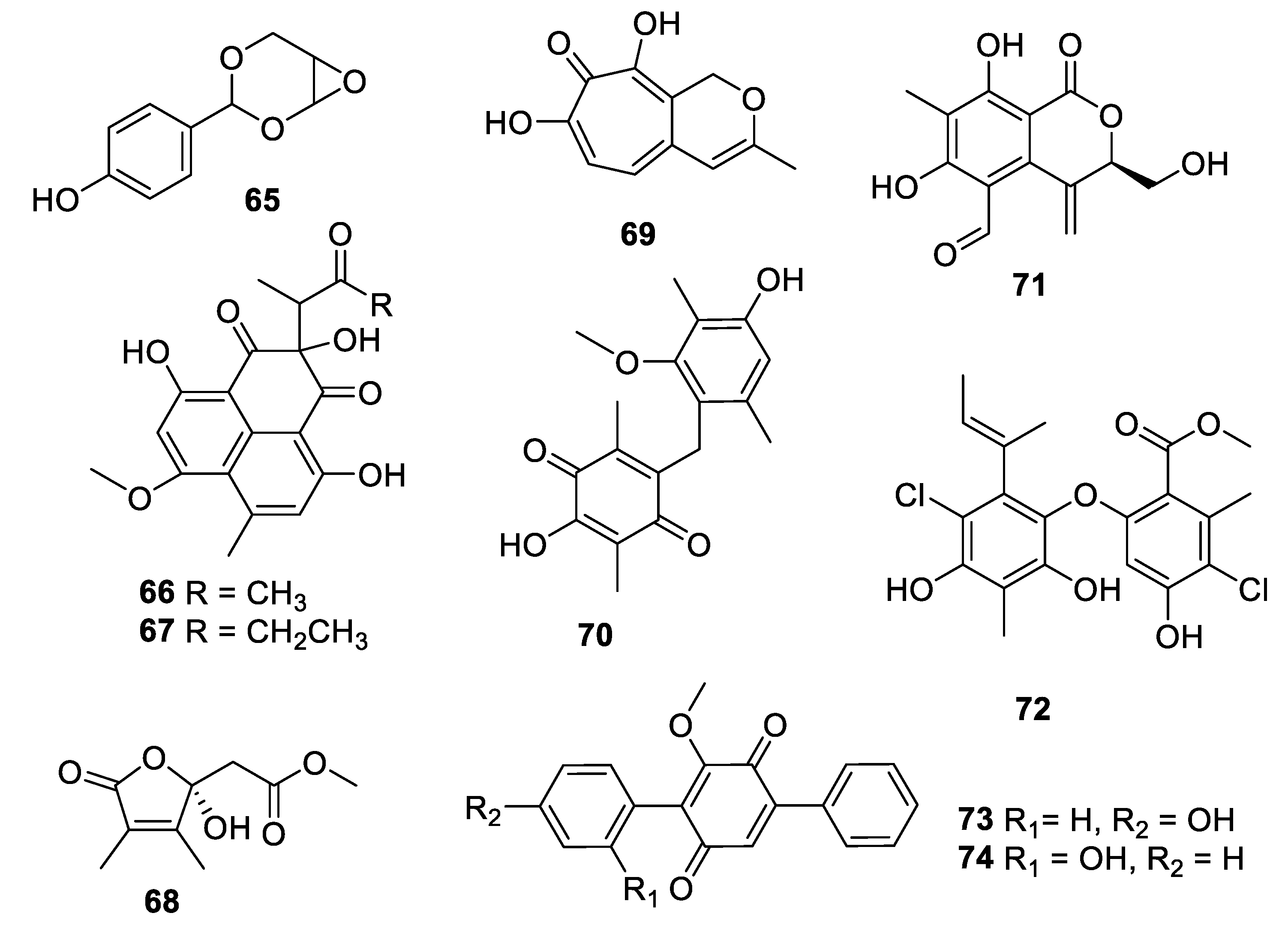
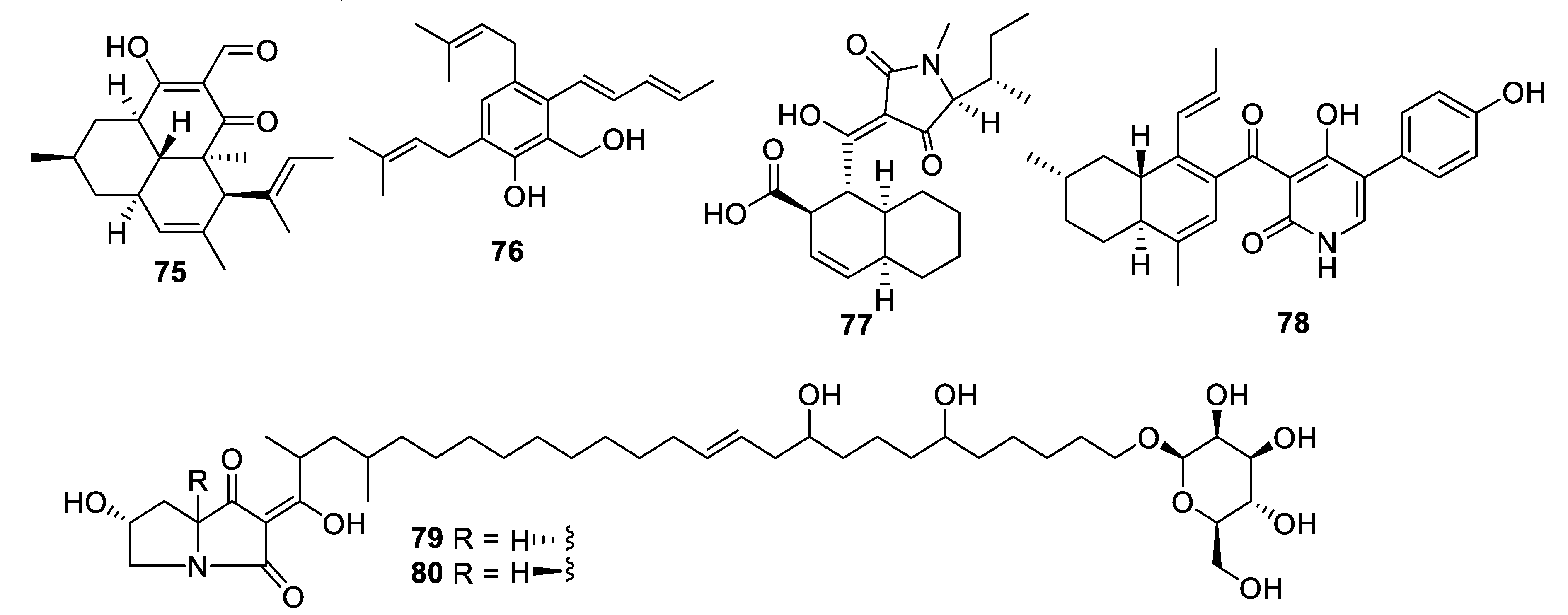
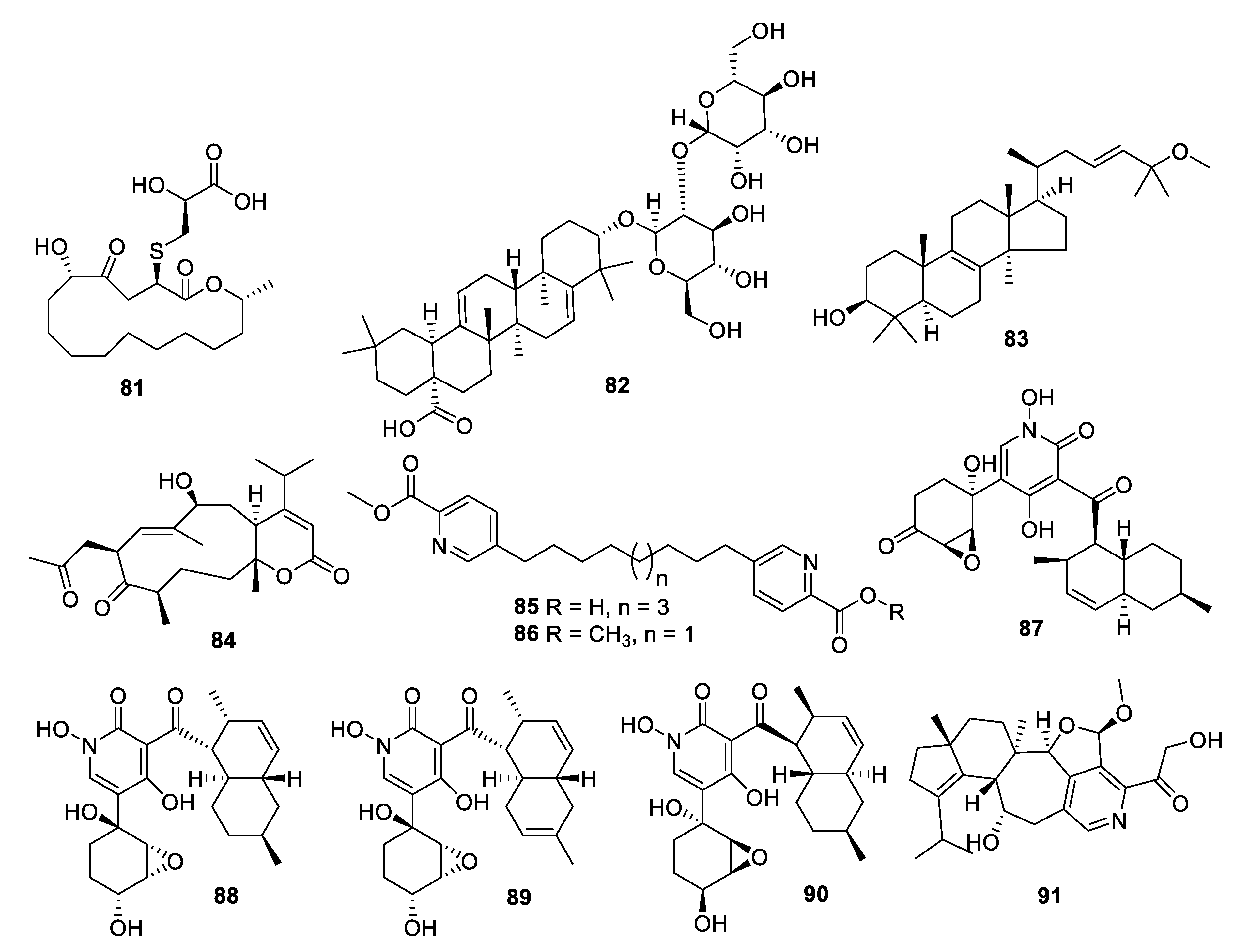
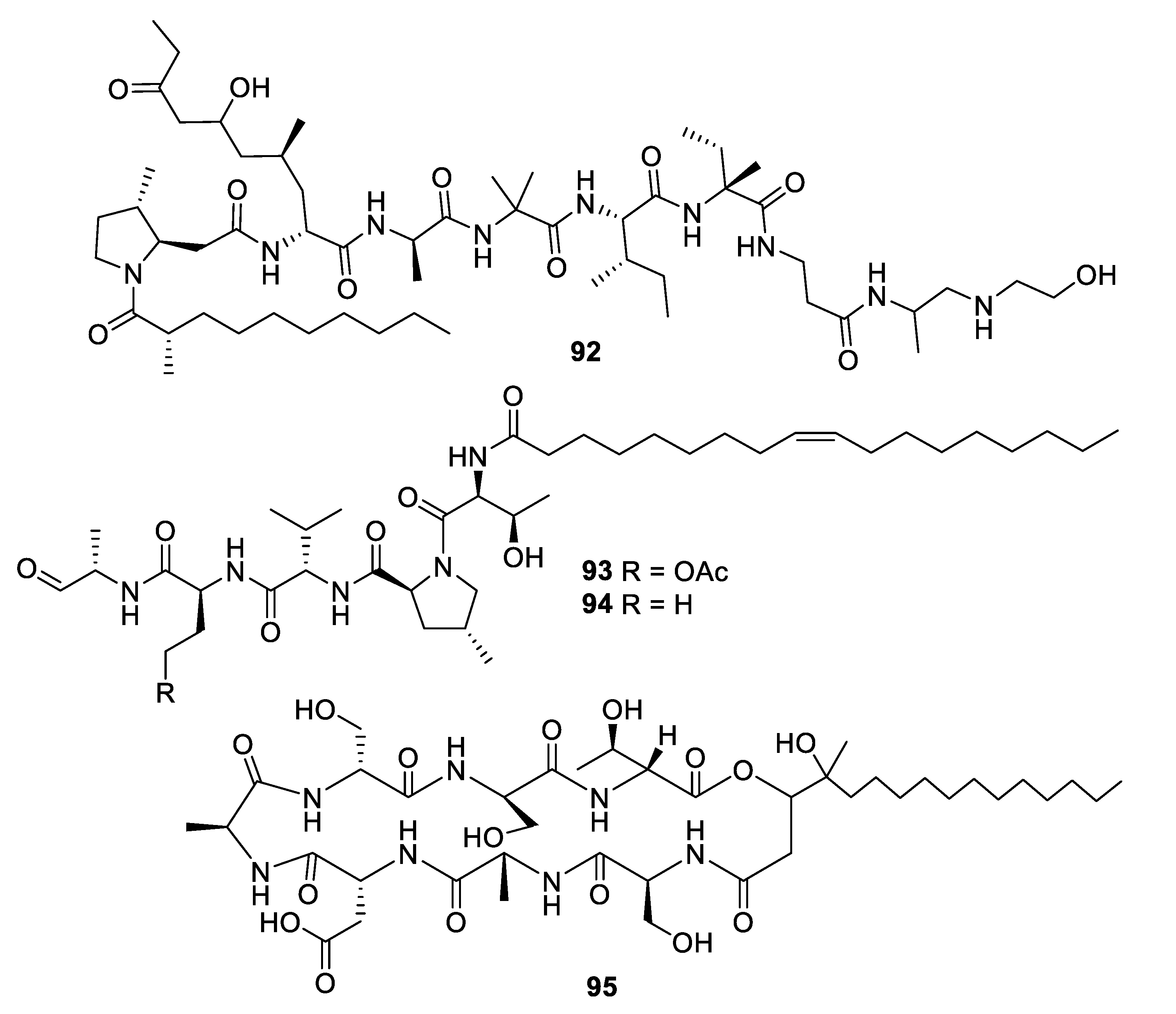
2.4. Natural Product Antifungal Leads from Fungi
3. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.; Denning, D. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases—Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pianalto, K.; Alspaugh, J. New Horizons in Antifungal Therapy. J. Fungi 2016, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery-Smith, A.; Taori, S.K.; Schelenz, S.; Jeffery, K.; Johnson, E.M.; Borman, A.; Manuel, R.; Brown, C.S. Candida auris: A Review of the Literature. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00029-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.; Wilson, D.; Drew, R.; Perfect, J. Azole antifungals: 35 years of invasive fungal infection management. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. 2015, 13, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Majumdar, S. Echinocandins in antifungal pharmacotherapy. J. Pharm. Pharm. 2017, 69, 1635–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotchev, S.B. Polyene macrolide antibiotics and their applications in human therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.C.; Palacios, D.S.; Dailey, I.; Endo, M.M.; Uno, B.E.; Wilcock, B.C.; Burke, M.D. Amphotericin primarily kills yeast by simply binding ergosterol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermes, A.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Dankert, J. Flucytosine: A review of its pharmacology, clinical indications, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and drug interactions. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfect, J.R. The impact of the host on fungal infections. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125, S39–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes-McAlister, J.; Shapiro, R.S. New pathogens, new tricks: Emerging, drug-resistant fungal pathogens and future prospects for antifungal therapeutics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1435, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revie, N.M.; Iyer, K.R.; Robbins, N.; Cowen, L.E. Antifungal drug resistance: Evolution, mechanisms and impact. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. Establishing a list of qualifying pathogens under the Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. Final rule. Fed. Regist. 2014, 79, 32464–32481. [Google Scholar]
- Perfect, J.R. The antifungal pipeline: A reality check. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortholand, J.Y.; Ganesan, A. Natural products and combinatorial chemistry: Back to the future. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A. The impact of natural products upon modern drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Jiang, Y.; Han, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Qu, X.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; et al. Bafilomycins and Odoriferous Sesquiterpenoids from Streptomyces albolongus Isolated from Elephas maximus Feces. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Han, L.; Huang, X.; Lu, T.; Jiang, C. The complete genome sequence of Streptomyces albolongus YIM 101047, the producer of novel bafilomycins and odoriferous sesquiterpenoids. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 262, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harunari, E.; Imada, C.; Igarashi, Y. Konamycins A and B and Rubromycins CA1 and CA2, Aromatic Polyketides from the Tunicate-Derived Streptomyces hyaluromycini MB-PO13 T. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Iwata, F.; Yamada, S.; Katayama, M. Neomaclafungins A–I: Oligomycin-Class Macrolides from a Marine-Derived Actinomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Hong, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. 1H and 13C assignments of two new macrocyclic lactones isolated from Streptomyces sp. 211726 and revised assignments of Azalomycins F3a, F4a and F5a. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2011, 49, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Hong, K.; Lin, H.; She, Z.; Li, J. New Azalomycin F Analogs from Mangrove Streptomyces sp. 211726 with Activity against Microbes and Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alferova, V.A.; Novikov, R.A.; Bychkova, O.P.; Rogozhin, E.A.; Shuvalov, M.V.; Prokhorenko, I.A.; Sadykova, V.S.; Kulko, A.B.; Dezhenkova, L.G.; Stepashkina, E.A.; et al. Astolides A and B, antifungal and cytotoxic naphthoquinone-derived polyol macrolactones from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 7442–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Victoria, I.; Oves-Costales, D.; Lacret, R.; Martín, J.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Díaz, C.; Cautain, B.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. Structure elucidation and biosynthetic gene cluster analysis of caniferolides A–D, new bioactive 36-membered macrolides from the marine-derived Streptomyces caniferus CA-271066. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 2954–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvariño, R.; Alonso, E.; Lacret, R.; Oves-Costales, D.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M. Caniferolide A, a Macrolide from Streptomyces caniferus, Attenuates Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, Amyloid-Beta, and Tau Pathology in Vitro. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, R.-H.; Li, T.-X.; Huang, S.-S.; Kong, L.-Y.; Yang, M.-H. Enduspeptides A-F, six new cyclic depsipeptides from a coal mine derived Streptomyces sp. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.; Kogler, H.; Heyse, W.; Matter, H.; Caspers, M.; Schummer, D.; Klemke-Jahn, C.; Bauer, A.; Penarier, G.; Debussche, L.; et al. Discovery, Structure Elucidation, and Biological Characterization of Nannocystin A, a Macrocyclic Myxobacterial Metabolite with Potent Antiproliferative Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10145–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Ji, J.; Zhang, S.-L.; He, Y. Novel nannocystin A analogues as anticancer therapeutics: Synthesis, biological evaluations and structure-activity relationship studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 170, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Falkinham, J.O.; Tawfik, K.A.; Jeffs, P.; Bray, B.; Dubay, G.; Cox, J.E.; Schmidt, E.W. Burkholdines from Burkholderia ambifaria: Antifungal Agents and Possible Virulence Factors. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Abumi, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Yano, S.; Nosaka, K. Structure activity relationship study of burkholdine analogues toward simple antifungal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3199–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, K.I.; Volz, C.; Jansen, R.; Wray, V.; Hoffmann, J.; Bernecker, S.; Wink, J.; Gerth, K.; Stadler, M.; Müller, R. Pinensins: The First Antifungal Lantibiotics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarif, W.M.; Al-Footy, K.O.; Zubair, M.S.; Halid PH, M.; Ghandourah, M.A.; Basaif, S.A.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Ayyad, S.-E.N.; Badria, F.A. The role of new eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoid and known eudesmane derivatives from the red alga Laurencia obtusa as potential antifungal–antitumour agents. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.-H.; Liu, D.-Q.; Liang, T.-J.; Yu, X.-Q.; Feng, M.-T.; Yao, L.-G.; Fang, Y.; Wang, B.; Feng, L.-H.; Zhang, M.-X.; et al. Caulerprenylols A and B, two rare antifungal prenylated para-xylenes from the green alga Caulerpa racemosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2491–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Quach, T.; Molinski, T.F. Liposomal Circular Dichroism. Assignment of Remote Stereocenters in Plakinic Acids K and L from a Plakortis–Xestospongia Sponge Association. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1524–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamison, M.T.; Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F. Peroxide Natural Products from Plakortis zyggompha and the Sponge Association Plakortis halichondrioides—Xestospongia deweerdtae: Antifungal Activity against Cryptococcus gattii. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, S.-J.; Song, Y.-L.; Jiao, W.-H.; Yang, F.; Liu, X.-F.; Chen, W.-S.; Han, B.-N.; Lin, H.-W. Hippolachnin A, a New Antifungal Polyketide from the South China Sea Sponge Hippospongia lachne. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3526–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, J.C.; Wood, J.L. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Hippolachnin a Analogues. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3788–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.-H.; Hong, L.-L.; Sun, J.-B.; Piao, S.-J.; Chen, G.-D.; Deng, H.; Wang, S.-P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.-W. (±)-Hippolide J - A Pair of Unusual Antifungal Enantiomeric Sesterterpenoids from the Marine Sponge Hippospongia lachne. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3421–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Nakamura, K.; Kurimoto, S.; Sakai, K.; Fromont, J.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Zamamidine D, a Manzamine Alkaloid from an Okinawan Amphimedon sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, Y.; Kubota, T.; Shibazaki, A.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Ceratinadins A–C, new bromotyrosine alkaloids from an Okinawan marine sponge Pseudoceratina sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4569–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, M.T.; Molinski, T.F. Antipodal Crambescin A2 Homologues from the Marine Sponge Pseudaxinella reticulata. Antifungal Structure–Activity Relationships. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, E.P.; Yu, L.C.; Molinski, T.F. Antifungal Diterpene Alkaloids from the Caribbean Sponge Agelas citrina: Unified Configurational Assignments of Agelasidines and Agelasines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5131–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.-J.; Tang, X.-L.; Qin, G.-F.; Sun, Y.-T.; Li, L.; de Voogd, N.J.; Li, P.-L.; Li, G.-Q. Pyrrole Derivatives and Diterpene Alkaloids from the South China Sea Sponge Agelas nakamurai. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1600446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Hamann, M.T.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Gong, X.-B.; Xiao, J.-R.; Chen, W.-S.; Lin, H.-W. Antimicrobial Metabolites from the Paracel Islands Sponge Agelas mauritiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias Silva, M.J.; Simonet, A.M.; Silva, N.C.; Dias, A.L.T.; Vilegas, W.; Macías, F.A. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Fungistatic Compounds from Mimosa caesalpiniifolia Leaves. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, D.B.; da Costa, R.C.; Araújo, R.M.; de Paula, J.E.; Silveira, E.R.; Braz-Filho, R.; Espindola, L.S. Activity of Fabaceae species extracts against fungi and Leishmania: Vatacarpan as a novel potent anti-Candida agent. Rev. Bras. Farm. 2015, 25, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.; Maciel, D.; Freitas, V.P.; Conserva, G.A.A.; Alexandre, T.R.; Purisco, S.U.; Tempone, A.G.; Melhem, M.S.C.; Kato, M.J.; Guimarães, E.F.; et al. Bioactivity-guided isolation of laevicarpin, an antitrypanosomal and anticryptococcal lactam from Piper laevicarpu (Piperaceae). Fitoterapia 2016, 111, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.R.; Tupe, S.G.; Gample, S.P.; Chandgude, M.G.; Sarkar, D.; Deshpande, M.V.; Joshi, S.P. Antifungal dimeric chalcone derivative kamalachalcone E from Mallotus philippinensis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.-W.; Xu, M.; Li, X.-C.; Yang, C.-R.; Zhu, H.-J.; Zhang, Y.-J. Eucalmaidials A and B, phloroglucinol-coupled sesquiterpenoids from the juvenile leaves of Eucalyptus maideni. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 21373–21378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Li, W.; Chen, F.-F.; Zhang, J.-S.; Tang, Y.-Q.; Chen, L.; Tang, G.-H.; Yin, S. Monoterpene indole alkaloids from Rhazya stricta. Fitoterapia 2018, 128, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-F.; Qin, X.-J.; Ding, C.-F.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Luo, J.-R.; Liu, L.; Khan, A.; Zhang, L.-C.; Xia, C.-F.; et al. Nepenthe-Like Indole Alkaloids with Antimicrobial Activity from Ervatamia chinensis. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4116–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollataghi, A.; Coudiere, E.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Mukhtar, M.R.; Awang, K.; Litaudon, M.; Ata, A. Anti-acetylcholinesterase, anti-α-glucosidase, anti-leishmanial and anti-fungal activities of chemical constituents of Beilschmiedia species. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, S.; Shan, L.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, W. Antifungal Cyclic Peptides from Psammosilene tunicoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subban, K.; Subramani, R.; Johnpaul, M. A novel antibacterial and antifungal phenolic compound from the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis mangiferae. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yue, Q.; Jayanetti, D.R.; Swenson, D.C.; Bartholomeusz, G.A.; An, Z.; Gloer, J.B.; Bills, G.F. Anti- Cryptococcus Phenalenones and Cyclic Tetrapeptides from Auxarthron pseudauxarthron. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Du, X.; Zang, X.; Dong, L.; Gu, Z.; Cao, L.; Chen, D.; Keyhani, N.O.; Yao, L.; Qiu, J.; et al. Extraction, identification and antimicrobial activity of a new furanone, grifolaone A, from Grifola frondosa. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornsakulkarn, J.; Saepua, S.; Suvannakad, R.; Supothina, S.; Boonyuen, N.; Isaka, M.; Prabpai, S.; Kongsaeree, P.; Thongpanchang, C. Cytotoxic tropolones from the fungus Nemania sp. BCC 30850. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 3505–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, X.X.; Zhang, W.J.; Hu, S.S.; Lin, L.P.; Huo, G.M.; Jiao, R.H.; Tan, R.X.; Ge, H.M. Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory compounds from a marine fungus Pleosporales sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 6183–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.-Y.; Wang, X.-B.; Yin, G.-P.; Liu, R.-H.; Kong, L.-Y.; Yang, M.-H. Isocoumarin derivatives from the endophytic fungus, Pestalotiopsis sp. Fitoterapia 2017, 122, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phainuphong, P.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Phongpaichit, S.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Diphenyl ethers and indanones from the soil-derived fungus Aspergillus unguis PSU-RSPG204. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 5920–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gao, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.-L.; Li, L.; Li, X.-B.; Chang, W.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-T.; Lou, H.-X. p -Terphenyl Derivatives from the Endolichenic Fungus Floricola striata. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chang, W.; Shi, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, W.; Lou, H. Floricolin C elicits intracellular reactive oxygen species accumulation and disrupts mitochondria to exert fungicidal action. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Phadke, S.; Lu, Z.; Beyhan, S.; Abdel Aziz, M.H.; Reilly, C.; Schmidt, E.W. Onydecalins, Fungal Polyketides with Anti- Histoplasma and Anti-TRP Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Kakule, T.B.; Reilly, C.A.; Beyhan, S.; Schmidt, E.W. Secondary Metabolites of Onygenales Fungi Exemplified by Aioliomyces pyridodomos. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Jamieson, C.S.; Ohashi, M.; Tang, M.-C.; Houk, K.N.; Tang, Y. Genome-Mined Diels–Alderase Catalyzes Formation of the cis -Octahydrodecalins of Varicidin A and B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Yuan, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, B.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Gao, Z. Heterologous Expression of Ilicicolin H Biosynthetic Gene Cluster and Production of a New Potent Antifungal Reagent, Ilicicolin J. Molecules 2019, 24, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Lacey, H.J.; Crombie, A.; Vuong, D.; Pitt, J.I.; Lacey, E.; Chooi, Y.-H.; Piggott, A.M. Discovery and Heterologous Biosynthesis of the Burnettramic Acids: Rare PKS-NRPS-Derived Bolaamphiphilic Pyrrolizidinediones from an Australian Fungus, Aspergillus burnettii. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierle, A.A.; Stierle, D.B.; Decato, D.; Priestley, N.D.; Alverson, J.B.; Hoody, J.; McGrath, K.; Klepacki, D. The Berkeleylactones, Antibiotic Macrolides from Fungal Coculture. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaad, A.S.; Al-Aonazi, N.K.; Al-Othman, M.R.; Zain, M.E.; El-Meligy, R.M.; El-Sayed, N. Anticandidal Activity of Extracts and a Novel Compound, Amnomopin, Isolated From Petriella setifera. Phyther. Res. 2017, 31, 1504–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandini, L.M.B.; Neto, A.T.; Pedroso, M.; Antoniolli, Z.I.; Burrow, R.A.; Bortoluzzi, A.J.; Mostardeiro, M.A.; da Silva, U.F.; Dalcol, I.I.; Morel, A.F. Lanostane-type triterpenes from the fungal endophyte Scleroderma UFSMSc1 (Persoon) Fries. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; He, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Antimicrobial Dolabellanes and Atranones from a Marine-Derived Strain of the Toxigenic Fungus Stachybotrys chartarum. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intaraudom, C.; Boonyuen, N.; Suvannakad, R.; Rachtawee, P.; Pittayakhajonwut, P. Penicolinates A–E from endophytic Penicillium sp. BCC16054. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, A.; Tamoto, H.; Ishino, M.; Kimura, E.; Sugita, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Takahashi, K.; Shiro, M.; Koyama, K. Pyridone Alkaloids from a Marine-Derived Fungus, Stagonosporopsis cucurbitacearum, and Their Activities against Azole-Resistant Candida albicans. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Bao, L.; Chen, Q.; Song, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, E.; et al. Decalin-containing tetramic acids and 4-hydroxy-2-pyridones with antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity from the fungus Coniochaeta cephalothecoides collected in Tibetan plateau (Medog). J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 11474–11486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, C.; Helaly, S.E.; Thongbai, B.; Hyde, K.D.; Stadler, M. Pyristriatins A and B: Pyridino-Cyathane Antibiotics from the Basidiomycete Cyathus cf. striatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1684–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz-López, F.J.; Monteiro, M.C.; González-Menéndez, V.; Tormo, J.R.; Genilloud, O.; Bills, G.F.; Vicente, F.; Zhang, C.; Roemer, T.; Singh, S.B.; et al. Cyclic colisporifungin and linear cavinafungins, antifungal lipopeptides isolated FROM Colispora cavincola. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoppey, D.; Lee, C.M.; Janoschke, M.; Lee, B.H.; Wan, K.F.; Dong, H.; Mathys, P.; Filipuzzi, I.; Schuhmann, T.; Riedl, R.; et al. The natural product cavinafungin selectively interferes with Zika and Dengue virus replication by inhibition of the host signal peptidase. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Ondeyka, J.; Harris, G.; Herath, K.; Zink, D.; Vicente, F.; Bills, G.; Collado, J.; Platas, G.; González del Val, A.; et al. Isolation, structure, and biological activity of phaeofungin, a cyclic lipodepsipeptide from a Phaeosphaeria sp. Using the genome-wide Candida albicans fitness test. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, I.; Kanasaki, R.; Yoshikawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Fujie, A.; Hamamoto, H.; Sekimizu, K. Discovery of a new antifungal agent ASP2397 using a silkworm model of Aspergillus fumigatus infection. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2017, 70, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, I.; Yoshimura, S.; Masaki, T.; Takase, S.; Ohsumi, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Furukawa, S.; Fujie, A. ASP2397: A novel antifungal agent produced by Acremonium persicinum MF-347833. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2017, 70, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, I.; Ohsumi, K.; Takeda, S.; Katsumata, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Akamatsu, S.; Mitori, H.; Nakai, T. ASP2397 is a novel natural compound that exhibits rapid and potent fungicidal activity AGAINST Aspergillus species through a specific transporter. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e02689-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
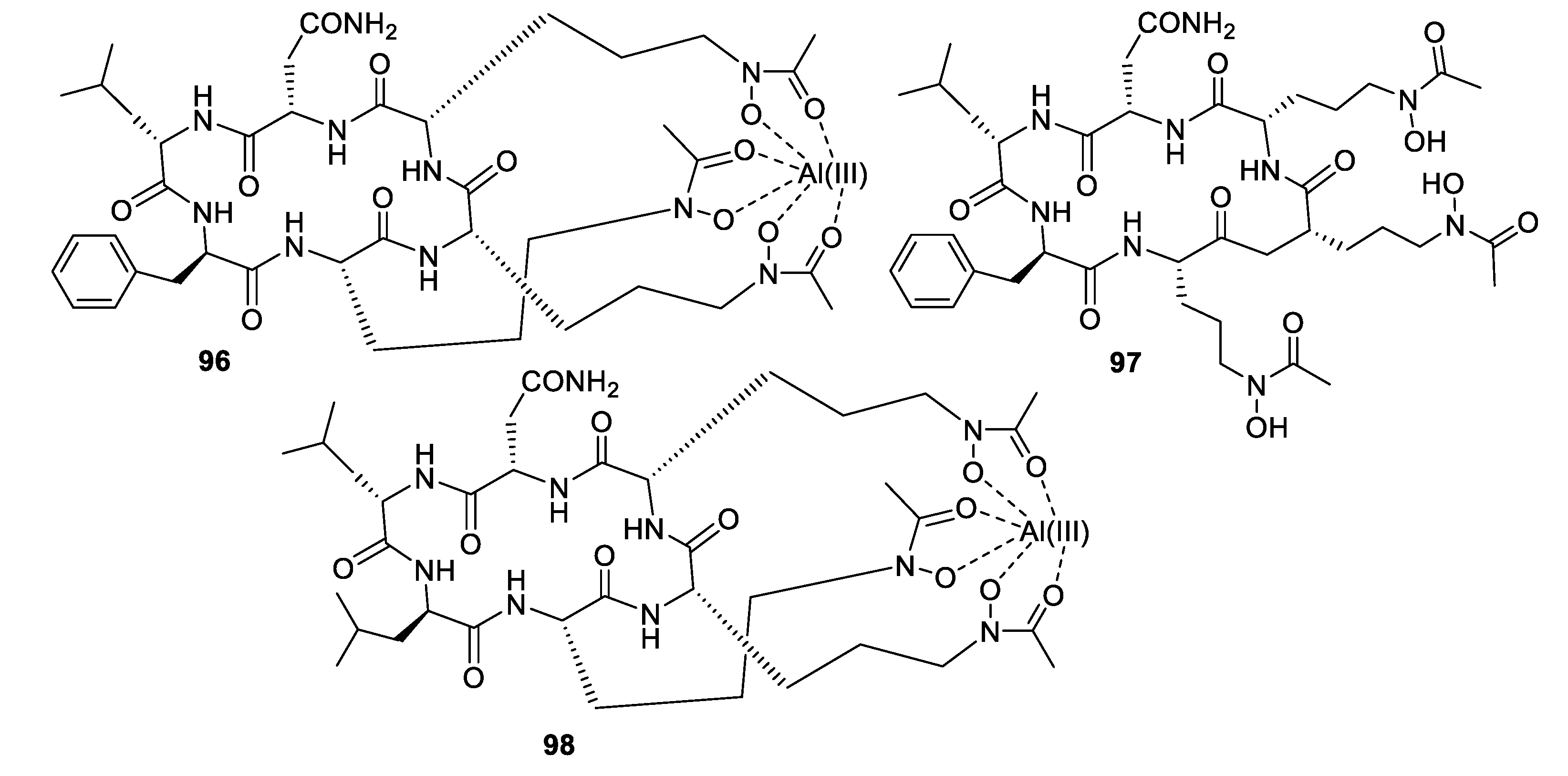
- Luo, M.; Zang, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Song, X.; Ju, J.; Huang, H. Natural hydroxamate-containing siderophore acremonpeptides A–D and an aluminum complex of acremonpeptide D from the marine-derived Acremonium persicinum SCSIO 115. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
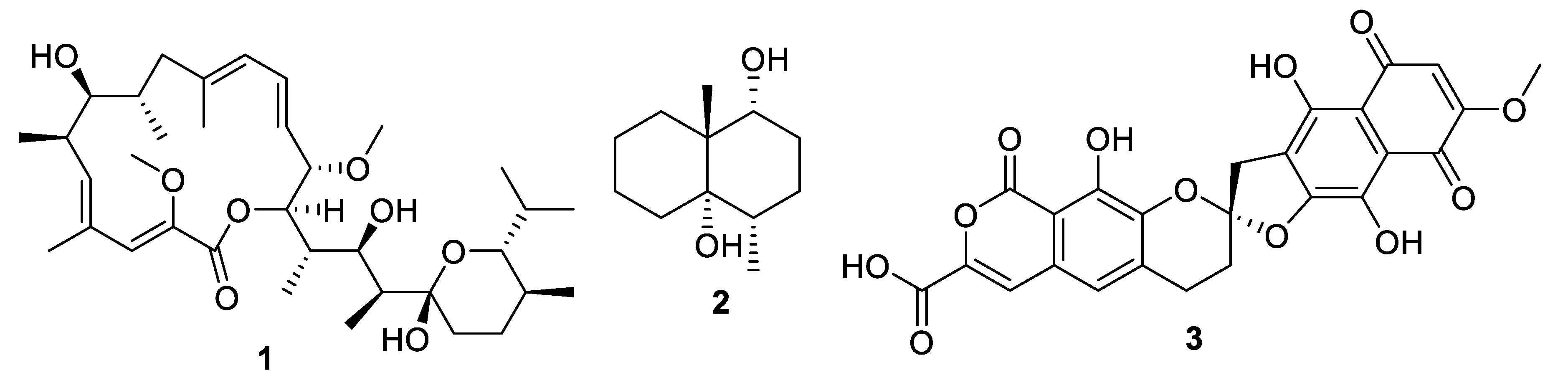
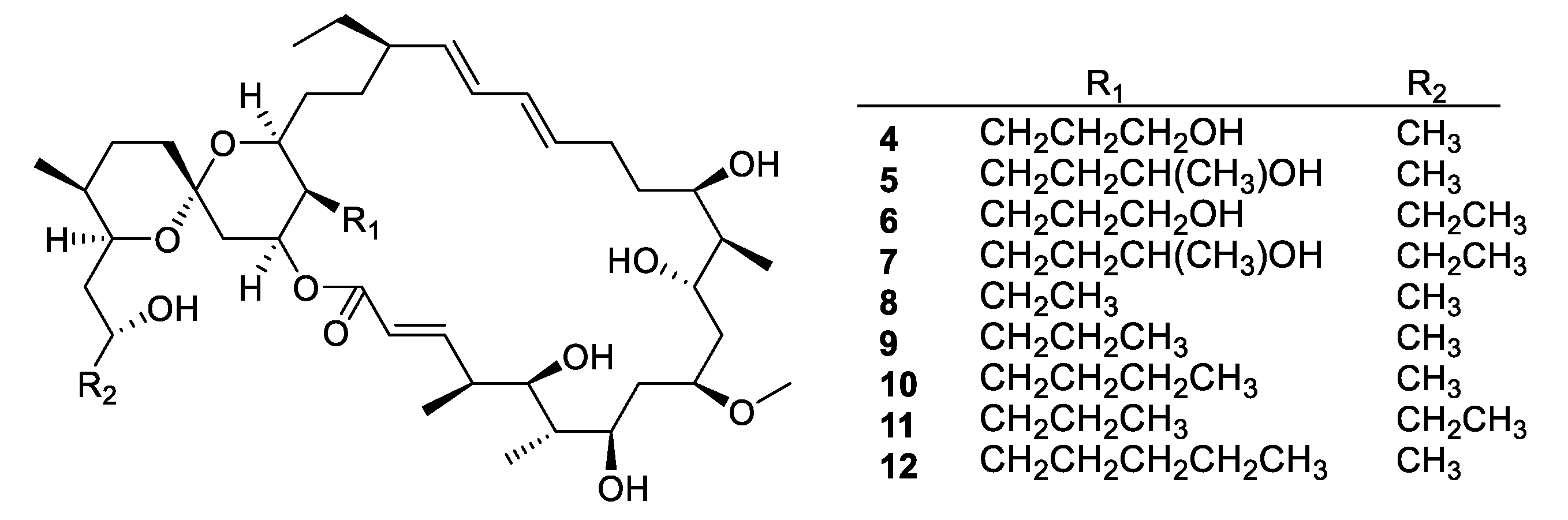
| Compound | MW | clogP | HBD | HBA | nrot | TPSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 607 | 4.8 | 3 | 8 | 10 | 115 |
| 2 | 198 | 2.1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 41 |
| 3 | 508 | 2.9 | 4 | 12 | 5 | 186 |
| 8 | 751 | 7.0 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 155 |
| 17 | 1123 | 7.6 | 13 | 18 | 26 | 312 |
| 21 | 1580 | 0.9 | 15 | 29 | 33 | 472 |
| 28 | 987 | 4.7 | 6 | 19 | 11 | 253 |
| 30 | 817 | 4.3 | 4 | 12 | 9 | 167 |
| 31 | 1200 | −5.7 | 23 | 32 | 36 | 546 |
| 35 | 2144 | −0.4 | 26 | 55 | 30 | 876 |
| 36 | 236 | 2.4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 41 |
| 37 | 274 | 3.0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 41 |
| 42 | 419 | 7.7 | 1 | 4 | 14 | 56 |
| 44 | 385 | 6.2 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 47 |
| 45 | 713 | 8.1 | 7 | 7 | 10 | 110 |
| 46 | 667 | 0.7 | 6 | 13 | 10 | 188 |
| 48 | 393 | 3.1 | 6 | 8 | 13 | 130 |
| 53 | 438 | 5.0 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 121 |
| 54 | 423 | 2.0 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 61 |
| 55 | 439 | 2.3 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 70 |
| 56 | 340 | 1.9 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 124 |
| 57 | 423 | 6.0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 68 |
| 58 | 297 | 2.7 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 48 |
| 59 | 1065 | 8.0 | 11 | 18 | 23 | 319 |
| 60 | 487 | 6.5 | 4 | 7 | 12 | 132 |
| 61 | 352 | 3.0 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 64 |
| 62 | 370 | 0.5 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 51 |
| 63 | 281 | 2.5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 33 |
| 64 | 901 | −0.1 | 10 | 21 | 9 | 303 |
| 65 | 194 | 1.3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 51 |
| 66 | 358 | 3.0 | 3 | 7 | 6 | 121 |
| 68 | 200 | −1.6 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 73 |
| 69 | 206 | −1.0 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 67 |
| 70 | 316 | 3.5 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 84 |
| 71 | 264 | 0.8 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 104 |
| 72 | 427 | 7.9 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 96 |
| 74 | 306 | 4.7 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 64 |
| 75 | 329 | 6.8 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 54 |
| 76 | 327 | 6.7 | 2 | 2 | 9 | 41 |
| 77 | 376 | 3.3 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 95 |
| 78 | 432 | 5.4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 87 |
| 79 | 770 | 3.2 | 8 | 13 | 35 | 218 |
| 81 | 405 | 2.3 | 3 | 7 | 6 | 146 |
| 82 | 779 | 6.4 | 8 | 13 | 14 | 216 |
| 83 | 457 | 9.5 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 30 |
| 84 | 391 | 2.7 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 81 |
| 85 | 399 | 5.1 | 1 | 6 | 14 | 89 |
| 87 | 444 | 1.4 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 128 |
| 90 | 446 | 3.5 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 131 |
| 91 | 442 | 3.5 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 89 |
| 92 | 1064 | 4.9 | 10 | 20 | 38 | 294 |
| 93 | 792 | 6.6 | 5 | 14 | 31 | 200 |
| 95 | 904 | −2.0 | 13 | 23 | 23 | 368 |
| 97 | 891 | −2.5 | 11 | 23 | 21 | 339 |
| Average | 569 | 3.4 | 5 | 10 | 11 | 155 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldholmi, M.; Marchand, P.; Ourliac-Garnier, I.; Le Pape, P.; Ganesan, A. A Decade of Antifungal Leads from Natural Products: 2010–2019. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040182
Aldholmi M, Marchand P, Ourliac-Garnier I, Le Pape P, Ganesan A. A Decade of Antifungal Leads from Natural Products: 2010–2019. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040182
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldholmi, Mohammed, Pascal Marchand, Isabelle Ourliac-Garnier, Patrice Le Pape, and A. Ganesan. 2019. "A Decade of Antifungal Leads from Natural Products: 2010–2019" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 4: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040182
APA StyleAldholmi, M., Marchand, P., Ourliac-Garnier, I., Le Pape, P., & Ganesan, A. (2019). A Decade of Antifungal Leads from Natural Products: 2010–2019. Pharmaceuticals, 12(4), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040182









