Chemical Probes for the Adenosine Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
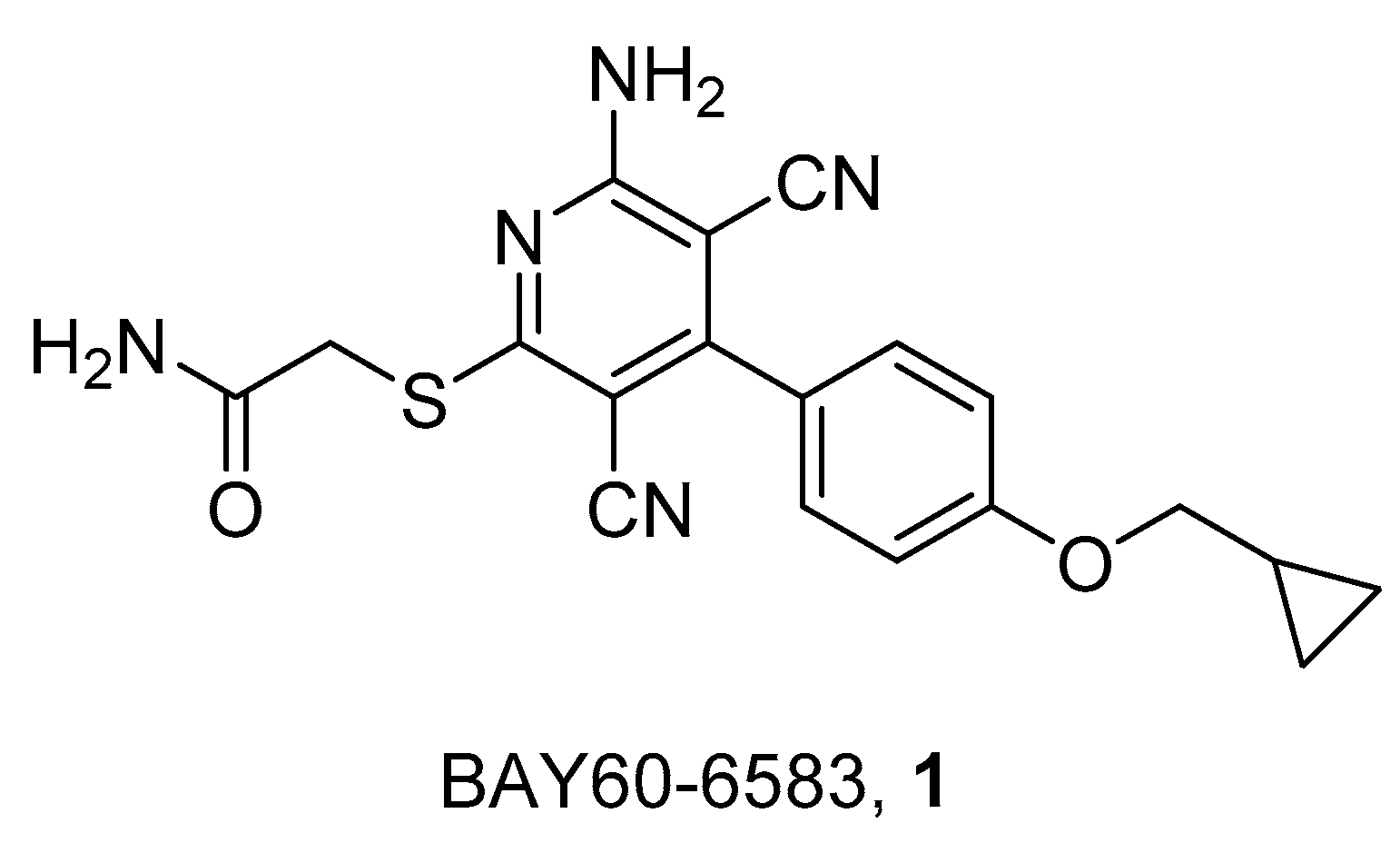
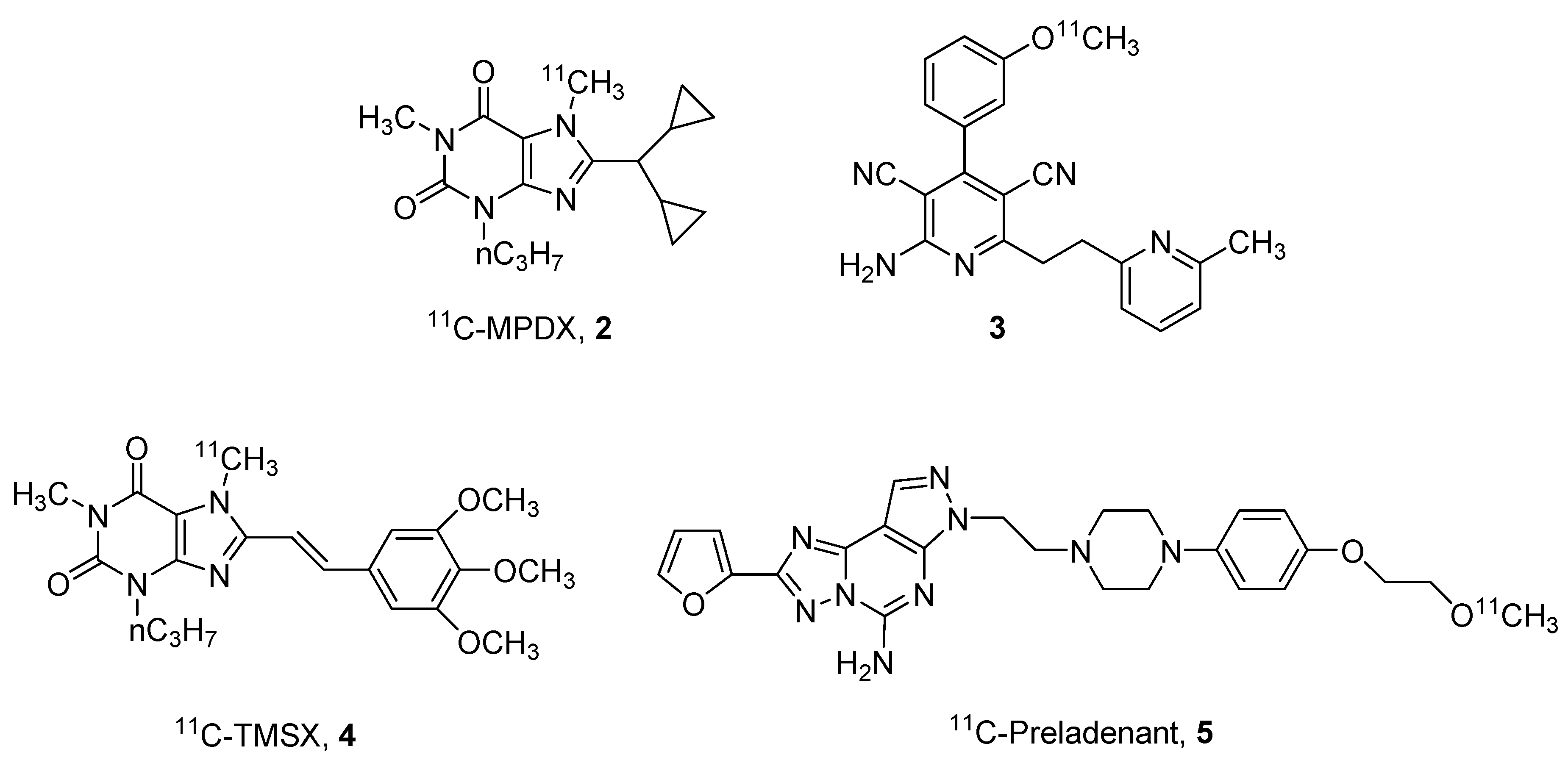
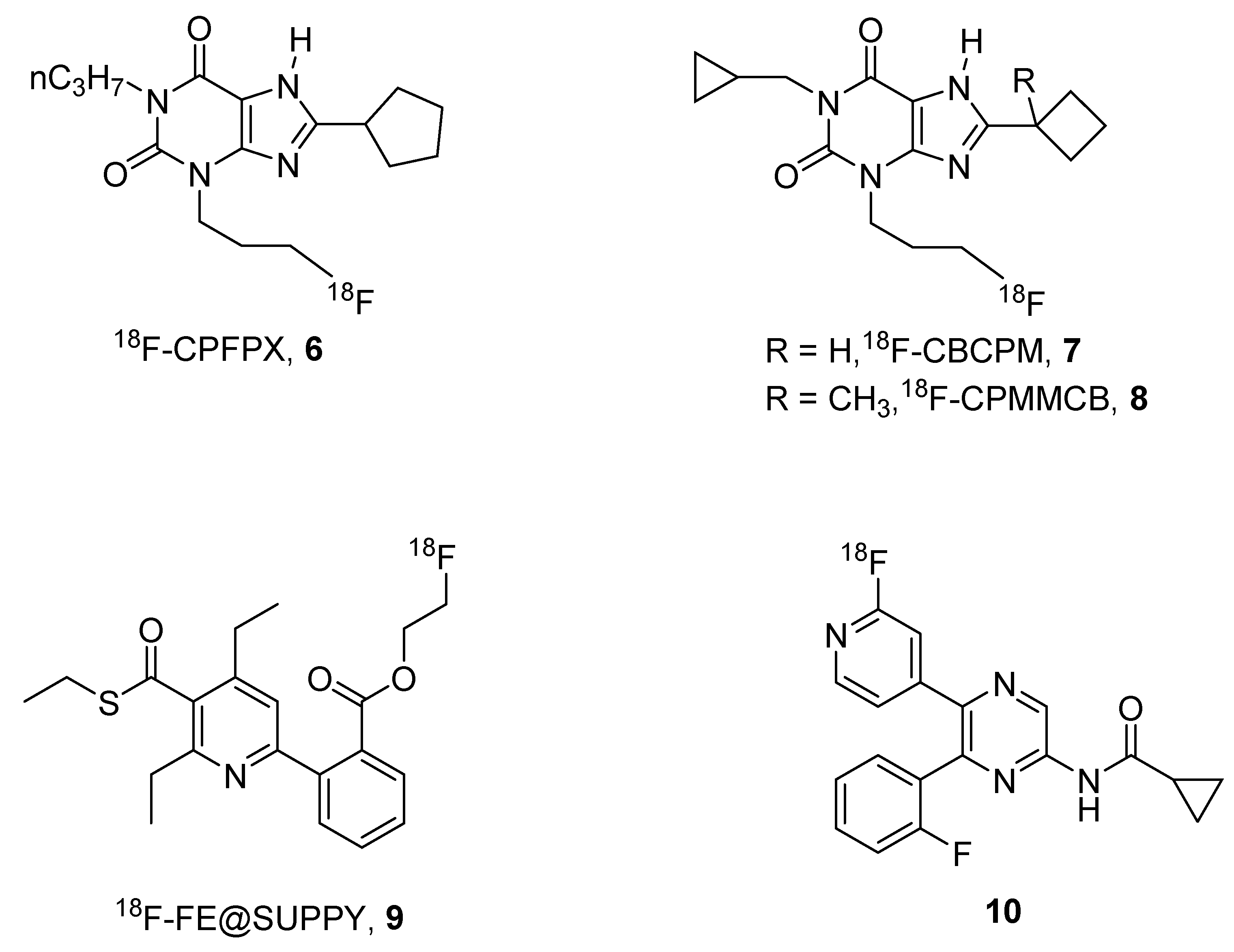
2. Radioligands and Radiotracers
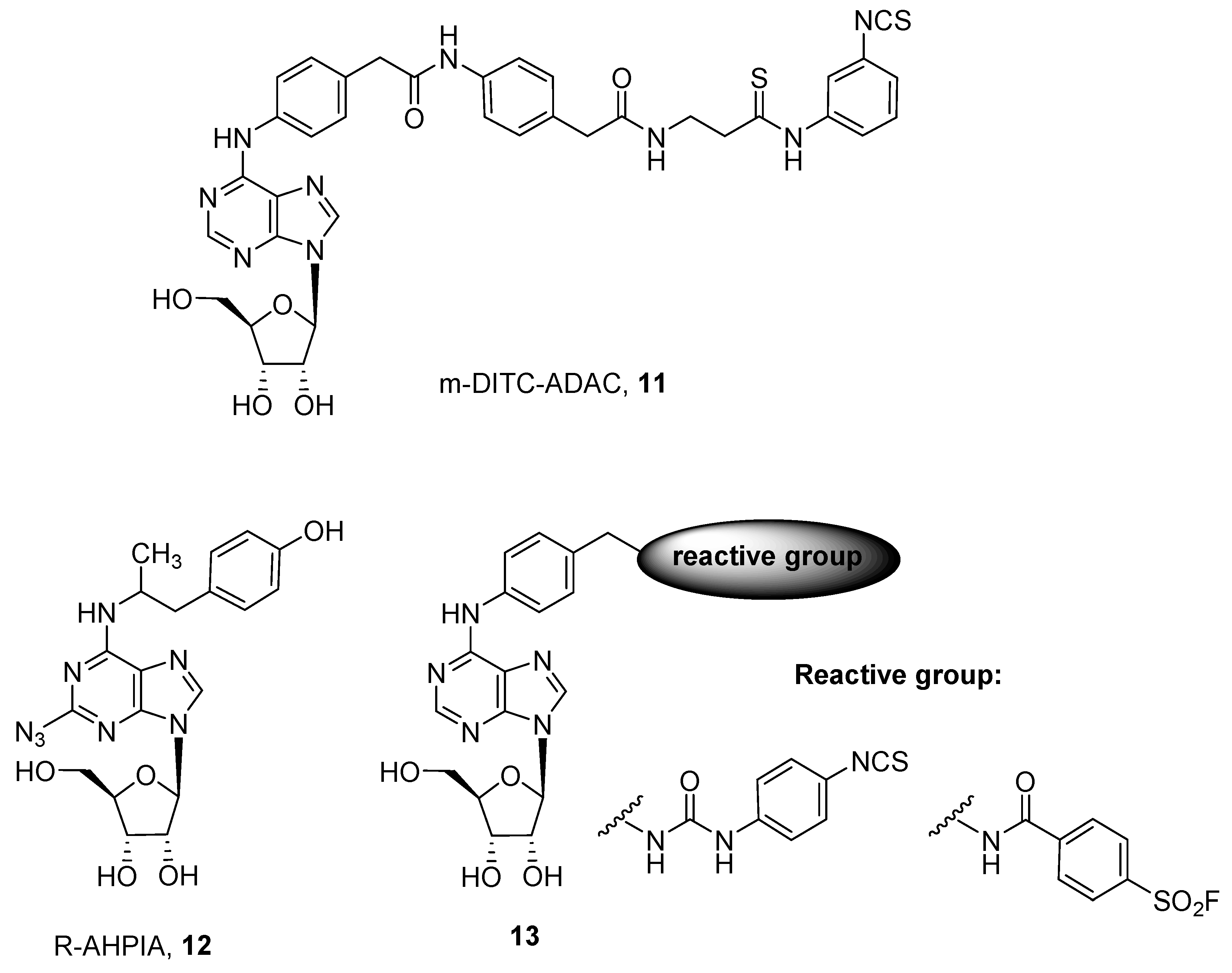
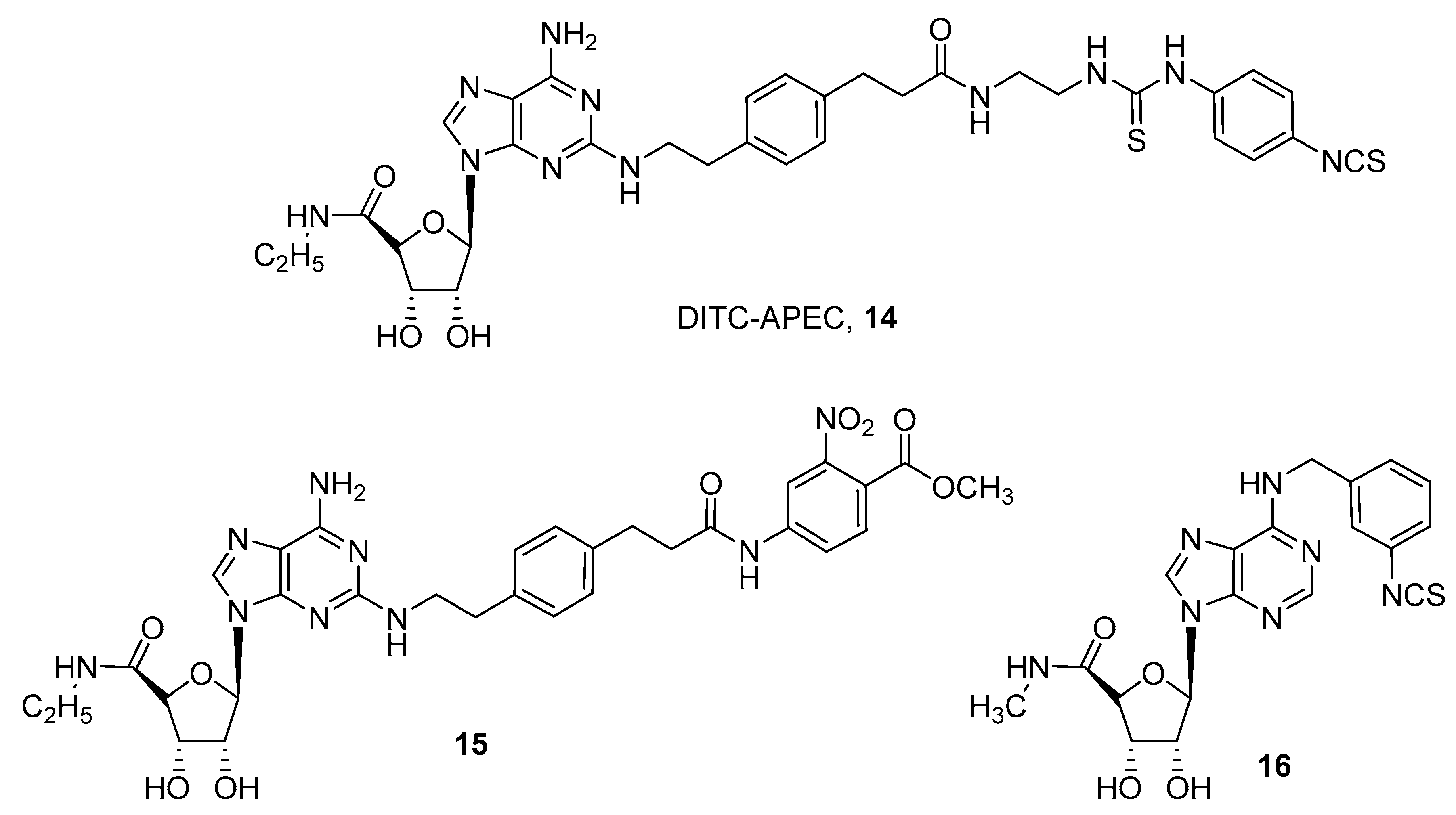
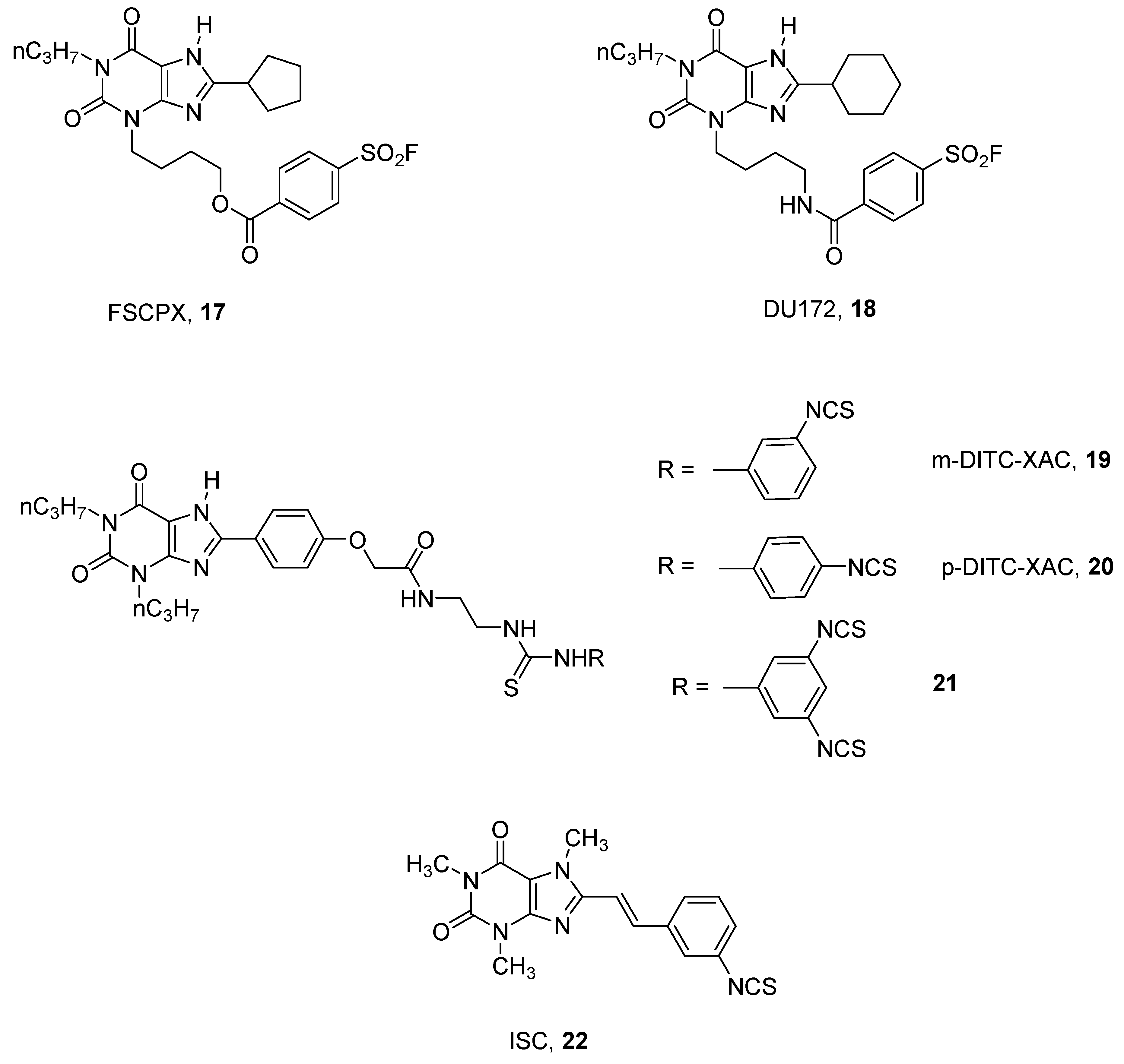
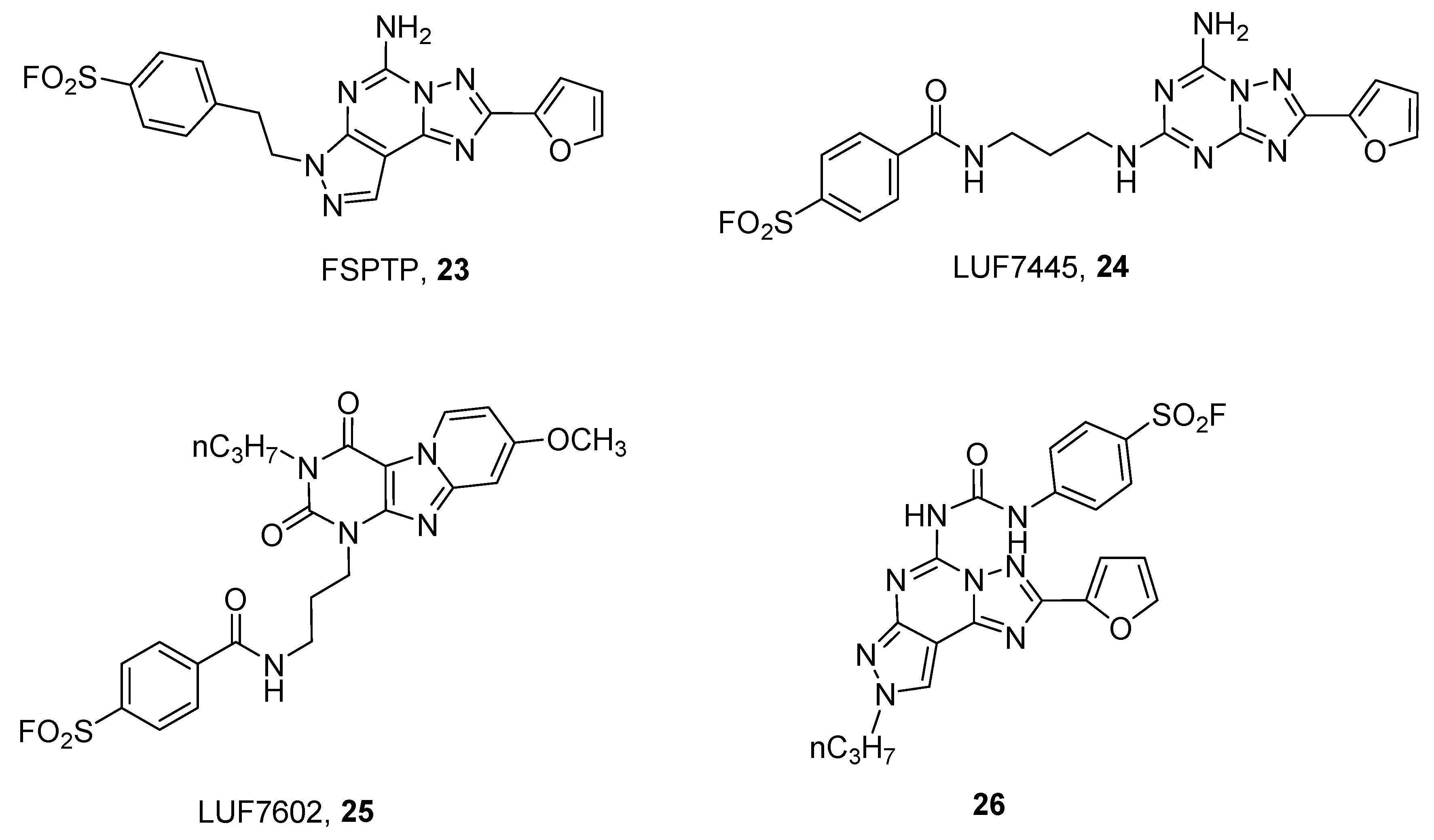
3. Covalent Ligands
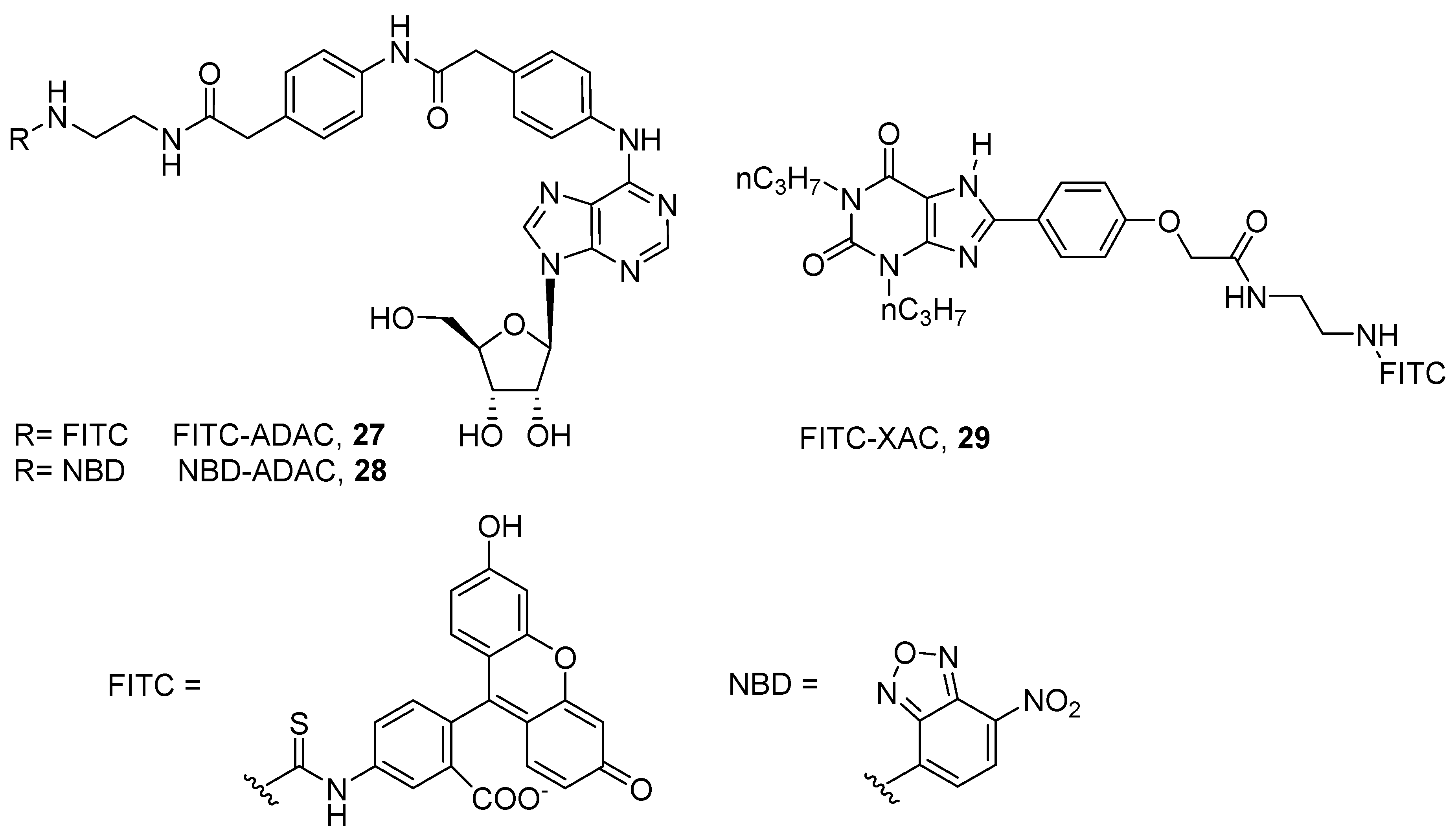
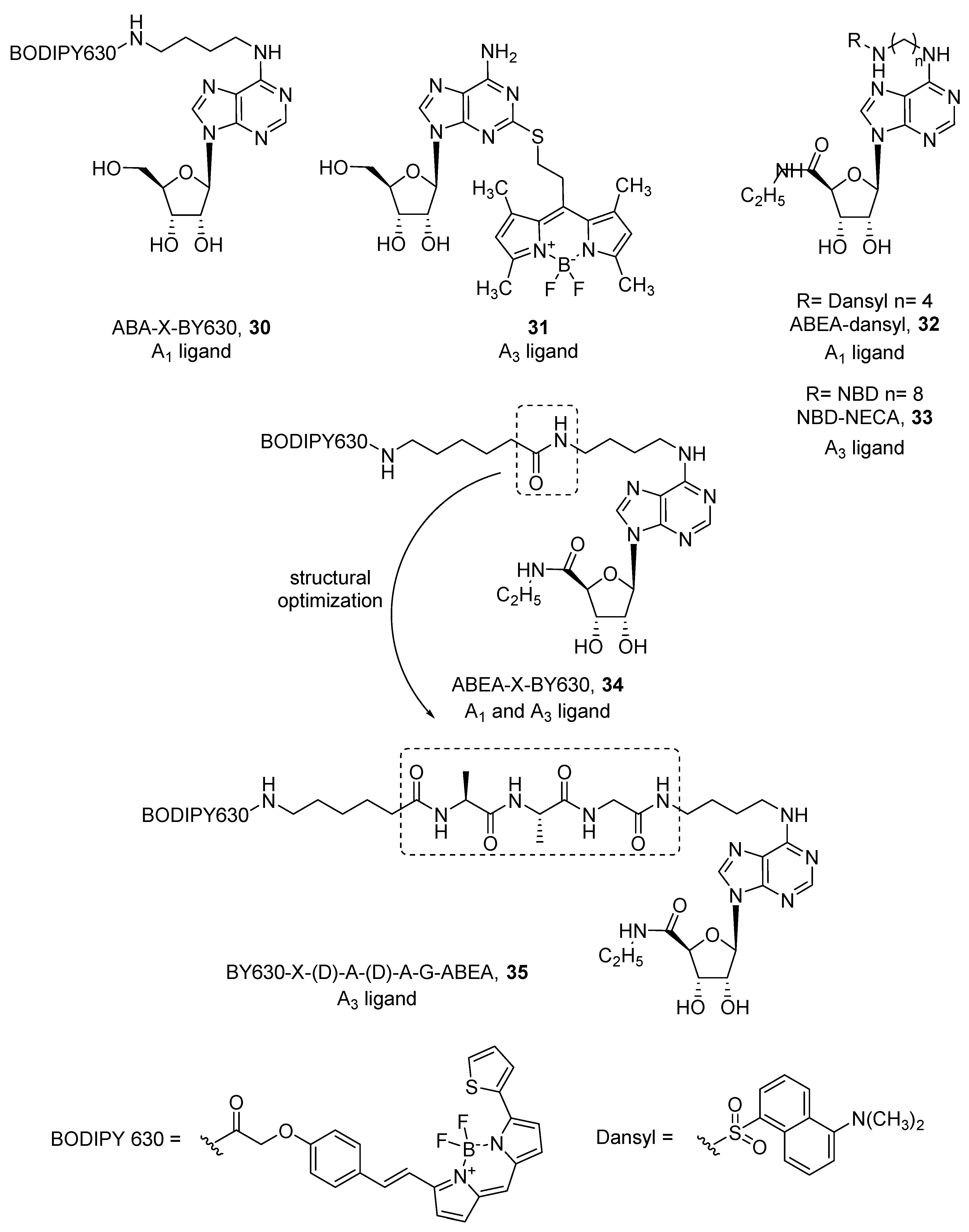
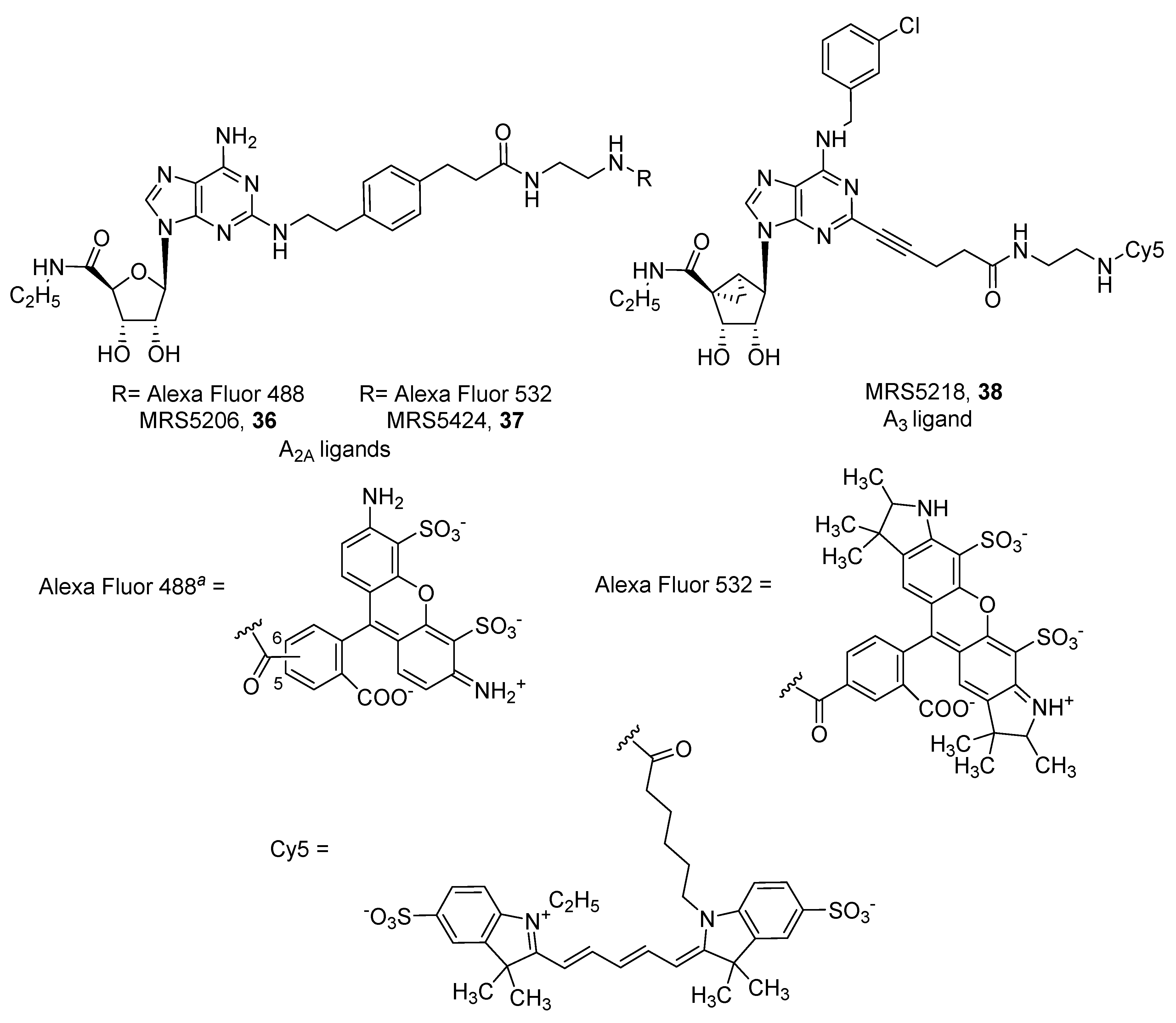
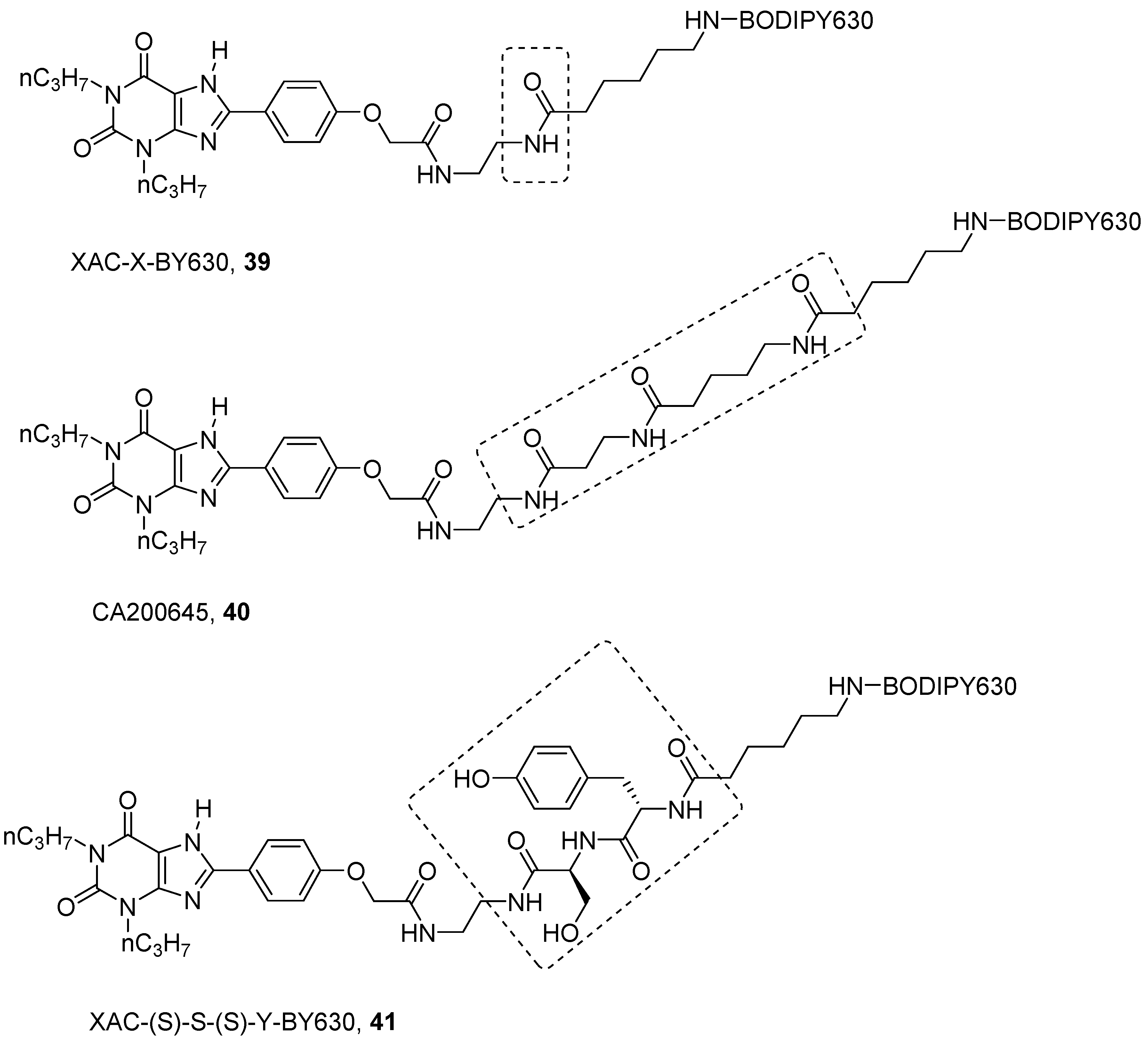
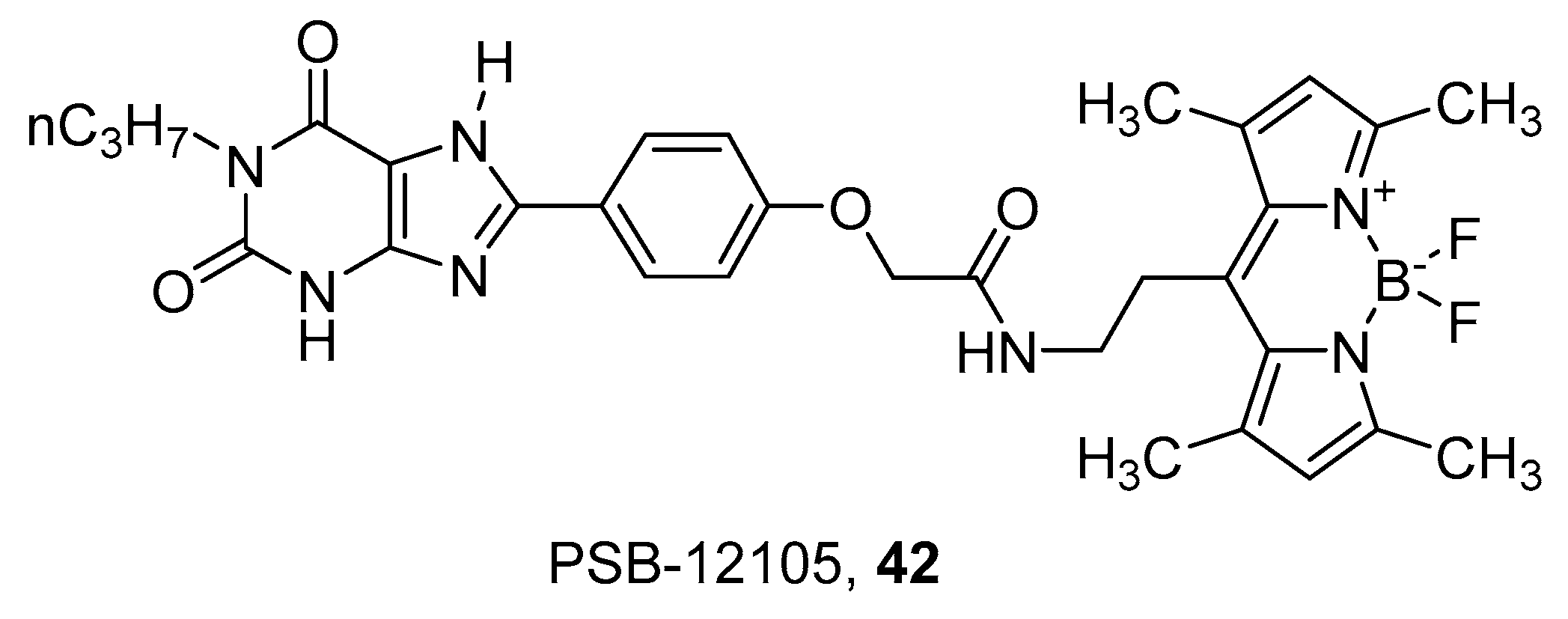
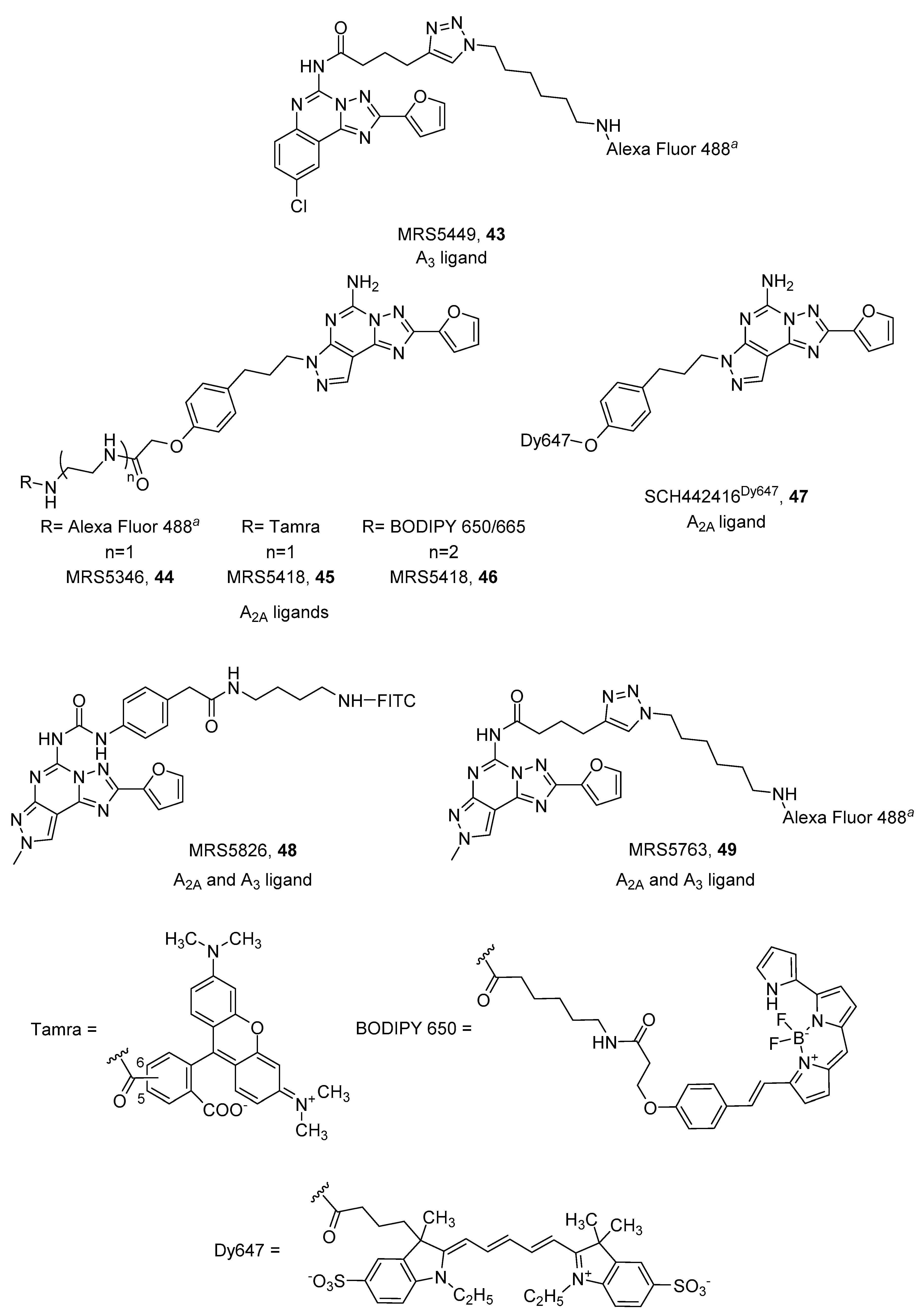
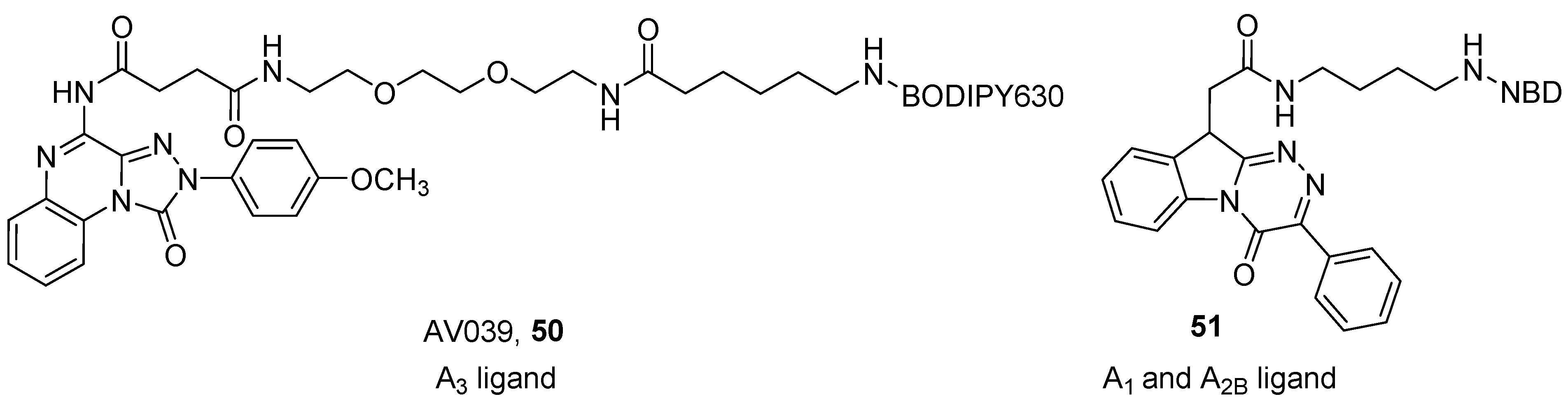
4. Fluorescent Ligands
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iizuka, H.; Adachi, K.; Halprin, K.M.; Levine, V. Adenosine and adenine nucleotides stimulation of skin (epidermal) adenylate cyclase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 1976, 444, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawynok, J.; Jhamandas, K.H. Inhibition of acetylcholine release from cholinergic nerves by adenosine, adenine nucleotides and morphine: Antagonism by theophylline. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1976, 197, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of adenosine receptors: The state of the art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.; Levitzki, A. Adenosine receptor permanently coupled to turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 2134–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, R.F. Adenosine receptor activation by adenine nucleotides requires conversion of the nucleotides to adenosine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1980, 315, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Klotz, K.N.; Linden, J. International Union of Pharmacology. XXV. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 527–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fredholm, B.B.; IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Linden, J.; Müller, C.E. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXXI. Nomenclature and classification of adenosine receptors—An update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciruela, F.; Jacobson, K.A.; Fernández-Dueñas, V. Portraying G protein-coupled receptors with fluorescent ligands. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.J.; Milligan, G. Structural and biophysical characterisation of G protein-coupled receptor ligand binding using resonance energy transfer and fluorescent labelling techniques. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichert, D.; Gmeiner, P. Covalent Molecular Probes for class A G protein-coupled receptors: Advances and applications. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xie, X. Tools for GPCR drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Bittner, G.C.; Ricq, E.L.; Hooker, J.M. A Philosophy for CNS radiotracer design. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.E.; Jacobson, K.A. Recent developments in adenosine receptor ligands and their potential as novel drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2011, 1808, 1290–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Waarde, A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Zhou, X.; Khanapur, S.; Tsukada, H.; Ishiwata, K.; Luurtsema, G.; de Vries, E.F.J.; Elsinga, P.H. Potential therapeutic applications of adenosine A2A receptor ligands and opportunities for A2A receptor imaging. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 5–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glukhova, A.; Thal, D.M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Vecchio, E.A.; Jörg, M.; Scammells, P.J.; May, L.T.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Structure of the adenosine A1 receptor reveals the basis for subtype selectivity. Cell 2017, 168, 867–877.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jörg, M.; Glukhova, A.; Abdul-Ridha, A.; Vecchio, E.A.; Nguyen, A.T.N.; Sexton, P.M.; White, P.J.; May, L.T.; Christopoulos, A.; Scammells, P.J. Novel irreversible agonists acting at the A1 adenosine receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 11182–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Furstenberg, A.; Huber, T. Labeling and single-molecule methods to monitor G proteincoupled receptor dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 186–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddart, L.A.; White, C.W.; Nguyen, K.; Hill, S.J.; Pfleger, K.D.G.G. Fluorescence-and bioluminescence-based approaches to study GPCR ligand binding. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 3028–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddart, L.A.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. Probing the pharmacology of G protein-coupled receptors with fluorescent ligands. Neuropharmacology 2015, 98, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauk, M.; Hoffmann, C. Intramolecular and intermolecular FRET sensors for GPCRs—Monitoring conformational changes and beyond. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, S.L.; Federico, S.; Venkatesan, G.; Mandel, A.L.; Shao, Y.-M.; Moro, S.; Spalluto, G.; Pastorin, G. The A3 adenosine receptor as multifaceted therapeutic target: Pharmacology, medicinal chemistry, and in silico approaches. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33, 235–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, K. Adenosine receptors and their ligands. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, S.; Gao, Z.; Jacobson, K.A.; Spalluto, G. Progress in the pursuit of therapeutic adenosine receptor antagonists. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 26, 131–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Pannell, L.K.; Ji, X.; Jarvis, M.F.; Williams, M.; Hutchison, A.J.; Barrington, W.W.; Stiles, G.L. Agonist derived molecular probes for A2 adenosine receptors. J. Mol. Recognit. 1989, 2, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, S.; Alnouri, W.M.; Pleiss, U.; Müller, C.E. Tritium-labeled agonists as tools for studying adenosine A2B receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Khanapur, S.; Sijbesma, J.W.; Ishiwata, K.; Elsinga, P.H.; Meerlo, P.; Dierckx, R.A.; van Waarde, A. Use of 11C-MPDX and PET to study adenosine A1 receptor occupancy by nonradioactive agonists and antagonists. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, S.; Inaji, M.; Nariai, T.; Oda, K.; Sakata, M.; Toyohara, J.; Ishii, K.; Ishiwata, K.; Maehara, T. Increased Binding Potential of Brain Adenosine A1 Receptor in Chronic Stages of Patients with Diffuse Axonal Injury Measured with [1-methyl-11C] 8-dicyclopropylmethyl-1-methyl-3-propylxanthine Positron Emission Tomography Imaging. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishina, M.; Ishii, K.; Kimura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kitamura, S.; Ishibashi, K.; Sakata, M.; Oda, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kimura, K.; et al. Adenosine A1 receptors measured with 11C-MPDX PET in early Parkinson’s disease. Synapse 2017, 71, e21979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Gao, Z.; Tyler, R.; Stodden, T.; Li, Y.; Ramsey, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, G.; Wiers, C.E.; Fowler, J.S.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of the first adenosine A1 receptor partial agonist radioligand for positron emission tomography imaging. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9966–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahesmaa, M.; Oikonen, V.; Helin, S.; Luoto, P.; Din, U.M.; Pfeifer, A.; Nuutila, P.; Virtanen, K.A. Regulation of human brown adipose tissue by adenosine and A2A receptors—Studies with [15O]H2O and [11C]TMSX PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Khanapur, S.; Huizing, A.P.; Zijlma, R.; Schepers, M.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Van Waarde, A.; De Vries, E.F.J.; Elsinga, P.H. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of 2-(2-furanyl)-7-[2-[4-[4-(2-[11C]methoxyethoxy)phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]7H-pyrazolo[4,3-e][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine-5-amine ([11C]preladenant) as a PET tracer for the imaging of. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9204–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Elsinga, P.H.; Khanapur, S.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; de Vries, E.F.J.; de Jong, J.R. Radiation dosimetry of a novel adenosine A2A receptor radioligand [11C]preladenant based on PET/CT imaging and ex vivo biodistribution in rats. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmenhorst, D.; Kroll, T.; Wedekind, F.; Weisshaupt, A.; Beer, S.; Bauer, A. In vivo kinetic and steady-state quantification of 18F-CPFPX binding to rat cerebral A1 Adenosine receptors: Validation by displacement and autoradiographic experiments. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmenhorst, D.; Meyer, P.T.; Matusch, A.; Winz, O.H.; Bauer, A. Caffeine occupancy of human cerebral A1 adenosine receptors: In vivo quantification with 18F-CPFPX and PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabbi-Schroeter, D.; Elmenhorst, D.; Oskamp, A.; Laskowski, S.; Bauer, A.; Kroll, T. Effects of long-term caffeine consumption on the adenosine A1 receptor in the rat brain: An in vivo PET study with [18F]CPFPX. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2018, 20, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreft, S.; Bier, D.; Holschbach, M.H.; Schulze, A.; Coenen, H.H. New potent A1 adenosine receptor radioligands for positron emission tomography. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadsak, W.; Mien, L.-K.; Shanab, K.; Ettlinger, D.E.; Haeusler, D.; Sindelar, K.; Lanzenberger, R.R.; Spreitzer, H.; Viernstein, H.; Keppler, B.K.; et al. Preparation and first evaluation of [18F]FE@SUPPY: A new PET tracer for the adenosine A3 receptor. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2008, 35, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, D.; Nics, L.; Mien, L.-K.; Ungersboeck, J.; Lanzenberger, R.R.; Shanab, K.; Sindelar, K.M.; Viernstein, H.; Wagner, K.-H.; Dudczak, R.; et al. [18F]FE@SUPPY and [18F]FE@SUPPY:2—Metabolic considerations. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2010, 37, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, M.; Hinz, S.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Namasivayam, V.; Dukic-Stefanovic, S.; Teodoro, R.; Toussaint, M.; Kranz, M.; Juhl, C.; Steinbach, J.; et al. Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of a fluorine-18 labeled pyrazine based radioligand for PET imaging of the adenosine A2B receptor. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4650–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Jacobson, K.A.; Downey, J.M. An irreversible A1-selective adenosine agonist preconditions rabbit heart. Can. J. Cardiol. 1996, 12, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Belardinelli, L.; Jacobson, K.A.; Otero, D.H.; Baker, S.P. Persistent activation by and receptor reserve for an irreversible A1 -adenosine receptor agonist in DDT 1 MF-2 cells and in guinea pig heart. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, K.N.; Cristalli, G.; Grifantini, M. Photoaffinity labeling of A1-adenosine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 14659–14664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Stiles, G.L.; Ji, X. Chemical modification and irreversible inhibition of striatal A2A adenosine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 42, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niiya, K.; Jacobson, K.A.; Silvia, S.K.; Olsson, R.A. Covalent binding of a selective agonist irreversibly activates guinea pig coronary artery A2 adenosine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1993, 347, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moss, S.M.; Jayasekara, P.S.; Paoletta, S.; Gao, Z.; Jacobson, K.A. Structure-based design of reactive nucleosides for site-specific modification of the A2A adenosine receptor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.D.; Gallo-Rodriguez, C.; Jacobson, K.A. A selective agonist affinity label for A3 adenosine receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van Muijlwijk-koezen, J.E.; Timmerman, H.; Van Der Sluis, R.P.; Van De Stolpe, A.C.; Menge, W.M.P.B.; Beukers, M.W.; Van Der Graaf, P.H.; Groote, D.; Ijzerman, A.P. Synthesis and use of FSCPX, an irreversible adenosine A1 antagonist, as a receptor knock-down tool. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauglehole, A.R.; Baker, P.; Scammells, P.J. New irreversible adenosine A1 antagonists based on FSCPX. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 3179–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauglehole, A.R.; Baker, S.P.; Scammells, P.J. Fluorosulfonyl-substituted xanthines as selective irreversible antagonists for the A1—Adenosine receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4973–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, M.; Shryock, J.C.; Scammells, P.J.; Ruble, J.; Baker, S.P.; Belardinelli, L. A novel irreversible antagonist of the A1-adenosine receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996, 50, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, A.; Beukers, M.W.; van der Graaf, P.H.; Lang, H.; van Muijlwijk-koezen, J.; de Groote, M.; Menge, W.; Schwabe, U.; Ijzerman, A.P. Modulation of agonist responses at the A1 adenosine receptor by an irreversible antagonist, receptor-G protein uncoupling and by the G protein activation state. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Barone, S.; Kammula, U.; Stiles, G.L. Electrophilic derivatives of purines as irreversible inhibitors of A1 adenosine receptors. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boring, D.L.; Ji, X.D.; Zimmet, J.; Taylor, K.E.; Stiles, G.L.; Jacobson, K.A. Trifunctional agents as a design strategy for tailoring ligand properties: Irreversible inhibitors of A1 adenosine receptors. Bioconjugate Chem. 1991, 2, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scammells, P.J.; Baker, S.P.; Belardinelli, L.; Olsson, R.A. Substituted 1, 3-Dipropylxanthines as irreversible antagonists of A1 adenosine receptors. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Callo-rodriguez, C.; Jacobson, K.A. 8-(3-Isothiocyanatostyryl) caffeine is a selective, irreversible inhibitor of striatal A2-Adenosine Receptors. Drug Dev. Res. 1993, 29, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shryock, J.C.; Snowdy, S.; Baraldi, P.G.; Cacciari, B.; Spalluto, G.; Monopoli, A.; Ongini, E.; Baker, S.P.; Belardinelli, L. A2A -Adenosine Receptor reserve for coronary vasodilation. Circulation 1998, 98, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; van Veldhoven, J.P.D.; Offringa, J.; Kuiper, B.J.; Lenselink, E.B.; Heitman, L.H.; van der Es, D.; IJzerman, A.P. Development of covalent ligands for G protein-coupled receptors: A case for the human adenosine A3 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3539–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Dong, G.; Michiels, T.J.M.; Lenselink, E.B.; Heitman, L.; Louvel, J.; IJzerman, A.P. A covalent antagonist for the human adenosine A2A receptor. Purinergic Signal. 2017, 13, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraldi, P.G.; Cacciari, B.; Moro, S.; Romagnoli, R.; Ji, X.; Jacobson, K.A.; Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Spalluto, G. Fluorosulfonyl- and bis-(β-chloroethyl)amino-phenylamino functionalized pyrazolo[4,3-e]1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidine derivatives: Irreversible antagonists at the human A3 adenosine receptor and molecular modeling studies. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Ukena, D.; Padgett, W.; Kirk, K.L.; Daly, J.W. Molecular probes for extracellular adenosine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, M.; Faklaris, O.; Zwier, J.M.; Trinquet, E.; Pin, J.-P.; Durroux, T. Original fluorescent ligand-based assays open new perspectives in G-protein coupled receptor drug screening. Pharmaceuticals 2011, 4, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, R.; Zuber, J.; Connelly, S.M.; Mathew, E.; Dumont, M.E. Fluorescent approaches for understanding interactions of ligands with G protein coupled receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Müller, C.E. Medicinal chemistry of adenosine, P2Y and P2X receptors. Neuropharmacology 2016, 104, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.; Choi, H.-K. Recent conjugation strategies of small organic fluorophores and ligands for cancer-specific bioimaging. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 248, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Ogawa, M.; Alford, R.; Choyke, P.L.; Urano, Y. New strategies for fluorescent probe design in medical diagnostic imaging. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2620–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nitschke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Method. 2008, 5, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozma, E.; Suresh Jayasekara, P.; Squarcialupi, L.; Paoletta, S.; Moro, S.; Federico, S.; Spalluto, G.; Jacobson, K.A. Fluorescent ligands for adenosine receptors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernall, A.J.; Hill, S.J.; Kellam, B. The evolving small-molecule fluorescent-conjugate toolbox for Class A GPCRs. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciruela, F.; Fernández-Dueñas, V.; Jacobson, K.A. Lighting up G protein-coupled purinergic receptors with engineered fluorescent ligands. Neuropharmacology 2015, 98, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, R.J.; Briddon, S.J.; Cordeaux, Y.; Yates, A.S.; Dale, C.L.; George, M.W.; Baker, J.G.; Hill, S.J.; Kellam, B. New fluorescent Adenosine A1—Receptor agonists that allow quantification of ligand−receptor interactions in microdomains of single living cells. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisig, F.; Gollos, S.; Freudenthal, S.J.; El-Tayeb, A.; Iqbal, J.; Müller, C.E. Synthesis of BODIPY derivatives substituted with various bioconjugatable linker groups: A construction kit for fluorescent labeling of receptor ligands. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.G.; Middleton, R.; Adams, L.; May, L.T.; Briddon, S.J.; Kellam, B.; Hill, S.J. Influence of fluorophore and linker composition on the pharmacology of fluorescent adenosine A1 receptor ligands: Themed section: Imaging in pharmacology research paper. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 772–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchia, M.; Salvetti, F.; Bertini, S.; Bussolo, D.; Gattuso, L.; Gesi, M.; Hamdan, M.; Klotz, K.; Laragione, T.; Lucacchini, A.; et al. 7-Nitrobenzofurazan (NBD) derivatives of 5-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA) as new fluorescent probes for human A3 adenosine receptors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 3023–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, C.L.; Hill, S.J.; Kellam, B. New potent, short-linker BODIPY-630/650TM labelled fluorescent adenosine receptor agonists. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 3, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchia, M.; Salvetti, F.; Barontini, S.; Calvani, F.; Gesi, M.; Hamdan, M.; Lucacchini, A.; Pellegrini, A.; Soldani, P.; Martini, C. Fluorescent probes for adenosine receptors: Synthesis and biology of N6-dansylaminoalkyl-substituted NECA derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 1998, 8, 3223–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, L.T.; Self, T.J.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. The effect of allosteric modulators on the kinetics of agonist-G protein-coupled receptor interactions in single living cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, L.T.; Bridge, L.J.; Stoddart, L.A.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. Allosteric interactions across native adenosine-A3 receptor homodimers: Quantification using single-cell ligand-binding kinetics. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3465–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddart, L.A.; Vernall, A.J.; Briddon, S.J.; Kellam, B.; Hill, S.J. Direct visualisation of internalization of the adenosine A3 receptor and localization with arrestin3 using a fluorescent agonist. Neuropharmacology 2015, 98, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, R.T.; Skolnick, P.; Jacobson, K.A. 2-[2-[4-[2-[2-[1,3-Dihydro-1,1-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-oxo-5-isobenzofuranthioureidyl]ethylaminocarbonyl]ethyl]phenyl]ethylamino]-5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (FITC-APEC): A fluorescent ligand for A2A-Adenosine receptors. J. Fluoresc. 1992, 2, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brand, F.; Klutz, A.M.; Jacobson, K.A.; Fredholm, B.B.; Schulte, G. Adenosine A2A receptor dynamics studied with the novel fluorescent agonist Alexa488-APEC. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 590, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Dueñas, V.; Gómez-Soler, M.; Jacobson, K.A.; Kumar, S.T.; Fuxe, K.; Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Ciruela, F. Molecular determinants of A2AR-D2R allosterism: Role of the intracellular loop 3 of the D2R. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Sanjayan, G.J.; Kecskés, M.; Yoo, L.; Gao, Z.G.; Jacobson, K.A. Nucleoside conjugates of quantum dots for characterization of G protein-coupled receptors: Strategies for immobilizing A2A adenosine receptor agonists. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosh, D.K.; Chinn, M.; Ivanov, A.A.; Klutz, A.M.; Gao, Z.; Jacobson, K.A. Functionalized congeners of A3 adenosine receptor-selective nucleosides containing a bicycle [3.1.0]hexane ring system. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7580–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosh, D.K.; Chinn, M.; Yoo, L.S.; Kang, D.W.; Luecke, H.; Gao, Z.; Jacobson, K.A. 2-Dialkynyl derivatives of (N)-methanocarba nucleosides: ‘Clickable’ A3 adenosine receptor-selective agonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tosh, D.K.; Deflorian, F.; Phan, K.; Gao, Z.; Wan, T.C.; Gizewski, E.; Auchampach, J.A.; Jacobson, K.A. Structure-guided design of A3 adenosine receptor-selective nucleosides: Combination of 2-arylethynyl and bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane substitutions. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4847–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, L.T.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. Antagonist selective modulation of adenosine A1 and A3 receptor pharmacology by the food dye brilliant black BN: Evidence for allosteric interactions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briddon, S.J.; Middleton, R.J.; Cordeaux, Y.; Flavin, F.M.; Weinstein, J.A.; George, M.W.; Kellam, B.; Hill, S.J. Quantitative analysis of the formation and diffusion of A1-adenosine receptor-antagonist complexes in single living cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4673–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kecskés, A.; Tosh, D.K.; Wei, Q.; Gao, Z.-G.; Jacobson, K.A. GPCR ligand dendrimer (GLiDe) conjugates: Adenosine receptor interactions of a series of multivalent xanthine antagonists. Bioconjugate Chem. 2011, 22, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Vernall, A.J.; Stoddart, L.A.; Briddon, S.J.; Ng, H.W.; Laughton, C.A.; Doughty, S.W.; Hill, S.J.; Kellam, B. Conversion of a non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist into A3-selective high affinity fluorescent probes using peptide-based linkers. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddart, L.A.; Vernall, A.J.; Denman, J.L.; Briddon, S.J.; Kellam, B.; Hill, S.J. Fragment screening at adenosine-A3 receptors in living cells using a fluorescence-based binding assay. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corriden, R.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Kellam, B.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. Kinetic analysis of antagonist-occupied adenosine-A3 receptors within membrane microdomains of individual cells provides evidence of receptor dimerization and allosterism. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4211–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzo-Lorenzo, M.; Stoddart, L.A.; Xia, L.; IJzerman, A.P.; Heitman, L.H.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. A live cell NanoBRET binding assay allows the study of ligand-binding kinetics to the adenosine A3 receptor. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.L.; Soave, M.; Jörg, M.; Scammells, P.J.; Woolard, J.; Hill, S.J. Probe dependence of allosteric enhancers on the binding affinity of adenosine A1—Receptor agonists at rat and human A1—Receptors measured using N ano BRET. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, M.; Gollos, S.; Karcz, T.; Fiene, A.; Heisig, F.; Behrenswerth, A.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Namasivayam, V.; Müller, C.E. Fluorescent-labeled selective adenosine A2B receptor antagonist enables competition binding assay by flow cytometry. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4301–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozma, E.; Kumar, T.S.; Federico, S.; Phan, K.; Balasubramanian, R.; Gao, Z.-G.; Paoletta, S.; Moro, S.; Spalluto, G.; Jacobson, K.A. Novel fluorescent antagonist as a molecular probe in A3 adenosine receptor binding assays using flow cytometry. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernall, A.J.; Stoddart, L.A.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J.; Kellam, B. Highly potent and selective fluorescent antagonists of the human adenosine A3 receptor based on the 1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one scaffold. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kecskés, M.; Kumar, T.S.; Yoo, L.; Gao, Z.G.; Jacobson, K.A. Novel Alexa Fluor-488 labeled antagonist of the A2A adenosine receptor: Application to a fluorescence polarization-based receptor binding assay. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.S.; Mishra, S.; Deflorian, F.; Yoo, L.S.; Phan, K.; Kecskés, M.; Szabo, A.; Shinkre, B.; Gao, Z.-G.; Trenkle, W.; et al. Molecular probes for the A2A adenosine receptor based on a pyrazolo[4,3-e][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-5-amine scaffold. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 2740–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, S.; Margiotta, E.; Paoletta, S.; Kachler, S.; Klotz, K.-N.; Jacobson, K.A.; Pastorin, G.; Moro, S.; Spalluto, G. Pyrazolo[4,3-e][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidines to develop functionalized ligands to target adenosine receptors: Fluorescent ligands as an example. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Duenas, V.; Taura, J.J.; Cottet, M.; Gomez-Soler, M.; Lopez-Cano, M.; Ledent, C.; Watanabe, M.; Trinquet, E.; Pin, J.-P.; Lujan, R.; et al. Untangling dopamine-adenosine receptor-receptor assembly in experimental parkinsonism in rats. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barresi, E.; Giacomelli, C.; Daniele, S.; Tonazzini, I.; Robello, M.; Salerno, S.; Piano, I.; Cosimelli, B.; Greco, G.; Da, F.; et al. Novel fluorescent triazinobenzimidazole derivatives as probes for labelling human A1 and A2B adenosine receptor subtypes. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5885–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redenti, S.; Ciancetta, A.; Pastorin, G.; Cacciari, B.; Moro, S.; Spalluto, G.; Federico, S. Pyrazolo[4,3-e][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidines and structurally simplified analogs. Chemistry and SAR profile as adenosine receptor antagonists. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 3224–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Thatikonda, S.K.; Kozma, E.E.; Spalluto, G.; Moro, S.; Federico, S. Fluorescent Antagonists of the A3 Adenosine Receptor. Patent US9227979B2, 5 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Federico, S.; Lassiani, L.; Spalluto, G. Chemical Probes for the Adenosine Receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040168
Federico S, Lassiani L, Spalluto G. Chemical Probes for the Adenosine Receptors. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040168
Chicago/Turabian StyleFederico, Stephanie, Lucia Lassiani, and Giampiero Spalluto. 2019. "Chemical Probes for the Adenosine Receptors" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 4: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040168
APA StyleFederico, S., Lassiani, L., & Spalluto, G. (2019). Chemical Probes for the Adenosine Receptors. Pharmaceuticals, 12(4), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040168




