Generation of a Triple-Transgenic Zebrafish Line for Assessment of Developmental Neurotoxicity during Neuronal Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
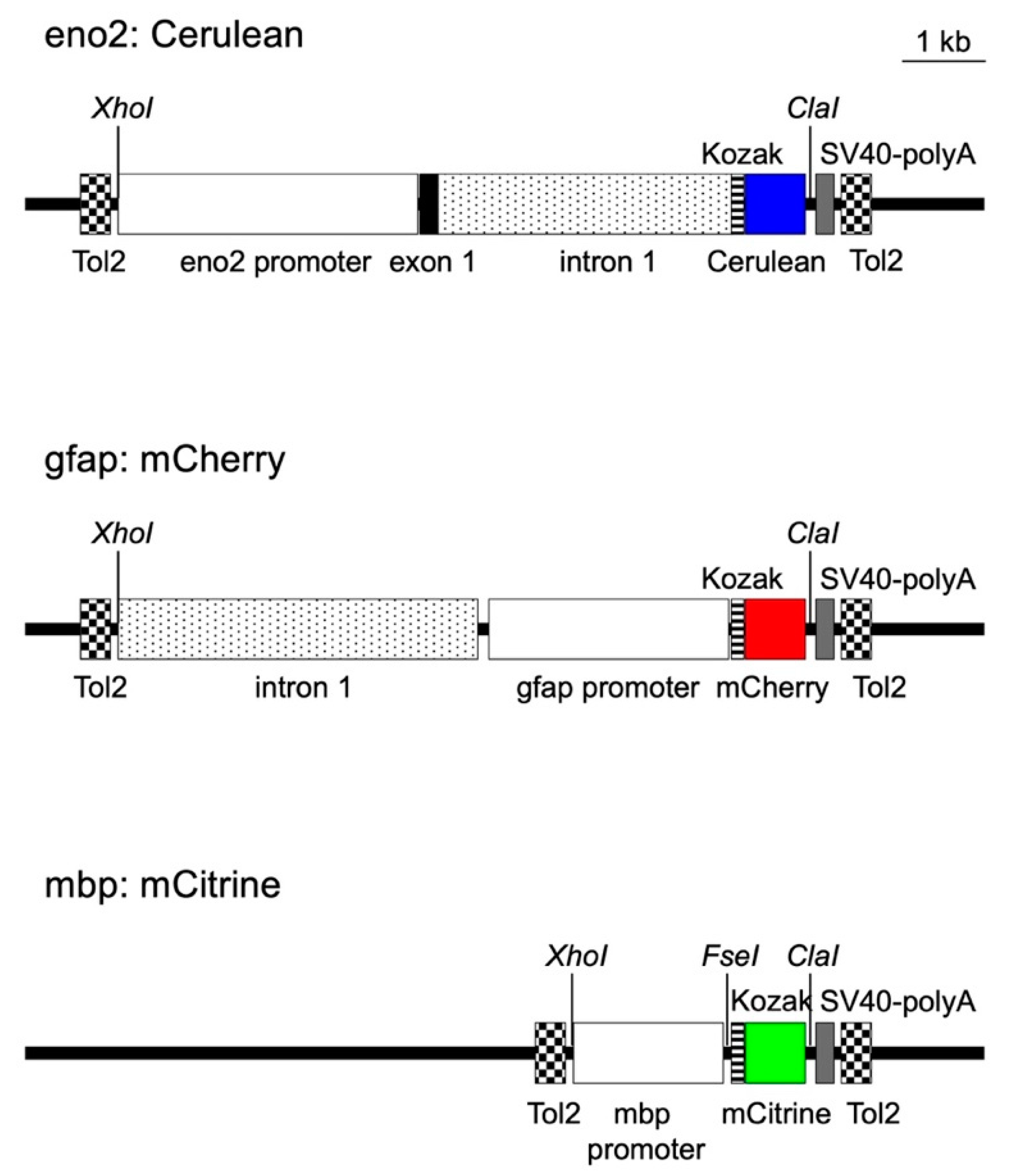
2.1. Construction of Transposon Vectors to Express Cerulean, Mcherry, and Mcitrine in Neurons, Astrocytes, and Oligodendrocytes
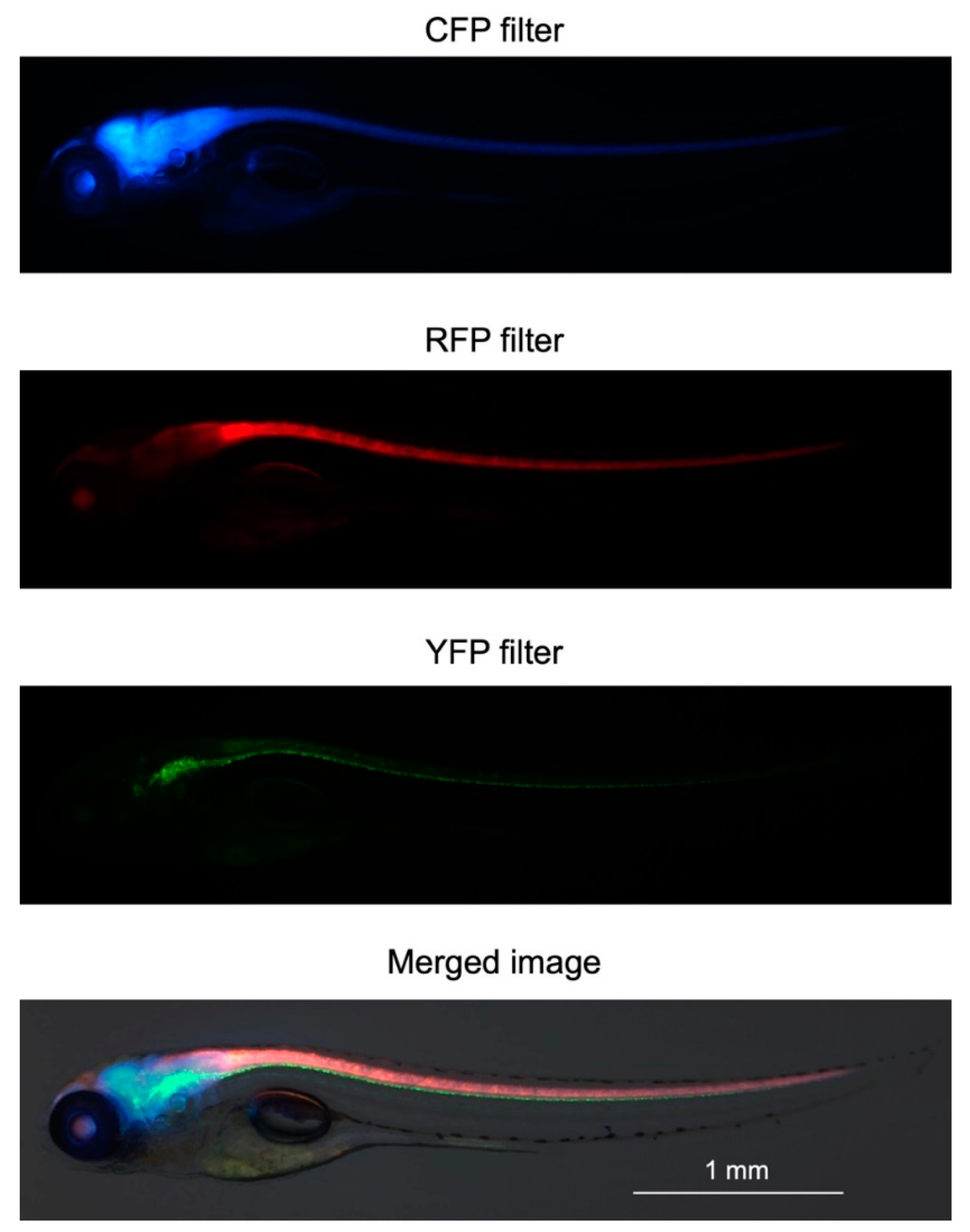
2.2. Generation of Triple-Tg Zebrafish
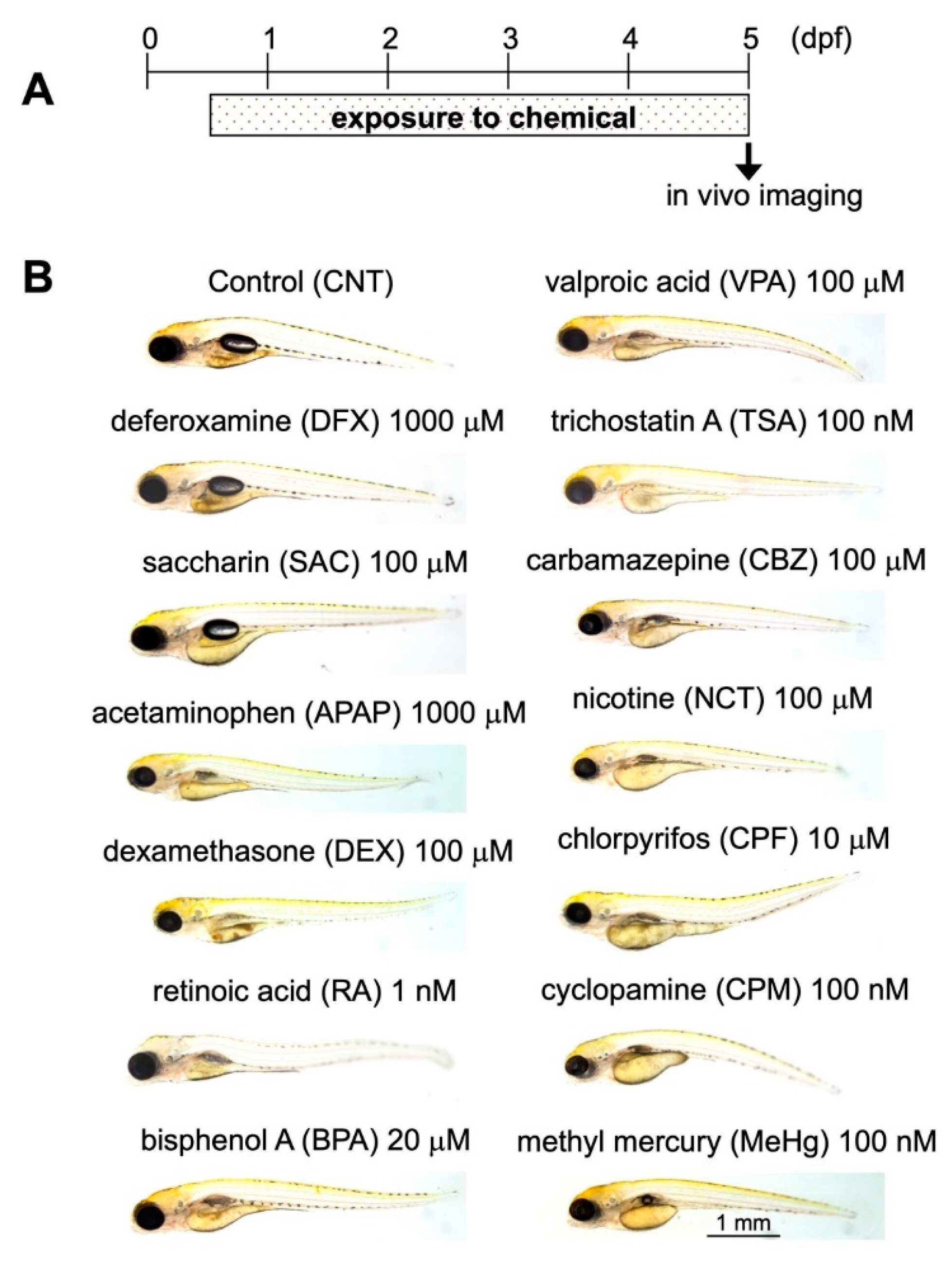
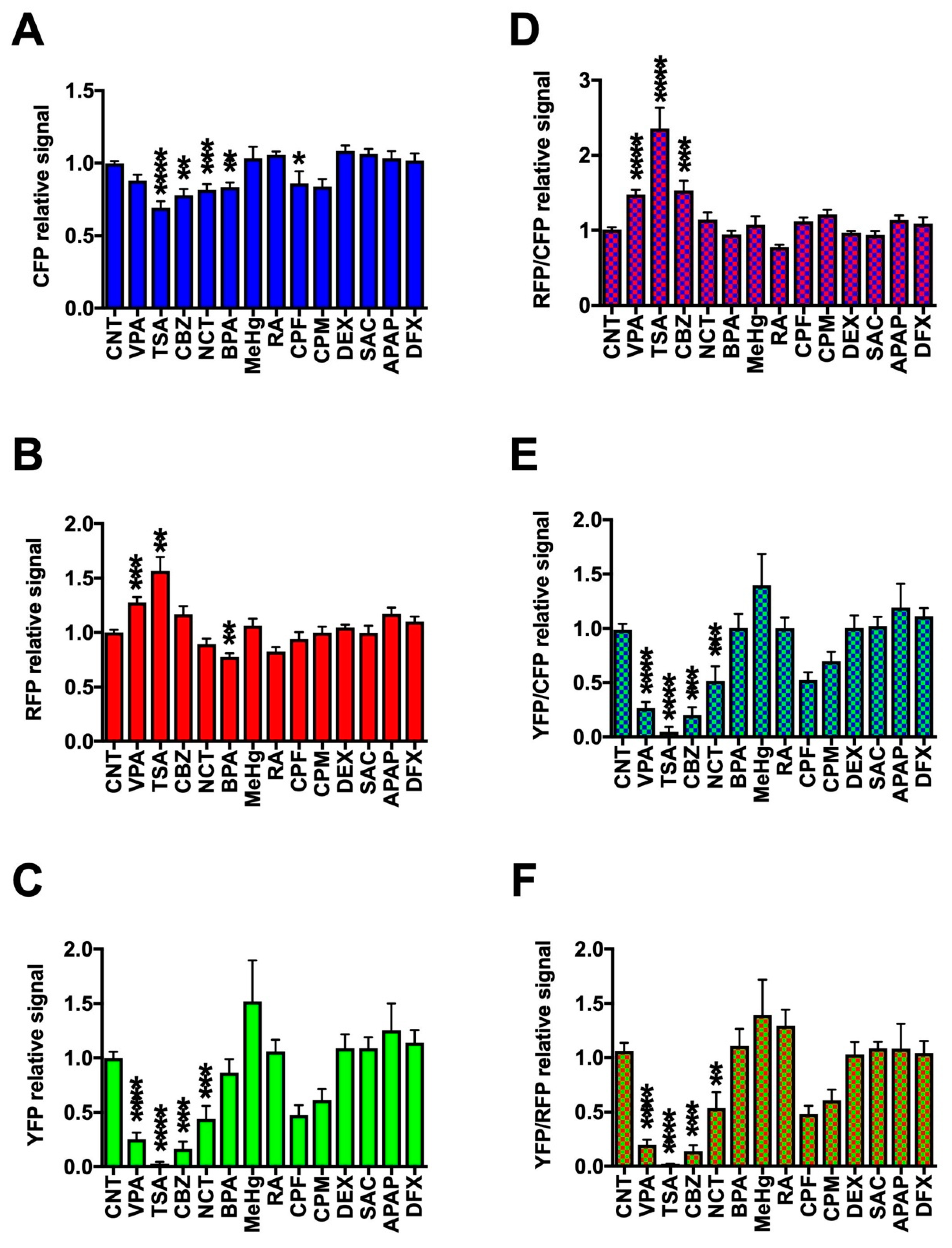
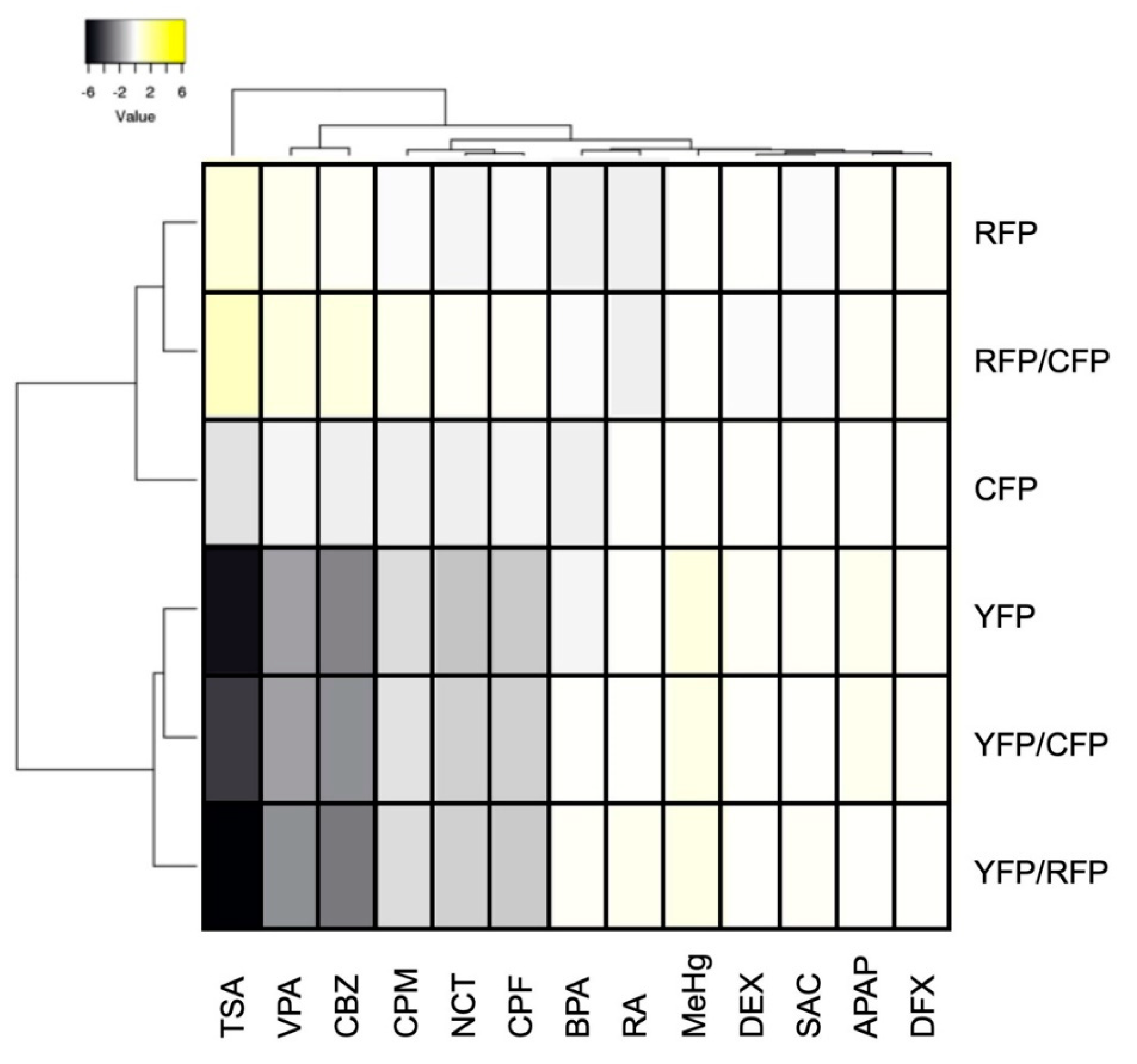
2.3. Assessment of DNT Using Triple-Tg Zebrafish
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Compounds
4.3. Zebrafish Husbandry
4.4. Generation of Tg (eno2:Cerulean, gfap:mCherry, mbp:mCitrine) Zebrafish
4.5. Exposure of Triple-Tg Zebrafish to Chemicals
4.6. In Vivo Imaging of Triple-Tg Zebrafish
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, L.G.; Steardo, L.; Cuomo, V. Structural Effects and Neurofunctional Sequelae of Developmental Exposure to Psychotherapeutic Drugs: Experimental and Clinical Aspects. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 103–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal-Price, A.; Hogberg, H.T.; Crofton, K.M.; Daneshian, M.; FitzGerald, R.E.; Fritsche, E.; Heinonen, T.; Hougaard Bennekou, S.; Klima, S.; Piersma, A.H.; et al. Prenatal exposure to drugs: Effects on brain development and implications for policy and education. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 303. [Google Scholar]
- Crofton, K.M.; Mundy, W.R.; Shafer, T.J. Developmental neurotoxicity testing: A path forward. Congenit. Anom. 2012, 52, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Murakami, S.; Ashikawa, Y.; Sasagawa, S.; Umemoto, N.; Shimada, Y.; Tanaka, T. Zebrafish as a systems toxicology model for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Congenit. Anom. 2015, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, H.; Takahashi, N.; Shutoh, Y.; Motomura, A.; Crofton, K.M. Developmental Neurotoxicology: History and Outline of Developmental Neurotoxicity Study Guidelines. Food Saf. 2015, 3, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grandjean, P.; Abdennebi-Najar, L.; Barouki, R.; Cranor, C.F.; Etzel, R.A.; Gee, D.; Heindel, J.J.; Hougaard, K.S.; Hunt, P.; Nawrot, T.S.; et al. Timescales of developmental toxicity impacting on research and needs for intervention. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 125, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohyama, C. Developmental neurotoxicity test guidelines: Problems and perspectives. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 41, SP69–SP79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G.; Chang, Y.C.; Cole, T.B. Developmental Neurotoxicity of Traffic-Related Air Pollution: Focus on Autism. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2017, 4, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.L.; Oberdörster, G.; Morris-Schaffer, K.; Wong, C.; Klocke, C.; Sobolewski, M.; Conrad, K.; Mayer-Proschel, M.; Cory-Slechta, D.A. Developmental neurotoxicity of inhaled ambient ultrafine particle air pollution: Parallels with neuropathological and behavioral features of autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders. NeuroToxicology 2017, 59, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, C.; Ceccatelli, S. Mechanistic insight into neurotoxicity induced by developmental insults. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, O.; Låg, M.; Villanger, G.D.; Oftedal, B.; Øvrevik, J.; Holme, J.A.; Aase, H.; Paulsen, R.E.; Bal-Price, A.; Dirven, H. Early life exposure to air pollution particulate matter (PM) as risk factor for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Need for novel strategies for mechanisms and causalities. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 354, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal-Price, A.; Pistollato, F.; Sachana, M.; Bopp, S.K.; Munn, S.; Worth, A. Strategies to improve the regulatory assessment of developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) using in vitro methods. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 354, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modabbernia, A.; Velthorst, E.; Reichenberg, A. Environmental risk factors for autism: An evidence-based review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyer, D.B.; Meredith, R.M. Environmental toxicology: Sensitive periods of development and neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurotoxicology 2017, 58, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattane, N.; Richetto, J.; Cattaneo, A. Prenatal exposure to environmental insults and enhanced risk of developing Schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorder: Focus on biological pathways and epigenetic mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Oecd Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals Test No. 426; Developmental Neurotoxicity Study; OECD iLibrary: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, R.; Crofton, K. Developmental neurotoxicity guideline study: Issues with methodology, evaluation and regulation. Congenit. Anom. 2012, 52, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwagata, M. Current problems of in vivo developmental neurotoxicity tests and a new in vivo approach focusing on each step of the developing central nervous system. Congenit. Anom. 2012, 52, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, H. Developmental neurotoxicity testing: Scientific approaches towards the next generation to protect the developing nervous system of children. An overview of the Developmental Neurotoxicity Symposium in 2011. Congenit. Anom. 2012, 52, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Inoue, A.; Sasagawa, S.; Koiwa, J.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kawase, R.; Maruyama, T.; Kim, S.; Tanaka, T. Using zebrafish in systems toxicology for developmental toxicity testing. Congenit. Anom. 2016, 56, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, E.; Grandjean, P.; Crofton, K.M.; Aschner, M.; Goldberg, A.; Heinonen, T.; Hessel, E.V.; Hogberg, H.T.; Bennekou, S.H.; Lein, P.J.; et al. Consensus statement on the need for innovation, transition and implementation of developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing for regulatory purposes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 354, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal-Price, A. Recommendation on test readiness criteria for new approach methods in toxicology: Exemplified for developmental neurotoxicity_suppl. ALTEX 2018, 35, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.W.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Yaghoobi, B.; Lein, P.J. Opportunities and challenges for using the zebrafish to study neuronal connectivity as an endpoint of developmental neurotoxicity. NeuroToxicology 2018, 67, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Settivari, R.; LeBaron, M.J.; Marty, M.S. An industry perspective: A streamlined screening strategy using alternative models for chemical assessment of developmental neurotoxicity. NeuroToxicology 2019, 73, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachana, M.; Bal-Price, A.; Crofton, K.M.; Bennekou, S.H.; Shafer, T.J.; Behl, M.; Terron, A. International Regulatory and Scientific Effort for Improved Developmental Neurotoxicity Testing. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 167, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamies, D.; Barreras, P.; Block, K.; Makri, G.; Kumar, A.; Wiersma, D.; Smirnova, L.; Zang, C.; Bressler, J.; Christian, K.M.; et al. A human brain microphysiological system derived from induced pluripotent stem cells to study neurological diseases and toxicity. ALTEX 2017, 34, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, E.; Barenys, M.; Klose, J.; Masjosthusmann, S.; Nimtz, L.; Schmuck, M.; Wuttke, S.; Tigges, J. Current Availability of Stem Cell-Based In Vitro Methods for Developmental Neurotoxicity (DNT) Testing. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 165, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuratani, Y.; Horie, M.; Leinala, E. Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment: OECD Activities on the Development and Use of Adverse Outcome Pathways and Case Studies. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandstrom, J.; Eggermann, E.; Charvet, I.; Roux, A.; Toni, N.; Greggio, C.; Broyer, A.; Monnet-Tschudi, F.; Stoppini, L. Development and characterization of a human embryonic stem cell-derived 3D neural tissue model for neurotoxicity testing. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 38, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Yu, K.N.; Kang, S.Y.; Kwon, S.J.; Kwon, P.S.; Dordick, J.S.; Kothapalli, C.R.; Lee, M.Y. 3D-cultured neural stem cell microarrays on a micropillar chip for high-throughput developmental neurotoxicology. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Sierra, G.; Sivapatham, R.; Swistowski, A.; Rao, M.S.; Zeng, X. A platform for rapid generation of single and multiplexed reporters in human iPSC lines. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.T.; Macrae, C.A. Systematic approaches to toxicology in the zebrafish. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, S.; Corum, D.; Padnos, B.; Hunter, D.; Beam, A.; Houck, K.; Sipes, N.; Kleinstreuer, N.; Knudsen, T.; Dix, D.; et al. Zebrafish developmental screening of the ToxCast™ Phase I chemical library. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekmann, H.; Hill, A. ADMETox in zebrafish. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 10, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amora, M.; Giordani, S. The Utility of Zebrafish as a Model for Screening Developmental Neurotoxicity. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Garver, J.A.; Hukriede, N.A.; Burton, E.A. Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 6501–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardos, R.L.; Raymond, P.A. GFAP transgenic zebrafish. Gene Expr. Patterns 2006, 6, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Kim, S.; Chung, A.Y.; Kim, H.T.; So, J.H.; Ryu, J.; Park, H.C.; Kim, C.H. Visualization of myelination in GFP-transgenic zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockway, N.L.; Cook, Z.T.; O’Gallagher, M.J.; Tobias, Z.J.C.; Gedi, M.; Carey, K.M.; Unni, V.K.; Pan, Y.A.; Metz, M.R.; Weissman, T.A. Multicolor lineage tracing using in vivo time-lapse imaging reveals coordinated death of clonally related cells in the developing vertebrate brain. Dev. Biol. 2019, 453, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K. Tol2: A versatile gene transfer vector in vertebrates. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Oecd Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals Test No. 236; Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity Test; OECD iLibrary: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mundy, W.R.; Padilla, S.; Breier, J.M.; Crofton, K.M.; Gilbert, M.E.; Herr, D.W.; Jensen, K.F.; Radio, N.M.; Raffaele, K.C.; Schumacher, K.; et al. Expanding the test set: Chemicals with potential to disrupt mammalian brain development. Neurotoxicol.Teratol. 2015, 52, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, M.; Ceccatelli, S.; Daneshian, M.; Fritsche, E.; Hasiwa, N.; Hartung, T.; Hogberg, H.T.; Leist, M.; Li, A.; Mundi, W.R.; et al. Reference compounds for alternative test methods to indicate developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) potential of chemicals: Example lists and criteria for their selection and use. ALTEX 2016, 34, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shen, S.; Li, J.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Histone modifications affect timing of oligodendrocyte progenitor differentiation in the developing rat brain. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, H.; Aonuma, M.; Sanosaka, T.; Kohyama, J.; Namihira, M.; Nakashima, K. Astrocyte Differentiation of Neural Precursor Cells is Enhanced by Retinoic Acid through a Change in Epigenetic Modification. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2744–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Dwyer, J.B.; Gautier, N.M.; Leslie, F.M.; Li, M.D. Central myelin gene expression during postnatal development in rats exposed to nicotine gestationally. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 553, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, B.; Yadav, A.; Tandon, A.; Shankar, J.; Chaturvedi, R.K. Carbofuran hampers oligodendrocytes development leading to impaired myelination in the hippocampus of rat brain. NeuroToxicology 2019, 70, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halluin, C.; Madelaine, R.; Naye, F.; Peers, B.; Roussigné, M.; Blader, P. Habenular Neurogenesis in Zebrafish Is Regulated by a Hedgehog, Pax6 Proneural Gene Cascade. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0158210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.W.; Chou, W.C.; Chen, K.H.; Cheng, A.L.; Mao, I.F.; Chao, H.R.; Chuang, C.Y. Visualized gene network reveals the novel target transcripts Sox2 and Pax6 of neuronal development in trans-placental exposure to bisphenol A. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kallur, T.; Gisler, R.; Lindvall, O.; Kokaia, Z. Pax6 promotes neurogenesis in human neural stem cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 38, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unoki, T.; Akiyama, M.; Kumagai, Y.; Gonçalves, F.M.; Farina, M.; Da Rocha, J.B.T.; Aschner, M. Molecular Pathways Associated With Methylmercury-Induced Nrf2 Modulation. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Lv, Q.; Zou, J.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z. Expression of Nrf2 Promotes Schwann Cell-Mediated Sciatic Nerve Recovery in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1879–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annau, Z.; Cuomo, V. Mechanisms of neurotoxicity and their relationship to behavioral changes. Toxicology 1988, 49, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimfarth, L.; Delgado, J.; Mignori, M.R.; Gelain, D.P.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Pessoa-Pureur, R. Developmental neurotoxicity of the hippocampus following in utero exposure to methylmercury: Impairment in cell signaling. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faigle, R.; Liu, L.; Cundiff, P.; Funa, K.; Xia, Z. Opposing effects of retinoid signaling on astrogliogenesis in embryonic day 13 and 17 cortical progenitor cells. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1681–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Slotkin, T.A.; Skavicus, S.; Seidler, F.J. Developmental neurotoxicity resulting from pharmacotherapy of preterm labor, modeled in vitro: Terbutaline and dexamethasone, separately and together. Toxicology 2018, 400, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanungo, J.; Lantz, S.; Paule, M.G. In vivo imaging and quantitative analysis of changes in axon length using transgenic zebrafish embryos. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, C.D.; Streissguth, A.P.; Riley, E.P. Prenatal alcohol exposure: Comparability of effects in humans and animal models. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1990, 12, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalberg, W.O.; Provost, B.; Tollison, S.J.; Tabachnick, B.G.; Robinson, L.K.; Hoyme, H.E.; Trujillo, P.M.; Buckley, D.; Aragón, A.S.; May, P.A. Comparison of Motor Delays in Young Children With Fetal Alcohol Syndrome to Those With Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and With No Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gong, Z. Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish Tg(nkx2.2a:mEGFP) Provides a Highly Sensitive Monitoring Tool for Neurotoxins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikawa, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Okabe, S.; Sasagawa, S.; Murakami, S.; Yuge, M.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kawase, R.; Tanaka, T. Activation of Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Factors by Fenofibrate and Gemfibrozil Stimulates Myelination in Zebrafish. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, C.-Y.; Song, J.; Oh, H.; Kim, C.-H.; Park, J.-H. Trimethyltin chloride inhibits neuronal cell differentiation in zebrafish embryo neurodevelopment. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 54, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; He, D.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, X.; Hassan, A.; et al. Hdac3 Interaction with p300 Histone Acetyltransferase Regulates the Oligodendrocyte and Astrocyte Lineage Fate Switch. Dev. Cell 2016, 36, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ye, J.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Wu, W.; Lin, W.; Lin, W.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, S. Valproic acid attenuates traumatic spinal cord injury-induced inflammation via STAT1 and NF-kappaB pathway dependent of HDAC3. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhoke, N.R.; Kalabathula, E.; Kaushik, K.; Geesala, R.; Sravani, B.; Das, A. Histone deacetylases differentially regulate the proliferative phenotype of mouse bone marrow stromal and hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 17, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, A.S.; Li, S.; Nicol, R.; Walsh, M.J. Carbamazepine is an inhibitor of histone deacetylases. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakèd, M.; Weissmüller, K.; Svoboda, H.; Hortschansky, P.; Nishino, N.; Wölfl, S.; Tucker, K.L. Histone Deacetylases Control Neurogenesis in Embryonic Brain by Inhibition of BMP2/4 Signaling. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterton, Z.; Hartley, B.J.; Seok, M.H.; Mendelev, N.; Chen, S.; Milekic, M.; Rosoklija, G.; Stankov, A.; Trencevsja-Ivanovska, I.; Brennand, K.; et al. In utero exposure to maternal smoking is associated with DNA methylation alterations and reduced neuronal content in the developing fetal brain. Epigenetics Chromatin 2017, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visan, A.; Hayess, K.; Sittner, D.; Pohl, E.E.; Riebeling, C.; Slawik, B.; Gulich, K.; Oelgeschläger, M.; Luch, A.; Seiler, A.E. Neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells as a tool to assess developmental neurotoxicity in vitro. NeuroToxicology 2012, 33, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incardona, J.P.; Gaffield, W.; Kapur, R.P.; Roelink, H. The teratogenic Veratrum alkaloid cyclopamine inhibits sonic hedgehog signal transduction. Development 1998, 125, 3553–3562. [Google Scholar]
- Traiffort, E.; Zakaria, M.; Laouarem, Y.; Ferent, J. Hedgehog: A Key Signaling in the Development of the Oligodendrocyte Lineage. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, C.; Duckworth, J.; Hermanson, O.; Ceccatelli, S. High susceptibility of neural stem cells to methylmercury toxicity: Effects on cell survival and neuronal differentiation. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangos, P.J.; Schmechel, D.E.; Parma, A.M.; Goodwin, F.K. Developmental profile of neuron-specific (NSE) and non-neuronal (NNE) enolase. Brain Res. 1980, 190, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avola, R.; Bramanti, V.; Tomassoni, D.; Avitabile, M.; Amenta, F. Biomarkers of glial cell proliferation and differentiation in culture. Front. Biosci. 2010, 2, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovcevski, I.; Filipovic, R.; Mo, Z.; Rakic, S.; Zecevic, N. Oligodendrocyte Development and the Onset of Myelination in the Human Fetal Brain. Front. Neuroanat. 2009, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, A.L.; Stedman, D.B.; Ball, J.; Hillegass, J.M.; Flood, A.; Zhang, C.X.; Panzica-Kelly, J.; Cao, J.; Coburn, A.; Enright, B.P.; et al. Inter-laboratory assessment of a harmonized zebrafish developmental toxicology assay—Progress report on phase I. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasagawa, S.; Nishimura, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Murakami, S.; Ashikawa, Y.; Yuge, M.; Okabe, S.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kawase, R.; Tanaka, T. E2F4 promotes neuronal regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury in zebrafish. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsh, R.N.; Brand, M.; Jiang, Y.J.; Heisenberg, C.P.; Lin, S.; Haffter, P.; Odenthal, J.; Mullins, M.C.; Van Eeden, F.J.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; et al. Zebrafish pigmentation mutations and the processes of neural crest development. Development 1996, 123, 369–389. [Google Scholar]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koiwa, J.; Shiromizu, T.; Adachi, Y.; Ikejiri, M.; Nakatani, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, Y. Generation of a Triple-Transgenic Zebrafish Line for Assessment of Developmental Neurotoxicity during Neuronal Differentiation. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040145
Koiwa J, Shiromizu T, Adachi Y, Ikejiri M, Nakatani K, Tanaka T, Nishimura Y. Generation of a Triple-Transgenic Zebrafish Line for Assessment of Developmental Neurotoxicity during Neuronal Differentiation. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040145
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoiwa, Junko, Takashi Shiromizu, Yuka Adachi, Makoto Ikejiri, Kaname Nakatani, Toshio Tanaka, and Yuhei Nishimura. 2019. "Generation of a Triple-Transgenic Zebrafish Line for Assessment of Developmental Neurotoxicity during Neuronal Differentiation" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 4: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040145
APA StyleKoiwa, J., Shiromizu, T., Adachi, Y., Ikejiri, M., Nakatani, K., Tanaka, T., & Nishimura, Y. (2019). Generation of a Triple-Transgenic Zebrafish Line for Assessment of Developmental Neurotoxicity during Neuronal Differentiation. Pharmaceuticals, 12(4), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040145






