Tamoxifen Protects from Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Mice and Virus
2.2. Plaque-Forming Assay
2.3. Histology
2.4. Neutralizing Antibody Assay
2.5. ELISA
2.6. RT-PCR Analyses
2.7. Flow Cytometry
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
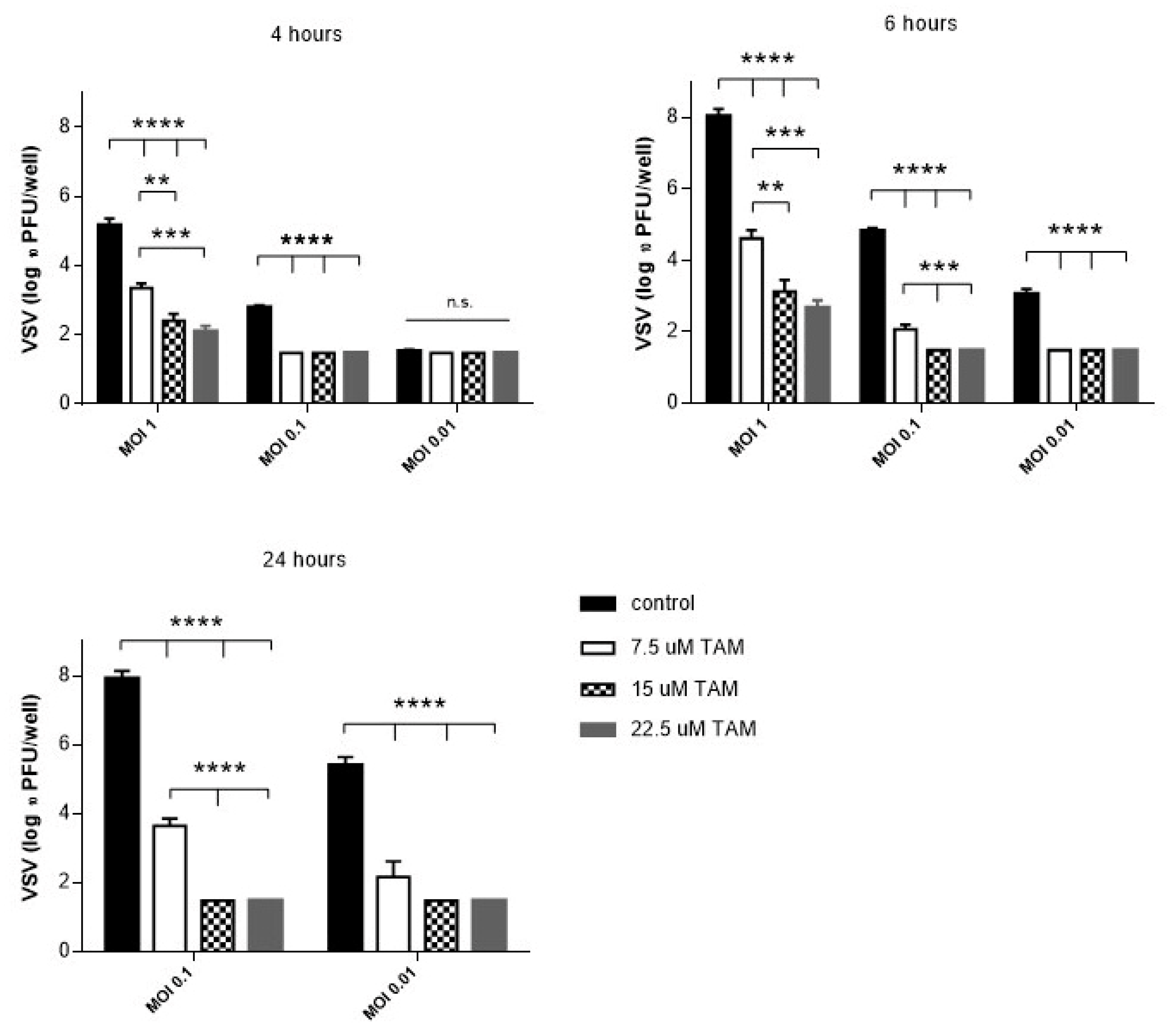
4.1. TAM Inhibits Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) In Vitro
4.2. TAM Pretreatment Protects from VSV Infection
4.3. TAM Pretreatment Reduces Antiviral Immune Response
4.4. Inhibitory Effect of TAM on Early VSV Replication Requires Interferon
5. Discussion
6. Declarations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grainger, D.J.; Metcalfe, J.C. Tamoxifen: Teaching an old drug new tricks? Nat. Med. 1996, 4, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, V.C. The science of selective estrogen receptor modulators: Concept to clinical practice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5010–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagufta; Ahmad, I. Tamoxifen a pioneering drug: An update on the therapeutic potential of tamoxifen derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heery, M.; Corbett, P.; Zelkowitz, R. Precautions for patients taking tamoxifen. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2018, 9, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allred, D.C.; Anderson, S.J.; Paik, S.; Wickerham, D.L.; Nagtegaal, I.D.; Swain, S.M.; Mamounas, E.P.; Julian, T.B.; Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Costantino, J.P.; et al. Adjuvant tamoxifen reduces subsequent breast cancer in women with estrogen receptor-positive ductal carcinoma in situ: a study based on NSABP protocol B-24. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Rasool, M.; Chaoudhry, H.; Pushparaj, P.N.; Jha, P.; Hafiz, A.; Mahfooz, M.; Sami, G.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Bashir, S.; et al. Molecular mechanisms and mode of tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Bioinformation 2016, 12, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes-Davies, L.; Caldas, C.; Wishart, G.C. Tamoxifen: The drug that came in from the cold. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 875–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, B.; Costantino, J.; Redmond, C.; Poisson, R.; Bowman, D.; Couture, J.; Domitrov, N.V.; Walmark, N.; Wickerham, D.L.; Fisher, E.R.; et al. A randomized clinical trial evaluating tamoxifen in the treatment of patients with node-negative breast cancer who have estrogen-receptor-positive tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obiorah, I.; Jordan, V.C. Progress in endocrine approaches to the treatment and prevention of breast cancer. Maturitas 2011, 70, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azvolinsky, A. ASCO: Long-Term Tamoxifen Benefit for Breast Cancer Confirmed. 2013. Available online: https://www.cancernetwork.com/breast-cancer/asco-long-term-tamoxifen-benefit-breast-cancer-confirmed (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: An overview of the randomized trials. Lancet 1998, 351, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogush, T.A.; Dudko, E.A.; Beme, A.A.; Bogush, E.A.; Polotskiĭ, B.E.; Tiuliandin, S.A.; Davydov, M.I. Estrogen receptor expression in tumors different from breast cancer. Antibiot. Khimioter. 2009, 54, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bogush, T.A.; Dudko, E.A.; Bogush, E.A.; Polotsky, B.E.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ryabov, A.B. Tamoxifen non-estrogen receptor mediated molecular targets. Oncol. Rev. 2012, 6, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Behjati, S.; Frank, M.H. The effects of tamoxifen on immunity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3076–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.C.; Su, S.; Fry, D.; Liebes, L. Combination therapy with irinotecan and protein kinase C inhibitors in malignant glioma. Cancer 2003, 97, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Cao, H.T.; Han, T.Y.; Jones, R.C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Jarman, M.; Hardcastle, I.R.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cabot, M.C. Tamoxifen induces selective membrane association of protein kinase C epsilon in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 28–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, H.I.; Won, M.; Seiferheld, W.F.; Schultz, C.J.; Choucair, A.K.; Brachman, D.G.; Demas, W.F.; Mehta, M.P. Phase 2 trial of radiation plus high-dose tamoxifen for glioblastoma multiforme: RTOG protocol BR-0021. Neuro. Oncol. 2006, 8, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skapek, S.X.; Anderson, J.R.; Hill, D.A.; Henry, D.; Spunt, S.L.; Meyer, W.; Kao, S.; Hoffer, F.A.; Grier, H.E.; Hawkins, D.S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of high-dose tamoxifen and sulindac for desmoid tumor in children: Results of a Children’s Oncology Group (COG) phase II study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2013, 60, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, M.C.; Krysan, D.J. Repurposing Estrogen Receptor Antagonists for the Treatment of Infectious Disease. MBio 2018, 9, e02272-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurence, J.; Cooke, H.; Sikder, S.K. Effect of tamoxifen on regulation of viral replication and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) long terminal repeat-directed transcription in cells chronically infected with HIV-1. Blood 1990, 75, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Watashi, K.; Inoue, D.; Hijikata, M.; Goto, K.; Aly, H.H.; Shimotohno, K. Anti-hepatitis C virus activity of tamoxifen reveals the functional association of estrogen receptor with viral RNA polymerase NS5B. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 32765–32772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, H.; Suzuki, T.; Wakita, T.; Murakami, Y.A. Cell-based, microplate colorimetric screen identifies 7,8-benzoflavone and green tea gallate catechins as inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Fukasawa, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Wakita, T.; Fukazawa, H. Selective estrogen receptor modulators inhibit hepatitis C virus infection at multiple steps of the virus life cycle. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Chen, M.; Xiang, Y.; Ma, K.; Jin, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 entry by chloride channel inhibitors tamoxifen and NPPB. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, P.B.; Panchal, R.G.; Warren, T.K.; Shurtleff, A.C.; Endsley, A.N.; Green, C.E.; Kolokoltsov, A.; Davey, R.; Manger, I.D.; Gilfillan, L.; et al. Evaluation of Ebola virus inhibitors for drug repurposing. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, U.; Steinhoff, U.; Reis, L.F.; Hemmi, S.; Pavlovic, J.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Aguet, M. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science 1994, 264, 1918–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, K.; Lang, K.S.; Manjarrez-Orduno, N.; Junt, T.; Senn, B.M.; Holdener, M.; Akira, S.; Zinkernagel, R.M.; Hengartner, H. Early type I interferon-mediated signals on B cells specifically enhance antiviral humoral responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honke, N.; Shaabani, N.; Merches, K.; Gassa, A.; Kraft, A.; Ehrhardt, K.; Häussinger, D.; Löhning, M.; Dittmer, U.; Hengel, H.; et al. Immunoactivation induced by chronic viral infection inhibits viral replication and drives immunosuppression through sustained IFN-I responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, D.J.; Kolla, V.; Kalvakolanu, D.V.; Borden, E.C. Tamoxifen enhanced interferon-regulated gene expression in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1997, 167, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, A.E.M.; Smid, M.; Nagelkerke, A.; Martens, J.W.M.; Bussink, J.; Sweep, F.C.G.J.; Span, P.N. Interferon-stimulated genes are involved in cross-resistance to radiotherapy in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, E.; Nagy, E.; Kwok, S.; McNicol, A.; Gerrard, J.; Berczi, I. Suppression of lymphocyte mitogenesis by tamoxifen: Studies on protein kinase C, calmodulin and calcium. Neuroimmunomodulation 2000, 7, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Rubin, D.; Mekori, T.; Segal, R.; Pollack, S. In vivo modulation of natural killer cell activity by tamoxifen in patients with bilateral primary breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 1993, 37, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Médina, P.; Favre, G.M.; Poirot, M. Multiple targeting by the antitumor drug tamoxifen: A structure-activity study. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 2004, 4, 491–508. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, L.M.; Brannan, J.M.; Delos, S.E.; Shoemaker, C.J.; Stossel, A.; Lear, C.; Hoffstrom, B.G.; Dewald, L.E.; Schornberg, K.L.; Scully, C.; et al. FDA-approved selective estrogen receptor modulators inhibits ebola virus infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 190ra79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suder, E.; Furuyama, W.; Feldmann, H.; Marzi, A.; De Wit, E. The vesicular stomatitis virus-based Ebola virus vaccine: From concept to clinical trials. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, M.K.; Lopez-Martinez, A.; Altomonte, J. Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus as a Viro-Immunotherapy: Defeating Cancer with a “Hammer” and “Anvil”. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishnoi, S.; Tiwari, R.; Gupta, S.; Byrareddy, S.N.; Nayak, D. Oncotargeting by Vesicular Stomatitis Virus (VSV): Advances in Cancer Therapy. Viruses 2018, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cham, L.B.; Friedrich, S.-K.; Adomati, T.; Bhat, H.; Schiller, M.; Bergerhausen, M.; Hamdan, T.; Li, F.; Machlah, Y.M.; Ali, M.; et al. Tamoxifen Protects from Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Infection. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040142
Cham LB, Friedrich S-K, Adomati T, Bhat H, Schiller M, Bergerhausen M, Hamdan T, Li F, Machlah YM, Ali M, et al. Tamoxifen Protects from Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Infection. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040142
Chicago/Turabian StyleCham, Lamin B., Sarah-Kim Friedrich, Tom Adomati, Hilal Bhat, Maximilian Schiller, Michael Bergerhausen, Thamer Hamdan, Fanghui Li, Yara Maria Machlah, Murtaza Ali, and et al. 2019. "Tamoxifen Protects from Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Infection" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 4: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040142
APA StyleCham, L. B., Friedrich, S.-K., Adomati, T., Bhat, H., Schiller, M., Bergerhausen, M., Hamdan, T., Li, F., Machlah, Y. M., Ali, M., Duhan, V., Lang, K. S., Friebus-Kardash, J., & Lang, J. (2019). Tamoxifen Protects from Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Infection. Pharmaceuticals, 12(4), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040142






