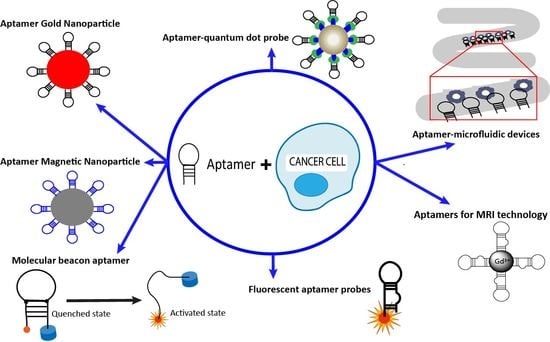
Aptamers as Diagnostic Tools in Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
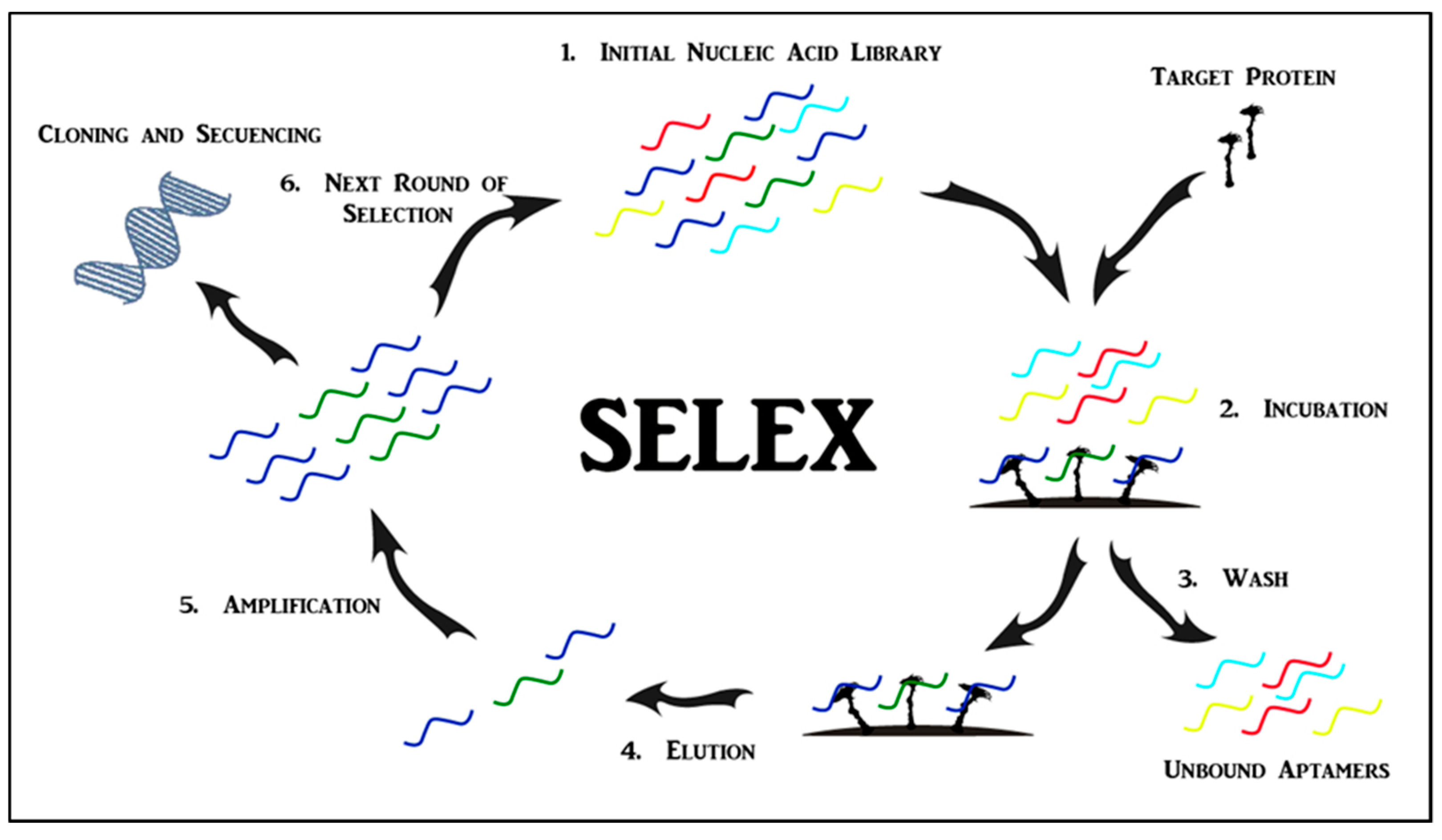
2. Aptamers
3. Applications of Aptamers in Cancer Imaging and Diagnostics
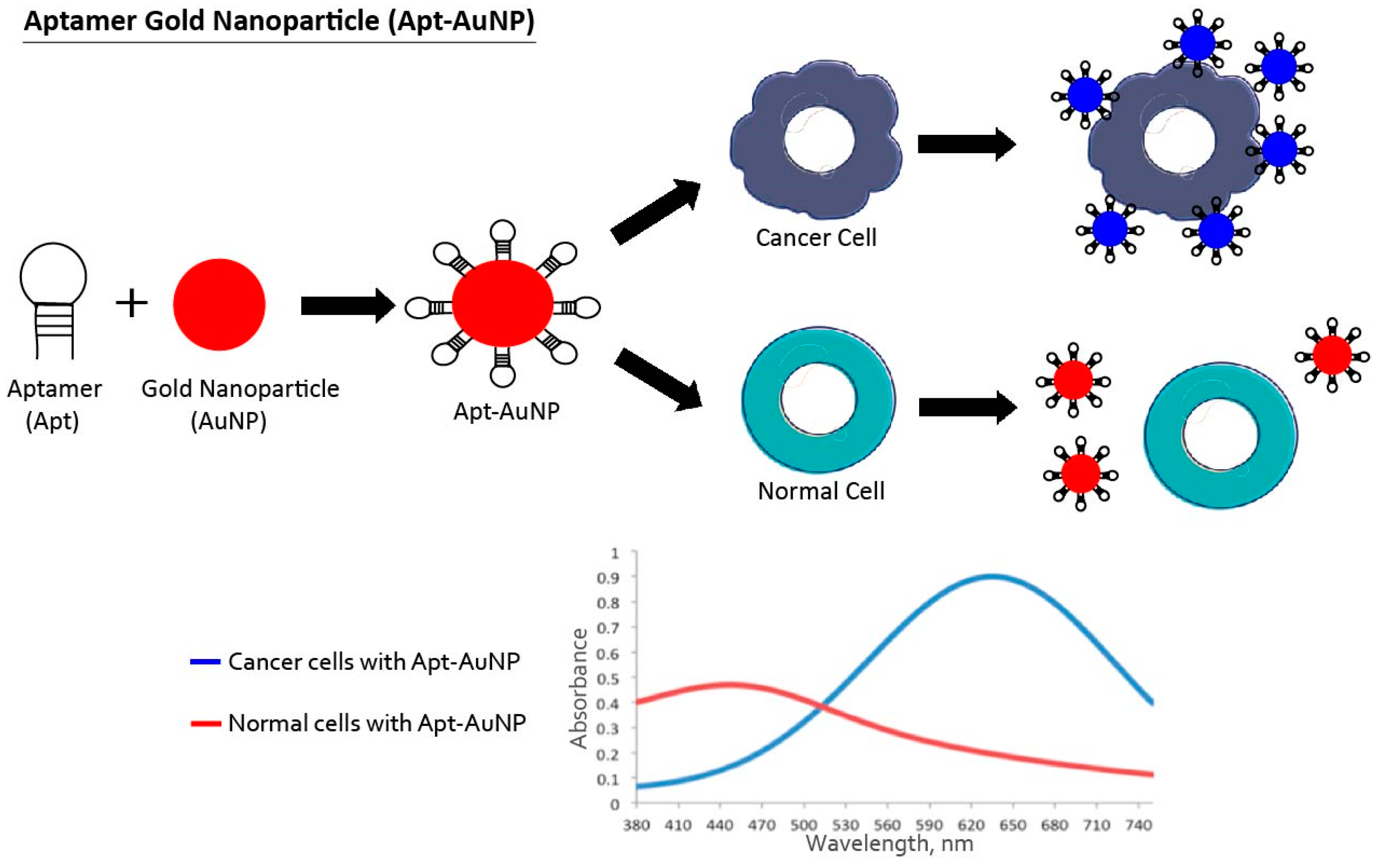
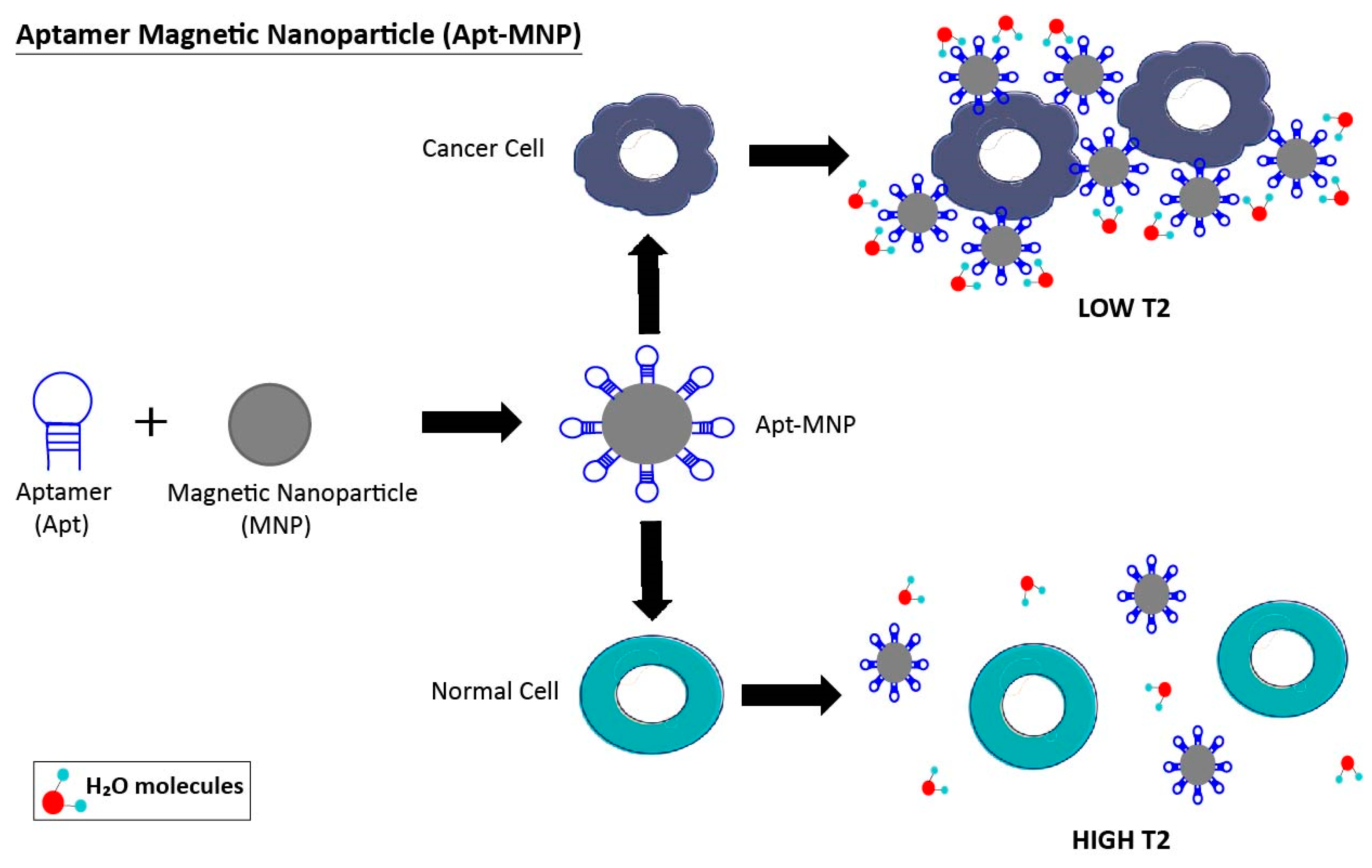
3.1. Aptamer-Nanoparticle System
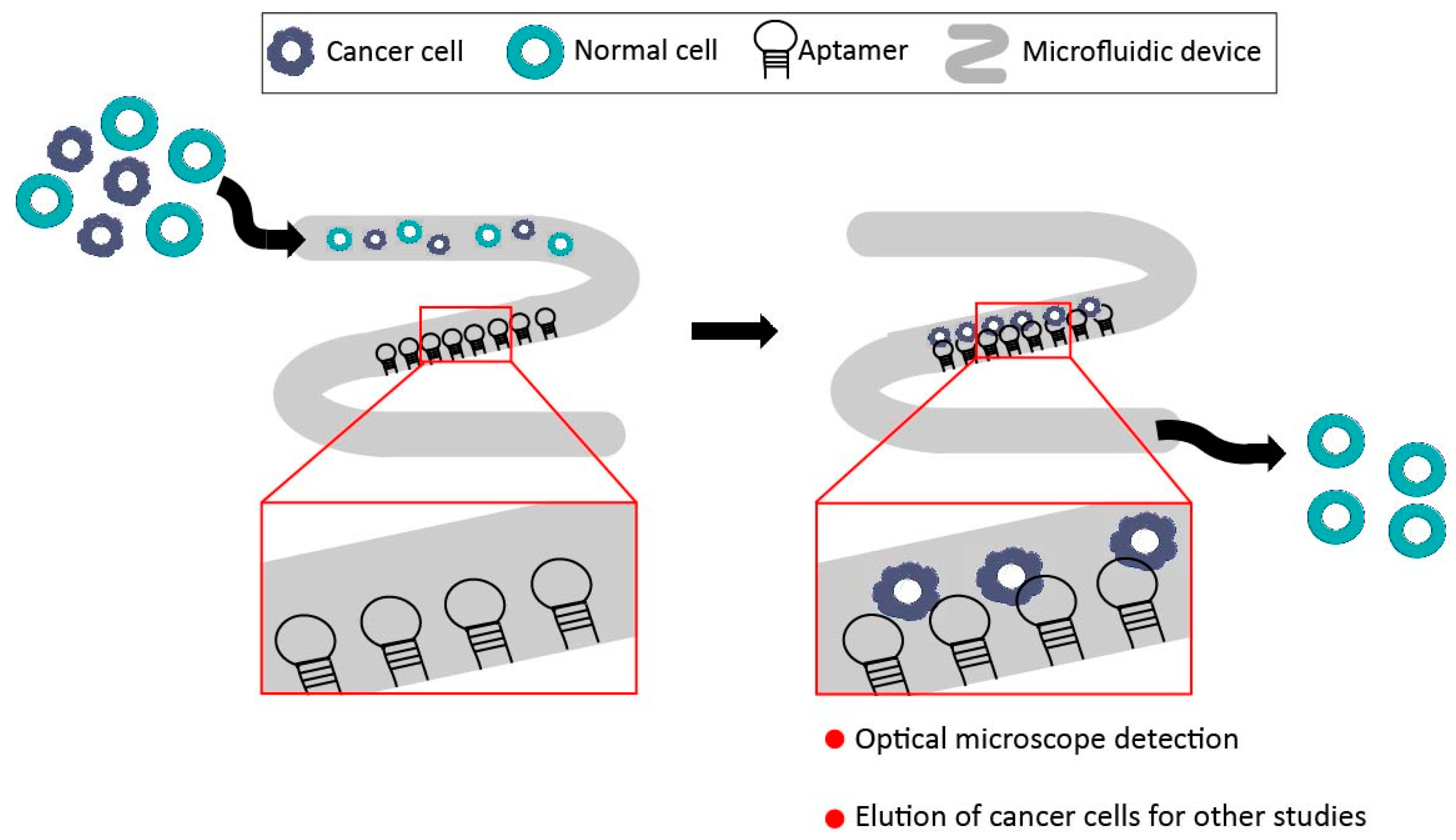
3.2. Aptamer-Microfluidic Devices
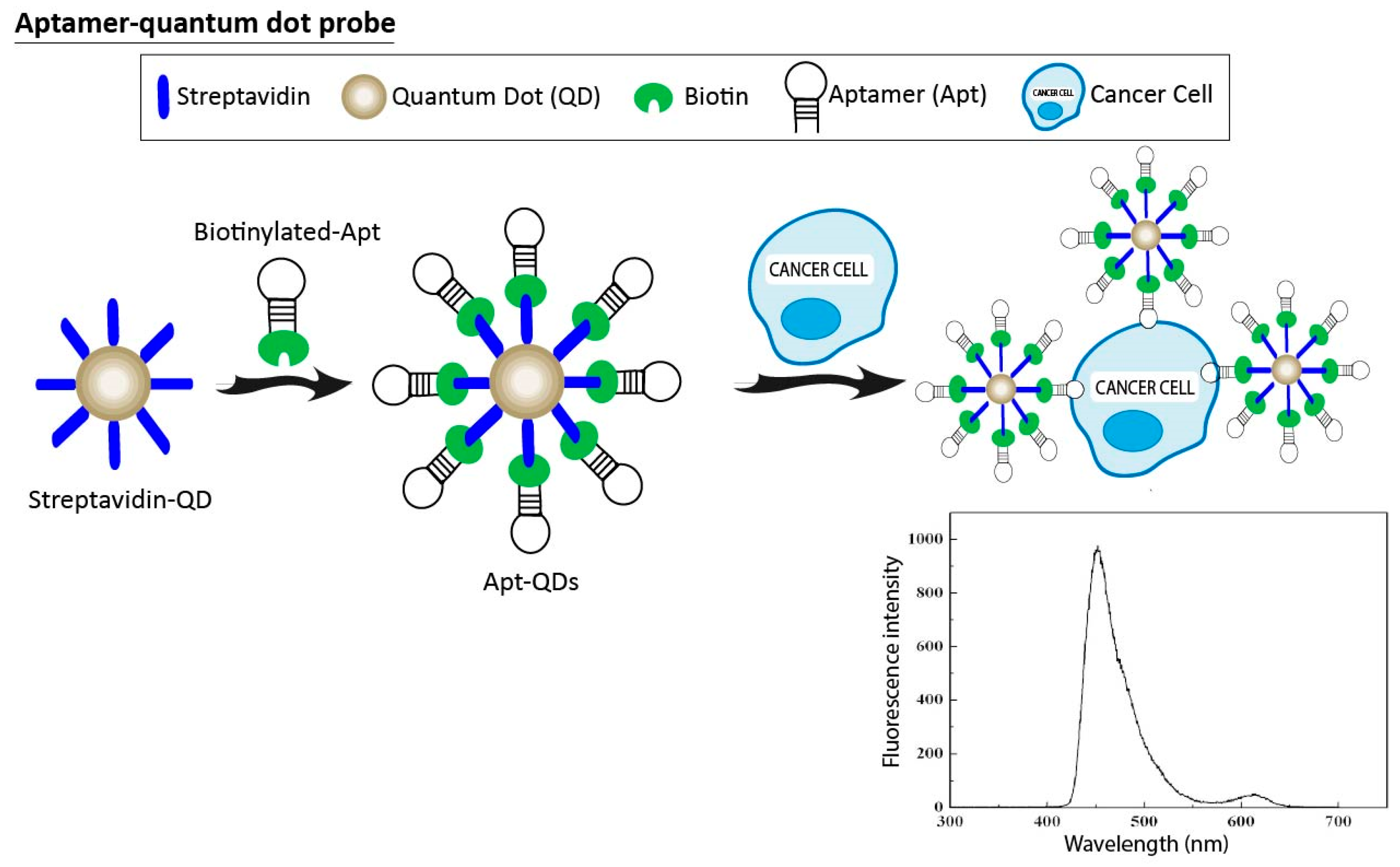
3.3. Aptamer-Quantum Dots Probes
3.4. Molecular Beacon Linked to Aptamers
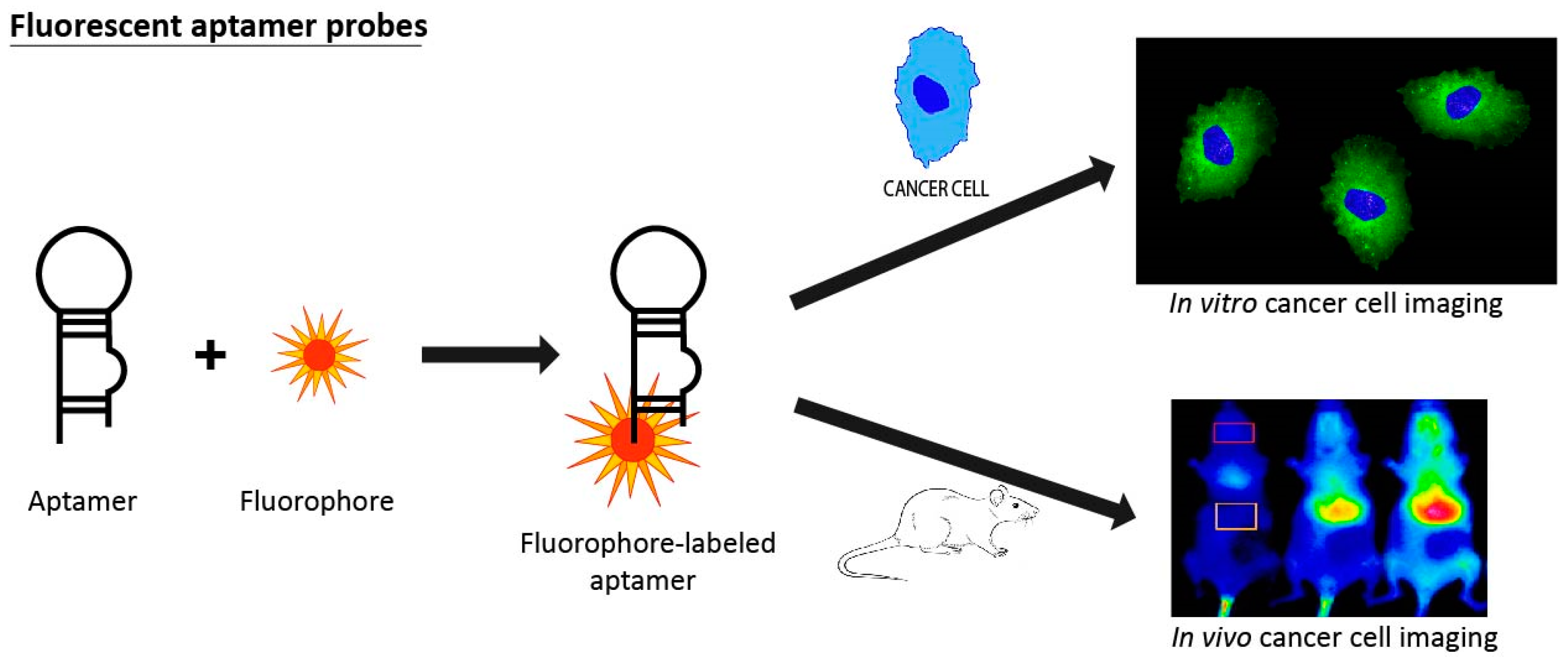
3.5. Fluorescent Aptamer Probes
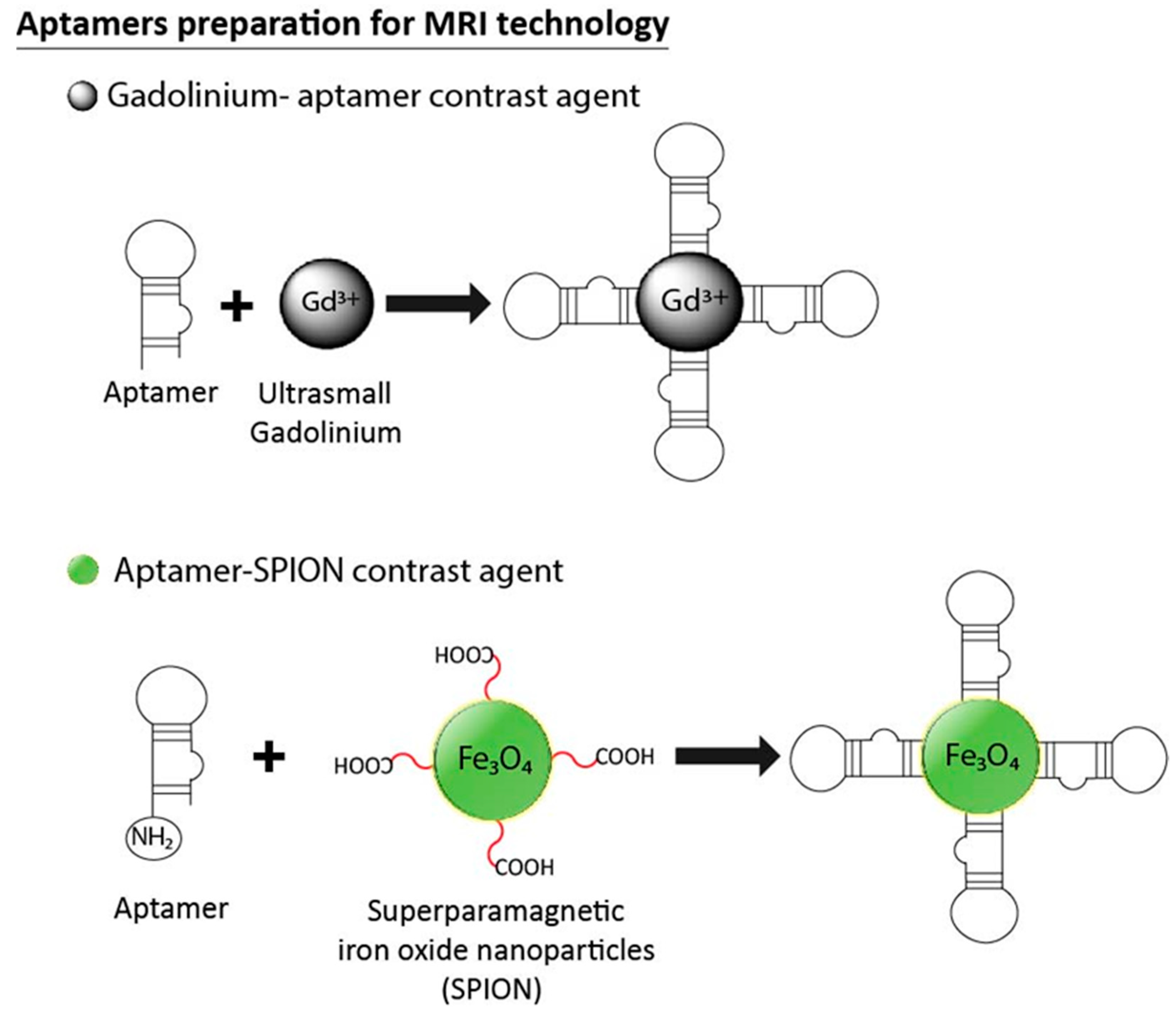
3.6. Aptamers in MRI Technology
4. Aptamers in Clinical Trials
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Miller, K.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Siegel, R.L.; Ward, E.M.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends—An Update. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, T.; Quyen, N. Molecular Imaging for Cancer Diagnosis and Surgery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Bao, J.; Zhou, X. Genome-wide mutational spectra analysis reveals significant cancer-specific heterogeneity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Ali, M.M.; Mahmood, M.A.I.; Labanieh, L.; Lu, M.; Iqbal, S.M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wan, Y. Nucleic acid aptamers in cancer research, diagnosis and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 1240–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, D.D.; Giangrande, P.H. Oligonucleotide Aptamers: A Next-Generation Technology for the Capture and Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Methods 2016, 97, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, K.; Lange, T.; Mittelberger, F.; Schumacher, U.; Hahn, U. Selection and Characterization of an α6β4 Integrin blocking DNA Aptamer. Mol. Ther.-Nucl. Acids 2016, 5, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.W.; Jeong, H.Y.; Kang, S.J.; Choi, M.J.; You, Y.M.; Im, C.S.; Lee, T.S.; Song, I.H.; Lee, C.G.; Rhee, K.J.; et al. Cancer-targeted Nucleic Acid Delivery and Quantum Dot Imaging Using EGF Receptor Aptamer-conjugated Lipid Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.C.; Han, C.L.; Yu, K.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Wu, K.P. Prioritization of cancer marker candidates based on the immunohistochemistry staining images deposited in the Human Protein Atlas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urak, K.T.; Shore, S.; Rockey, W.M.; Chen, S.; Mccaffrey, A.P.; Giangrande, P.H.; City, I.; States, U.; Diego, S.; States, U.; et al. In vitro RNA SELEX for the generation of chemically-optimized therapeutic RNA drugs. Methods 2016, 103, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szostak, J.; Ellington, A. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment: RNA Ligands to Bacteriophage T4 DNA Polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, L.C.; Griffin, L.C.; Latham, J.; Vermaas, E.H.; Toole, J.J. Selection of single-stranded DNA molecules that bind and inhibit human thrombin. Nature 1992, 355, 564–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, K.W.; Giangrande, P.H. Therapeutic Applications of DNA and RNA Aptamers. Oligonucleotides 2009, 19, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.; Tan, G.; Jiang, X.; Wu, K.; Tan, W.; Tan, Y. Suppression of FOXM1 Transcriptional Activities via a Single-Stranded DNA Aptamer Generated by SELEX. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, W.H.; Giangrande, P.H. Analyzing HT-SELEX data with the Galaxy Project tools—A web based bioinformatics platform for biomedical research. Methods 2014, 97, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, W.H.; Bair, T.; Peek, A.S.; Liu, X.; Dassie, J.; Stockdale, K.R.; Behlke, M.A.; Miller, F.J.; Giangrande, P.H. Rapid Identification of Cell-Specific, Internalizing RNA Aptamers with Bioinformatics Analyses of a Cell-Based Aptamer Selection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, W.H. Galaxy Workflows for Web-based Bioinformatics Analysis of Aptamer High-throughput Sequencing Data. Mol. Ther.-Nucl. Acids 2016, 5, e345. [Google Scholar]
- Avci-adali, M. Selection and Application of Aptamers and Intramers. Med. Biol. 2016, 917, 241–258. [Google Scholar]
- Cerchia, L.; de Franciscis, V. Targeting cancer cells with nucleic acid aptamers. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestourie, C.; Cerchia, L.; Gombert, K.; Aissouni, Y.; Boulay, J.; De Franciscis, V.; Libri, D.; Tavitian, B.; Ducongé, F. Comparison of different strategies to select aptamers against a transmembrane protein target. Oligonucleotides 2006, 16, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasset, D.M.; Kubik, M.F.; Steiner, W. Oligonucleotide inhibitors of human thrombin that bind distinct epitopes. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 272, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, J.; Liu, Y.; Rabbani, Z.N.; Yang, Z.; Urban, J.H.; Sullenger, A.; Clary, B.M. In vivo selection of tumor-targeting RNA motifs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangguan, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Cao, Z.C.; Chen, H.W.; Mallikaratchy, P.; Sefah, K.; Yang, C.J.; Tan, W. Aptamers evolved from live cells as effective molecular probes for cancer study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11838–11843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.Y.; Yuan, A.H.; Shi, X.S.; Chen, W.; Miao, Y. Evolution of a gastric carcinoma cell-specific DNA aptamer by live cell-SELEX. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.F.; Yin, C.Q.; Wang, B.C.; Peng, C.W.; Liu, S.P.; Wang, F.B. Identification of an aptamer through whole cell-SELEX for targeting high metastatic liver cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8282–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.J.; Nguyen, P.D.M.; Callaway, M.K.; Johnson, M.C.; Burke, D.H. RNA-protein interactions govern antiviral specificity and encapsidation of broad spectrum anti-HIV reverse transcriptase aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 6087–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedi, V.; Kim, Y.P. Detection and characterization of cancer cells and pathogenic bacteria using aptamer-based nano-conjugates. Sensors 2014, 14, 18302–18327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamay, G.S.; Ivanchenko, T.I.; Zamay, T.N.; Grigorieva, V.L.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Garanzha, I.V.; Barinov, A.A.; Krat, A.V.; Mironov, G.G.; et al. DNA Aptamers for the Characterization of Histological Structure of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Ther.-Nucl. Acids 2017, 6, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohuchi, S. Cell-SELEX Technology. Biores. Open Access 2012, 1, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefah, K.; Shangguan, D.; Xiong, X.; O’Donoghue, M.B.; Tan, W. Development of DNA aptamers using Cell-SELEX. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Shangguan, D.; Wang, K.; Shi, H.; Sefah, K.; Mallikratchy, P.; Chen, H.W.; Li, Y.; Tan, W. Selection of Aptamers for Molecular Recognition and Characterization of Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4900–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, C.H.; Yang, Y.F.; Yin, C.Q.; Guan, Q.; Wang, F.B.; Tu, J.C. Subtractive Cell-SELEX Selection of DNA Aptamers Binding Specifically and Selectively to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells with High Metastatic Potential. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5735869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, M.; Khanahmad, H.; Palizban, A. Selection and characterization of single-stranded DNA aptamers binding human B-cell surface protein CD20 by cell-SELEX. Molecules 2018, 23, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Tan, W.; Fang, X. Introduction to Aptamer and Cell-SELEX. In Aptamers Selected by Cell-SELEX for Theranostics; Fang, X., Tan, W., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, R.L.; Nascimento, I.C.; Santos, A.P.; Ogusuku, I.E.Y.; Lameu, C.; Mayer, G.; Ulrich, H. Aptamers: Novelty tools for cancer biology. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26934–26953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, N.N.; Perret, G.; Ducongé, F. Applications of High-Throughput Sequencing for In Vitro Selection and Characterization of Aptamers. Pharmaceutical 2016, 9, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Scoville, D.J.; Uhm, T.K.B.; Shallcross, J.A.; Whelan, R.J. Selection of DNA Aptamers for Ovarian Cancer Biomarker CA125 Using One-Pot SELEX and High-Throughput Sequencing. J. Nucleic Acids 2017, 2017, 9879135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A.C.; Levy, M. Aptamer-Mediated Delivery and Cell-Targeting Aptamers: Room for Improvement. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018, 28, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohuchi, S.P.; Ohtsu, T.; Nakamura, Y. Selection of RNA aptamers against recombinant transforming growth factor-β type III receptor displayed on cell surface. Biochimie 2006, 88, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, G.; Ahmed, M.S.L.; Dolf, A.; Endl, E.; Knolle, P.A.; Famulok, M. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting for aptamer SELEX with cell mixtures. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.G.; Marangoni, K.; Fujimura, P.T.; Alves, P.T.; Silva, M.J.; Bastos, V.A.F.; Goulart, L.R.; Goulart, V.A. 3D Cell-SELEX: Development of RNA aptamers as molecular probes for PC-3 tumor cell line. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 341, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.C.; Ellington, A.D. Automated selection of anti-protein aptamers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, F.; Tolle, F.; Rosenthal, M.; Brändle, G.M.; Ewers, J.; Mayer, G. Identification and characterization of nucleobase-modified aptamers by click-SELEX. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1153–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, W.H.; Thiel, K.W.; Flenker, K.S.; Bair, T.; Dupuy, A.J.; McNamara, J.O., II; Miller, F.J.; Giangrande, P.H. Cell-Internalization SELEX: Method for Identifying Cell-Internalizing RNA Aptamers for Delivering siRNAs to Target Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1218, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, H.; Trujillo, C.A.; Nery, A.A.; Alves, J.M.; Majumder, P.; Resende, R.R.; Martins, A.H. DNA and RNA aptamers: From tools for basic research towards therapeutic applications. Comb. Chem. High Throughout Screen. 2006, 9, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J.M.; Lewis, S.D.; Kurz, M.; Boomer, R.M.; Thompson, K.M.; Wilson, C.; McCauley, T.G. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of novel aptamer compositions. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 2234–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, A.D.; Cload, S.T. SELEX with modified nucleotides. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratschmer, C.; Levy, M. Effect of Chemical Modifications on Aptamer Stability in Serum. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, R.; Sousa, R. Efficient synthesis of nucleic acids heavily modified with non-canonical ribose 2’-groups using a mutant T7 RNA polymerase (RNAP). Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirao, I.; Kimoto, M.; Mitsui, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Kawai, R.; Sato, A.; Harada, Y.; Yokoyama, S. An unnatural hydrophobic base pair system: Site-specific incorporation of nucleotide analogs into DNA and RNA. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenblum, G.T.; Lopez, V.G.; Vitullo, A.D. Aptamers: Current Challenges and Future Prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Deng, J.; Jin, H.; Yang, X.; Fan, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Chemical modification improves the stability of the DNA aptamer GBI-10 and its affinity towards tenascin-C. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, S.; Gassò, P.; Álvarez, S.; Parellada, E.; Bernardo, M.; Lafuente, A. Intuitive pharmacogenetics: Spontaneous risperidone dosage is related to CYP2D6, CYP3A5 and ABCB1 genotypes. Pharmacogenomics J. 2012, 12, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruta, K.; Otaki, N.; Nagamine, M.; Kayo, T.; Sasaki, A.; Hiramoto, S.; Takahashi, M.; Hota, K.; Sato, H.; Yamazaki, H. A Novel PEGylation Method for Improving the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Anti-Interleukin-17A RNA Aptamers. Nucleic Acids Ther. 2016, 27, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boomer, R.M.; Lewis, S.D.; Healy, J.M.; Kurz, M.; Wilson, C.; McCauley, T.G. Conjugation to Polyethylene Glycol Polymer Promotes Aptamer Biodistribution to Healthy and Inflamed Tissues. Oligonucleotides 2005, 15, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Mehran, R.; Povsic, T.J.; Zelenkofske, S.L.; Huang, Z.; Armstrong, P.W.; Steg, P.G.; Bode, C.; Cohen, M.G.; Buller, C.; et al. Effect of the REG1 anticoagulation system versus bivalirudin on outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention (REGULATE-PCI): A randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganson, N.J.; Povsic, T.J.; Sullenger, B.A.; Alexander, J.H.; Zelenkofske, S.L.; Sailstad, J.M.; Rusconi, C.P.; Hershfield, M.S. Pre-existing anti-polyethylene glycol antibody linked to first-exposure allergic reactions to pegnivacogin, a PEGylated RNA aptamer. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2016, 137, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, A.D.; Pai, S.; Ellington, A. Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiviyanathan, V.; Gorenstein, D.G. Aptamers and the next generation of diagnostic reagents. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.W.M.; Shima, D.T.; Calias, P.; Cunningham, E.T.; Guyer, D.R.; Adamis, A.P. Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, G. The chemical biology of aptamers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2672–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassie, J.P.; Liu, X.; Thomas, G.S.; Whitaker, R.M.; Kristina, W.; Stockdale, K.R.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Mccaffrey, A.P.; Mcnamara, J.O.; Giangrande, P.H. Systemic administration of optimized aptamer-siRNA chimeras promotes regression of PSMA-expressing tumors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, S.F.; Qiao, S.; Tran, P.H.L.; Pu, C.; Li, Y.; Kong, L.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Lin, J.; et al. Superior performance of aptamer in tumor penetration over antibody: Implication of aptamer-based theranostics in solid tumors. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orava, E.W.; Cicmil, N.; Gariépy, J. Delivering cargoes into cancer cells using DNA aptamers targeting internalized surface portals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 2190–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, R.; Grody, W. General Considerations in the Use and Application of Laboratory Tests for the Evaluation of Cancer. In Cancer Diagnostic: Current and Future Trends; Nakamura, R., Grody, W., Wu, J., Nagle, R., Eds.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fass, L. Imaging and cancer: A review. Mol. Oncol. 2008, 2, 115–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimse, S.B.; Sonawane, M.D.; Song, K.S.; Kim, T. Biomarker detection technologies and future directions. Analyst 2015, 141, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badalà, F.; Nouri-mahdavi, K.; Raoof, D.A. Aptamer in Bioanalytical Applications. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4440–4452. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.; Shigdar, S.; Qiao, G.; Wang, T.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Zhou, S. Nucleic Acid Aptamer-Guided Cancer Therapeutics and Diagnostics: The Next Generation of Cancer Medicine. Theranostics 2015, 5, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Hwang, K.; Li, J.; Torabi, S.F.; Lu, Y. DNA Aptamer Technology for Personalized Medicine. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2014, 4, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medley, C.D.; Bamrungsap, S.; Tan, W.; Smith, J.E. Aptamer-Conjugated Nanoparticles for Cancer Cell Detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 83, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Mao, X.; Phillips, J.A.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Zeng, L. Aptamer-nanoparticle strip biosensor for sensitive detection of cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 10013–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medley, C.D.; Smith, J.E.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Bamrungsap, S.; Tan, W. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for the direct detection of cancerous cells. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghei, Y.S.; Hosseini, M.; Dadmehr, M.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Sheikhnejad, R. Visual detection of cancer cells by colorimetric aptasensor based on aggregation of gold nanoparticles induced by DNA hybridization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 904, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Tan, J.; Lai, Z.; Zheng, R.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, N.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Aptamer Combined with Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Detection of Hepatoma Cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Yang, N.; Hu, Z.; Su, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xue, D.; Huang, Y.; et al. Aptamer-Functionalized Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive Detection of Leukemia Cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.M.; Bachelet, I.; Church, G.M. A Logic-Gated Nanorobot for Targeted Transport of Molecular Payloads. Science 2012, 335, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamrungsap, S.; Chen, T.; Shukoor, M.I.; Chen, Z.; Sefah, K.; Chen, Y.; Tan, W. Pattern Recognition of Cancer Cells Using Aptamer-Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3974–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Wei, S.; Liu, H. Electrochemiluminescent Determination of Cancer Cells Based on Aptamers, Nanoparticles, and Magnetic Beads. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 7263–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, H. Sensitive cancer cell detection based on Au nanoparticles enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdS nanocrystal film supplemented by magnetic separation. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 25, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tan, T.; Fub, J.J.; Zhengb, T.; Zhub, J.J. A novel aptamer-based competition strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of leukemia cells. Analyst 2013, 138, 6323–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshfetrat, S.M.; Mehrgardi, M.A. Amplified detection of leukemia cancer cells using an aptamer-conjugated gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles on a nitrogen-doped graphene modified electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 2016, 114, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashkavayi, A.B.; Raoof, J.B.; Ojani, R.; Kavoosian, S. Ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor based on sandwich architecture for selective label-free detection of colorectal cancer (CT26) cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 92, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; He, M.Q.; Zhai, F.H.; He, R.H.; Yu, Y.L. A novel electrochemical biosensor based on polyadenine modified aptamer for label-free and ultrasensitive detection of human breast cancer cells. Talanta 2017, 166, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashefi-Kheyrabadi, L.; Mehrgardi, M.A.; Wiechec, E.; Turner, A.P.F.; Tiwari, A. Ultrasensitive Detection of Human Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Using a Label-Free Aptasensor. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4956–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari-bafrooei, E.; Shamszadeh, N.S. Electrochemical bioassay development for ultrasensitive aptasensing of prostate specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 15, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crulhas, B.P.; Karpik, A.E.; Delella, F.K.; Castro, G.R.; Pedrosa, V.A. Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensor developed to monitor PSA and VEGF released by prostate cancer cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6771–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, S.; Mohammad, N.; Ramezani, M. A novel electrochemical aptasensor based on Y-shape structure of dual-aptamer-complementary strand conjugate for ultrasensitive detection of myoglobin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 532–537. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, J.A.; Xu, Y.; Xia, Z.; Fan, Z.H.; Tan, W. Enrichment of cancer cells using aptamers immobilized on a microfluidic channel. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Phillips, J.A.; Yan, J.; Li, Q.; Fan, Z.H.; Tan, W. Aptamer-based microfluidic device for enrichment, sorting, and detection of multiple cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7436–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, C.H.; Bose, S.; Guo, D.; Shen, C.; Wong, W.P. Bioinspired multivalent DNA network for capture and release of cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19626–19631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Ji, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S. A chemiluminescence imaging array for the detection of cancer cells by dual-aptamer recognition and bio-bar-code nanoprobe-based rolling circle amplification. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3452–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, W. Cascade Signal Amplification Based on Copper Nanoparticle-Reported Rolling Circle Amplification for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection of the Prostate Cancer Biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Georgiev, T.Z.; Sheng, W.; Zheng, X.; Varillas, J.I.; Zhang, J.; Hugh Fan, Z. Tumor cell capture patterns around aptamer-immobilized microposts in microfluidic devices. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 54110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Chen, T.; Tan, W.; Fan, Z.H. Multivalent DNA Nanospheres for Enhanced Capture of Cancer Cells in Microfluidic Devices. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7067–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.J.; Chae, J.R.; Cho, Y.L.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, S. Multiplex imaging of single tumor cells using quantum-dot-conjugated aptamers. Small 2009, 5, 2519–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, S.H.; Zhang, P.F.; Gong, P.; Hu, D.H.; Shi, B.H.; Zeng, C.C.; Cai, L.T. A Universal Quantum Dots-Aptamer Probe for Efficient Cancer Detection and Targeted Imaging. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7703–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kang, H.J.; Jang, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Ali, B.A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Kim, S. Simultaneous imaging of two different cancer biomarkers using aptamer-conjugated quantum dots. Sensors 2015, 15, 8595–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, G.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, Y. A fluorescent polymeric quantum dot/aptamer superstructure and its application for imaging of cancer cells. Chem.-Asian J. 2014, 9, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; He, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, N. DNA-Programmed Quantum Dot Polymerization for Ultrasensitive Molecular Imaging of Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9355–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Huang, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, T.; Tan, Y.; Pi, J.; Pi, L.; Cheng, S.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, Y. Aptamer-conjugated PEGylated quantum dots targeting epidermal growth factor receptor variant III for fluorescence imaging of glioma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3899–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Ji, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, K. A recognition-before-labeling strategy for sensitive detection of lung cancer cells with a quantum dot–aptamer complex. Analyst 2015, 140, 6100–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, X.; Ye, X.; Guo, Q.; Tan, W.; Qing, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhou, B. Activatable aptamer probe for contrast-enhanced in vivo cancer imaging based on cell membrane protein-triggered conformation alteration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3900–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Tung, C.H.; Zu, Y. A cancer cell-activatable aptamer-reporter system for one-step assay of circulating tumor cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Mu, Y.; Qian, S.; Lu, J.; Wan, Y.; Fu, G.; Liu, S. Synthesis of fluorescent dye-doped silica nanoparticles for target-cell-specific delivery and intracellular microRNA imaging. Analyst 2015, 140, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, K.J.; Lee, M.; Jo, M.H.; Kim, S. Molecular imaging of a cancer-targeting theragnostics probe using a nucleolin aptamer- and microRNA-221 molecular beacon-conjugated nanoparticle. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Wu, C.; You, M.; Han, D.; Chen, T.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, J.; Yu, R.; Tan, W. A Targeted, Self-delivered and Photocontrolled Molecular Beacon for mRNA Detection in Living Cells Liping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12925–12955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zu, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.J. Detection of DNA methyltransferase activity using allosteric molecular beacons. Analyst 2016, 141, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Tan, J.; Wan, R.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. An “activatable” aptamer-based fluorescence probe for the detection of HepG2 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, S.T.; Han, H.S.; Kim, K.; Han, J.S. Optical aptamer probes of fluorescent imaging to rapid monitoring of circulating tumor cell. Sensors 2016, 16, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, N.; Zeng, Z.; Feng, Y.; Tung, C.H.; Chang, C.C.; Zu, Y. Using an RNA aptamer probe for flow cytometry detection of CD30-expressing lymphoma cells. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Tang, Z.; Kim, Y.; Nie, H.; Huang, Y.F.; He, X.; Deng, K.; Wang, K.; Tan, W. In vivo fluorescence imaging of tumors using molecular aptamers generated by cell-SELEX. Chem.-Asian J. 2010, 5, 2209–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Cui, W.; He, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, K.; Ye, X.; Tang, J. Whole Cell-SELEX Aptamers for Highly Specific Fluorescence Molecular Imaging of Carcinomas In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, K.; Meng, X.; Huang, Z.; Wen, X. Metastatic cancer cell and tissue-specific fluorescence imaging using a new DNA aptamer developed by Cell-SELEX. Talanta 2017, 170, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryza, D.; Debordeaux, F.; Azema, L.; Hassan, A.; Paurelle, O.; Schulz, J.; Savona-Baron, C.; Charignon, E.; Bonazza, P.; Taleb, J.; et al. Ex vivo and in vivo imaging and biodistribution of aptamers targeting the human Matrix MetalloProtease-9 in melanomas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boros, E.; Gale, E.M.; Caravan, P. MR Imaging Probes: Design and Applications. Dalt Trans. 2015, 44, 4804–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; You, J.; Dai, Y.; Shi, M.; Han, C.; Xu, K. Gadolinium oxide nanoparticles and aptamer-functionalized silver nanoclusters-based multimodal molecular imaging nanoprobe for optical/magnetic resonance cancer cell imaging. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11306–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.Z.; Bagalkot, V.; Vasilliou, C.C.; Gu, F.; Alexis, F.; Zhang, L.; Shaikh, M.; Yuet, K.; Cima, M.J.; Langer, R.; et al. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Aptamer Bioconjugates for Combined Prostate Cancer Imaging and Therapy. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.K.; Kim, D.; Lee, I.H.; So, J.S.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Jon, S. Image-Guided Prostate Cancer Therapy Using Aptamer-Functionalized Thermally Cross-Linked Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Small 2011, 7, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.G.; Tu, R.; Peng, M.L.; Bai, Y.J.; Tan, M.; Li, H.J.; Guan, J.; Wen, L.J. Molecular magnetic resonance probe targeting VEGF165: Preparation and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2014, 9, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mi, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; et al. Multifunctional nanoprobe for cancer cell targeting and simultaneous fluorescence/magnetic resonance imaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 938, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshtkar, M.; Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D.; Khoshfetrat, S.M.; Mehrgardi, M.A.; Aghaei, M. Aptamer-conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles as Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent for Breast Cancer. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2016, 6, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clinicaltrials.gov US National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03385148 (accessed on 28 December 2017).
- Clinicaltrials.gov US National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02957370 (accessed on 7 November 2016).
- Jung, Y.J.; Katilius, E.; Ostroff, R.M.; Kim, Y.; Seok, M.; Lee, S.; Jang, S.; Kim, W.S.; Choi, C.M. Development of a Protein Biomarker Panel to Detect Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Korea. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, e99–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Novotny, W. Bevacizumab (Avastin), a humanized anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody for cancer therapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, J.; Araujo, J.; Yang, J.; Reich, M.; Oldendorp, A.; Shiu, V.; Quarmby, V.; Lowman, H.; Lien, S.; Gaudreault, J.; et al. Ranibizumab inhibits multiple forms of biologically active vascular endothelial growth factor in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 85, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeraro, F.; Morescalchi, F.; Duse, S.; Parmeggiani, F.; Gambicorti, E.; Costagliola, C. Aflibercept in wet AMD: Specific role and optimal use. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 7, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, P.J.; Kahlon, J.B.; Thomas, S.D.; Trent, J.O.; Miller, D.M. Antiproliferative activity of G-rich oligonucleotides correlates with protein binding. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26369–26377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoellenriegel, J.; Zboralski, D.; Maasch, C.; Rosin, N.Y.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, J.; Kruschinski, A.; Burger, J.A.; Hoellenriegel, J.; Zboralski, D.; et al. The Spiegelmer NOX-A12, a novel CXCL12 inhibitor, interferes with chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell motility and causes chemosensitization. Blood 2014, 123, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinicaltrials.gov US National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00512083 (accessed on 7 August 2007).
- Clinicaltrials.gov US National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00740441 (accessed on 25 August 2008).
- Clinicaltrials.gov US National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01486797 (accessed on 7 December 2011).
- Clinicaltrials.gov US National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01521533 (accessed on 30 January 2012).
- Clinicaltrials.gov US National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03168139 (accessed on 30 May 2017).
- Dunn, M.R.; Jimenez, R.M.; Chaput, J.C. Analysis of aptamer discovery and technology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.W.; Ko, H.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, H.; Ryu, S.H.; Song, I.C.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, S. A Nucleolin-Targeted Multimodal Nanoparticle Imaging Probe for Tracking Cancer Cells Using an Aptamer. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.J.; Fang, X.; Tan, W. Molecular aptamer beacons for real-time protein recognition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 292, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaught, J.D.; Bock, C.; Carter, J.; Fitzwater, T.; Otis, M.; Schneider, D.; Rolando, J.; Waugh, S.; Wilcox, S.K.; Eaton, B.E. Expanding the chemistry of DNA for in vitro selection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4141–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Katilius, E.; Olivas, E.; Dumont Milutinovic, M.; Walt, D.R. Incorporation of Slow Off-Rate Modified Aptamers Reagents in Single Molecule Array Assays for Cytokine Detection with Ultrahigh Sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8385–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.J.; Wang, X.; Diaz, A.; Goos-Root, D.M.; Bock, C.; Vaught, J.D.; Sun, W.; Strom, C.M. Measurement of Cetuximab and Panitumumab-Unbound Serum EGFR Extracellular Domain Using an Assay Based on Slow Off-Rate Modified Aptamer (SOMAmer) Reagents. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohloff, J.C.; Gelinas, A.D.; Jarvis, T.C.; Ochsner, U.A.; Schneider, D.J.; Gold, L.; Janjic, N. Nucleic acid ligands with protein-like side chains: Modified aptamers and their use as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Mol. Ther.-Nucl. Acids 2014, 3, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerchia, L.; Esposito, C.L.; Camorani, S.; Rienzo, A.; Stasio, L.; Insabato, L.; Affuso, A.; De Franciscis, V. Targeting Axl with an high-affinity inhibitory aptamer. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.Y.; Ortube, M.C.; McCannel, C.A.; Sarraf, D.; Hubschman, J.P.; McCannel, T.A.; Gorin, M.B. Sustained elevated intraocular pressures after intravitreal injection of bevacizumab, ranibizumab, and pegaptanib. Retina 2011, 31, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.J.; Lee, J.W.; Ellington, A.D. Applications of Aptamers as Sensors. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2009, 2, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Aptamer Name | Nature | Ligand/Target | Cancer | Affinity (nM) 1 | Reference in the Review |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD05 | DNA | Immunoglobulin heavy constant mu (IGHM) | Burkitt Lymphoma | 74.7 | [33,75,81,115] |
| TE02 | DNA | Ramos cells | Burkitt Lymphoma | 0.76 | [33,75] |
| AS1411 | DNA | Nucleolin | Expressed in different cancers | 169 | [77,99,100,101,108,109,110,120,125] |
| TLS11a | DNA | HepG2 cells (also LH86 cells) | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 7 | [78,112,124] |
| Sgc8 | DNA | Tyrosine-protein kinase-like 7 (PTK7) | T-cell leukemia | 0.8 | [79,80,81,85,92,93,94,97,106] |
| 41t | DNA | Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) | --- | 1 | [80] |
| TE17 | DNA | CCRF-CEM cells | T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia | 675 | [80] |
| KDED 2a-3 | DNA | DLD-1 cells | Colorectal cancer | 29.2 | [81] |
| KCHA10 | DNA | HCT 116 cells | Colorectal cancer | 21.3 | [81] |
| Sgd5 | DNA | Toledo cells | nonHodgkin’s B cell lymphoma | 70.8 | [93] |
| TTA1 | DNA | Tenacin C | Expressed in different cancers | 5 | [99,101] |
| MUC-1 | DNA | Mucin 1 | Adenocarcinoma | 27 | [99] |
| A32 | DNA | Epidermal growth factor receptor III (EGFRIII) | Glioma | 0.62 | [104] |
| S11e | DNA | A549 cells | Lung | 46.2 | [105] |
| --- | RNA | CD30 | Lymphoma | 0.11 | [114] |
| S6 | DNA | A549 cells | Lung | 28.2 | [116] |
| J3 | DNA | LoVo cells | Colorectal carcinoma | 138.2 | [117] |
| F3B | RNA | Human matrix metalloprotease-9 (hMMP-9) | Malignant melanoma | 20 | [118] |
| A10 | RNA | Prostate membrane antigen (PSMA) | Prostate | 11.9 | [121,122] |
| VEGF165 | RNA | Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF-165) | Expressed in different cancers | 50 | [123] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz Ciancio, D.; Vargas, M.R.; Thiel, W.H.; Bruno, M.A.; Giangrande, P.H.; Mestre, M.B. Aptamers as Diagnostic Tools in Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030086
Ruiz Ciancio D, Vargas MR, Thiel WH, Bruno MA, Giangrande PH, Mestre MB. Aptamers as Diagnostic Tools in Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2018; 11(3):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030086
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz Ciancio, Dario, Mauricio R. Vargas, William H. Thiel, Martin A. Bruno, Paloma H. Giangrande, and María Belén Mestre. 2018. "Aptamers as Diagnostic Tools in Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 11, no. 3: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030086
APA StyleRuiz Ciancio, D., Vargas, M. R., Thiel, W. H., Bruno, M. A., Giangrande, P. H., & Mestre, M. B. (2018). Aptamers as Diagnostic Tools in Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 11(3), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030086