Materials-Driven Advancements in Chipless Radio-Frequency Identification and Antenna Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
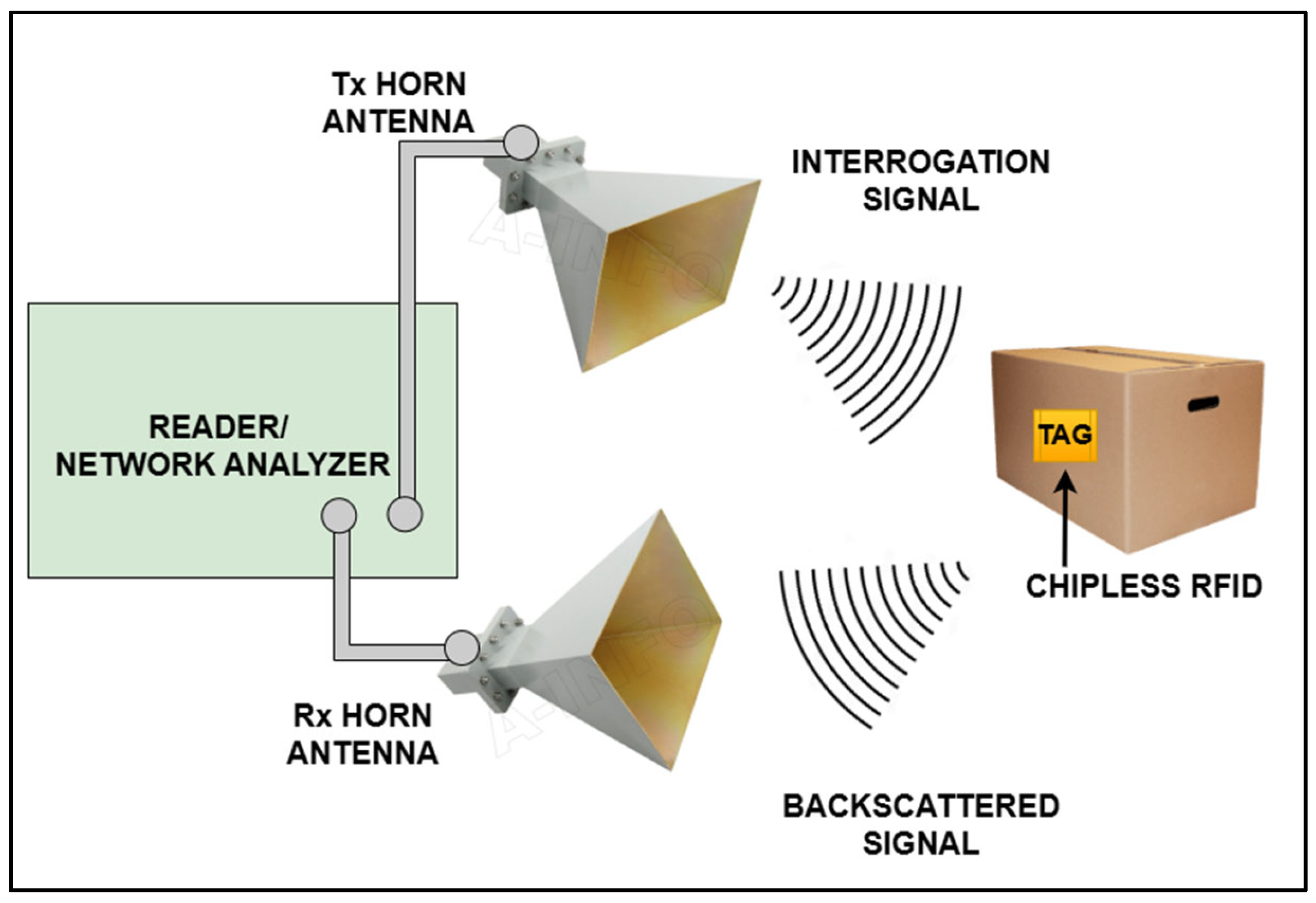
2. Working Principle of CRFID Tags
3. Substrate Material
3.1. Rigid Materials
3.2. Flexible Materials
3.2.1. Paper as Flexible Substrate
3.2.2. Textile as Flexible Substrate
3.2.3. Polymers as Flexible Substrate
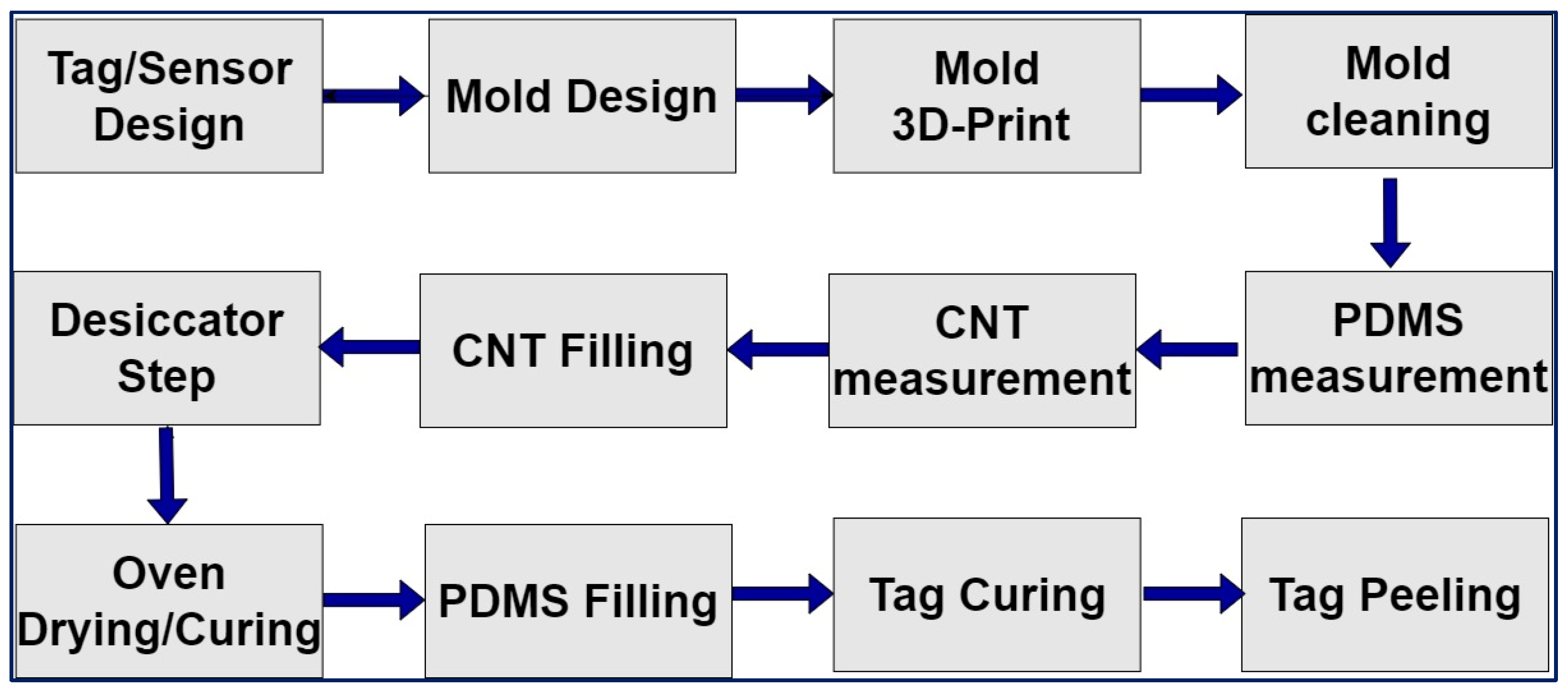
3.3. 3D-Printable Materials
- Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers;
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printers;
- Selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printers.
3.4. Advanced Substrates
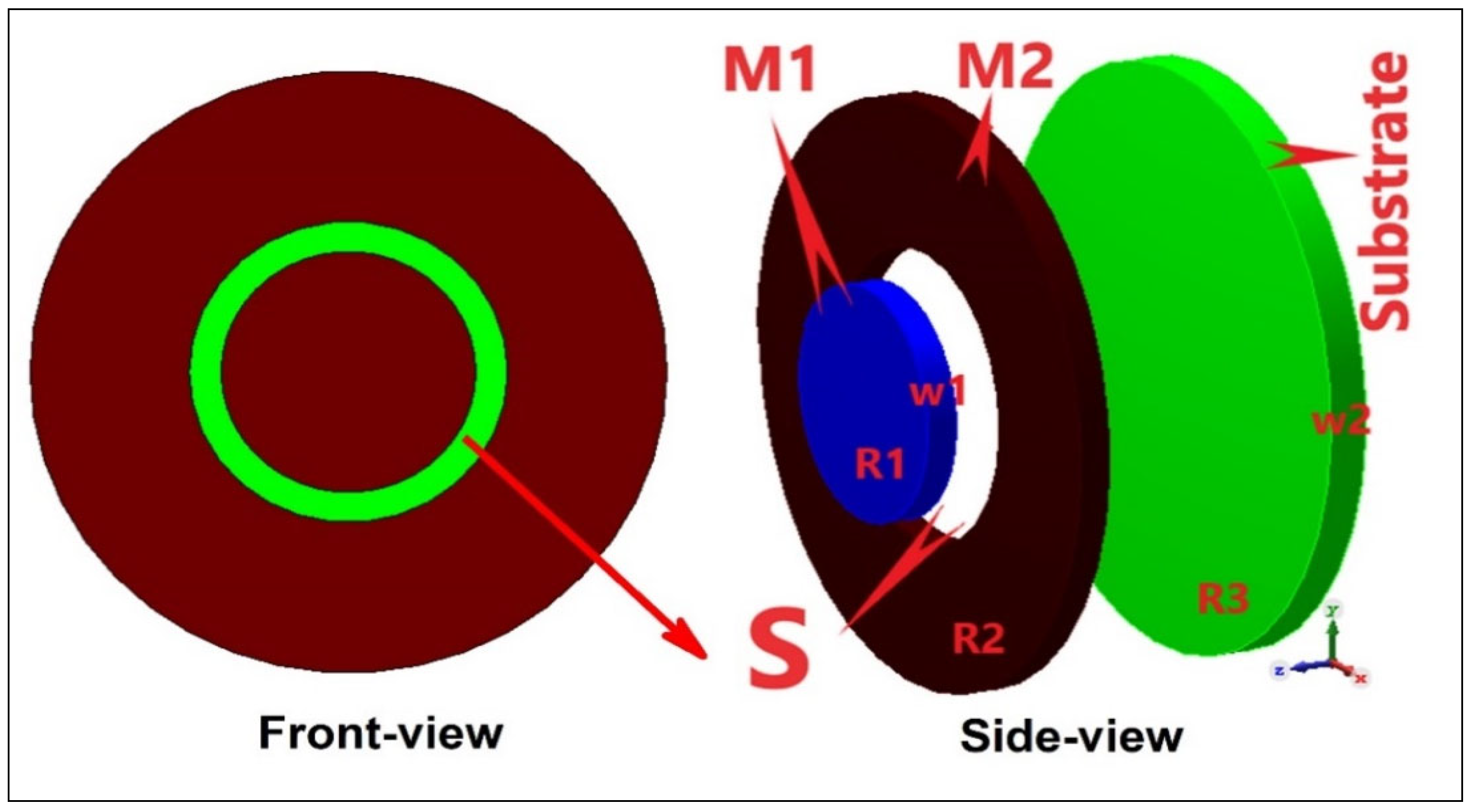
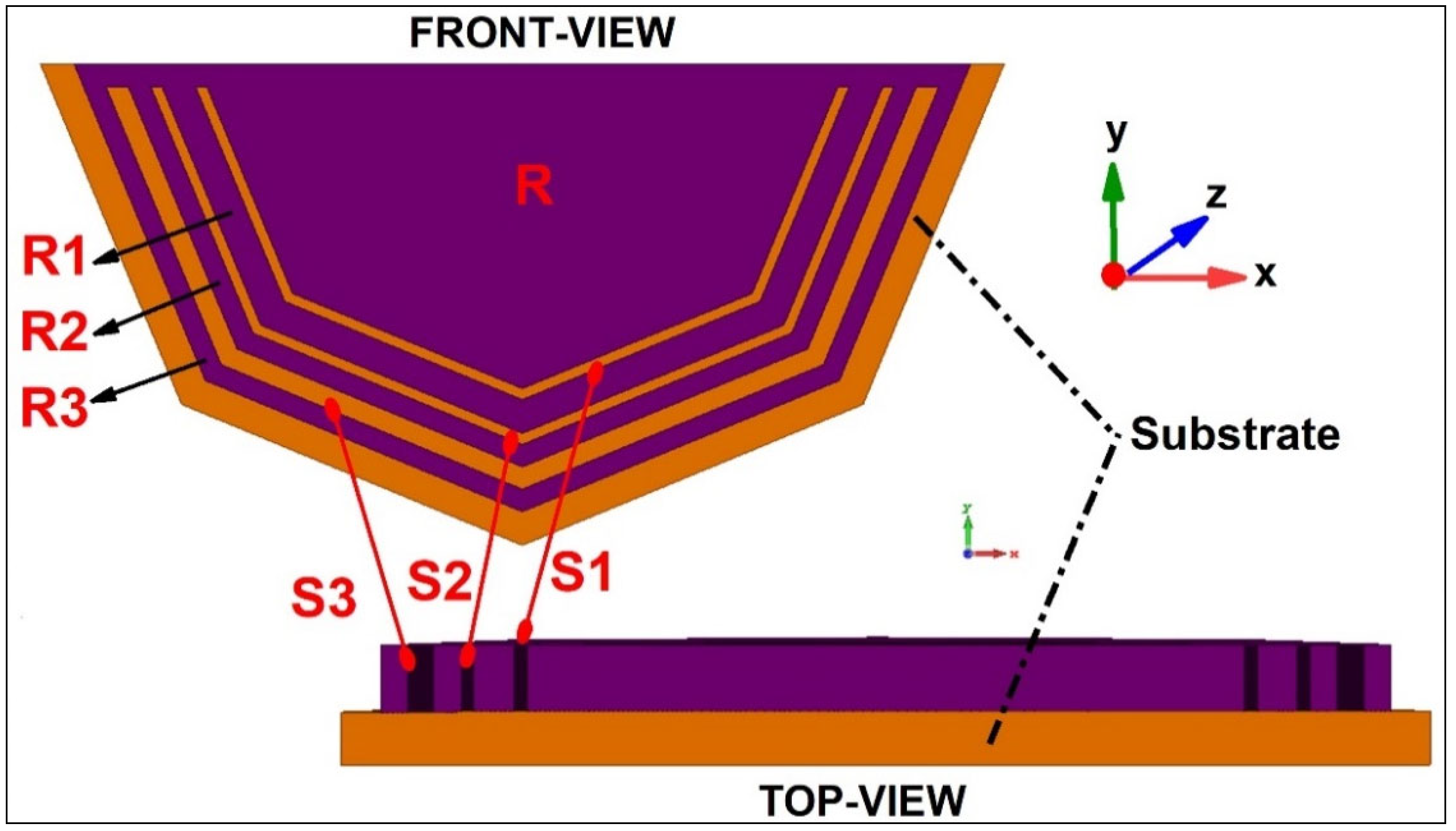
4. Radiator Material
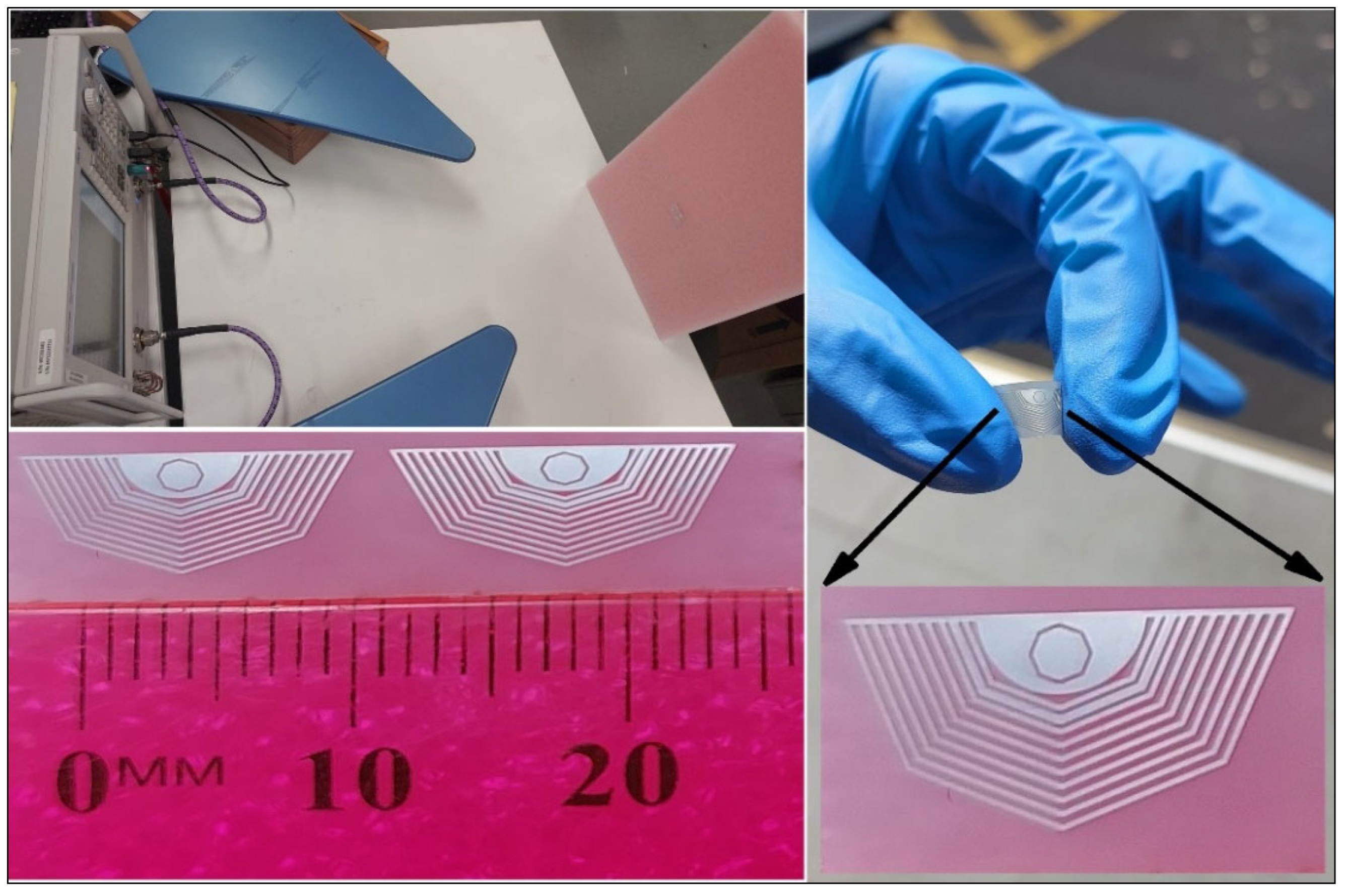
4.1. Conventional Metals
4.2. Flexible Radiating Materials
4.3. Stretchable Radiators
4.4. Ink-Based Tags/Antennas
4.5. Advanced Materials
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, Z.; Perret, E. A Simple RCS Calibration Approach for Depolarizing Chipless RFID Tags. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–25 June 2021; pp. 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobkin, D.M. The RF in RFID: Passive UHF RFID in Practice; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; ISBN 978-0-7506-8209-1. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.U.A. Polymer-Based Flexible Antennas and Chipless RFID Tags for General IoT Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Mejia, G.; Martinez-Castillo, J.; Diaz-Sanchez, A.; Rocha-Perez, J.M.; Herrera-May, A.L.; Zapata-Rodriguez, U.G.; Carbajal-Gomez, V.H. A Self-Powered UHF Passive Tag for Biomedical Temperature Monitoring. Electronics 2022, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Khaliel, M.; Zantah, Y.; Vinck, A.J.H.; Kaiser, T.; El-Awamry, A. Motion Modulation Backscattering of Linear Chipless RFID Tags: THz Measurements. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Mobile and Miniaturized Terahertz Systems (ICMMTS), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 23–26 February 2025; pp. 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZOIN Market Research Homepage. Available online: https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/report/chipless-rfid-market (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Chipless RFID Market Homepage. Available online: https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-chipless-rfid-market/36436/ (accessed on 26 July 2023).
- Habib, A.; Mirza, A.; Umair, M.Y.; Salimi, M.N.; Ahmed, S.; Amin, Y. Data dense chipless RFID tag with efficient band utilization. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) 2022, 152, 154220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, E.; Nair, R.S.; Kamel, E.B.; Vena, A.; Tedjini, S. Chipless RFID tags for passive wireless sensor grids. In Proceedings of the 2014 XXXIth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), Beijing, China, 16–23 August 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.; Pinho, P.; Carvalho, N.B.; Tentzeris, M.M. Humidity passive sensors based on UHF RFID using cork dielectric slabs. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Lisbon, Portugal, 13–17 April 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Sáez, A.; Sakaki, M.; Sánchez-Pastor, J.; Schüßler, M.; Jakoby, R.; Benson, N. Ceramic-Based High-Q Retroreflectors for Sub-mm Localization in High-Temperature Environments. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Mobile and Miniaturized Terahertz Systems (ICMMTS), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 23–26 February 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vena, A.; Sydänheimo, L.; Ukkonen, L.; Tentzeris, M.M. A fully inkjet-printed chipless RFID gas and temperature sensor on paper. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE RFID Technology and Applications Conference (RFID-TA), Tampere, Finland, 8–9 September 2014; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliri, A.; Galehdar, A.; John, S.; Wang, C.H.; Rowe, W.S.T.; Ghorbani, K. Wireless strain measurement using circular microstrip patch antennas. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 184, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, J.R.; Malocha, D.C. Wireless SAW Strain Sensor Using Orthogonal Frequency Coding. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5527–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M.; Amber, S.F.; Ejaz, A.; Habib, A.; Jafri, S.I.; Amin, Y. Design and analysis of C shaped chipless RFID tag. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Wireless Systems and Networks (ISWSN), Lahore, Pakistan, 19–22 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, L.-R. Low-Cost Printed Chipless RFID Humidity Sensor Tag for Intelligent Packaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.; Majumder, S.P. Improvement of the read range of a chipless RFID for MPSK UWB system in outdoor and farm NLOS environment using receiver diversity with maximal ratio combining. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 22–23 December 2014; pp. 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Karmakar, N.C. Analysis of real-world implementation challenges of chipless RFID tag. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2019, 13, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulloni, V.; Marchi, G.; Valt, A.G.M.; Donelli, M.; Lorenzelli, L. Applications of Chipless RFID Humidity Sensors to Smart Packaging Solutions. Sensors 2024, 24, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Agarwal, M.; Khanna, R. An ultrathin compact orientation insensitive chipless RFID tag with high bit capacity. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 21–22 March 2024; pp. 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, C.D.; Narbudowicz, A. Chipless RFID Sensor on Paper Substrate. In Proceedings of the 2024 18th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Glasgow, UK, 17–22 March 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, M.; Anandarajah, P.; Collins, D. A Review of Chipless Remote Sensing Solutions Based on RFID Technology. Sensors 2019, 19, 4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulloni, V.; Donelli, M. Chipless RFID Sensors for the Internet of Things: Challenges and Opportunities. Sensors 2020, 20, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, A.; Sarhaddi, A.H.; Emami, H. A Review on Chipless RFID Tag Design. Majlesi J. Electr. Eng. 2013, 7, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Patre, S.R. Passive Chipless RFID Sensors: Concept to Applications—A Review. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2022, 6, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessky, V.; Lamothe, M. Ultra-wide-band SAW RFID/sensors. In Proceedings of the 2014 European Frequency and Time Forum (EFTF), Neuchatel, Switzerland, 23–26 June 2014; pp. 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anam, H.; Abbas, S.M.; Collings, I.B.; Mukhopadhyay, S. A PDMS/MWCNTs RFID Flexible Tag with Advanced Resonator Design for Read Range Enhancement in IoT Monitoring Systems. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anam, H.; Rafique, U.; Agarwal, S.; Abbas, S.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Metallic Crack Detection Using Chipless RFID Single-bit Sensor Tag. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Microwaves, Antennas, and Propagation Conference (MAPCON), Ahmedabad, India, 11–14 December 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anam, H.; Abbas, S.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Collings, I. Material Classification and Accuracy Testing Using Passive CRFID Transponder in Recycle Unit. In Proceedings of the 2023 16th International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Hyderabad, India, 17–20 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Khaliel, M.; Fawky, A.; El-Awamry, A.; Kaiser, T. Frequency-Coded Chipless RFID Tags: Notch Model, Detection, Angular Orientation, and Coverage Measurements. Sensors 2020, 20, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anam, H.; Abbas, S.M.; Mukhopadhahy, S.; Collings, I. Dual Sided Data Dense 25-bit Chipless RFID Tag. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (USNC-URSI), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 July 2023; pp. 1487–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- SemiConductor Engineering Homepage, Giving A Flexible Edge To The IoT. Available online: https://semi.semiengineering.com/giving-a-flexible-edge-to-the-iot/ (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- RFID4u Homepage. Available online: https://rfid4u.com/dig-deep-construction-of-rfid-tags/ (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Ali, A.; Smartt, C.; Im, J.; Williams, O.; Lester, E.; Greedy, S. Impact of dielectric substrates on chipless RFID tag performance. International Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2023, 15, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.G.; Rafique, U.; Ullah, S.; Khan, S.; Abbas, S.M.; Ali, E.M.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Dalarsson, M. Novel MIMO Antenna System for Ultra Wideband Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, S.H.; Khan, M.A.; Rafique, U.; Marey, M.; Alharbi, A.G.; Mostafa, H.; Khan, M.A.; Abbas, S.M. High Performance Eight-Port Dual-Band MIMO Antenna System for 5G Devices. Micromachines 2022, 13, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Rafique, U.; Savci, H.Ş.; Nordin, A.N.; Kiani, S.H.; Abbas, S.M. Ultra-Wideband Pentagonal Fractal Antenna with Stable Radiation Characteristics for Microwave Imaging Applications. Electronics 2022, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Zahra, H.; Abbas, S.M.; Ahmed, M.I.; Varshney, G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Mahmoud, A. Compact Four-Port Circularly Polarized MIMO X-Band DRA. Sensors 2022, 22, 4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Zahra, H.; Dardeer, O.M.; Hussain, N.; Abbas, S.M.; Abdelghany, M.A. Slotted Antenna Array with Enhanced Radiation Characteristics for 5G 28 GHz Communications. Electronics 2022, 11, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, U.; Khan, S.; Abbas, S.M.; Dalal, P. Uni-planar MIMO Antenna for Sub-6 GHz 5G Mobile Phone Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Wireless Antenna and Microwave Symposium (WAMS), Rourkela, India, 5–8 June 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabavathi, P.; Rani, S.S. Design of Frequency-Signature Based Multiresonators Using Quarter Wavelength Open Ended Stub for Chipless RFID Tag. In Proceedings of the 2019 National Conference on Communications (NCC), Bangalore, India, 20–23 February 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.P.; Mishra, D.P.; Das, T.K.; Behera, S.K. Design of a Chipless RFID Tag for 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz ISM Band Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), Bhopal, India, 22–23 February 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, N.; Habib, A.; Noor, T.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. RFID Enabled Chipless Humidity Sensor. Nucl. A Q. Int. Sci. J. 2019, 56, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, I.; Ejaz, A.; Akram, A.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. Miniaturized Slot Based Chipless RFID Tag for IoT Applications. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering (RAEE), Islamabad, Pakistan, 28–29 August 2019; Volume 4, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.A.; Salimi, M.N.; Riaz, M.A.; Shahid, H.; Asghar, M.A.; Amin, Y. An RFID Enabled Miniaturized Chipless Tag for IoT Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Multitopic Conference (INMIC), Bahawalpur, Pakistan, 5–7 November 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhat, H.A.; El-Refaay, E.A.; Zainud-Deen, S.H. Compact Multi-bits Chipless-RFID Curl Resonator Tag with Temperature Sensing Capability. In Proceedings of the 2021 38th National Radio Science Conference (NRSC), Mansoura, Egypt, 27–29 July 2021; pp. 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-P.; Chang, C.-H.; Cheng, Y.T.; Jou, C.F. Development of a Flexible SU-8/PDMS-Based Antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, A.I.; Neebha, T.M.; Sumi, M. Implementation of Hexagonal Open-Loop Resonators Utilizing the FSC Technique for Chipless RFID Tag Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Intelligent Control, Computing and Communications (IC3), Mathura, India, 13–14 February 2025; pp. 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Qu, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, T.; Chen, H.; Lu, W. A flexible wearable dual-frequency antenna of ISM band. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications (IMWS-AMP), Nanjing, China, 9–11 November 2024; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, L.; Luo, G.Q. A Flexible Millimeter-Wave Endfire Antenna Based on Spoof Surface Plasmon Polaritons. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L. Flexible dual-band LCP antenna for RFID applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory, Hiroshima, Japan, 20–24 May 2013; pp. 973–976. [Google Scholar]
- Khaleel, H.R.; Al-Rizzo, H.M.; Rucker, D.G.; Al-Naiemy, Y. Flexible printed monopole antennas for WLAN applications. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011; pp. 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, H.R.; Abbosh, A.I.; Al-Rizzo, H.M.; Rucker, D.G. Flexible and Compact AMC Based Antenna for Telemedicine Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srifi, M.N.; Podilchak, S.K.; Essaaidi, M.; Antar, Y.M.M. Compact Disc Monopole Antennas for Current and Future Ultrawideband (UWB) Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 4470–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, M.; Lv, X.; Chamani, S.; Lai, J.; Yang, Y. Dielectric Target Imaging with THz Chipless RFID Technology. In Proceedings of the 2025 6th Australian Microwave Symposium (AMS), Gold Coast, Australia, 10–11 February 2025; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzebiatowski, K.; Kalista, W.; Kulas, L.; Nyka, K. RCS Enhancement of Millimeter-Wave LTCC Van Atta Arrays With 3-D Printed Lenses for Chipless RFID Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2025, 24, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.-P.; Chen, Y.-S. A Broadband Dual-Polarized Antenna with Pattern Reconfigurability for Multi-Tag Detection in Chipless RFID. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2025, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelle, E.; Vuong, T.-P.; Ardila, G.; Hemour, S.; Wu, K. Miniaturized Antenna on a Paper Substrate. In Proceedings of the 2019 49th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Paris, France, 1–3 October 2019; pp. 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.I.; Ismail, M.Y.; Mokhtar, M.H. Design Optimization of Reflectarray Antenna Fabricated above Paper Based Substrate Materials. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2019, 11, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutarboush, H.F.; Shamim, A. A Reconfigurable Inkjet-Printed Antenna on Paper Substrate for Wireless Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscato, S.; Moro, R.; Pasian, M.; Bozzi, M.; Perregrini, L. Innovative manufacturing approach for paper-based substrate integrated waveguide components and antennas. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2016, 10, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preradovic, S.; Roy, S.M.; Karmakar, N.C. RFID System Based on Fully Printable Chipless Tag for Paper-/Plastic-ltem Tagging. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2011, 53, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, J.; Almajali, E.; Najjar, M.E.; Amir, A.; Altaf, A.; Elahi, M.; Alja’afreh, S.S.; Rmili, H. Flexible, Fully Printable, and Inexpensive Paper-Based Chipless Arabic Alphabet-Based RFID Tags. Sensors 2022, 22, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, T.; Alam, T.; Mitu, N.J.; Hoque, A.; Alam, M.S.; Islam, M.T. Design and Performance Analysis of Textile-based RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Tag Antenna. In Proceedings of the 2021 Sixth International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, India, 25–27 March 2021; pp. 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xiong, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, Q.; Xue, Z.; Zeng, X. Development of a Traceability Tag Based Data Warehouse for Textile Supply Chain. In Proceedings of the 2023 18th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering (ISKE), Fuzhou, China, 17–19 November 2023; pp. 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchia, L.; Monti, G.; Tarricone, L. A Fully-Textile Chipless Tag. In Proceedings of the 2018 48th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Madrid, Spain, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Volakis, J.L. Textile antennas for wearable radio frequency applications. Text. Light Ind. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Dierck, A.; Declercq, F.; Rogier, H. Review of active textile antenna co-design and optimization strategies. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on RFID-Technologies and Applications, Sitges, Spain, 15–16 September 2011; pp. 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayem, A.S.M.; Simorangkir, R.B.V.B.; Esselle, K.P.; Hashmi, R.M. Development of Robust Transparent Conformal Antennas Based on Conductive Mesh-Polymer Composite for Unobtrusive Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 7216–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, Z.; Wojkiewicz, J.-L.; Pud, A.A.; Kone, L.; Belaabed, B.; Bergheul, S.; Lasri, T. Dual-Band Elliptical Planar Conductive Polymer Antenna Printed on a Flexible Substrate. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 5864–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Jung, C.W. A flexible and transparent antenna on a polyimide substrate for laptop computers. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19–24 July 2015; pp. 930–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, D.; Haase, K.; Hübler, A.; Ellinger, F. Bending and Folding Effect Study of Flexible Fully Printed and Late-Stage Codified Octagonal Chipless RFID Tags. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 2815–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.T.; Sharma, S.K. Inkjet-Printed Wideband Circularly Polarized Microstrip Patch Array Antenna on a PET Film Flexible Substrate Material. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M.O.; Kandil, S.M.; Volski, V.; Vandenbosch, G.A.E.; Soliman, E.A. Wideband CPW-Fed Flexible Bow-Tie Slot Antenna for WLAN/WiMax Systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 4274–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, M.S.; Ghafouri-Shiraz, H. Liquid Crystalline Polymer Substrate-Based THz Microstrip Antenna Arrays for Medical Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramiabarghouei, H.; Porter, E.; Santorelli, A.; Gosselin, B.; Popović, M.; Rusch, L.A. Flexible 16 Antenna Array for Microwave Breast Cancer Detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2516–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.-Z.; Zhu, L.-X.; Yang, Z.-P.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.-Y.; Nie, Y. A CPW-fed UWB Flexible Antenna with Double Band-notched Characteristics. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Xi’an, China, 16–19 October 2019; pp. 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-D.; Du, C.-Z. Compact Triple-Band Liquid Crystal Polymer Based Flexible Antenna for WiMAX/WLAN/5G Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Workshop on Electromagnetics: Applications and Student Innovation Competition (iWEM), Qingdao, China, 18–20 September 2019; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, S.F.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Alomainy, A. Inkjet-Printed Millimetre-Wave PET-Based Flexible Antenna for 5G Wireless Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on 5G Hardware and System Technologies (IMWS-5G), Dublin, Ireland, 30–31 August 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshenko, A.; Lomovskaya, K.; Levanov, A.; Borodulin, E.; Belousov, E. Analysis and design of planar flexible antenna prototype. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE East-West Design & Test Symposium (EWDTS), Yerevan, Armenia, 14–17 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elobaid, H.A.E.; Rahim, S.K.A.; Himdi, M.; Castel, X.; Kasgari, M.A. A Transparent and Flexible Polymer-Fabric Tissue UWB Antenna for Future Wireless Networks. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1333–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, H.; Wojkiewicz, J.-L.; Alexander, P.; Kone, L.; Belkacem, B.; Bergheul, S.; Lasri, T. Design fabrication and characterisation of polyaniline and multiwall carbon nanotubes composites-based patch antenna. IET Microwaves Antennas Propag. 2016, 10, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, R.; Sukumaran, S.K. Flexible Ultra Wide Band Antenna for WBAN Applications. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, H.; Mirbozorgi, S.A.; Ameli, R.; Rusch, L.A.; Gosselin, B. Flexible, Polarization-Diverse UWB Antennas for Implantable Neural Recording Systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarfoth, R.; Zhou, Y.; Sievenpiper, D. Flexible Patch Antennas Using Patterned Metal Sheets on Silicone. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1354–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Battiato, P.; Abdinia, S.; Jacobs, S.; Chartier, I.; Coppard, R.; Klink, G.; Cantatore, E.; Ragonese, E.; Palmisano, G. An Integrated 13.56-MHz RFID Tag in a Printed Organic Complementary TFT Technology on Flexible Substrate. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Raad, R.; Foroughi, J.; Tubbal, F.; Theoharis, P.I.; Raheel, M.S. Effects of Bending Bow-Tie Chipless RFID Tag for Different Polymer Substrates. In Proceedings of the 2019 13th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), Gold Coast, Australia, 16–18 December 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satti, J.A.; Habib, A.; Zeb, S.; Amin, Y. Highly dense flexible chipless RFID tag. IEICE Electron. Express 2017, 14, 20170750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, N.; Azam, M.A.; Qazi, I.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. Data-Dense Chipless RFID Multisensor for Aviculture Industry. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2020, 30, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, S.; Satti, J.A.; Habib, A.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. Dual-polarized data dense chipless RFID tag towards IoT applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Wireless Systems and Networks (ISWSN), Lahore, Pakistan, 19–22 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, S.; Ullah, H.; Tahir, F.A. A 26 Bit Alternating U-shaped Chipless RFID Tag Using Slot Length Variation Technique. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Microwave, Antennas & Circuits (ICMAC), Islamabad, Pakistan, 21–22 December 2021; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, I.; Ejaz, A.; Kabir, S.M.; Akram, A.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. Octagonal Shaped Flexible Chipless RFID Tag for Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical, Communication, and Computer Engineering (ICECCE), Swat, Pakistan, 24–25 July 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, N.; Simorangkir, R.B.V.B.; Buckley, J.; O’Flynn, B. Flexible and Semi-transparent Chipless RFID Tag based on PDMS-Conductive Fabric Composite. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Workshop on Antenna Technology (iWAT), Dublin, Ireland, 16–18 May 2022; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, S.; Habib, A.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H.; Loo, J. Green Electronic Based Chipless Humidity Sensor for IoT Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech), Austin, TX, USA, 4–6 April 2018; pp. 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.M.; Nassar, J.M.; Hussain, M.M. Paper as a Substrate and an Active Material in Paper Electronics. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 30–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarreta-Andrés, J.; Melià-Seguí, J.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Vilajosana, X.; Sarma, S.E. Toward Low-Cost RF-Based Bulk Fabric Classification for the Textile Industry. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 16586–16594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, H. Innovation in Wearable and Flexible Antennas; Wit Press: Southampton, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1845649869. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally, A.; Topsakal, E. Textile-Based Incognito RFID for Patient Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2025 United States National Committee of URSI National Radio Science Meeting (USNC-URSI NRSM), Boulder, CO, USA, 7–10 January 2025; p. 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.; Chowdhury, A.; Bairagi, S.; Banerjee, S. Green nanomaterials for multifunctional textile finishes. In Green Functionalized Nanomaterials for Environmental Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaze, M.; Harifi, T. Nanosurface activation. In Nanofinishing of Textile Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, M.; Harifi, T. Nanofinishing of Textile Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moučka, R.; Sedlačík, M.; Osička, J.; Pata, V. Mechanical properties of bulk Sylgard 184 and its extension with silicone oil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.-Z.; Yan, J.; Yu, Y. Design of Multibeam Conformal Antenna Based on Liquid Metal. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bayram, Y.; Volakis, J.L. Embroidered Conductive Fibers on Polymer Composite for Conformal Antennas. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 4141–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajkovikj, J.; Zürcher, J.-F.; Skrivervik, A.K. PDMS, A Robust Casing for Flexible W-BAN Antennas [EurAAP Corner]. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2013, 55, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Kumar, V.; Ko, U.H.; Zhou, Y.; Hoque, J.; Arya, G. Supporting Information for “Microengineered materials with self-healing features for soft robotics”. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, V.; Rebello, P.; Correra, F.S. Design of Flexible and Rigid RFID Chipless Tag using High Performance Substrates. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 13th International Conference on RFID Technology and Applications (RFID-TA), Aveiro, Portugal, 4–6 September 2023; pp. 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Raad, R.; Foroughi, J.; Tubbal, F.E.; Xi, J. Novel Bow-Tie Chip-less RFID Tag for Wearable Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 19th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 25–27 September 2019; pp. 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, R.; Bozzi, M.; Collado, A.; Georgiadis, A.; Via, S. Plastic-based Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) components and antennas. In Proceedings of the 2012 42nd European Microwave Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 October–1 November 2012; pp. 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 802.15.6-2012; IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Part 15.6: Wireless Body Area Networks. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–271. [CrossRef]
- Mcgarry, M.P.; Iyer, M.K.; Lee, M. Broadband Millimeter-Wave Dielectric Properties of Liquid Crystal Polymer Materials. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 12, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.-J.; Oh, J.-I.; Jo, H.-W.; Kim, K.-S.; Yu, J.-W.; Lee, D.-J. 28 GHz and 38 GHz Dual-Band Vertically Stacked Dipole Antennas on Flexible Liquid Crystal Polymer Substrates for Millimeter-Wave 5G Cellular Handsets. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 3223–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; You, D.; Fu, X.; Lee, H.; Li, Z.; Awaji, D.; Pang, J.; Shirane, A.; Sakamoto, H.; Okada, K. A Flexible Implementation of Ka-Band Active Phased Array for Satellite Communication. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium—IMS 2022, Denver, CO, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, R.; Shen, X.; Yan, N.; Safdar, G.A.; Ur-Rehman, M. A 60 GHz Broadband Wearable Antenna for Body-to-Body Communications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 14th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), Kunming, China, 26–29 October 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marnat, L.; Shamim, A. Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) based antenna for flexible system on package (SoP) applications. In Proceedings of the 2012 15 International Symposium on Antenna Technology and Applied Electromagnetics, Toulouse, France, 25–28 June 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.V.; Madhav, B.T.P.; Anilkumar, T.; Prudhvinadh, B. Circularly polarized flexible antenna on liquid crystal polymer substrate material with metamaterial loading. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omnexus Homepage. Available online: https://omnexus.specialchem.com/selection-guide/polyimide-pi-plastic (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Morris, S.; Chandran, A.R.; Timmons, N.; Morrison, J. The fabrication and analysis of a polyimide-based loop antenna for 2.45GHz WBAN applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 14–15 November 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleel, H.R.; Al-Rizzo, H.M.; Rucker, D.G. Compact Polyimide-Based Antennas for Flexible Displays. J. Disp. Technol. 2012, 8, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshan, S.H.; Hasan, R.R.; Al Mamun Sarker, A.; Zabin, S.; Tusher, R.T.H.; Rahman, M.A. Brain tumor detection by Kapton Polyimide based on-body patch antenna in K band. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 7–8 January 2023; pp. 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, S.; Gulan, H.; Rusch, C.; Zwick, T. Integrated 122-GHz Antenna on a Flexible Polyimide Substrate with Flip Chip Interconnect. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeya, M.; Shimasaki, H. Studies on a cavity-backed slot antenna made of a conductive textile bent along a spherical surface. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory, Hiroshima, Japan, 20–24 May 2013; pp. 561–564. [Google Scholar]
- C-MAC Innovative metal Solutions Homepage. Available online: https://www.cmac.com.au/blog/top-10-materials-used-industrial-3d-printing (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Formlabs Homepage. Available online: https://formlabs.com/asia/blog/3d-printing-materials/ (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Guo, Y.J.; Guo, C.A.; Li, M.; Latva-aho, M. Antenna Technologies for 6G—Advances and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2025, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhao, G.; Yang, M.; Chen, P.-Y. Review on Wearable Antennas: Part 2: Recent advances and applications. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2025, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Wei, Z.; Ding, J.; Guo, C. Broaden the bandwidth of patch antenna by using inhomogeneous metamaterial substrate. In Proceedings of the Electromagnetics Research Symposium Proceedings, Xi’an, China, 22–26 March 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, A.; Vakula, D. Metamaterial Superstrate Based High Gain Antenna for Wi-Fi Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Wireless Antenna and Microwave Symposium (WAMS), Rourkela, India, 5–8 June 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafell, I.; Ferrer, P.J.; González-Arbesú, J.M.; Romeu, J. Microstrip patch antenna design using artificial material loadings. In Proceedings of the Fourth European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, Barcelona, Spain, 12–16 April 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Hua, C.; Lu, Z.; Liu, L. A Metamaterial-Inspired RFID Tag Antenna. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT), Guangzhou, China, 19–22 May 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.C.; Huang, X.J.; Tong, M.S. A Metamaterial-Inspired Structure for UHF RFID Tag Antenna. In Proceedings of the 2018 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS-Toyama), Toyama, Japan, 1–4 August 2018; pp. 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Jeoti, V.; Soeung, S.; Drieberg, M.; Goh, M.; Aslam, M.Z. A Comparative Survey on Silicon Based and Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW)-Based RFID Tags: Potentials, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91624–91647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zomorrodi, M. mm-Wave EM-Imaging Chipless RFID System. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.C. Invisible RFID Ink Safe for Cattle and People, Company Says. Available online: https://www.informationweek.com/it-leadership/invisible-rfid-ink-safe-for-cattle-and-people-company-says (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Louis, S. SOMARK’s Chipless RFID Ink Tattoo Field Demo Brings the Company Closer to Launch. 2008. Available online: https://www.theforcefield.net/podcast/somarks-chipless-rfid-ink-tattoo-field-demo-brings-the-company-closer-to-launch-851/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Kim, Y.; Lee, B.; Yang, S.; Byun, I.; Jeong, I.; Cho, S.M. Use of copper ink for fabricating conductive electrodes and RFID antenna tags by screen printing. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia Homepage. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RFID_on_metal (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Madhav, A.; Sumi, M.; Harikrishnan, A.I. A Study on Chipless RFID Tag Structures. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electronics and Renewable Systems (ICEARS), Tuticorin, India, 16–18 March 2022; pp. 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savill, T.; Jewell, E. Design of a Chipless RFID Tag to Monitor the Performance of Organic Coatings on Architectural Cladding. Sensors 2022, 22, 3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Dong, L.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Xie, X. Passive Ultra High Frequency RFID sensor with reference tag for crack detection of aluminum alloy structure. J. Instrum. 2021, 16, P11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyaoui, A.; Elsharabasy, A.; Yousaf, J.; Sedraoui, K.; Rmili, H. MIIM-based optical log spiral rectenna for efficient IR energy harvesting. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 8897–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothama, J.M.; Lopez-Soriano, S.; Vena, A.; Sorli, B.; Susanti, I.; Perret, E. Electronically Rewritable Chipless RFID Tags Fabricated Through Thermal Transfer Printing on Flexible PET Substrates. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 1908–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Karmakar, N.C. Towards an inexpensive paper based flexible chipless RFID tag with increased data capacity. In Proceedings of the 2017 Eleventh International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Sydney, Australia, 4–6 December 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Huang, K. Design of Compact Trapezoidal Bow-Tie Chipless RFID Tag. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2015, 502938–502945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polivka, M.; Svanda, M.; Havlicek, J.; Machac, J. Detuned dipole array backed by rectangular plate applied as chipless RFID tag. In Proceedings of the 2017 Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium—Spring (PIERS), St. Petersburg, Russia, 22–25 May 2017; pp. 3314–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, I.; Ejaz, A.; Rahman, M.U.; Naghshvarianjahromi, M.; Khan, M.J.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. Data-Dense and Miniature Chipless Moisture Sensor RFID Tag for Internet of Things. Electronics 2019, 8, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Williams, O.; Lester, E.; Greedy, S. High Code Density and Humidity Sensor Chipless RFID Tag. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Split/Bol, Croatia, 5–8 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solid-Signal-Blog Homepage. Available online: https://blog.solidsignal.com/tutorials/good-material-antenna/ (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Zhao, Y.; Genovesi, S.; Jiang, T.; Manara, G.; Costa, F. High Capacity Chipless RFID System Enabled by Machine Learning Predictive Models. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Smartt, C.; Lester, E.; Williams, O.; Greedy, S. High capacity chipless RFID tags for biomass tracking application. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2022, 15, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-H.; Li, J.-S. Jeans Textile Antenna for Smart Wearable Antenna. In Proceedings of the 2018 12th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory (ISAPE), Hangzhou, China, 3–6 December 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Hirayama, H. On a transmission efficiency of tape-wound spiral antenna for coupled resonant wireless power transfer. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Okinawa, Japan, 24–28 October 2016; pp. 528–529. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, A.I.; Cifci, A.; Gozel, M.A.; Kahriman, M. Electromagnetic absorption efficiency of aluminum doped composite materials recycled from waste Tetra Pak packages in the frequency range 1.8 GHz to 5 GHz. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- hcdx Antennas Homepage. Available online: https://www.hard-core-dx.com/nordicdx/antenna/hidden/indoor.html (accessed on 9 July 2022).
- Kumar, A.; Utsav, A.; Badhai, R.K. A novel copper-tape wideband wearable textile antenna for WBAN applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Applied Electromagnetics Conference (AEMC), Aurangabad, India, 19–22 December 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Sharma, S.; Henderson, R.; Ashrafi, S.; MacFarlane, D. Ka band 3D printed horn antennas. In Proceedings of the 2017 Texas Symposium on Wireless and Microwave Circuits and Systems (WMCS), Waco, TX, USA, 30–31 March 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masihi, S.; Panahi, M.; Bose, A.K.; Maddipatla, D.; Hanson, A.J.; Narakathu, B.B.; Bazuin, B.J.; Atashbar, M.Z. Rapid Prototyping of a Tunable and Compact Microstrip Antenna by Laser Machining Flexible Copper Tape. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Glasgow, UK, 8–10 July 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeian, F.; Karmakar, N.; Komeily-Nia, Z.; Sutti, A. Towards an Objective and Precise Moisture Content Measurement of Textiles Using a Chipless RFID Tag-Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE SENSORS, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, M.I.; Malek, M.F.; Jamlos, M.F.; Jusoh, M. Conductive E-textile analysis of 1.575 GHz rectangular antenna with H-slot for GPS application. In Proceedings of the 2012 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference (LAPC), Loughborough, UK, 12–13 November 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, S.; Chaudhari, S.; Inshaar, A.; Shah, H.; Zou, C.; Harne, R.L.; Kiourti, A. E-Textile Origami Dipole Antennas with Graded Embroidery for Adaptive RF Performance. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 2218–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web Search W-IoT. Available online: https://www.rfid-wiot-search.com/primo1d-e-thread-technology-each-product-is-given-its-native-digital-id (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Benouakta, S.; Hutu, F.D.; Duroc, Y. UHF RFID Temperature Sensor Tag Integrated into a Textile Yarn. Sensors 2022, 22, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annalakshmi, T.; Kiruthika, K.; Maiyuri, R.; Menaka, A. NPSB Logo Patch Antenna Using Conductive Thread –UWB. IJAREEIE 2017, 6, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, T.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Design and Optimization of Embroidered Antennas on Textile Using Silver Conductive Thread for Wearable Applications. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 2900–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Kiourti, A.; Sebastian, T.; Bayram, Y.; Volakis, J.L. Conformal Load-Bearing Spiral Antenna on Conductive Textile Threads. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiourti, A.; Lee, C.; Volakis, J.L. Fabrication of Textile Antennas and Circuits With 0.1 mm Precision. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiourti, A.; Volakis, J.L.; Simorangkir, R.B.V.B.; Abbas, S.M.; Esselle, K.P. UWB antennas on conductive textiles. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Fajardo, PR, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1941–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, P.; Shrestha, S.; Yerramilli, R.; Karmakar, N.; Bhattacharya, S. Screen printed chipless RFID tags on packaging substrates. Flex. Print. Electron. 2021, 6, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htwe, Y.Z.N.; Mariatti, M. Printed graphene and hybrid conductive inks for flexible, stretchable, and wearable electronics: Progress, opportunities, and challenges. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deavours, D.D.; Demarest, K.; Syed, A. Effects of Antenna Material on the Performance of UHF RFID Tags. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on RFID, Grapevine, TX, USA, 26–28 March 2007; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtania, S.G.; Elger, A.W.; Hasan, M.R.; Wisniewska, A.; Sekhar, K.; Karacolak, T.; Sekhar, P.K. Flexible Antennas: A Review. Micromachines 2020, 11, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ahmadi, M.; Fargas, G.; Perinka, N.; Reguera, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Llanes, L.; Jiménez-Piqué, E. Silver Nanoparticles for Conductive Inks: From Synthesis and Ink Formulation to Their Use in Printing Technologies. Metals 2022, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, N.; Habib, A.; Amin, Y.; Tenhunen, H. Miniaturized flexible chipless RFID tag for IoT market. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Communication, Computing and Digital Systems (C-CODE), Islamabad, Pakistan, 8–9 March 2017; pp. 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, M.R.; Ibrahim, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Abidin, I.S.Z.; Ain, M.F. Stretchable Conductive Ink Based on Polysiloxane−Silver Composite and Its Application as a Frequency Reconfigurable Patch Antenna for Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28033–28042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paula, I.L.; Rogier, H.; Van Torre, P. Conformal Integration of Efficient Conductive-Ink-Printed Antennas in Smart Suitcases for LPWAN-Based Luggage Tracking. Sensors 2022, 22, 4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labiano, I.I.; Alomainy, A. Flexible inkjet-printed graphene antenna on Kapton. Flex. Print. Electron. 2021, 6, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Wei, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z. Tunable wideband slot antennas based on printable graphene inks. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 10949–10955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Hanagata, N.; Huangfu, J.; Xu, M. High-performance printable 2.4 GHz graphene-based antenna using water-transferring technology. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.G.; Sorathiya, V. Ultra-Wideband Graphene-Based Micro-Sized Circular Patch-Shaped Yagi-like MIMO Antenna for Terahertz Wireless Communication. Electronics 2022, 11, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Navani, N.K.; Manhas, S.K. Altering the Schottky Barrier Height and Conductance by Using Metal Nanoparticles in Carbon Nanotubes-Based Devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 2789–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, D.; Takida, Y.; Kawano, Y.; Minamide, H.; Terasaki, N. Carbon nanotube-based, serially connected terahertz sensor with enhanced thermal and optical efficiencies. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2022, 23, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gross, A.; Kim, N.Y. Numerical Studies of Optimized Designs for Carbon Nanotube Microstrip Antennas. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.09084. [Google Scholar]
- Hajjyahya, M.; Ishtaiwi, M.; Sayyed, J.; Saddouq, A. Design of Carbon Nanotube Antenna in Nanoscale Range. Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 9, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abohmra, A.; Abbas, H.; Alomainy, A.; Imran, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H. Flexible Terahertz Antenna Arrays Based on Graphene for Body-Centric Wireless Communication. In Proceedings of the 2023 17th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Florence, Italy, 26–31 March 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, H. Advancements in the use of carbon nanotubes for antenna realization. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 136, 153753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. Rapid mold-free fabrication of long functional PDMS fibers. NPG Asia Mater. 2022, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Prashalee, P. High Gain Compact Multiband Cavity-Backed SIW and Metamaterial Unit Cells with CPW Feed Antenna for S, and Ku Band Applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 118, 1621–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Akhtar, S.; Inam, F.A. Hyperbolic metamaterial-based metal–dielectric resonator-antenna designs for GHz photon collection rates from wide-range solid-state single-photon sources. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2020, 37, 3469–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, M.A.S.R.; Maguire, A.; Pottackal, N.T.; Thakur, M.S.H.; Ikram, M.M.; Hart, A.J.; Ajayan, P.M.; Rahman, M.M. Direct Ink Writing: A 3D Printing Technology for Diverse Materials. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2108855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Siddiquei, H.R.; Alahi, M.E.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. An IoT-enabled portable sensing system with MWCNTs/PDMS sensor for nitrate detection in water. Measurement 2021, 178, 109424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhiuzzi, C.; Rida, A.; Marrocco, G.; Tentzeris, M.M. Passive ammonia sensor: RFID tag integrating carbon nanotubes. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 3–8 July 2011; pp. 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Dong, J. Liquid Metal-Embedded Layered-PDMS Antenna for Flexible and Conformal Applications. Opt. Photonics 2022, 10, 872992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christydass, S.P.J.; Gunavathi, N. Octa-Band Metamaterial Inspired Multiband Monopole Antenna for Wireless Application. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2021, 113, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, B.; Adepu, V.; Sahatiya, P.; Nandi, S. An MXene based flexible patch antenna for pressure and level sensing applications. FlatChem 2022, 33, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Cao, M.-S.; Cao, W.-Q.; Yuan, J. Developing MXenes from Wireless Communication to Electromagnetic Attenuation. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhu, M.; Schmidt, O.G. Flexible MXene films for batteries and beyond. Carbon Energy 2022, 4, 598–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedambaimoole, V.; Harsh, K.; Rajanna, K.; Sen, P.; Nayak, M.M.; Kumar, S. MXene wearables: Properties, fabrication strategies, sensing mechanism and applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 3784–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Liu, Y.; Rakhmanov, R.; Israel, C.; Tajin, M.A.S.; Friedman, G.; Volman, V.; Hoorfar, A.; Dandekar, K.R.; Gogotsi, Y. Solution-Processed Ti3C2Tx MXene Antennas for Radio-Frequency Communication. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2003225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yuan, J.; Lin, L.; Lei, Z. A Dual-Band Cross-Shaped Microstrip Antenna Based on Ti3C2Tx MXene. In Proceedings of the 2024 20th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (ICNC-FSKD), Guangzhou, China, 27–29 July 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wei, L.; Wu, X.; Jiang, C.; Yao, Y.; Peng, B.; Chen, H.; Huangfu, J.; Ying, Y.; Zhang, C.J.; et al. Room-temperature high-precision printing of flexible wireless electronics based on MXene inks. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.A.; Sazegar, M.; Sullivan, P. Enabling A Hyper-Connected World: Advanced Antenna Design Using Liquid Crystals and LCD Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the International Display Workshops, Virtual, 9–11 December 2020; Volume 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Zhang, Y. Design of a liquid crystal beam-steerable antenna with characteristic mode analysis. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2022, 16, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Temiz, M.; Makadema, A.E. Determining dielectric properties of nematic liquid crystals at microwave frequencies using inverted microstrip lines. Liq. Cryst. 2022, 49, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Koloor, S.S.R.; Alshehri, A.H.; Arockiarajan, A. Carbon nanotube characteristics and enhancement effects on the mechanical features of polymer-based materials and structures—A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 6495–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Li, H.; Ren, L.; Perini, S.; Lanagan, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H. Highly stretchable and mechanically tunable antennas based on three-dimensional liquid metal network. Mater. Lett. 2020, 270, 127727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. A liquid crystal leaky-wave antenna with fixedfrequency beam scanning and open-stop-band suppression. Liq. Cryst. 2022, 49, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Raad, R.; Foroughi, J. A Fibre Embroidered Chipless RFID Tag on Cotton Fabrics for Wearable Applications. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2020—2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, D.; Christodoulou, C.; Jackson, N. A Stretchable Liquid Metal Antenna Array. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (APS/URSI), Singapore, 4–10 December 2021; pp. 1777–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Soad, O.H.R.; Fu, J.; Wu, Q. A tunable ⵣ-shaped microstrip leaky wave antenna based on liquid crystal. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2022, 35, 5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahmar, L.; Errkik, A.; Zbitou, J.; Bouzida, I.; Lakhssassi, A.; Latrach, M. A new flexible passive UHF RFID tag antenna using meander line. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2752, 070002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrich, L.; Zenkouar, L. Microruban dipole antenna for RFID applications at 2.45 GHz. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. (IJECE) 2016, 6, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, H.A.; Rahim, R.A.; Soh, P.J.; Akkaraekthalin, P. Liquid-based reconfigurable antenna technology: Recent developments, challenges and future. Sensors 2021, 21, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girmilla, K.; Sethy, P.; Behera, S.K. A Frequency Domain 8-Bit Chipless RFID tag for IoT and Sensor Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Wireless Antenna and Microwave Symposium (WAMS), Visakhapatnam, India, 29 February–3 March 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Sethy, P.; Behera, S.K. A 6-bit Asymmetric Floral Shaped Chipless RFID for WiMAX Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference for Women in Innovation, Technology & Entrepreneurship (ICWITE), Bangalore, India, 16–17 February 2024; pp. 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anam, H.; Abbas, S.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Towards Array and Curve Analysis: Flexible Passive Chipless RFID Tags. In Proceedings of the 2024 18th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Glasgow, UK, 17–22 March 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltresy, N.A.; Elhamid, A.E.M.A.; Elsheakh, D.M.; Elhennawy, H.M.; Abdallah, E.A. Silver Sandwiched ITO Based Transparent Antenna Array for RF Energy Harvesting in 5G Mid-Range of Frequencies. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 49476–49486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltresy, N.A.; Dardeer, O.M.; Al-Habal, A.; Elhariri, E.; Abotaleb, A.M.; Elsheakh, D.N.; Khattab, A.; Taie, S.A.; Mostafa, H.; Elsadek, H.A.; et al. Smart Home IoT System by Using RF Energy Harvesting. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 8828479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.R.T.D.; Lee, J.S. Applications of Nanomaterials in RFID Wireless Sensor Components. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Sinha, R.; Das, D.; Choubey, A.; Barde, C.; Ranjan, P.; Kumar, S. A recent survey on zeroth-order resonant (ZOR) antennas. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2022, 112, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TUBALLTM Homepage. Available online: https://tuball.com/about-tuball?gclid=CjwKCAjwsMGYBhAEEiwAGUXJafPgm0SuEnzozF2RcesGLaFq7CXTiDDKHbX7LOZ0DM1DQ6Ckzo5lTRoC2TcQAvD_BwE (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- AlOmairi, A.; Atilla, D.C. Ultra-wide-band microstrip patch antenna design for breast cancer detection. Electrica 2022, 22, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Liu, C.; Hao, S.; Fu, W.; Peng, J.; Wu, B.; Zheng, N. Antioxidant high-conductivity copper paste for low-cost flexible printed electronics. npj Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairath, K.; Singh, N.; Shabaz, M.; Jagota, V.; Singh, B.K. Performance Analysis of Metamaterial-Inspired Structure Loaded Antennas for Narrow Range Wireless Communication. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 7940319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshikenari, M.; Ali, E.M.; Soruri, M.; Dalarsson, M.; Naser-Moghadasi, M.; Virdee, B.S.; Stefanovic, C.; Pietrenko-Dabrowska, A.; Koziel, S.; Szczepanski, S.; et al. A Comprehensive Survey on Antennas On-Chip Based on Metamaterial, Metasurface, and Substrate Integrated Waveguide Principles for Millimeter-Waves and Terahertz Integrated Circuits and Systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 3668–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.N.; Gaofeng, Z.; Kiani, S.H.; Rafique, U.; Abbas, S.M.; Alibakhshikenari, M.; Dalarsson, M. H-Shaped Eight-Element Dual-Band MIMO Antenna for Sub-6 GHz 5G Smartphone Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 85619–85629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.T.; Salama, R.; Abbas, S.M.; Liyanapathirana, R. Review of Antenna Technologies and Designs for Various Wearable and Integrated Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 10th International Conference on Information and Automation for Sustainability (ICIAfS), Negambo, Sri Lanka, 11–13 August 2021; pp. 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chakraborty, S.; Dhar, A.; Sangani, C.B.; Duan, Y.; Pansuriya, B.R.; Vekariya, R.L. Graphene, an epoch-making material in RFID technology: A detailed overview. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 18700–18721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y. MXenes: Trends, growth, and future directions. Graphene 2D Mater. 2022, 7, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Advances in multifunctional flexible MXene-based stress sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 7845–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuck, C.E.; Sarycheva, A.; Anayee, M.; Levitt, A.; Zhu, Y.; Uzun, S.; Balitskiy, V.; Zahorodna, V.; Gogotsi, O.; Gogotsi, Y. Scalable Synthesis of Ti3C2Tx MXene. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otgonbayar, Z.; Yang, S.; Kim, I.-J.; Oh, W.-C. Recent Advances in Two-Dimensional MXene for Supercapacitor Applications: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yuan, X.; Tang, Y.; Wageh, S.; Al-Hartomy, O.A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Yang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Y. MXene sensors based on optical and electrical sensing signals: From biological, chemical, and physical sensing to emerging intelligent and bionic devices. PhotoniX 2023, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; Burden, E.; Shaffer, M.; Noack, T.; Mueller, M.; Walker, J.; MacDonald, E.; Cortes, P.; Quintana, J. A copper pyramidal fractal antenna fabricated with green-laser powder bed fusion. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 7, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
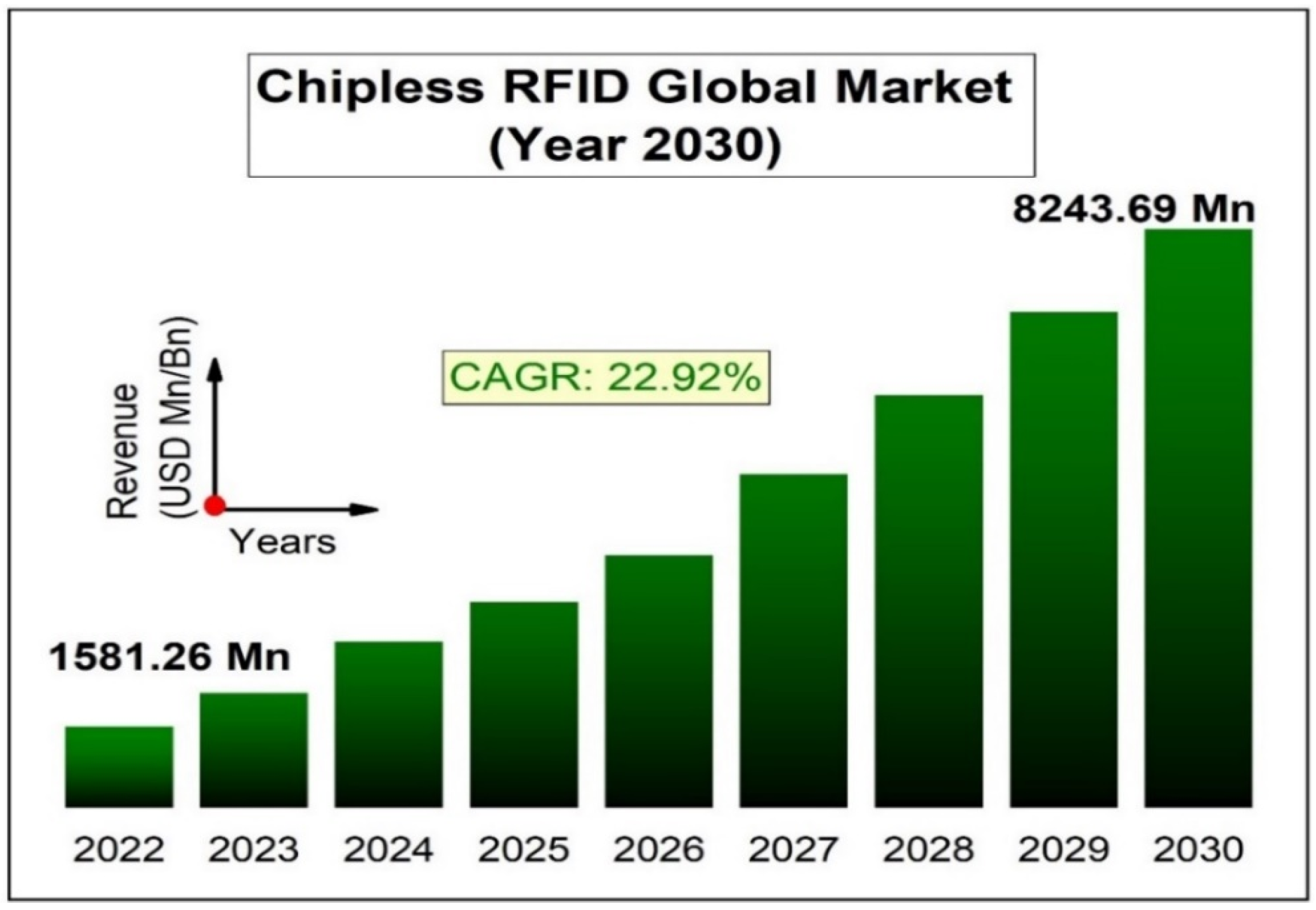
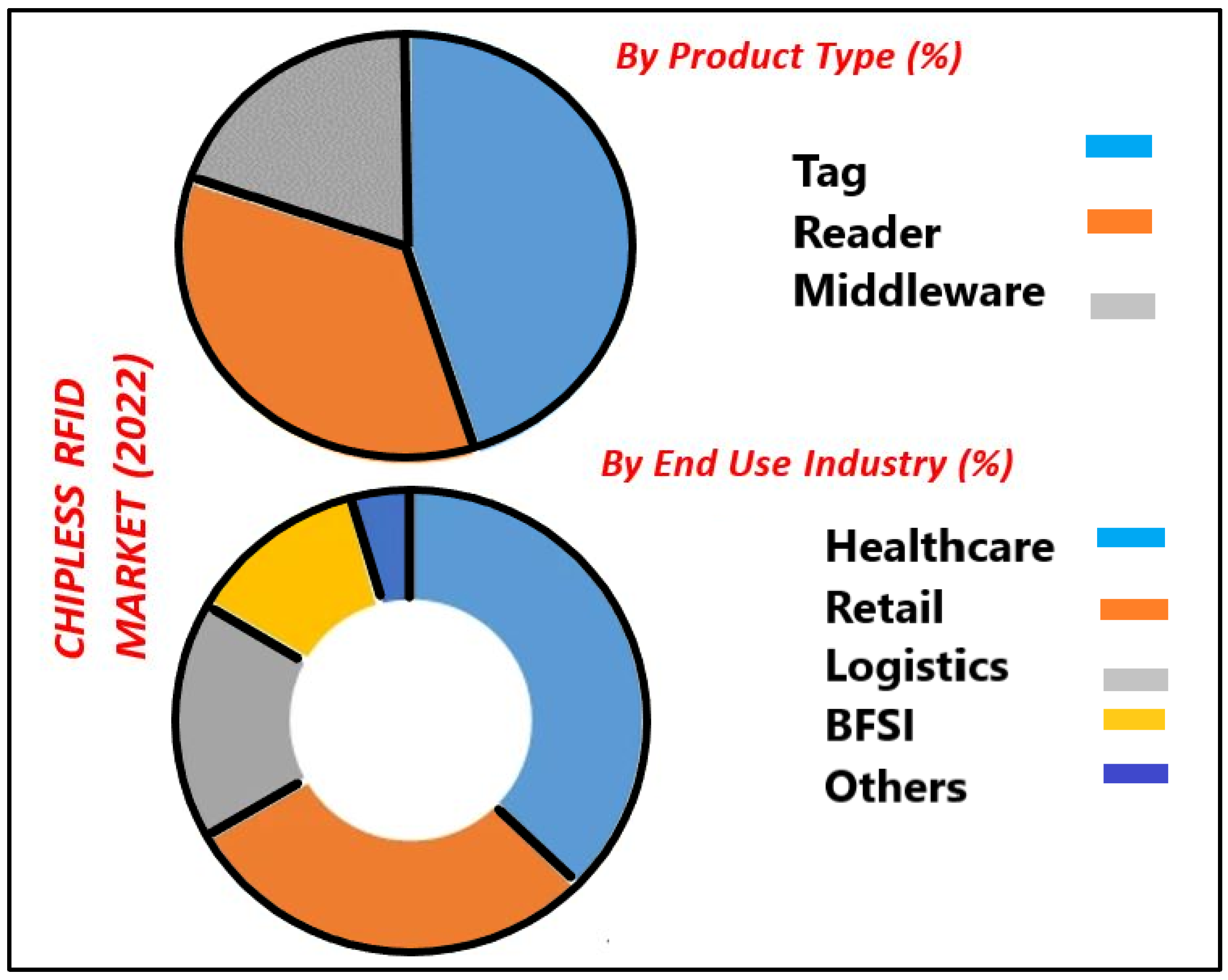
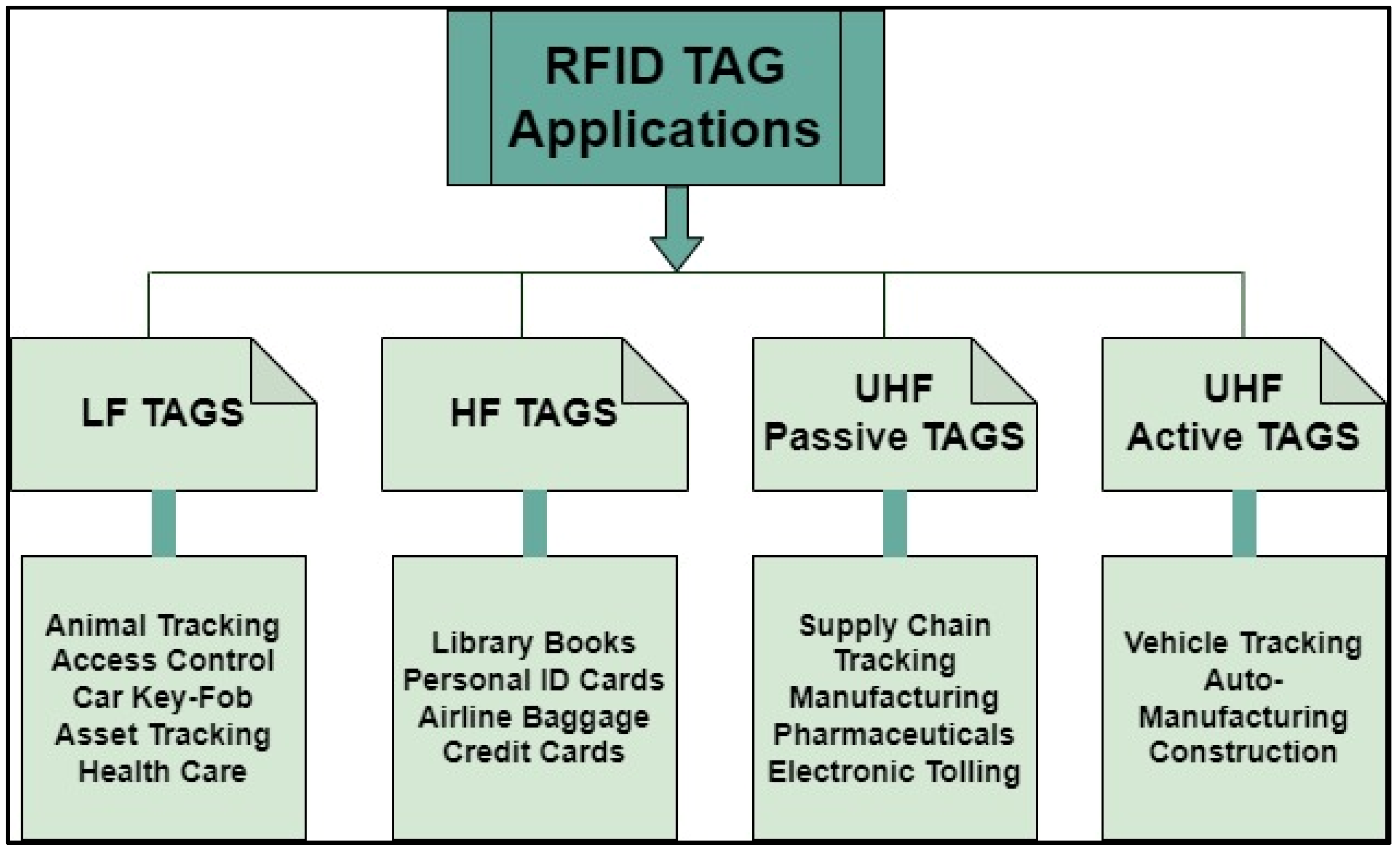

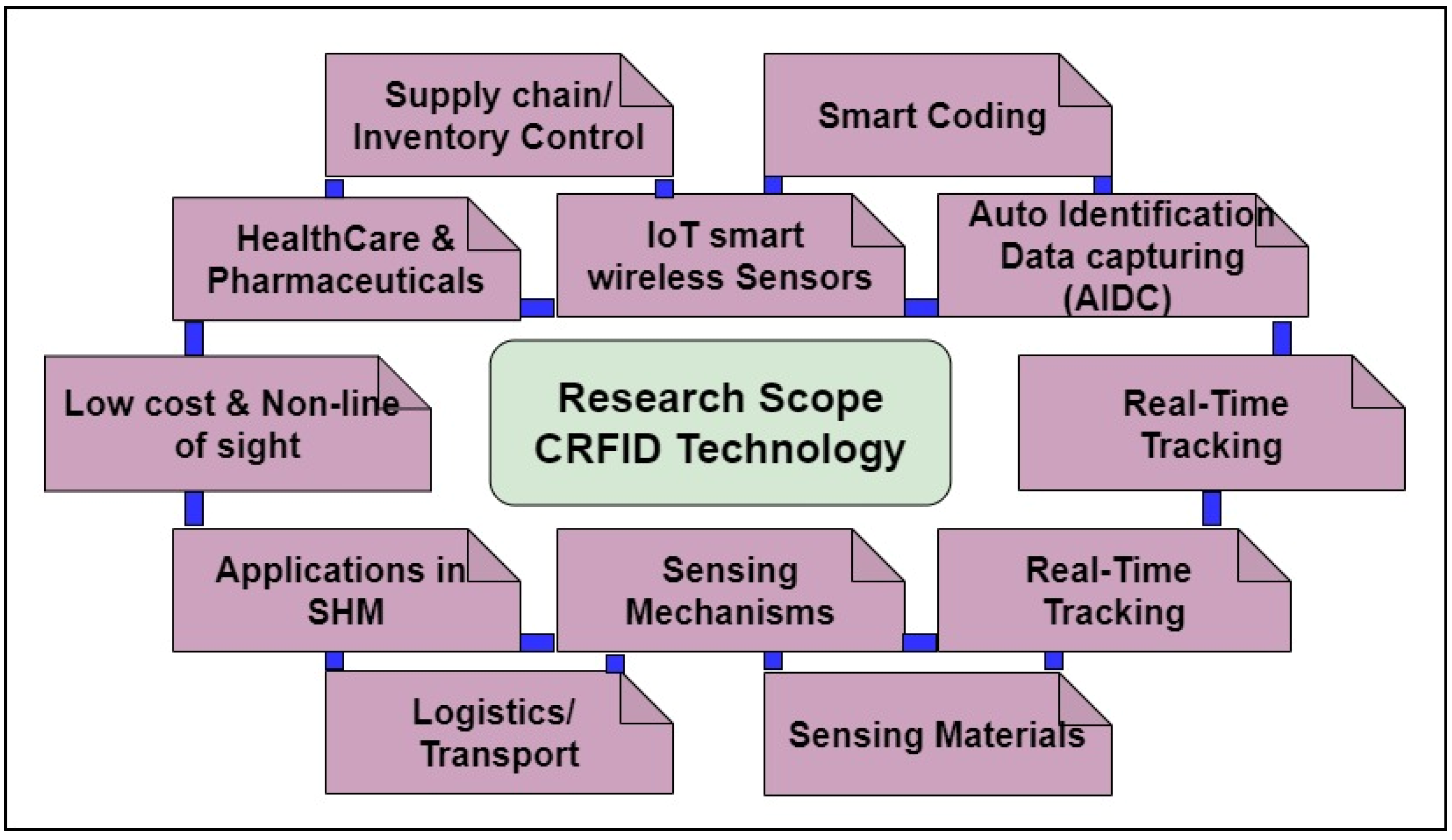





| Materials | Rel. Permittivity | Loss Tangent | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR4 | 4.3 | 0.025 | x |
| Taconic TLX-0 | 2.45 | 0.0019 | x |
| Taconic TLX-8 | 2.55 | 0.0019 | x |
| Rogers RT/duroid 5870 | 2.33 | 0.0009 | x |
| Rogers RT/duroid 5880 | 2.20 | 0.0009 | √ |
| Thermoset Polyester | 4.0 | 0.0050 | x |
| Kapton® HN | 3.5 | 0.0026 | √ |
| PDMS | 2.76–3.00 | 0.01–0.05 | √ |
| SYLGARD™ 527 Silicone Dielectric Gel | 2.85 | 0.0001 | √ |
| SYLGARD™ 170 Silicone Elastomer | 2.5 | 0.0002 | √ |
| SYLGARD™ 182 Silicone Elastomer | 2.65 | 0.0005 | √ |
| SYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer Kit | 2.68 | 0.00133 | √ |
| PET | 3 | 0.0025 | √ |
| HP Photopaper | 3.2 | 0.04 | √ |
| Teflon (PTFE) | 2.1 | 0.00015–0.0003 | √ |
| PE | 2.25 | 0.0005 | √ |
| Parylene C | 2.7 | 0.1 | √ |
| Parylene N | 2.7 | 0.0006 | √ |
| PLA | 3.11 ± 0.07 | 0.013 ± 0.001 | x |
| ABS | 2.0–3.5 | 0.00500–0.0190 | x |
| Nylon | 2.4 | 0.0083 | √ |
| Desmopan® TPU | 8.0–4.0 | <0.02 | √ |
| Ref # | Substrate | Permittivity/ Loss Tangent | Thickness (mm) | Oper. Freq./ Freq. Band (GHz) | Design | Area (mm2) | Gain (dBi) | Radiation Efficiency (%) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [36] | FR-4 laminate | 4.3 - | 1.6 | 9.33 2.77–12 | MIMO antenna | 90 × 90 | 5 | >75 | UWB MIMO applications |
| [37] | FR-4 | 4.4 - | 0.8 | 3.5/4.8 | MIMO antenna | 150 × 75 | >2 | 55/72 | 5G Communication |
| [38] | Rogers RT/duroid 5880 | 2.2 - | 0.787 | 8.5 3–12.7 | UWB-Fractal antenna | 24 × 30 | 3.6 | 88 | Microwave imaging applications |
| [39] | - | 10.2 - | 0.762 | 10.5 9.2–10.1 | CP MIMO antenna | 35 × 30 | 6 | - | X-band applications |
| [40] | Rogers RT/duroid 4003 | 3.55 0.0027 | 0.203 | 28 | Linear antenna array | 39.5 × 39.5 | 13.01 | 83.05 | 5G new radio (NR) comm. |
| [41] | FR-4 | 4.4 - | 1.6 | 3.21–3.81 | MIMO antenna | 150 × 75 | 3.64 | >90 | 5G mobile applications |
| Ref # | Substrate | Thickness (mm) | Radiator | No. of Bits | Area (mm2) | Freq. Band (GHz) | Sensing | No. of Tagged Items | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | FR4 | 1.6 | Copper | 10 | 23.8 × 17 | 2–4 | x | 1024 | Identification |
| [43] | FR4 | 0.8 | Copper | 2 | 21 × 21 | 2–4 | x | 4 | ISM band |
| [31] | FR4 | 0.5 | Copper | 25 | 27 × 12.5 | 4.5–12.5 | x | 33,554,432 | Tracking |
| [44] | FR4 | 0.5 | Copper | 9 | 12.4 × 6 | 6–16 | x | 512 | Pharmaceutical industries |
| [45] | Taconic TLX-0 | 0.635 | Copper | 13 | 16.65 × 17 | 3–12 | x | 8192 | Item-level tagging |
| [44] | Taconic TLX-0 | 0.5 | Copper | 9 | 12.4 × 6 | 6–16 | √ | 512 | RFID sensing |
| [46] | Rogers-RT/duroid 5870 | 1.575 | Copper | 10 | 10.8 × 10.8 | 3.5–7.5 | x | 1024 | IoT market |
| [47] | Rogers RO4003 | 0.88 | Copper | 12 | 29.75 × 34 | 3–7 | √ | 4096 | Temp. sensor |
| Ref # | Substrate | Thickness (mm) | Radiator | No. of Bits | Area (mm2) | Freq. Band (GHz) | Sensing | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [90] | Kapton HN | 0.125 | Silver nano-ink | 27 | 22 × 22 | 3.7–15.1 | x | Flexible identification |
| [91] | Kapton HN | 0.125 | Copper | 22 | 171.9 | 4–25 | √ | Aviculture industry |
| [92] | Rogers RT/duroid 5880 | 0.508 | Copper | 38 | 29 × 29 | 4.7–14.8 | x | Smart IoT applications |
| [93] | Rogers RT/duroid 5880 | 1.575 | - | 26 | 20 × 20 | 3.5–8 | x | Item-level tracking |
| [94] | PET | 0.1 | Copper | 9 | - | 4.7–13.7 | x | IoT enabler |
| [3] | PET | 0.07 | Gold | 8 | 25 × 25 | 4–18 | x | |
| [95] | PDMS | 0.4 | Nickel–copper coated ripstop | 6 | 25 × 25 | 3.1–10.6 | x | WBAN IoT |
| [96] | HP Photopaper | 0.25 | Silver nano-ink | 15 | 20 × 10 | 2.4–14.6 | √ | Smart green electronics |
| No. | Material | Printing Technique | Characteristics | Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ABS | FDM 3D Printing | Temp. resistant | Functional prototypes |
| 2 | PLA | FDM 3D Printing | Easy printing | Resemblance models |
| 3 | PETG | FDM 3D Printing | Moisture resistant | Moisture-resistant applications |
| 4 | Nylon | FDM 3D Printing | Complicated printing | Lightweight applications |
| 5 | TPU | FDM 3D Printing | Flexible | Stretchable prototypes |
| 6 | PVA | FDM 3D Printing | Water soluble | Assistant/holding material |
| 7 | HIPS | FDM 3D Printing | Soluble support | Aid/support material |
| 8 | Standard Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Even surface | Pretend prototypes |
| 9 | Clear Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Optical transparency | Millifluidics |
| 10 | Draft Resin | SLA 3D Printing | Rapid printing | Faster iterations |
| 11 | Tough Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Stretchable, durable | Connectors |
| 12 | Rigid Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Sustains the load | Automotive housing |
| 13 | High Temp. Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Elevated accuracy | Temperature resistant housings |
| 14 | Flexible Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Withstands bending/flexible | Medical/robotics applications |
| 15 | Medical Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Biocompatible | Medical/dental equipment |
| 16 | Ceramic Resins | SLA 3D Printing | Resembles stone | Art applications |
| 17 | Nylon 12 | SLS 3D Printing | Temperature, moisture resistant | Medical instruments/gadgets |
| 18 | Nylon 11 | SLS 3D Printing | Temperature, humidity resistant | Medical equipment |
| 19 | TPU | SLS 3D Printing | Deformation adaptable | Stretchable medical equipment |
| 20 | Nylon Composites | SLS 3D Printing | Strength | Effective prototyping |
| Ref # | Substrate | Operational Frequency (GHz) | Design | Dimensions (mm2) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [131] | Homogeneous | 2.45 | Patch antenna | 35.9 × 3 | Efficient miniaturization |
| [132] | Metamaterial | 0.906 | RFID tag antenna | 60 × 19.89 | High-efficiency |
| [133] | Metamaterial | 2.4 | RFID tag antenna | 42.6 × 42.6 | RF devices/optical devices |
| Material | Conductivity (Sm−1) | Resistivity (Ω-m) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m) | Density (g/cm3) | Printing Tech. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 5.96 × 107 | 1.7 × 10−8 | 401 | 8.9 | Etching |
| Aluminum | 3.56 × 107 | 2.8 × 10−8 | 237 | 2.7 | |
| Silver | 9 × 106 | 1.6 × 10−8 | 429 | 10.5 | Printing |
| Graphene | 1 × 105 | 1 × 10–8 | 4.84 × 103 | 2.267 | - |
| HCGAF | 1.82 × 106 | 6.5 × 10−8 | - | - | - |
| Gold | 44.2 × 106 | 2.4 × 10−8 | 317 | 19.4 | - |
| MWCNT | 1 × 105 | 1.74 × 10−8 | 2586 | 2.3 | - |
| SWCNT | 102 to 106 | 5.34 × 103 | 3000 | 1.8 | - |
| MXene (Ti3C2Tx) | 150 | - | - | - | - |
| Ref # | Radiator | Thickness (mm) | Substrate | No. of Bits | Area (mm2) | Freq. Band (GHz) | Sensing | Flexibility | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [43] | Copper | FR4 | 2 | 21 × 21 | 1–8 | x | x | ISM band | |
| [44] | Copper | 0.035 | Taconic TLX-0 | 9 | 12.4 × 6 | 6–16 | √ | x | Low-cost ID |
| [145] | Copper | 0.035 | Paper | 30 | - | 22–26.5 | x | √ | Flexible detection |
| [146] | Copper | - | FR-4 | 12 | 35 × 33 | 3.1–10.6 | x | x | Identification |
| [147] | Metallic | - | Rogers RO4350 | 20 | 60 × 60 | 3.1–3.9 | x | x | Data-dense identification |
| [148] | Copper | 0.035 | Roger RT/duroid/5880 | 20 | 25 × 17 | 4.1–16 | √ | √ | Conformal applications |
| [148] | Copper | 0.035 | Taconic TLX-0 | 20 | 25 × 17 | 3.8–15 | x | x | Identification |
| [149] | Copper | 0.012 | PET | 18 | 20 × 20 | 3.5–16 | √ | √ | Biomass tracking |
| [3] | Gold | 0.1 | PET | 8 | 25 × 25 | 4–12 | x | √ | Identification |
| [3] | Gold | 0.1 | PET | 8 | 13.44 × 11.56 | 8–18 | x | √ | Identification |
| Ref # | Radiator | Thickness (mm) | Substrate | Rel. Permittivity | Area (mm2) | Operating Freq. (GHz) | Freq. Band (GHz) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [153] | Copper tape | 0.03 | Kapton HN | 3.5 | 65 × 46 | 2.4 | - | ISM band |
| [157] | Copper tape | 0.05 | Denim jeans | 1.54 | 46 × 16 | 2.45 5.8 | - | ISM band Wearable applications |
| [158] | Copper tape | - | Cloth fabric | 1.8 | 30 × 30 | - | 3.1–10.6 | WBAN-UWB Biomedical applications |
| [159] | Copper tape | 0.07 | ABS | 2.8 | 27.8 × 36.8 | 28 | - | Commercial applications |
| Ref # | Radiator | Substrate | Thickness (mm) | Rel. Permittivity | Loss Tangent | No. of Bits | Area (mm2) | Freq. Band (GHz) | Sensing | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | Nickel–copper fabric | PDMS | 0.4 | 2.77 | 0.02–0.076 | 6 | 25 × 25 | 3.1–10.6 | x | Wireless identification |
| [164] | Textile yarn | No substrate | - | 2 | - | - | 135 × 0.44 | 0.864–0.867 | √ | E-Thread temp. sensor |
| Ref # | Radiator | Conductivity (S/m) | Surface Resistance (Ω) | Substrate | Area (mm2) | Oper. Freq./Range (GHz) | Radiation Efficiency | Gain (dB) | S11 (dB) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [161] | Zelt Copper Taffeta Shieldit Super | 1.479 × 105 2.5 × 105 6.67 × 105 | 0.05 0.05 1 | Foam (3 mm, Ɛr = 1.006) | 120 × 120 | 1.575 | 0.858 0.8962 0.978 | 6.735 7.564 7.7 | −17.6 −14.5 −13.9 | GPS applications |
| [162] | E-Threads | - | 1.9 | Felt | 0.76–1.015 | - | - | Flexible applications | ||
| [165] | Copper E-Threads | - | Cotton fabric | 40 × 40 | 3.1–10.6 | - | 3 | - | Military applications | |
| [166] | Silver conductive thread/Rayon thread | - | 0.70 | Nylon (0.35 mm) | 90 × 10 | 0.880–0.990 | - | - | Smart wearable applications | |
| [167] | E-Threads | - | 1.9 | Kevlar fabric (0.59 mm) (Ɛr = 2.6, Tanδ = 0.006) | 160 × 160 | 0.3–3 | - | 6.5 | - | Airborne and wearables |
| [168] | Elektrisola E-Threads | - | 1.9 | PDMS (1.5 mm) (Ɛr = 3, Tanδ <0.01) | 160 × 160 | 1–5 | - | - | Medical applications | |
| [169] | Elektrisola E-Threads | - | 1.9 | PDMS (Ɛr = 3, Tanδ = 0.004) | 160 × 160 | 1–6 | - | 6 | - | Flexible applications |
| Ref # | Radiator | Thickness (mm) | Substrate | No. of Bits | Area (mm2) | Freq. Band (GHz) | Sensing | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [175] | Silver ink | 0.015 | Kapton HN | 9 | 10.5 × 15 | 8–19 | x | Ubiquitous sensor network |
| [175] | Silver ink | 0.015 | PET | 9 | 10.5 × 15 | 8.5–20 | x | Ubiquitous sensor network |
| Ref # | Radiator | Conductivity (s/m) | Substrate | Thickness (mm) | Dielectric Constant | Area (mm2) | Oper. Freq. | Freq. Band/ Band Width | Gain (dBi) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [164] | Graphene ink | FR4 | 1.6 | 4.4 | 2.45 GHz | 2.421–2.474 GHz 74.5 MHz | 0.94 | ISM band | ||
| [176] | Silver ink | 0.1–0.7 | Sylgard 184 (PDMS) | 3 | 3.0 | 60 × 20 | 2.50 GHz | - 105 MHz | - | Stretchable electronics |
| [177] | Silver ink | 6.8 × 106 | PP foil | 0.15 | 6.03 | - | 895 MHz | 860–928 MHz - | 2.8 1.5 | Bluetooth Wi-Fi |
| [178] | Graphene ink | 2.5 × 104 | Kapton HN | 0.125 | 3.5 | 30 × 20 | 5.65 GHz | 3.5–6.5 GHz 3 GHz | - | WLAN 5G appl. |
| [179] | Graphene ink | - | Teflon | 0.8 | 2.65 | 25 × 15 | - | 2.83–6 GHz | −1.7 | Flexible, printable electronics |
| [180] | Graphene ink | - | Paper | - | - | 43 × 3 | 2.4 GHz | 2.297–2.510 GHz | 0.7 | IoT sensing |
| [181] | Graphene ink | 108 | Polyimide | 0.016 | 4.3 | 0.62 × 0.8 | 7.5 THz | 1–30 THz 10.96 THz | 7 | Terahertz communications |
| Ref # | Radiator | Thickness (mm) | Substrate | Dielectric Constant | Loss Tangent | Area (mm2) | Freq. Band /Op. Freq. | Sensing | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [183] | CNT film | 0.0014 | Polyimide film | - | - | 0.35 × 0.35 | 1.5 THz 361 THz | √ | THz sensing |
| [192] | MWCNTs | 0.5 | PDMS | 2.76 | 0.01 | 110 × 78 | - | √ | Water quality monitoring |
| [193] | SWCNT | 0.032 | Polyamide membrane | - | - | 80 × 180 | 0.5–1.5 GHz | √ | Ammonia sensor |
| [194] | Liquid metal (LM) | - | PDMS (Sylgard 184) | 2.68 | 0.0375 | 30 × 12 | 2.4 GHz 5.8 GHz | x | Wrist-worn applications |
| [195] | Hybrid metamaterial | - | FR4 | 4.3 | 0.025 | 28 × 32 | 2.25–9.47 GHz | x | Multi-band wireless applications |
| Ref # | Radiator | Conductivity (S/m) | Thickness (mm) | Antenna | Substrate | Area (mm2) | Oper. Freq./Range (GHz) | Refl. Coefficient/Gain (dBi) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [206] | 3D LM composite | 8.1 × 105–1.3 × 106 | - | Dipole | PDMS | 72 × 40 | 1.55–0.45 | −30 | Wireless strain sensor |
| [207] | E7-LC | 0.254 | Leaky wave (LWA) | Rogers 4350B (ε = 3.48, Tanδ = 0.0037) | - | 26–30 | 5.5 | Flexible antennas | |
| [208] | (a) HC12-Thread (b) LCP-(LIBERATOR 40) | 5000 | 0.09 0.12 | 4-bit tag | Plain cotton (0.25) | 25 × 25 | 8–18 | - | Smart textile applications |
| [209] | LC | - | - | Antenna array | - | - | 2.4 | 3.5 | Antenna array systems |
| [210] | N-LC | - | - | Microstrip leaky wave antenna (MLWA) | Rogers RT5880 (0.254 mm, Ɛr = 2.2, Tanδ = 0.0009) | 157.5 × 36 | 8.4–10.5 | 7.53 | Satellite and radar communication |
| [211] | Liquid metal (LM) | - | - | IFA antenna | PDMS (4.5 mm, Ɛr = 2.68, Tanδ = 0.0375) | 30 × 12 | 2.4 5.8 | 5.55 1.66 | Wearable applications |
| Ref. No. | Antenna/Tag Geometry | Material Type | Substrate Material | Flexibility | Operating Frequency (GHz) | Gain (dBi) | Bandwidth (MHz) | Bits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | Square slot | Silver ink | PET | Flexible | 1.35–6.9 | N/A | N/A | 3 |
| [27] | Square slot | CNT | PDMS | Flexible | 1.35–6.9 | N/A | N/A | 3 |
| [45] | C-shaped slot | Copper | Taconic TLX-0 | Non-flexible | 3–12 | N/A | N/A | 13 |
| [64] | Square slot | Copper | Paper | Flexible | 1–12 | N/A | N/A | 28 |
| [212] | Meander line | Silver ink | Kapton | Flexible | 0.868 | 1.66 | 5 | N/A |
| [212] | Meander line | Silver ink | PET | Flexible | 0.868 | 1.66 | 5 | N/A |
| [213] | Dipole | Copper | FR4 | Non-flexible | 2.45 | 2.1 | N/A | N/A |
| [214] | Loop resonator | Liquid metal | PDMS | Flexible | 0.868 | 2.7 | N/A | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anam, H.; Abbas, S.M.; Collings, I.B.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Materials-Driven Advancements in Chipless Radio-Frequency Identification and Antenna Technologies. Sensors 2025, 25, 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092867
Anam H, Abbas SM, Collings IB, Mukhopadhyay S. Materials-Driven Advancements in Chipless Radio-Frequency Identification and Antenna Technologies. Sensors. 2025; 25(9):2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092867
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnam, Hafsa, Syed Muzahir Abbas, Iain B. Collings, and Subhas Mukhopadhyay. 2025. "Materials-Driven Advancements in Chipless Radio-Frequency Identification and Antenna Technologies" Sensors 25, no. 9: 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092867
APA StyleAnam, H., Abbas, S. M., Collings, I. B., & Mukhopadhyay, S. (2025). Materials-Driven Advancements in Chipless Radio-Frequency Identification and Antenna Technologies. Sensors, 25(9), 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25092867










