Abstract
In order to meet the demand for high-frequency current sensors in 5G communication and new energy fields, there is an urgent need to develop high-performance nickel-zinc ferrite-based co-fired ceramic magnetic cores. In this study, a nickel-zinc ferrite core based on low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology was developed. The regulation mechanism of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping on the low-temperature sintering characteristics of NiZn ferrites was systematically investigated. The results show that the introduction of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 reduces the sintering temperature to 900 °C and significantly improves the density and grain uniformity of ceramics. When the doping amount is 0.75 wt%, the sample exhibits the lowest coercivity of 35.61 Oe and the following optimal soft magnetic properties: initial permeability of 73.74 (at a frequency of 1 MHz) and quality factor of 19.64 (at a frequency of 1 MHz). The highest saturation magnetization reaches 66.07 emu/g at 1 wt% doping. The results show that BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping can regulate the grain boundary liquid phase distribution and modulate the magnetocrystalline anisotropy, which provides an experimental basis and optimization strategy for the application of LTCC technology in high-frequency current sensors.
1. Introduction
The progress of modern electronic technology promotes the development of communication equipment in the direction of high frequency, miniaturization, and multi-function. As a key component in the communication system, the performance of the multi-layer co-fired device directly determines the overall efficiency of the system [1,2,3,4,5,6]. To meet these requirements, the selection of substrate materials is critical. Ferrite materials emerge as ideal candidates for high-frequency device substrates and sensor applications due to their moderate permeability, low loss, and high magnetization characteristics [7,8,9]. Among them, NiZn ferrites have shown significant advantages in high-frequency current sensors due to their high permeability, low magnetic loss, and excellent chemical stability.
However, the relatively high sintering temperature of NiZn ferrites imposes significant constraints on their application in low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. To achieve process compatibility with silver electrode co-firing, the sintering temperature must be strictly maintained below the melting point of silver (approximately 961 °C). Conventional NiZn ferrite systems typically exhibit microstructural defects such as inhomogeneous grain growth and insufficient densification under low-temperature sintering conditions, leading to substantial degradation of both magnetic and dielectric properties [17]. To address these technical challenges, researchers commonly employ the strategy of adding sintering aids (e.g., Bi2O3, B2O3) [18], aiming to achieve effective regulation of sintering temperature and optimization of material microstructure. Nevertheless, such additives may introduce non-magnetic ionic impurities, thereby adversely affecting the magnetic performance of the material.
In recent years, researchers have focused on enhancing the low-temperature sintering characteristics of NiZn ferrites through process optimization and the development of novel sintering aids. For instance, the preparation of ultrafine ferrite powder matrices through chemical synthesis techniques, including co-precipitation, hydrothermal processing, microwave heating, and sol-gel combustion, has proven effective in reducing sintering temperature. Furthermore, advanced sintering techniques such as spark plasma sintering, flash sintering, hot-press sintering, and microwave sintering have demonstrated significant potential in enhancing ferrite densification efficiency while reducing sintering temperature. Industrial production puts forward higher requirements for cost and efficiency. The research on oxide doping sintering technology is of great value. This technology can effectively reduce the sintering temperature of NiZn ferrites and significantly improve the material properties. Reducing the sintering temperature of NiZn ferrites is a key breakthrough for enabling its co-firing with silver electrodes. At present, many methods have been developed to reduce the sintering temperature of NiZn ferrites, such as adding low melting point oxide V2O5 [19]; at the same time, in order to improve the magnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrites, the methods of introducing additives such as MoO3-WO3 [20] and Bi2O3-Li2CO3 [21] have been explored.
BaBiO3 is a kind of ceramic material with special properties, which has a high dielectric constant, low loss factor, and good thermal stability, and is widely used in the field of electronics and optoelectronics. The excellent performance of BaBiO3 makes it an ideal choice to improve the performance of other materials, especially in magnetic materials, as an additive to enhance their performance. In NiZn ferrite materials, the addition of BaBiO3 as an additive can significantly improve the magnetic properties of the material, especially in the low-temperature sintering process. Because BaBiO3 has good dielectric and magnetic properties, it can improve the permeability, saturation magnetization, and temperature stability of NiZn ferrite by adjusting the lattice structure of NiZn ferrite and increasing the interaction between magnetic particles. In this way, BaBiO3 can help NiZn ferrites perform more stably in high-frequency applications, reduce electromagnetic losses, and improve overall performance. In addition, the addition of BaBiO3 can also promote the low-temperature sintering process of NiZn ferrite. BaBiO3 has high sintering activity, which can promote the sintering of NiZn ferrite at lower temperatures, thereby reducing energy consumption and increasing the density of the material. The incorporation of cobalt oxide mainly enhances the magnetism of the material by providing Co2+ ions. Co2+ ion has a high magnetic moment, so its addition can effectively improve the saturation magnetization and coercivity of NiZn ferrite. Co2+ ions can also promote the uniform growth of grains, thereby improving the magnetic domain structure of the material and improving its magnetic permeability and high-frequency performance. Therefore, we try to improve the properties of NiZn ferrite by adding the Co element into BaBiO3 as an additive.
The novel sintering aid BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 demonstrates exceptional magnetic property regulation capabilities. The purpose of this paper is to investigate its effect as an additive on the low-temperature sintering properties of NiZn ferrites. By adjusting the doping ratio, the influence of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 on the microstructure and magnetic properties of the material was studied, and its application potential in LTCC technology and high-frequency laminated devices was explored. We expect to obtain NiZn ferrite materials with high permeability, low loss, and high magnetization by optimizing the additional amount of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, which provides a new solution for the miniaturization and high performance of electronic components. Through this study, we hope to provide a new idea for the low-temperature sintering technology of NiZn ferrite material and lay a theoretical foundation for its application in high-frequency current sensors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
NiZn ferrite ceramic samples were prepared using the oxide ceramic method. High-purity BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 precursors (BaCO3, Co2O3, and Bi2O3, purity ≥99.99%, purchased from Aladdin, Shanghai, China) were precisely weighed and mixed with deionized water according to stoichiometric ratios, followed by 6-h planetary ball milling. The mixed powder was then pre-sintered in a muffle furnace at 725 °C for 2 h to complete solid-state reactions.
2.2. I Preparation of Composite Ceramic Samples
Commercial NiZn ferrite powder was blended with sintering aids ((1 − x)Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 + xBaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, 0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.01). The mixed powder underwent 6-h wet ball milling with deionized water, followed by vacuum drying. Then, 8% weight polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) binder was added for spray granulation. The dried powder was uniaxially pressed at 20 MPa into standard toroidal green compacts (outer diameter 20 mm, inner diameter 10 mm, thickness 5 mm), followed by sintering at 900 °C for 1 h in an air atmosphere.
2.3. Characterization
Bulk density was determined by the Archimedes drainage method using a precision densitometer. Crystal structure analysis was performed with an Empyrean PIXcel3D X-ray (PANalytical, Almelo, The Netherlands) diffractometer, with diffraction data refined by Jade 6.5 software using the Rietveld method. Microstructural characterization and elemental distribution analysis were conducted using a QUANTA 450-FEG (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA) field-emission scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS, Oxford X-Max20, Oxford Instruments plc, Oxford, UK). Complex permeability spectra were measured by an Agilent E4991B (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) impedance analyzer. The hysteresis loop is obtained by multiple measurements using the Lake Shore 7404-S (Lake Shore Cryotronics Inc., Westerville, OH, USA) vibrating sample magnetometer. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was obtained by the ESCALAB 250 XI (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) spectrometer.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Analysis
Figure 1 shows the XRD pattern of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, and the diffraction peak of the sample corresponds well to JCPDS PDF#38-1151, which proves the successful synthesis of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3. Figure 2a shows the XRD pattern of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4/BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 composite ceramic samples. All samples exhibit a single spinel phase structure, where the primary diffraction peaks correspond to the (111), (022), (113), (222), (004), (224), (333), and (044) crystal planes, showing excellent agreement with the NiZn ferrites with reference JCPDS PDF#52-0277. Figure 2b shows the Rietveld refinement results of ceramic samples with a doping amount of 0.75 wt%. Through the refinement of XRD diffraction data, the Rietveld method was used to accurately fit the diffraction patterns of the samples. During the refinement process, the position, strength, and lattice parameters of each crystal phase in the sample were determined by analyzing the shape and strength of the diffraction peaks. The refinement results show that the crystal structure of the ceramic sample does not change significantly after adding 0.75 wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, and all diffraction peaks are still consistent with the expected NiZn ferrite and BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, which proves the composite stability of the two materials. The refined calculation results further obtained the lattice constants of each phase and confirmed that the formation of NiZn ferrite phase was not affected by the addition of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, thus proving the successful synthesis of the composite material. The diffraction peak position did not change with the addition of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, indicating that the formation of the NiZn ferrites phase was not affected. XRD analysis confirms that the crystal structure of NiZn ferrites remains intact without phase transformation during sintering with this sintering aid.
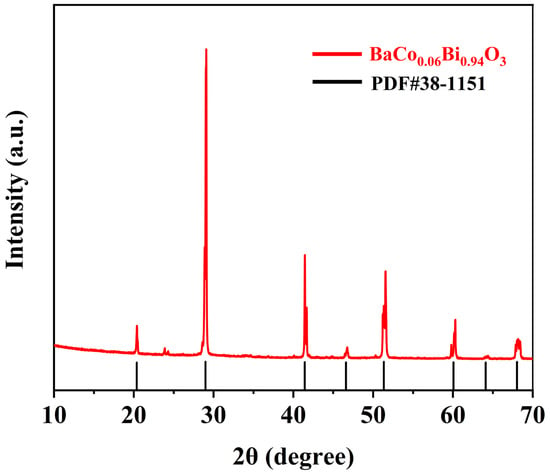
Figure 1.
The XRD patterns of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3.
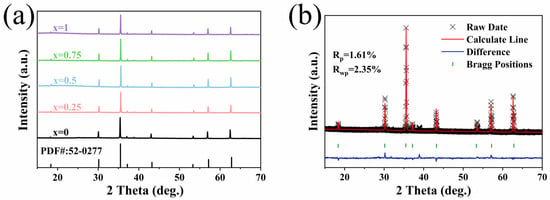
Figure 2.
(a) The XRD patterns of ceramic samples doped with x wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 and (b) Rietveld refinement XRD results of ceramic samples doped with 0.75 wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3.
The surface structure of the composite NiZn ferrite ceramics was characterized by XPS. As shown in Figure 3a, the characteristic peaks of Ba 3d, Co 2p, and Bi 4f can be clearly identified in the full spectrum of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doped samples. XPS spectra combined with XRD patterns can further illustrate that the formation of the NiZn ferrite phase structure is not affected by additives or the successful introduction of additives. Figure 3b further demonstrates the high-resolution XPS spectra of 0.75 wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3-doped NiZn ferrites sintered at 900 °C. The peak positions of Fe 2p and Fe 2p can reflect the valence state characteristics of iron ions: the sample shows a significant main peak of Fe 2p3/2 at 710.8 eV and 713.7 eV, Fe 2p1/2 at 725.2 eV and 722.2 eV, and a typical satellite peak appears near 719 eV, 732.5 eV, indicating that the iron element in the system exists in the form of Fe3+, and the characteristic signal of Fe2+ is not detected [22]. This result indicates that the electron transfer between Fe3+ and Fe2++ is weak, which may be one of the important mechanisms for the low magnetic loss characteristics of the doped NiZn ferrite [23,24].
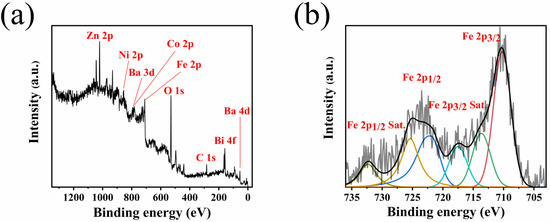
Figure 3.
XPS spectra (a) and Fe high-resolution spectra (b) of NiZn ferrite ceramics with a BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping ratio of 0.75 wt%.
3.2. Microstructure Analysis
Figure 4 shows the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4/BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 composite ceramics sintered at 900 °C for 1 h. When the doping amount of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 is 0 wt%, the sintered body exhibits small grain sizes with larger size differences. The sample is composed of grain clusters showing a loose structure. The grains inside the clusters are in close contact to form grain boundaries, while there is less contact between the clusters, and there are a large number of interconnected pores (Figure 4a,b). This microstructure characteristic leads to low sample density. The main reason for its formation is the volume shrinkage caused by the density difference between the amorphous phase and the crystalline phase [25].
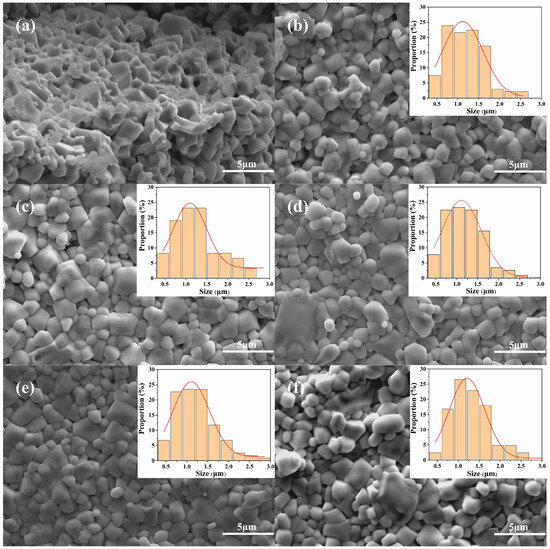
Figure 4.
SEM images of (1 − x) Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 + x BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.01) composite ceramic samples: (a) x = 0, (b) x = 0, (c) x = 0.0025, (d) x = 0.005, (e) x = 0.0075, (f) x = 0.01.
When the doping ratio of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 increases to 0.25 wt% and 0.75 wt%, the contact tightness between grains is significantly enhanced, the grain boundaries become clearer, and the number of pores is significantly reduced. At the same time, the morphology of the grains gradually tends to be regularized (Figure 4c,e) and the uniformity of the microstructure is improved, accompanied by an increase in the density of the sample. However, when the doping amount increases to 0.5 wt% and 1 wt%, abnormal grain growth and uneven pore distribution appear along the grain boundary region (Figure 4d,f), which may be the main reason for the sample density fluctuation. The increase of density may have an important influence on the improvement of magnetic properties.
When the doping ratio of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 increases to 1 wt%, dense small-sized grains and abnormally grown super-large grains appear in the grain boundary region (Figure 4f). Excessive doping-induced abnormal grain growth led to the formation of a supersaturated liquid phase at grain boundaries or within grains [26]. This liquid phase not only inhibited the normal growth of other grains but also caused an anomalous increase in average grain size while promoting intergranular pore formation and reducing material density. This phenomenon is the main factor that causes the magnetic properties to show the first enhancement and then deterioration, as shown in Table 1 (). SEM analysis shows that the grain growth of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite during sintering is significantly affected by BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping. Combined with the experimental results, the appropriate amount of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping can reduce the sintering temperature of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite to 900 °C.

Table 1.
The performance parameters of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite with BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 addition sintered at 900 °C.
3.3. Magnetic Properties
Figure 5 displays the magnetic hysteresis loops of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4/BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 composite ceramics at room temperature. The data in Table 1 show that the saturation magnetization of the Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4/BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 composite ceramic sample decreases slightly and then continues to rise when the doping ratio is 0.25 wt% compared with the undoped sample. All the samples show a typical hysteresis under the applied magnetic field and have low coercivity (). When the BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping concentration reached 0.75 wt%, the composite ceramic achieved magnetization saturation at a 600 Oe magnetic field while obtaining the minimum coercivity of 35.61 Oe. With the doping ratio increased to 1 wt%, the sample demonstrated the maximum saturation magnetization of 66.07 emu/g (Table 1). This enhancement of magnetization is essential to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of high-precision magnetic sensors because it is directly related to the detection sensitivity to magnetic flux. This enhancement in magnetization originated from the optimal addition of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, which improved grain size uniformity and increased sample density through reduced sintering temperature, thereby facilitating magnetization improvement. The improvement in saturation magnetization is due to the addition of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3, which not only reduces the sintering temperature of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite but also improves the uniformity of grain size and increases the density of the sample, thus promoting the increase in saturation magnetization. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) microstructural analysis presented in Figure 4 further corroborated this mechanism.
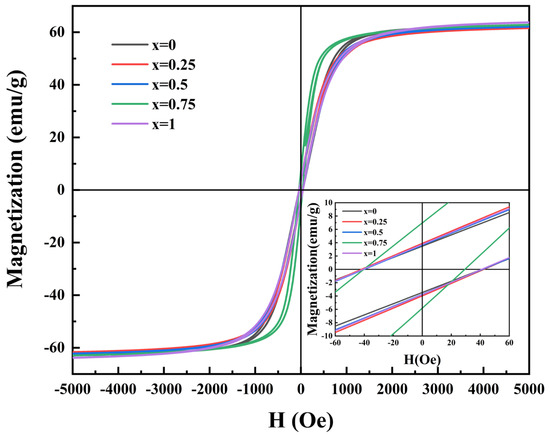
Figure 5.
The magnetic hysteresis loops of ceramic samples doped with x wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3.
The magnetism of spinel ferrite is mainly due to the difference in magnetic moments between A () and B () sublattices. The net magnetic moment () of the crystal can be defined as follows:
When the doping content reached 0.25 wt%, the saturation magnetization () decreased to 63.79 emu/g. This phenomenon can be attributed to the excess nonmagnetic BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3. These ions (mainly Ba2+ and Bi3+) lead to the redistribution of metal cations at the B site by replacing Fe3+ ions. Such redistribution reduces the magnetic moment () of B-site lattice ions, consequently leading to the observed decline in saturation magnetization [27]. At a doping ratio of 0.75 wt%, the coercivity () of sintered samples reached a minimum value of 35.61 Oe. As described by Brown’s relation [28], coercivity exhibits a functional relationship with saturation magnetization (), the anisotropy constant (), and the magnetostriction coefficient ():
This relationship indicates that coercivity () is inversely proportional to saturation magnetization () and directly proportional to the magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant (). As the BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 content increases from 0 wt% to 0.5 wt%, the coercivity of the samples exhibits an initial increase followed by a decrease, which can be explained by the dominant effect of significantly reduced grain size on magnetocrystalline anisotropy [29,30]. When the BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 content exceeds 0.75 wt%, the variation in coercivity is predominantly governed by saturation magnetization. The study reveals that 1 wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 represents the optimal doping concentration for enhancing the saturation magnetization of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite, while 0.75 wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 enables the Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite to achieve the lowest coercivity value.
Figure 6 demonstrates the frequency response characteristics of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4/BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 composite ceramics after sintering at 900 °C for 1 h. Within the 1–1000 MHz frequency range, the real part of permeability (μ′) for all samples exhibited three-stage evolution characteristics: maintaining stable values in the low-frequency region (<10 MHz), showing a gradual increase in the mid-frequency region, and demonstrating a sharp decline in the high-frequency region. As seen in Figure 6a, a significant increase in the initial permeability and a decrease in the cut-off frequency are observed, which is consistent with Snoek’s law [31]. The results show that the appropriate amount of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 can significantly improve the permeability of the sample. When the doping amount is 0.75 wt%, the maximum initial permeability is about 73.74 (at a frequency of 1 MHz).
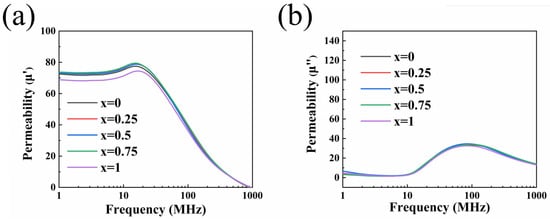
Figure 6.
Complex permeability (a) real part and (b) imaginary part of ceramic samples doped with x wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3.
The experimental observations can be attributed to permeability evolution induced by distinct magnetization mechanisms. In the low-frequency range, the initial permeability can be expressed as complex permeability, which mainly comes from the two main magnetization mechanisms of spin rotation and magnetic domain wall motion [32,33]:
where and represent the magnetic susceptibility corresponding to spin rotation and domain wall motion, respectively. For multi-domain samples, the magnetization mechanism is predominantly governed by domain wall motion [34]. Accordingly, Equation (3) can be rewritten as
In the formula, is the saturation magnetization, D is the average grain size, and is the domain wall energy. Van der Zaag reported that when the size of NiZn ferrites is less than 2 µm, the grains reach a single domain state [35]. As shown in Table 1, the grains in the ferrites we prepared are determined to be single-domain states, and the main contribution mechanism of dynamic magnetization changes from domain wall motion to spin rotation magnetization mechanism. Based on this analysis, Equation (3) can be simplified to the following expression [36,37]:
Here, , , and denote saturation magnetization, demagnetizing field, and magnetocrystalline anisotropy field, respectively. The increase in the permeability of the 0.75 wt% doped sample can be explained by the decrease in and the increase in caused by the increase in sample density. The results show that the Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite doped with 0.75 wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 has the highest permeability in the frequency range of 1~10 MHz.
Low magnetic loss is an important parameter for high-performance NiZn ferrites. BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 can effectively reduce the magnetic loss of NiZn ferrites and achieve saturation magnetization characteristics at low applied magnetic field strength. The mechanism of action is derived from the optimal regulation of the microstructure of the material.
The quality factor is an important parameter to measure the loss characteristics of ferrite materials under an AC magnetic field, which is usually used to evaluate the energy loss and performance of materials. Figure 7a shows the fluctuation curves of the quality factor and density of the samples with the doping ratio of the additives. For ferrites, especially soft magnetic ferrites for high frequency applications, the quality factor is usually calculated by the following formula:
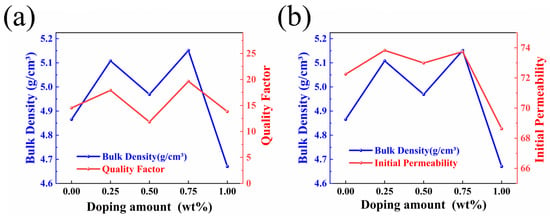
Figure 7.
The (a) quality factor and initial (b) permeability of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4/BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 composite ceramics change with density.
Figure 8 shows the magnetic loss of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4/BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 composite ceramics sintered at 900 °C in the frequency range of 1 MHz~1 GHz. The magnetic loss characteristics can be quantitatively described by the following mathematical expression:
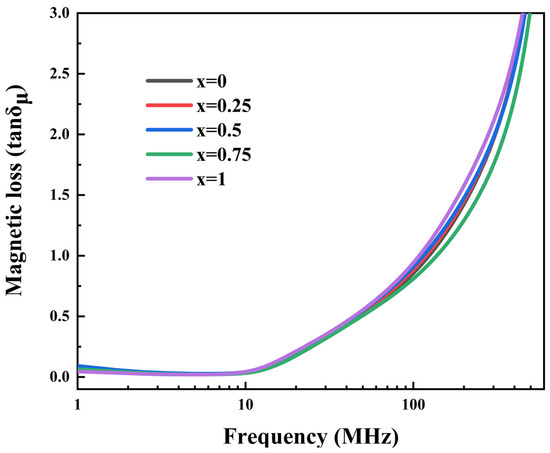
Figure 8.
The magnetic loss of ceramic samples doped with x wt% BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 in the frequency range of 1 MHz~1 GHz was measured.
Undoped samples exhibited a relatively low-quality factor at 1 MHz. The maximum Q value of 19.64 (at a frequency of 1 MHz) was achieved when the doping concentration of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 reached 0.75 wt%. As shown in Figure 7a, both sample density and quality factor followed consistent variation patterns with increasing BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 content, demonstrating that densification plays a critical role in enhancing the quality factor. As shown in Figure 7a,b, with the change in BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping concentration, the density, quality factor, and initial permeability of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite show a synergistic change rule. The material density significantly affects the change trend of the initial permeability and quality factor. The experimental results show that BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping can effectively regulate the material properties in the 1–10 MHz frequency band: the magnetic loss is significantly reduced, and the initial permeability and quality factor are improved.
Figure 9a is the structure diagram of Hall current sensor. After integrating the optimized magnetic ring (Figure 9b) into the above current sensor, the high permeability, low coercivity, high frequency, low loss, high density, and other characteristics of the magnetic ring can provide sensitivity improvement, dynamic response acceleration, noise suppression, reliability enhancement, and other multiple advantages for the Hall current sensor [38]. According to the magnetic circuit model of the magnetic core in the Hall current sensor, the output magnetic induction intensity B is closely related to the initial permeability μ and the saturation magnetization M of the material. By introducing Ba impurity, the density of the NiZn ferrite core increases from 4.87 g/cm3 to 5.15 g/cm3, the microstructure is more compact, the porosity is reduced, and the magnetic flux conduction ability is effectively enhanced. The experimental results show that the initial permeability of the material increases from 72.25 to 73.83, an increase of about 2.2%. According to the formula
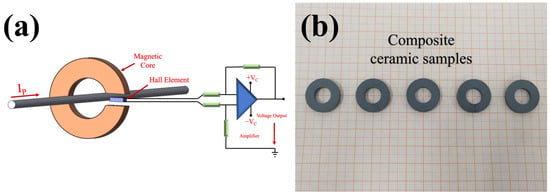
Figure 9.
(a) Application of the magnetic core in the Hall sensor and (b) composite ceramic samples.
It can be seen that the corresponding Hall output voltage will also be positively correlated, which will help to improve the sensitivity of the sensor. The formula shows that the material can still maintain a linear response under higher current conditions, which expands the linear working range of the sensor and improves its adaptability to high current signals. In summary, the density improvement and magnetic performance optimization achieved by doping control show consistency in both theoretical models and experimental data, which significantly enhances the comprehensive performance of the magnetic core in the application of Hall current sensors. In the future, multi-gap core design or gradient doping strategy can be further explored to meet the needs of 5G communication and miniaturized current sensors for high frequency and integration.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, the effect of BaCo0.06Bi0.94O3 doping on the low-temperature sintering properties of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite was systematically studied. The results show that proper doping can significantly reduce the sintering temperature of Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 ferrite to 900 °C and optimize its microstructure and magnetic properties. The sample with 0.75 wt% doping exhibited optimal comprehensive performance: uniform grain size (1.21 μm), minimum coercivity (35.61 Oe), highest quality factor (19.64 at a frequency of 1 MHz), and permeability (73.74 at a frequency of 1 MHz), along with significantly reduced magnetic losses. Excessive doping (≥0.75 wt%) induced abnormal grain growth and increased porosity, resulting in notable deterioration of magnetic properties. XRD and SEM analysis confirmed that the doping did not change the main phase structure of spinel. The magnetocrystalline anisotropy is affected by the liquid phase distribution at the grain boundary. The research results provide theoretical support for the development of high-frequency and low-loss LTCC components in current sensors, and 1 wt% and 0.75 wt% are established as the optimal doping thresholds for improving saturation magnetization (66.07 emu/g) and optimizing dynamic magnetic properties, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation, methodology, and writing—original draft preparation, S.-P.J.; writing—review and editing, supervision, and project administration, C.-L.Y. and W.L.; resources and funding acquisition, J.-T.Z., L.L. and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52261005), the Central Government Guided Local Science and Technology Development Fund Project (ZY22096009), and the Guangxi Project of Science and Technology (Grant No. AB22080062). The authors also acknowledge the Program for Bagui Scholars of Guangxi, China.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liang, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. An LC wireless microfluidic sensor based on low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) technology. J. Sens. 2019, 19, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrila, I. Annealing Temperature Effects on Humidity Sensor Properties for Mg0.5W0.5Fe2O4 Spinel Ferrite. J. Sens. 2022, 22, 9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, G.; Coisson, M.; Celegato, F.; Martino, L.; Tiwari, P.; Verma, R.; Kane, S.N.; Mazaleyrat, F. Specific Loss Power of Co/Li/Zn-Mixed Ferrite Powders for Magnetic Hyperthermia. J. Sens. 2020, 20, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Fu, G.; Li, Y. Research on a Defects Detection Method in the Ferrite Phase Shifter Cementing Process Based on a Multi-Sensor Prognostic and Health Management (PHM) System. J. Sens. 2016, 16, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-J.; Sim, H.-J. Development and Evaluation of Ferrite Core Inductively Coupled Plasma Radio Frequency Ion Source for High-Current Ion Implanters in Semiconductor Applications. J. Sens. 2024, 24, 5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.; Lim, T.H.; Kang, E.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, K.B. Design of a Miniaturized Rectangular Multiturn Loop Antenna for Shielding Effectiveness Measurement. J. Sens. 2020, 20, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Acharya, S.; Popov, M.; Sauyet, T.; Pfund, J.; Bidthanapally, R. A Novel Spinel Ferrite-Hexagonal Ferrite Composite for Enhanced Magneto-Electric Coupling in a Bilayer with PZT. J. Sens. 2023, 23, 9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshaka, K.; Twomey, K. A Ceramic Thick Film Humidity Sensor Based on MnZn Ferrite. J. Sens. 2002, 2, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Lu, D.; Cui, B.; Lin, A.; Liu, M.; Ye, Y. Establishment of a Mass Concrete Strength-Monitoring Method Using Barium Titanate–Bismuth Ferrite/Polyvinylidene Fluoride Nanocomposite Piezoelectric Sensors with Temperature Stability. J. Sens. 2024, 24, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Li, J.; Su, H.; Zhou, T.C.; Long, Y.; Zheng, Z.L. Development and application of ferrite materials for low temperature co-fired ceramic technology. J. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 117504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węglarski, M.; Jankowski-Mihułowicz, P.; Pitera, G.; Jurków, D. LTCC Flow Sensor with RFID Interface. J. Sens. 2020, 20, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowski, A.; Nawrot, W.; Czok, M.; Babij, M.; Bielówka, P. LTCC Strip Electrode Arrays for Gas Electron Multiplier Detectors. J. Sens. 2022, 22, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Passive Wireless LC Proximity Sensor Based on LTCC Technology. J. Sens. 2019, 19, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molins-Benlliure, J.; Cabedo-Fabrés, M.; Antonino-Daviu, E.; Ferrando-Bataller, M. Miniaturized On-Ground 2.4 GHz IoT LTCC Chip Antenna and Its Positioning on a Ground Plane. J. Sens. 2023, 23, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanowska, P.; Nowak, D.; Piasecki, T. Performance Evaluation of Miniature Integrated Electrochemical Cells Fabricated Using LTCC Technology. J. Sens. 2019, 19, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecha, K.; Jasińska, L.; Grytsko, A.; Drzozga, K.; Słobodzian, P.; Cabaj, J. Monolithic Microwave-Microfluidic Sensors Made with Low Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic (LTCC) Technology. J. Sens. 2019, 19, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Gan, G.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of highly uniform and compact lithium zinc ferrite ceramics via an efficient low temperature approach. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 4512–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.T.; Hsiang, H.I.; Hsu, W.H. Varistor and magnetic properties of nickel copper zinc niobium ferrite doped with B2O3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 3918–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaee, O.; Golozar, M.A.; Shafyei, A. Influence of V2O5 as an effective dopant on the microstructure development and magnetic properties of Ni0.64Zn0.36Fe2O4 soft ferrites. J. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; Jing, Y. Effects of MoO3 and WO3 additives on densification and magnetic properties of highly permeable NiCuZn ferrites. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 102, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Tang, X.; Zhang, H.; Su, H. Effects of Li2CO3 addition on the microstructure and magnetic properties of low-temperature-fired NiCuZn ferrites. J. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 14609–14613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Dube, D.C. Processing of nickel-zinc ferrites via the citrate precursor route for high-frequency applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Zhou, J.; Gui, Z.; Li, L. Magnetic and electrical properties of low-temperature sintered Mn-doped NiCuZn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 264, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yi, Z.; Li, J.J.; Qiu, T.; Min, F.F.; Zhang, M.X. Microwave Sintering of Nanocrystalline Ni1−xZnxFe2O4 Ferrite Powder and Their Magnetic Properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliman, L.B.; Bouchet, R.; Gouvea, D.; Soudant, P.; Steil, M.C. Flash sintering of ionic conductors: The need of a reversible electrochemical reaction. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, K.; Ma, Y.; Huang, F.; Lv, F. On the structure and some properties of LaCo Co-substituted NiZn ferrites prepared using the standard ceramic technique. J. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2016, 35, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D. Ferromagnetism; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Maisnam, M.; Phanjoubam, S.; Sarma, H.N.K.; Devi, L.R.; Thakur, O.P.; Prakash, C. Hysteresis and initial permeability behavior of vanadium-substituted lithium-zinc-titanium ferrite. J. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2004, 352, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lan, Z.; Jiang, X.; Yu, Z.; Sun, K.; Li, L.; Liu, P. Effects of sintering temperature and Bi2O3 content on microstructure and magnetic properties of LiZn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T. Snoek’s limit in high-frequency permeability of polycrystalline NiZn, Mg-Zn, and NiZn-Cu spinel ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutaoka, T.; Ueshima, M.; Tokunaga, T.; Nakamura, T.; Hatakeyama, K. Frequency dispersion and temperature variation of complex permeability of NiZn ferrite composite materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 3983–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, G.; Li, L. Contribution of magnetization mechanisms in nickel-zinc ferrites with different grain sizes and its temperature relationship. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 175, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, T.Y.; Byeon, S.C.; Hong, K.S.; Kim, C.K. Factors affecting initial permeability of Co-substituted NiZn-Cu ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 3445–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Zaag, P.J.; Kolenbrander, M.; Rekveldt, M.T. The effect of intragranular domain walls in MgMnZn-ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 6870–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yan, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Nie, Y. Monodomain design and permeability study of high-Q-factor NiCuZn ferrites for near-field communication application. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 4367–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Nie, Y. Monodomain MgCuZn ferrite with equivalent permeability and permittivity for broad frequency band applications. J. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5974–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Oh, Y.; Oh, S.; Chae, H. Low power CMOS-based Hall sensor with simple structure using double-sampling delta-sigma ADC. J. Sens. 2020, 20, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).