Three-Station Non-Contrast MR Angiography of the Lower Extremities Using Standard and Centric Fresh Blood Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
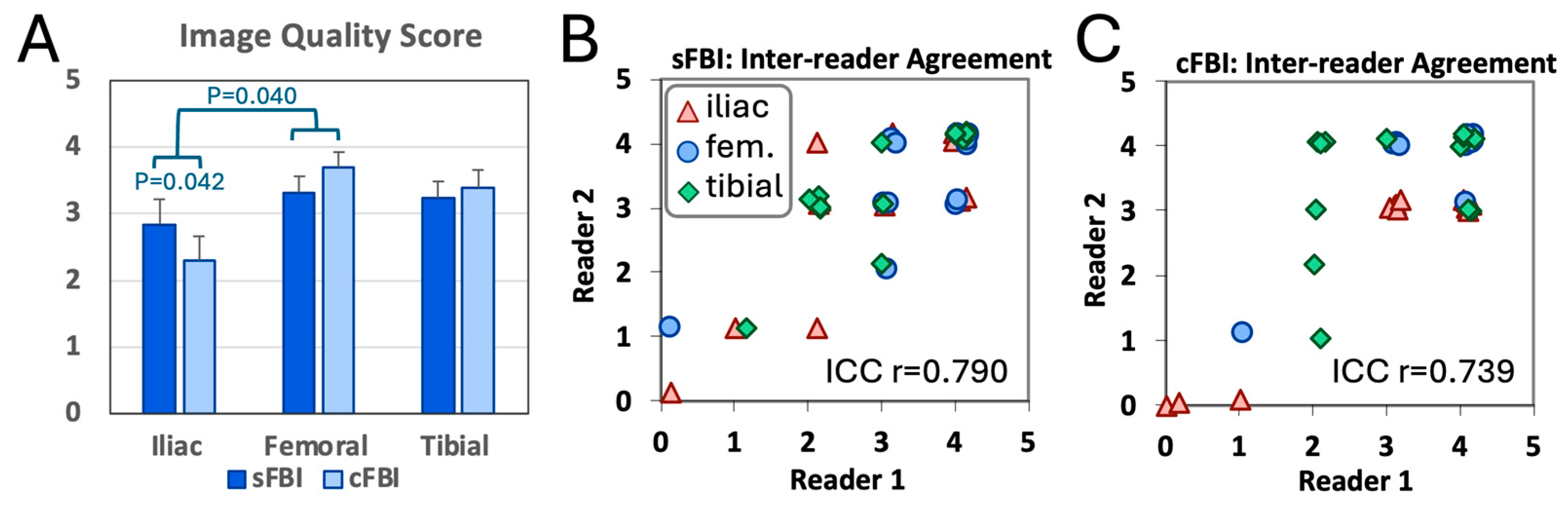
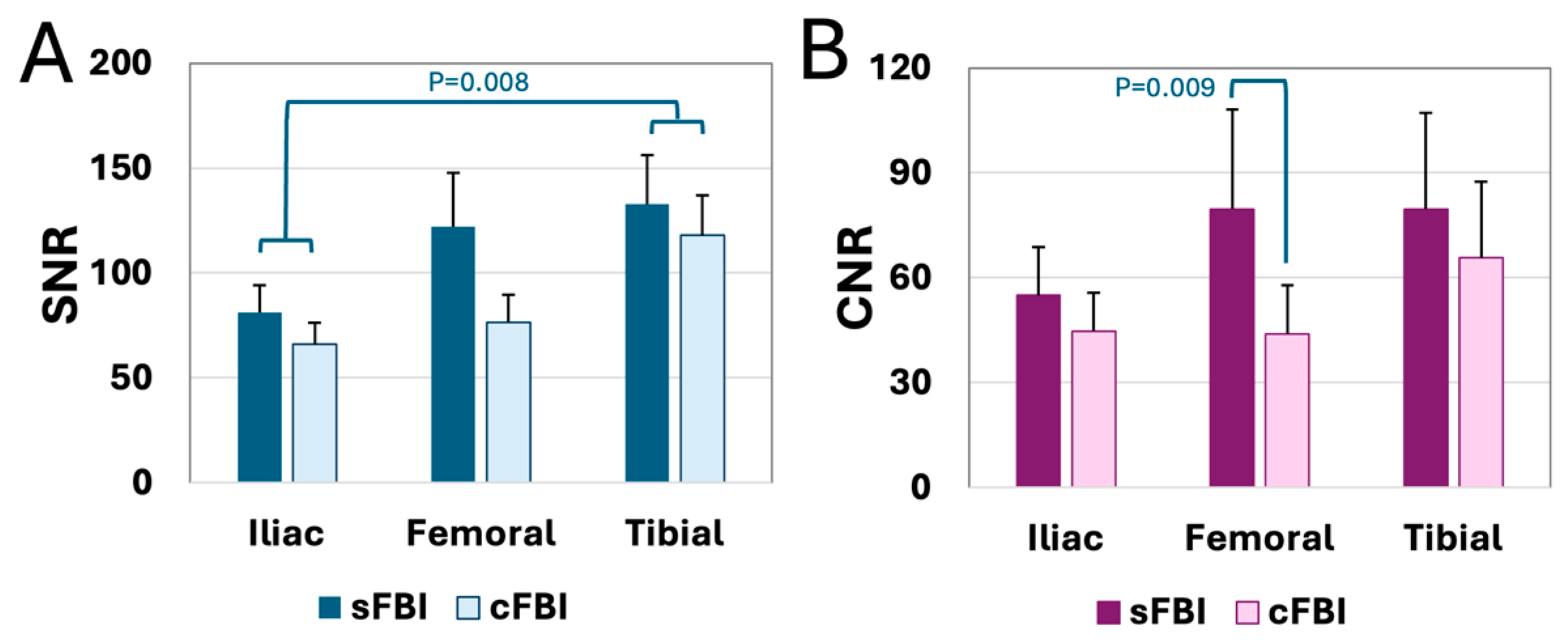
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selvin, E.; Erlinger, T.P. Prevalence of and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2000. Circulation 2004, 110, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, C.A.; Thal, E.R.; Redman, H.C.; Gibson, P. Intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography in the evaluation of peripheral vascular trauma. Ann. Surg. 1989, 210, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, R.; Santoro, M.; Marano, R.; Di Stasi, C.; Dattesi, R.; Kirchin, M.; Tinelli, G.; Snider, F.; Bonomo, L. Low-dose multidetector CT angiography in the evaluation of infrarenal aorta and peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Radiology 2012, 263, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolski, G.J.; Stavropoulos, S.W. Contrast alternatives for iodinated contrast allergy and renal dysfunction: Options and limitations. J. Vasc. Surg. 2013, 57, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, D.; Hallett, R.L.; Rubin, G.D. CT angiography of peripheral arterial disease. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 17, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLoach, S.S.; Mohler, E.R., 3rd. Peripheral arterial disease: A guide for nephrologists. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.A.; Debatin, J.F. Three-dimensional contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of the thoracic vasculature. Eur. Radiol. 1997, 7, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.Y.; Leiner, T.; de Haan, M.W.; Kessels, A.G.; Kitslaar, P.J.; van Engelshoven, J.M. Peripheral vascular tree stenoses: Evaluation with moving-bed infusion-tracking MR angiography. Radiology 1998, 206, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm223966.htm (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Aime, S.; Caravan, P. Biodistribution of gadolinium-based contrast agents, including gadolinium deposition. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Ishii, K.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kitajima, K.; Takenaka, D. High signal intensity in the dentate nucleus and globus pallidus on unenhanced T1-weighted MR images: Relationship with increasing cumulative dose of a gadolinium-based contrast material. Radiology 2014, 270, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Osawa, M.; Oba, H.; Toyoda, K.; Kotoku, J.; Haruyama, T.; Takeshita, K.; Furui, S. High Signal Intensity in Dentate Nucleus on Unenhanced T1-weighted MR Images: Association with Linear versus Macrocyclic Gadolinium Chelate Administration. Radiology 2015, 275, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Jentoft, M.E.; Murray, D.L.; Thielen, K.R.; Williamson, E.E.; Eckel, L.J. Intracranial Gadolinium Deposition after Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging. Radiology 2015, 275, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, M.; Sugiura, S.; Tateishi, F.; Wada, H.; Kassai, Y.; Abe, H. Non-contrast-enhanced MR angiography using 3D ECG-synchronized half-Fourier fast spin echo. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Takai, H.; Sugiura, S.; Wada, H.; Kuwahara, R.; Urata, J. Peripheral MR angiography: Separation of arteries from veins with flow-spoiled gradient pulses in electrocardiography-triggered three-dimensional half-Fourier fast spin-echo imaging. Radiology 2003, 227, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, R.R.; Sheehan, J.J.; Dunkle, E.; Schindler, N.; Carr, J.; Koktzoglou, I. Quiescent-interval single-shot unenhanced magnetic resonance angiography of peripheral vascular disease: Technical considerations and clinical feasibility. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 63, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Sheehan, J.; Bi, X.; Liu, X.; Carr, J.; Li, D. 3D noncontrast MR angiography of the distal lower extremities using flow-sensitive dephasing (FSD)-prepared balanced SSFP. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Bi, X.; Dharmakumar, R.; Carr, J.C.; Li, D. Determination of the optimal first-order gradient moment for flow-sensitive dephasing magnetization-prepared 3D noncontrast MR angiography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.; Hu, B.S.; Nishimura, D.G. Off-resonance-robust velocity-selective magnetization preparation for non-contrast-enhanced peripheral MR angiography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.; Qin, Q.; Park, J.Y.; Crawford, R.S.; Rajagopalan, S. Identification and reduction of image artifacts in non-contrast-enhanced velocity-selective peripheral angiography at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, M.; Lee, V.S. Nonenhanced MR angiography. Radiology 2008, 248, 20–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Akahane, M. Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: Established techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, A.J.; Miyazaki, M. Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: Physical principles. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaryk, T.J.; Laub, G.A.; Modic, M.T.; Ross, J.S.; Haacke, E.M. Carotid-CNS MR flow imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1990, 14, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, N.; Rijsman, L.H.; Nieuwets, A.; Groenendaal, F.; NeoQflow Study, G. Cerebral Blood Flow Measured by Phase-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Angiography in Preterm and Term Neonates. Neonatology 2019, 115, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Kuroki, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Hiramine, A.; Admiraal-Behloul, F. Noncontrast-enhanced peripheral MRA: Technical optimization of flow-spoiled fresh blood imaging for screening peripheral arterial diseases. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaney, J.F. Magnetic resonance angiography of the peripheral arteries: Current status. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 836–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, R.R.; Koktzoglou, I. Noncontrast MR angiography: An update. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.C.; Kramer, C.M. Recent advances in magnetic resonance imaging for peripheral artery disease. Vasc. Med. 2018, 23, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, H.; Rybicki, F.J. MR angiography of the lower extremities. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Murase, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Shibutani, O.; Takata, S.; Kobashi, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Deep vein thrombosis using noncontrast-enhanced MR venography with electrocardiographically gated three-dimensional half-Fourier FSE: Preliminary experience. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Murase, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Shibutani, O.; Takata, S.; Kobashi, Y.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Deep venous thrombosis: Diagnostic value of non-contrast-enhanced MR venography using electrocardiography-triggered three-dimensional half-Fourier FSE. Magn. Reson. Med. 2010, 64, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malis, V.; Vucevic, D.; Bae, W.C.; Yamamoto, A.; Kassai, Y.; Lane, J.; Hsiao, A.; Nakamura, K.; Miyazaki, M. Fast Non-contrast MR Angiography Using a Zigzag Centric k(y) − k(z) k-space Trajectory and Exponential Refocusing Flip Angles with Restoration of Longitudinal Magnetization. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2025, 24, mp-2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, W.C.; Hahn, L.; Malis, V.; Mesa, A.; Vucevic, D.; Miyazaki, M. Peripheral Non-Contrast MR Angiography Using FBI: Scan Time and T2 Blurring Reduction with 2D Parallel Imaging. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Morita, Y.; Vucevic, D.; Higuchi, S.; Takagi, H.; Kutsuna, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Kim, P.; Miyazaki, M. Motion robust coronary MR angiography using zigzag centric ky-kz trajectory and high-resolution deep learning reconstruction. MAGMA 2024, 37, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.P.; Weavers, P.T.; Borisch, E.A.; Grimm, R.C.; Hulshizer, T.C.; LaPlante, C.C.; Rossman, P.J.; Glockner, J.F.; Young, P.M.; Riederer, S.J. Three-station three-dimensional bolus-chase MR angiography with real-time fluoroscopic tracking. Radiology 2014, 272, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A.U.; Koktzoglou, I.; Edelman, R.R.; Gilkeson, R.; Mihai, G.; Shin, T.; Rajagopalan, S. Noncontrast Magnetic Resonance Angiography for the Diagnosis of Peripheral Vascular Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e008844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, M.; Furudate, N.; Chotiyanonta, J.S.; Yamamoto, A.; Nakamura, K. A Simple Noncontrast FBI Technique for Peripheral Run-Offs: Development of Automatic Algorithm to Find Systolic and Diastolic Triggering Delays; ISMRM: Concord, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 20, p. 3349. [Google Scholar]
- Boujan, T.; Neuberger, U.; Pfaff, J.; Nagel, S.; Herweh, C.; Bendszus, M.; Mohlenbruch, M.A. Value of Contrast-Enhanced MRA versus Time-of-Flight MRA in Acute Ischemic Stroke MRI. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 1710–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnam, M.S.; Tomasian, A.; Deshpande, V.; Tran, L.; Laub, G.; Finn, J.P.; Ruehm, S.G. Noncontrast 3D steady-state free-precession magnetic resonance angiography of the whole chest using nonselective radiofrequency excitation over a large field of view: Comparison with single-phase 3D contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography. Investig. Radiol. 2008, 43, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasp Team. JASP (Version 0.18.3) [Computer Software]. 2025. Available online: https://jasp-stats.org/faq/how-do-i-cite-jasp/ (accessed on 1 November 2025).
- Nielsen, Y.W.; Thomsen, H.S. Contrast-enhanced peripheral MRA: Technique and contrast agents. Acta Radiol. 2012, 53, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.; Menon, R.G.; Thomas, R.B.; Cavallo, A.U.; Sarkar, R.; Crawford, R.S.; Rajagopalan, S. Unenhanced Velocity-Selective MR Angiography (VS-MRA): Initial Clinical Evaluation in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolen, S.A.; Shankar, P.R.; Gagnier, J.J.; MacEachern, M.P.; Singer, L.; Davenport, M.S. Risk of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis in Patients with Stage 4 or 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Receiving a Group II Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheith, O.; Farouk, N.; Nampoory, N.; Halim, M.A.; Al-Otaibi, T. Diabetic kidney disease: World wide difference of prevalence and risk factors. J. Nephropharmacol. 2016, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyoye, D.O.; Abiodun, O.O.; Ikem, R.T.; Kolawole, B.A.; Akintomide, A.O. Diabetes and peripheral artery disease: A review. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

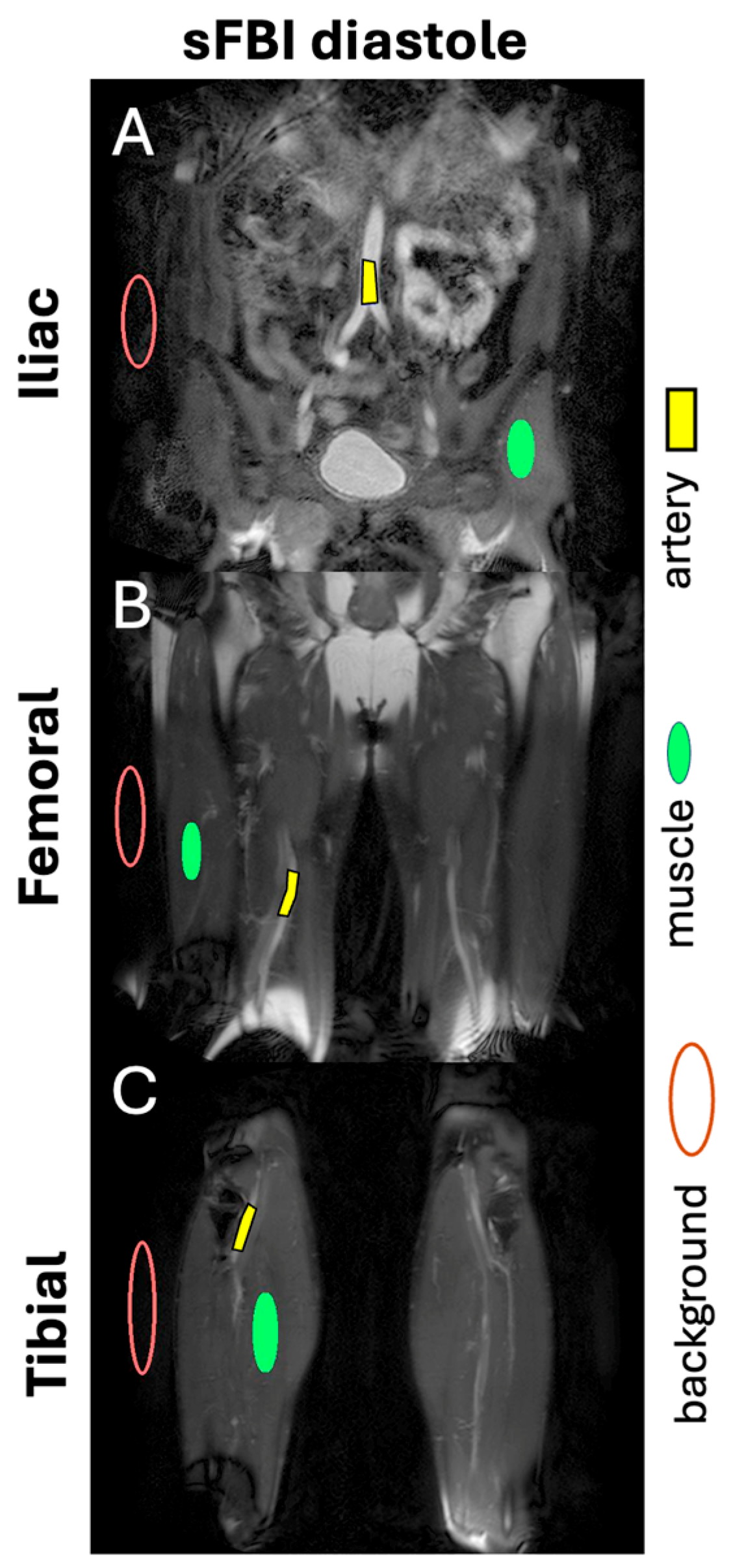
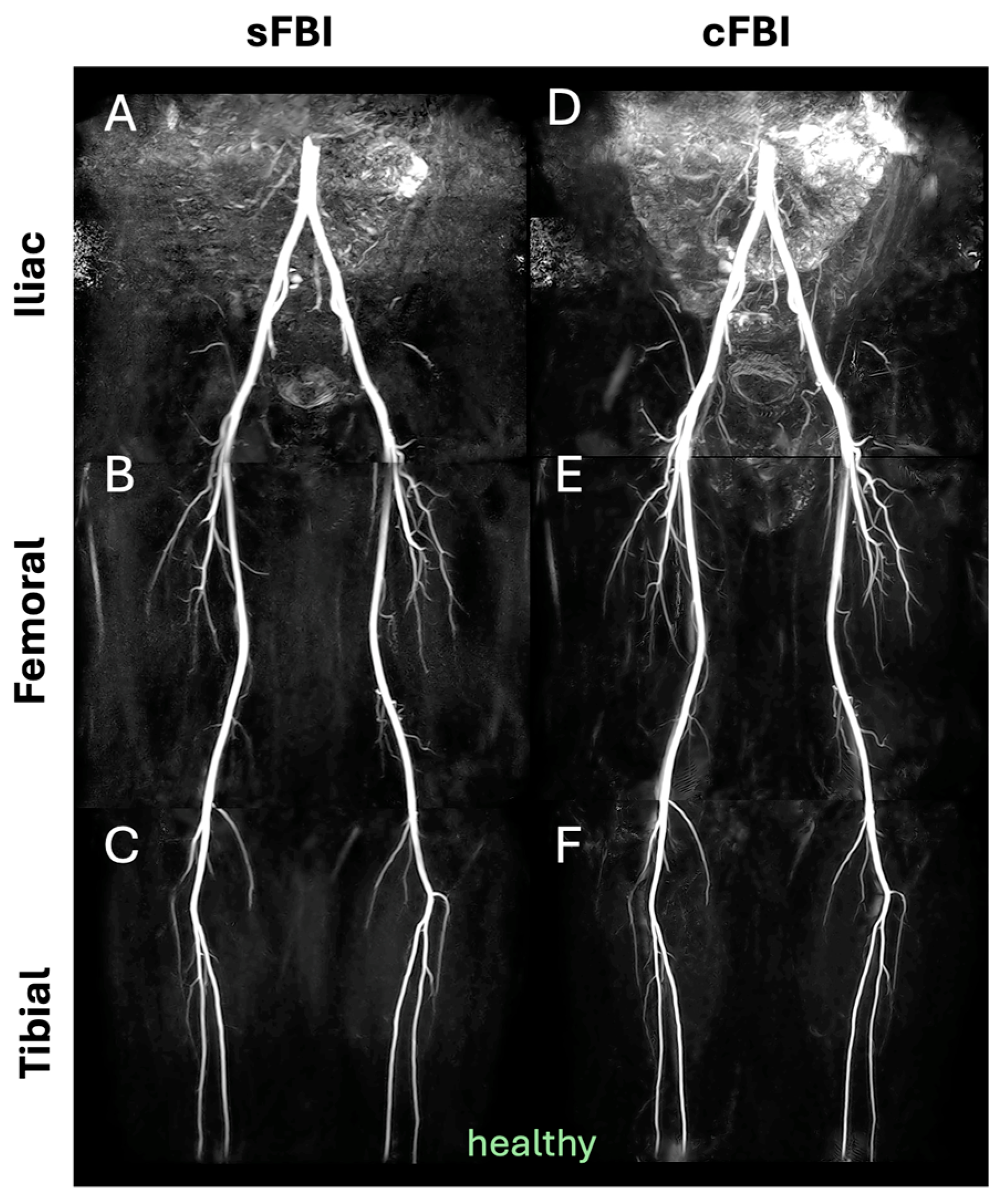
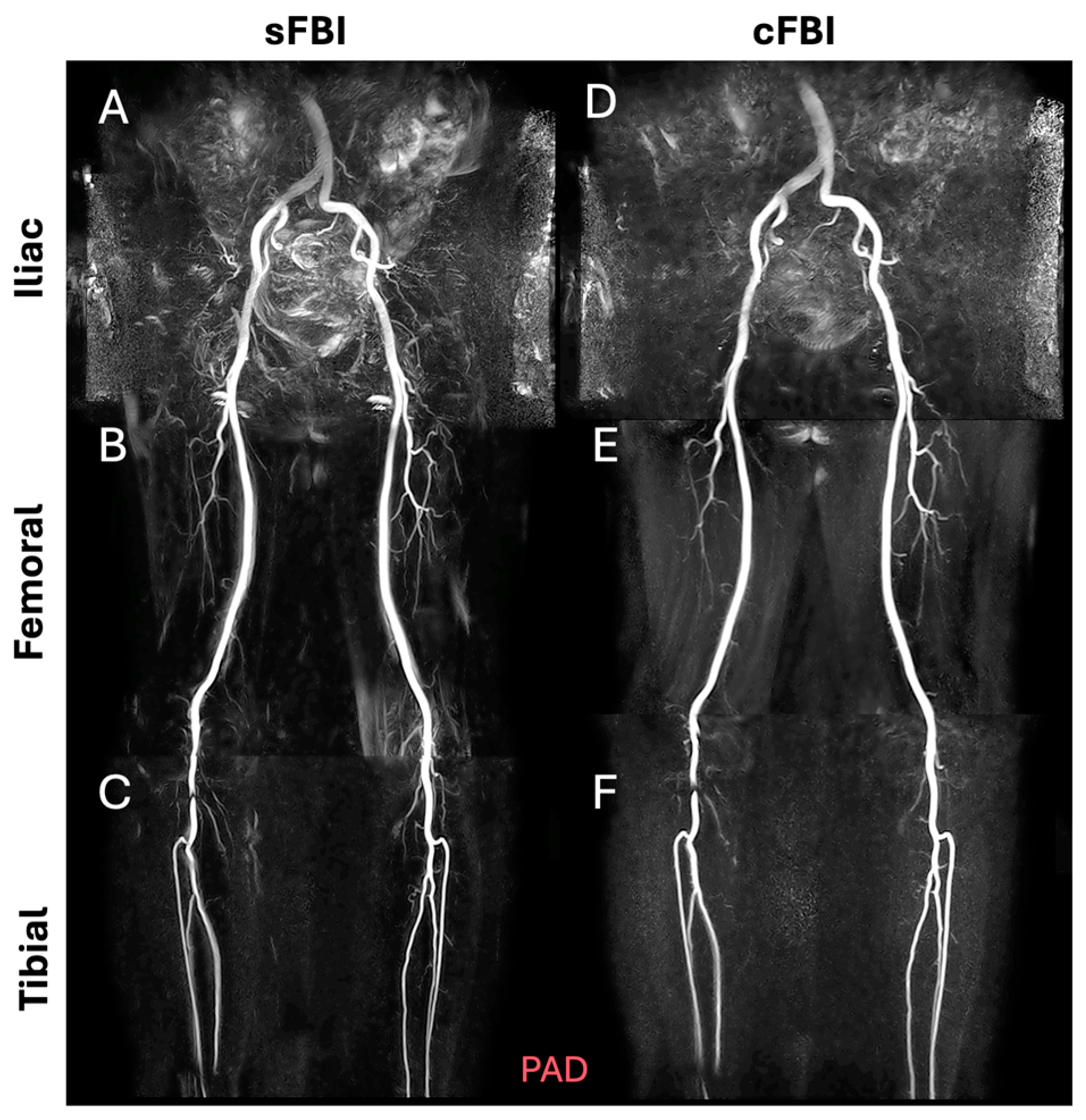
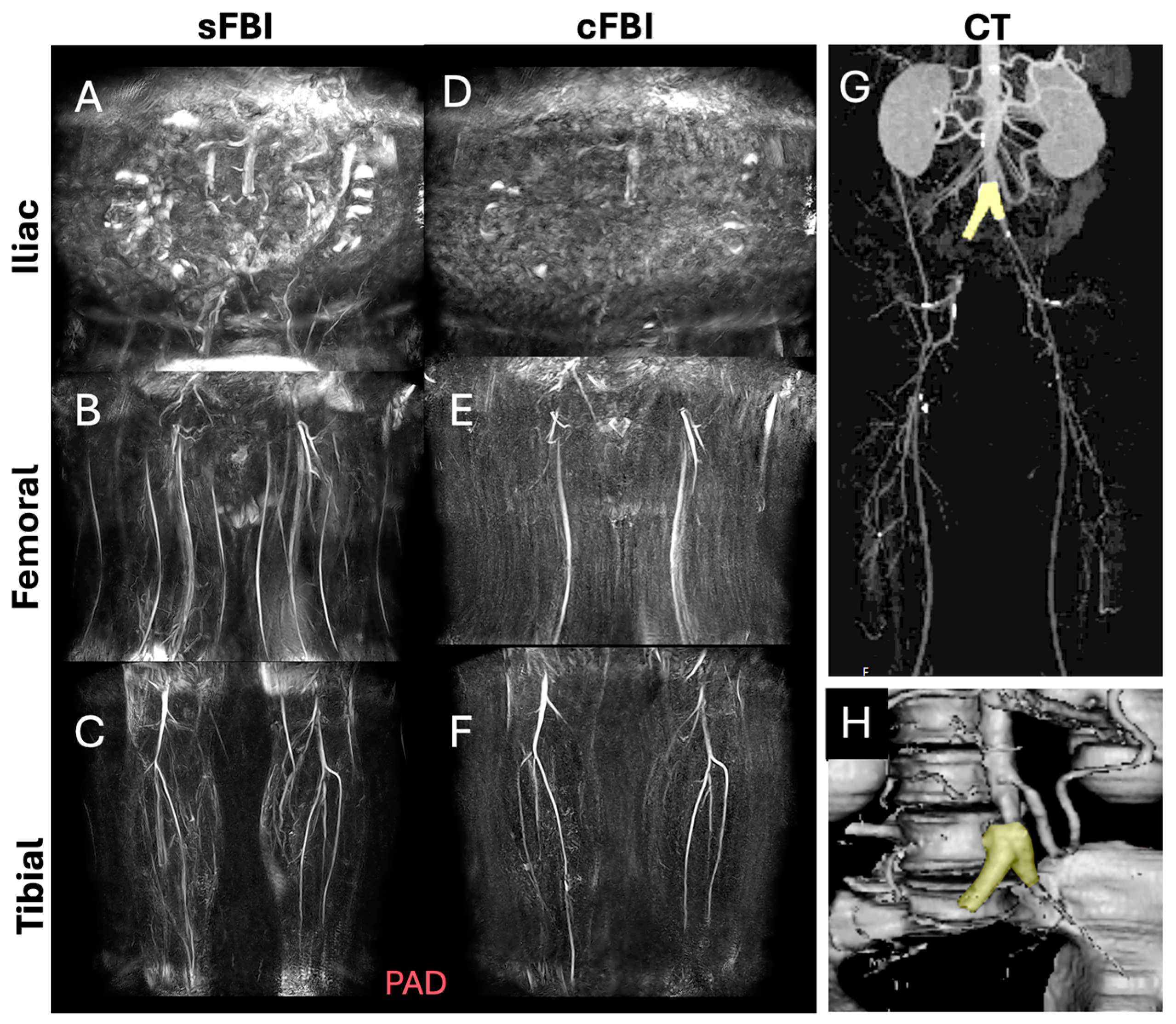
| Subject ID | Age (years) | Sex | HR (bpm) | BMI (kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 | F | 55 | 18.6 |
| 2 | 23 | F | 50 | 29.3 |
| 3 | 51 | M | 64 | 24.5 |
| 4 | 32 | M | 90 | 25.2 |
| 5 | 39 | F | 57 | 20.2 |
| 6 | 32 | M | 64 | 25.4 |
| 7 | 52 | M | 82 | 25.1 |
| 8 | 79 | F | 78 | 25.7 |
| 9 | 50 | F | 61 | 23.2 |
| 10 | 58 | M | 66 | 23.7 |
| 11 (PAD) | 46 | M | 96 | 30.2 |
| 12 (PAD) | 53 | M | 77 | 23 |
| 13 (PAD) | 74 | F | 44 | 21.7 |
| mean | 47.3 | 6 female | 68.0 | 24.3 |
| S.D. | 17.1 | 7 male | 15.6 | 3.2 |
| sFBI [s] | cFBI [s] | |
|---|---|---|
| Iliac | 173.8 (34.1) | 105.9 (30.4) |
| Femoral | 158.4 (38.3) | 95.5 (30.0) |
| Calf | 136.2 (31.0) | 82.7 (22.3) |
| 3 Station Total | 468 (88) | 291 (80) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, W.C.; Mesa, A.; Malis, V.; Kuwatsuru, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Gaffey, A.; Miyazaki, M. Three-Station Non-Contrast MR Angiography of the Lower Extremities Using Standard and Centric Fresh Blood Imaging. Sensors 2025, 25, 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247429
Bae WC, Mesa A, Malis V, Kuwatsuru Y, Nakamura K, Gaffey A, Miyazaki M. Three-Station Non-Contrast MR Angiography of the Lower Extremities Using Standard and Centric Fresh Blood Imaging. Sensors. 2025; 25(24):7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247429
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Won C., Anya Mesa, Vadim Malis, Yoshiki Kuwatsuru, Katsumi Nakamura, Ann Gaffey, and Mitsue Miyazaki. 2025. "Three-Station Non-Contrast MR Angiography of the Lower Extremities Using Standard and Centric Fresh Blood Imaging" Sensors 25, no. 24: 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247429
APA StyleBae, W. C., Mesa, A., Malis, V., Kuwatsuru, Y., Nakamura, K., Gaffey, A., & Miyazaki, M. (2025). Three-Station Non-Contrast MR Angiography of the Lower Extremities Using Standard and Centric Fresh Blood Imaging. Sensors, 25(24), 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247429





