LDLK-U-Mamba: An Efficient and Highly Accurate Method for 3D Rock Pore Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose a 3D rock pore segmentation model, termed LDLK-U-Mamba, which is based on the mamba network for precise and efficient 3D rock pore segmentation.
- (2)
- We propose a Lightweight Dynamic Large Kernel (LDLK) module to capture global contextual information and design an InceptionDSConv3d module to fuse and refine multi-scale features, thereby achieving more accurate segmentation results.
- (3)
- We propose a Basic Residual Depthwise Separable Block (BasicResDWSBlock) module, which employs separable convolutions and the Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) module to reduce model parameters and computational complexity.
- (4)
- The comparative experiments demonstrate LDLK-U-Mamba outperforms the existing 3D segmentation networks.
2. Related Work
2.1. 2D Image Segmentation
2.2. 3D Image Segmentation
2.3. Neural Network Lightweighting
3. Methods
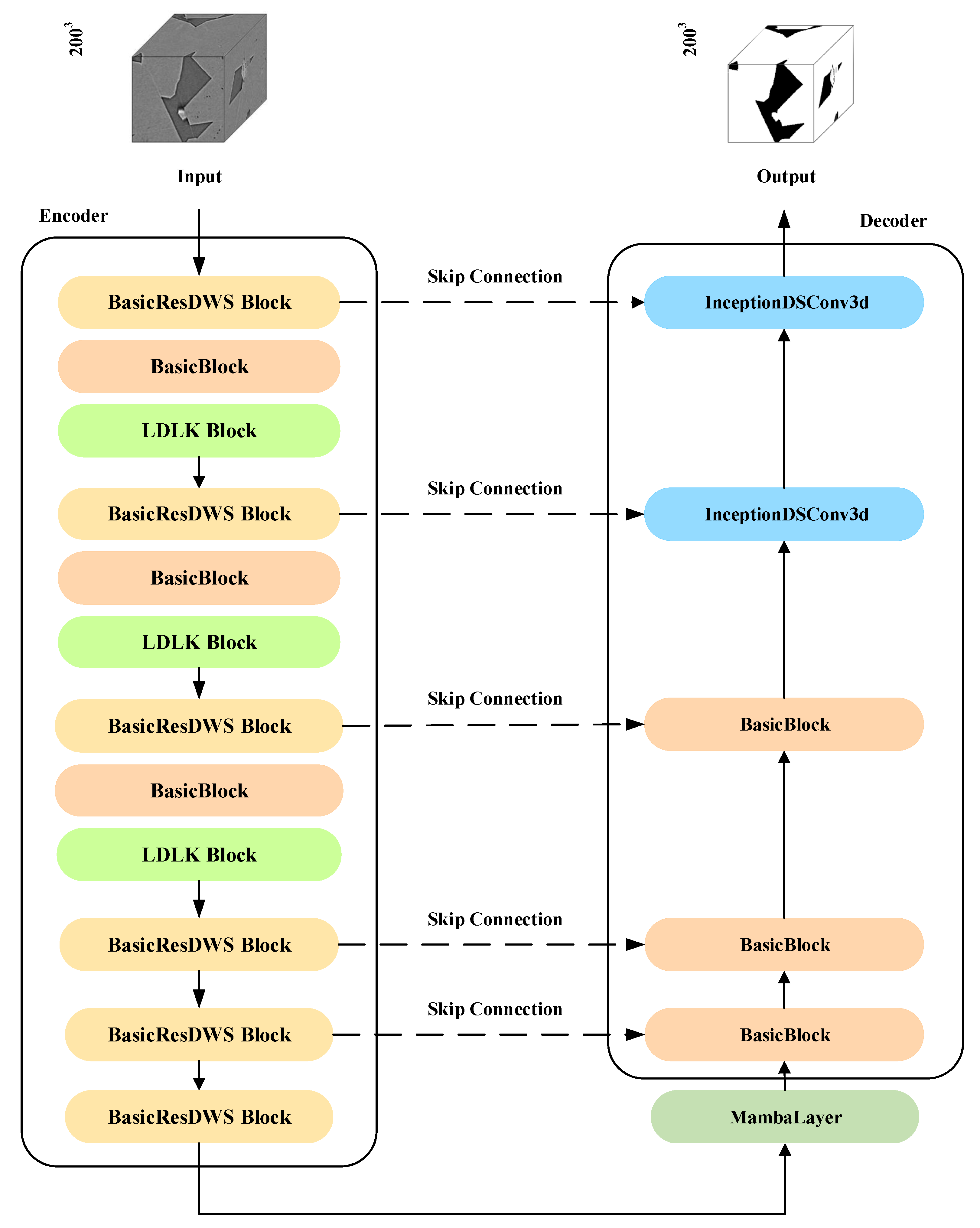
3.1. Overview
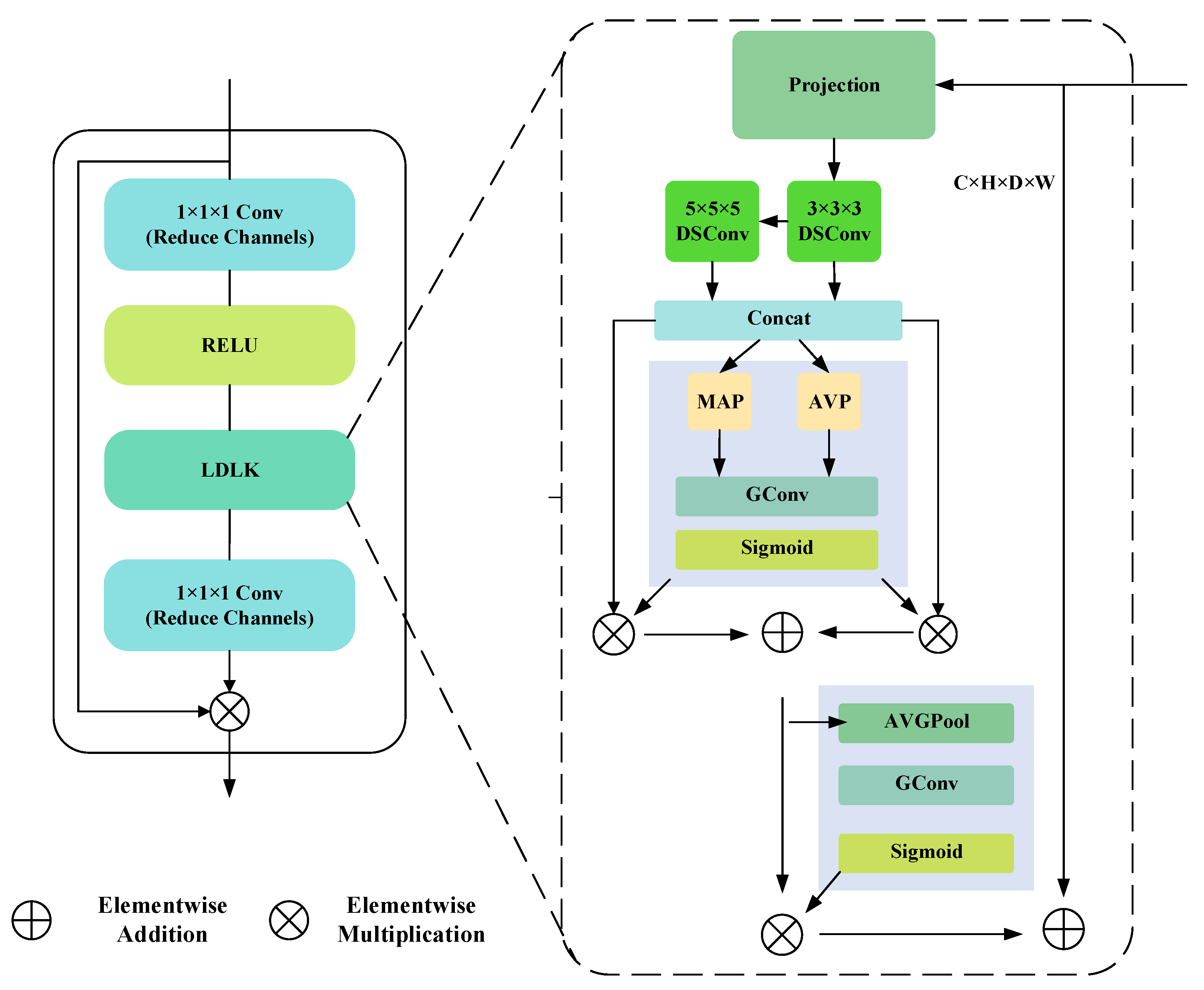
3.2. The LDLK Module
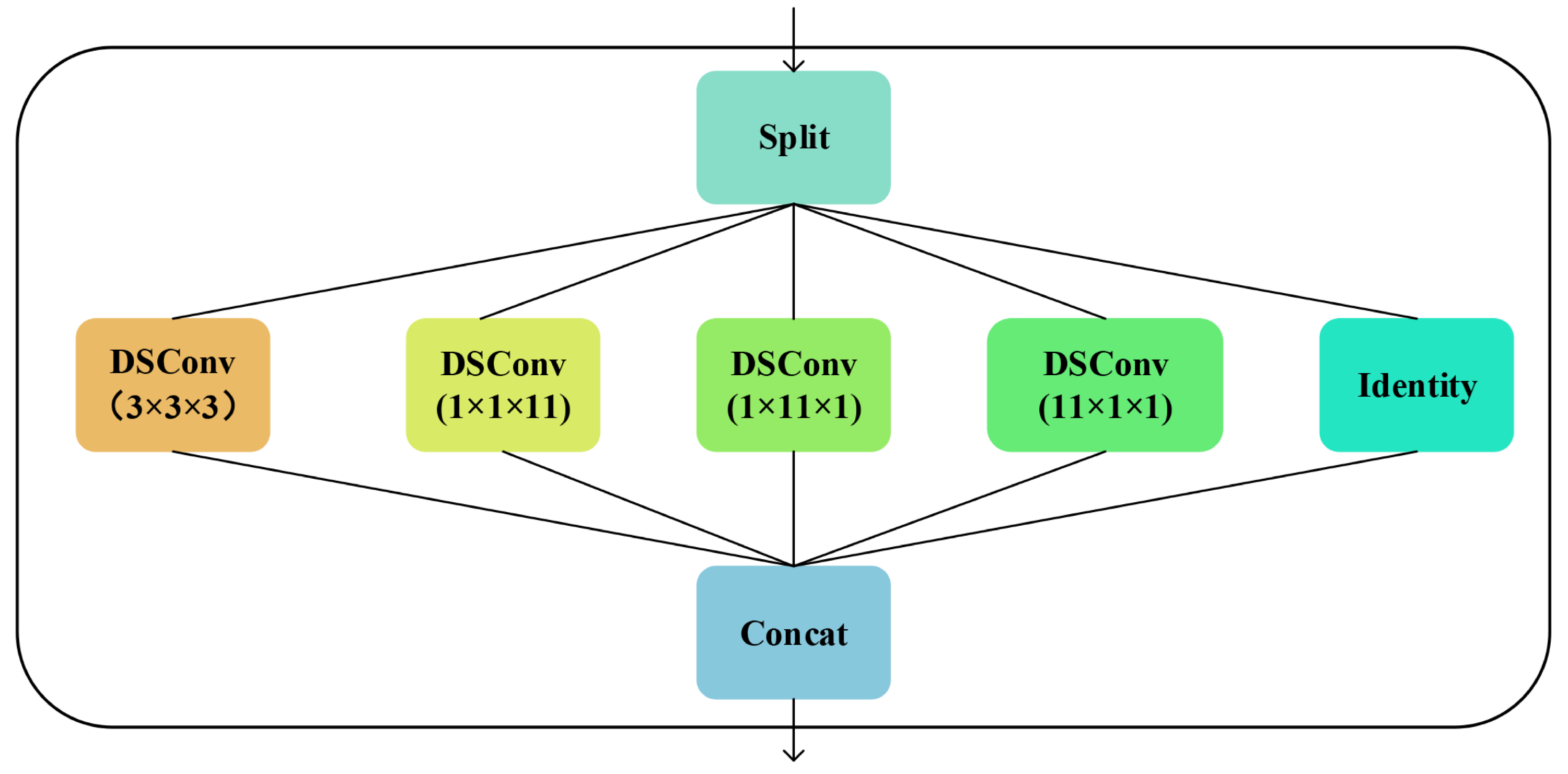
3.3. The InceptionDSConv3d Module
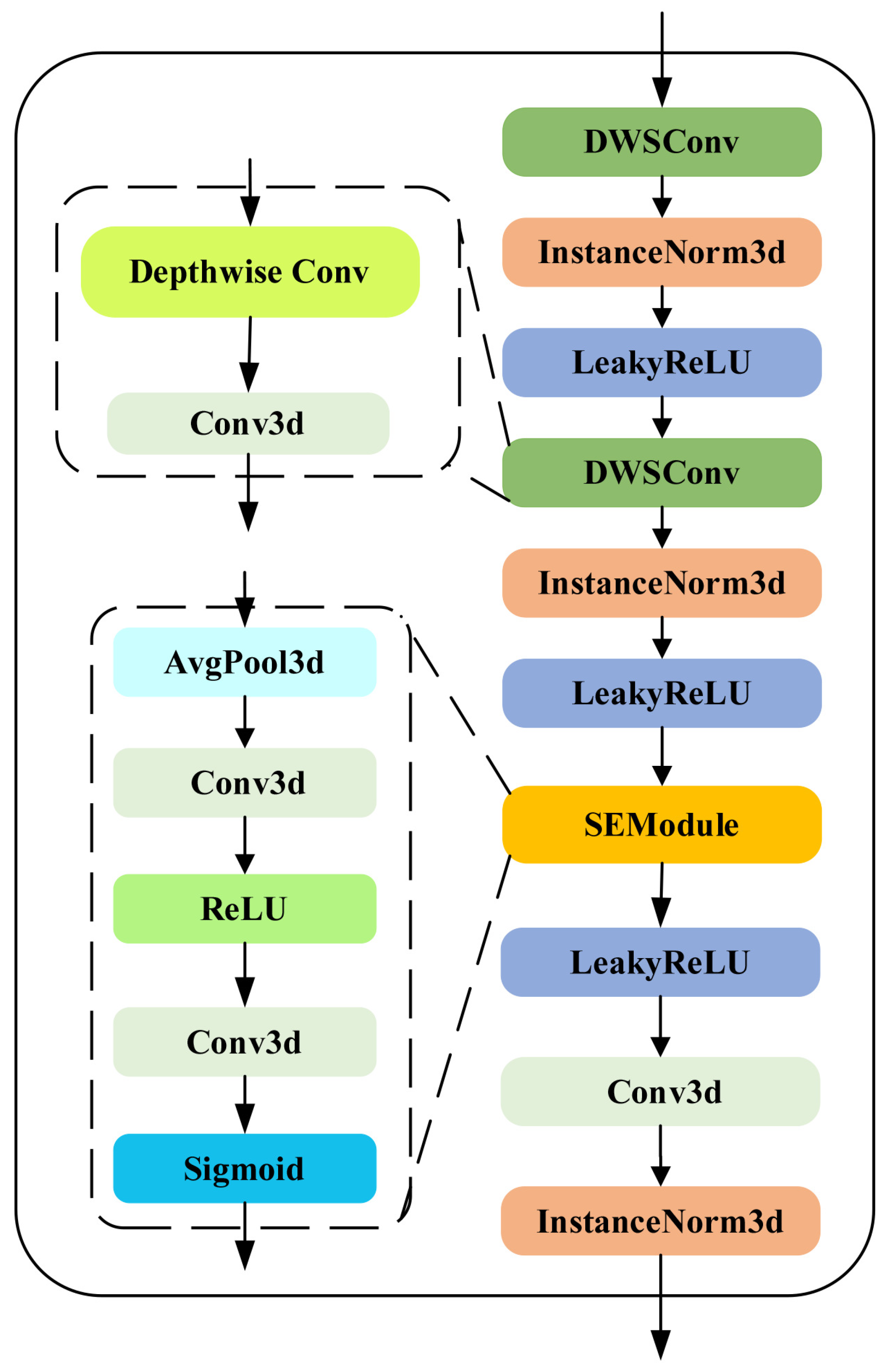
3.4. The BasicResDWSBlock Module
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Data Acquisition and Labeling
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Assessment of Indicators
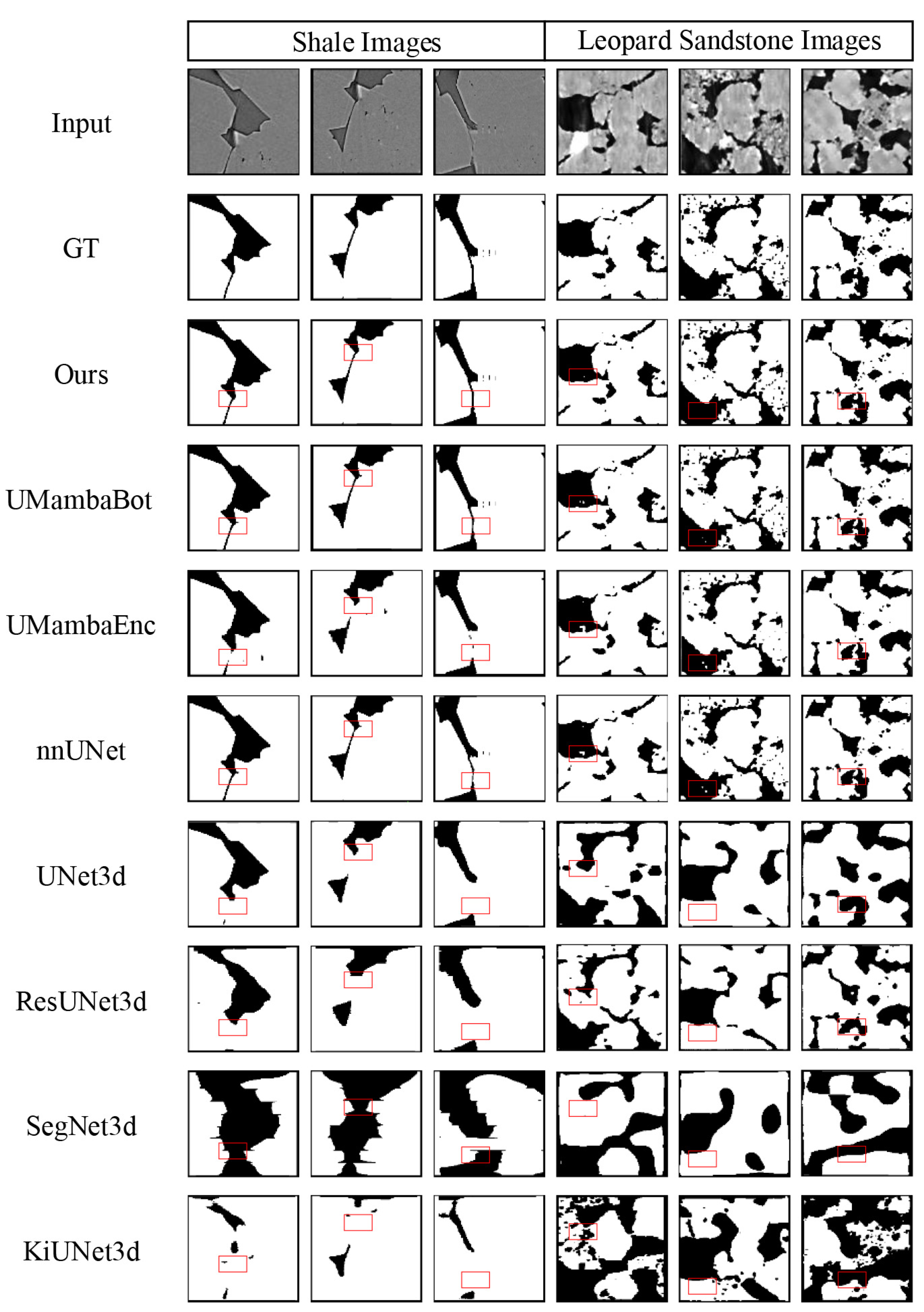
4.4. Comparison of Different Segmentation Networks
4.5. Ablation Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karimpouli, S.; Tahmasebi, P. Segmentation of digital rock images using deep convolutional autoencoder networks. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 126, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeev, I.; Yakimchuk, I.; Safonov, I. An Application of Deep Neural Networks for Segmentation of Microtomographic Images of Rock Samples. Computers 2019, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, D.; Tassara, A.; Abarca, R.; Melnick, D.; Madella, A. Frictional Segmentation of the Chilean Megathrust from a Multivariate Analysis of Geophysical, Geological and Geodetic Data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB020647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, J.; Lu, W.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; Li, L. A Review of Deep Learning-Based Methods for Road Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Advances in Medical Image Segmentation: A Comprehensive Review of Traditional, Deep Learning and Hybrid Approaches. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; Part II 19. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Shabaninejad, M.; Armstrong, R.T.; Mostaghimi, P. Deep neural networks for improving physical accuracy of 2D and 3D multi-mineral segmentation of rock micro-CT images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 104, 107185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y. Dense U-net based on patch-based learning for retinal vessel segmentation. Entropy 2019, 21, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Chen, H.; Cui, T.; Li, H. SFMRNet: Specific Feature Fusion and Multibranch Feature Refinement Network for Land Use Classification. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. IEEE J. 2024, 17, 16206–16221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S. A Separate 3D-SegNet Based on Priority Queue for Brain Tumor Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC), Hangzhou, China, 22–23 August 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Valanarasu, J.M.J.; Sindagi, V.A.; Hacihaliloglu, I.; Patel, V.M. KiU-Net: Overcomplete Convolutional Architectures for Biomedical Image and Volumetric Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 41, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-Net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision, Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Yang, D.; Roth, H.; Xu, D. UNETR: Transformers for 3D Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Virtual, 3–8 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Li, F.; Wang, B. U-mamba: Enhancing long-range dependency for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.04722. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; He, X.; Kwak, H.; Gao, J.; Sun, S.; Yan, B. Enhancing rock image segmentation in digital rock physics: A fusion of generative ai and state-of-the-art neural networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.06079. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, N.; Kang, J.; Xiong, G. Construction of pore structure and lithology of digital rock physics based on laboratory experiments. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2021, 11, 2113–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Xiang, Z. A method of blasted rock image segmentation based on improved watershed algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, L.; Soille, P. Watersheds in digital spaces: An efficient algorithm based on immersion simulations. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1991, 13, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, M.; Jacob, A.; Sadeghnejad, S.; Cappuccio, F.; Arnold, P.; Frank, S.; Enzmann, F.; Kersten, M. Benchmarking conventional and machine learning segmentation techniques for digital rock physics analysis of fractured rocks. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunair, H.; Hamza, A.B. Masked supervised learning for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.00923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D.; Shabaninejad, M.; Armstrong, R.T.; Mostaghimi, P. Physical Accuracy of Deep Neural Networks for 2D and 3D Multi- Mineral Segmentation of Rock micro-CT Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.05322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 27 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Ding, M.; Li, J.; Zha, S. TransBTS: Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Transformer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Qiu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Marcus, D.S.; Sotiras, A. D-net: Dynamic large kernel with dynamic feature fusion for volumetric medical image segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, W.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Luo, P. Differentiable learning-to-group channels via groupable convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3542–3551. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Yun, S.; Heo, B.; Yoo, Y. Rethinking channel dimensions for efficient model design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 732–741. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Zhou, P.; Yan, S.; Wang, X. InceptionNeXt: When Inception Meets ConvNeXt. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, B.C.; Torralba, A.; Murphy, K.P.; Freeman, W.T. LabelMe: A Database and Web-Based Tool for Image Annotation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 77, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, V.G.; Silva, L.R.D.D.; Carvalho, B.M.; Lucena, L.R.F.D.; Vieira, M.M. Deep Learning-Based Pore Segmentation of Thin Rock Sections for Aquifer Characterization Using Color Space Reduction. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP), Osijek, Croatia, 5–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Purswani, P.; Karpyn, Z.T.; Enab, K.; Xue, Y.; Huang, X. Evaluation of image segmentation techniques for image-based rock property estimation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
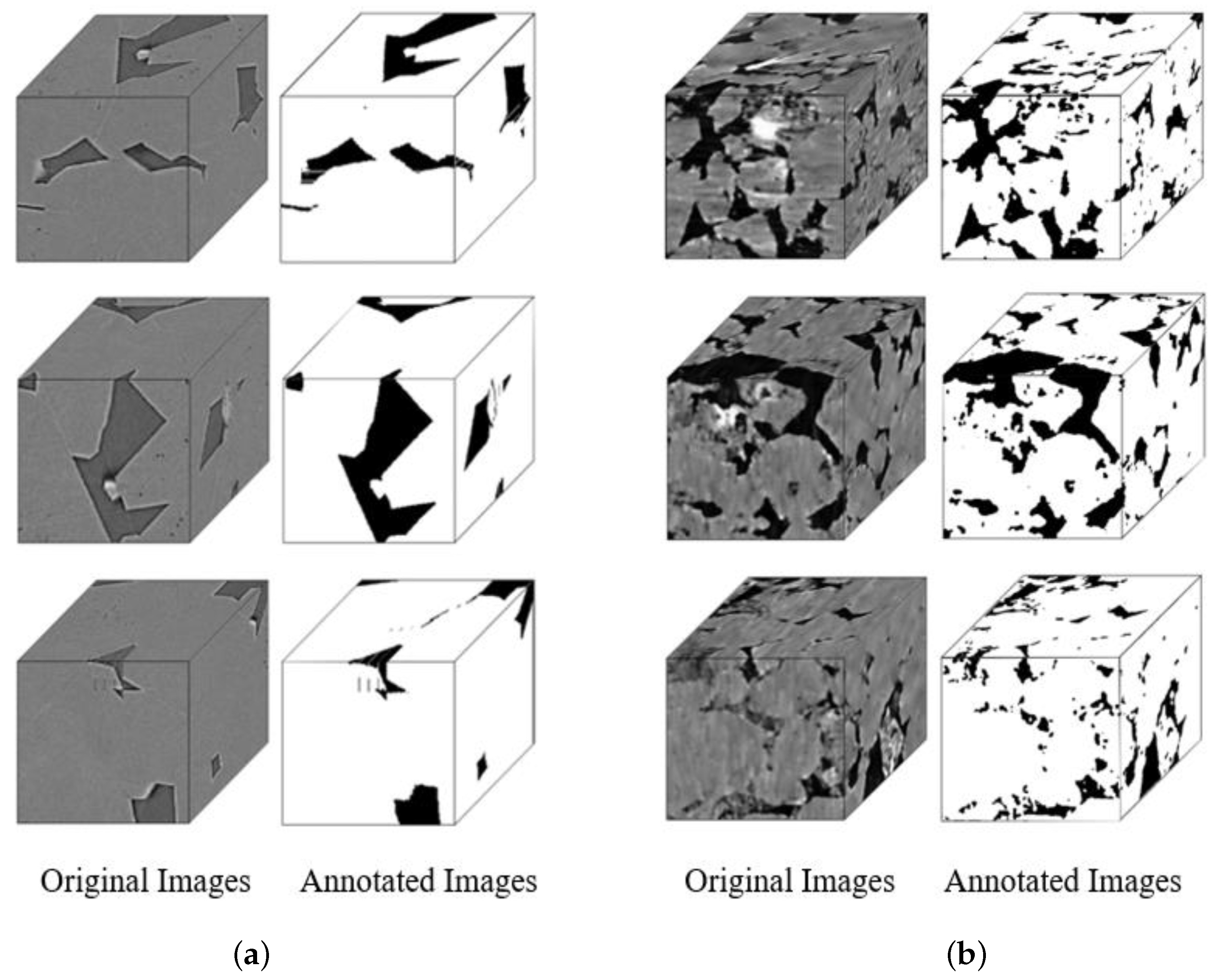
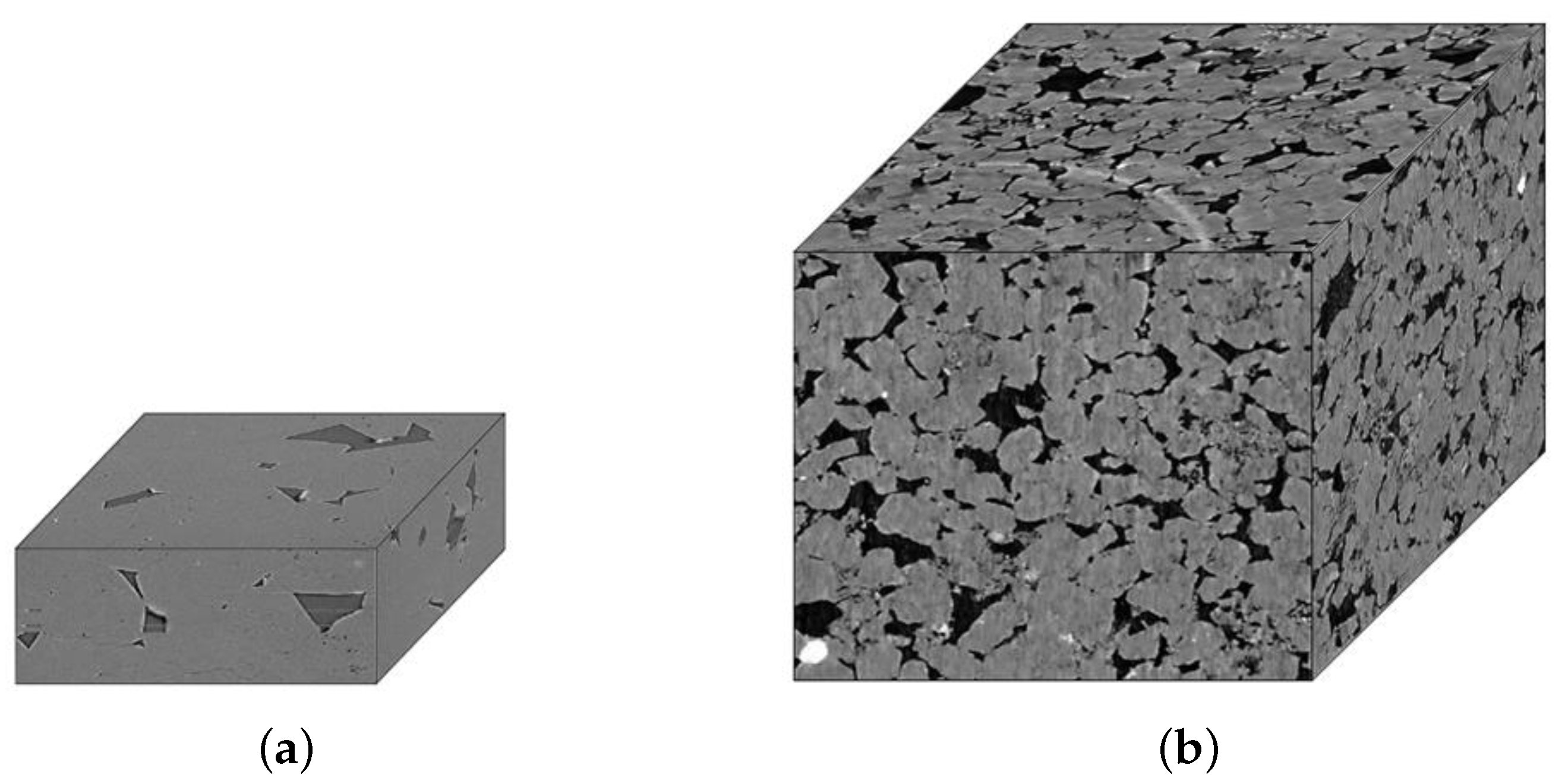

| Dataset | Resolution | Train | Validation | Test | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shale Images | 200 × 120 × 120 | 683 | 171 | 170 | 1024 |
| Leopard Sandstone Images | 250 × 250 × 250 | 144 | 36 | 36 | 216 |
| Category | Configuration |
|---|---|
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 24 G |
| System environment | Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Torch version | 2.6.0 + cu118 |
| Programming language | Python 3.10.16 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) ↑ | Dice (%) ↑ | IOU (%) ↑ | Params (M) ↓ | FLOPs (G) ↓ | Time (ms) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D U-Net [6] | 98.13 | 82.74 | 70.74 | 2.32 | 117.98 | 82.5 |
| 3D U-ResNet [24] | 94.84 | 35.12 | 21.37 | 9.49 | 1699.84 | 1180.3 |
| 3D SegNet [12] | 73.40 | 26.10 | 15.08 | 2.33 | 116.52 | 76.8 |
| 3D KiUNet [13] | 94.57 | 55.90 | 39.09 | 2.33 | 130.17 | 89.2 |
| nnUNet [14] | 99.32 | 93.32 | 87.51 | 31.19 | 534.03 | 365.7 |
| U-Mamba-Enc [17] | 98.79 | 87.58 | 78.07 | 42.75 | 990.65 | 620.4 |
| U-Mamba-Bot [17] | 99.34 | 93.50 | 87.84 | 42.12 | 973.91 | 598.1 |
| Ours | 99.46 | 94.67 | 89.90 | 14.03 | 426.64 | 295.3 |
| Method | Accuracy (%) ↑ | Dice (%) ↑ | IOU (%) ↑ | Params (M) ↓ | FLOPs (G) ↓ | Time (ms) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D U-Net [6] | 88.77 | 92.90 | 86.74 | 2.32 | 117.98 | 83.2 |
| 3D U-ResNet [24] | 86.32 | 91.36 | 84.10 | 9.49 | 1660.00 | 1165.8 |
| 3D SegNet [12] | 65.44 | 75.55 | 60.74 | 2.33 | 116.54 | 77.4 |
| 3D KiUNet [13] | 57.72 | 67.08 | 50.54 | 2.33 | 178.73 | 91.6 |
| nnUNet [14] | 98.04 | 98.80 | 97.66 | 31.19 | 534.03 | 368.2 |
| U-Mamba-Enc [17] | 81.13 | 89.55 | 81.13 | 42.75 | 990.65 | 625.1 |
| U-Mamba-Bot [17] | 98.22 | 98.90 | 97.89 | 42.12 | 973.91 | 602.5 |
| Ours | 99.38 | 99.62 | 99.25 | 13.97 | 426.64 | 298.8 |
| A | B | C | Accuracy (%) ↑ | Dice (%) ↑ | IOU (%) ↑ | Params (M) ↓ | FLOPs (G) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 99.34 | 93.50 | 87.84 | 42.12 | 973.91 | |||
| ✓ | 99.32 | 93.28 | 87.45 | 13.96 | 425.28 | ||
| ✓ | 99.43 | 94.39 | 89.40 | 42.12 | 975.00 | ||
| ✓ | 99.42 | 94.25 | 89.16 | 42.12 | 974.18 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 99.46 | 94.67 | 89.90 | 14.03 | 426.64 |
| A | B | C | Accuracy (%) ↑ | Dice (%) ↑ | IOU (%) ↑ | Params (M) ↓ | FLOPs (G) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 98.22 | 98.90 | 97.89 | 42.12 | 973.91 | |||
| ✓ | 97.27 | 98.31 | 96.76 | 13.96 | 425.28 | ||
| ✓ | 99.37 | 99.61 | 99.23 | 42.12 | 974.78 | ||
| ✓ | 99.34 | 99.60 | 99.20 | 42.12 | 974.18 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 99.38 | 99.62 | 99.25 | 13.97 | 426.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Li, P.; Kong, Y. LDLK-U-Mamba: An Efficient and Highly Accurate Method for 3D Rock Pore Segmentation. Sensors 2025, 25, 7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227039
Chen G, Li H, Liu C, Li P, Kong Y. LDLK-U-Mamba: An Efficient and Highly Accurate Method for 3D Rock Pore Segmentation. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227039
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guojun, Huihui Li, Chang Liu, Pengxia Li, and Yunyi Kong. 2025. "LDLK-U-Mamba: An Efficient and Highly Accurate Method for 3D Rock Pore Segmentation" Sensors 25, no. 22: 7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227039
APA StyleChen, G., Li, H., Liu, C., Li, P., & Kong, Y. (2025). LDLK-U-Mamba: An Efficient and Highly Accurate Method for 3D Rock Pore Segmentation. Sensors, 25(22), 7039. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227039






