Environmental Context Indicator for Evaluating Quality of GNSS Observation Environment Using Android Smartphone
Abstract
1. Introduction
Key Contributions
- A raw-data-based, interpretable, and simple framework capable of real-time monitoring of both observation environments and smartphone GNSS quality.
- Utilization of key indicators directly associated with positioning performance—including C/N0, PDOP, and the number of visible satellites—for straightforward integration with real-time operation and positioning algorithms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment
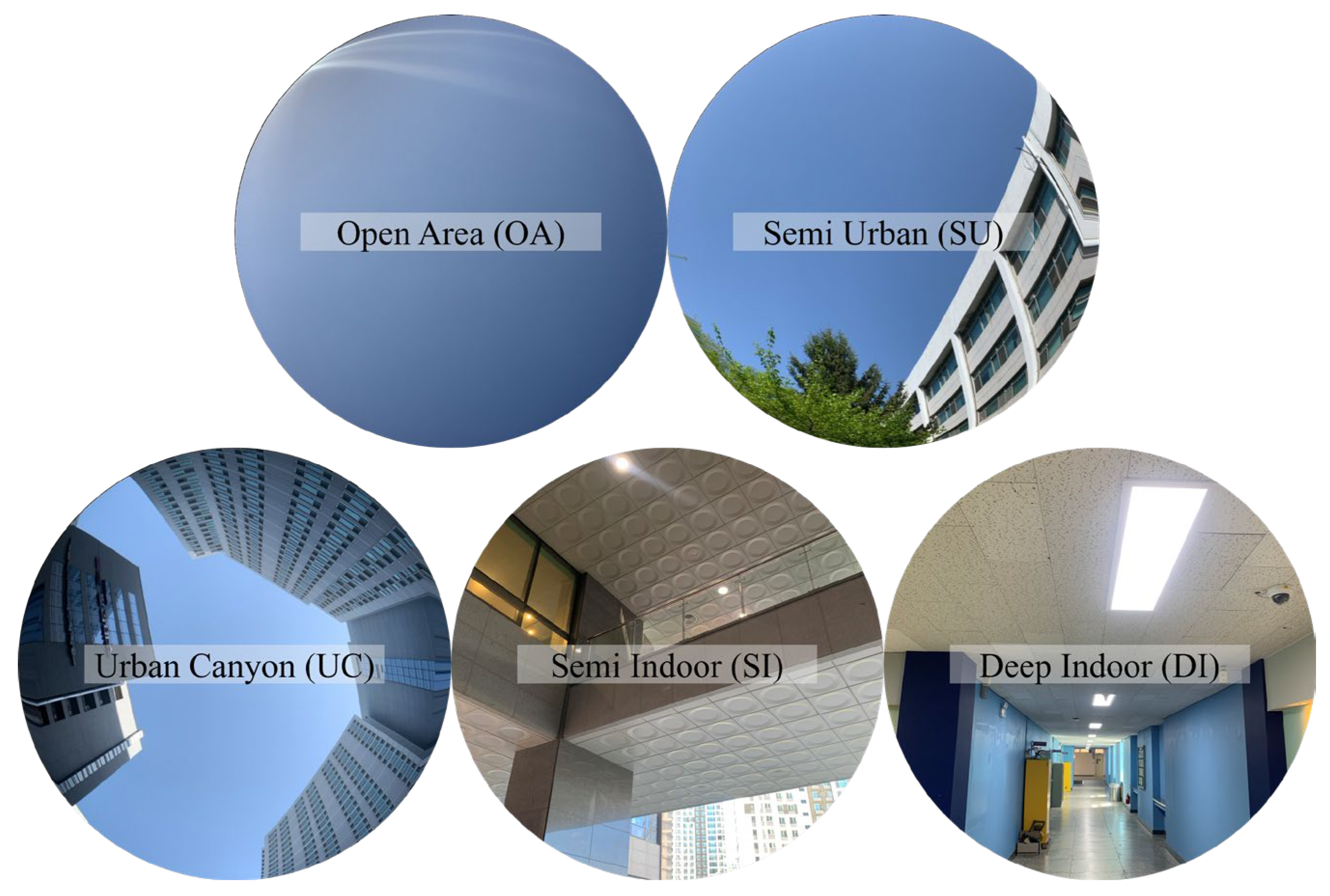
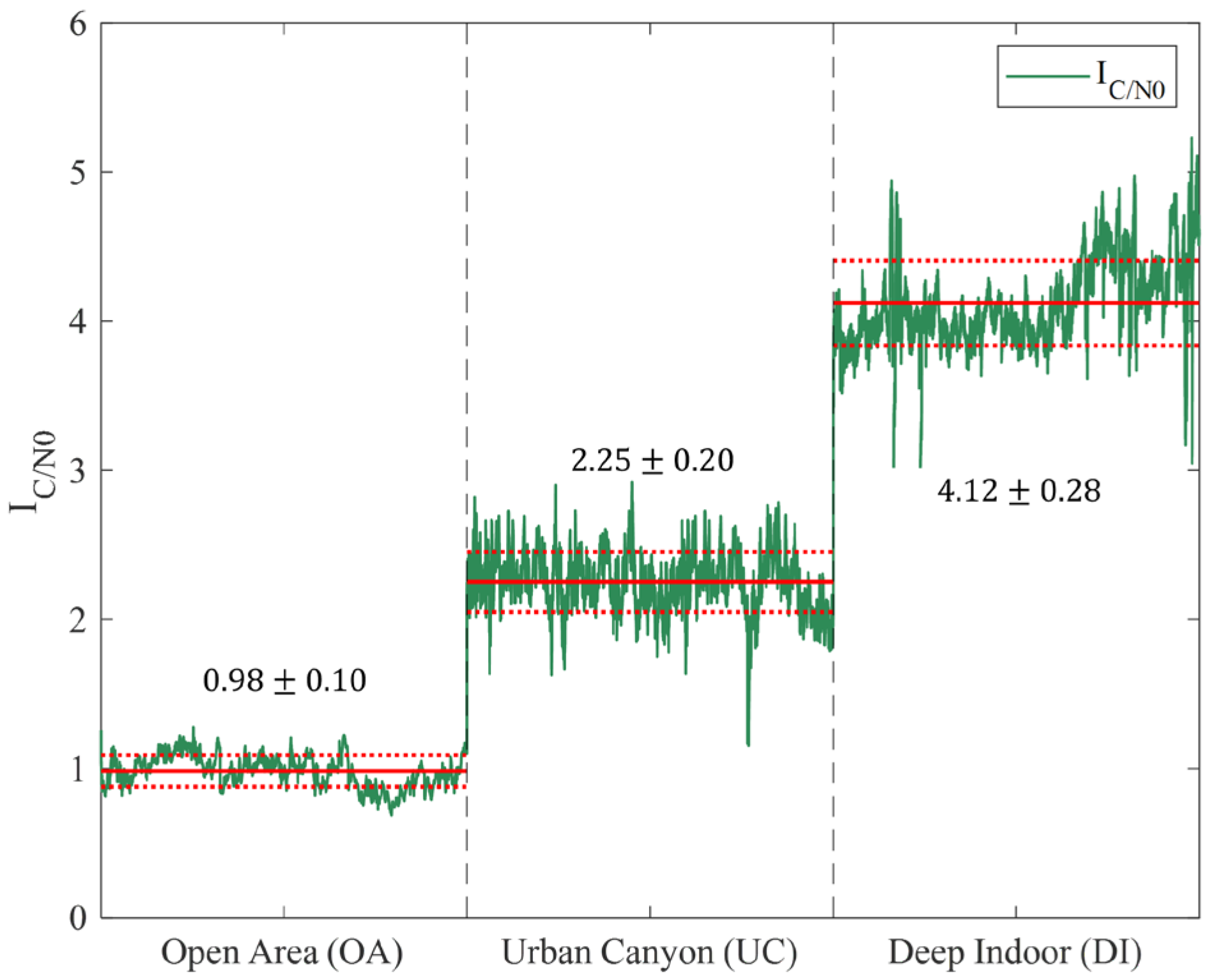
2.2. Definition of Observation Environment
2.3. Process of ECI Calculation
2.4. Generation of ECI-F
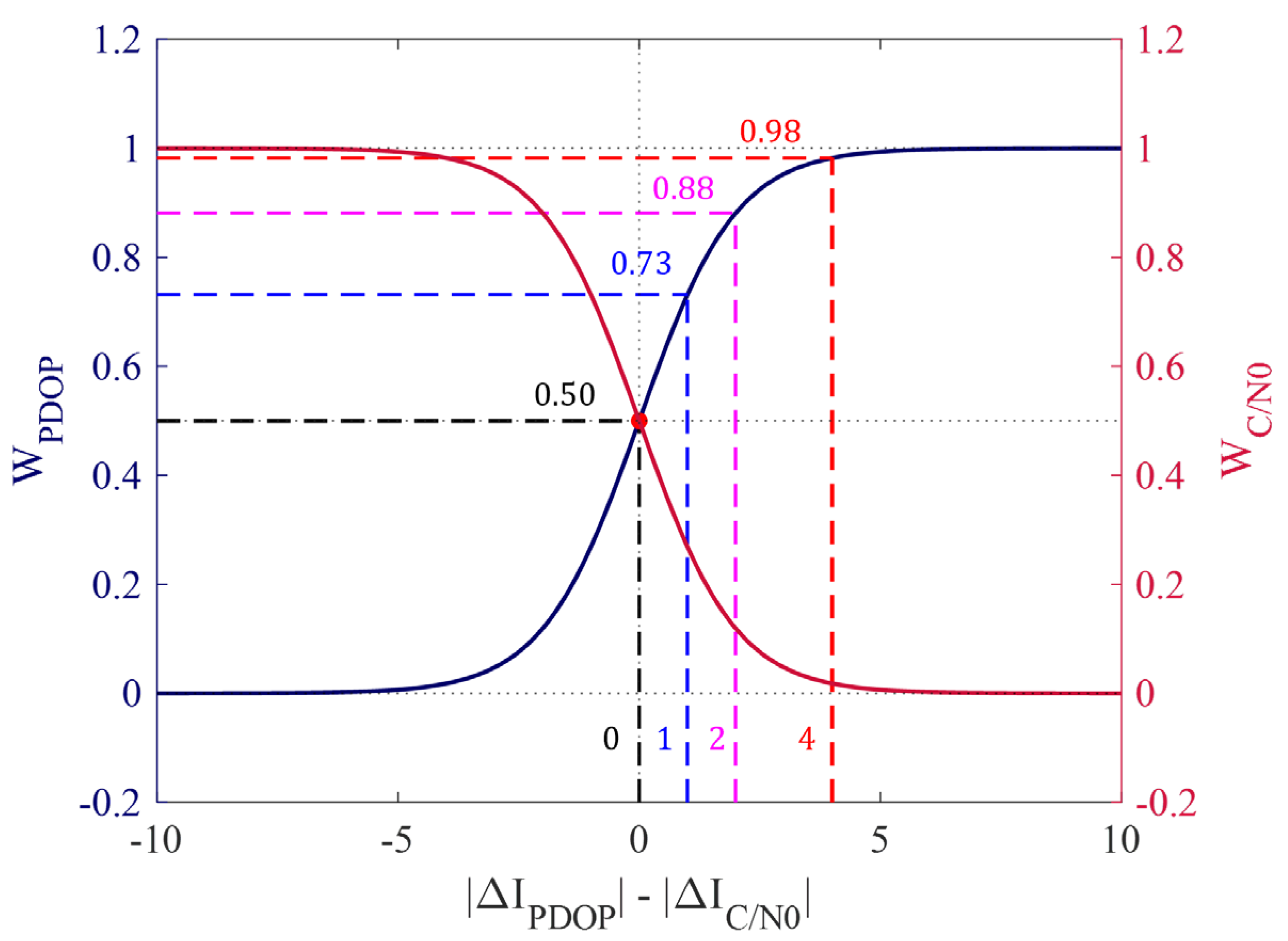
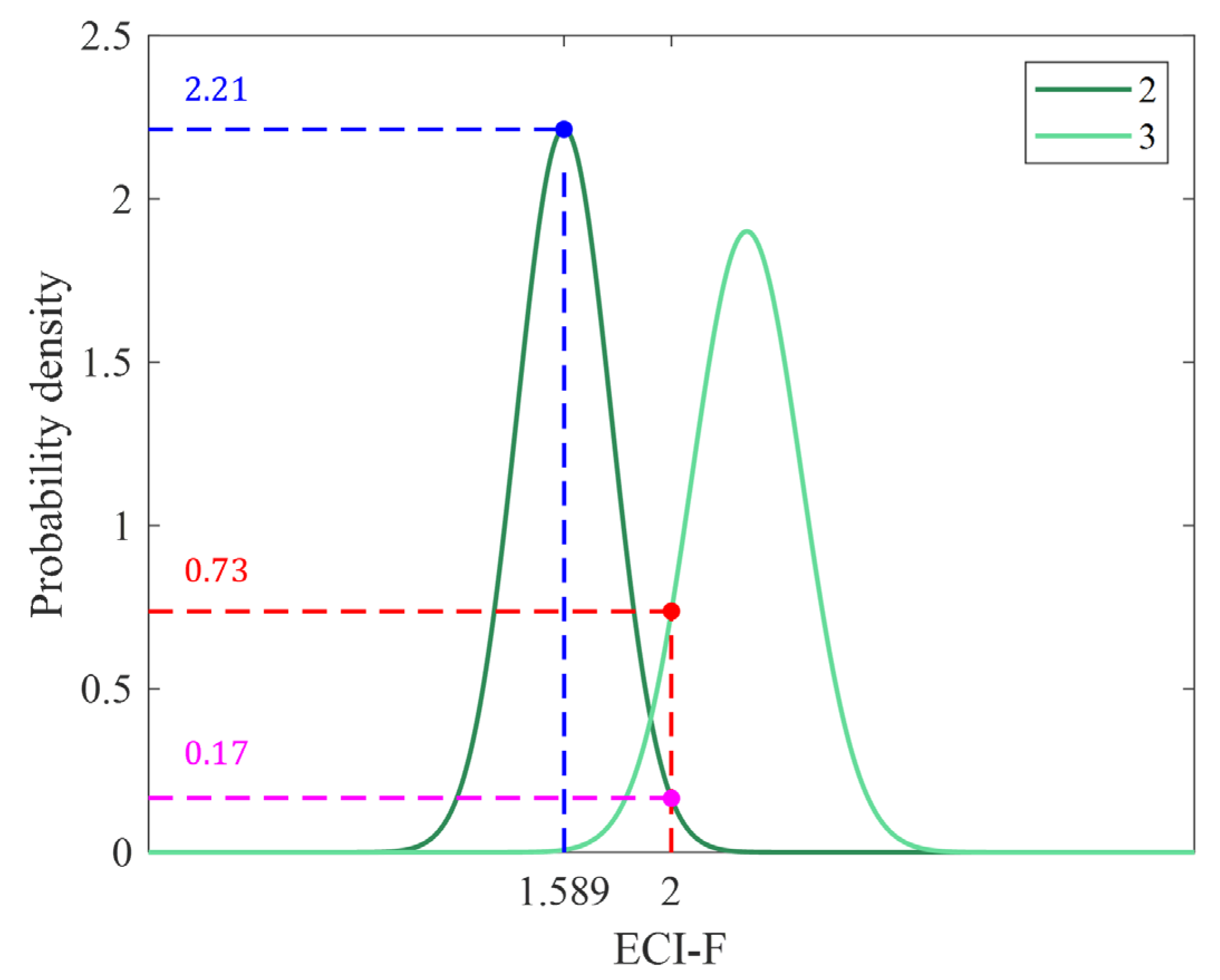
2.5. Conversion to ECI-I
2.6. Calculation of ECI-R
3. Results
3.1. Summary of Test Scenario
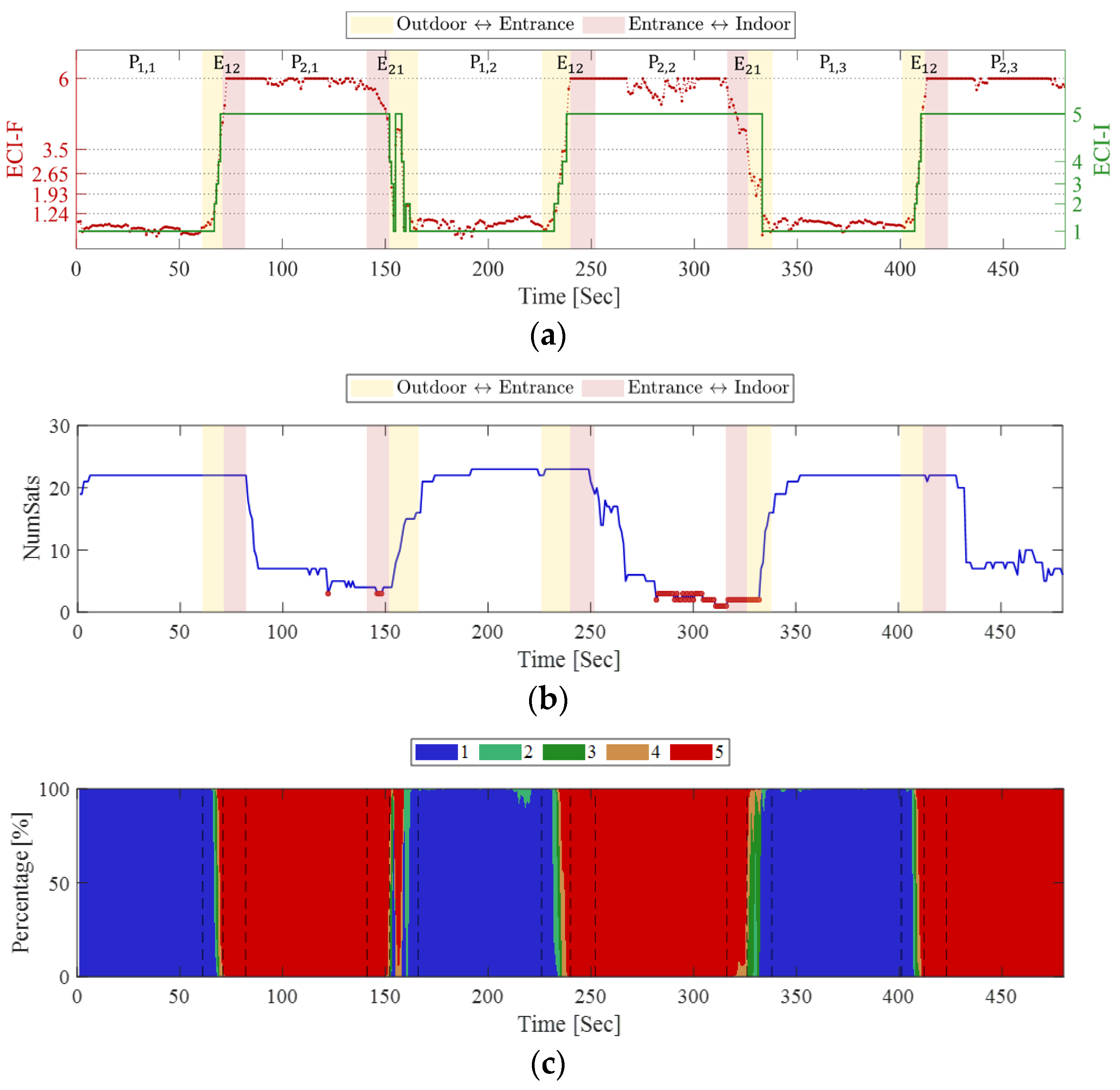
3.2. Indoor-Outdoor Transition Test
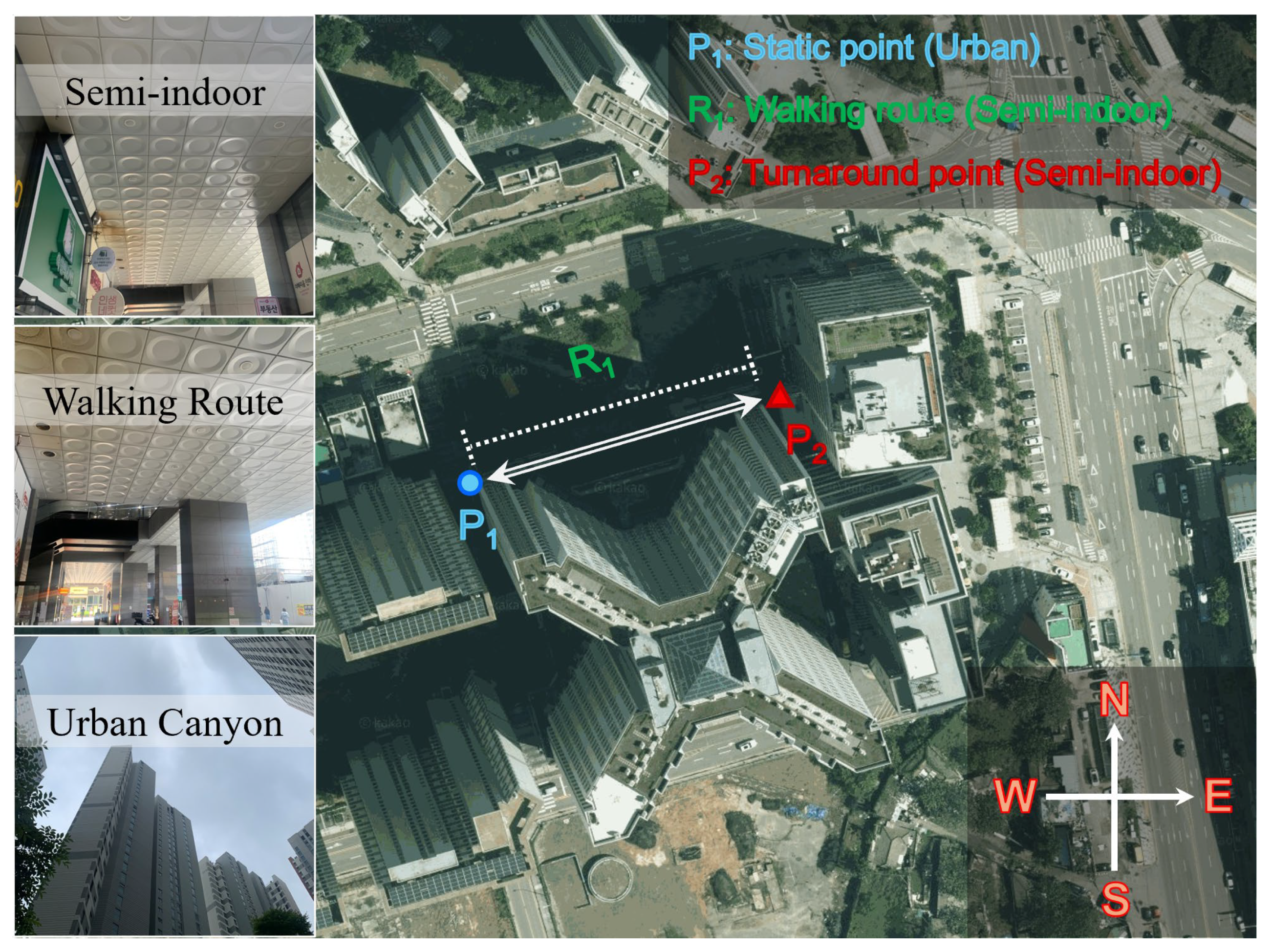
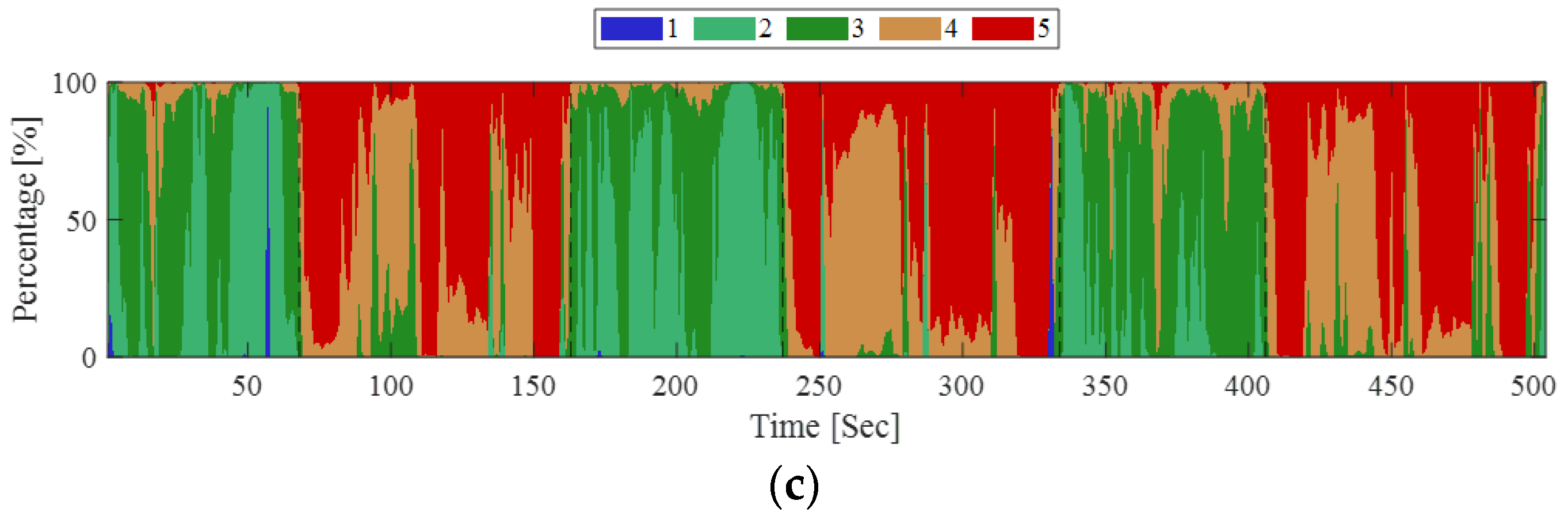
3.3. Static-Kinematic Test in Urban and Semi-Indoor Environment
3.4. Kinematic Test in Open Area and Urban Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| LBS | Location-Based Services |
| ECI | Environmental Context Indicator |
| C/N0 | Carrier-to-Noise Density Ratio |
| PDOP | Position Dilution of Precision |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| HMM | Hidden Markov Model |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long-Short Term Memory |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| OA | Open Area |
| SU | Semi Urban |
| UC | Urban Canyon |
| SI | Semi Indoor |
| DI | Deep Indoor |
| ECI-F | Real-valued ECI |
| ECI-I | Integer-valued ECI |
| ECI-R | Probability Density Ratio |
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
References
- Using GNSS Raw Measurements on Android Devices. Available online: https://galileognss.eu/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Using-GNSS-Raw-Measurements-on-Android-devices.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Huang, H.; Gartner, G.; Krisp, J.M.; Raubal, M.; Van De Weghe, N. Location based services: Ongoing evolution and research agenda. J. Locat. Based Serv. 2018, 12, 63–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisnath, S.; Aggrey, J. Current Limitations and Prospects for Smartphone GNSS Precise Positioning. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 26–29 January 2024; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cai, C.; Xu, Z. A Combined Elevation Angle and C/N0 Weighting Method for GNSS PPP on Xiaomi MI8 Smartphones. Sensors 2022, 22, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, P.; Bisnath, S. Enhancing smartphone precise point positioning to sub-meter accuracy in suburban environments: A new stochastic model and outlier diagnosis. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-D.; Yoon, W.-J.; Lee, J.-S. Reduction of Multipath Effect in GNSS Positioning by Applying Pseudorange Acceleration as Weight. Sensors 2024, 24, 6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-I.; Park, K.-D. Satellite Positioning Accuracy Improvement in Urban Canyons Through a New Weight Model Utilizing GPS Signal Strength Variability. Sensors 2025, 25, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Mi, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, B.; Jiang, D.; Liu, W. A Robust Adaptive Filtering Algorithm for GNSS Single-Frequency RTK of Smartphone. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chang, Q.; Li, Q.; Shi, Z.; Chen, W. Indoor-Outdoor Detection Using a Smart Phone Sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, Q.; Adeel, M.; Qian, J.; Jin, X.; Ying, R. Urban environment recognition based on the GNSS signal characteristics. J. Inst. Navig. 2019, 66, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wu, C. Environment scenario identification based on GNSS recordings for agricultural tractors. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 195, 106829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Groves, P.D. Environmental Context Detection for Adaptive Navigation using GNSS Measurements from a Smartphone. Navigation 2018, 65, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Groves, P.D. Improving environment detection by behavior association for context-adaptive navigation. Navigation 2020, 67, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Groves, P.D. Context Detection for Advanced Self-Aware Navigation using Smartphone Sensors. In Proceedings of the International Navigation Conference, Brighton, UK, 27–30 November 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Luo, K.; Tao, X.; Zhang, X. Deep Learning Based Vehicle-Mounted Environmental Context Awareness via GNSS Signal. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 9498–9511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Chen, W.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X. Constructing Context-Aware GNSS Stochastic Model for Code-Based Resilient Positioning in Urban Environment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 10, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, P.; Zhang, G.; Hsu, L.-T. GNSS-based Environment Retrieval: A Deep Learning Approach for Fine-grained Environment Perception. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Pan, S.; Gao, W.; Yu, B.; Gan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q. Recurrent neural network based scenario recognition with Multi-constellation GNSS measurements on a smartphone. Measurement 2020, 153, 107420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Luo, J. No Perfect Outdoors: Towards a Deep Profiling of GNSS-Based Location Contexts. Future Internet 2021, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yao, Z.; Cao, X.; Cai, X.; Sheng, M. Enhancing Navigation Adaptability for Ground Vehicles: Fine-Grained Urban Environment Recognition Based on GNSS Measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 8509412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Qian, C.; Huang, W.; Yang, Z. A Deep-Learning Based GNSS Scene Recognition Method for Detailed Urban Static Positioning Task via Low-Cost Receivers. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhai, C.; Li, F.; Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Feng, Y. Deep-Learning-Based Scenario Recognition With GNSS Measurements on Smartphones. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 23, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ahmed, A.; Shah, M.A.; Katyara, S.; Staszewski, L.; Magsi, H. On Mitigating the Effects of Multipath on GNSS Using Environmental Context Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Sieradzki, R.; Baryla, R. Signal characterization and assessment of code GNSS positioning with low-power consumption smartphones. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Fortunato, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Odolinski, R. An analysis of multi-GNSS observations tracked by recent Android smartphones and smartphone-only relative positioning results. Measurement 2021, 175, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, T.E.; Murrian, M.; van Diggelen, F.; Podshivalov, S.; Pesyna, K.M. On the feasibility of cm-accurate positioning via a smartphone’s antenna and GNSS chip. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Savannah, GA, USA, 11–14 April 2016; pp. 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, X.; Zhu, F.; Shi, X.; Wang, F. Quality assessment of GNSS observations from an Android N smartphone and positioning performance analysis using time-differenced filtering approach. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, F.; Sang, J.; Lin, X.; Gong, X.; Zhang, W. Characteristics Analysis of Raw Multi-GNSS Measurement from Xiaomi Mi 8 and Positioning Performance Improvement with L5/E5 Frequency in an Urban Environment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Li, R.; Liu, A. Real-time GNSS precise point positioning with smartphones for vehicle navigation. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Hou, Z.; Meng, Y.; Cai, M.; Chan, Y. Characterization and mitigation of urban GNSS multipath effects on smartphones. Measurement 2023, 223, 113766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Groves, P.D.; Ziebart, M.K. Smartphone Shadow Matching for Better Cross-street GNSS Positioning in Urban Environments. J. Navig. 2014, 68, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrisano, A.; Gaglione, S. Smartphone GNSS Performance in an Urban Scenario with RAIM Application. Sensors 2022, 22, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaštík, J.; Olcina, J.H.; Saloň, Š.; Tunák, D. Pixel 5 Versus Pixel 9 Pro XL—Are Android Devices Evolving Towards Better GNSS Performance? Sensors 2025, 25, 4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Enge, P. Global Positioning System: Signals, Measurements, and Performance, 2nd ed.; Ganga-Jamuna Press: Lincoln, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Wen, Y.; Cao, X. Realistic stochastic modeling considering the PDOP and its application in real-time GNSS point positioning under challenging environments. Measurement 2022, 197, 111342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Ning, B.; Ke, Q.; Zhang, C. A Fast Indoor/Outdoor Transition Detection Algorithm Based on Machine Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Category | Specification |
|---|---|
| Device | Samsung Galaxy S21+ (Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suwon, Republic of Korea) |
| OS version | Android 14 |
| SoC/CPU | Exynos 2100 (1 × Cortex-X1 ~2.9 GHz + 3 × A78 ~2.8 GHz + 4 × A55 ~2.2 GHz, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suwon, Republic of Korea) |
| GPU/RAM | Mali-G78 MP14, 8 GB RAM |
| GNSS constellations | GPS, Galileo, BeiDou, GLONASS, QZSS |
| GNSS signals | L1/E1/B1/G1 + L5/E5a |
| Logging app/rate | Custom-build logger/1 Hz |
| Duty cycling | Off |
| Environment | Description | Representative C/N0 Range (dB-Hz) | Satellite Visibility (Multi-Constellation) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open area | Outdoor area with sparse obstacles | 35–45 | 18–25 | [4,9,28,29] |
| Semi urban | Densely built-up area with low-rise buildings | 20–40 | 12–20 | [30,31] |
| Urban canyon | Densely built-up area with high-rise buildings | 20–35 | 10–18 | [12,31,32] |
| Semi indoor | Partially covered outdoor spaces/Partially opened indoor space | <32 | 8–15 | [33] |
| Deep indoor | Indoor area with limited visibility | <25 | 0–8 | [9,12] |
| Scenario | Characteristics | Data Type | Walking Speed (m/s) | Duration (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indoor-outdoor transition | Abrupt changes in satellite visibility | static, kinematic | 0.50 | 480 |
| Urban, semi-indoor walking | severe signal degradation | static, kinematic | 0.65 | 504 |
| Open area, urban walking | gradual signal degradation | Kinematic | 1.30 | 525 |
| Metrics | P1,1 | P1,2 | P1,3 | P2,1 | P2,2 | P2,3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean of ECI-F | 0.78 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 6.00 | 5.98 | 6.00 |
| Std. of ECI-F | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 |
| Mode of ECI-I | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 1 (%) | 99.93 | 93.30 | 98.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 2 (%) | 0.07 | 6.70 | 1.80 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 3 (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 4 (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 5 (%) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 99.85 | 99.87 | 98.85 |
| Segment | Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Outdoor static | 100.00% | 92.15% | 96.04% |
| Outdoor → Entrance | 72.22% | ||
| Entrance → Outdoor | 57.14% | ||
| Indoor static | 100.00% | 100.00% | |
| Indoor → Entrance | 100.00% | ||
| Entrance → Indoor | 100.00% | ||
| Metrics | P1,1 | P1,2 | P1,3 | R1,1 | R1,2 | R1,3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean of ECI-F | 1.98 | 1.93 | 2.18 | 3.68 | 3.75 | 3.76 |
| Std. of ECI-F | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.97 | 1.02 | 0.96 |
| Mode of ECI-I | 3 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 1 (%) | 1.66 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.01 | 0.00 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 2 (%) | 42.54 | 53.86 | 20.83 | 0.98 | 2.15 | 0.01 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 3 (%) | 48.46 | 42.05 | 66.14 | 9.08 | 5.08 | 9.12 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 4 (%) | 6.96 | 3.88 | 12.25 | 36.21 | 33.99 | 34.96 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 5 (%) | 0.38 | 0.16 | 0.78 | 53.73 | 57.77 | 55.91 |
| Metrics | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean of ECI-F | 0.47 | 1.63 | 1.93 |
| Std. of ECI-F | 0.21 | 0.41 | 0.50 |
| Mode of ECI-I | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 1 (%) | 99.26 | 21.42 | 7.30 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 2 (%) | 0.74 | 56.73 | 34.59 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 3 (%) | 0.00 | 16.12 | 51.13 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 4 (%) | 0.00 | 4.63 | 6.72 |
| Avg. of ECI-I = 5 (%) | 0.00 | 1.10 | 0.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, B.-G.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.-S.; Park, K.-D. Environmental Context Indicator for Evaluating Quality of GNSS Observation Environment Using Android Smartphone. Sensors 2025, 25, 6452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206452
Park B-G, Kim M, Lee J-S, Park K-D. Environmental Context Indicator for Evaluating Quality of GNSS Observation Environment Using Android Smartphone. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206452
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Bong-Gyu, Miso Kim, Jong-Sung Lee, and Kwan-Dong Park. 2025. "Environmental Context Indicator for Evaluating Quality of GNSS Observation Environment Using Android Smartphone" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206452
APA StylePark, B.-G., Kim, M., Lee, J.-S., & Park, K.-D. (2025). Environmental Context Indicator for Evaluating Quality of GNSS Observation Environment Using Android Smartphone. Sensors, 25(20), 6452. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206452






