VLA-MP: A Vision-Language-Action Framework for Multimodal Perception and Physics-Constrained Action Generation in Autonomous Driving
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a unified end-to-end VLA framework that integrates multimodal BEV perception, vision-language understanding, and physically constrained action generation, achieving seamless mapping from sensor observations and natural language instructions to executable control commands, with demonstrated closed-loop operation and competitive driving performance in the CARLA simulation environment.
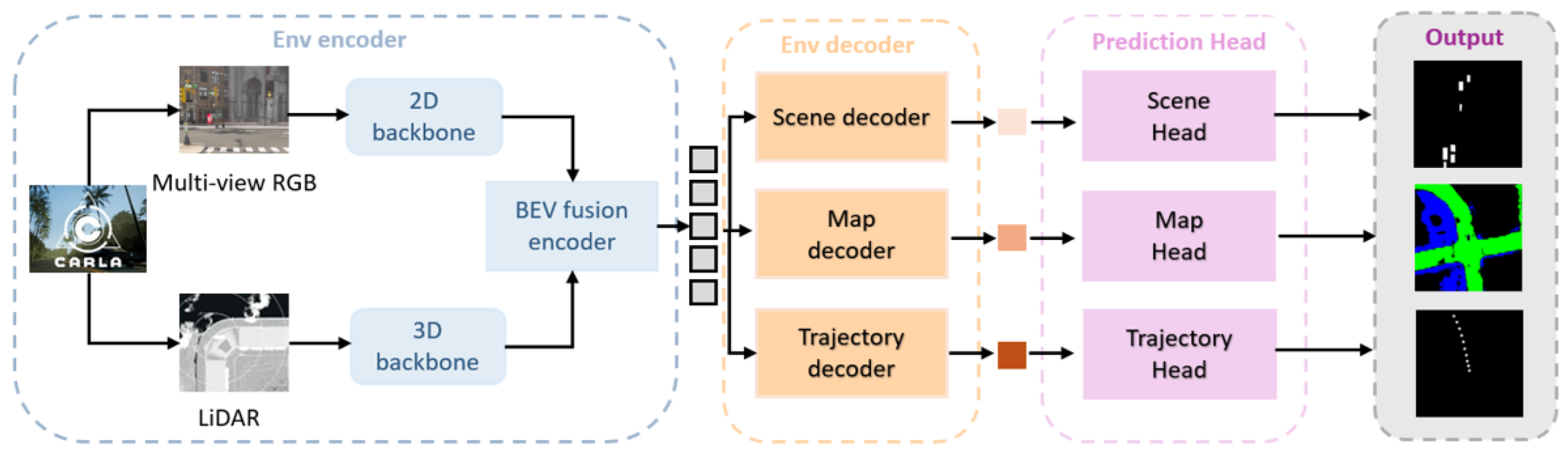
- We extract hierarchical map, scene, and trajectory features from BEV space, characterizing static road topology, dynamic traffic participants, and future motion trends, respectively, and pass these features to the large language model to bridge perception and cognition.
- We design a GRU-bicycle model cascade adapter where the GRU processes temporal semantic information and the bicycle model ensures trajectory compliance with vehicle dynamics constraints, guaranteeing physical feasibility and executability of generated trajectories.
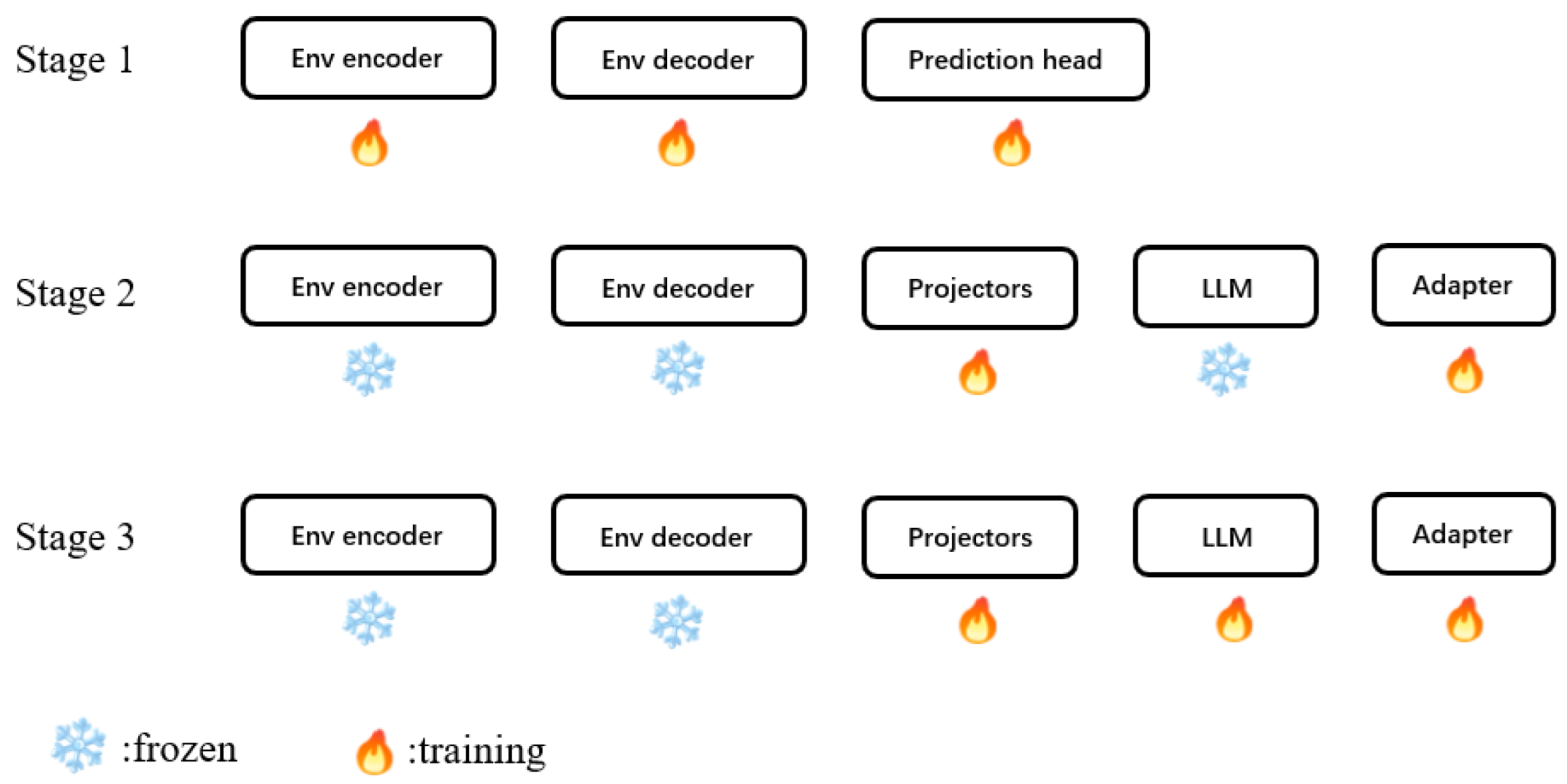
- We develop a three-stage progressive training strategy encompassing environmental perception pre-training, vision-language alignment, and end-to-end fine-tuning, enabling effective knowledge transfer and stable convergence in the complex multimodal learning process.
2. Related Works
2.1. End-to-End Autonomous Driving
2.2. Multimodal Perception and BEV Fusion
2.3. Vision–Language Models in Autonomous Driving
3. Methodology
3.1. Multimodal Environmental Perception Module
3.2. Vision–Language Bridge and Large Language Action Model
| Algorithm 1 Vision–Language Bridge and Cross-Modal Alignment |
| Require:BEV decoder features ; instruction T Ensure :waypoints // Cross-Modal Feature Projection 1 Fuse environmental features: ; 2 Initialize learnable query tokens ; 3 Cross-attention interaction: ; 4 Project to LLM space: ; // Multimodal Token Fusion 5 Text embedding: ; 6 Token concatenation: ; // LLM Reasoning and Decision Generation 7 ; 8 waypoints ← WaypointsDecoder(); |
3.3. Physics-Constrained Action Generation
| Algorithm 2 Physics-Constrained Action Generation |
| Require:LLM hidden states ; initial state Ensure :control commands // Initialize GRU temporal state modeling 1 ; 2 state ; ; 3 waypoints ; // Iterative trajectory generation with bicycle model 4 for step = 1 to 5 do; 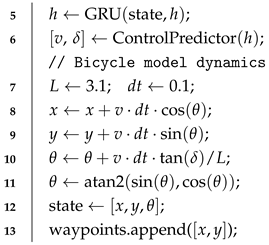 // Convert waypoints to control commands 14 ; |
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Results and Analysis
4.4.1. Overall Performance Comparison
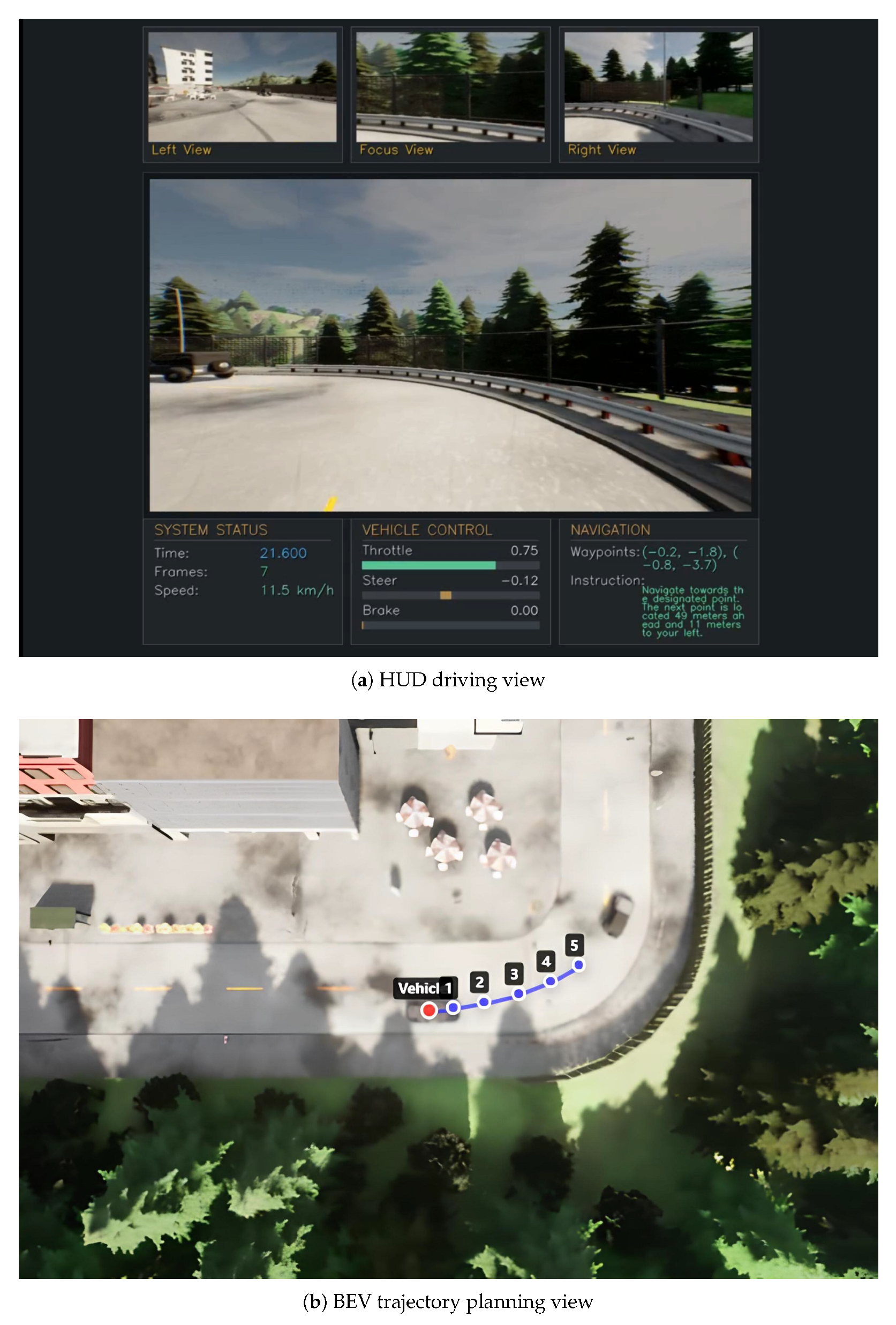
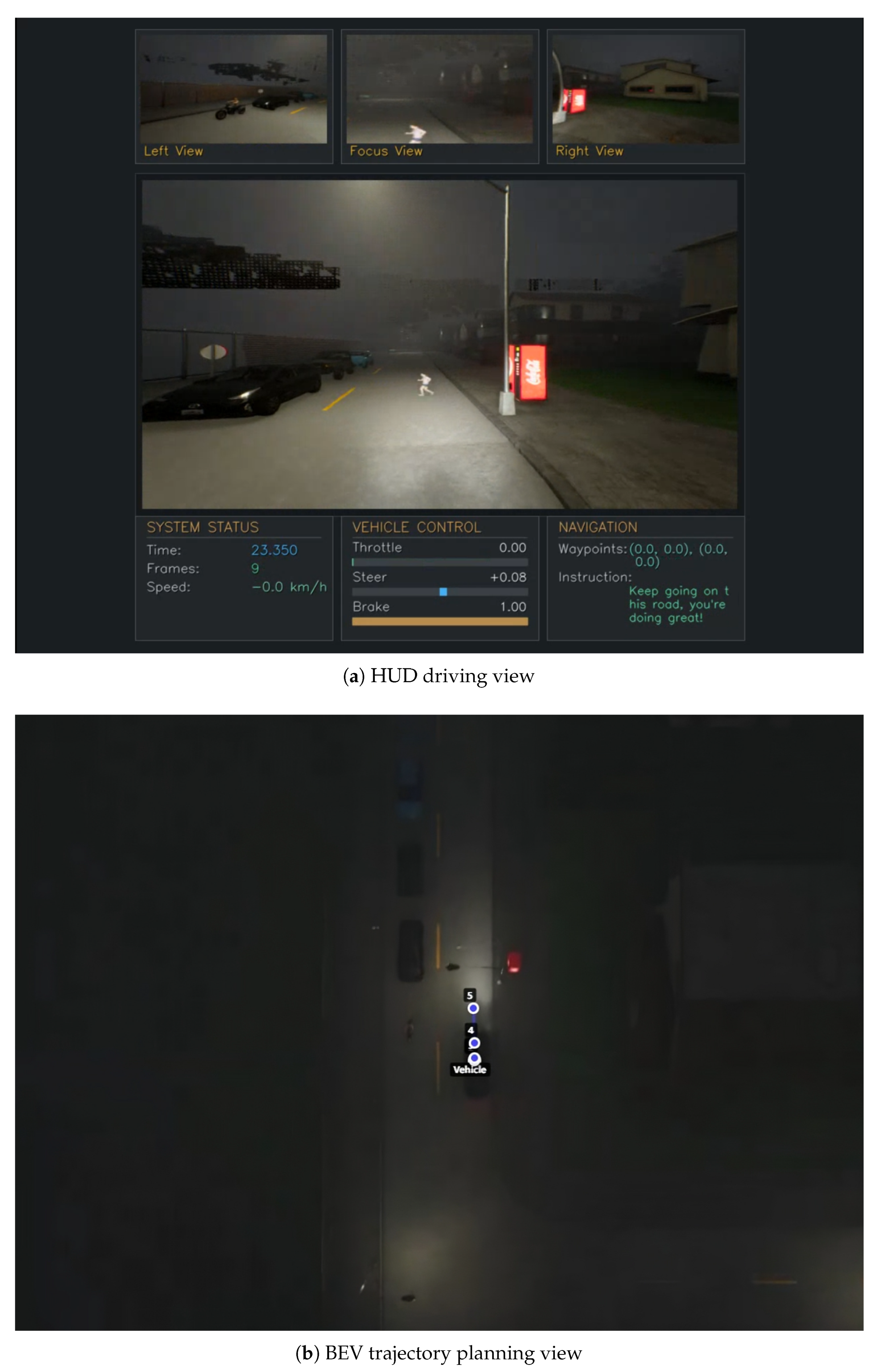
4.4.2. Qualitative Visualization Results
4.4.3. Dynamic Video Demonstrations
4.4.4. Ablation Studies
4.4.5. Computational Efficiency Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VLA | Vision–Language–Action |
| BEV | Bird’s Eye View |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| DS | Driving Score |
| RC | Route Completion |
| IS | Infraction Score |
| HUD | Head-Up Display |
References
- Yang, Z.; Jia, X.; Li, H.; Yan, J. Llm4drive: A survey of large language models for autonomous driving. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.01043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, P.; Chitta, K.; Jaeger, B.; Geiger, A.; Li, H. End-to-end autonomous driving: Challenges and frontiers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 10164–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapkota, R.; Cao, Y.; Roumeliotis, K.I.; Karkee, M. Vision-language-action models: Concepts, progress, applications and challenges. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.04769. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Huang, Z.; Qian, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, T.; Zhong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Kong, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, S.; et al. A Survey on Vision-Language-Action Models for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.24044. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Yurtsever, E.; Zagar, B.L.; Zimmer, W.; Cao, H.; Knoll, A.C. Vision language models in autonomous driving: A survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, K.; Azer, M.; Flohr, F.B. BEVDriver: Leveraging BEV Maps in LLMs for Robust Closed-Loop Driving. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.03074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cai, T.; Zhao, S.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Ma, J. AutoVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for End-to-End Autonomous Driving with Adaptive Reasoning and Reinforcement Fine-Tuning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.13757. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, A.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chai, J.; Cao, Q.; Heng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Dong, Y.; et al. Diffvla: Vision-language guided diffusion planning for autonomous driving. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.19381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Han, X.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; Knoll, A.C. Opendrivevla: Towards end-to-end autonomous driving with large vision language action model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.23463. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, H.; Miwa, K.; Sasaki, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Aoki, S.; Yamamoto, I. Covla: Comprehensive vision-language-action dataset for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Tucson, AZ, USA, 26 February–6 March 2025; pp. 1933–1943. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, E.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wong, K.Y.K.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H. Drivegpt4: Interpretable end-to-end autonomous driving via large language model. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 8186–8193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, G.; Waslander, S.L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Lmdrive: Closed-loop end-to-end driving with large language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 15120–15130. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Qian, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y. Gpt-driver: Learning to drive with gpt. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.01415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Ma, J. DSDrive: Distilling Large Language Model for Lightweight End-to-End Autonomous Driving with Unified Reasoning and Planning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.05360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, J.; Zhuo, L. BEV perception for autonomous driving: State of the art and future perspectives. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 258, 125103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Amini, A.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Rus, D.; Han, S. Bevfusion: Multi-task multi-sensor fusion with unified bird’s-eye view representation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.13542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Xie, E.; Sima, C.; Lu, T.; Yu, Q.; Dai, J. Bevformer: Learning bird’s-eye-view representation from lidar-camera via spatiotemporal transformers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 47, 2020–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, D.; Gosala, N.; Kumar, V.R.; Borse, S.; Valada, A.; Yogamani, S. Multi-camera Bird’s Eye View Perception for Autonomous Driving. In Computer Vision; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ge, Z.; Yu, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z. Bevdepth: Acquisition of reliable depth for multi-view 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; pp. 1477–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliari, F.; Hasan, I.; Cristani, M.; Galasso, F. Transformer networks for trajectory forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 10335–10342. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Ma, X.; Ren, J.; Zhao, H.; Yi, S. Spatio-temporal graph transformer networks for pedestrian trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 507–523. [Google Scholar]
- Lai-Dang, Q.V. A survey of vision transformers in autonomous driving: Current trends and future directions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.07542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Li, K.; Sima, C.; Zhu, X.; Chai, S.; Du, S.; Lin, T.; Wang, W.; et al. Planning-oriented autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17853–17862. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Ma, Y.; Cao, X.; Ye, W.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, K.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, Z.; Liao, K.D.; et al. A survey on multimodal large language models for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 958–979. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Chen, S.; Fu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Fan, L.; An, D.; Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Meng, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Multimodal fusion and vision-language models: A survey for robot vision. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.02477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Haß, E.L.; Chao, K.Y.; Petrovic, N.; Song, Y.; Wu, C.; Knoll, A. A Unified Perception-Language-Action Framework for Adaptive Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.23540. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Chen, S.; Xu, Q.; Liao, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Huang, C.; Wang, X. Vad: Vectorized scene representation for efficient autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 8340–8350. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Lin, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H.; Zheng, S. Sparsedrive: End-to-end autonomous driving via sparse scene representation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.19620. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Chen, L.; Wu, P.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Tao, D. St-p3: End-to-end vision-based autonomous driving via spatial-temporal feature learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 533–549. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Safety-enhanced autonomous driving using interpretable sensor fusion transformer. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 726–737. [Google Scholar]
- Hanselmann, N.; Renz, K.; Chitta, K.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Geiger, A. King: Generating safety-critical driving scenarios for robust imitation via kinematics gradients. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 335–352. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Jia, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, J.; Li, H.; Qiao, Y. Trajectory-guided control prediction for end-to-end autonomous driving: A simple yet strong baseline. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 6119–6132. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fu, H.; Tai, C.L. Transfusion: Robust lidar-camera fusion for 3d object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1090–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Miao, Z.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L. Deepinteraction: 3d object detection via modality interaction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 1992–2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, D.; Fang, J.; Yin, J.; Bin, Z.; Zhang, L. Fusionpainting: Multimodal fusion with adaptive attention for 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 3047–3054. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Jia, F.; Li, S.; Gao, A.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X. Petrv2: A unified framework for 3d perception from multi-camera images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 3262–3272. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Liu, H. Adapt: Action-aware driving caption transformer. In Proceedings of the CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Panchal, J.; Wang, Z. Personalized autonomous driving with large language models: Field experiments. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 27th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 24–27 September 2024; pp. 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Han, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Xu, C.z.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J. Language prompt for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; pp. 8359–8367. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, B.; Chitta, K.; Geiger, A. Hidden biases of end-to-end driving models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 8240–8249. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Caesar, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Beijbom, O. Pointpillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12697–12705. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, T.; Zhou, X.; Krahenbuhl, P. Center-based 3d object detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11784–11793. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 19730–19742. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Lee, Y.J. Improved baselines with visual instruction tuning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 26296–26306. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Hui, B.; Zheng, B.; Yu, B.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, F.; Wei, H.; et al. Qwen2.5 Technical Report. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.15115. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2412.15115 (accessed on 20 August 2025). [CrossRef]
- LaValle, S.M. Planning Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Ros, G.; Codevilla, F.; Lopez, A.; Koltun, V. CARLA: An open urban driving simulator. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Mountain View, CA, USA, 13–15 November 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- CARLA Team. CARLA Autonomous Driving Leaderboard. 2020. Available online: https://leaderboard.carla.org/ (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, H. Ad-h: Autonomous driving with hierarchical agents. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.03474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, P.; Zhao, X.; Lan, B.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. FastDriveVLA: Efficient End-to-End Driving via Plug-and-Play Reconstruction-based Token Pruning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.23318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q. Transfuse: Fusing transformers and cnns for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]

| LLM Backbone | LangAuto | LangAuto-Short | LangAuto-Tiny | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS ↑ | RC ↑ | IS ↑ | DS ↑ | RC ↑ | IS ↑ | DS ↑ | RC ↑ | IS ↑ | |
| Random Init. | 10.7 | 16.2 | 0.63 | 14.2 | 20.1 | 0.72 | 20.1 | 24.7 | 0.75 |
| LMdrive (LLaMA-7B) [12] | 31.3 | 37.1 | 0.82 | 42.8 | 49.1 | 0.87 | 52.5 | 57.8 | 0.91 |
| LMdrive (LLaVA-7B) | 36.2 | 46.5 | 0.81 | 50.6 | 60.0 | 0.84 | 66.5 | 77.9 | 0.85 |
| AD-H (LLaVA-7B) [52] | 44.0 | 53.2 | 0.83 | 56.1 | 68.0 | 0.78 | 77.5 | 85.1 | 0.91 |
| AD-H (Mipha-3B) | 41.1 | 48.5 | 0.86 | 54.3 | 61.8 | 0.86 | 68.0 | 74.4 | 0.87 |
| BEVdriver (Llama3.1-8B-I) [6] | 33.1 | 40.7 | 0.83 | 60.9 | 65.8 | 0.92 | 66.0 | 69.9 | 0.90 |
| DSDrive (LLaMA-1B) [14] | 29.5 | 39.3 | 0.77 | 62.0 | 76.1 | 0.81 | 60.6 | 72.5 | 0.84 |
| Ours VLA-MP (LLaVA-7B) | 44.3 | 49.6 | 0.89 | 63.5 | 71.1 | 0.90 | 78.4 | 82.3 | 0.95 |
| Module Design | DS ↑ | RC ↑ | IS ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ours(VLA-MP) | 78.4 | 82.3 | 0.95 |
| w/o Projector | 67.5 | 75.0 | 0.91 |
| w/o Physical-Constrained | 58.0 | 64.0 | 0.92 |
| w/o Env Pre-training | 42.3 | 61.1 | 0.69 |
| Metric | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Total Time | 125.04 | ms |
| Visual Processing | 43.78 | ms |
| LLM Inference | 20.91 | ms |
| Physics Control | 0.25 | ms |
| FPS | 8.0 | frames/s |
| Peak GPU Memory | 13.7 | GB |
| Model Parameters | 6.9 | B |
| Hardware Platform | RTX 3090 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, M.; Ohtani, K.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Takeda, K. VLA-MP: A Vision-Language-Action Framework for Multimodal Perception and Physics-Constrained Action Generation in Autonomous Driving. Sensors 2025, 25, 6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196163
Ge M, Ohtani K, Niu Y, Zhang Y, Takeda K. VLA-MP: A Vision-Language-Action Framework for Multimodal Perception and Physics-Constrained Action Generation in Autonomous Driving. Sensors. 2025; 25(19):6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196163
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Maoning, Kento Ohtani, Yingjie Niu, Yuxiao Zhang, and Kazuya Takeda. 2025. "VLA-MP: A Vision-Language-Action Framework for Multimodal Perception and Physics-Constrained Action Generation in Autonomous Driving" Sensors 25, no. 19: 6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196163
APA StyleGe, M., Ohtani, K., Niu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Takeda, K. (2025). VLA-MP: A Vision-Language-Action Framework for Multimodal Perception and Physics-Constrained Action Generation in Autonomous Driving. Sensors, 25(19), 6163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196163







