Revealing Lunar Far-Side Polarization Characteristics via FeO Abundance Distribution Correlations with Ground-Based Polarimetric Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
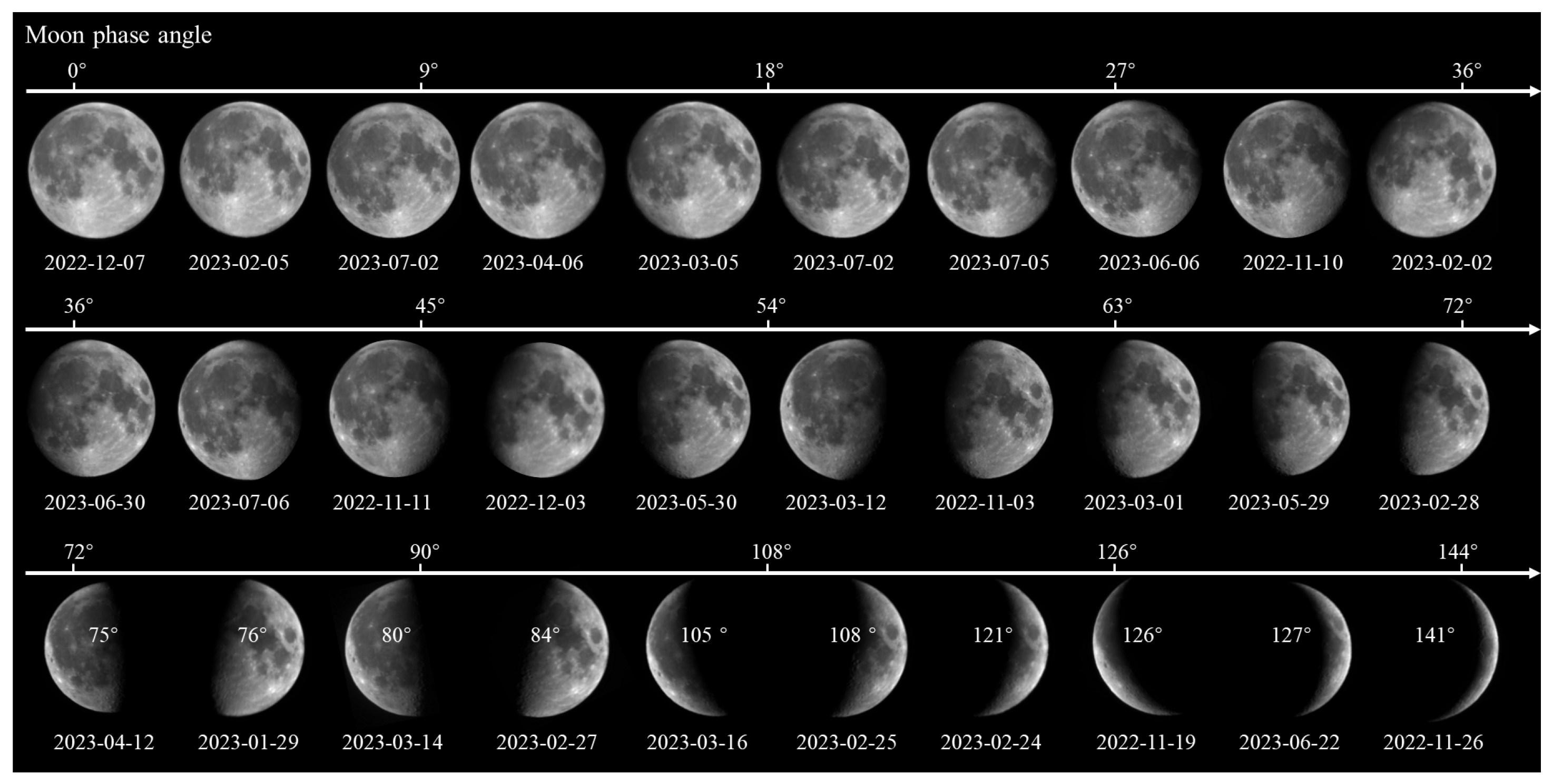
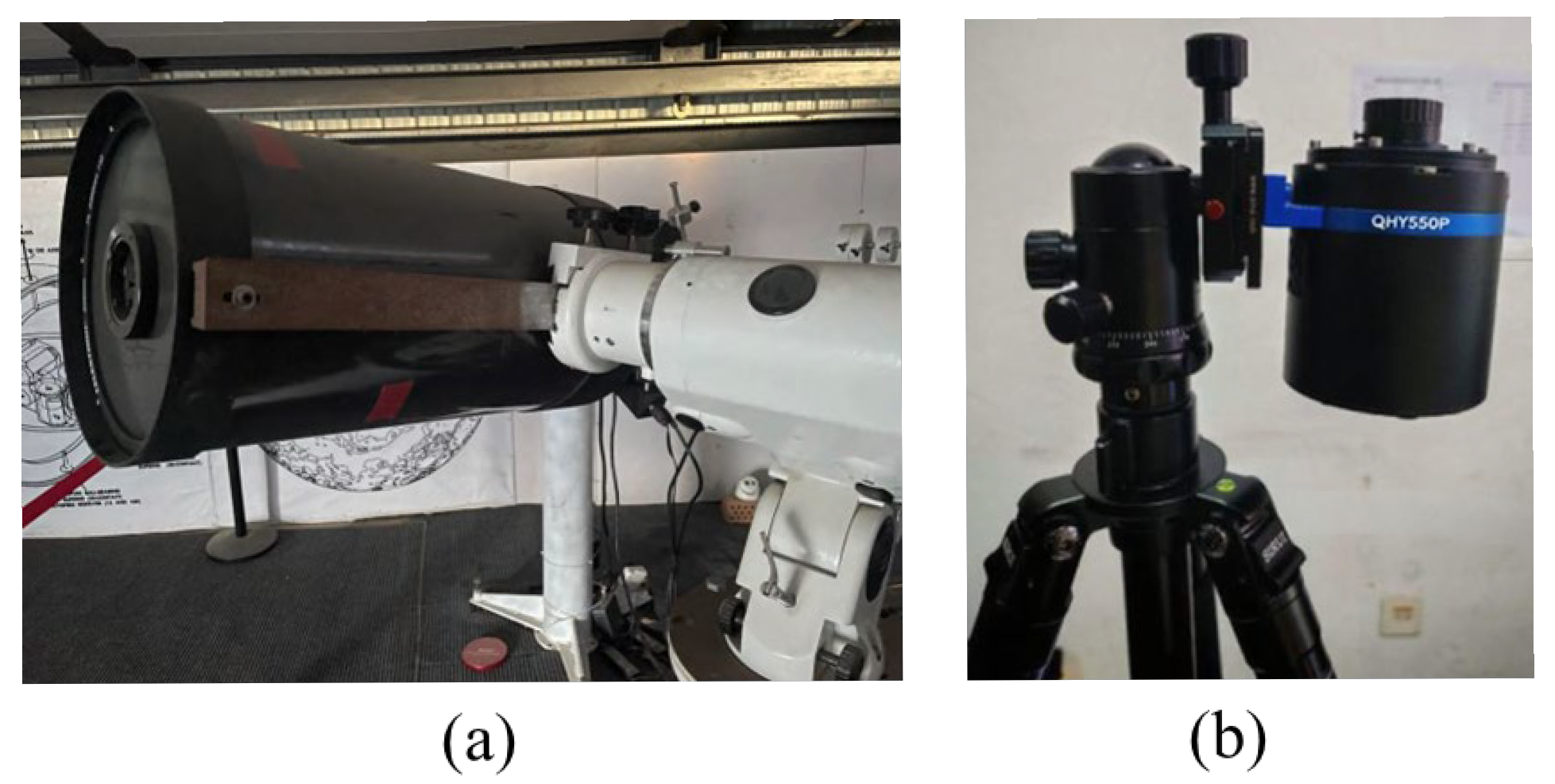
2.1. Polarization Data from DoFP Camera
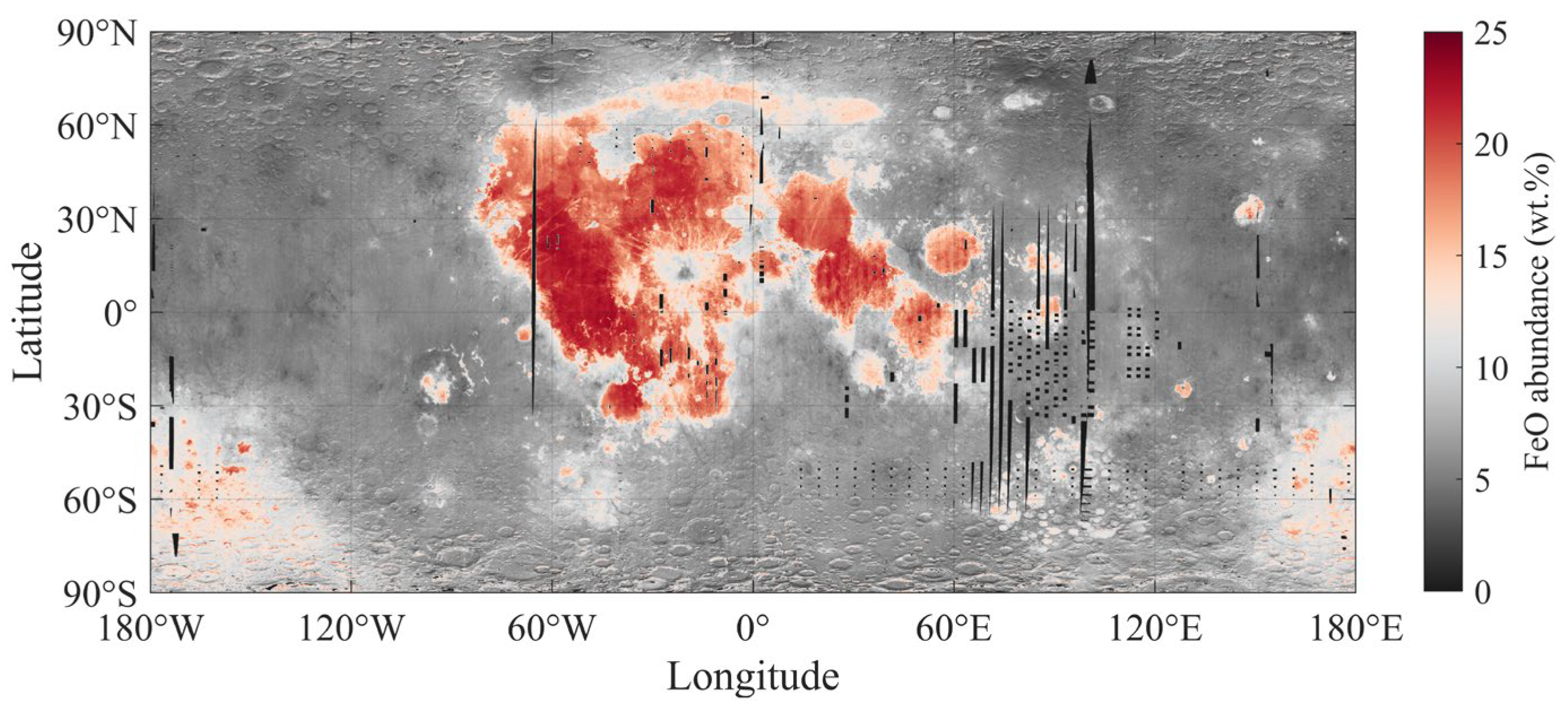
2.2. Lunar Surface FeO Abundance
3. Method
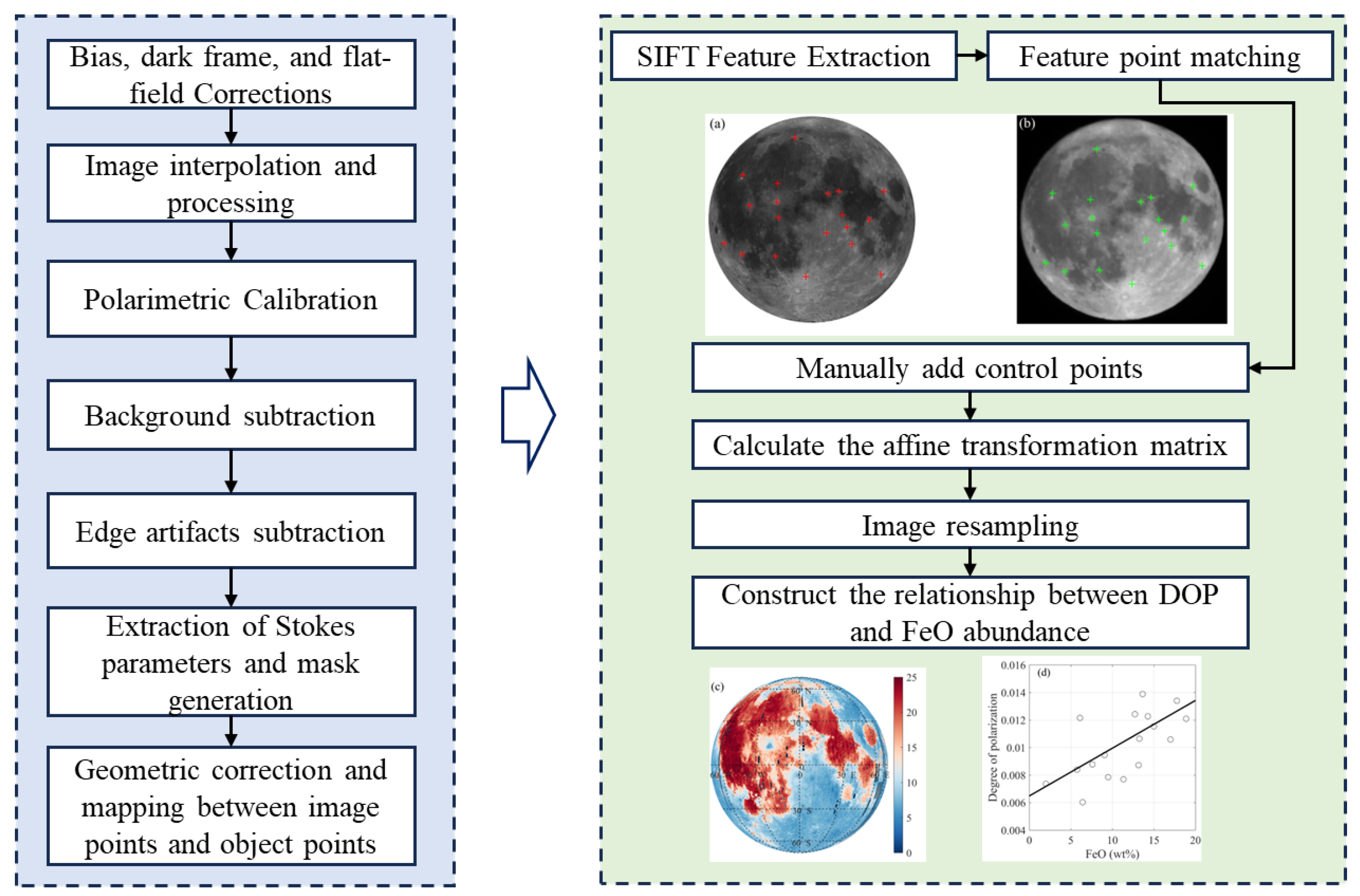
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Image Registration
4. Results
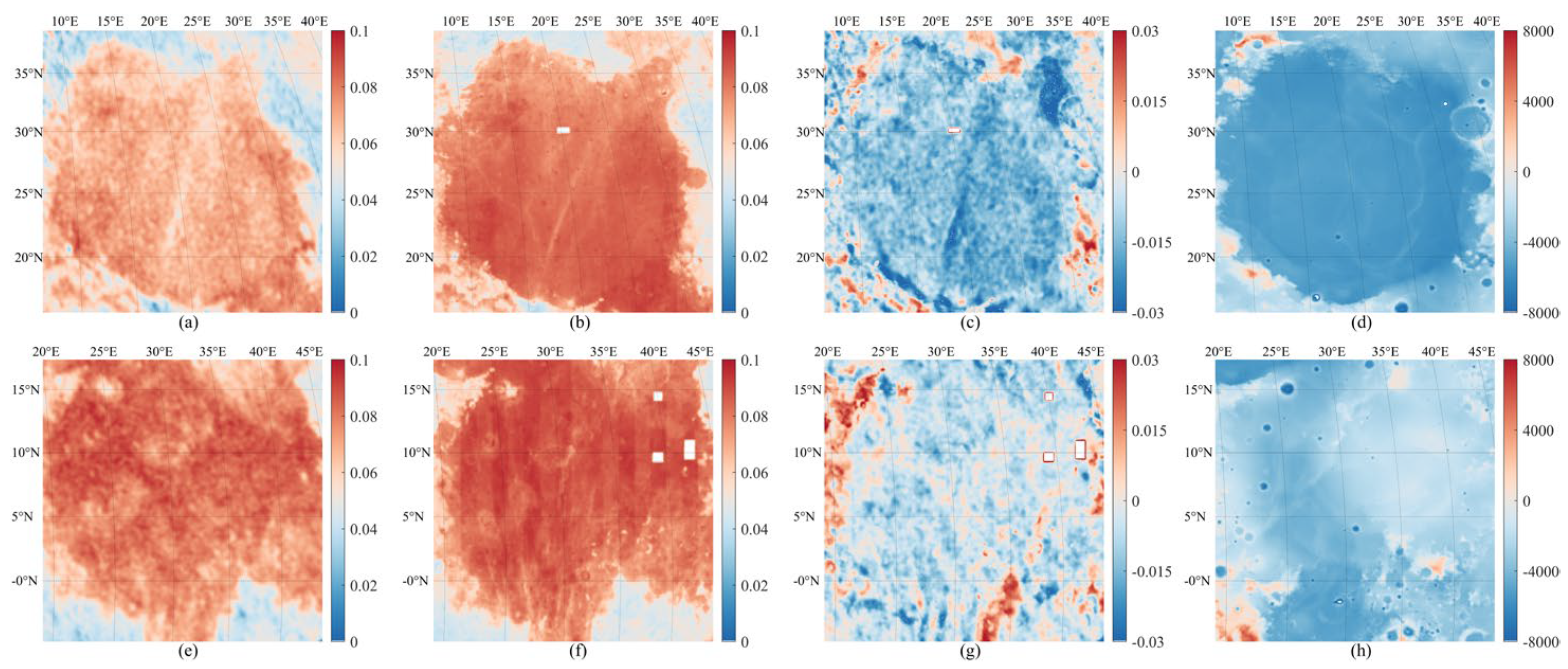
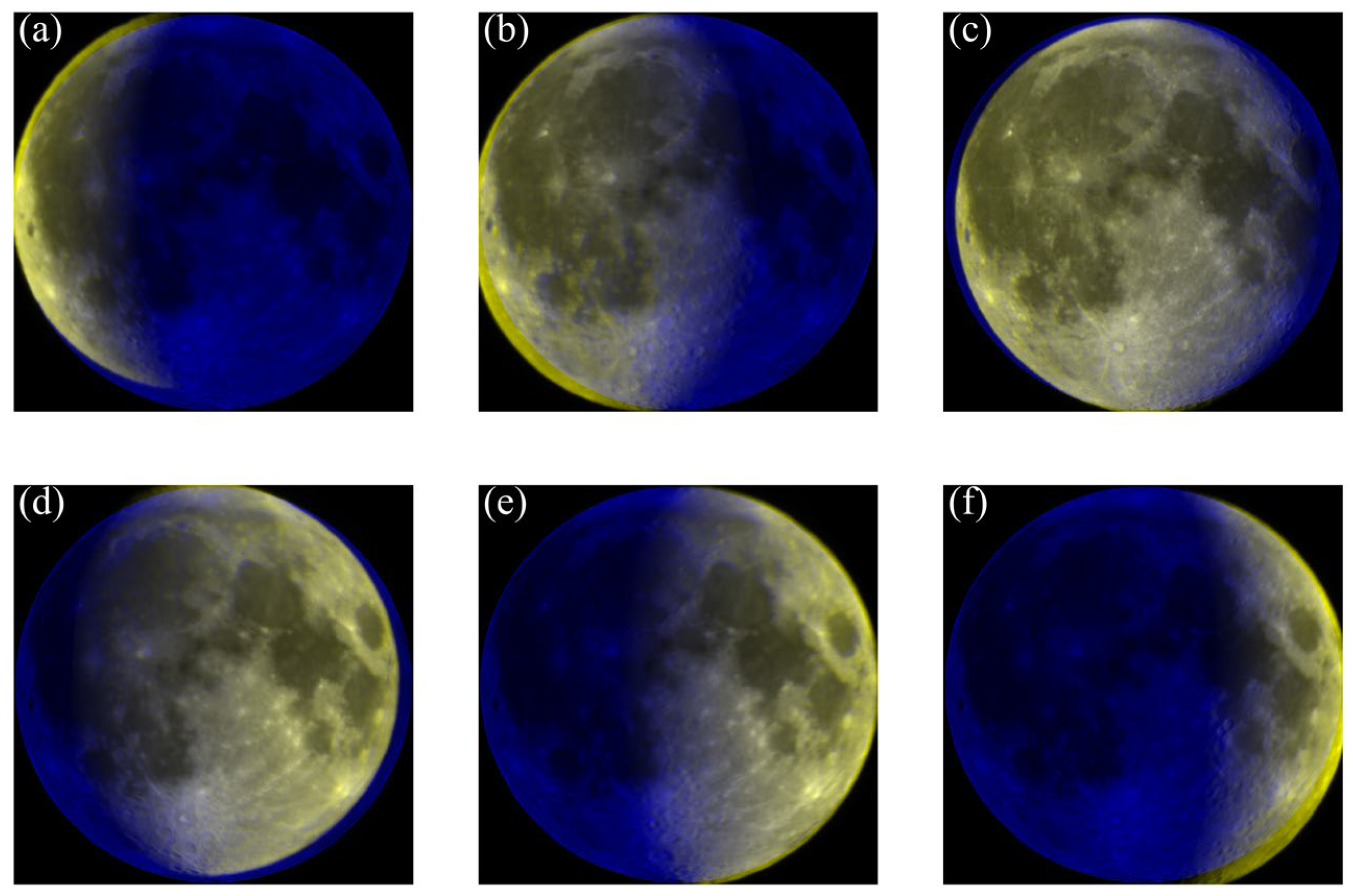
4.1. Analysis of the DOP Distribution
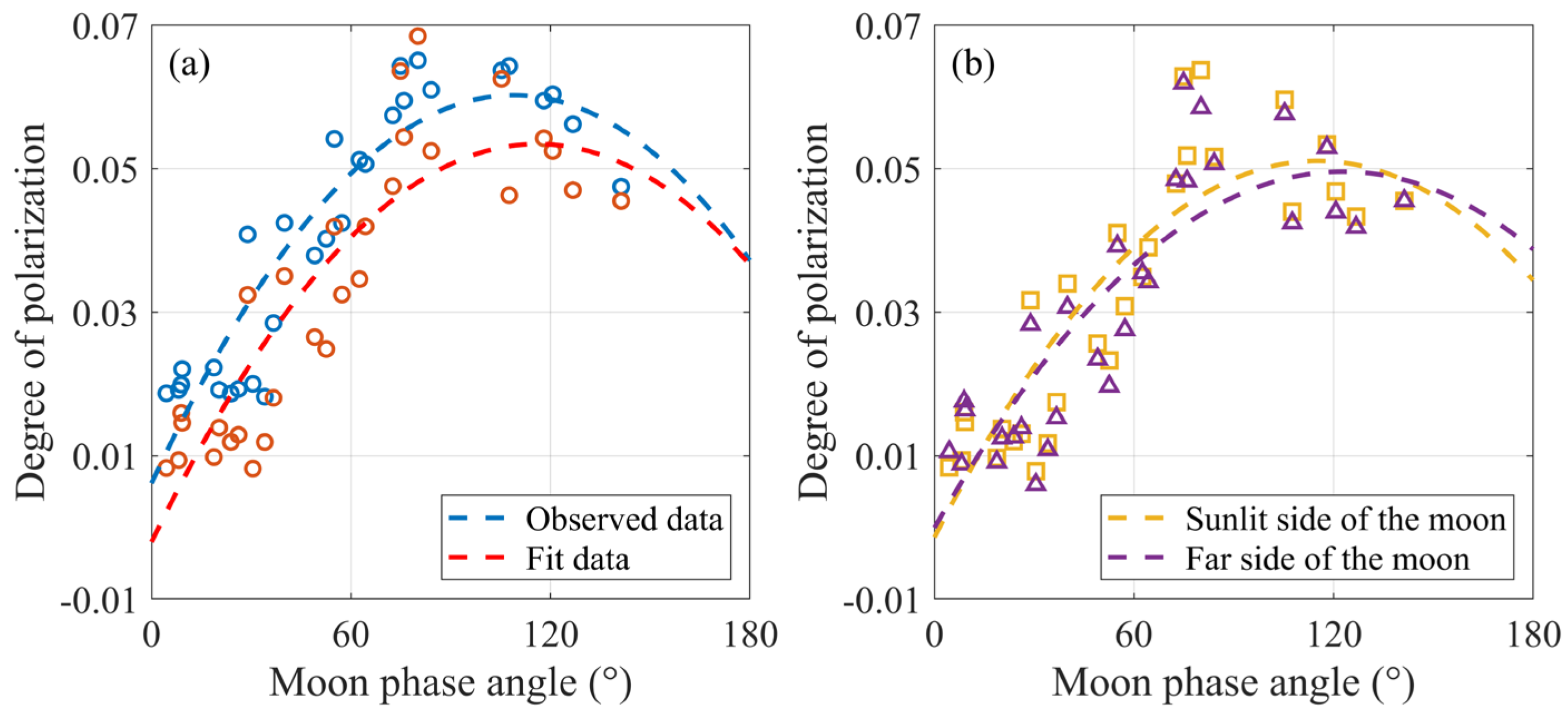
4.2. Relationship Between the Mean DOP and Lunar Phase Angles
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spudis, P.D. The case for renewed human exploration of the Moon. Earth Moon Planets 1999, 87, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilevsky, A.T. Exploration of the Moon by Soviet spacecraft. Encycl. Space Sci. Technol. 2003, 1, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delano, J.W. Scientific exploration of the Moon. Elements 2009, 5, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Li, C.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lü, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zuo, W.; Su, Y.; Wen, W.; et al. Primary scientific results of Chang’E-1 lunar mission. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1565–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Kamimori, N.; Takizawa, Y.; Kato, M.; Oda, M.; Wakabayashi, S.; Kawamoto, S.; Okada, T.; Iwata, T.; Ohtake, M. Japanese lunar exploration long-term plan. Acta Astronaut. 2006, 59, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Lin, Y. China’s present and future lunar exploration program. Science 2019, 365, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y. China’s lunar exploration program: Present and future. Planet. Space Sci. 2008, 56, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.; Korotev, R.L.; Gillis, J.J.; Taylor, L.A.; Lawrence, D.; Campbell, B.A.; Elphic, R.; Feldman, B.; Hood, L.L.; Hunten, D.; et al. Understanding the lunar surface and space-Moon interactions. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2006, 60, 83–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, I.; Anand, M.; Cockell, C.; Falcke, H.; Green, D.; Jaumann, R.; Wieczorek, M. Back to the Moon: The scientific rationale for resuming lunar surface exploration. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 74, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrajsek, J.; McKissock, D.; Woytach, J.; Zakrajsek, J.; Oswald, F.; McEntire, K.; Hill, G.; Abel, P.; Eichenberg, D.; Goodnight, T. Exploration rover concepts and development challenges. In Proceedings of the 1st Space Exploration Conference: Continuing the Voyage of Discovery, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 January–1 February 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, H.; Yang, M.-F.; Pei, Z.-Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, D.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. Characteristics of the lunar samples returned by the Chang’E-5 mission. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jia, X.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, X.; Qu, Y. Vision-based sampling implementation in the Chang’e-6 lunar farside sample return mission. Light Adv. Manuf. 2025, 6, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, C.; Yuan, L.; Lv, G.; Xu, S.; Li, F.; Jin, J.; Wang, Z.; Pan, W.; Wang, R.; et al. Lunar mineralogical spectrometer on Chang’E-5 mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2022, 218, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Ren, X.; Mou, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lü, C.; Liu, J.; Zuo, W.; Su, Y.; et al. The global image of the Moon obtained by the Chang’E-1: Data processing and lunar cartography. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vondrak, R.; Keller, J.; Chin, G.; Garvin, J. Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO): Observations for lunar exploration and science. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 150, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, P. Ground-based observation system development for the moon hyper-spectral imaging. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2017, 129, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Sun, J.; Huang, L.; Jiang, P.; Wang, X.; Ding, C. Moon imaging performance of FAST radio telescope in bistatic configuration with other radars. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, A.T. New generation ground-based optical/infrared Telescopes. Encycl. Sol. Syst. 2014, 59, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E. Least-squares wavelet and cross-wavelet analyses of VLBI baseline length and temperature time series: Fortaleza–Hartebeesthoek–Westford–Wettzell. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2021, 133, 014502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ni, S.; Xiao, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, H. Study on the Feasibility and Performance Evaluation of High-Orbit Spacecraft Orbit Determination Based on GNSS/SLR/VLBI. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesulu, E.; Shaw, J.A. Polarization images of the Moon as a function of the lunar phase. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 24275–24292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ping, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Ye, H.; Han, X.; Kou, S. A New Method for Ground-Based Optical Polarization Observation of the Moon. Sensors 2024, 24, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapke, B. Lunar surface: Composition inferred from optical properties. Science 1968, 159, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Lucey, P.G.; Fisher, E.A. Using polarized infrared spectroscopy to characterize surface adsorbed and internal water in planetary materials. Icarus 2024, 411, 115924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkuratov, Y.; Opanasenko, N.; Zubko, E.; Grynko, Y.; Korokhin, V.; Pieters, C.; Videen, G.; Mall, U.; Opanasenko, A. Multispectral polarimetry as a tool to investigate texture and chemistry of lunar regolith particles. Icarus 2007, 187, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, R.; Bao, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Feng, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H. Imaging Chain Modelling and a Scaling Experiment for Optical Remote Sensing of Lunar Surface. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollfus, A. Lunar surface imaging polarimetry: I. Roughness and Grain Size. Icarus 1998, 136, 69–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Yan, L. Estimation of rock characteristics based on polarization spectra: Surface roughness, composition, and density. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2021, 87, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, E. Investigation of the Polarization Properties of the Surface of the Moon. Moon 1962, 14, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Kim, S.S.; Garrick-Bethell, I.; Park, S.-M.; Sim, C.K.; Jin, H.; Min, K.W.; Choi, Y.-J. Multi-band polarimetry of the lunar surface. I. Global Properties. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2015, 221, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, I.A.; Wiersema, K.; McCall, C.; Newsam, A.; Shrestha, M. Optical Polarimetry of the May 2022 Lunar Eclipse. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 518, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaut, M.; Wöhler, C.; Bhatt, M. The Moon Polarizes and It Matters: New Lunar Spectropolarimetric Datasets, Effects and Models. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Division for Planetary Sciences, San Antonio, TX, USA, 1–6 October 2023; Available online: https://baas.aas.org/pub/2023n8i101p05 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Venkatesulu, E.; Dabby, S.L.; Shaw, J.A. Disk-resolved and disk-integrated polarization state of moonlight as a function of lunar phase. In Proceedings of the Polarization Science and Remote Sensing XI, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–22 August 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreslavsky, M.; Kim, S.; Jeong, M.; Choi, Y.-J.; Sim, C.; Shkuratov, Y.; Farrand, W.; Videen, G.; Moon, B.; Kang, K.-I. Polarization Signatures of Young Lunar Craters from Danuri PolCam Observations. In Proceedings of the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 11–15 March 2024; Available online: https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2024/pdf/2502.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Dollfus, A.; Titulaer, C. Polarimetric Properties of the Lunar Surface and Its Interpretation. Part III Astron. Astrophys. 1971, 12, 199. Available online: https://adsabs.harvard.edu/full/1971A%26A....12..199D (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Gehrels, T.; Coffeen, T.; Owings, D. Wavelength dependance of polarization III. the lunar surface. Astron. J. 1964, 69, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Han, S.I.; Har, D. Operational Tests for Delay-Tolerant Network between the Moon and Earth Using the Korea Pathfinder Lunar Orbiter in Lunar Orbit. Electronics 2024, 13, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, C.K.; Kim, S.S.; Jeong, M.; Choi, Y.-J.; Shkuratov, Y.G. Observational strategy for KPLO/PolCam measurements of the lunar surface from orbit. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2019, 132, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-N.; Ping, J.-S.; Wang, M.-Y.; Zhang, W.-Z.; Ye, H.-L.; Han, X.-W.; Kou, S.-F. The First Ground-based White Light Lunar Polarization Imaging: A New Kind of FeO Observation on the Near Side of the Moon. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 24, 061001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, H.-Y.; Meng, Z.-G.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Lu, Y.; Cai, Z.-C.; Ping, J.-S.; Gusev, A.; Hu, S. Retrieving volume FeO and TiO2 abundances of lunar regolith with CE-2 CELMS data using BPNN method. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 19, 066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, Z.; Ping, J.; Zhang, Y. A new brightness temperature mapping method for weakening latitude effect with Chang’e-2 MRM data and its geologic significances. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4512712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Yang, G.; Ping, J.; Cai, Z.; Gusev, A.; Osei, E.M. Influence of (FeO+TiO2) abundance on the microwave thermal emissions of lunar regolith. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prettyman, T.H.; Hagerty, J.; Elphic, R.; Feldman, W.; Lawrence, D.; McKinney, G.; Vaniman, D. Elemental composition of the lunar surface: Analysis of gamma ray spectroscopy data from Lunar Prospector. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2006, 111, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Gruev, V. Bilinear and bicubic interpolation methods for division of focal plane polarimeters. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 26161–26173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, B.M.; LaCasse, C.F.; Scott Tyo, J. Interpolation strategies for reducing IFOV artifacts in microgrid polarimeter imagery. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 9112–9125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, G. Sift-the scale invariant feature transform. Int. J. 2004, 2, 2. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/19d1/c9a4546d840269ef534f6c1c8e3798ce81ac.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Shkuratov, Y.G.; Opanasenko, N. Polarimetric and photometric properties of the moon: Telescope observation and laboratory simulation: 2. The positive polarization. Icarus 1992, 99, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, D.T.; Lucey, P.G.; Hawke, B.R.; Jolliff, B.L. Clementine images of the lunar sample-return stations: Refinement of FeO and TiO2 mapping techniques. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1997, 102, 16319–16325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, C.; Brennan, R.; Burkhard, L.; Costello, E.; Sandford, M.; Sun, L. Multispectral polarization measurements of eight lunar soils. Polarization 2018, 2083, 1718. Available online: https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2018/pdf/1718.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Nozette, S.; Rustan, P.; Pleasance, L.; Kordas, J.; Lewis, I.; Park, H.; Priest, R.; Horan, D.; Regeon, P.; Lichtenberg, C. The Clementine mission to the Moon: Scientific overview. Science 1994, 266, 1835–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Sasaki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Iijima, Y.; Takizawa, Y. The Japanese lunar mission SELENE: Science goals and present status. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 42, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, J.; Annadurai, M. Chandrayaan-1: India’s first planetary science mission to the Moon. Curr. Sci. 2009, 96, 486–491. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24105456 (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Zhao, B.; Yang, J.; Wen, D.; Gao, W.; Chang, L.; Song, Z.; Xue, B.; Zhao, W. Overall scheme and on-orbit images of Chang’E-2 lunar satellite CCD stereo camera. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 2237–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, L. Thermophysical properties of the regolith on the lunar far side revealed by the in situ temperature probing of the Chang’E-4 mission. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, H.; Yang, M.-F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, D.; Zeng, X.; Zuo, W. Nature of the lunar far-side samples returned by the Chang’E-6 mission. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Yang, M.-H.; Li, Q.-L.; Liu, Y.; Yue, Z.-Y.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, L.-Y.; Ma, H.-X.; Yang, S.-H.; Tang, X.; et al. Lunar farside volcanism 2.8 billion years ago from Chang’e-6 basalts. Nature 2025, 643, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai Udovicic, C.; Costello, E.; Ghent, R.; Edwards, C. New constraints on the lunar optical space weathering rate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL092198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.; Wöhler, C.; Rogall, J.; Aravind, K.; Ganesh, S.; Bhardwaj, A. Unique regolith characteristics of the lunar swirl reiner gamma as revealed by imaging polarimetry at large phase angles. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 674, A82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Site | Longitude | Latitude | DOP | Fitted DOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apollo 11-average (in the literature) | 23.473° E | 0.673° N | 0.109 | 0.091 |
| luna16-average (in the literature) | 56.364° E | 0.514° S | 0.107 | 0.098 |
| luna20-average (in the literature) | 56.624° E | 3.786° N | 0.056 | 0.030 |
| Apollo 15 average | 3.638° E | 26.132° N | 0.074 | 0.061 |
| Apollo 16 average | 15.504° E | 8.973° S | 0.040 | 0.022 |
| Apollo 17 average | 30.766° E | 20.192° N | 0.066 | 0.062 |
| CE-5 | 51.916° W | 43.057° N | 0.108 | 0.095 |
| Apollo 11-average (in the literature) | 23.473° E | 0.673° N | 0.109 | 0.091 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, H.; Wang, W.; Ping, J.; Jin, Y. Revealing Lunar Far-Side Polarization Characteristics via FeO Abundance Distribution Correlations with Ground-Based Polarimetric Data. Sensors 2025, 25, 5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185666
Ye H, Wang W, Ping J, Jin Y. Revealing Lunar Far-Side Polarization Characteristics via FeO Abundance Distribution Correlations with Ground-Based Polarimetric Data. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185666
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Hanlin, Weinan Wang, Jinsong Ping, and Yin Jin. 2025. "Revealing Lunar Far-Side Polarization Characteristics via FeO Abundance Distribution Correlations with Ground-Based Polarimetric Data" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185666
APA StyleYe, H., Wang, W., Ping, J., & Jin, Y. (2025). Revealing Lunar Far-Side Polarization Characteristics via FeO Abundance Distribution Correlations with Ground-Based Polarimetric Data. Sensors, 25(18), 5666. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185666








