Rapid Identification of Dendrobium Species Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.1.1. Collection of Dendrobium Samples
2.1.2. Preparation of Dendrobium Samples
2.2. Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging System
2.2.1. Components of Near-Infrared Hyperspectral System
2.2.2. The Advantages of Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Compared to RGB Imaging
2.3. Hyperspectral Data Acquisition of Dendrobium Samples
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4.1. Sample Partitioning
2.4.2. Spectral Preprocessing
2.4.3. Characteristic Wavelength Selection Methods
2.5. Classification Modeling and Evaluation Methods for Dendrobium Samples
2.5.1. Modeling Method
2.5.2. Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectral Analysis
3.2. Classification Model Analysis Based on Full Wavelengths
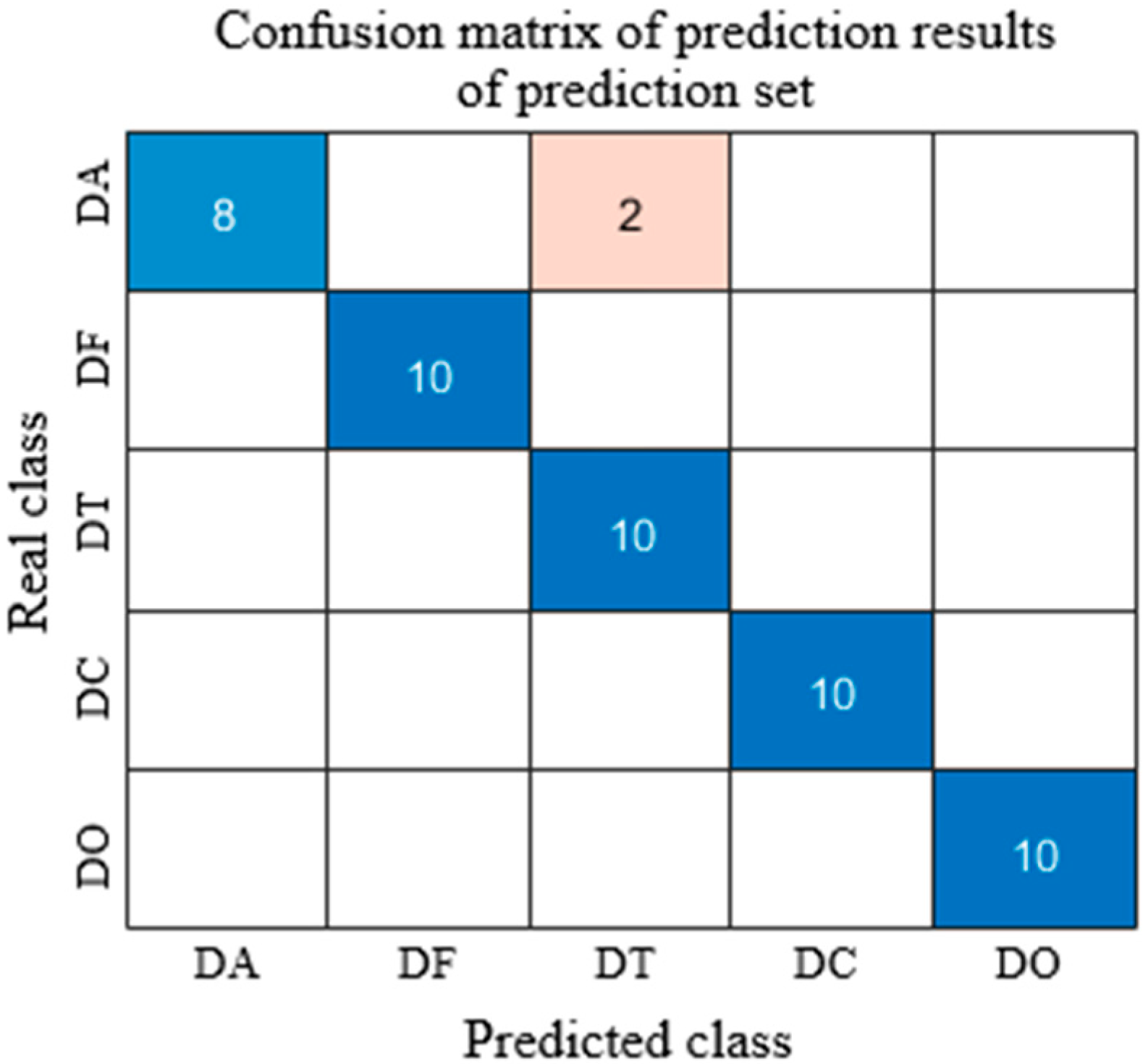
3.3. Classification Model Analysis Based on Feature Wavelength Selection
3.3.1. Modeling Results Based on CARS Feature Wavelength Selection
3.3.2. Modeling Results Based on SPA Feature Wavelength Selection
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, N.; Jia, X.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, M.; Li, J. Comparative study on pharmacognostical characteristics of Dendrobium huoshanense and Dendrobium henanense. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2016, 28, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Bushueva, A.; Adeleye, T.; Roy, P. Socioeconomic and Environmental Prospects of the Food Industry. Agric. Rural Stud. 2024, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, X. Big food vision and food security in China. Agric. Rural Stud. 2023, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, T.; Abay, C. Malian farmers’ perception of sustainable agriculture: A case of southern Mali farmers. Agric. Rural Stud. 2024, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, Â.; Schneider, S. The relationship between agri-food production and macro-economic dynamics: A study on soybeans in Brazilian south and Chinese mainland. Agric. Rural Stud. 2023, 1, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, B.; Ye, Y. Identification of common confounding and counterfeit products of Dendrobium officinale and its processed products. Green Sci. Technol. 2020, 94–95, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Pharmacognostic Identification Study of Dendrobium huoshanense. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Comparative Identification and Histochemical Localization Study of Dendrobium huoshanense and Its Related Species. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N. Rapid identification of Dendrobium huoshanense, Dendrobium officinale and Dendrobium henanense flower tea using multi-level infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Cai, J.; Wang, X. Identification of Dendrobium officinale using DNA barcoding method combined with HRM and qPCR technology. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dong, C.; Yan, S.; Lin, J.; Bao, H.; Tang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. Identification of Dendrobium officinale species and authentication of commercial products by DNA barcoding and high-resolution melting analysis. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2025, 46, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Liu, X.; Shao, J.; Lin, T.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H. Simultaneous identification and evaluation of multiple Dendrobium species by HPLC. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2018, 14, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; She, X.; Cao, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Su, L.; Wu, M.; Tong, H.; Ji, X. Comprehensive evaluation of Dendrobium officinale from different geographical origins using near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 277, 121249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Niu, Y.; Wei, S.; Tong, H.; Wu, M.; Yang, Y. Rapid Measurement of Antioxidant Properties of Dendrobium officinale Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Foods 2024, 13, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.Z. Authentication of Dendrobium Officinale from similar species with infrared and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopies with data visualization and mining. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1774–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancewicz, L.J.; Swift, M.L.; Penner, G.B.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Koenig, K.M.; Chibisa, G.E.; He, M.L.; McKinnon, J.J.; Yang, W.Z.; McAllister, T.A. Development of near-infrared spectroscopy calibrations to estimate fecal composition and nutrient digestibility in beef cattle. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 97, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, J.; Kong, W.; Huang, J. Trends in digital detection for the quality and safety of herbs using infrared and Raman spectroscopy. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1128300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, C.; Ding, Y.; Sun, H. Rapid indentification of auramine O dyeing adulteration in Dendrobium officinale, Saffron and Curcuma by SERS Raman spectroscopy combined with SSA-BP neural networks model. Foods 2023, 12, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Hu, W.; Wu, F.; He, Y. Polysaccharide determination and habitat classification for fresh Dendrobiums with hyperspectral imagery and modified RBFNN. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Sun, Z.; Qu, J.; He, Y.; Ma, F.; Sun, S. Structural analysis and identification of three Dendrobium species and their extracts using infrared spectroscopy. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 3407–3413. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.A.; Zhang, C.Y.; Li, L.; Si, M.Z. Comparative analysis of infrared spectra of four Dendrobium species. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2022, 42, 2989–2994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Cui, H.; Li, C.; Lin, L. A novel polyethylene oxide/Dendrobium officinale nanofiber: Preparation, characterization and application in pork packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 21, 100329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wan, J.; Liao, Y.; Liu, S.; Wei, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Dendrobium species regulate energy homeostasis in neurodegenerative diseases: A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 2151–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Cao, Y.; Yin, X.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Lee, Y.-W. Rapid and nondestructive quantification of deoxynivalenol in individual wheat kernels using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging and chemometrics. Food Control 2022, 131, 108420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Nirere, A.; Dusabe, K.D.; Yuhao, Z.; Adrien, G. Rapid and nondestructive watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) seed viability detection based on visible near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technology and machine learning algorithms. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 4403–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Yao, K.; Cao, Y.; Tang, N. Identification of maize seed varieties based on stacked sparse autoencoder and near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheto, J.H.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Ren, Y.; Bonah, E.; Alenyorege, E.A.; Lv, R.; Dai, C. Combination of spectra and image information of hyperspectral imaging data for fast prediction of lipid oxidation attributes in pork meat. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, e13225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aheto, J.H.; Huang, X.; Xiaoyu, T.; Bonah, E.; Ren, Y.; Alenyorege, E.A.; Chunxia, D. Investigation into crystal size effect on sodium chloride uptake and water activity of pork meat using hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 5009.3-2016; Determination of Moisture in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Kong, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Yuan, C.; Hou, L.; Wen, S. Discussion of Key Issues and Methodological Optimization in GB 5009.3—2016 National Food Safety Standard: Determination of Moisture in Food. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2025, 16, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Nirere, A.; Sun, J.; Atindana, V.A.; Hussain, A.; Zhou, X.; Yao, K. A comparative analysis of hybrid SVM and LS-SVM classification algorithms to identify dried wolfberry fruits quality based on hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16320. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, S.; Mao, H.; Wu, X.; Li, Q. Classification of black beans using visible and near infrared hyperspectral imaging. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1687–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, J.; Lu, B.; Chen, Q.; Xun, W.; Jin, Y. Classification of oolong tea varieties based on hyperspectral imaging technology and BOSS-LightGBM model. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, e13289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Nirere, A.; Wu, X.; Dai, R. Classification detection of saccharin jujube based on hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; Lu, B.; Dai, C. Research on apple origin classification based on variable iterative space shrinkage approach with stepwise regression–support vector machine algorithm and visible-near infrared hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, V.; Nourian, S.; Zhou, Z.; Rahimi, S.; Avramidis, S.; Cool, J. Classification and characterization of thermally modified timber using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy and artificial neural networks: A comparative study on the performance of different NDE methods and ANNs. Wood Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1093–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xuan, G.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y. Detection of adulterants and authenticity discrimination for coarse grain flours using NIR hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| System Components | Technical Index | Parameter Values |
|---|---|---|
| Imaging Spectrometer | Model | GaiaField-N17E, (Shuangli Hepu Technology Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China) |
| Spectral range | 870~1720 nm | |
| Spectral resolution | 5 nm | |
| Spectral sampling points | 3 nm | |
| Slit size | 30 μm × 12.5 nm | |
| Focal length | 30 mm | |
| Stray | <0.45% | |
| Luminous Efficiency | >50% | |
| Relative aperture | F/2.0 | |
| Imaging Lens | Type | HSIA-OLES30, (Shuangli Hepu Technology Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China) |
| Transmittance | ≥90% | |
| Field of view length | 300 nm | |
| Camera | Model | HSIA-CT, (Shuangli Hepu Technology Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China) |
| Full frame pixel count (spatial Dimension x spectral dimension) | 270 × 310 | |
| Time of exposure | 1~500 ms | |
| Calibrate Whiteboard | Size | 150 mm × 150 mm |
| tungsten-halogen lamp | Model | ModelsXC-130, (Shuangli Hepu Technology Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China) |
| Power | 150 W | |
| Electric Displacement Platform | Model | PSA200-11-X, (Shuangli Hepu Technology Co., Ltd., Wuxi, China) |
| Transmission speed | 0~25 mm/s |
| Pretreatment | Type | Calibration Set | Prediction Set | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | ||
| Raw | DA | 95 | 95 | 95 | 86 | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | 84 |
| DF | 100 | 90.91 | 83.33 | 100 | 90.91 | 83.33 | |||
| DT | 95 | 79.17 | 67.86 | 90 | 75 | 64.29 | |||
| DC | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| DO | 40 | 57.14 | 100 | 30 | 46.15 | 100 | |||
| Smoothing | DA | 95 | 95 | 95 | 88 | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | 84 |
| DF | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | 100 | 90.91 | 83.33 | |||
| DT | 95 | 79.17 | 67.86 | 90 | 75 | 64.29 | |||
| DC | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| DO | 50 | 66.67 | 100 | 30 | 46.15 | 100 | |||
| Normalize | DA | 95 | 97.44 | 100 | 97 | 40 | 57.14 | 100 | 88 |
| DF | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| DT | 100 | 97.56 | 95.24 | 100 | 76.92 | 62.5 | |||
| DC | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| DO | 90 | 94.74 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| SGolay | DA | 95 | 97.44 | 100 | 89 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 86 |
| DF | 85 | 91.89 | 100 | 80 | 88.89 | 100 | |||
| DT | 65 | 78.79 | 100 | 50 | 66.67 | 100 | |||
| DC | 100 | 93.02 | 86.96 | 100 | 90.91 | 83.33 | |||
| DO | 100 | 83.33 | 71.43 | 100 | 80 | 66.67 | |||
| Baseline | DA | 70 | 80 | 93.33 | 87 | 70 | 82.35 | 100 | 88 |
| DF | 95 | 90.48 | 86.36 | 100 | 90.91 | 83.33 | |||
| DT | 90 | 78.27 | 69.23 | 100 | 83.33 | 71.43 | |||
| DC | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |||
| DO | 80 | 86.49 | 94.12 | 70 | 82.35 | 100 | |||
| Pretreatment | Type | Calibration Set | Prediction Set | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | ||
| Raw | DA | 85 | 85 | 85 | 77 | 90 | 87.8 | 85.71 | 76 |
| DF | 90 | 81.82 | 75 | 90 | 83.33 | 76.19 | |||
| DT | 85 | 70.83 | 60.71 | 80 | 69.57 | 59.26 | |||
| DC | 90 | 90 | 90 | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | |||
| DO | 35 | 51.85 | 87.5 | 30 | 42.86 | 85.71 | |||
| Smoothing | DA | 85 | 85 | 85 | 79 | 90 | 87.8 | 85.71 | 76 |
| DF | 90 | 85.71 | 81.82 | 90 | 83.33 | 76.19 | |||
| DT | 85 | 70.83 | 60.71 | 80 | 69.57 | 59.26 | |||
| DC | 90 | 90 | 90 | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | |||
| DO | 45 | 60 | 81.82 | 30 | 42.86 | 85.71 | |||
| Normalize | DA | 85 | 87.18 | 89.47 | 87 | 40 | 52.17 | 85.71 | 80 |
| DF | 90 | 85.71 | 81.82 | 90 | 91.84 | 90 | |||
| DT | 90 | 87.8 | 85.71 | 90 | 70.59 | 57.14 | |||
| DC | 90 | 90 | 90 | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | |||
| DO | 80 | 85.11 | 90.91 | 90 | 91.84 | 90 | |||
| SGolay | DA | 85 | 87.18 | 89.47 | 80 | 90 | 91.84 | 90 | 78 |
| DF | 75 | 82.76 | 92.31 | 70 | 81.82 | 90 | |||
| DT | 55 | 70.97 | 91.67 | 40 | 60.87 | 87.50 | |||
| DC | 90 | 83.72 | 78.26 | 90 | 83.33 | 76.19 | |||
| DO | 90 | 75 | 64.29 | 90 | 73.47 | 60 | |||
| Baseline | DA | 65 | 72.22 | 81.25 | 78 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 80 |
| DF | 85 | 81.4 | 77.78 | 90 | 83.33 | 76.19 | |||
| DT | 80 | 70.59 | 63.16 | 90 | 76.19 | 64 | |||
| DC | 90 | 90 | 90 | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | |||
| DO | 70 | 77.78 | 87.50 | 60 | 75 | 90 | |||
| Method | Type | Calibration Set | Prediction Set | Independent Validation Set | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | ||
| CARS | DA | 95 | 95 | 95 | 98 | 100 | 95.24 | 90.91 | 96 | 100 | 97.09 | 94.34 | 98 |
| DF | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90.91 | 83.33 | 100 | 92.31 | 85.71 | ||||
| DT | 95 | 95 | 95 | 90 | 75 | 64.29 | 90 | 76.60 | 66.67 | ||||
| DC | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100.00 | 100.00 | ||||
| DO | 100 | 100 | 100 | 30 | 46.15 | 100 | 40 | 57.14 | 100.00 | ||||
| Method | Type | Calibration Set | Prediction Set | Independent Validation Set | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | Precision (%) | Model Accuracy (%) | ||
| SPA | DA | 80 | 82.05 | 84.21 | 93 | 50 | 62.50 | 83.33 | 88 | 60 | 70.59 | 85.71 | 90 |
| DF | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||
| DT | 85 | 82.93 | 80.95 | 90 | 75 | 64.29 | 90 | 78.26 | 69.23 | ||||
| DC | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||
| DO | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Guo, Y.; Zhong, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, B.; Fang, H.; Yao, L.; Zhao, C. Rapid Identification of Dendrobium Species Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Sensors 2025, 25, 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185625
Li K, Guo Y, Zhong H, Jin Y, Li B, Fang H, Yao L, Zhao C. Rapid Identification of Dendrobium Species Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185625
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kaixuan, Yijun Guo, Haosheng Zhong, Yiqi Jin, Bin Li, Huimin Fang, Lijian Yao, and Chao Zhao. 2025. "Rapid Identification of Dendrobium Species Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Technology" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185625
APA StyleLi, K., Guo, Y., Zhong, H., Jin, Y., Li, B., Fang, H., Yao, L., & Zhao, C. (2025). Rapid Identification of Dendrobium Species Using Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Sensors, 25(18), 5625. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185625








