Robust Visual-Inertial Odometry with Learning-Based Line Features in a Illumination-Changing Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We present a novel learning-based visual-inertial odometry system that incorporates illumination-invariant line features trained via attraction fields.
- (2)
- We develop an efficient filtering and matching pipeline that ensures geometric consistency of extracted lines, even under changing light and noisy conditions.
- (3)
- We validate our method on challenging benchmark datasets with synthetic lighting perturbations, demonstrating significant improvements in trajectory accuracy and robustness over existing point- and line-based VIO systems.
2. Related Work
2.1. Visual-Inertial Odometry
2.2. Line Features in SLAM and VIO
2.3. Deep Learning for SLAM and Feature Detection
2.4. Our Contribution
3. Methodology
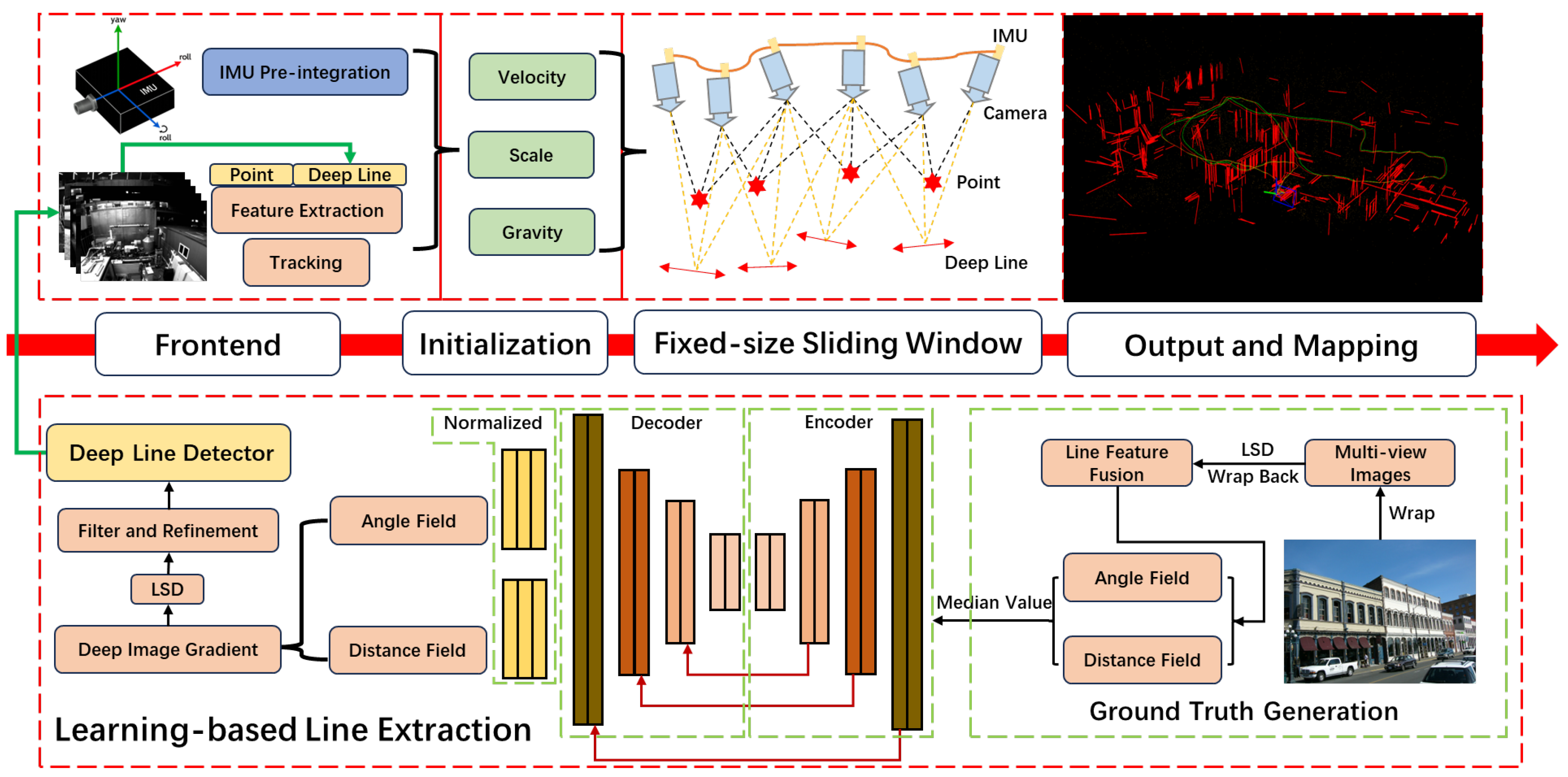
3.1. System Overview
- A.
- Feature Extraction and Tracking
- B.
- IMU Pre-integration Modeling
- C.
- Visual-Inertial Initialization
- D.
- Sliding Window Optimization and Residual Modeling
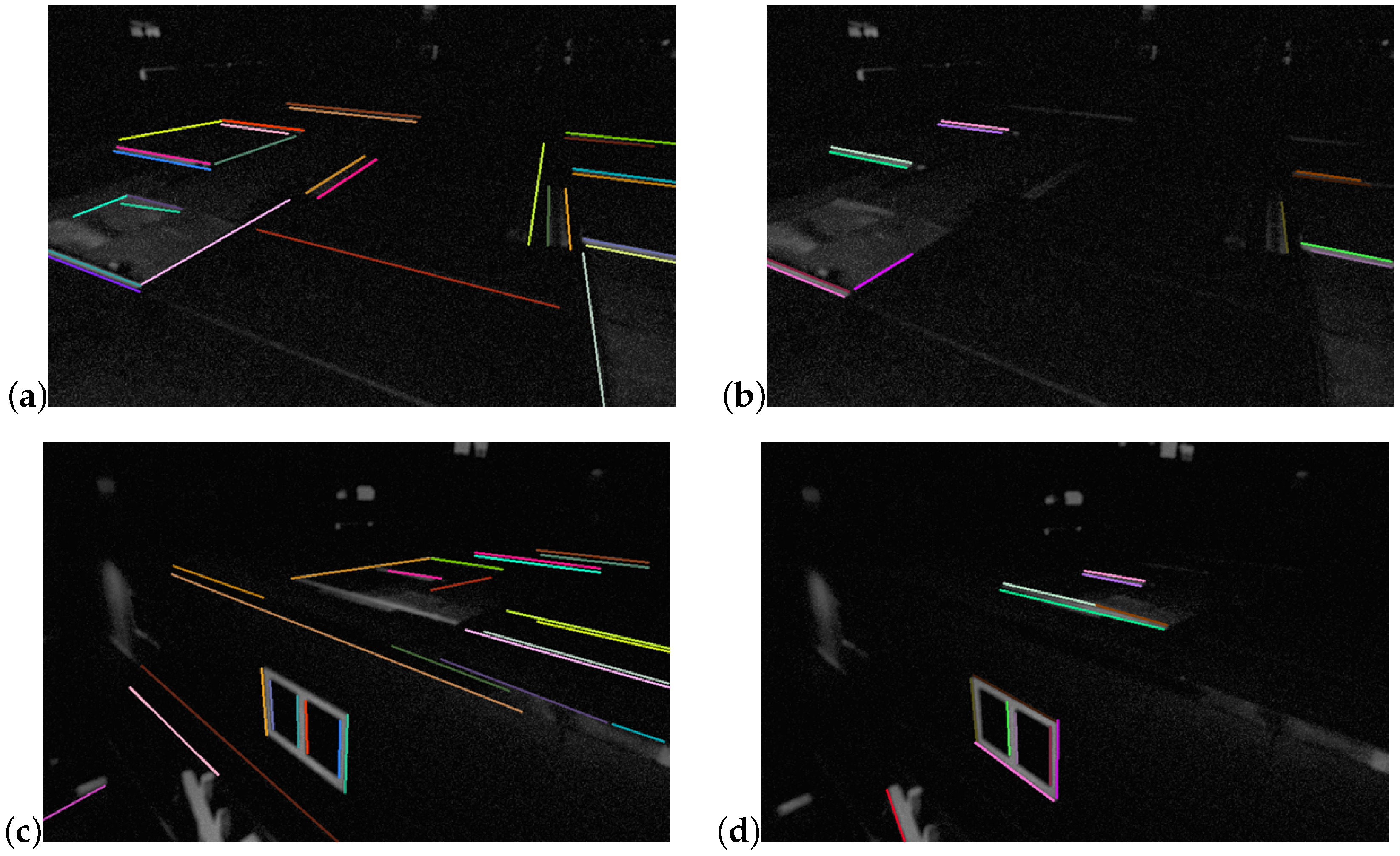
3.2. Learning-Based Line Extraction
3.3. DeepLine-Enhanced Visual-IMU Odometry with Efficient Line Filtering and Matching
4. Experimental Results
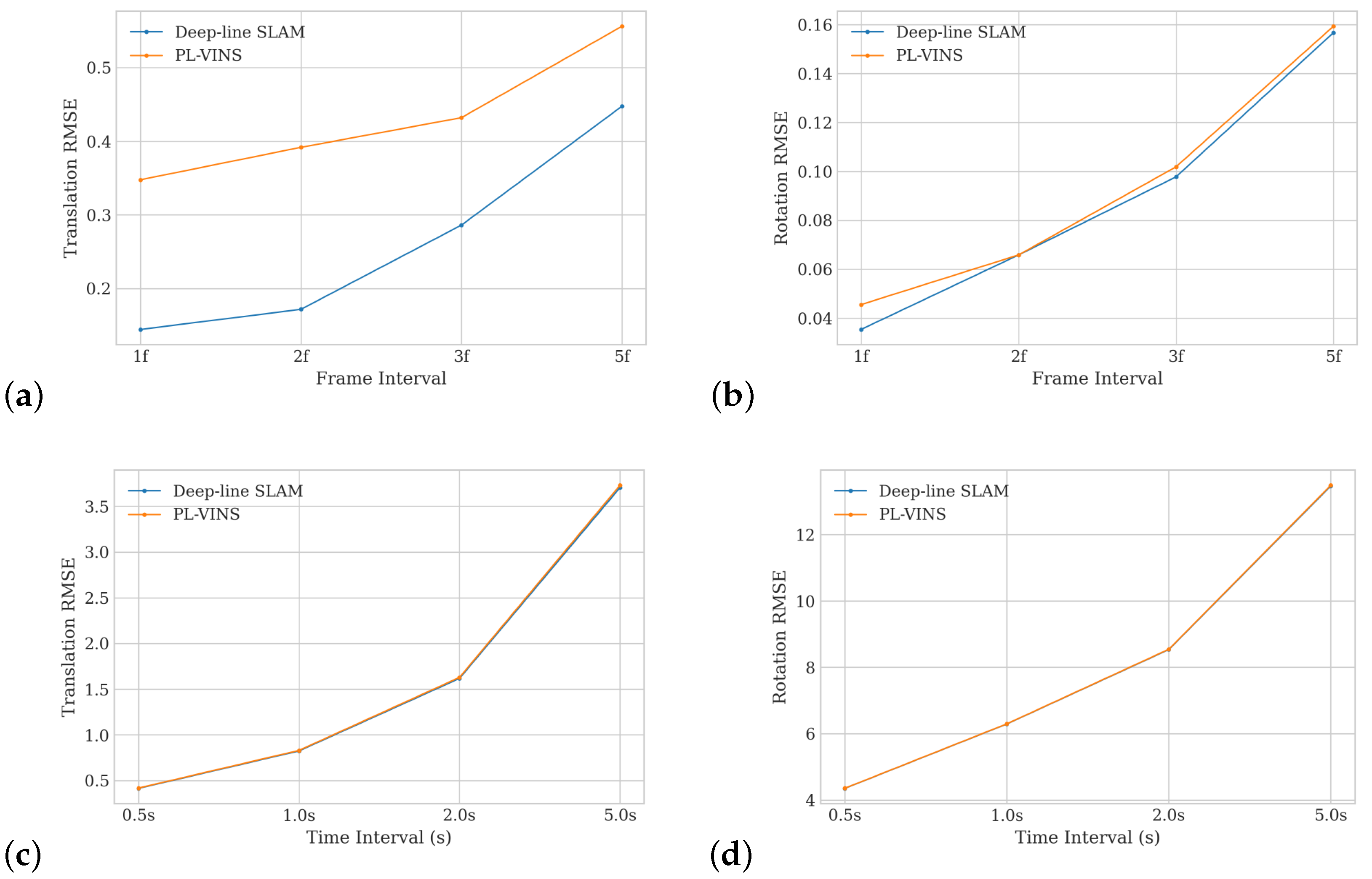
4.1. Accuracy
4.2. Real-Time Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Yuan, S.; Cao, M.; Nguyen, T.M.; Cao, K.; Xie, L. HCTO: Optimality-aware LiDAR inertial odometry with hybrid continuous time optimization for compact wearable mapping system. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 211, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; Liang, F.; Yang, B.; Dong, Z. Reliable-loc: Robust sequential LiDAR global localization in large-scale street scenes based on verifiable cues. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2025, 224, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Habib, A. NRLI-UAV: Non-rigid registration of sequential raw laser scans and images for low-cost UAV LiDAR point cloud quality improvement. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 158, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nguyen, T.M.; Cao, M.; Yuan, S.; Hung, T.Y.; Xie, L. Graph Optimality-Aware Stochastic LiDAR Bundle Adjustment with Progressive Spatial Smoothing. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.14565. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhou, W.; Cao, Y.; Zha, H. Adaptive vio: Deep visual-inertial odometry with online continual learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 18019–18028. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, C.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X. A Low-Cost 3D SLAM System Integration of Autonomous Exploration Based on Fast-ICP Enhanced LiDAR-Inertial Odometry. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, H.; Xia, Z.C. SLAM; definition and evolution. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 97, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Leng, Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, T.; Cao, M.; Nguyen, T.M.; Yuan, S.; Cao, K.; Xie, L. HelmetPoser: A Helmet-Mounted IMU Dataset for Data-Driven Estimation of Human Head Motion in Diverse Conditions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.05006. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G. Visual-inertial navigation: A concise review. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 9572–9582. [Google Scholar]
- Santoso, F.; Garratt, M.A.; Anavatti, S.G. Visual–inertial navigation systems for aerial robotics: Sensor fusion and technology. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourikis, A.I.; Roumeliotis, S.I. A multi-state constraint Kalman filter for vision-aided inertial navigation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 3565–3572. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Li, P.; Shen, S. Vins-mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutenegger, S. Okvis2: Realtime scalable visual-inertial slam with loop closure. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.09199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Geneva, P.; Eckenhoff, K.; Huang, G. Visual-inertial odometry with point and line features. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 4–8 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 2447–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Ali, I.; Guo, F.; He, Y.; Zhang, H. PL-VINS: Real-time monocular visual-inertial SLAM with point and line features. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.07462. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Park, S.Y. PLF-VINS: Real-time monocular visual-inertial SLAM with point-line fusion and parallel-line fusion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7033–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Dong, Z.; Yang, B. DeepAAT: Deep Automated Aerial Triangulation for Fast UAV-based Mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 134, 104190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokssit, S.; Licea, D.B.; Guermah, B.; Ghogho, M. Deep learning techniques for visual SLAM: A survey. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 20026–20050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, S.; Gu, D. DeepSLAM: A robust monocular SLAM system with unsupervised deep learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yin, M.; Li, G.; Yang, F. SP-Flow: Self-supervised optical flow correspondence point prediction for real-time SLAM. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 2020, 82, 101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grompone von Gioi, R.; Jakubowicz, J.; Morel, J.M.; Randall, G. LSD: A fast line segment detector with a false detection control. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, K.; Yuan, S.; Xie, L. Ua-mpc: Uncertainty-aware model predictive control for motorized lidar odometry. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 3652–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Yuan, S.; Xu, F.; Xie, L. Limo-calib: On-site fast lidar-motor calibration for quadruped robot-based panoramic 3d sensing system. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12655. [Google Scholar]
- Seok, H.; Lim, J. ROVINS: Robust omnidirectional visual inertial navigation system. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6225–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; He, W.; Yuan, K. PL-VIO: Tightly-coupled monocular visual–inertial odometry using point and line features. Sensors 2018, 18, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Pang, M.; Wang, M. A new visual inertial simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm based on point and line features. Drones 2022, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Fang, Z.; Luo, X.; Liu, W. Accurate and robust visual SLAM with a novel ray-to-ray line measurement model. Image Vis. Comput. 2023, 140, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, J.; Qiu, X.; Rong, Z.; Zou, X. Dynamic-SLAM: Semantic monocular visual localization and mapping based on deep learning in dynamic environment. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 117, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Luo, S.; Huang, X. Real-time dynamic SLAM algorithm based on deep learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 87754–87766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautrat, R.; Barath, D.; Larsson, V.; Oswald, M.R.; Pollefeys, M. Deeplsd: Line segment detection and refinement with deep image gradients. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17327–17336. [Google Scholar]
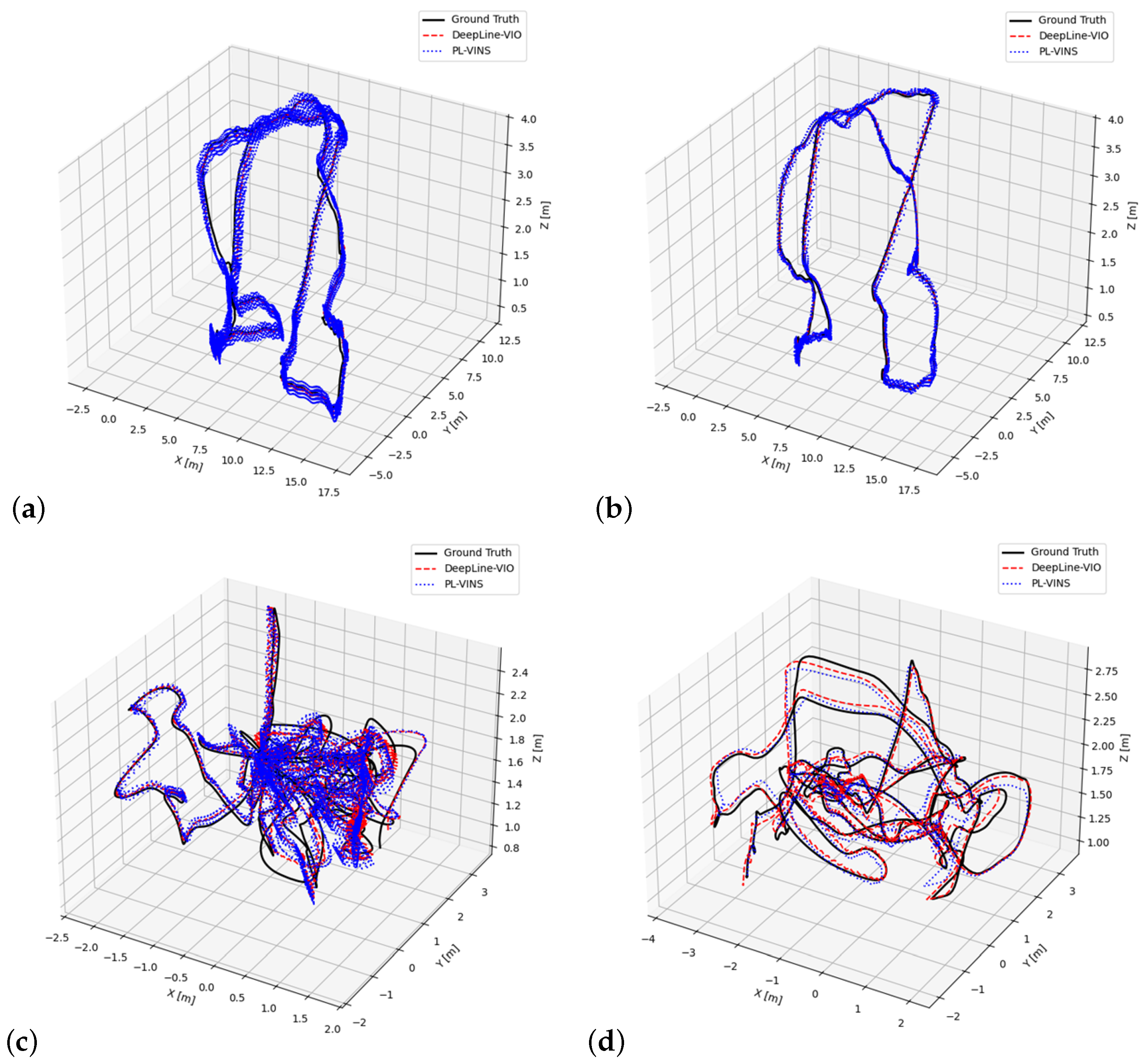



| Dataset | PL-VINS | DeepLine-VIO | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MH_05_difficult | 0.3329 | 0.2801 | 15.87 |
| MH_04_difficult | 0.2707 | 0.2305 | 14.85 |
| V1_03_difficult | 0.1663 | 0.1473 | 11.41 |
| V2_03_difficult | 0.2412 | 0.2127 | 11.82 |
| MH_03_medium | 0.2320 | 0.2254 | 2.86 |
| V1_02_medium | 0.1249 | 0.1243 | 0.49 |
| V2_02_medium | 0.1375 | 0.1284 | 6.67 |
| MH_02_easy | 0.1621 | 0.1618 | 0.15 |
| MH_01_easy | 0.1473 | 0.1473 | 0.04 |
| V1_01_easy | 0.0744 | 0.0737 | 0.92 |
| Dataset | PL-VINS | DeepLine-VIO | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outdoors1 | 58.6819 | 55.3845 | 5.62 |
| Outdoors2 | 118.3505 | 114.9687 | 2.86 |
| Outdoors3 | 25.0901 | 21.6994 | 13.51 |
| Outdoors4 | 9.5543 | 9.6601 | −1.11 |
| Outdoors5 | 24.8762 | 15.0594 | 39.46 |
| Outdoors6 | 133.5429 | 118.7678 | 11.06 |
| Outdoors7 | 33.0223 | 31.2352 | 5.41 |
| Outdoors8 | 24.2436 | 24.0311 | 0.88 |
| Dataset | PL-VINS | DeepLine-VIO | Change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trans_RMSE | Rot_RMSE | Trans_RMSE | Rot_RMSE | Trans_RMSE | Rot_RMSE | |
| MH_05_difficult | 0.3477 | 0.0455 | 0.1445 | 0.0354 | 58.43% | 22.30% |
| MH_04_difficult | 0.2283 | 0.0497 | 0.1462 | 0.0550 | 35.95% | −10.56% |
| V1_03_difficult | 0.1694 | 0.1306 | 0.1319 | 0.1031 | 22.14% | 21.03% |
| V2_03_difficult | 0.1090 | 0.1562 | 0.1088 | 0.1620 | 0.18% | −3.71% |
| MH_03_medium | 0.1641 | 0.0469 | 0.1617 | 0.0618 | 1.44% | −31.79% |
| V1_02_medium | 0.1453 | 0.1706 | 0.1453 | 0.1706 | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| V2_02_medium | 0.1209 | 0.1024 | 0.1195 | 0.1200 | 1.19% | −17.13% |
| MH_02_easy | 0.0780 | 0.0627 | 0.0780 | 0.0627 | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| MH_01_easy | 0.0801 | 0.0635 | 0.0801 | 0.0635 | −0.01% | 0.00% |
| V1_01_easy | 0.0751 | 0.0876 | 0.0751 | 0.0876 | −0.01% | 0.00% |
| Dataset | PL-VINS | DeepLine-VIO | Change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trans_RMSE | Rot_RMSE | Trans_RMSE | Rot_RMSE | Trans_RMSE | Rot_RMSE | |
| MH_05_difficult | 3.7319 | 13.4837 | 3.7060 | 13.4624 | −0.69% | −0.16% |
| MH_04_difficult | 4.0944 | 13.9614 | 4.0567 | 13.9507 | −0.92% | −0.08% |
| V1_03_difficult | 0.1380 | 27.7495 | 0.1428 | 27.7437 | 3.47% | −0.02% |
| V2_03_difficult | 4.9929 | 28.4594 | 5.0185 | 28.3558 | 0.51% | −0.36% |
| MH_03_medium | 8.1860 | 15.7445 | 8.1816 | 15.7446 | −0.05% | 0.00% |
| V1_02_medium | 1.2568 | 26.4574 | 1.2578 | 26.4575 | 0.08% | 0.00% |
| V2_02_medium | 4.5907 | 26.3838 | 4.5908 | 26.4043 | 0.00% | 0.08% |
| MH_02_easy | 4.6397 | 14.8012 | 4.6396 | 14.8014 | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| MH_01_easy | 3.8185 | 14.0366 | 3.8184 | 14.0363 | 0.00% | 0.00% |
| V1_01_easy | 0.4343 | 20.1465 | 0.4341 | 20.1458 | −0.05% | 0.00% |
| Dataset | PL-VINS | DeepLine-VIO | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MH_05_difficult | 22.6305 | 32.9479 | 45.59 |
| MH_04_difficult | 23.7498 | 30.6881 | 29.21 |
| V1_03_difficult | 16.0668 | 18.3584 | 14.26 |
| V2_03_difficult | 15.0747 | 16.8990 | 12.10 |
| Threads | Modules | Times (ms) | System Frame Rate (Hz) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL-VINS | Deepline-VIO | PL-VINS | Deepline-VIO | ||
| 1 | Point Detection and Tracking | 6.1 | 6.01 | ||
| Line Detection | 5.3 | 44.5 | 10 | 10 | |
| Line Tracking | 9.3 | 9.61 | |||
| 2 | Local VIO | 43.2 | 43.8 | 10 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, C.; Yan, X. Robust Visual-Inertial Odometry with Learning-Based Line Features in a Illumination-Changing Environment. Sensors 2025, 25, 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165029
Li X, Liu C, Yan X. Robust Visual-Inertial Odometry with Learning-Based Line Features in a Illumination-Changing Environment. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinkai, Cong Liu, and Xu Yan. 2025. "Robust Visual-Inertial Odometry with Learning-Based Line Features in a Illumination-Changing Environment" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165029
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, C., & Yan, X. (2025). Robust Visual-Inertial Odometry with Learning-Based Line Features in a Illumination-Changing Environment. Sensors, 25(16), 5029. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165029






