Measuring Asymmetric Ionic Current Waveform Through Micropores for Detecting Reduced Red Blood Cell Deformability Due to Plasmodium falciparum Infection
Abstract
Highlights
- A microfluidic RBC deformability sensor was developed using the resistive pulse method.
- The asymmetric waveform detected by the sensor may be a reliable indicator of reduced deformability.
- This novel sensor allows for a detailed single-cell analysis of malaria-associated deformability reduction.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
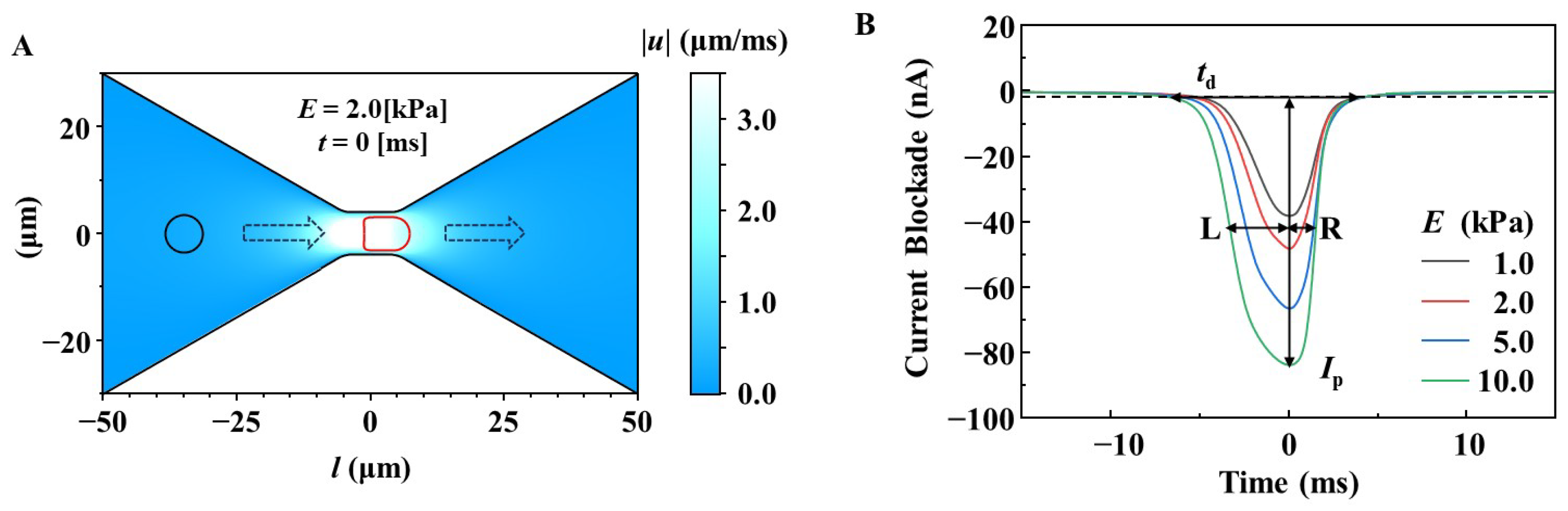
2.1. Multiphysics Simulations of Ionic Current Waveform for RBCs with Different Membrane Stiffness
2.2. Parasite Culture
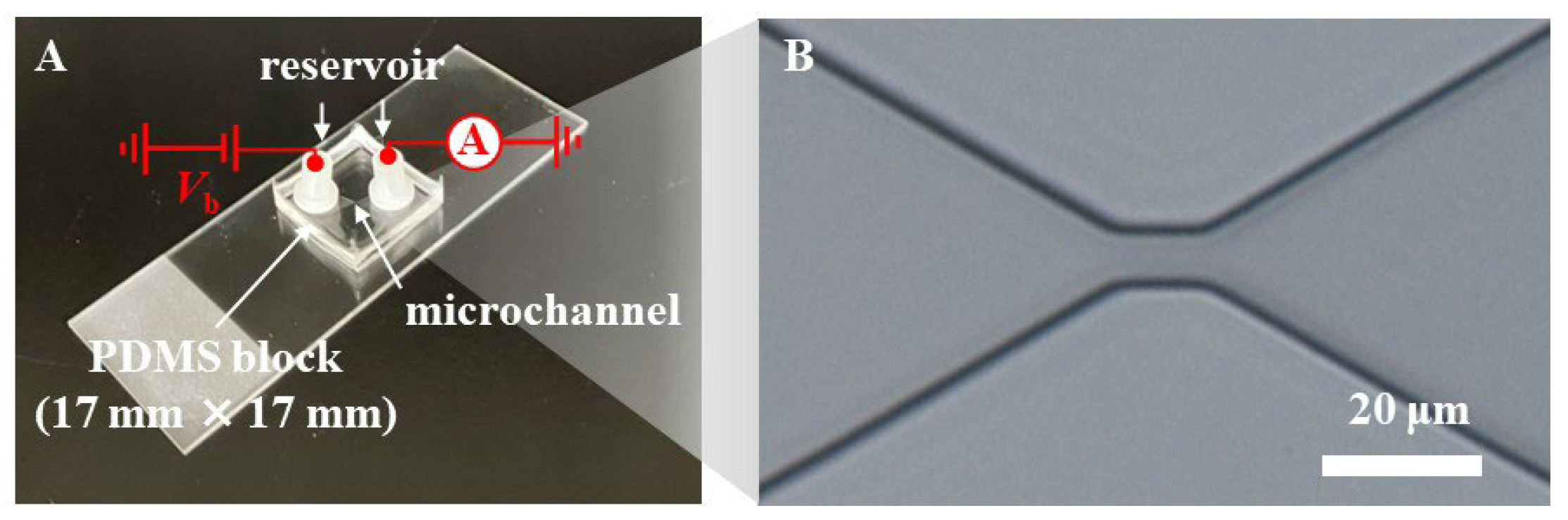
2.3. Preparation of Microfluidic RBC Deformability Sensor
2.4. Ionic Current Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design of Microfluidic RBC Deformability Sensors for Measuring RBC Deformability Using a Multi-Physics Simulation Approach
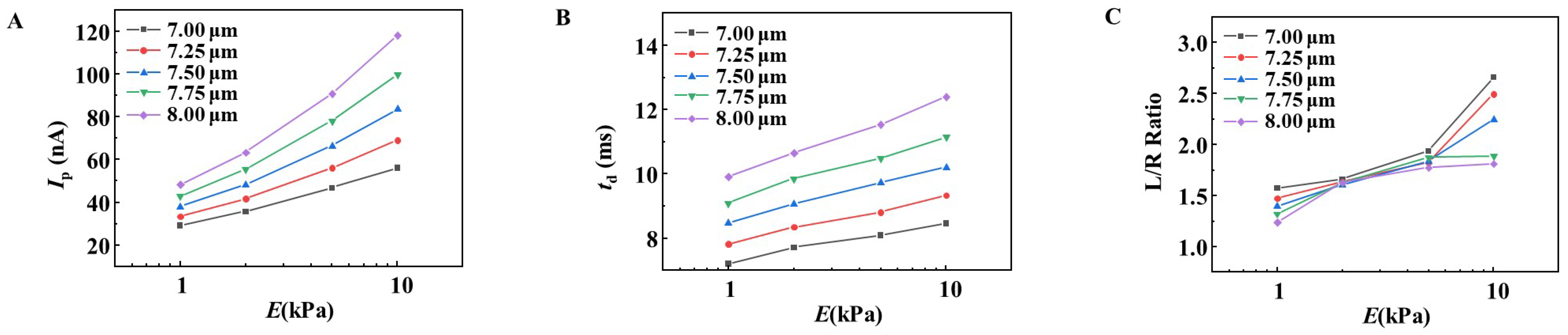
3.2. Simulation of the Effect of RBC Size on the Changes in Ip, td, and L/R Ratio
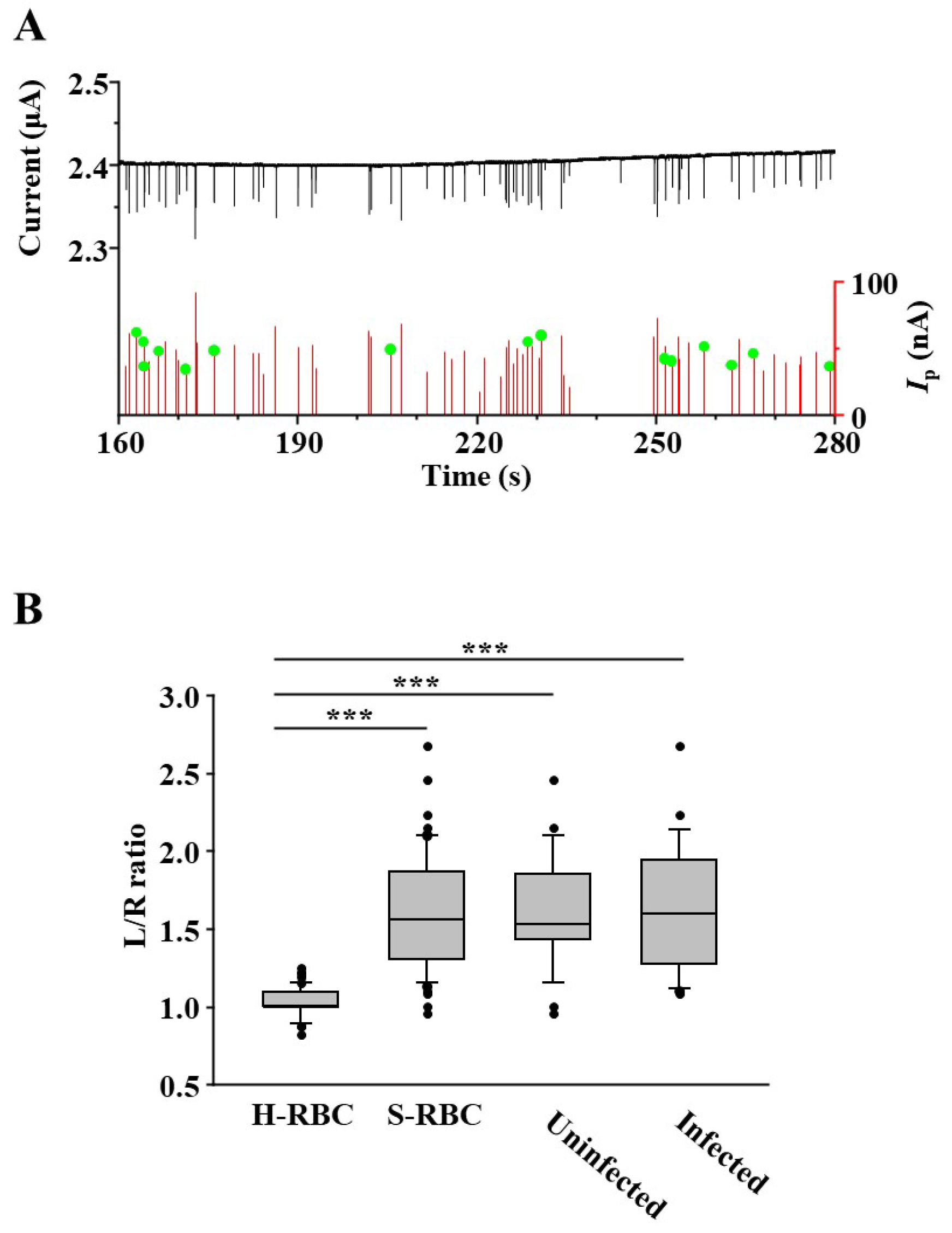
3.3. Measurement of Deformability of P. falciparum-Infected RBCs Using a Microfluidic RBC Deformability Sensor
3.4. Detection of RBC with P. falciparum Inside Using Microfluidic RBC Deformability Sensors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parthasarathi, K.; Lipowsky, H.H. Capillary recruitment in response to tissue hypoxia and its dependence on red blood cell deformability. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, H2145–H2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHedlishvili, G. Disturbed blood flow structuring as critical factor of hemorheological disorders in microcirculation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 1998, 19, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barshtein, G.; Ben-Ami, R.; Yedgar, S. Role of red blood cell flow behavior in hemodynamics and hemostasis. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2007, 5, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Gelmont, D.; Meiselman, H.J. Red blood cell deformability in sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, J.; Johnson, C.S. Rheology of the sickle cell disorders. Baillieres Clin. Haematol. 1987, 1, 747–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrean, V.; Suciu, I.; Sampelean, D.; Cozma, A. Rheological changes in diabetic microangiopathy. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 42, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Kowal, P.; Marcinkowska-Gapinska, A. Hemorheological changes dependent on the time from the onset of ischemic stroke. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 258, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Angus, B.J.; Hardeman, M.R.; Chotivanich, K.T.; Silamut, K.; Ruangveerayuth, R.; Kager, P.A.; White, N.J.; Vreeken, J. Prognostic significance of reduced red blood cell deformability in severe falciparum malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 57, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranston, H.A.; Boylan, C.W.; Carroll, G.L.; Sutera, S.P.; Williamson, J.R.; Gluzman, I.Y.; Krogstad, D.J. Plasmodium falciparum maturation abolishes physiologic red cell deformability. Science 1984, 223, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.E.; Russell, B.; Grigg, M.J.; Zhang, R.; William, T.; Amir, A.; Lau, Y.L.; Chatfield, M.D.; Dondorp, A.M.; Anstey, N.M.; et al. Reduced red blood cell deformability in Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, K.M.; Jones, G.L.; Saul, A.; Smith, R. A Plasmodium falciparum exo-antigen alters erythrocyte membrane deformability. FEBS Lett. 1991, 292, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioka, H.; Ghose, A.; Charunwatthana, P.; Maude, R.; Plewes, K.; Kingston, H.; Intharabut, B.; Woodrow, C.; Chotivanich, K.; Sayeed, A.A.; et al. Sequestration and Red Cell Deformability as Determinants of Hyperlactatemia in Falciparum Malaria. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnam, J.T.T.; Grigg, M.J.; Dondorp, A.M.; William, T.; Rajasekhar, M.; Rajahram, G.; Simpson, J.A.; Barber, B.E.; Anstey, N.M. Reduced Red Blood Cell Deformability in Vivax Malaria. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 231, e566–e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, J.; Buffet, P.A.; Ciceron, L.; Milon, G.; Mercereau-Puijalon, O.; Safeukui, I. Reduced erythrocyte deformability associated with hypoargininemia during Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Hardeman, M.R.; Uyuklu, M.; Ulker, P.; Cengiz, M.; Nemeth, N.; Shin, S.; Alexy, T.; Meiselman, H.J. Parameterization of red blood cell elongation index--shear stress curves obtained by ektacytometry. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2009, 69, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, K.; Lamoureux, E.S.; Myrand-Lapierre, M.E.; Duffy, S.P.; Ma, H. Technologies for measuring red blood cell deformability. Lab. Chip 2022, 22, 1254–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Microfluidic and Nanofluidic Resistive Pulse Sensing: A Review. Micromachines 2017, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, M.; Yoshida, T.; Yokota, K.; Yasaki, H.; Yasui, T.; Arima, A.; Tonomura, W.; Nagashima, K.; Yanagida, T.; Kaji, N.; et al. Discriminating single-bacterial shape using low-aspect-ratio pores. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusko, E.C.; Bruhn, B.R.; Eggenberger, O.M.; Houghtaling, J.; Rollings, R.C.; Walsh, N.C.; Nandivada, S.; Pindrus, M.; Hall, A.R.; Sept, D.; et al. Real-time shape approximation and fingerprinting of single proteins using a nanopore. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryuzaki, S.; Tsutsui, M.; He, Y.; Yokota, K.; Arima, A.; Morikawa, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Kawai, T. Rapid structural analysis of nanomaterials in aqueous solutions. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 155501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmandi, N.; Van Roy, W.; Lagae, L.; Borghs, G. Measuring the electric charge and zeta potential of nanometer-sized objects using pyramidal-shaped nanopores. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8490–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Nguyen, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y. Electrical measurement of red blood cell deformability on a microfluidic device. Lab. Chip 2013, 13, 3275–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvish, A.; Goyal, G.; Aneja, R.; Sundaram, R.V.; Lee, K.; Ahn, C.W.; Kim, K.B.; Vlahovska, P.M.; Kim, M.J. Nanoparticle mechanics: Deformation detection via nanopore resistive pulse sensing. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14420–14431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yatsushiro, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Kajimoto, K.; Ido, Y.; Abe, K.; Sofue, Y.; Nogami, T.; Hayashi, T.; Nagatomi, K.; et al. Development of a highly sensitive, quantitative, and rapid detection system for Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells using a fluorescent blue-ray optical system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.K.; Kong, T.F.; Ng, C.S.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Bhagat, A.A.; Nguyen, N.T.; Preiser, P.R.; Han, J. Micromagnetic resonance relaxometry for rapid label-free malaria diagnosis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Kajimoto, K.; Tanaka, M.; Murayama, S.; Tsutsui, M.; Nakajima, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Kataoka, M. Effect of Electrolyte Concentration on Cell Sensing by Measuring Ionic Current Waveform through Micropores. Biosensors 2021, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodeyri, Z.; Taghipoor, M. Multivariate analysis of nanoparticle translocation through a nanopore to improve the accuracy of resistive pulse sensing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 5097–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruatrachue, M.; Na-Nakorn, S. Red blood cell morphology in falciparum malaria. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 47, 665–669. [Google Scholar]
- Ciasca, G.; Papi, M.; Di Claudio, S.; Chiarpotto, M.; Palmieri, V.; Maulucci, G.; Nocca, G.; Rossi, C.; De Spirito, M. Mapping viscoelastic properties of healthy and pathological red blood cells at the nanoscale level. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17030–17037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safeukui, I.; Correas, J.M.; Brousse, V.; Hirt, D.; Deplaine, G.; Mulé, S.; Lesurtel, M.; Goasguen, N.; Sauvanet, A.; Couvelard, A.; et al. Retention of Plasmodium falciparum ring-infected erythrocytes in the slow, open microcirculation of the human spleen. Blood 2008, 112, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Miao, J.; Cui, L.; Guan, W. High-throughput and label-free parasitemia quantification and stage differentiation for malaria-infected red blood cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yokota, K.; Hirano, K.; Kajimoto, K.; Hashimoto, M. Measuring Asymmetric Ionic Current Waveform Through Micropores for Detecting Reduced Red Blood Cell Deformability Due to Plasmodium falciparum Infection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154722
Yokota K, Hirano K, Kajimoto K, Hashimoto M. Measuring Asymmetric Ionic Current Waveform Through Micropores for Detecting Reduced Red Blood Cell Deformability Due to Plasmodium falciparum Infection. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154722
Chicago/Turabian StyleYokota, Kazumichi, Ken Hirano, Kazuaki Kajimoto, and Muneaki Hashimoto. 2025. "Measuring Asymmetric Ionic Current Waveform Through Micropores for Detecting Reduced Red Blood Cell Deformability Due to Plasmodium falciparum Infection" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154722
APA StyleYokota, K., Hirano, K., Kajimoto, K., & Hashimoto, M. (2025). Measuring Asymmetric Ionic Current Waveform Through Micropores for Detecting Reduced Red Blood Cell Deformability Due to Plasmodium falciparum Infection. Sensors, 25(15), 4722. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154722





