Electric Field Measurement in Radiative Hyperthermia Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. E-Field Sensor’s Structure
2.2. Simulation Analysis
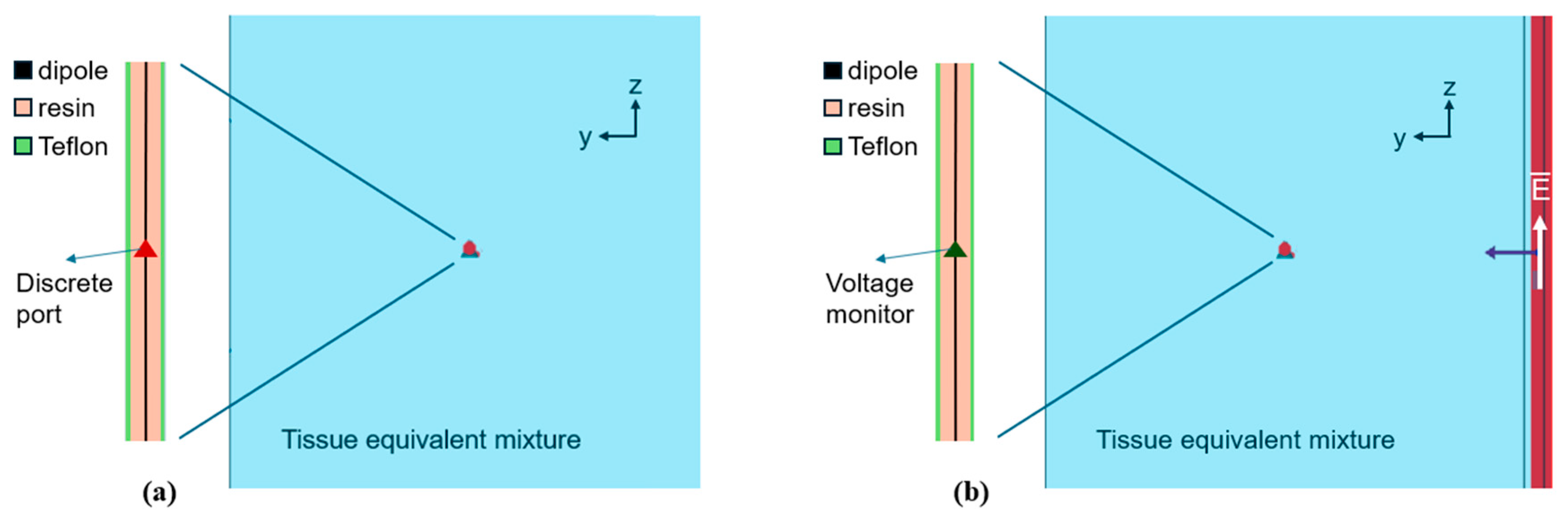
2.2.1. Electromagnetic Simulations
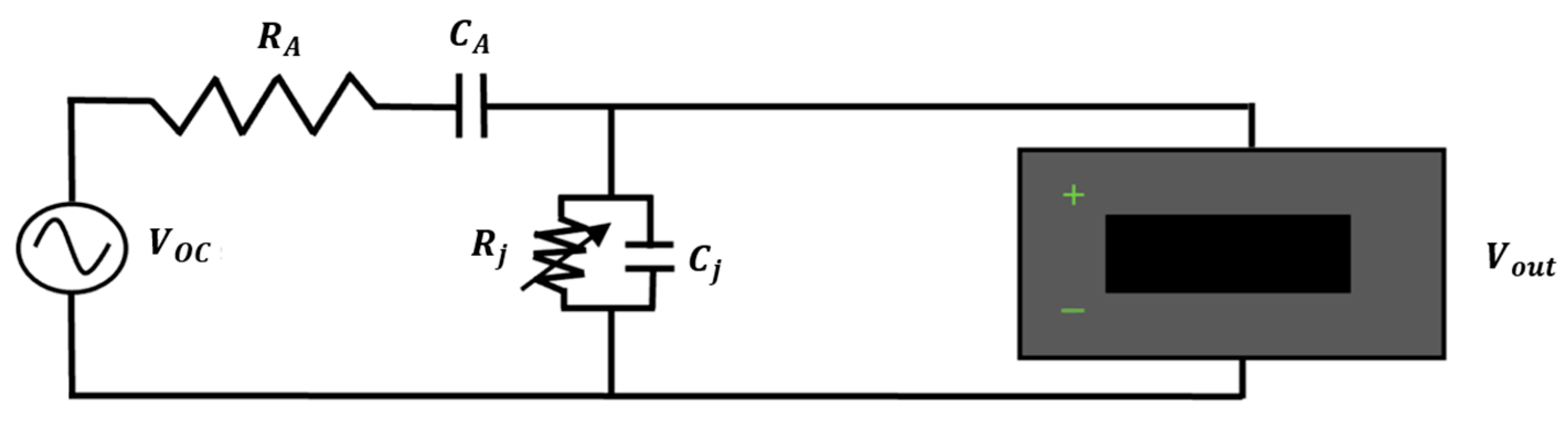
2.2.2. Circuit Simulation
2.3. Experimental Analysis
2.3.1. Choice of the Optimal Sensor Configuration
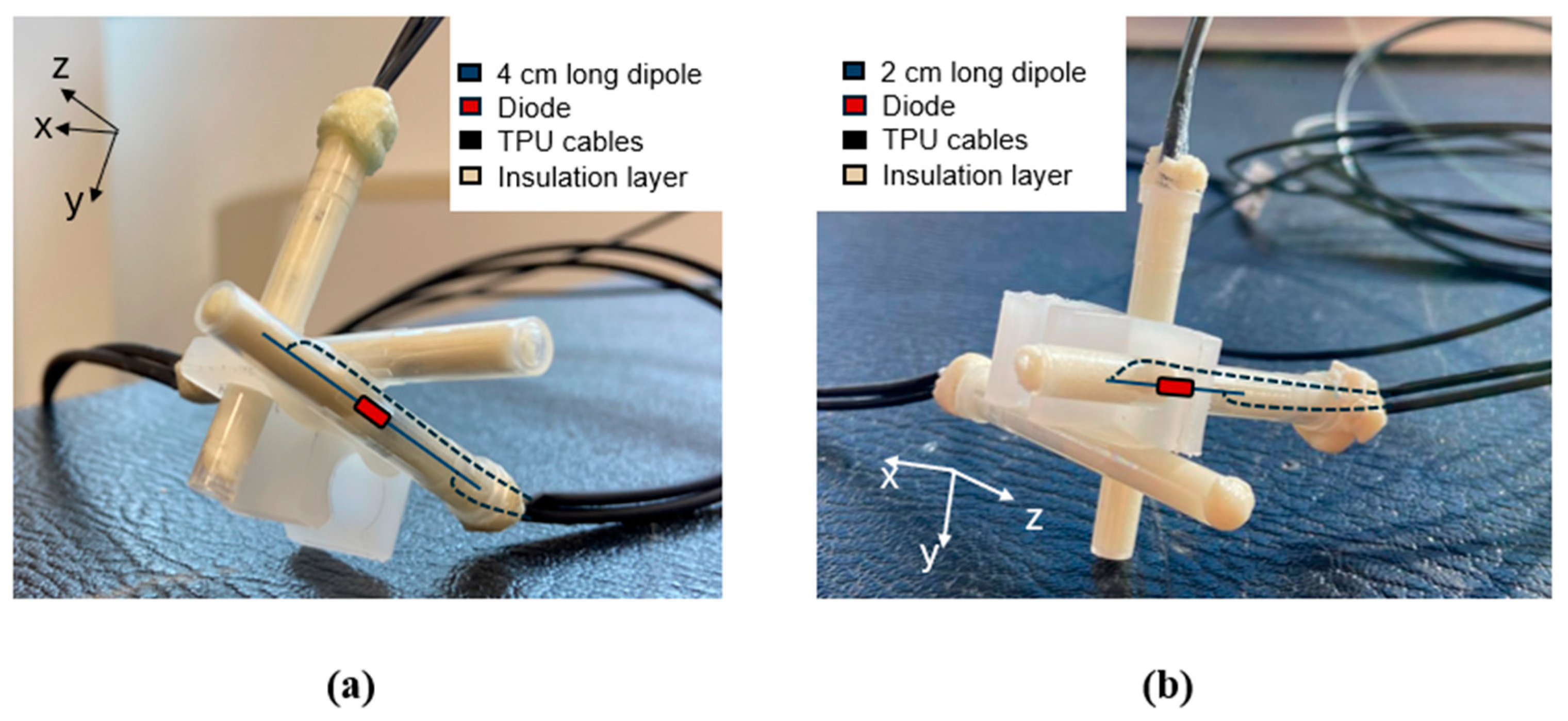
2.3.2. Realization of the E-Field Sensors
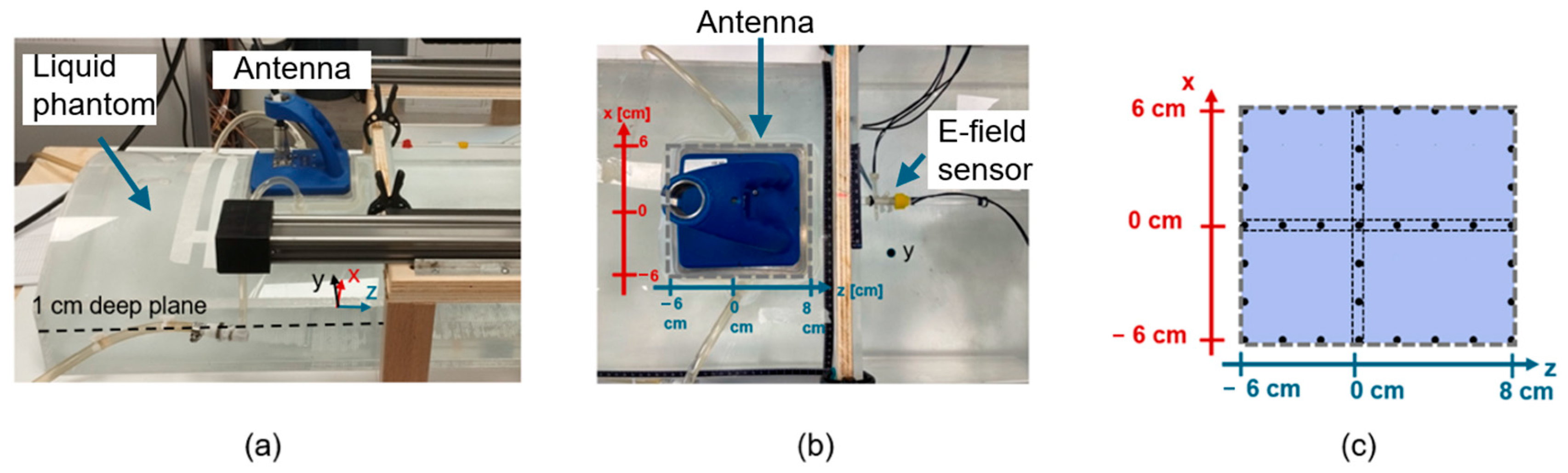
2.3.3. Experimental Setup: Phantoms and Mixtures
2.3.4. Measurements’ Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Numerical Results
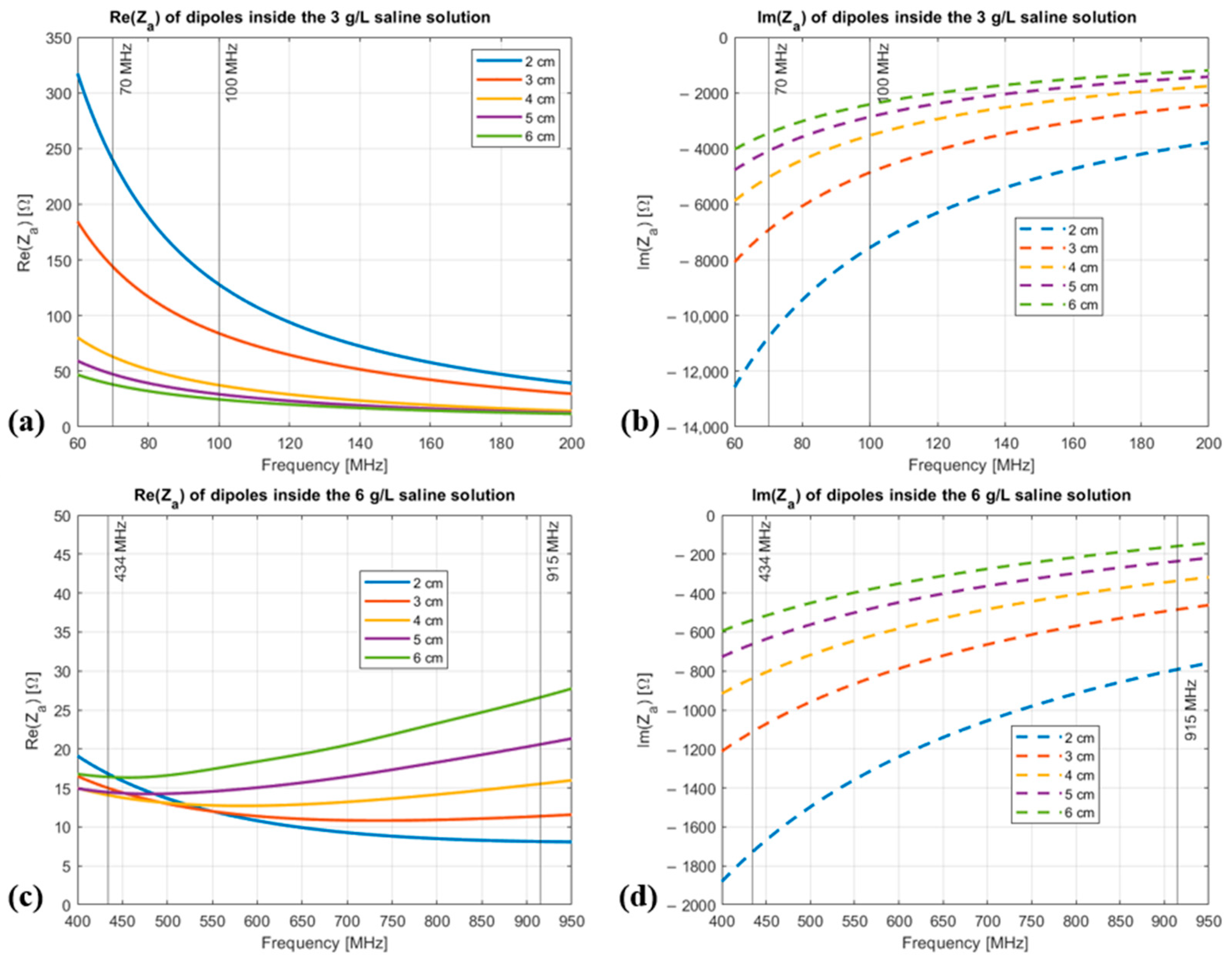
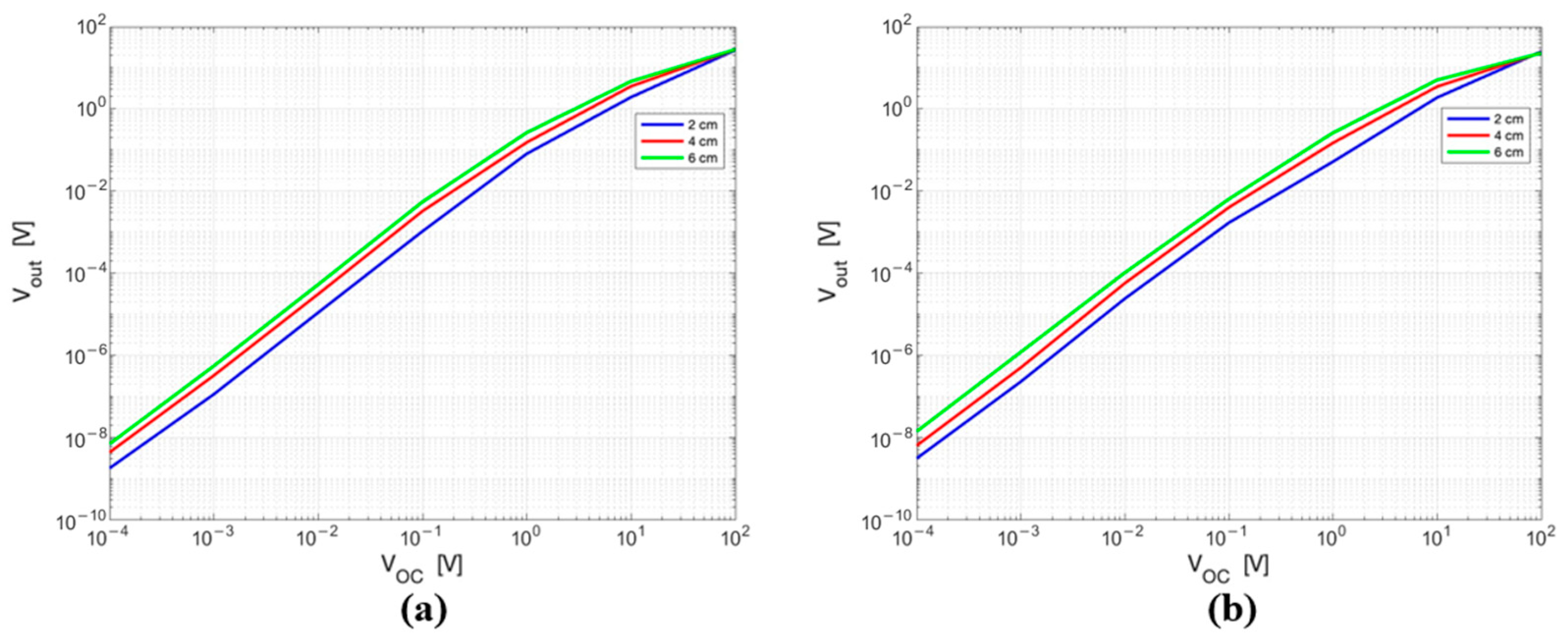
3.1.1. Results of Electromagnetic Simulations
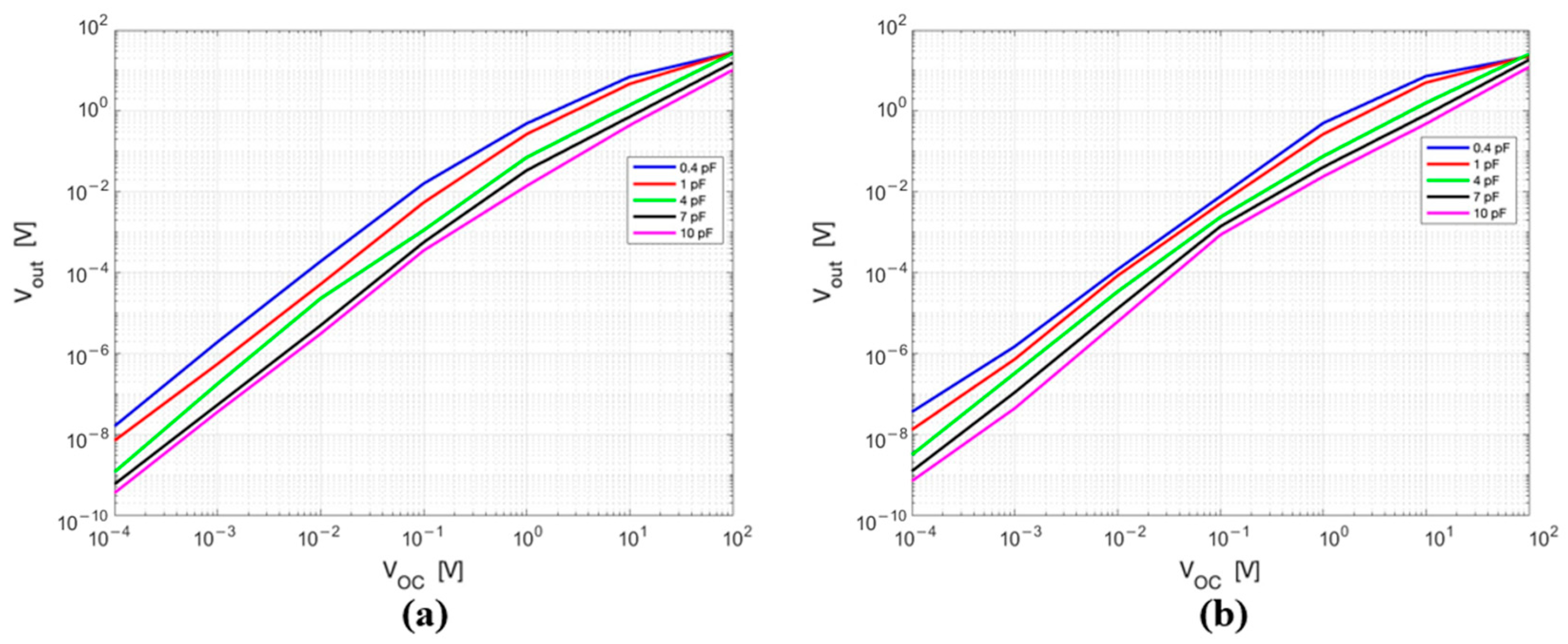
3.1.2. Circuit Simulations
3.2. Optimal Configuration and Realisation of the E-Field Sensors
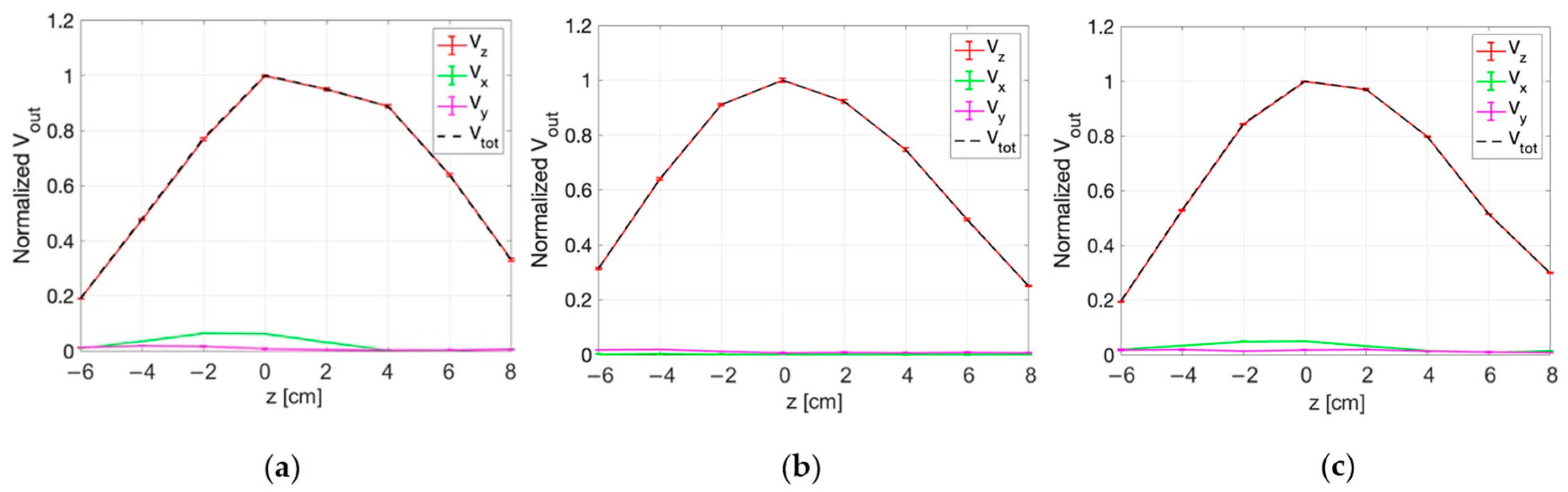
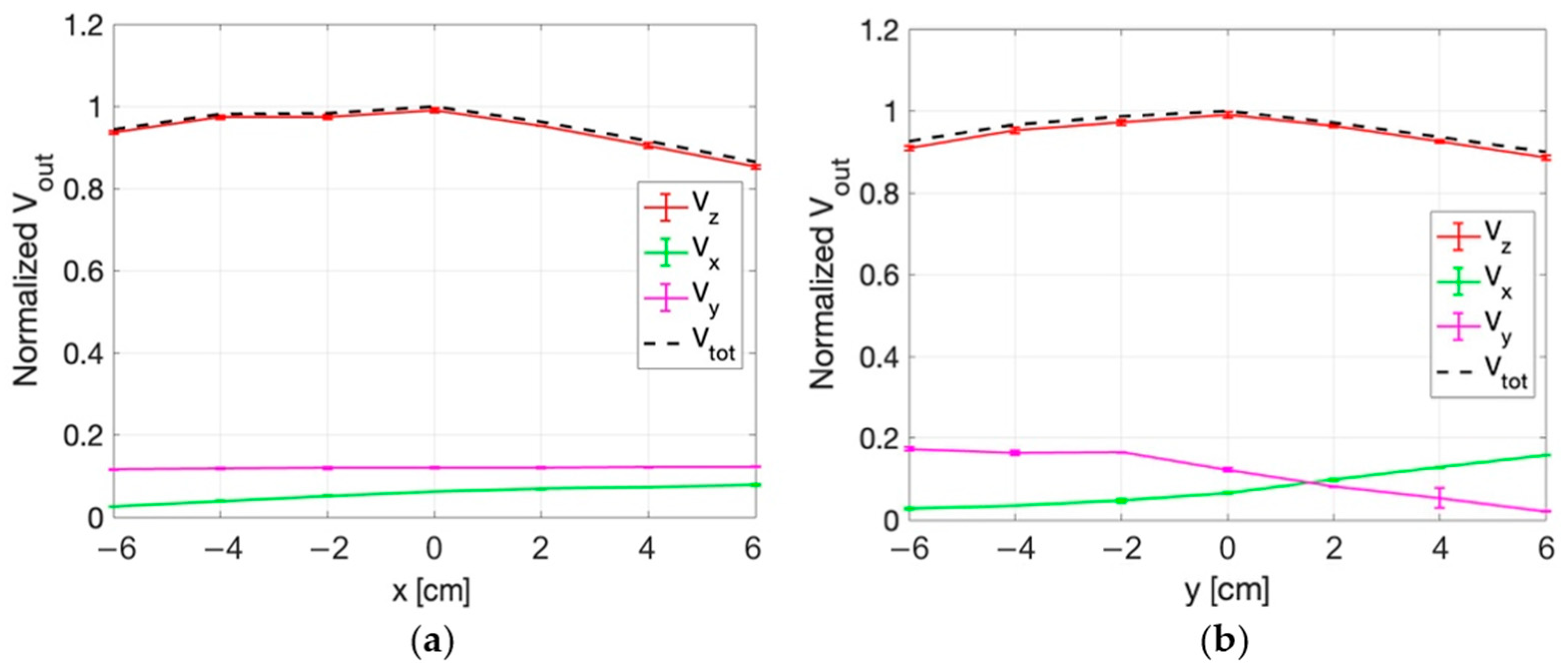
3.3. Measurements Results
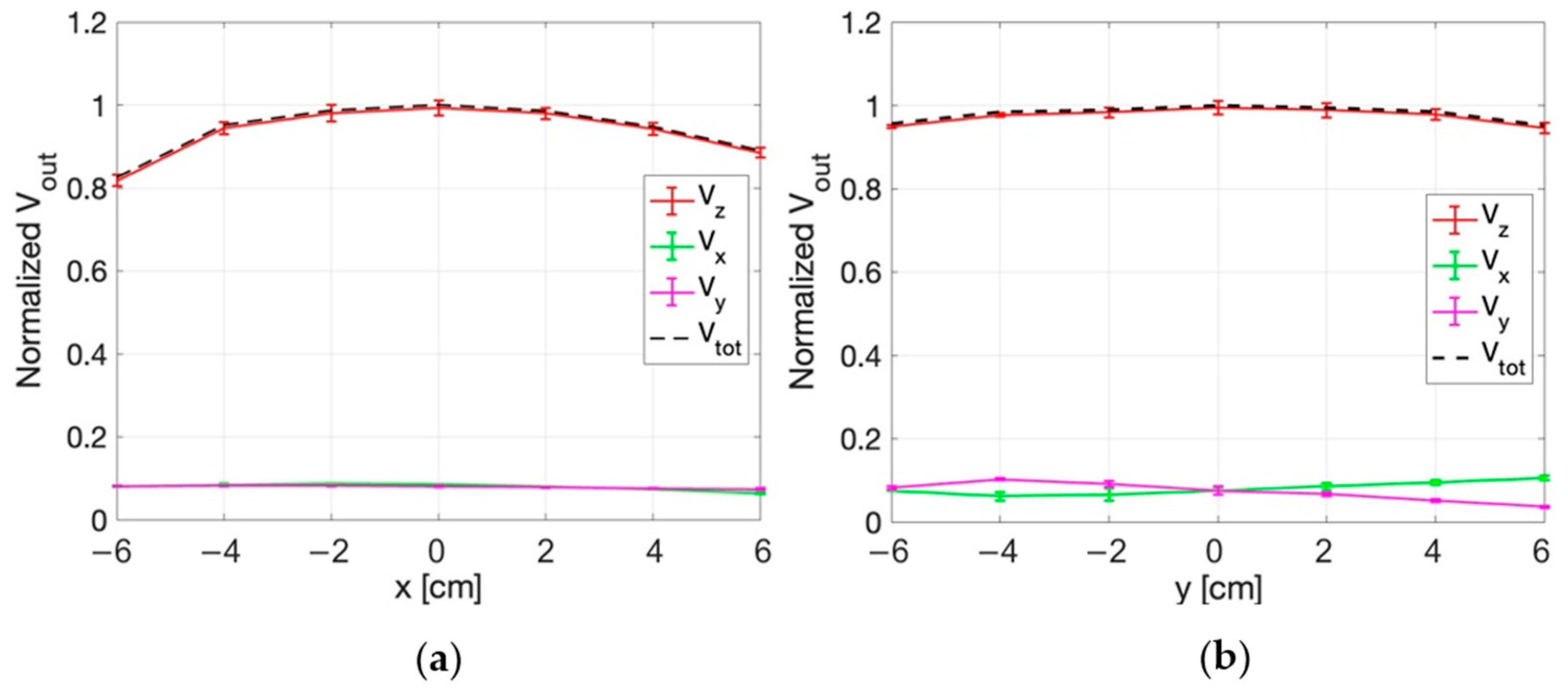
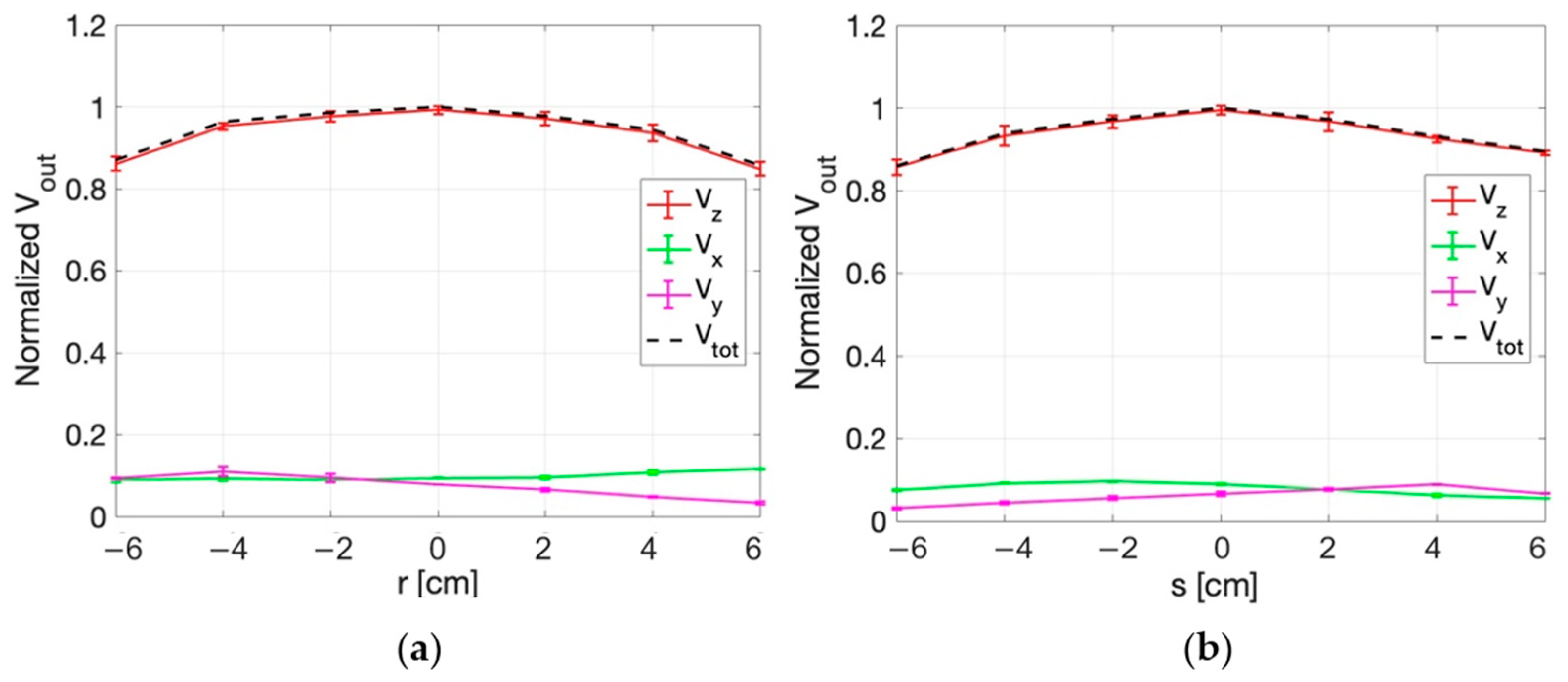
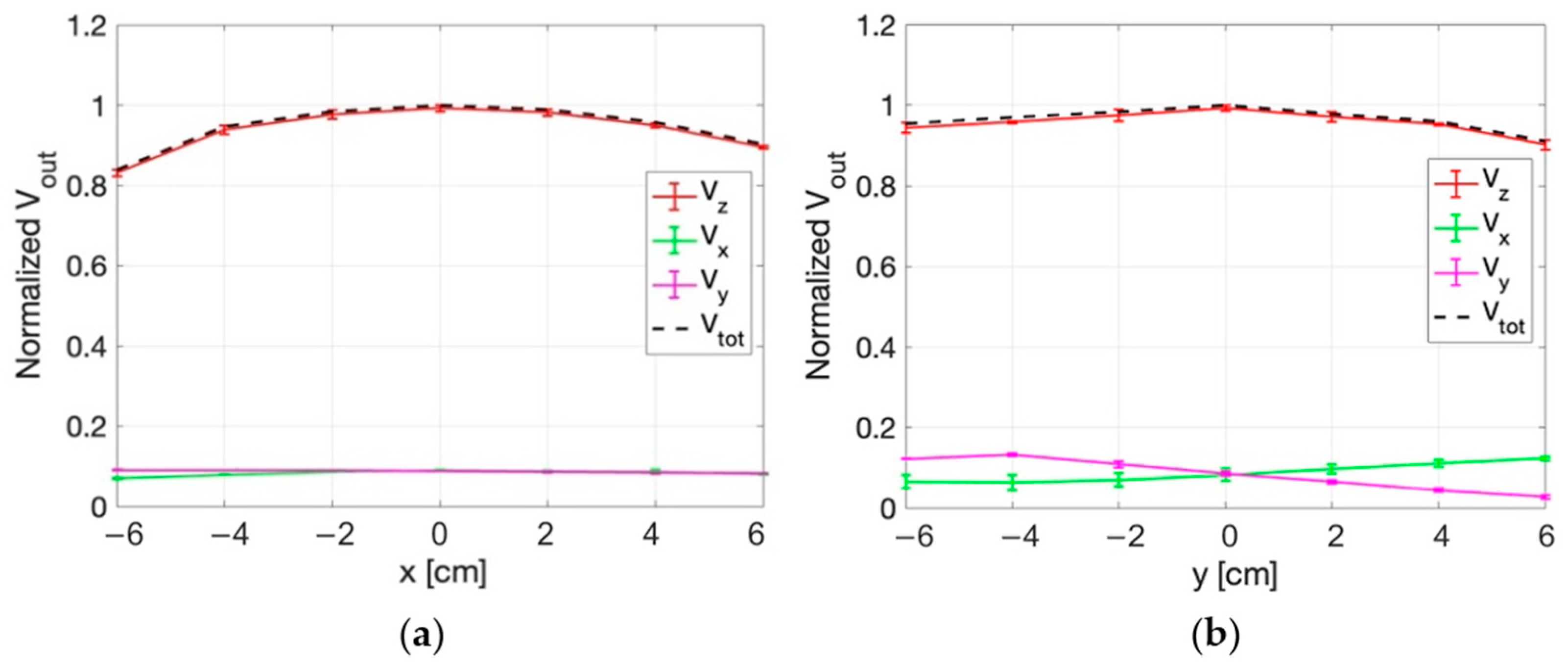
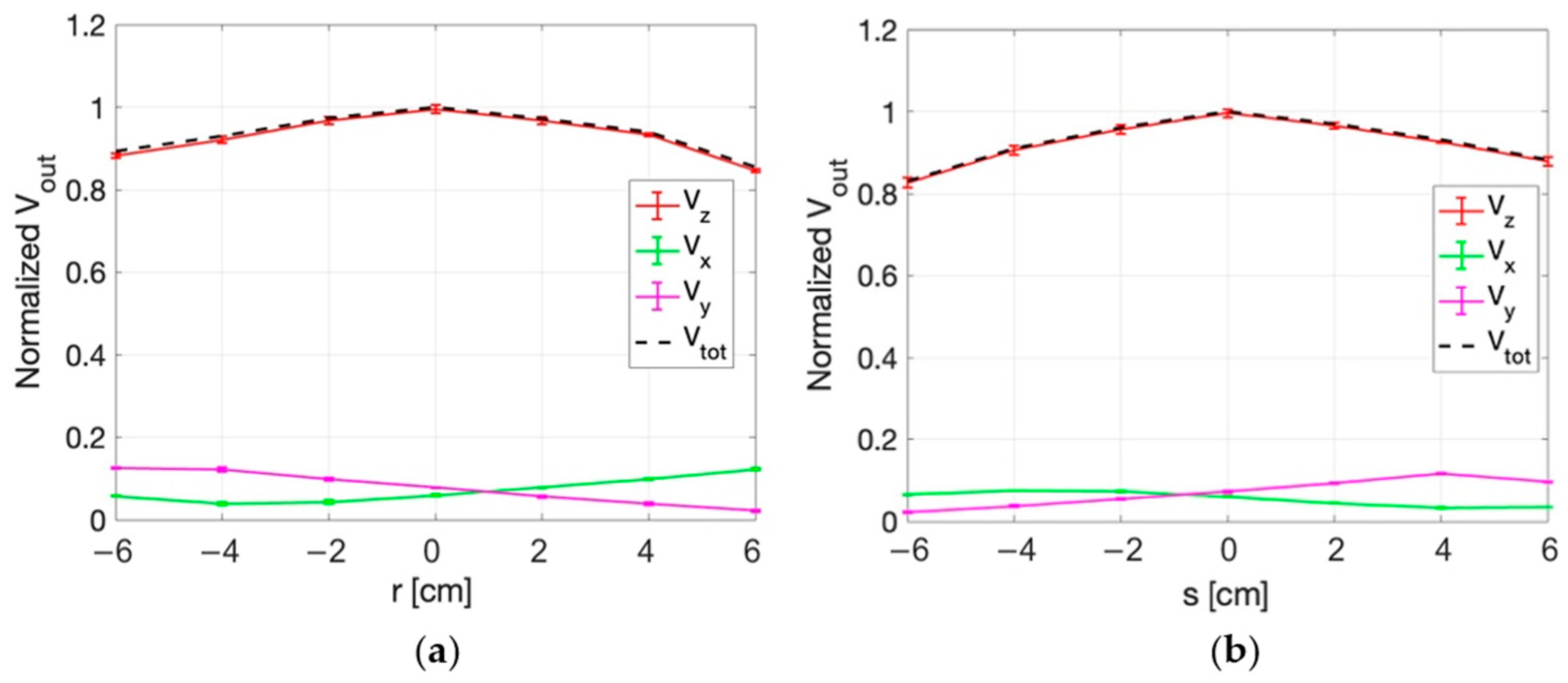
3.3.1. E-Field Measurements for Superficial HT
3.3.2. E-Field Measurements for Deep HT
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chicheł, A.; Skowronek, J.; Kubaszewska, M.; Kanikowski, M. Hyperthermia—Description of a method and a review of clinical applications. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2007, 12, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, G.M. Hyperthermia for the engineer: A short biological primer. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1984, 31, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Zee, J.; González, D.; van Rhoon, G.C.; van Dijk, J.D.; van Putten, W.L.; Hart, A.A. Comparison of radiotherapy alone with radiotherapy plus hyperthermia in locally advanced pelvic tumours: A prospective, randomised, multicentre trial. Lancet 2000, 355, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, N.R.; Ordóñez, S.G.; Gaipl, U.S.; Paulides, M.M.; Crezee, H.; Gellermann, J.; Marder, D.; Puric, E.; Bodis, S. Local hyperthermia combined with radiotherapy and-/or chemotherapy: Recent advances and promises for the future. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issels, R.D.; Lindner, L.H.; Verweij, J.; Wust, P.; Reichardt, P.; Schem, B.-C.; Abdel-Rahman, S.; Daugaard, S.; Salat, C.; Wendtner, C.-M.; et al. Neo-adjuvant chemotherapy alone or with regional hyperthermia for localised high-risk soft-tissue sarcoma: A randomised phase 3 multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wust, P.; Hildebrandt, B.; Sreenivasa, G.; Rau, B.; Gellermann, J.; Riess, H.; Felix, R.; Schlag, P.M. Hyperthermia in combined treatment of cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, D.S.; Petersen, I.A.; Cox, R.S.; Hahn, G.M.; Fessenden, P.; Prionas, S.D.; Lee, E.R.; Meyer, J.L.; Samulski, T.V.; Bagshaw, M.A. Two or six hyperthermia treatments as an adjunct to radiation therapy yield similar tumor responses: Results of a randomized trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1990, 19, 1481–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, A.L.; Vriend, L.E.M.; Crezee, J.; Franken, N.A.; Krawczyk, P.M. Effects of hyperthermia on DNA repair pathways: One treatment to inhibit them all. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulides, M.M.; Dobsicek Trefna, H.; Curto, S.; Rodrigues, D.B. Recent technological advancements in radiofrequency and microwave mediated hyperthermia for enhancing drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 163–164, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rhoon, G.C.; Paulides, M.M.; van Holthe, J.M.L.; Franckena, M. Hyperthermia by electromagnetic fields to enhanced clinical results in oncology. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Crezee, J.; Zweije, R.; Sikbrands, J.; Kok, H.P. RF and MW System for Hyperthermia of Challenging Tumor Locations. In Proceedings of the European Microwave Conference in Central Europe (EuMCE), Prague, Czech Republic, 13–15 May 2019; pp. 432–435. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, H.P.; Navarro, F.; Strigari, L.; Cavagnaro, M. Crezee Locoregional hyperthermia of deep-seated tumours applied with capacitive and radiative systems: A simulation study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 714–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Hiraoka, M.; Takahashi, M.; Egawa, S.; Matsuda, C.; Onoyama, Y.; Morita, K.; Kakehi, M.; Sugahara, T. Multi-institutional Studies on Hyperthermia using an 8-MHz Radiofrequency Capacitive Heating Device (Thermotron RF-8) in Combination with Radiation for cancer therapy. Cancer 1986, 58, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, M.; Wust, P.; Oberacker, E.; Rattunde, A.; Päßler, T.; Chrzon, B.; Ghadjar, P. Experimental and computational evaluation of capacitive hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobsicek Trefna, H.; Crezee, J.; Schmidt, M.; Marder, D.; Lamprecht, U.; Ehmann, M.; Nadobny, J.; Hartmann, J.; Lomax, N.; Abdel-Rahman, S.; et al. Quality assurance Guidelines for superficial hyperthermia clinical trials: II. Technical requirements for heating devices. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2017, 193, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggmoser, G. Some aspects of quality management in deep regional hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 2012, 28, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crezee, H.; Crezee, H.; Schmidt, M.; Marder, D.; Lamprecht, U.; Ehmann, M.; Hartmann, J.; Nadobny, J.; Gellermann, J.; van Holthe, N.; et al. Quality assurance Guidelines for superficial hyperthermia clinical trials: I. Clinical requirements. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 471–482. [Google Scholar]
- Pennes, H.H. Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in resting forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1948, 1, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristofano, M.; Cavagnaro, M. Analysis of the Influence of Phantom Design in Superficial Hyperthermia Quality Assurance Procedures. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2025; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassen, H.I.; Smith, G.S. Electric Field Probe—A Review. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1983, 31, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, M. Analytical and Numerical Techniques for Analyzing an Electrically Short Dipole with a Nonlinear Load. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1980, 28, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivkovic, Z.; Senic, D.; Sarolic, A.; Vucic, A. Design and testing of a diode-based electric field probe prototype. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks, Split, Croatia, 15–17 September 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- IEC/IEEE 62209-1528:2020; Measurement Procedure for the Assessment of Specific Absorption Rate of Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Fields from Handheld and Body-Mounted Wireless Communication Devices—Human Models, Instrumentation, and Procedures—Part 1528: General Requirements for Using the Frequency Range 4 MHz to 10 GHz. IEC/IEEE: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Pokovic, K. Robust setup for precise calibration of E-field probes in tissue simulating liquids at mobile communication frequencies. In IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility; ICECOM: Garðabær, Iceland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, K.; Burkhardt, M.; Schmid, T.; Kuster, N. Broadband calibration of E-field probes in lossy media [mobile telephone safety application]. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1996, 44, 1954–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Van Dijk, J.D.P. Visualization by a matrix of light-emitting diodes of interference effects from a radiative four-applicator hyperthermia system. Int. J. Hyperth. 1991, 7, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; van Dijk, J.D.P.; Sijbrands, J.; van Os, R.; van Stam, G.; Vörding, P.J.Z.V.S.; Lamaitre, G.; Postma, A.; Koenis, F. Visualization of interfering RF-electric fields in a lossy liquid simulating a patient’s body in a hyperthermia treatment by a LED-matrix. In Proceedings of the 1992 14th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Paris, France, 29 October–1 November 1992; pp. 256–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, M. An isotropic Electric-Field probe with tapered resistive dipoles for broad-band use, 100 kHz to 18 GHz. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1987, 35, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, D.B. Small Antenna Design, 1st ed.; Newnes/Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yuan, Y. Study on the Effect of SiO2 Content on the Properties of Epoxy Resin. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2713, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H. The Design of CMOS Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liporace, F.; Di Cristofano, M.; Cavagnaro, M. Muscle and fat equivalent mixtures at radiative hyperthermia frequencies. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Conference on Antenna Measurements and Applications (CAMA), Genoa, Italy, 15–17 November 2023; pp. 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvio, G.; Vaselli, M.; Lopresto, V.; Pinto, R.; Farina, L.; Cavagnaro, M. Comparison of different methods for dielectric properties measurements in liquid sample media. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Aided Eng. 2018, 28, e21215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuchly, M.A.; Stuchly, S.S. Coaxial line reflection methods for 723 measuring dielectric properties of biological substances at radio and 724 microwave frequencies—A review. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1980, 29, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelvich, E.A.; Mazokhin, V.N. Contact flexible microstrip applicators (CFMA) in a range from microwaves up to short waves. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamaitret, G.; Van Dijk, J.D.P.; Gelvich, E.A.; Wiersma, J.; Schneider, C.J. SAR characteristics of three types of Contact Flexible Microstrip Applicators for superficial hyperthermia. Int. J. Hyperth. 1996, 12, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petra Kok, H.; Correia, D.; De Greef, M.; Van Stam, G.; Bel, A.; Crezee, J. SAR deposition by curved CFMA-434 applicators for superficial hyperthermia: Measurements and simulations. Int. J. Hyperth. 2010, 26, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweije, R.; Kok, H.P.; Bakker, A.; Bel, A.; Crezee, J. Technical and Clinical Evaluation of the ALBA-4D 70MHz Loco-Regional Hyperthermia System. In Proceedings of the 2018 48th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Madrid, Spain, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, H.P.; van der Zee, J.; Guirado, F.N.; Bakker, A.; Datta, N.R.; Abdel-Rahman, S.; Crezee, J. Treatment planning facilitates clinical decision making for hyperthermia treatments. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 532–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A.; Zweije, R.; Kok, H.P.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Westerveld, G.H.; Hinnen, K.A.; Crezee, H. Comparison of the clinical performance of a hybrid Alba 4D and the AMC-4 locoregional hyperthermia systems. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instek, G.W. GDM-8341 5½ Digit Dual Measurement Multimeter Datasheet; Good Will Instrument Co., Ltd.: New Taipei City, Taiwan, 2014; Available online: https://www.gwinstek.com/en-global/products/detail/GDM-8341 (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pokovic, K.; Schmid, T.; Kuster, N. Millimeter-resolution E-field probe for isotropic measurement in lossy media between 100 MHz and 20 GHz. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2000, 49, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S. A Comparison of Electrically Short Bare and Insulated Probes for Measuring the Local Radio Frequency Electric Field in Biological Systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1975, 22, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.J.; Van Dijk, J.D.P.; De Leeuw, A.A.C.; Wust, P. Quality assurance in various radiative hyperthermia systems applying a phantom with LED matrix. Int. J. Hyperth. 1994, 10, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Dipole Length | 70 MHz | 100 MHz | 434 MHz | 915 MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 cm | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.029 | 0.061 |
| 3 cm | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.043 | 0.091 |
| 4 cm | 0.009 | 0.013 | 0.058 | 0.122 |
| 5 cm | 0.012 | 0.017 | 0.072 | 0.152 |
| 6 cm | 0.014 | 0.020 | 0.087 | 0.183 |
| Dipole Length | 70 MHz | 100 MHz | 434 MHz | 915 MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 cm | 0.0081 | 0.0115 | 0.0501 | 0.1057 |
| 3 cm | 0.0121 | 0.0173 | 0.0752 | 0.1585 |
| 4 cm | 0.0162 | 0.0231 | 0.1002 | 0.2113 |
| 5 cm | 0.0202 | 0.0289 | 0.1253 | 0.2641 |
| 6 cm | 0.0242 | 0.0346 | 0.1503 | 0.3170 |
| Dipole Length | 70 MHz | 100 MHz | 434 MHz | 915 MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 cm | 0.90 cm | 1.00 cm | 1.00 cm | 1.30 cm |
| 3 cm | 1.40 cm | 1.70 cm | 1.60 cm | \ |
| 4 cm | 1.80 cm | 2.10 cm | 2.40 cm | \ |
| 5 cm | 2.30 cm | 2.70 cm | \ | \ |
| 6 cm | 2.80 cm | 3.30 cm | \ | \ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Cristofano, M.; Lalli, L.; Paglialunga, G.; Cavagnaro, M. Electric Field Measurement in Radiative Hyperthermia Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144392
Di Cristofano M, Lalli L, Paglialunga G, Cavagnaro M. Electric Field Measurement in Radiative Hyperthermia Applications. Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144392
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Cristofano, Marco, Luca Lalli, Giorgia Paglialunga, and Marta Cavagnaro. 2025. "Electric Field Measurement in Radiative Hyperthermia Applications" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144392
APA StyleDi Cristofano, M., Lalli, L., Paglialunga, G., & Cavagnaro, M. (2025). Electric Field Measurement in Radiative Hyperthermia Applications. Sensors, 25(14), 4392. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144392







