An Experimental 10-Port Microwave System for Brain Stroke Diagnosis—Potentials and Limitations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
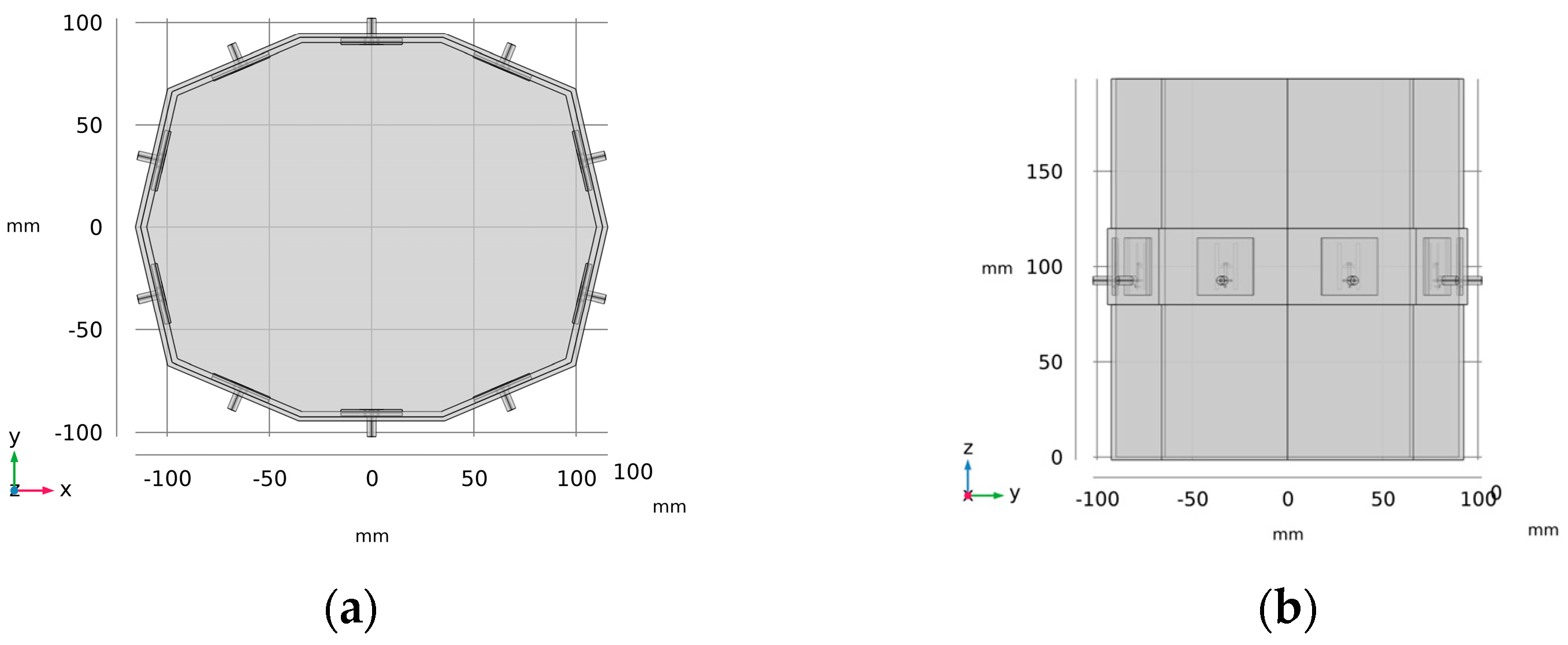
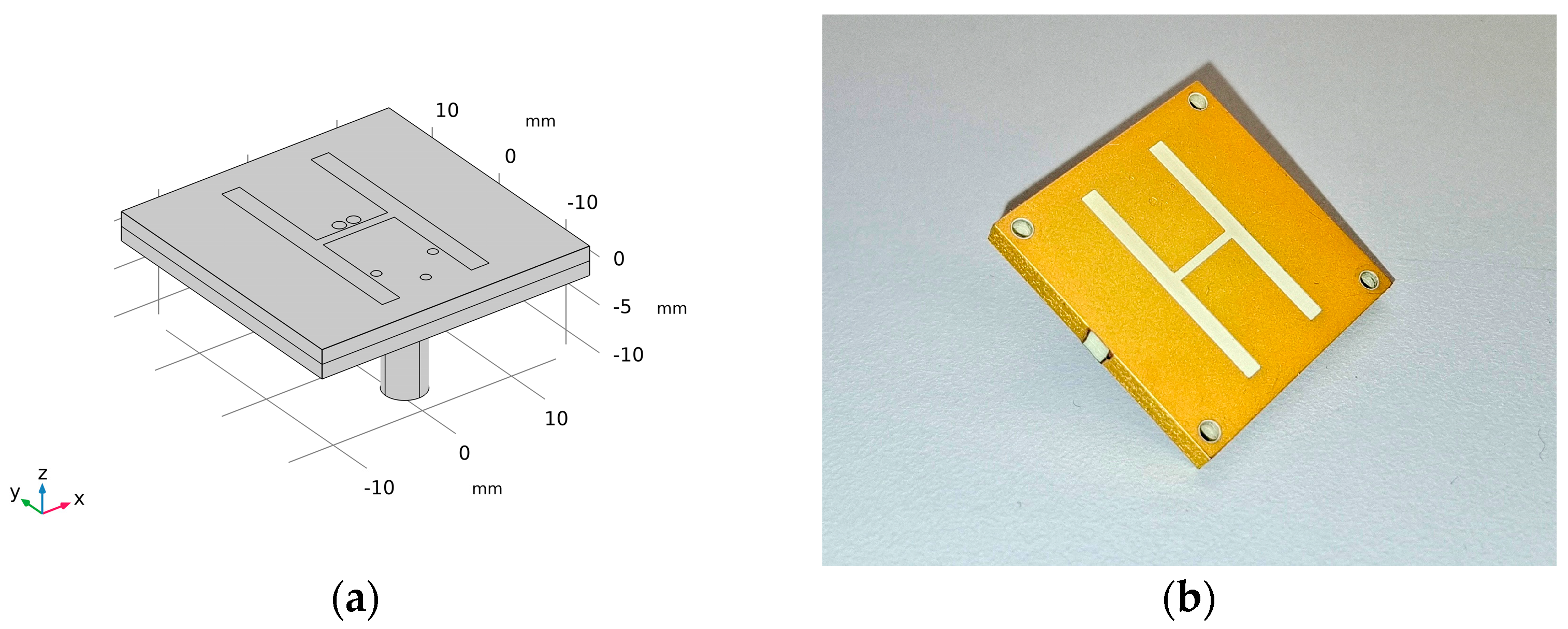
2.1. Microwave System for Head Stroke Measurements
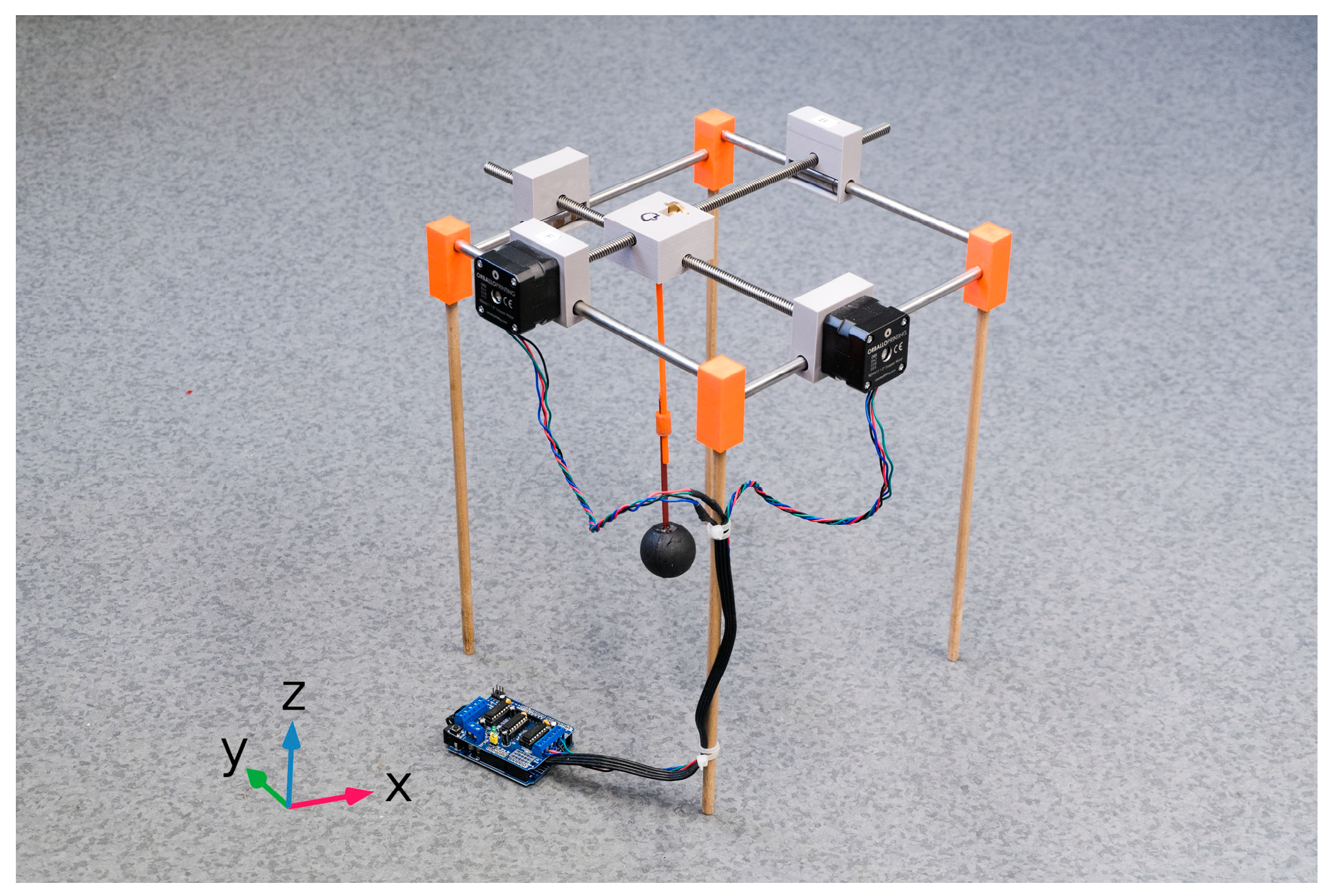
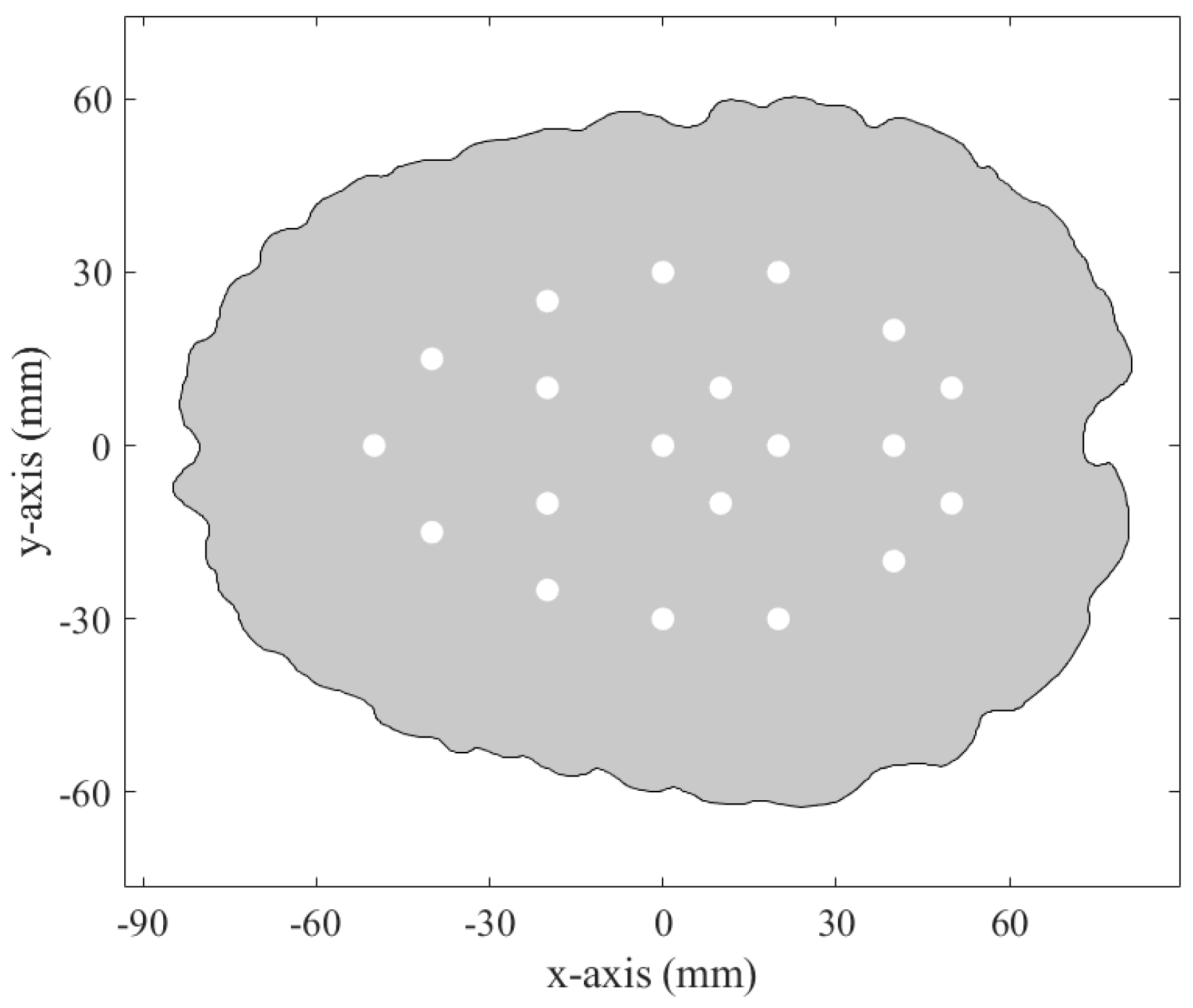
2.2. Experimental Measurement
2.3. Classification of Stroke Type Using SVM and PCA
2.4. Differential Forward Scattering and Linear Inverse Scattering Solution
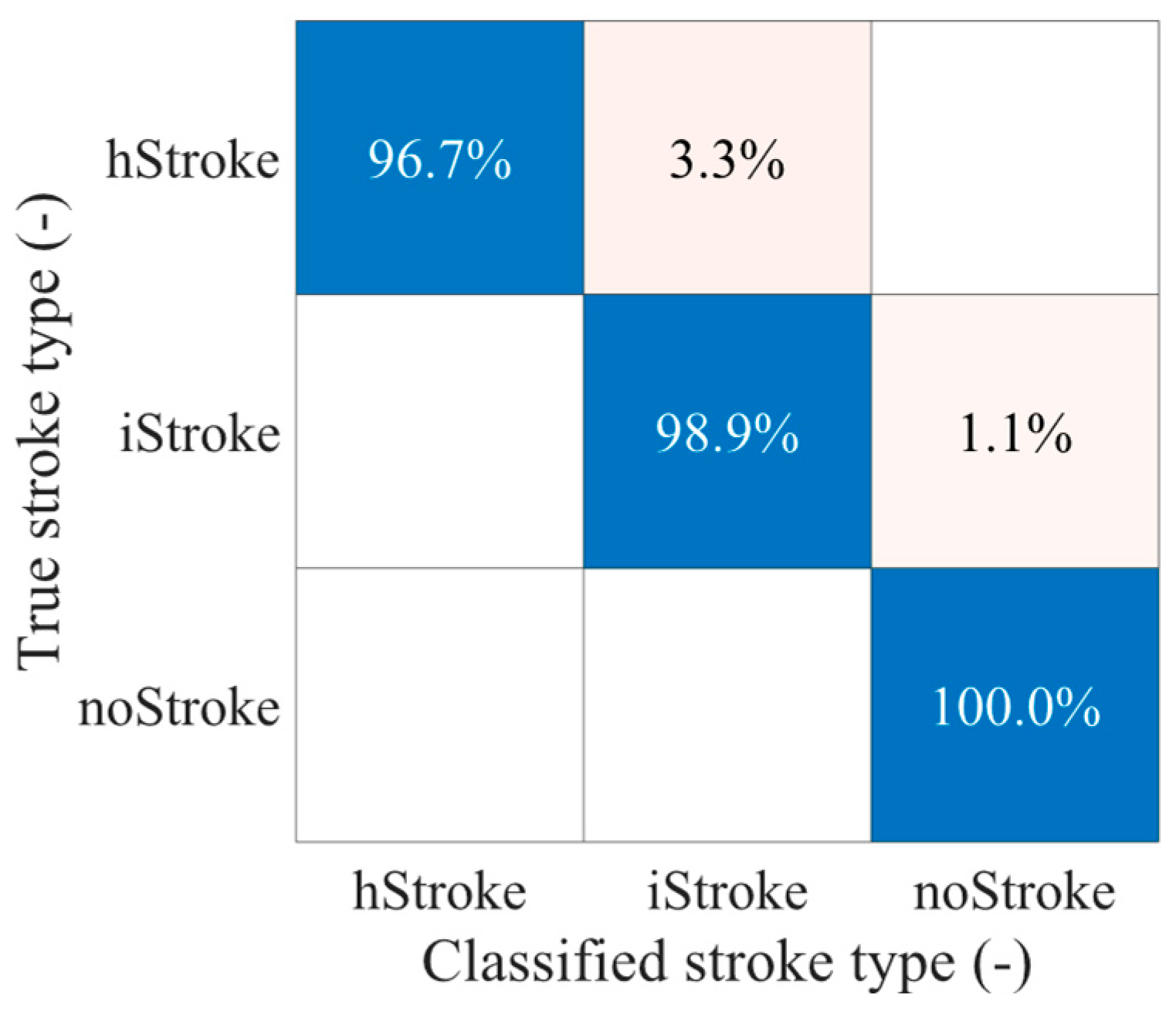
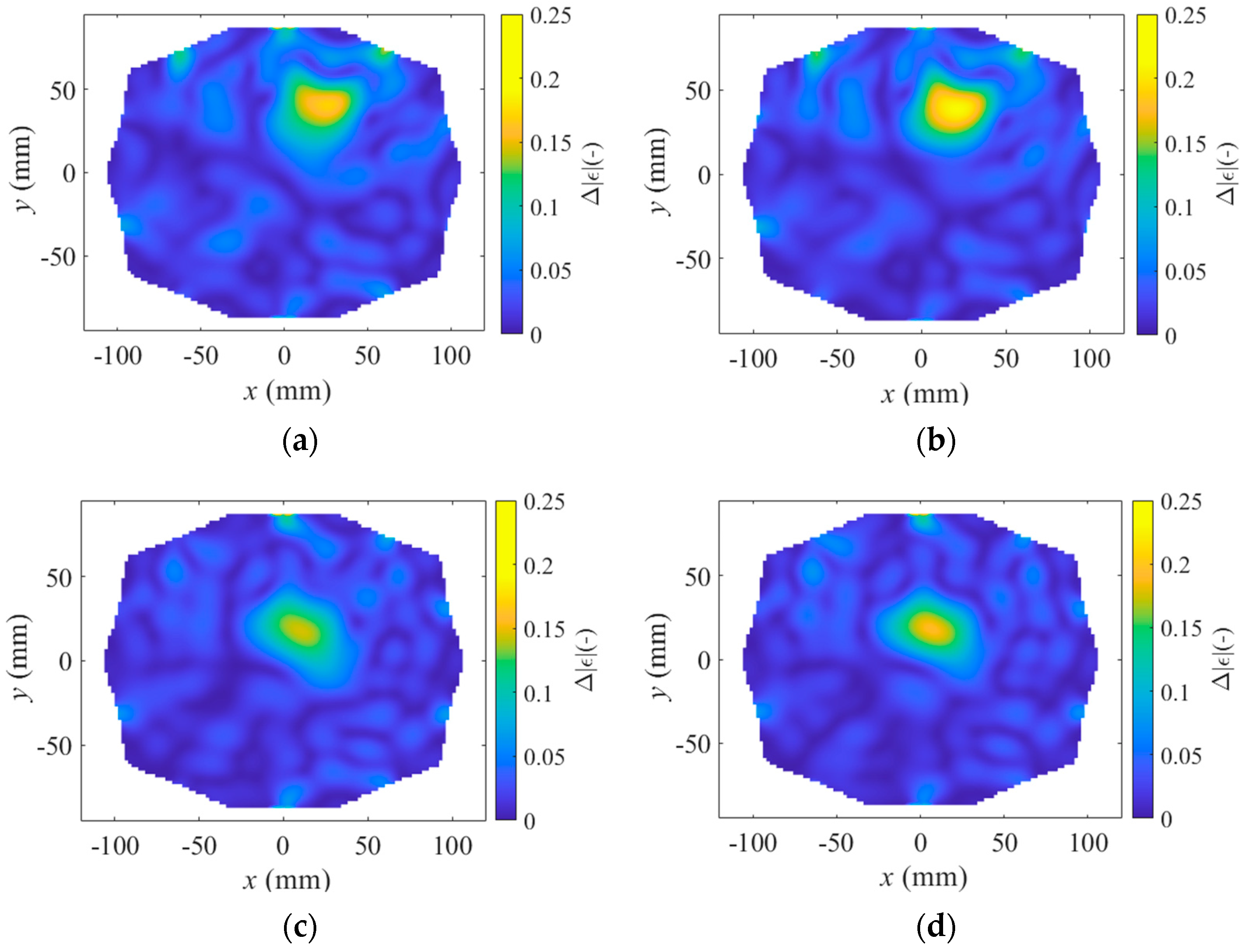
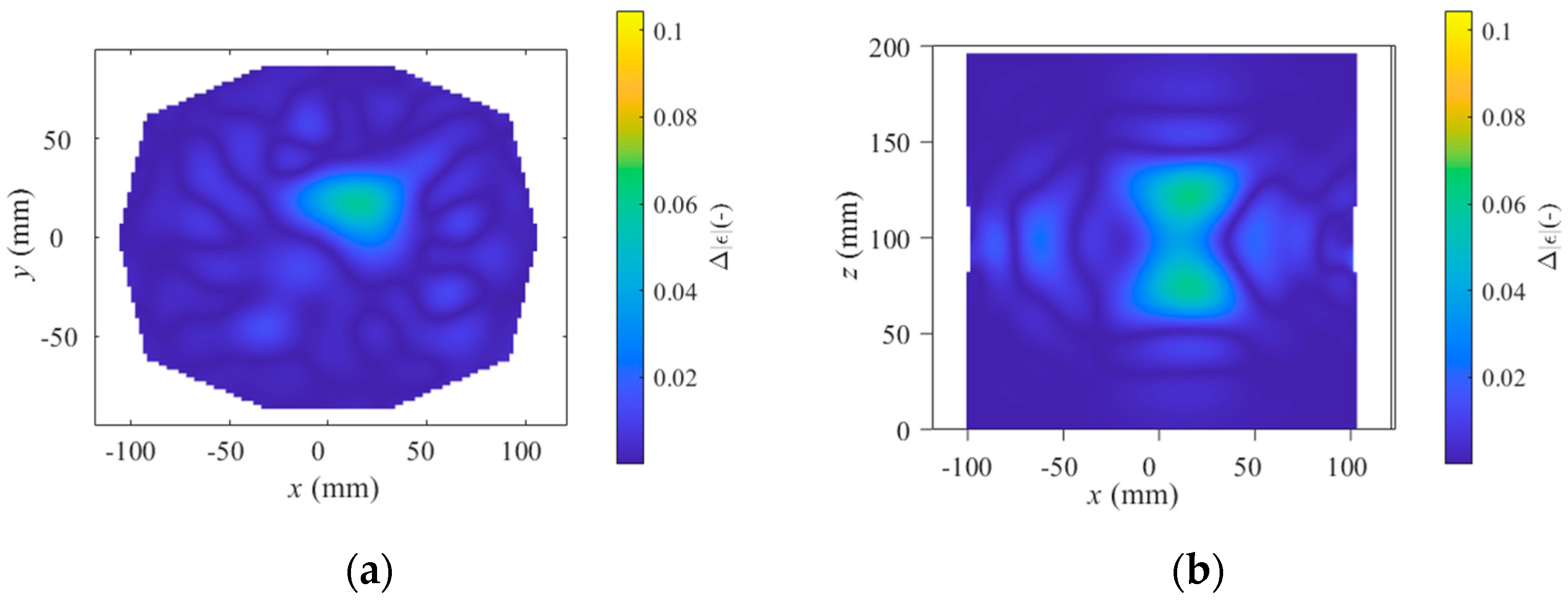
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Hacke, W.; Fisher, M.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetto, M.; Wechsler, P.M.; Merkler, A.E. Stroke Treatment in the Era of COVID-19: A Review. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2022, 24, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zong, M.; Suo, C.; Man, Q.; Xiong, L. Global Burden, Risk Factor Analysis, and Prediction Study of Ischemic Stroke, 1990–2030. Neurology 2023, 101, e137–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Almekhlafi, M.A.; Bala, F.; Ademola, A.; Coutts, S.B.; Deschaintre, Y.; Khosravani, H.; Buck, B.; Appireddy, R.; Moreau, F.; et al. Effect of Time to Thrombolysis on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Treated with Tenecteplase Compared to Alteplase: Analysis erom the AcT Randomized Controlled Trial. Stroke 2023, 54, 2766–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiftsis, D.; Manioti, E.A.; Touris, G.; Kyriakakis, E.; Tsamopoulos, N.; Gamvroudi, M. “etecting Stroke at the Emergency Department by a Point of Care Device: A Multicenter Feasibility Study. Med. Devices 2024, 17, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungqvist, J.; Candefjord, S.; Persson, M.; Jönsson, L.; Skoglund, T.; Elam, M. Clinical Evaluation of a Microwave-Based Device for Detection of Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, T.; Sahebdivan, S.; Planas, R.; Brunner, C.; Kellermair, L.; Guger, M.; Struhal, W.; Fuchs, P.; Reichl, J.; Stelzer, A.; et al. Human Brain Imaging by Electromagnetic Tomography: A mobile brain scanner for clinical settings. In Proceedings of the 2022 16th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Madrid, Spain, 27 March–1 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fedeli, A.; Schenone, V.; Randazzo, A.; Pastorino, M.; Henriksson, T.; Semenov, S. Nonlinear S-Parameters Inversion for Stroke Imaging. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 1760–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbosh, A.; Bialkowski, K.; Guo, L.; Al-Saffar, A.; Zamani, A.; Trakic, A.; Brankovic, A.; Bialkowski, A.; Zhu, G.; Cook, D.; et al. Clinical electromagnetic brain scanner. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.; Brown, H.; Widanapathirana, I.; Shah, D.; Walsham, J.; Trakic, A.; Zhu, G.; Zamani, A.; Guo, L.; Brankovic, A.; et al. Case Report: Preliminary Images from an Electromagnetic Portable Brain Scanner for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Acute Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 765412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.; Balabanski, A.; Cook, D.; Crozier, S.; Bialkowski, K.; Langenberg, F.; Bivard, A.; Bishop, L.; Easton, D.; Donnan, G.A.; et al. Abstract 129: Electromagnetic Portable Brain Imaging for Stroke. Stroke 2022, 53 (Suppl. S1), A129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapaticci, R.; Tobon, J.; Bellizzi, G.; Vipiana, F.; Crocco, L. Design and Numerical Characterization of a Low-Complexity Microwave Device for Brain Stroke Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 7328–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Duarte, D.O.; Tobon Vasquez, J.A.; Scapaticci, R.; Turvani, G.; Cavagnaro, M.; Casu, M.R.; Crocco, L.; Vipiana, F. Experimental Validation of a Microwave System for Brain Stroke 3-D Imaging. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Duarte, D.O.; Origlia, C.; Vasquez, J.A.T.; Scapaticci, R.; Crocco, L.; Vipiana, F. Experimental Assessment of Real-Time Brain Stroke Monitoring via a Microwave Imaging Scanner. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2022, 3, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisio, I.; Fedeli, A.; Garibotto, C.; Lavagetto, F.; Pastorino, M.; Randazzo, A. Two Ways for Early Detection of a Stroke Through a Wearable Smart Helmet: Signal Processing vs. Electromagnetism. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccaro, A.; Dell’Aversano, A.; Basile, B.; Maisto, M.A.; Solimene, R. Subcranial Encephalic Temnograph-Shaped Helmet for Brain Stroke Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidul Islam, M.; Islam, M.T.; Hoque, A.; Islam, M.T.; Amin, N.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. A Portable Electromagnetic Head Imaging System Using Metamaterial Loaded Compact Directional 3D Antenna. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 50893–50906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Lu, X.; Ding, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, G.; Yu, M.; et al. Classification and Location of Cerebral Hemorrhage Points Based on SEM and SSA-GA-BP Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 2505714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Guanghong, L.; Qingxin, G.; De, Z.; Mingqiang, L.; Xiaolin, L. Wideband Microwave System for Brain Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Communication and Information Systems (ICCIS), Wuhan, China, 21–23 December 2019; pp. 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Abbosh, Y.M.; Sultan, K.; Guo, L.; Abbosh, A. Non-Uniform Antenna Array for Enhanced Medical Microwave Imaging. Sensors 2025, 25, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Thayabaranathan, T.; Donnan, G.A.; Howard, G.; Howard, V.J.; Rothwell, P.M.; Feigin, V.; Norrving, B.; Owolabi, M.; Pandian, J.; et al. Global Stroke Statistics 2019. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 1747493020909545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saver Jeffrey, L. Time Is Brain—Quantified. Stroke 2006, 37, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Stroke Organisation (ESO) Executive Committee; ESO Writing Committee Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 25, 457–507. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Smith, E.E.; Fonarow, G.C.; Reeves, M.J.; Zhao, X.; Olson, D.M.; Schwamm, L.H. The “Golden Hour” and Acute Brain Ischemia. Stroke 2010, 41, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musuka, T.D.; Wilton, S.B.; Traboulsi, M.; Hill, M.D. Diagnosis and management of acute ischemic stroke: Speed is critical. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2015, 187, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flibotte, J.J.; Hagan, N.; O’Donnell, J.; Greenberg, S.M.; Rosand, J. Warfarin, hematoma expansion, and outcome of intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2004, 63, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGurgan, I.J.; Ziai, W.C.; Werring, D.J.; Salman, R.A.-S.; Parry-Jones, A.R. Acute intracerebral haemorrhage: Diagnosis and management. Pract. Neurol. 2021, 21, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordonnier, C.; Demchuk, A.; Ziai, W.; Anderson, C.S. Intracerebral haemorrhage: Current approaches to acute management. Lancet 2018, 392, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moullaali, T.J.; Wang, X.; Sandset, E.C.; Woodhouse, L.J.; Law, Z.K.; Arima, H.; Butcher, K.S.; Chalmers, J.; Delcourt, C.; Edwards, L.; et al. Early lowering of blood pressure after acute intracerebral haemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassi, N.; Zhao, H.; Churilov, L.; Campbell, B.C.V.; Wu, T.; Ma, H.; Cheung, A.; Kleinig, T.; Brown, H.; Choi, P.; et al. Tranexamic acid for intracerebral haemorrhage within 2 hours of onset: Protocol of a phase II randomised placebo-controlled double-blind multicentre trial. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2022, 7, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesarik, J.; Pokorny, T.; Vrba, J. Dielectric sensitivity of different antennas types for microwave-based head imaging: Numerical study and experimental verification. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2020, 12, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scapaticci, R.; Bjelogrlic, M.; Tobon Vasquez, J.A.; Vipiana, F.; Mattes, M.; Crocco, L. Microwave Technology for Brain Imaging and Monitoring: Physical Foundations, Potential and Limitations. In Emerging Electromagnetic Technologies for Brain Diseases Diagnostics, Monitoring and Therapy; Crocco, L., Karanasiou, I., James, M.L., Conceição, R.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 7–35. ISBN 978-3-319-75007-1. [Google Scholar]
- Scapaticci, R.; Di Donato, L.; Catapano, I.; Crocco, L. A Feasibility Study on Microwave Imaging for Brain Stroke Monitoring. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2012, 40, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorny, T.; Vrba, J.; Fiser, O.; Vrba, D.; Drizdal, T.; Novak, M.; Tosi, L.; Polo, A.; Salucci, M. On the Role of Training Data for SVM-Based Microwave Brain Stroke Detection and Classification. Sensors 2023, 23, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokorny, T.; Vrba, D.; Fiser, O.; Salucci, M.; Vrba, J. Systematic Optimization of Training and Setting of SVM-Based Microwave Stroke Classification: Numerical Simulations for 10 Port System. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2024, 8, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorny, T.; Vrba, D.; Tesarik, J.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Vrba, J. Anatomically and Dielectrically Realistic 2.5D 5-Layer Reconfigurable Head Phantom for Testing Microwave Stroke Detection and Classification. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2019, 2019, 5459391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorny, T.; Drizdal, T.; Novak, M.; Vrba, J. Automated, Reproducible, and Reconfigurable Human Head Phantom for Experimental Testing of Microwave Systems for Stroke Classification. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2024, 34, e23200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasgall, P.A.; Di Gennnaro, F.; Baumgartner, C.; Neufeld, E.; Lloyd, B.; Gosselin, M.C.; Payne, D.; Klingenböck, A.; Kuster, N. IT’IS Database for Thermal and Electromagnetic Parameters of Biological Tissues, Version 4.0. 2018. Available online: https://itis.swiss/virtual-population/tissue-properties/downloads/database-v4-0/ (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Scapaticci, R.; Bucci, O.M.; Catapano, I.; Crocco, L. Differential Microwave Imaging for Brain Stroke Followup. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 312528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, M.; Boccacci, P.; De Mol, C. Introduction to Inverse Problems in Imaging, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-0-367-47005-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Olaiya, M.T.; De Silva, D.A.; Norrving, B.; Bosch, J.; De Sousa, D.A.; Christensen, H.K.; Ranta, A.; Donnan, G.A.; Feigin, V.; et al. Global stroke statistics 2023: Availability of reperfusion services around the world. Int. J. Stroke 2024, 19, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
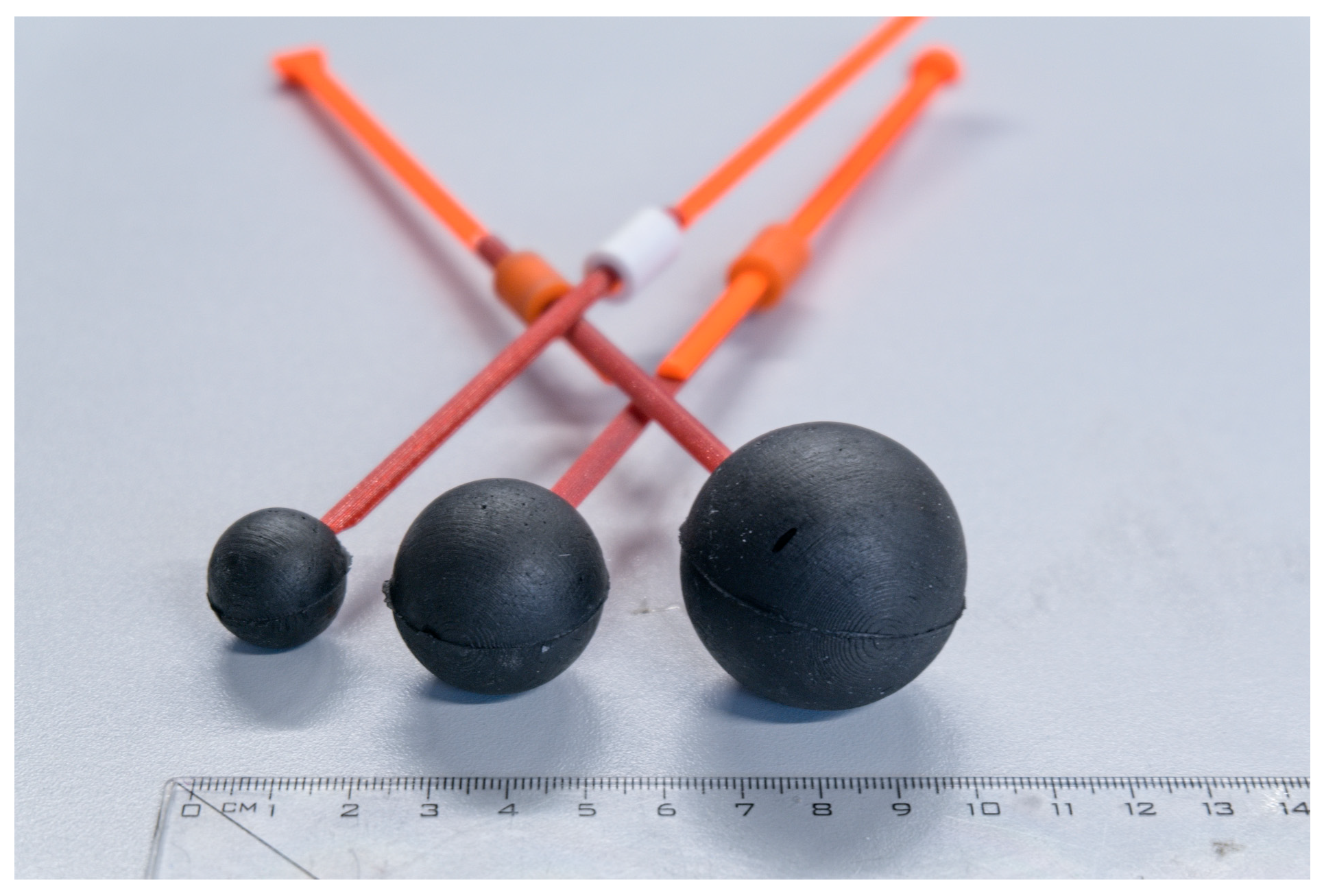



| Tissue Layer | Urethane Rubber (%) | Graphite Powder (%) | Carbon Black Powder (%) | Acetone (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemorrhagic stroke | 61.5 | 22.0 | 3.5 | 13 |
| Ischemic stroke | 66.0 | 22.7 | 2.3 | 9 |
| Liquid brain | 61.15% deionized water + 38% isopropanol + 0.85% NaCl | |||
| Tissue Layer | εr (-) | σ (S/m) |
|---|---|---|
| Human head * | 41.40 ± 0.71 | 1.04 ± 0.01 |
| Ischemic stroke | 31.72 ± 4.43 | 0.92 ± 0.07 |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | 52.73 ± 7.39 | 2.85 ± 0.58 |
| DataSet (-) | Stroke Type (-) | Stroke Sizes (mm) | Stroke Positions (-) | Operating Frequency (GHz) | DataSet Size (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | hStroke | 20, 30, 40 | Fixed 20 | 1 | 60 |
| iStroke | 60 | ||||
| noStroke | 40 | ||||
| M2 | hStroke | 20, 30, 40 | Random 30 * | 1 | 90 |
| iStroke | 90 | ||||
| noStroke | 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pokorny, T.; Redr, J.; Laierova, H.; Smahelova, B.; Kollar, J. An Experimental 10-Port Microwave System for Brain Stroke Diagnosis—Potentials and Limitations. Sensors 2025, 25, 4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144360
Pokorny T, Redr J, Laierova H, Smahelova B, Kollar J. An Experimental 10-Port Microwave System for Brain Stroke Diagnosis—Potentials and Limitations. Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144360
Chicago/Turabian StylePokorny, Tomas, Jan Redr, Hana Laierova, Barbora Smahelova, and Jakub Kollar. 2025. "An Experimental 10-Port Microwave System for Brain Stroke Diagnosis—Potentials and Limitations" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144360
APA StylePokorny, T., Redr, J., Laierova, H., Smahelova, B., & Kollar, J. (2025). An Experimental 10-Port Microwave System for Brain Stroke Diagnosis—Potentials and Limitations. Sensors, 25(14), 4360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144360







