A Ka-Band Omnidirectional Metamaterial-Inspired Antenna for Sensing Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Omni Metamaterial-Inspired Antenna Design
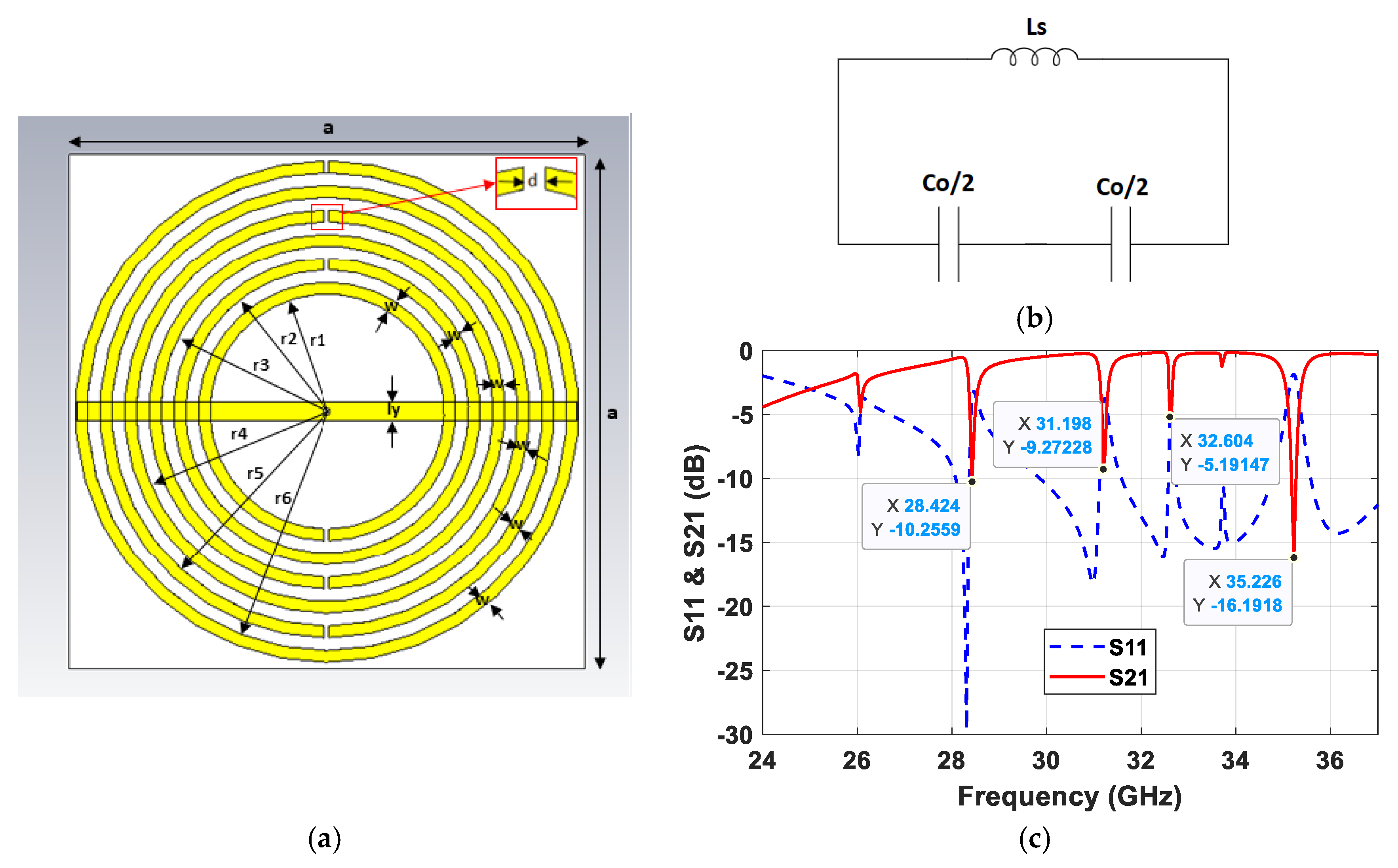
2.1. Metamaterial Structure Design
2.2. Metamaterial Antenna Design
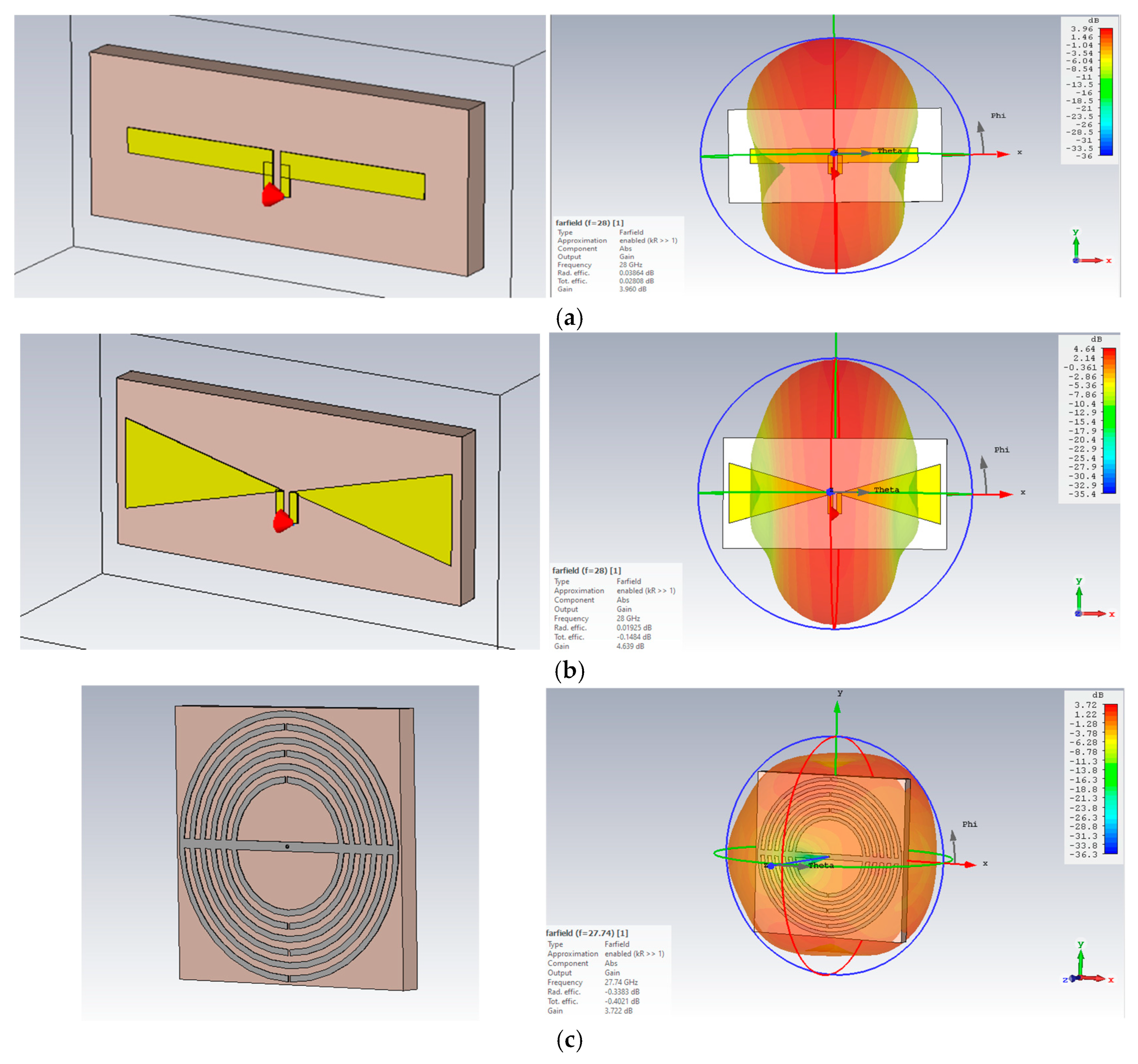
2.2.1. Antenna Geometry
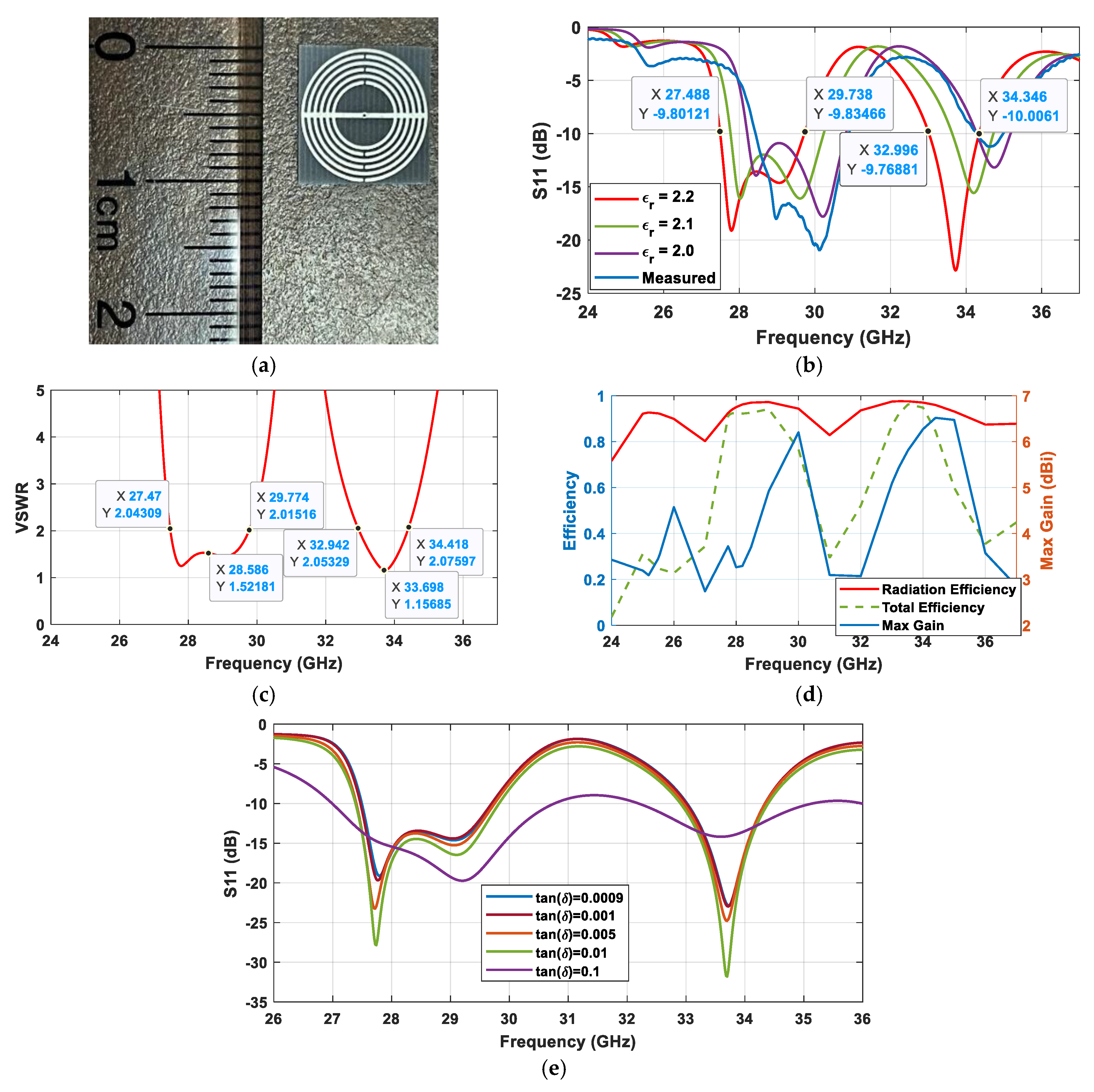
2.2.2. Antenna Design Optimization
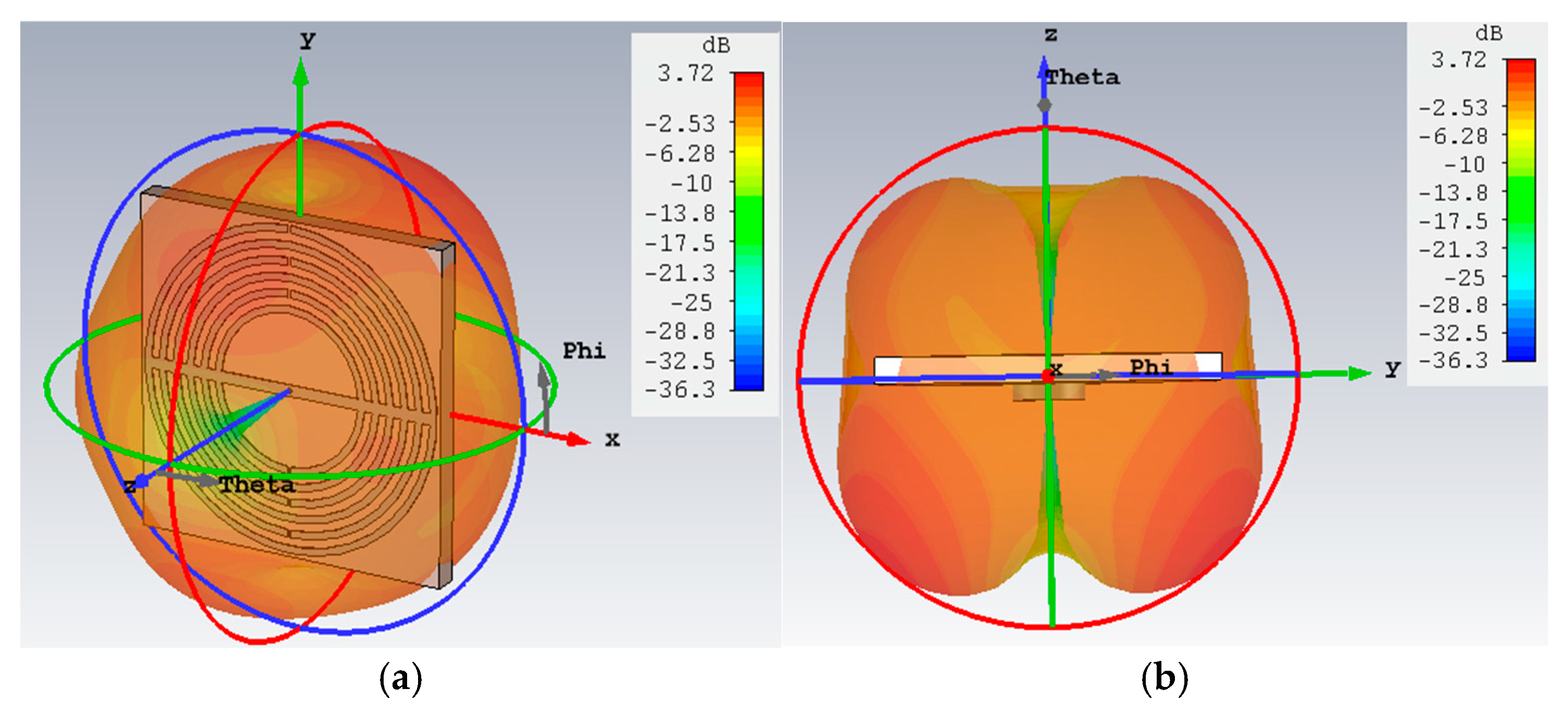
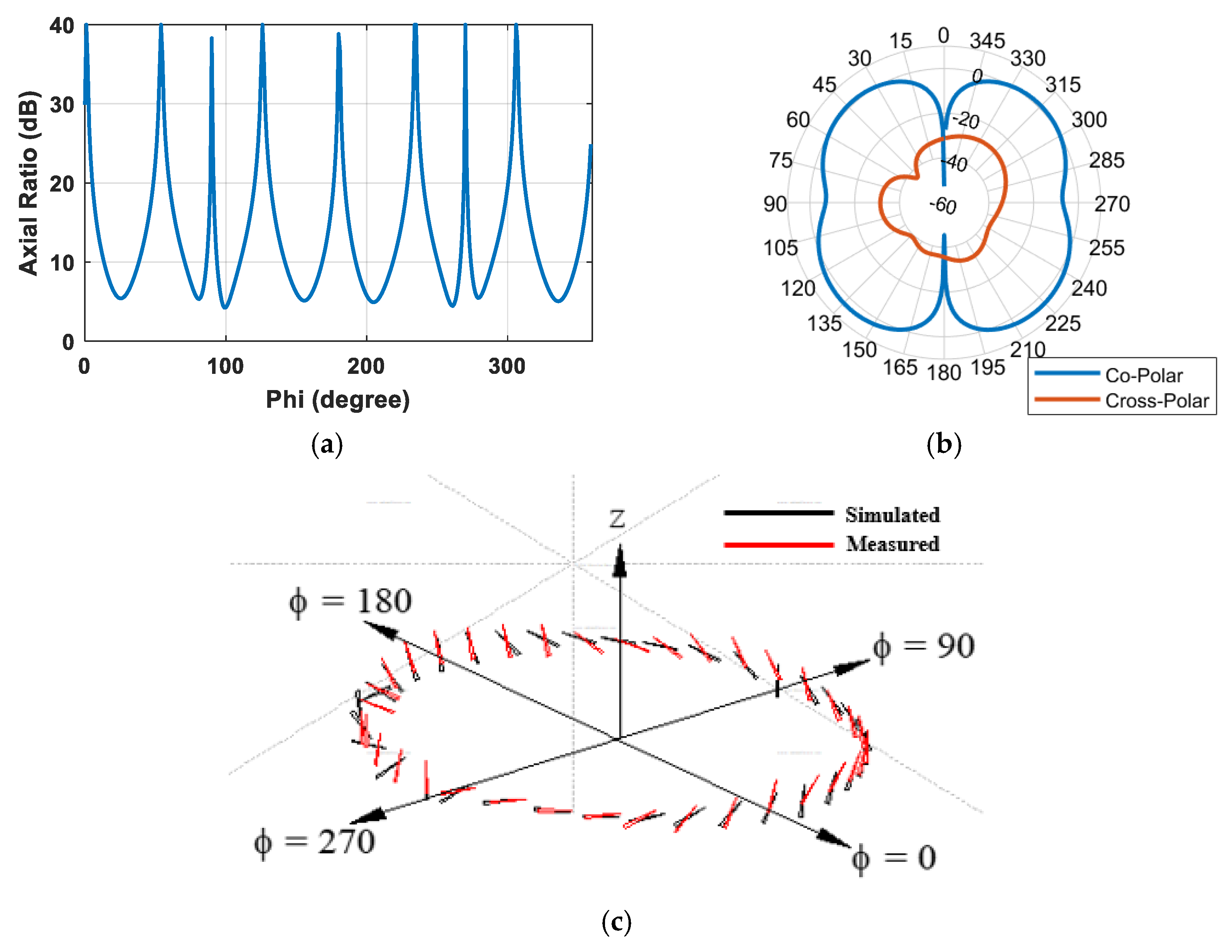
2.2.3. Final Design and Results
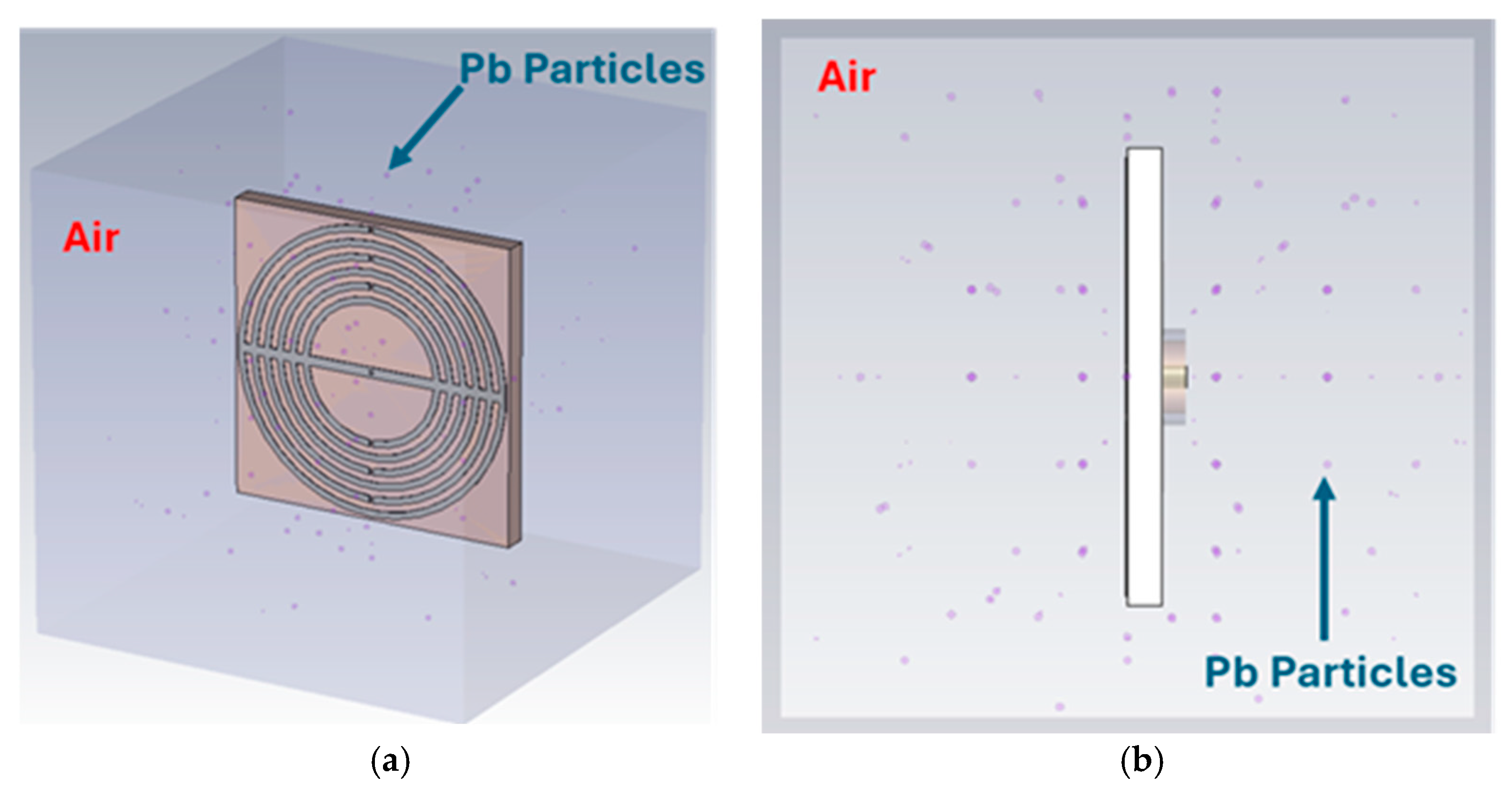
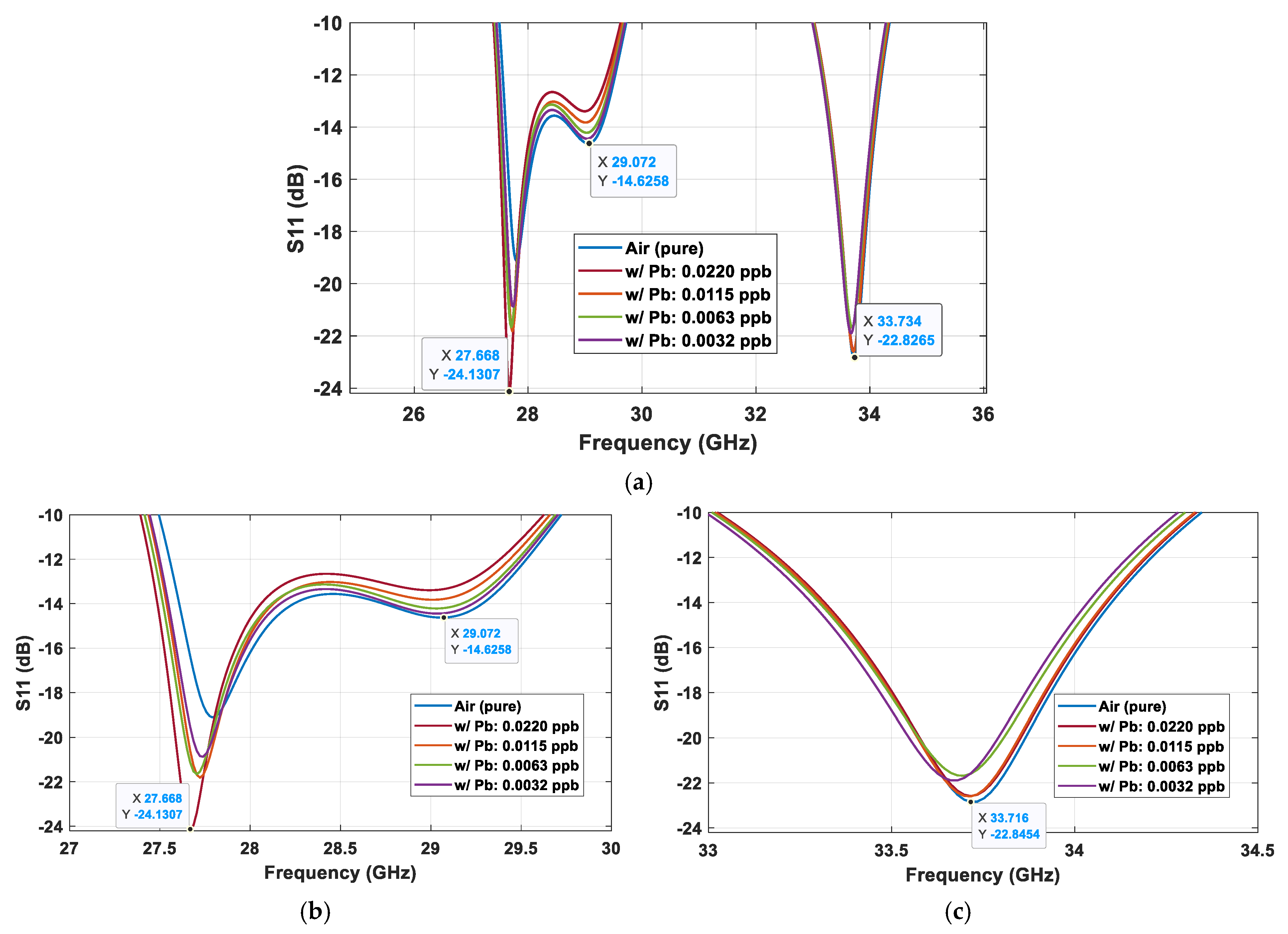
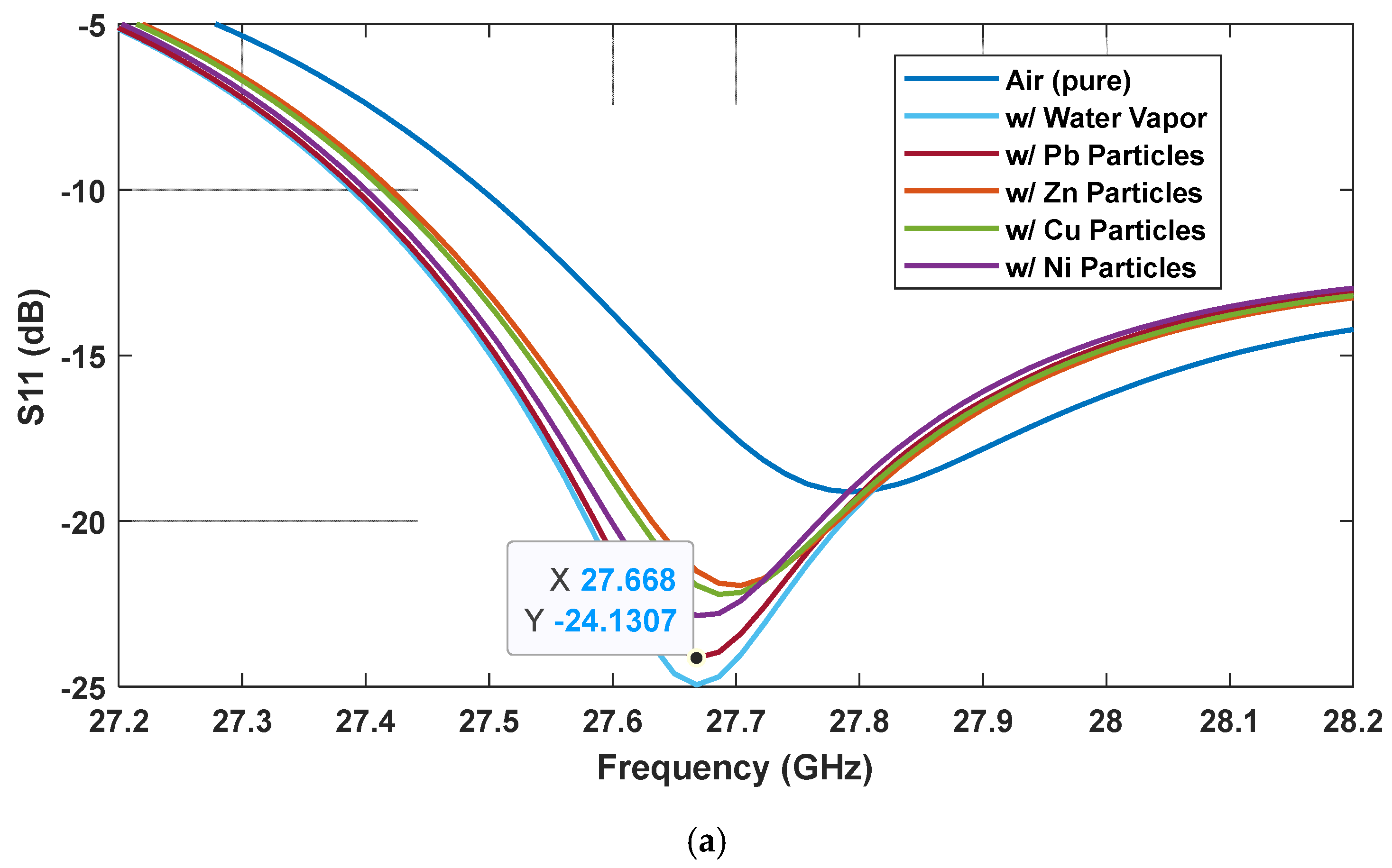
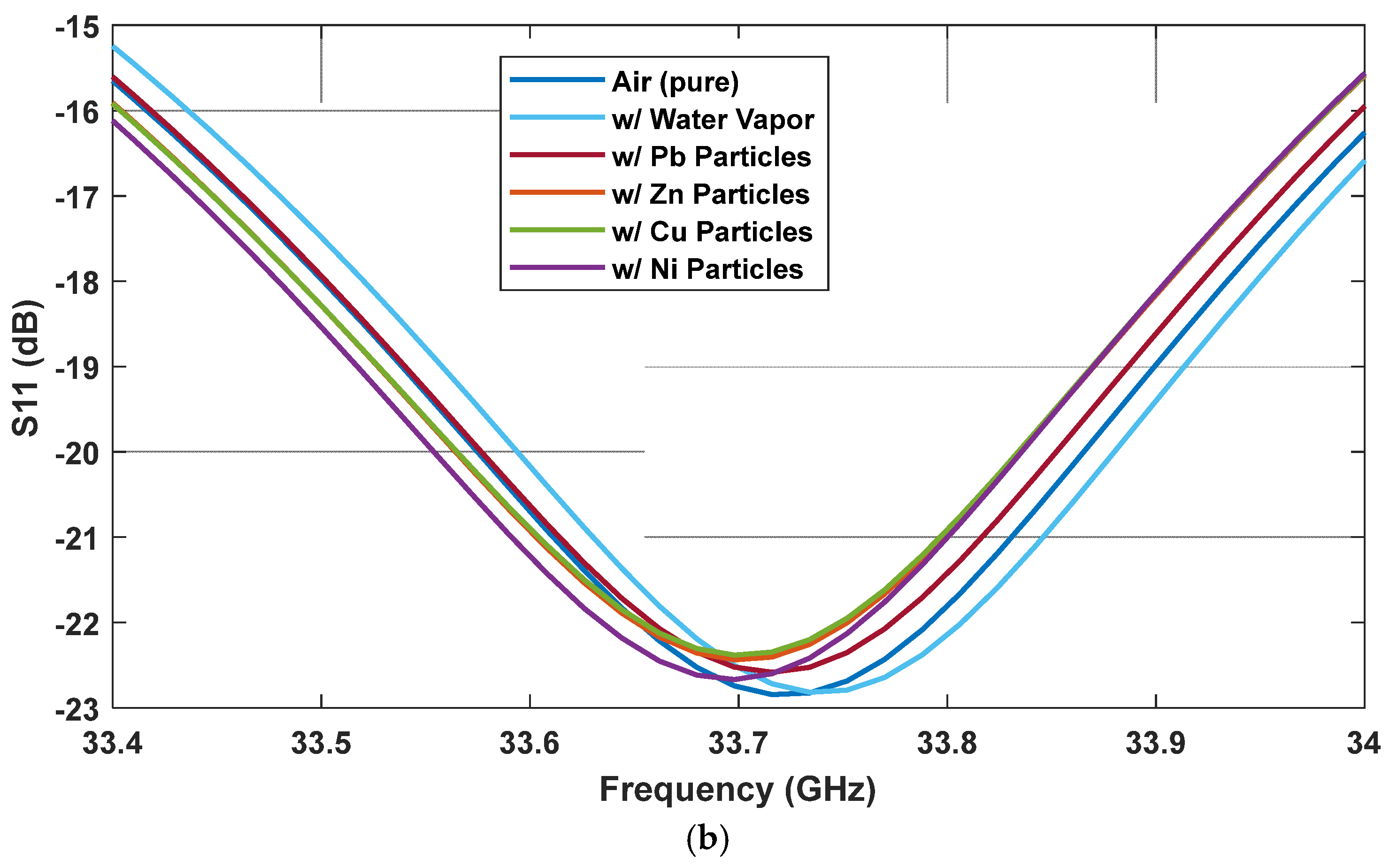
3. Sensing Performance Demonstration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.omnisense.com/ (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Available online: https://arguscontrols.com/ (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Jeon, H.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, S.J.; Lim, G. Omni-Purpose Stretchable Strain Sensor Based on a Highly Dense Nanocracking Structure for Whole-Body Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41712–41721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Shibata, T.; Ishiguro, H. Visual data mining using omni-directional sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, MFI2003, Tokyo, Japan, 30 July–1 August 2003; pp. 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkasem, N.; Cabrera, G. Multiple-Point Metamaterial-Inspired Microwave Sensors for Early-Stage Brain Tumor Diagnosis. Sensors 2024, 24, 5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Duhni, G.; Wongkasem, N. Metal discovery by highly sensitive microwave multi-band metamaterial-inspired sensors. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2021, 93, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; ShafieiDarabi, M.; Wang, X.; Slowinski, S.; Li, S.; Abbasi, Z.; Rezanezhad, F.; Van Cappellen, P.; Ren, C.L. Detection of microplastics by microfluidic microwave sensing: An exploratory study. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2025, 383, 116154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckl, G.; Atxutegi, A.; Bellinghausen, S.; Heinrich, S. Employing a multi-resonance microwave sensor for in-line moisture monitoring of fluidized bed agglomeration. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particle Size Monitoring. Available online: https://envea.global/design/pdf/envea-paddy-particle-size-monitoring-pi-en.pdf (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Tsai, T.-T.; Fang, Y.-C.; Wu, S.-K.; Chang, R.-H.; Chien, W.-C.; Chang, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-S.; Kuo, W. High throughput and label-free particle sensor based on microwave resonators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 285, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, N.A.; Meltzer, G.Y.; Avenbuan, O.N.; Raja, A.; Zelikoff, J.T. Particulate Matter and Associated Metals: A Link with Neurotoxicity and Mental Health. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, S.; Mohammed, A.S.B.; Ain, M.F.; Najmi, F.; Hussin, R.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Ullah, U.; Othman, M.; Ab Rahman, M.F. A novel lumped LC resonator antenna with air-substrate for 5G mobile terminals. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2020, 88, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Kroll, N. Negative refractive index in left-handed materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 2933–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Si, L.-M.; Hu, W.; Lv, X. A Symmetrical Dual-Beam Bowtie Antenna with Gain Enhancement Using Metamaterial for 5G MIMO Applications. IEEE Photon. J. 2019, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.; Hamad, E.K.I. Isolation enhancement of 5G multiple-input multiple-output microstrip patch antenna using metamaterials and the theory of characteristic modes. Int. J. RF Microw. Comput. Eng. 2020, 30, 22416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.M.Z.; Wongkasem, N. Development of microwave metamaterial-inspired sensors with multiple-band reactivity for mercury contamination detection. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2021, 36, 520–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabib-Azar, M.; Chowdhury, M.A.H. A 10 GHz Metamaterial Sensor to Detect SARS COV-2 and Dust Particles in Free Space. IEEE Sensors J. 2022, 22, 12846–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaina, N.; Lemoult, F.; Fink, M.; Lerosey, G. Negative refractive index and acoustic superlens from multiple scattering in single negative metamaterials. Nature 2015, 525, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Yi, F.; Cubukcu, E. Plasmonic metamaterial absorber for broadband manipulation of mechanical resonances. Nat. Photon 2016, 10, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, N.-S.; Yang, X.-S.; Chen, Z.N.; Wang, B.-Z. A Low-Profile Wideband Hybrid Metasurface Antenna Array for 5G and WiFi Systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, Z.; Abegaonkar, M.P.; Koul, S.K. A 28-GHz antenna for 5G MIMO applications. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2018, 78, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, E.K.I.; Abdalaziz, A. Metamaterial superstrate microstrip patch antenna for 5G wireless communication based on the theory of characteristic modes. J. Electr. Eng. 2019, 70, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Sindreu, M.; Naqui, J.; Paredes, F.; Bonache, J.; Martín, F. Electrically Small Resonators for Planar Metamaterial, Microwave Circuit and Antenna Design: A Comparative Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.; Martín, F.; Sorolla, M. Metamaterials with Negative Parameters: Theory, Design and Microwave Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Baena, J.; Bonache, J.; Martin, F.; Sillero, R.; Falcone, F.; Lopetegi, T.; Laso, M.; Garcia-Garcia, J.; Gil, I.; Portillo, M.; et al. Equivalent-circuit models for split-ring resonators and complementary split-ring resonators coupled to planar transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Grzegorczyk, T.M.; Wu, B.-I.; Pacheco, J.J.; Kong, J.A. Robust method to retrieve the constitutive effective parameters of metamaterials. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 016608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shorbagy, M.; Shubair, R.M.; AlHajri, M.I.; Mallat, N.K. On the design of millimetre-wave antennas for 5G. In Proceedings of the 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 14–16 November 2016; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Khalily, M.; Tafazolli, R.; Xiao, P.; Kishk, A.A. Broadband mm-Wave Microstrip Array Antenna with Improved Radiation Characteristics for Different 5G Applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 4641–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Bashir, S.; Chu, S. Dual band omnidirectional millimeter wave antenna for 5G communications. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2019, 33, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| r1 | 2.36 mm | Dw | 0.15 mm |
| W | 0.23 mm | Ly | 0.35 mm |
| G | 0.26 mm | Lg | 5.25 mm |
| D | 0.1 mm | A | 10.3 mm |
| Ref. | Band (GHz) | Size (mm3) | Radiation Pattern | Number of Bands | Rad. Eff. (%) | Gain (dBi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | 27.74–28.45 | 15 × 15 × 0.6 | Directional | Single | 97 | 8.8 |
| [29] | 24.35–31.13 | 6.2 × 7 × 0.2 | Directional | Single | 86 | 8.2 |
| [30] | 26.65–29.2 | 14 × 12 × 0.3 | Omni | Single | 78 | 1.7 |
| [22] | 26–31 | 11 × 31 × N/A | Directional | Single | N/A | 10 |
| [15] | 24.25–27.5 | 30 × 30 × 0.5 | Directional | Single | N/A | 7.4 |
| This work | 27.49–29.72 | 10.3 × 10.3 × 0.7 | Omni | Dual | 97 | 5.5 |
| Metal Particles | Mass Concentration (g/m3) |
|---|---|
| Pb | 126.30 |
| Zn | 99.83 |
| Cu | 79.53 |
| Ni | 99.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassan, K.M.Z.; Wongkasem, N.; Foltz, H. A Ka-Band Omnidirectional Metamaterial-Inspired Antenna for Sensing Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113545
Hassan KMZ, Wongkasem N, Foltz H. A Ka-Band Omnidirectional Metamaterial-Inspired Antenna for Sensing Applications. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113545
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassan, Khan Md. Zobayer, Nantakan Wongkasem, and Heinrich Foltz. 2025. "A Ka-Band Omnidirectional Metamaterial-Inspired Antenna for Sensing Applications" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113545
APA StyleHassan, K. M. Z., Wongkasem, N., & Foltz, H. (2025). A Ka-Band Omnidirectional Metamaterial-Inspired Antenna for Sensing Applications. Sensors, 25(11), 3545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113545







