Rowhammer Attacks in Dynamic Random-Access Memory and Defense Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. DRAM Background
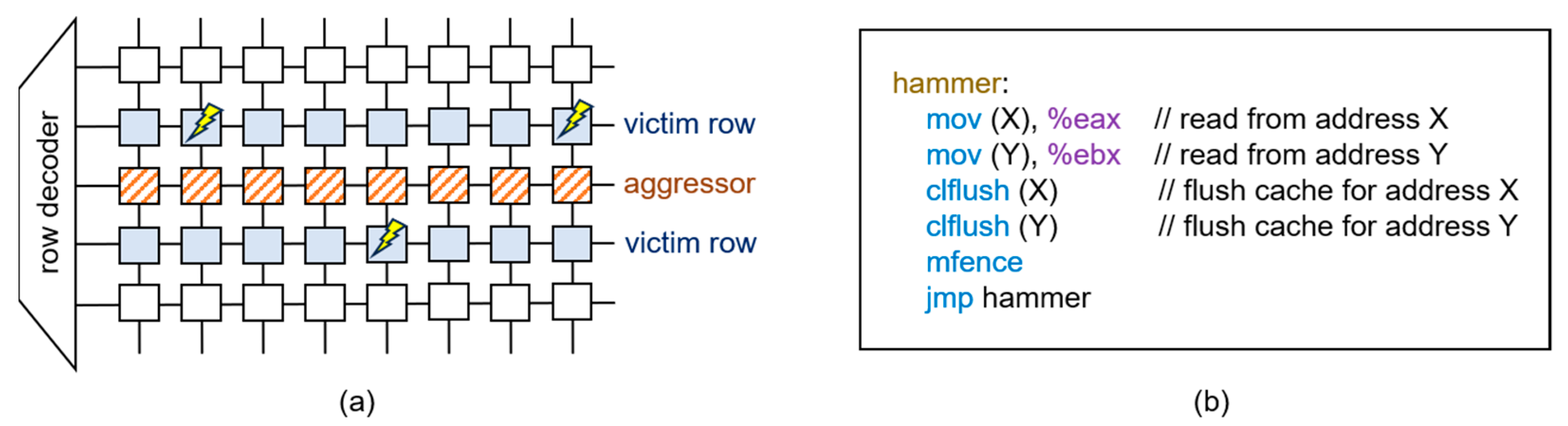
2.2. Rowhammer Mechanism
- (1)
- (2)
- (3)
- Hot carrier injection: Prolonged toggling of a word-line can lead to hot-carrier injection [53]. The injection of hot carriers into adjacent rows may escalate charge leakage from victim cells.
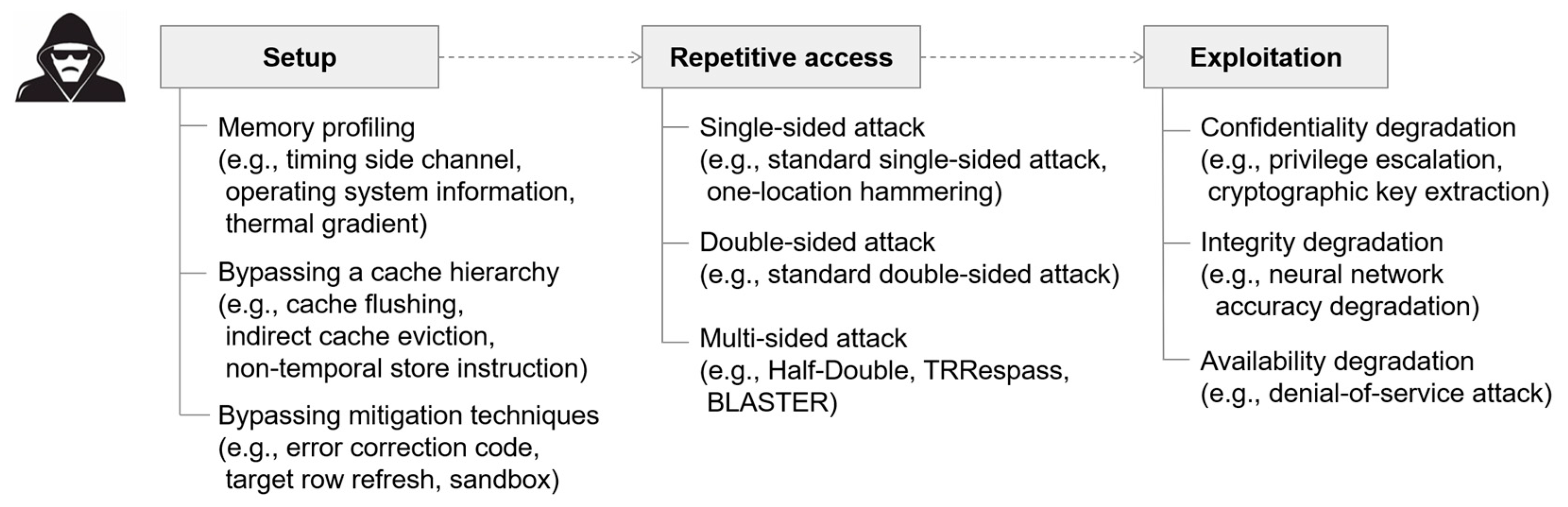
3. Setup for Rowhammer
3.1. Memory Profiling
3.2. Bypassing a Cache Hierarchy
3.3. Escaping a Sandbox
3.4. Bypassing Target Row Refresh
4. Repetitive Access Patterns for Rowhammer
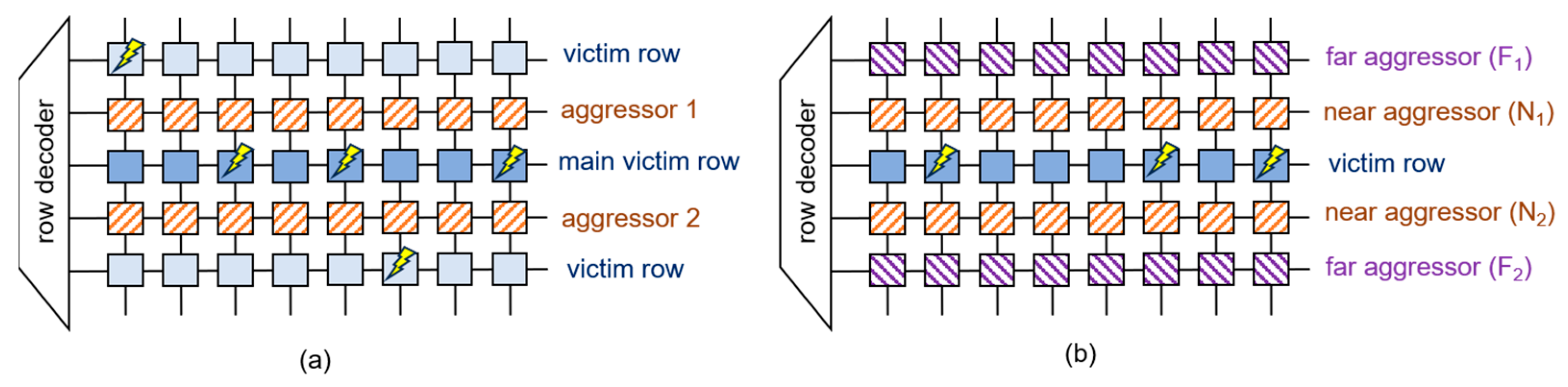
4.1. Single-Sided Attack
4.2. Double-Sided Attack
4.3. Multi-Sided Attack
5. Exploitation of Rowhammer
5.1. Confidentiality Degradation
5.2. Integrity Degradation
5.3. Availability Degradation
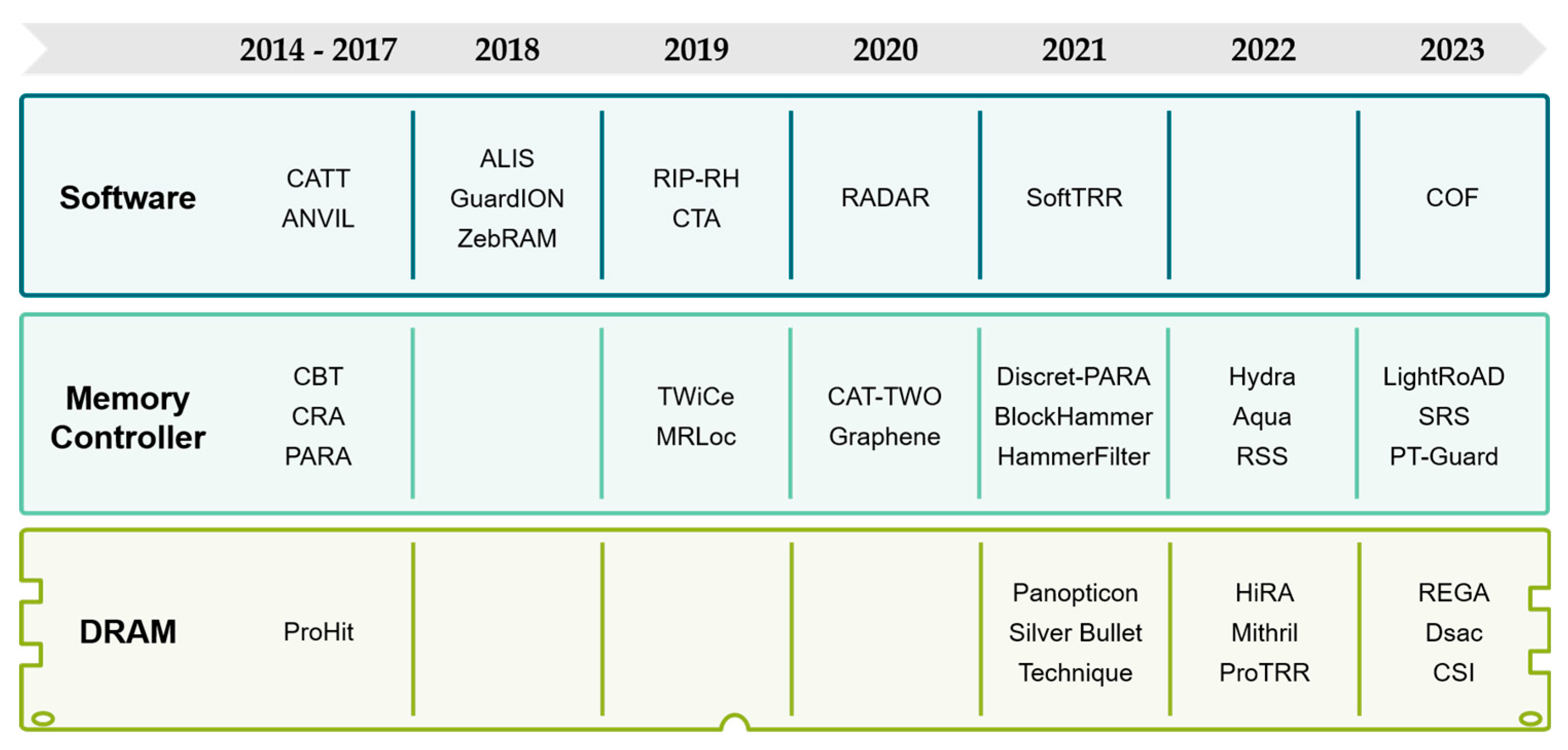
6. Rowhammer Defenses
6.1. Software-Based Mitigations
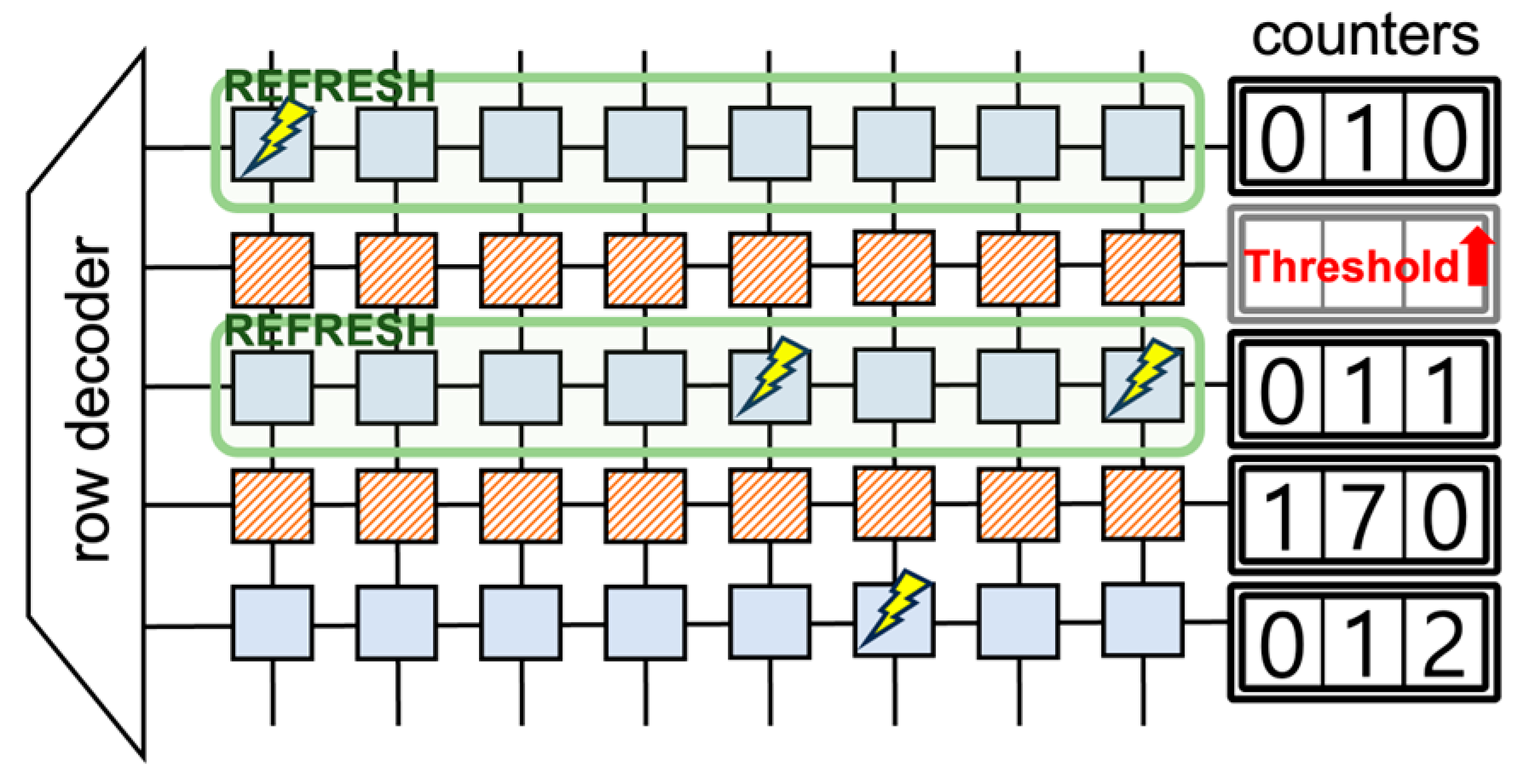
6.1.1. Heuristic-Based Attack Detection
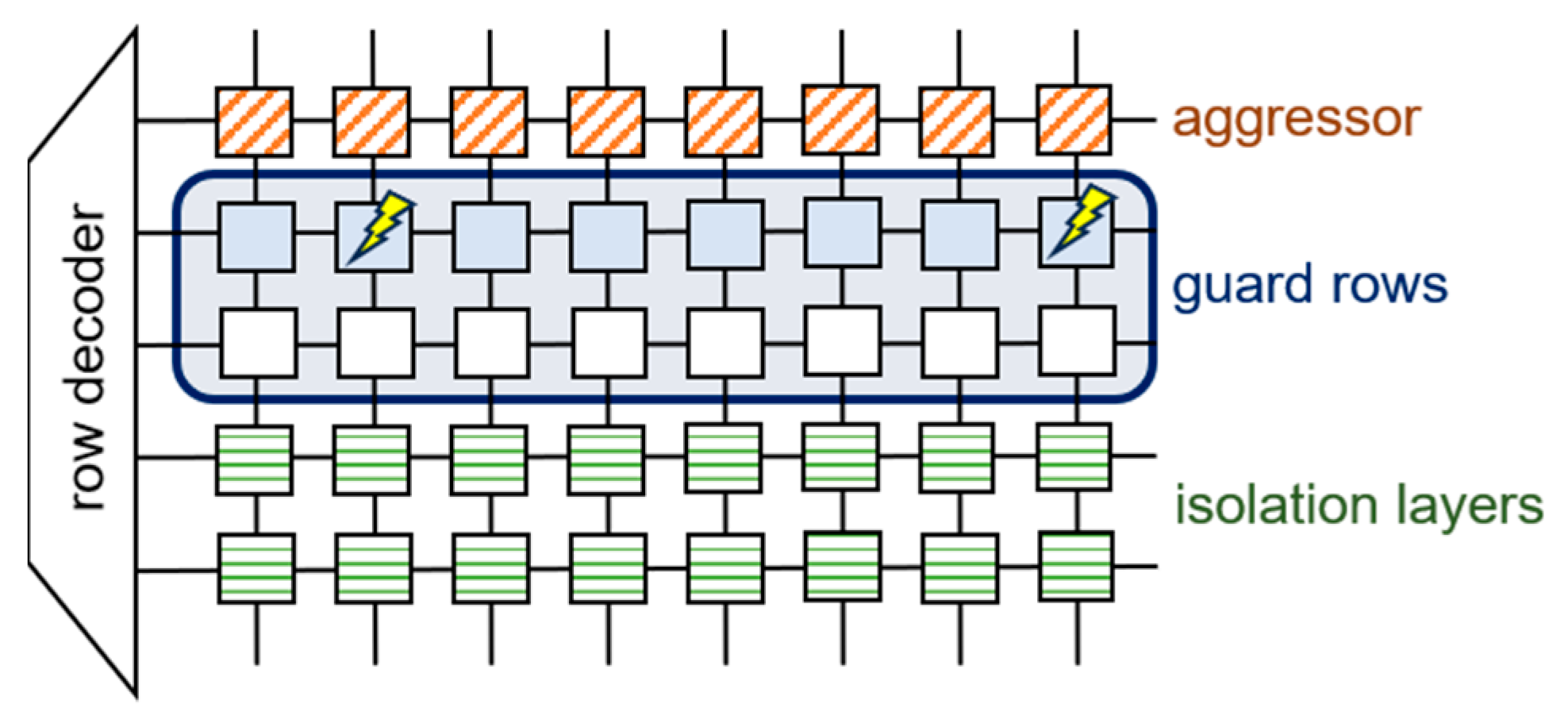
6.1.2. Physical Isolation
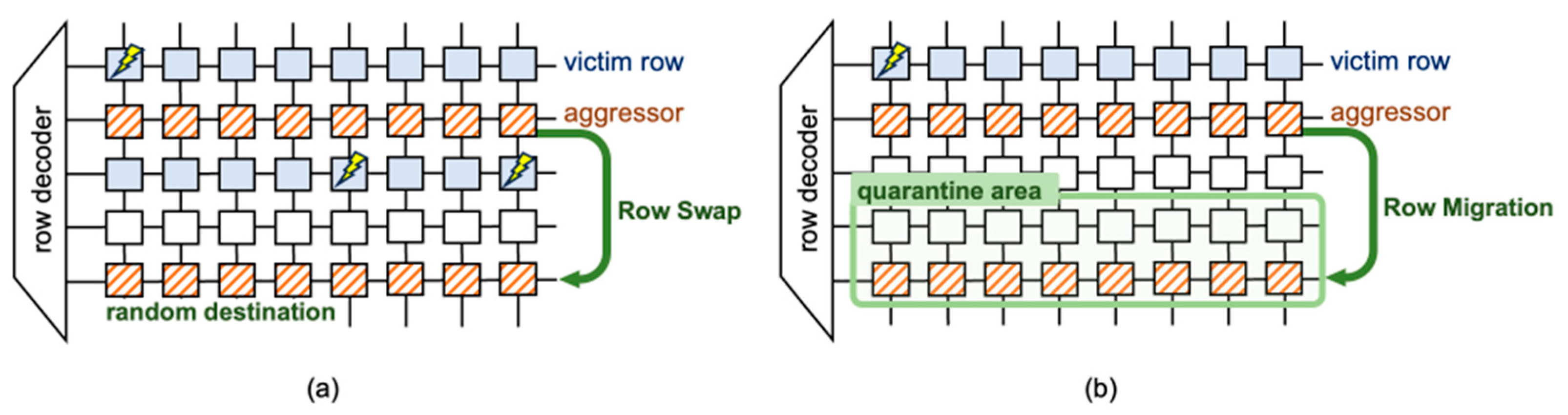
6.2. Memory Controller-Based Mitigations
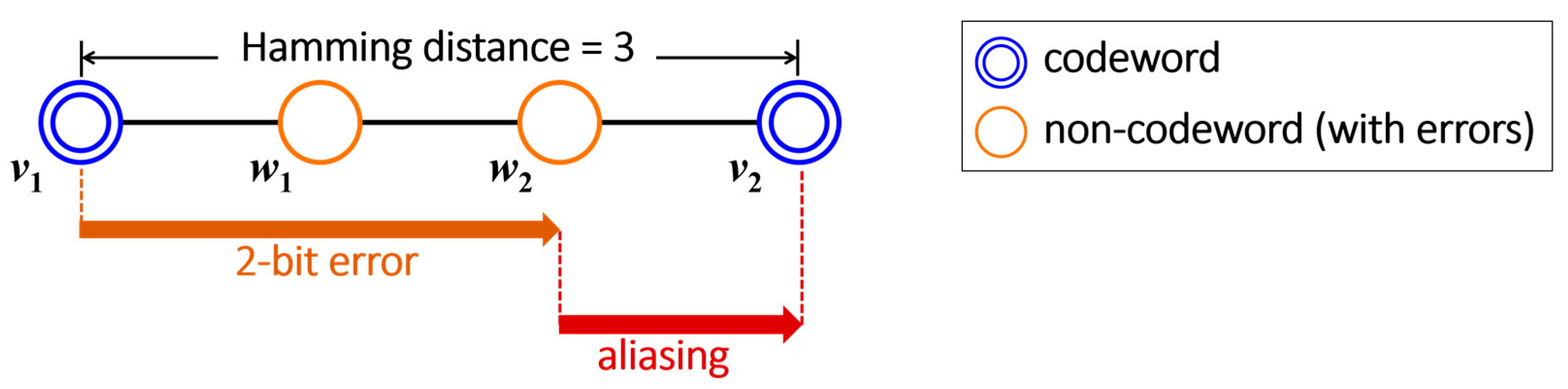
6.3. DRAM-Based Mitigations
7. Discussion: Rowhammer on DDR5 DRAM
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.; Daly, R.; Kim, J.; Fallin, C.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.; Wilkerson, C.; Lai, K.; Mutlu, O. Flipping bits in memory without accessing them: An experimental study of DRAM disturbance errors. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 2014, 42, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, A.; Genkin, D.; Gruss, D.; Yarom, Y. Rambleed: Reading bits in memory without accessing them. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–21 May 2020; pp. 695–711. [Google Scholar]
- Seaborn, M.; Dullien, T. Exploiting the DRAM rowhammer bug to gain kernel privileges. Black Hat 2015, 15, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kaveh, R.; Gras, B.; Bosman, E.; Preneel, B.; Giuffrida, C.; Bos, H. Flip feng shui: Hammering a needle in the software stack. In Proceedings of the 25th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 16), Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2016; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Teodorescu, R. One bit flips, one cloud flops:{Cross-VM} row hammer attacks and privilege escalation. In Proceedings of the 25th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 16), Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2016; pp. 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, G.; Maurice, C.; Mangard, S. Rowhammer. js: A remote software-induced fault attack in javascript. In Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment: 13th International Conference, DIMVA 2016, San Sebastián, Spain, 7–8 July 2016; Proceedings 13; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 300–321. [Google Scholar]
- Lucian, C.; Razavi, K.; Giuffrida, C.; Bos, H. Exploiting correcting codes: On the effectiveness of ecc memory against rowhammer attacks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2019; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, G.; Lipp, M.; Schwarz, M.; Genkin, D.; Juffinger, J.; O’Connell, S.; Schoechl, W.; Yarom, Y. Another flip in the wall of rowhammer defenses. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 245–261. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, T. SGX-Bomb: Locking down the processor via Rowhammer attack. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on System Software for Trusted Execution, Shanghai, China, 28 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Birhanu, A.Z.; Yitbarek, S.F.; Qiao, R.; Das, R.; Hicks, M.; Oren, Y.; Austin, T. ANVIL: Software-based protection against next-generation rowhammer attacks. ACM SIGPLAN Notices 2016, 51, 743–755. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, M.; He, W.; Wang, W.; Nepal, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C. {SoftTRR}: Protect Page Tables against Rowhammer Attacks using Software-only Target Row Refresh. In Proceedings of the 2022 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 22), Carlsbad, CA, USA, 11–13 July 2022; pp. 399–414. [Google Scholar]
- Moinuddin, Q.; Rohan, A.; Saileshwar, G.; Nair, P.J. Hydra: Enabling low-overhead mitigation of row-hammer at ultra-low thresholds via hybrid tracking. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, New York, NY, USA, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 699–710. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.S.; Jones, A.K.; Melhem, R. Counter-based tree structure for row hammering mitigation in DRAM. IEEE Comput. Archit. Lett. 2016, 16, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Eojin, L.; Kang, I.; Lee, S.; Suh, G.E.; Ahn, J.H. TWiCe: Preventing row-hammering by exploiting time window counters. In Proceedings of the 46th International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 22–26 June 2019; pp. 385–396. [Google Scholar]
- Yeonhong, P.; Kwon, W.; Lee, E.; Ham, T.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Lee, J.W. Graphene: Strong yet lightweight row hammer protection. In Proceedings of the 2020 53rd Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2020; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yağlikçi, A.G.; Patel, M.; Kim, J.S.; Azizi, R.; Olgun, A.; Orosa, L.; Hassan, H.; Park, J.; Kanellopoulos, K.; Shahroodi, T.; et al. Blockhammer: Preventing rowhammer at low cost by blacklisting rapidly-accessed dram rows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 February–3 March 2021; pp. 345–358. [Google Scholar]
- Michele, M.; Jattke, P.; Solt, F.; Razavi, K. Protrr: Principled yet optimal in-dram target row refresh. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2022; pp. 735–753. [Google Scholar]
- Min, Y.J.; Yang, J.-S. MRLoc: Mitigating Row-hammering based on memory Locality. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Design Automation Conference 2019, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2–6 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Saileshwar, G.; Juffinger, J.; Kogler, A.; Gruss, D.; Qureshi, M. PT-Guard: Integrity-Protected Page Tables to Defend Against Breakthrough Rowhammer Attacks. In Proceedings of the 2023 53rd Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN), Porto, Portugal, 27–30 June 2023; pp. 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ingab, K.; Lee, E.; Ahn, J.H. CAT-TWO: Counter-based adaptive tree, time window optimized for DRAM row-hammer prevention. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 17366–17377. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Oh, R.; Yoo, C.; Hwang, S.; Lee, J. Dsac: Low-cost rowhammer mitigation using in-dram stochastic and approximate counting algorithm. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.03591. [Google Scholar]
- Jaemin, K.M.; Park, J.; Park, Y.; Doh, W.; Kim, N.; Ham, T.J.; Lee, J.W.; Ahn, J.H. Mithril: Cooperative row hammer protection on commodity dram leveraging managed refresh. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2–6 April 2022; pp. 1156–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinand, B.; Davi, L.; Gens, D.; Liebchen, C.; Sadeghi, A.-R. {CAn’t} Touch This: Software-only Mitigation against Rowhammer Attacks targeting Kernel Memory. In Proceedings of the 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–18 August 2017; pp. 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Nair, P.J.; Qureshi, M.K. Architectural support for mitigating row hammering in DRAM memories. IEEE Comput. Archit. Lett. 2014, 14, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanj, B.; Saroiu, S.; Wolman, A.; Cojocar, L. Panopticon: A complete in-dram rowhammer mitigation. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on DRAM Security (DRAMSec), Virtual, 17 June 2021; Volume 22, p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Son, M.; Park, H.; Ahn, J.; Yoo, S. Making DRAM stronger against row hammering. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Design Automation Conference 2017, Austin, TX, USA, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Carsten, B.; Brasser, F.; Gens, D.; Liebchen, C.; Sadeghi, A.-R. Rip-rh: Preventing rowhammer-based inter-process attacks. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Auckland, New Zealand, 9–12 July 2019; pp. 561–572. [Google Scholar]
- Andrei, T.; Konoth, R.K.; Athanasopoulos, E.; Giuffrida, C.; Bos, H.; Razavi, K. Throwhammer: Rowhammer attacks over the network and defenses. In Proceedings of the 2018 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC 18), Boston, MA, USA, 11–13 July 2018; pp. 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen, V.; Lindorfer, M.; Fratantonio, Y.; Pillai, H.P.; Vigna, G.; Kruegel, C.; Bos, H.; Razavi, K. Guardion: Practical mitigation of dma-based rowhammer attacks on arm. In Detection of Intrusions and Malware, and Vulnerability Assessment: 15th International Conference, DIMVA 2018, Saclay, France, 28–29 June 2018; Proceedings 15; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 92–113. [Google Scholar]
- Konoth, R.K.; Oliverio, M.; Tatar, A.; Andriesse, D.; Bos, H.; Giuffrida, C.; Razavi, K. {ZebRAM}: Comprehensive and Compatible Software Protection Against Rowhammer Attacks. In Proceedings of the 13th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 18), Carlsbad, CA, USA, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 697–710. [Google Scholar]
- Gururaj, S.; Wang, B.; Qureshi, M.; Nair, P.J. Randomized row-swap: Mitigating row hammer by breaking spatial correlation between aggressor and victim rows. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 28 February–4 March 2022; pp. 1056–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Anish, S.; Saileshwar, G.; Nair, P.J.; Qureshi, M. Aqua: Scalable rowhammer mitigation by quarantining aggressor rows at runtime. In Proceedings of the 2022 55th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Chicago, IL, USA, 1–5 October 2022; pp. 108–123. [Google Scholar]
- Michele, M.; Solt, F.; Jattke, P.; Takashi, K.; Razavi, K. REGA: Scalable Rowhammer Mitigation with Refresh-Generating Activations. In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP 2023), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Giray, Y.A.; Olgun, A.; Patel, M.; Luo, H.; Hassan, H.; Orosa, L.; Ergin, O.; Mutlu, O. HiRA: Hidden row activation for reducing refresh latency of off-the-shelf DRAM chips. In Proceedings of the 2022 55th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Chicago, IL, USA, 1–5 October 2022; pp. 815–834. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, J.; Lamster, L.; Kogler, A.; Eichlseder, M.; Lipp, M.; Gruss, D. CSI: Rowhammer–Cryptographic Security and Integrity against Rowhammer. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–24 May 2022; pp. 1702–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Balasubramanian, D.; Li, B.; Volgyesi, P.; Koutsoukos, X. Leveraging em side-channel information to detect rowhammer attacks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–21 May 2020; pp. 729–746. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.-C.; Sherwood, T.; Chong, F.T.; Li, Y. Protecting page tables from rowhammer attacks using monotonic pointers in dram true-cells. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, Providence, RI, USA, 13–17 April 2019; pp. 645–657. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.; Saileshwar, G.; Nair, P.J. Scalable and Secure Row-Swap: Efficient and Safe Row Hammer Mitigation in Memory Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 25 February–1 March 2023; pp. 374–389. [Google Scholar]
- Di Dio, A.; Koning, K.; Bos, H.; Giuffrida, C. Copy-on-Flip: Hardening ECC Memory Against Rowhammer Attacks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 27 February–3 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kwangrae, K.; Woo, J.; Kim, J.; Chung, K.-S. Hammerfilter: Robust protection and low hardware overhead method for rowhammer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 39th International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Storrs, CT, USA, 24–27 October 2021; pp. 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Z. Discreet-PARA: Rowhammer Defense with Low Cost and High Efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 39th International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Storrs, CT, USA, 24–27 October 2021; pp. 433–441. [Google Scholar]
- Mottaqiallah, T.; Reinbrecht, C.; Hamdioui, S.; Sepúlveda, J. LightRoAD: Lightweight Rowhammer Attack Detector. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI), Virtual, 7–9 July 2021; pp. 362–367. [Google Scholar]
- Yağlıkçı, A.G.; Kim, J.S.; Devaux, F.; Mutlu, O. Security Analysis of the Silver Bullet Technique for RowHammer Prevention. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.07084. [Google Scholar]
- Jamie, L.; Jaiyen, B.; Kim, Y.; Wilkerson, C.; Mutlu, O. An experimental study of data retention behavior in modern DRAM devices: Implications for retention time profiling mechanisms. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 2013, 41, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Restle, Park, and Lloyd. DRAM variable retention time. In Proceedings of the 1992 International Technical Digest on Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–16 December 1992; pp. 807–810.
- Lois, O.; Yaglikci, A.G.; Luo, H.; Olgun, A.; Park, J.; Hassan, H.; Patel, M.; Kim, J.S.; Mutlu, O. A deeper look into rowhammer’s sensitivities: Experimental analysis of real dram chips and implications on future attacks and defenses. In Proceedings of the MICRO-54: 54th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Virtual, 18–22 October 2021; pp. 1182–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Patel, M.; Yağlıkçı, A.G.; Hassan, H.; Azizi, R.; Orosa, L.; Mutlu, O. Revisiting rowhammer: An experimental analysis of modern dram devices and mitigation techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Valencia, Spain, 30 May–3 June 2020; pp. 638–651. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.-F.; Yang, H.-Y.; Chao, M.C.-T.; Lin, S.-C. Alternate hammering test for application-specific DRAMs and an industrial case study. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 1012–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Redeker, M.; Cockburn, B.F.; Elliott, D.G. An investigation into crosstalk noise in DRAM structures. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Workshop on Memory Technology, Design and Testing (MTDT2002), Bendor, France, 12 July 2002; pp. 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ars, Z.; Hamdioui, S.; Van De Goor, A.; Gaydadjiev, G.; Vollrath, J. DRAM-specific space of memory tests. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Test Conference, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 22–27 October 2006; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, M.C.T.; Yang, H.Y.; Huang, R.F.; Lin, S.C.; Chin, C.Y. Fault models for embedded-DRAM macros. In Proceedings of the 46th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–31 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Min, D.S.M.D.S.; Seo, D.I.S.D.I.; You, J.Y.J.; Cho, S.C.S.; Chin, D.C.D.; Park, Y.E. Wordline coupling noise reduction techniques for scaled DRAMs. In Proceedings of the Digest of Technical Papers, 1990 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Honololu, HI, USA, 7–9 June 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, P.C.F.; Wen, S.J.; Baeg, S.H. New DRAM HCI qualification method emphasizing on repeated memory access. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Integrated Reliability Workshop Final Report, South Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 17–21 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shutemov, K.A. Pagemap: Do Not Leak Physical Addresses to Non-Privileged Userspace. Available online: https://lwn.net/Articles/642074/ (accessed on 10 November 2015).
- Peter, P.; Gruss, D.; Maurice, C.; Schwarz, M.; Mangard, S. {DRAMA}: Exploiting {DRAM} Addressing for {Cross-CPU} Attacks. In Proceedings of the 25th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 16), Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2016; pp. 565–581. [Google Scholar]
- Matthias, J.; Rheinländer, C.C.; Weis, C.; Wehn, N. Reverse engineering of DRAMs: Row hammer with crosshair. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on Memory Systems, Alexandria, VA, USA, 3–6 October 2016; pp. 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Jeremie, K.; Patel, M.; Hassan, H.; Mutlu, O. Solar-DRAM: Reducing DRAM access latency by exploiting the variation in local bitlines. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 36th International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Orlando, FL, USA, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Donghyuk, L.; Khan, S.; Subramanian, L.; Ghose, S.; Ausavarungnirun, R.; Pekhimenko, G.; Seshadri, V.; Mutlu, O. Design-induced latency variation in modern DRAM chips: Characterization, analysis, and latency reduction mechanisms. Proc. ACM Meas. Anal. Comput. Syst. 2017, 1, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Andrei, T.; Giuffrida, C.; Bos, H.; Razavi, K. Defeating software mitigations against rowhammer: A surgical precision hammer. In Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses: 21st International Symposium, RAID 2018, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 10–12 September 2018; Proceedings 21; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- van Der Veen, V.; Fratantonio, Y.; Lindorfer, M.; Gruss, D.; Maurice, C.; Vigna, G.; Bos, H.; Razavi, K.; Giuffrida, C. Drammer: Deterministic rowhammer attacks on mobile platforms. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 October 2016; pp. 1675–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Q.; Seaborn, M. A new approach for rowhammer attacks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), McLean, VA, USA, 3–5 May 2016; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, K.; Juffinger, J.; Qazi, S.; Kim, Y.; Lipp, M.; Boichat, N.; Shiu, E.; Nissler, M.; Gruss, D. {Half-Double}: Hammering From the Next Row Over. In Proceedings of the 31st USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 22), Boston, MA, USA, 10–12 August 2022; pp. 3807–3824. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, Z.; Jattke, P.; Marazzi, M.; Razavi, K. BLASTER: Characterizing the Blast Radius of Rowhammer. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on DRAM Security (DRAMSec) Co-Located with ISCA 2023, Virtual, 17 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, G.; Bidner, D.; Mangard, S. Practical memory deduplication attacks in sandboxed javascript. In Computer Security—ESORICS 2015: 20th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Vienna, Austria, 21–25 September 2015; Proceedings, Part I 20; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Yossef, O.; Kemerlis, V.P.; Sethumadhavan, S.; Keromytis, A.D. The spy in the sandbox: Practical cache attacks in javascript and their implications. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Denver, CO, USA, 12–16 October 2015; pp. 1406–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Pietro, F.; Vannacc, E.; Hassan, H.; Van Der Veen, V.; Mutlu, O.; Giuffrida, C.; Bos, H.; Razavi, K. TRRespass: Exploiting the many sides of target row refresh. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–21 May 2020; pp. 747–762. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, J.; Van Der Veen, V.; Frigo, P.; Gunter, S.; Razavi, K. Blacksmith: Scalable rowhammering in the frequency domain. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2022; pp. 716–734. [Google Scholar]
- Onur, M.; Kim, J.S. Rowhammer: A retrospective. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 39, 1555–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.T. Modern Dram Memory Systems: Performance Analysis and Scheduling Algorithm. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitris, K.; Stuecheli, J.; John, L.K. Minimalist open-page: A DRAM page-mode scheduling policy for the many-core era. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 3–7 December 2011; pp. 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, O.D.; Jeffrey, R.W. Method for Dynamically Adjusting a Memory Page Closing Policy. U.S. Patent 6,799,241, 28 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Siraj, R.A.; He, Z.; Fan, D. Bit-flip attack: Crushing neural network with progressive bit search. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1211–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Dahoon, P.; Kwon, K.-W.; Im, S.; Kung, J. ZeBRA: Precisely Destroying Neural Networks with Zero-Data Based Repeated Bit Flip Attack. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.01080. [Google Scholar]
- Ramprasaath, R.S.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, Z.; Tomer, L.E.V.Y. Throttling Support for Row-Hammer Counters. U.S. Patent 9,251,885, 2 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Minesh, P.; Kim, J.S.; Shahroodi, T.; Hassan, H.; Mutlu, O. Bit-exact ECC recovery (BEER): Determining DRAM on-die ECC functions by exploiting DRAM data retention characteristics. In Proceedings of the 2020 53rd Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2020; pp. 282–297. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.S.; Jones, A.K.; Melhem, R. Mitigating wordline crosstalk using adaptive trees of counters. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM/IEEE 45th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; pp. 612–623. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, J.; David, G. Finding repeated elements. Sci. Comput. Program. 1982, 2, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onur, M.; Olgun, A.; Yağlıkcı, A.G. Fundamentally understanding and solving rowhammer. In Proceedings of the 28th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 16–19 January 2023; pp. 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- About the Security Content of Mac EFI Security Update 2015-001; Apple Inc.: Cupertino, CA, USA, June 2015; Available online: https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT204934 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Fridley, T.; Omar, S. Mitigations Available for the DRAM Row Hammer Vulnerability. 2015. Available online: https://blogs.cisco.com/security/mitigations-available-for-the-dram-row-hammer-vulnerability (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Enterprise, Hewlett-Packard. HP Moonshot Component Pack Version 2015.05.0. 2015. Available online: https://support.hpe.com/hpesc/public/docDisplay?docId=c04676483&docLocale=en_US (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- JESD79-5; JEDEC Standard, DDR5 SDRAM. JEDEC Solid State Technology Association: Arlington, VA, USA, July 2020.
- Kim, D.; Park, M.; Jang, S.; Song, J.Y.; Chi, H.; Choi, G.; Choi, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.; et al. 23.2 a 1.1 V 1ynm 6.4 Gb/s/pin 16Gb DDR5 SDRAM with a Phase-Rotator-Based DLL, high-speed SerDes and RX/TX equalization scheme. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pae, S.I.; Kozhikkottu, V.; Somasekar, D.; Wu, W.; Ramasubramanian, S.G.; Dadual, M.; Cho, H.; Kwon, K.W. Minimal aliasing single-error-correction codes for dram reliability improvement. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 29862–29869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, J.J.; Joo, K.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.T.; Na, W.J.; Choi, I.; Yu, H.S.; Kim, W.; et al. Industry’s First 7.2 Gbps 512GB DDR5 Module. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Hot Chips 33 Symposium (HCS), Palo Alto, CA, USA, 22–24 August 2021; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, N.H.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; Jin, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Hwang, Y.C.; Kim, H.S.; Pae, S. Development and Product Reliability Characterization of Advanced High Speed 14nm DDR5 DRAM with On-die ECC. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Monterey, CA, USA, 26–30 March 2023. [Google Scholar]



| Setup | Cited Paper | Year | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Memory profiling | Project Zero [3] | 2015 | Pagemap/Huge pages/Timing |
| Pagemap [54] | 2015 | Pagemap | |
| DRAMA [55] | 2015 | Pagemap/Huge pages/Timing | |
| Cross-VM Row Hammer [5] | 2015 | Timing | |
| Rambleed [2] | 2020 | Pagemap | |
| Row hammer with crosshair [56] | 2016 | The retention error behavior with respect to the temperature | |
| Solar-DRAM [57] | 2018 | Timing | |
| Design-induced latency variation [58] | 2017 | Timing | |
| A surgical precision hammer [59] | 2018 | Pagemap/Huge pages/Timing | |
| Drammer [60] | 2016 | Pagemap/Huge pages/Timing | |
| Bypassing a cache hierarchy | DRAM disturbance errors [1] | 2014 | Cache Flushing |
| A new approach [61] | 2016 | Non-temporal store-based bypassing | |
| Half-Double [62] | 2022 | Cache Eviction | |
| BLASTER [63] | 2023 | Cache Eviction | |
| Bypassing mitigation techniques | Memory deduplication attacks in sandboxed JavaScript [64] | 2015 | Escaping a Sandbox |
| The spy in the sandbox [65] | 2015 | Escaping a Sandbox | |
| Rowhammer.js [6] | 2016 | Escaping a Sandbox | |
| TRRespass [66] | 2020 | Bypassing TRR | |
| BLACKSMITH [67] | 2022 | Bypassing TRR |
| CIA Triad | Cited Paper | Year | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality degradation | Project Zero [3] | 2015 | An operating system for privilege escalation |
| Drammer [60] | 2016 | An ARM-based device for privilege escalation | |
| Cross-VM Row Hammer [5] | 2016 | The physical hardware in virtual machines (VMs) | |
| Flip Feng Shui [4] | 2016 | The memory-storing cryptographic keys | |
| RAMBleed [2] | 2020 | An operating system for privilege escalation | |
| Integrity degradation | Cross-VM Row Hammer [5] | 2016 | Withing an OpenSSH server |
| Rowhammer.js [6] | 2016 | Within a remote computing system | |
| ECCploit [7] | 2019 | Within error correction code (ECC) memory | |
| Bit-flip attack [72] | 2019 | Within the neural network, parameter bits stored in DRAM | |
| ZeBRA [73] | 2021 | Within the neural network, parameter bits stored in DRAM | |
| Availability degradation | SGX-Bomb [9] | 2017 | Accessibility in the cloud |
| Another Flip [8] | 2018 | Accessibility in the cloud |
| Location | Mechanism | Year | Protection Concepts | Tracking Mechanism | Remedy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software | COF [39] | 2023 | Deterministic | Counter | Physical Isolation |
| SoftTRR [11] | 2021 | Deterministic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| RADAR [36] | 2020 | Deterministic | - | Reactive Refresh | |
| RIP-RH [27] | 2019 | Deterministic | - | Physical Isolation | |
| CTA [37] | 2019 | Deterministic | - | Physical Isolation | |
| ALIS [28] | 2018 | Deterministic | - | Physical Isolation | |
| GuardION [29] | 2018 | Deterministic | - | Physical Isolation | |
| ZebRAM [30] | 2018 | Deterministic | - | Physical Isolation | |
| CATT [23] | 2017 | Deterministic | Cache | Physical Isolation | |
| ANVIL [10] | 2016 | Probabilistic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| Memory Controller | LightRoAD [42] | 2023 | Deterministic | Counter, Cache | Reactive Refresh |
| SRS [38] | 2023 | - | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| PT-Guard [19] | 2023 | ||||
| Hydra [12] | 2022 | - | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| Aqua [32] | 2022 | Probabilistic | - | Physical Isolation | |
| RSS [31] | 2022 | Probabilistic | - | Physical Isolation | |
| Discreet-PARA [41] | 2021 | Probabilistic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| BlockHammer [16] | 2021 | Deterministic | Counter | Proactive Throttling | |
| HammerFilter [40] | 2021 | Deterministic | Counter | Proactive Throttling | |
| CAT-TWO [20] | 2020 | Deterministic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| Graphene [15] | 2020 | Deterministic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| TWiCe [14] | 2019 | Deterministic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| MRLoc [18] | 2019 | Probabilistic | Counter, Queue | Reactive Refresh | |
| CBT [13] | 2016 | Probabilistic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| CRA [24] | 2015 | Probabilistic | Counter, Cache | Reactive Refresh | |
| PARA [1] | 2014 | Probabilistic | - | Increased Refresh Rate | |
| DRAM | REGA [33] | 2023 | Deterministic | - | Reactive Refresh |
| Dsac [21] | 2023 | Probabilistic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| CSI [35] | 2023 | - | - | - | |
| HiRA [34] | 2022 | Probabilistic | - | Reactive Refresh | |
| Mithril [22] | 2022 | Deterministic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| ProTRR [17] | 2022 | Probabilistic | Counter | Reactive Refresh | |
| Silver Bullet Technique [43] | 2021 | Probabilistic | - | Reactive Refresh | |
| Panopticon [25] | 2021 | Deterministic | Counter, Queue | Reactive Refresh | |
| ProHIT [26] | 2017 | Probabilistic | Queue | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Park, H.; Yeo, I.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.-M.; Kwon, K.-W. Rowhammer Attacks in Dynamic Random-Access Memory and Defense Methods. Sensors 2024, 24, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020592
Kim D, Park H, Yeo I, Lee YK, Kim Y, Lee H-M, Kwon K-W. Rowhammer Attacks in Dynamic Random-Access Memory and Defense Methods. Sensors. 2024; 24(2):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020592
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dayeon, Hyungdong Park, Inguk Yeo, Youn Kyu Lee, Youngmin Kim, Hyung-Min Lee, and Kon-Woo Kwon. 2024. "Rowhammer Attacks in Dynamic Random-Access Memory and Defense Methods" Sensors 24, no. 2: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020592
APA StyleKim, D., Park, H., Yeo, I., Lee, Y. K., Kim, Y., Lee, H.-M., & Kwon, K.-W. (2024). Rowhammer Attacks in Dynamic Random-Access Memory and Defense Methods. Sensors, 24(2), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020592