Online Handwritten Signature Verification Method Based on Uni-Feature Correlation Coefficient between Signatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
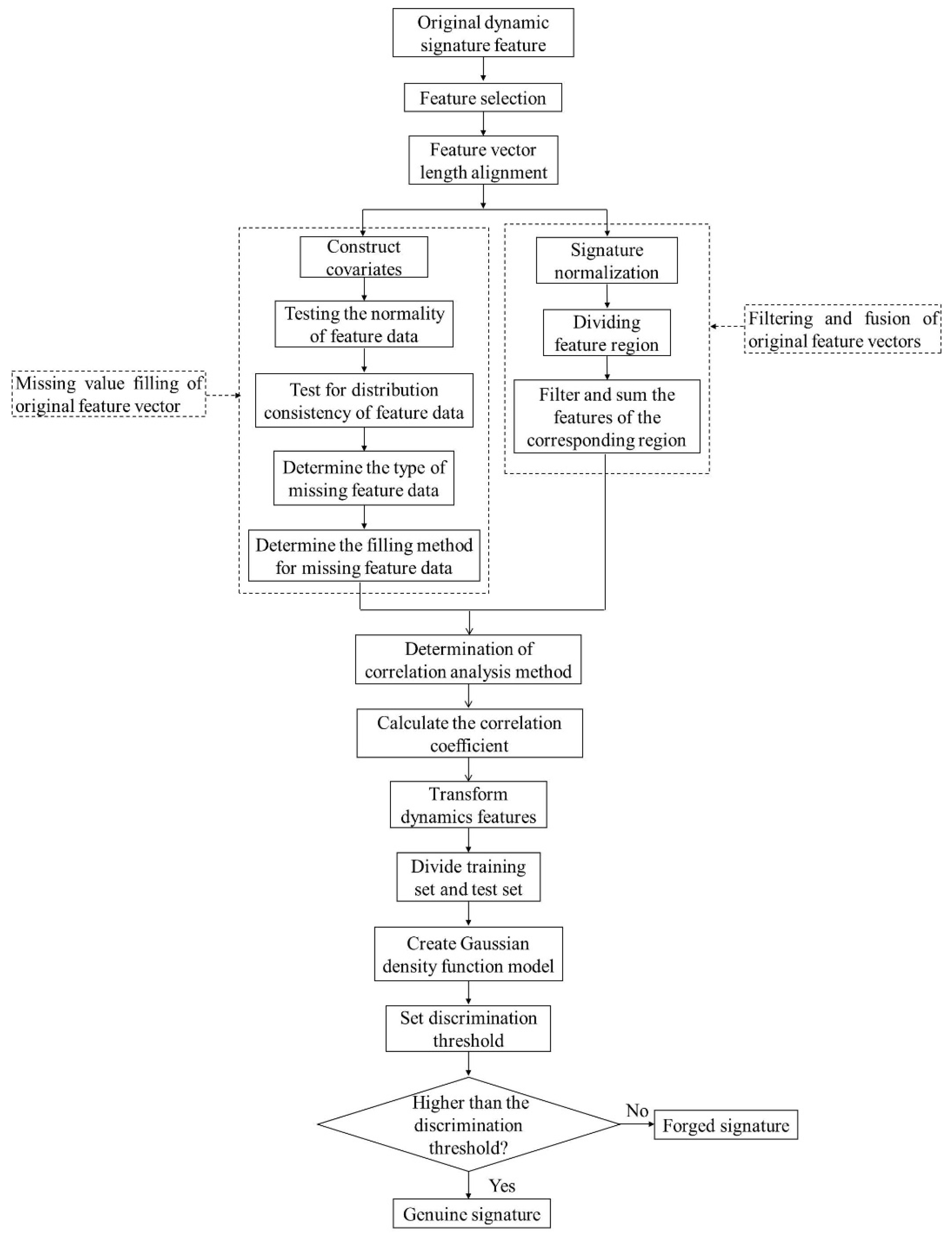
2. Online Signature Verification Method Based on Uni-Features
2.1. Feature Selection
2.2. Feature Vector Length Alignment Method
2.2.1. Feature Vector Length Alignment Method by Filling the Missing Value according to Original Feature Vector Missing Situation
2.2.2. Feature Vector Length Alignment Method Based on Original Feature Vector Filtering and Fusion
2.3. Online Signature Verification
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, X.Q.; Li, X. Computer Writer Identification and Verification Theory and Method; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 1–278. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jin, X.Y.; Jiang, Q. Online handwritten signature verification based on the most stable feature and partition. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, F.; Plamondon, R. Automatic signature verification: The state of the art-1989–1993. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 1994, 8, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Kumar, V. A novel approach to validate online signature using dynamic features based on locally weighted learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 40959–40976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorugunti, C.S.; Pulabaigari, V.; Mukherjee, P.; Gautam, A. COMPOSV: Compound feature extraction and depthwise separable convolution-based online signature verification. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 10901–10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Luan, F.J.; Yuan, S. Multi-scale residual based siamese neural network for writer-independent online signature verification. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 14571–14589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrabian, K.; Babaali, B. Usage of autoencoders and Siamese networks for online handwritten signature verification. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 9321–9334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.H.; Song, X.Y.; Luan, F.G.; Zhang, J.G.; Chen, Z.L.; Ma, X.F. Discriminative feature selection for on-line signature verification. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sundaram, S. On the exploration of information from the DTW cost matrix for online signature verification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 48, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, M. Online signature verification using single-template matching through locally and globally weighted dynamic time warping. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2020, 103, 2701–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Tam, H.; Huang, Z.C. Online handwritten signature verification based on association of curvature and torsion feature with Hausdorff distance. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 19253–19278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowal, P.; Banerjee, D.; Malakar, S.; Sarkar, R. A two-tier ensemble approach for writer dependent online signature verification. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 13, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Lai, S.X.; Jin, L.W.; Zhu, Y.C. DsDTW: Local representation learning with deep soft-dtw for dynamic signature verification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 17, 2198–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikin, I.; Anisimova, E. Framework for biometric user authentication based on a dynamic handwritten signature. Cyber-Phys. Syst. Intell. Models 2022, 417, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Kimura, A.; Iwana, B.K.; Uchida, S.; Kashino, K. Deep dynamic time warping: End-to-end local representation learning for online signature verification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), Sydney, Australia, 20–25 September 2019; pp. 1103–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Kovari, B. K-nearest neighbour and dynamic time warping for online signature verification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning Techniques and Data Science (MLDS 2021), Zurich, Switzerland, 20–21 November 2021; pp. 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Foroozandeh, A.; Hemmat, A.A.; Rabbani, H. Online handwritten signature verification and recognition based on dual-tree complex wavelet packet transform. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2020, 10, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- AbuAlghanam, O.; Albdour, L.; Adwan, O. Multimodal biometric fusion online handwritten signature verification using neural network and support vector machine. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2021, 17, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parziale, A.; Diaz, M.; Ferrer, M.A.; Marcelli, A. SM-DTW: Stability modulated dynamic time warping for signature verification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 121, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawa, M. Time-series averaging and local stability-weighted dynamic time warping for online signature verification. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 112, 107699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.S.; Govindaraju, V. A comparative study on the consistency of features in on-line signature verification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2005, 26, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamski, M.; Saeed, K. Online signature classification and its verification system. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Information Systems and Industrial Management Applications, Ostrava, Czech Republic, 26–28 June 2008; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, K.D.; De Sá, C.R.; Poel, M.; Carvalho, T.; Mendes-Moreira, J.; Cardoso, J.M.P.; de Carvalho, A.C.P.L.F.; Kok, J.N. An ensemble of autonomous auto-encoders for human activity recognition. Neurocomputing 2021, 439, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverko, Z.; Vrankic, M.; Vlanhinic, S.; Rogelj, P. Complex Pearson correlation coefficient for EEG connectivity analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, R.B.; Aqila, T.; Maharjan, M.; Mamun, A.A.; Mondal, A.M. Graph theoretic and Pearson correlation-based discovery of network biomarkers for cancer. Data 2019, 4, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiao, H.Y.J.; Cheng, J. Human posture estimation and correction based on the CPM and the Pearson correlation coefficient. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sensors and Instruments (ICSI 2021), Qingdao, China, 2 July 2021; pp. 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Bommisetty, R.M.; Prakash, O.; Khare, A. Keyframe extraction using Pearson correlation coefficient and color moments. Multimed. Syst. 2020, 26, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.; Weisshaar, J.C. Modified Pearson correlation coefficient for two-color imaging in spherocylindrical cells. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Khan, M.A.; Yasmin, M.; Shah, J.H.; Gabryel, M.; Scherer, R.; Damaševičcius, R. Pearson correlation-based feature selection for document classification using balanced training. Sensors 2020, 20, 6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.; Nixo, M.S.; Komogortsev, O.V. Method to assess the temporal persistence of potential biometric features: Application to oculomotor, gait, face and brain structure databases. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.Z.; Jin, R.H.; Shi, H.F.; Lu, X.J. Research on recognition of motor imagination based on connectivity features of brain functional network. Neural Plast. 2021, 2021, 6655430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Maggioni, V.; Houser, P.; Xue, Y.; Mei, Y.W. The impact of weather condition and social activity on COVID-19 transmission in the United States. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zeng, P.F.; Wu, Q.S.; Chen, F.G. Feature selection of converter steelmaking process based on the improved genetic algorithm. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 40, 185–195. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailoghli, M.; Quiané-Ruiz, J.A.; Abedjan, Z. COCOA: Correlation coefficient-aware data augmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT 2021), Nicosia, Cyprus, 23–26 March 2021; pp. 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Jones, R.B.; Fodor, A.A. Inference-based accuracy of metagenome prediction tools varies across sample types and functional categories. Microbiome 2020, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Li, C.; Cui, L.; Tian, C.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Ge, Q. M-BLUE protocol for coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) patients: Interobserver variability and correlation with disease severity. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, E.; Liu, A.A.S.; Duizer, L.M.; Darlington, G.; Duncan, A.M.; Haines, J.; Ma, D.W.L. Taste sensitivity and taste preference measures are correlated in healthy young adults. Chem. Senses 2019, 44, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, Y.A.C.; Rêgo, L.C.; Ospina, R. Online handwritten signature verification via network analysis. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2022, 600, 127582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.K.; Wong, S.K.; Chim, L.C.J. A prototype of mathematical treatment of pen pressure data for signature verification. J. Forensic Sci. 2018, 63, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.N.; Xin, Y.Z.; Li, Y. Online signature verification method based on Pearson correlation coefficient. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2022, 43, 279–287. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosana, R.; Vera-Rodriguez, R.; Fierrez, J.; Ortega-Garci, J. Reducing the template ageing effect in on-line signature biometrics. IET Biom. 2019, 8, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbally, J.; Martinez-Diaz, M.; Fierrez, J. Aging in biometrics: An experimental analysis on on-line signature. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, D.Y.; Chang, H.; Xiong, Y.; George, S.; Kashi, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Rigoll, G. Svc2004: First international signature verification competition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometric Authentication (ICBA 2004), Hong Kong, China, 15–17 July 2004; pp. 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, N.J.; Laird, N.M. Maximum likelihood analysis of generalized linear models with missing covariates. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.X.; Shan, L.B.; He, D.Q.; Tang, R. Processing method of missing data and its developing tendency. Stat. Decis. 2019, 23, 28–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.J.A.; Rubin, D.B. Statistical Analysis with Missing Data, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Jin, Y.J.; Dai, M.F. Discussion on testing the mechanism of missing data. Math. Pract. Theory 2013, 43, 166–173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Pandey, C.M.; Singh, U.; Gupta, A.; Sahu, C.; Keshri, A. Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, B.W.; Sim, C.H. Comparisons of various types of normality tests. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2011, 81, 2141–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertagova, E.; Ostertag, O.; Kováč, J. Methodology and application of the Kruskal-Wallis test. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 611, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.R.; Royston, P.; Wood, A.M. Multiple imputation using chained equations: Issues and guidance for practice. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am. J. Psychol. 1904, 15, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, J.C.F.; Gosling, S.D.; Potter, J. Comparing the Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients across distributions and sample sizes: A tutorial using simulations and empirical data. Psychol. Methods 2016, 21, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsby, P.D.; Weatherall, M. Statistics: An introduction to basic principles. Postgrad. Med. J. 2022, 98, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Kovari, B. Online signature verification using signature down-sampling and signer-dependent sampling frequency. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cpałka, K.; Zalasinski, M. On-line signature verification using vertical signature partitioning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4170–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Singh, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Ganesh, K.V.K.S.; Sravya, L.; Kumar, B.P. A novel approach to validate online signature using machine learning based on dynamic features. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 12347–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalasiński, M.; Cpałka, K.; Niksa-Rynkiewicz, T. The online signature verification using population-based vertical partitioning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing (ICONIP 2020), Bangkok, Thailand, 23–27 November 2020; pp. 569–579. [Google Scholar]
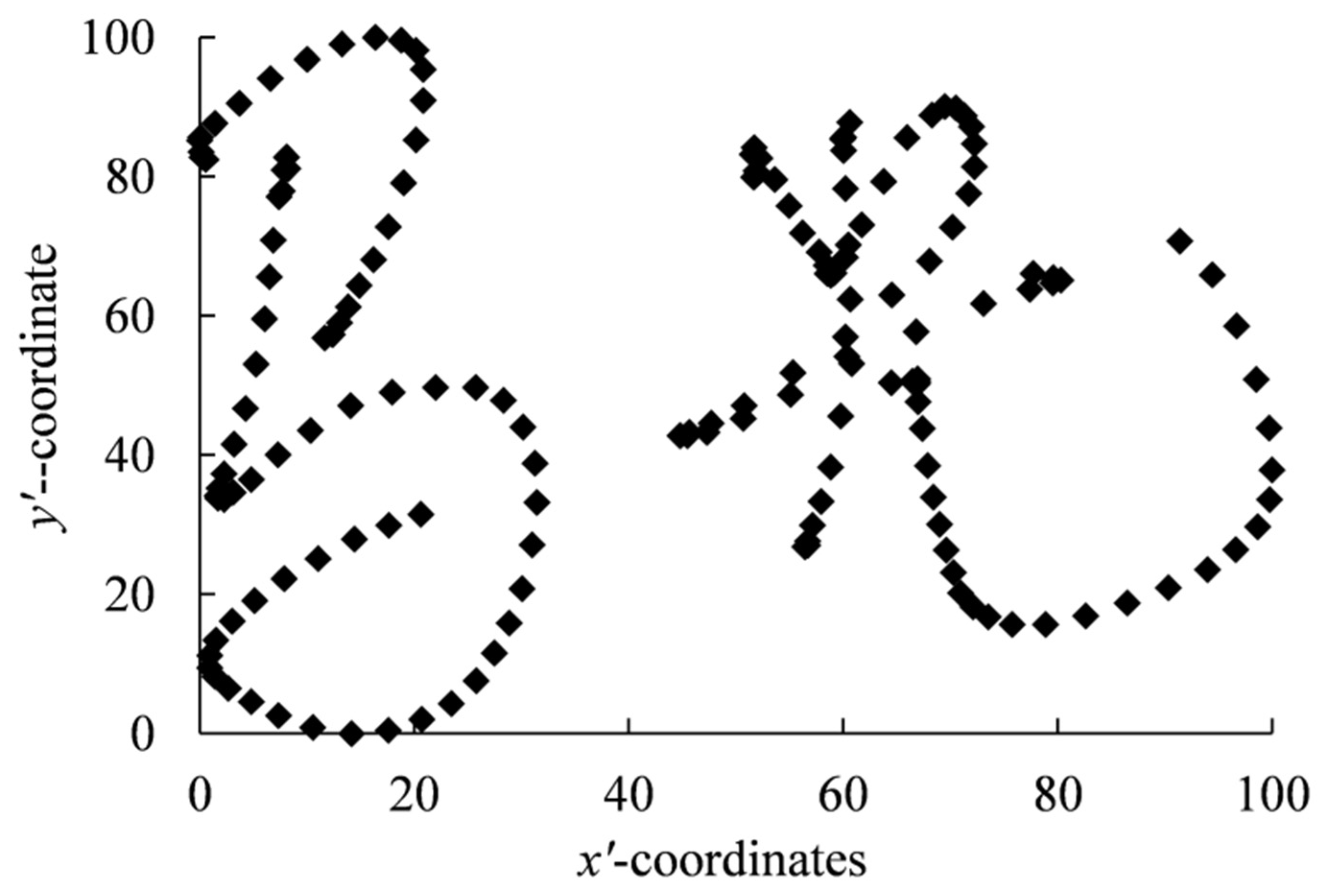

| New Pen Pressure Feature Vector | [0, 20) | [20, 40) | [40, 60) | [60, 80) | [80, 100] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Pen Pressure Feature Vector | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filling Method | Feature | xLongSignDB DataSet | SVC 2004 DataSet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRR | FAR | ACC | FRR | FAR | ACC | ||
| MEI | X | 0.297 | 0.183 | 73.78% | 0.287 | 0.278 | 71.93% |
| Y | 0.309 | 0.272 | 70.22% | 0.317 | 0.292 | 69.93% | |
| P | 0.115 | 0.148 | 87.46% | 0.200 | 0.134 | 84.07% | |
| T | 0.142 | 0.186 | 84.43% | 0.207 | 0.219 | 78.52% | |
| A | 0.132 | 0.176 | 85.48% | 0.238 | 0.201 | 78.67% | |
| MI | X | 0.287 | 0.176 | 74.71% | 0.282 | 0.061 | 86.51% |
| Y | 0.215 | 0.257 | 77.32% | 0.269 | 0.103 | 84.15% | |
| P | 0.058 | 0.110 | 92.58% | 0.082 | 0.057 | 93.46% | |
| T | 0.133 | 0.162 | 85.79% | 0.240 | 0.073 | 87.11% | |
| A | 0.114 | 0.138 | 87.88% | 0.207 | 0.053 | 89.56% | |
| Zero | X | 0.385 | 0.207 | 66.88% | 0.322 | 0.356 | 65.56% |
| Y | 0.376 | 0.310 | 64.37% | 0.333 | 0.378 | 63.70% | |
| P | 0.147 | 0.307 | 80.46% | 0.273 | 0.143 | 81.41% | |
| T | 0.166 | 0.342 | 78.58% | 0.211 | 0.248 | 76.44% | |
| A | 0.179 | 0.328 | 77.53% | 0.249 | 0.221 | 76.96% | |
| Feature | xLongSignDB DataSet | SVC 2004 DataSet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRR | FAR | ACC | FRR | FAR | ACC | |
| X | 0.279 | 0.221 | 73.87% | 0.400 | 0.222 | 71.85% |
| Y | 0.297 | 0.252 | 71.68% | 0.415 | 0.260 | 68.81% |
| P | 0.142 | 0.072 | 87.88% | 0.298 | 0.170 | 78.74% |
| T | 0.285 | 0.189 | 74.39% | 0.302 | 0.247 | 73.48% |
| A | 0.654 | 0.203 | 77.32% | 0.278 | 0.267 | 72.96% |
| Literature | DataSet | Method | Feature | FRR | FAR | EER | ACC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lei et al. [21] | SVC | DTW | X | - | - | 0.251 | - |
| Y | - | - | 0.187 | - | |||
| P | - | - | 0.256 | - | |||
| T | - | - | 0.291 | - | |||
| A | - | - | 0.266 | - | |||
| Friedman et al. [22] | SVC | DTW + Feature Normalization | P | - | - | - | 75.40% |
| T | - | - | - | 57.50% | |||
| A | - | - | - | 73.30% | |||
| Saleem et al. [55] | SVC | Signer-Dependent Sampling Frequency | X | - | - | 0.178 | - |
| Y | - | - | 0.163 | - | |||
| P | - | - | 0.138 | - | |||
| Cpałka et al. [56] | SVC | Signature Partitioning + Fuzzy Classifier | (X,Y) | 0.109 | 0.105 | - | 89.30% |
| Shen et al. [6] | SVC | Siamese Neural Network | (X,Y,P) | 0.186 | 0.208 | - | 80.05% |
| Chandra et al. [57] | SVC | Random Forest | (X,Y,P,T,A) | 0.063 | 0.058 | - | 94.00% |
| Zalasiński et al. [58] | xLongSignDB | Signature Partitioning + Fuzzy Classifier | (X,Y,P,V) | 0.029 | 0.041 | - | 96.52% |
| Our paper | SVC | Multiple Imputation + Correlation Coefficient + Gaussian Density Function | X | 0.282 | 0.061 | 0.139 | 86.51% |
| Y | 0.269 | 0.103 | 0.187 | 84.15% | |||
| P | 0.082 | 0.057 | 0.076 | 93.46% | |||
| T | 0.240 | 0.073 | 0.138 | 87.11% | |||
| A | 0.207 | 0.053 | 0.109 | 89.56% | |||
| Our paper | xLongSignDB | Multiple Imputation + Correlation Coefficient + Gaussian Density Function | X | 0.287 | 0.176 | 0.270 | 74.71% |
| Y | 0.215 | 0.257 | 0.262 | 77.32% | |||
| P | 0.058 | 0.110 | 0.089 | 92.58% | |||
| T | 0.133 | 0.162 | 0.172 | 85.79% | |||
| A | 0.114 | 0.138 | 0.148 | 87.88% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Xin, Y. Online Handwritten Signature Verification Method Based on Uni-Feature Correlation Coefficient between Signatures. Sensors 2023, 23, 9341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239341
Liu R, Xin Y. Online Handwritten Signature Verification Method Based on Uni-Feature Correlation Coefficient between Signatures. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239341
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ruonan, and Yizhong Xin. 2023. "Online Handwritten Signature Verification Method Based on Uni-Feature Correlation Coefficient between Signatures" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239341
APA StyleLiu, R., & Xin, Y. (2023). Online Handwritten Signature Verification Method Based on Uni-Feature Correlation Coefficient between Signatures. Sensors, 23(23), 9341. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239341





