Binary Hunter–Prey Optimization with Machine Learning—Based Cybersecurity Solution on Internet of Things Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
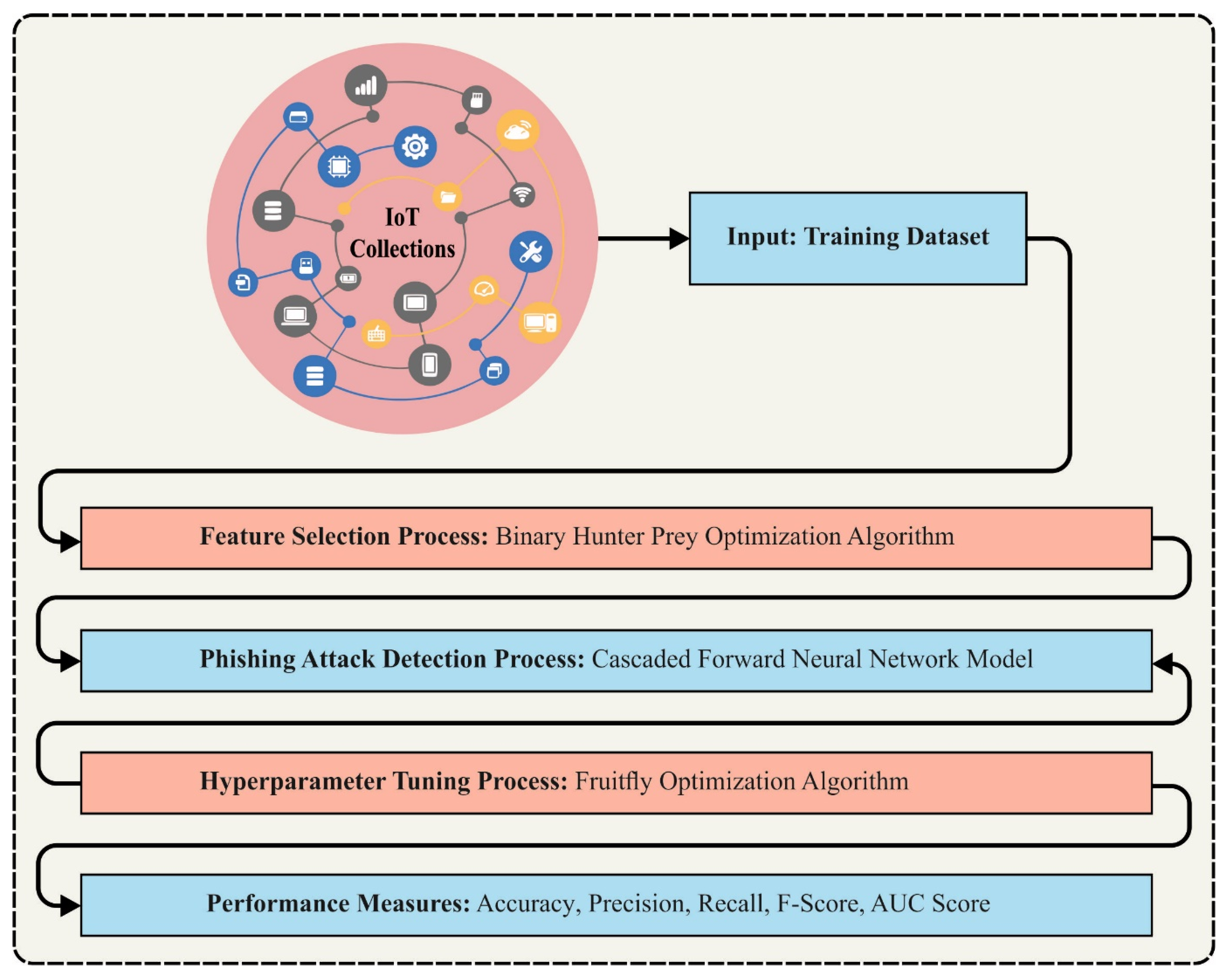
3. The Proposed Model
3.1. BHPO-Based Feature Selection
3.2. Phishing Attack Detection
3.3. VFFO-Based Parameter Tuning
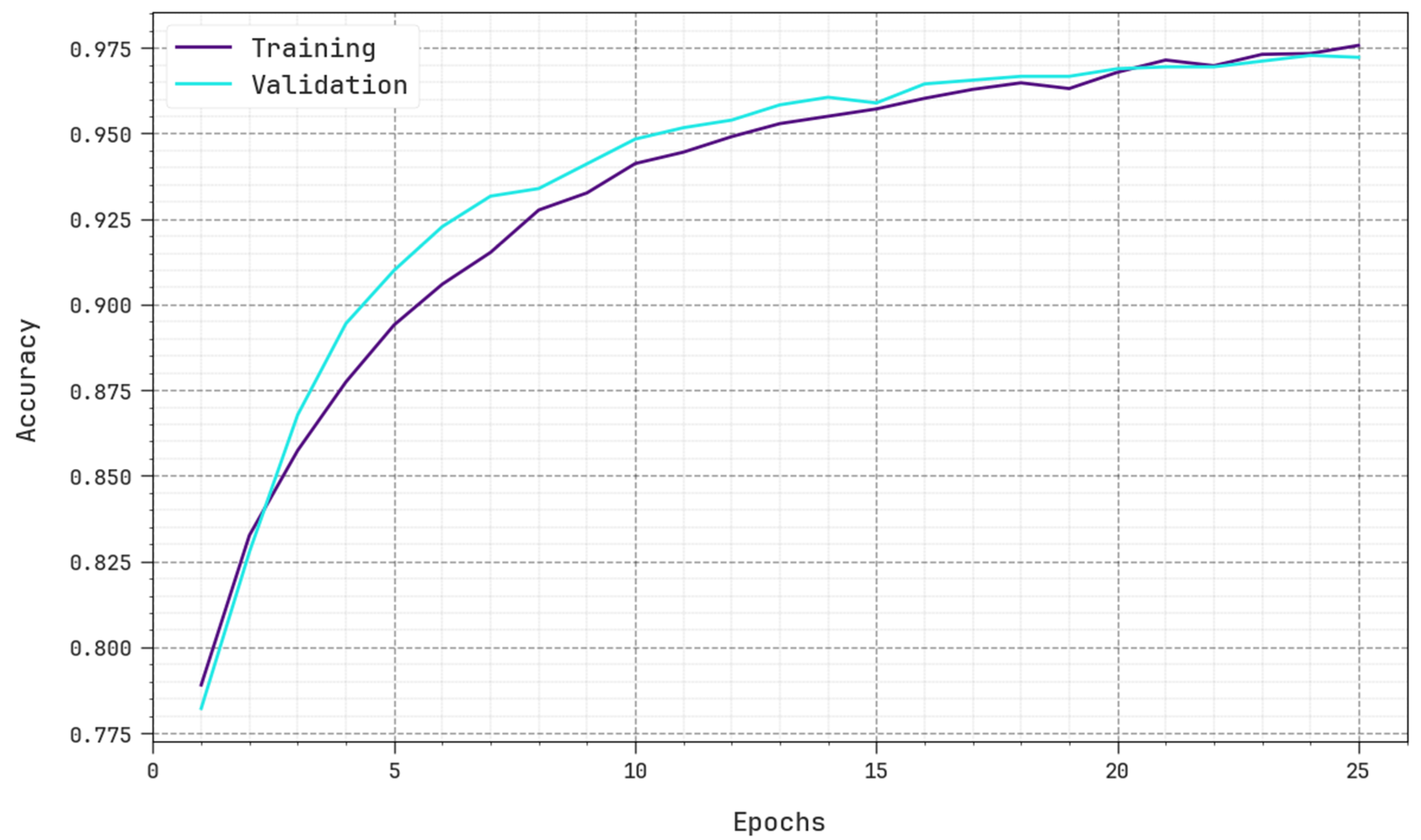
4. Experimental Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ansari, M.F.; Sharma, P.K.; Dash, B. Prevention of phishing attacks using AI-based Cybersecurity Awareness Training. Prevention 2022, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Venkatachalam, N.; Rajendran, R. A Novel Phishing Attack Prediction Model With Crowdsouring in Wireless Networks. In Perspectives on Social Welfare Applications’ Optimization and Enhanced Computer Applications; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Basit, A.; Zafar, M.; Liu, X.; Javed, A.R.; Jalil, Z.; Kifayat, K. A comprehensive survey of AI-enabled phishing attacks detection techniques. Telecommun. Syst. 2021, 76, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andryukhin, A.A. Phishing attacks and preventions in blockchain based projects. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Computer Science (EnT), Moscow, Russia, 26–27 March 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Al-Haija, Q.; Zein-Sabatto, S. An efficient deep-learning-based detection and classification system for cyber-attacks in IoT communication networks. Electronics 2020, 9, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheri, M.; Ragab, M. Quantum Cat Swarm Optimization Based Clustering with Intrusion Detection Technique for Future Internet of Things Environment. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 46, 3783–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsisi, M.; Tran, M.Q.; Mahmoud, K.; Mansour, D.E.A.; Lehtonen, M.; Darwish, M.M. Towards secured online monitoring for digitalized GIS against cyber-attacks based on IoT and machine learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78415–78427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanathan, A.; Gharakheili, H.H.; Sivaraman, V. Managing IoT cyber-security using programmable telemetry and machine learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2020, 17, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, M.; Abd Allah, A.M.; Hassanien, A.E. Developing an efficient feature engineering and machine learning model for detecting IoT-botnet cyber attacks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 91038–91052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Sarma, D.; Lima, F.F.; Saha, I.; Hossain, S. August. In Phishing attacks detection using machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 Third International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), Tirunelveli, India, 20–22 August 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1173–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, B.; Simba, J.; Fuertes, W.; Benavides, E.; Andrade, R.; Toulkeridis, T. December. In Phishing attack detection: A solution based on the typical machine learning modeling cycle. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 5–7 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.B.; Jain, A.K. Phishing attack detection using a search engine and heuristics-based technique. J. Inf. Technol. Res. 2020, 13, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demertzis, K.; Iliadis, L. Cognitive web application firewall to critical infrastructures protection from phishing attacks. J. Comput. Model. 2019, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Alsariera, Y.A.; Adeyemo, V.E.; Balogun, A.O.; Alazzawi, A.K. Ai meta-learners and extra-trees algorithm for the detection of phishing websites. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 142532–142542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsufyani, A.A.; Alzahrani, S.M. Social Engineering Attack Detection Using Machine Learning: Text Phishing Attack. Indian J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2021, 12, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughaid, A.; AlZu’bi, S.; Hnaif, A.; Taamneh, S.; Alnajjar, A.; Elsoud, E.A. An intelligent cyber security phishing detection system using deep learning techniques. Clust. Comput. 2022, 25, 3819–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrahman, M.D.; Alhassan, J.K.; Adebayo, O.S.; Ojeniyi, J.A.; Olalere, M. Phishing attack detection based on random forest with wrapper feature selection method. Int. J. Inf. Process. Commun. 2019, 7, 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.K.; Gupta, B.B. PHISH-SAFE: URL features-based phishing detection system using machine learning. In Cyber Security: Proceedings of CSI 2015; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Qin, J.; Wen, W. Phishing URL detection via capsule-based neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on Anti-Counterfeiting, Security, and Identification (ASID), Xiamen, China, 25–27 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zabihimayvan, M.; Doran, D. Fuzzy rough set feature selection to enhance phishing attack detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–26 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A.K.; Gupta, B.B. Detection of phishing attacks in financial and e-banking websites using link and visual similarity relation. Int. J. Inf. Comput. Secur. 2018, 10, 398–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, N.A.; Misra, S.; Margaret, I.A.; Fernandez-Sanz, L. Adopting automated whitelist approach for detecting phishing attacks. Comput. Secur. 2021, 108, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, R.; Al-Turaiki, I.; Alakeel, F. Mitigating email phishing attacks using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 19–21 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alrowais, F.; Althahabi, S.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Mohamed, A.; Hamza, M.A.; Marzouk, R. Automated machine learning enabled cyber security threat detection in Internet of things environment. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Villafranca, S.; Carrillo-Mondéjar, J.; Castelo Gómez, J.M.; Roldán-Gómez, J. MECInOT: A multi-access edge computing and industrial internet of things emulator for the modelling and study of cybersecurity threats. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 11895–11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rookard, C.; Khojandi, A. Applying Deep Reinforcement Learning for Detection of Internet-of-Things Cyber Attacks. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 13th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–11 March 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Mengash, H.A.; Alzahrani, J.S.; Eltahir, M.M.; Al-Wesabi, F.N.; Mohamed, A.; Hamza, M.A.; Marzouk, R. Search and Rescue Optimization with Machine Learning Enabled Cybersecurity Model. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Rui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tu, Z. Topology Optimization of Continuum Structures Based on Binary Hunter-Prey Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruei, I.; Keynia, F.; Sabbagh Molahosseini, A. Hunter–prey optimization: Algorithm and applications. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 1279–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdelAty, A.M.; Yousri, D.; Chelloug, S.; Alduailij, M.; Abd Elaziz, M. Fractional order adaptive hunter-prey optimizer for feature selection. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 75, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Khushnood, R.A.; Fawad, M. A hybrid data-driven and metaheuristic optimization approach for the compressive strength prediction of high-performance concrete. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhasawneh, M.S.; Tay, L.T. A hybrid intelligent system integrating the cascade forward neural network with elman neural network. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 6737–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tao, D.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y. Adaptive Image Enhancement Algorithm Based on Variable Step Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm and Nonlinear Beta Transform. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, W.; Zheng, L.; Ling, S.; Fu, W. Adaptive co-simulation method and platform application of drive mechanism based on Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2022, 153, 104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.S.; Ke, X.T.; Liao, J.G.; Shen, Y.J. DSLC-FOA: Improved fruit fly optimization algorithm for application to structural engineering design optimization problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 55, 314–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, N.; Jill, S. UNSW-NB15: A comprehensive data set for network intrusion detection systems (UNSW-NB15 network data set). In Proceedings of the Military Communications and Information Systems Conference (MilCIS), Canberra, Australia, 10–12 November 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]




| Reference | Year | Method | Performance | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mughaid et al. [16] | 2022 | ML models such as SVM, DT, LR, NN, and decision forest | Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F-Score | Phishing email collection dataset |
| Abdulrahman et al. [17] | 2019 | Random Forest and CAER feature selection | TPR, FPR, Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F-Measure | UCI phishing website dataset |
| Jain et al. [18] | 2018 | PHISH-SAFE, an ML-based classifier | Accuracy | PhishTank URL dataset |
| Huang et al. [19] | 2019 | Capsule-based neural network | TPR, FPR, Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F-Measure | PhishTank and Openphish data |
| Zabihimayvan and Doran [20] | 2019 | Fuzzy Rough Set | F-measure | UCI Phishing and Mendeley dataset |
| Jain and Gupta [21] | 2018 | Link and visual similarity relation | TPR, FPR | - |
| Azeez et al. [22] | 2021 | Whitelist approach | TPR, TNR, FPR, FNR, Accuracy | PhishTank and Alexa data |
| Alotaibi et al. [23] | 2020 | CNN | Accuracy | PhishingCorpus and SpamAssassin |
| Alrowais et al. [24] | 2023 | Mayfly optimization with RELM | Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F-score | N-BaIoT dataset |
| Ruiz-Villafranca et al. [25] | 2023 | MECInOT | Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F-score | Mendeley dataset |
| Rookard and Khojandi [26] | 2023 | Deep Q-network | Accuracy | - |
| Mengash et al. [27] | 2023 | SRO-MLCOSN model | Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F-score | - |
| Class | No. of Samples |
|---|---|
| Normal | 1000 |
| Fuzzers | 1000 |
| DoS | 1000 |
| Analysis | 1000 |
| Exploits | 1000 |
| Generic | 1000 |
| Total Number of Samples | 6000 |
| Class | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Phase (70%) | |||||
| Normal | 99.38 | 98.30 | 98.02 | 98.16 | 98.84 |
| Fuzzers | 99.33 | 97.69 | 98.26 | 97.98 | 98.90 |
| DoS | 99.02 | 97.00 | 97.40 | 97.20 | 98.38 |
| Analysis | 99.19 | 98.80 | 96.20 | 97.48 | 97.99 |
| Exploits | 98.81 | 95.20 | 97.68 | 96.42 | 98.36 |
| Generic | 98.93 | 97.11 | 96.42 | 96.76 | 97.92 |
| Average | 99.11 | 97.35 | 97.33 | 97.33 | 98.40 |
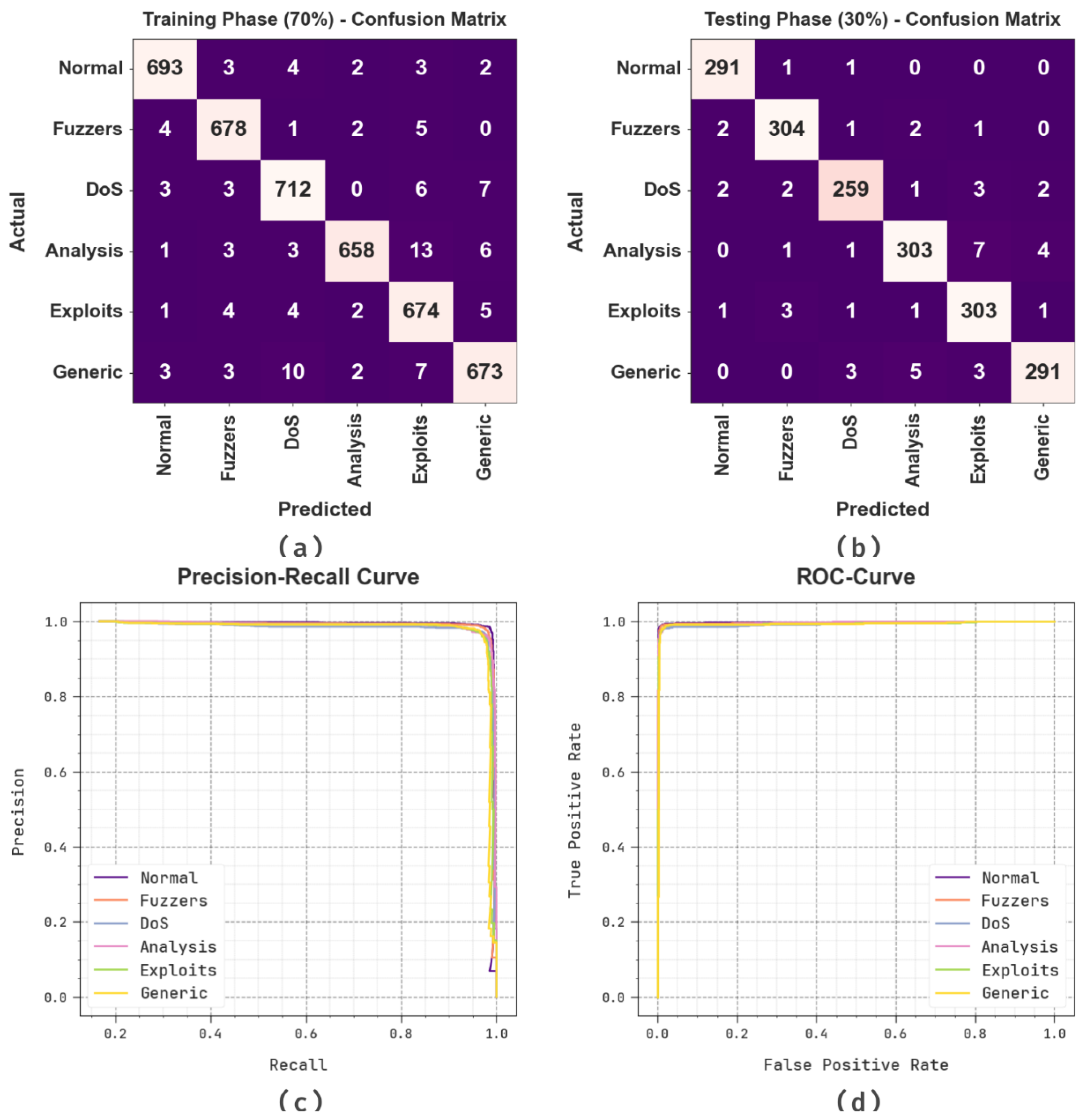
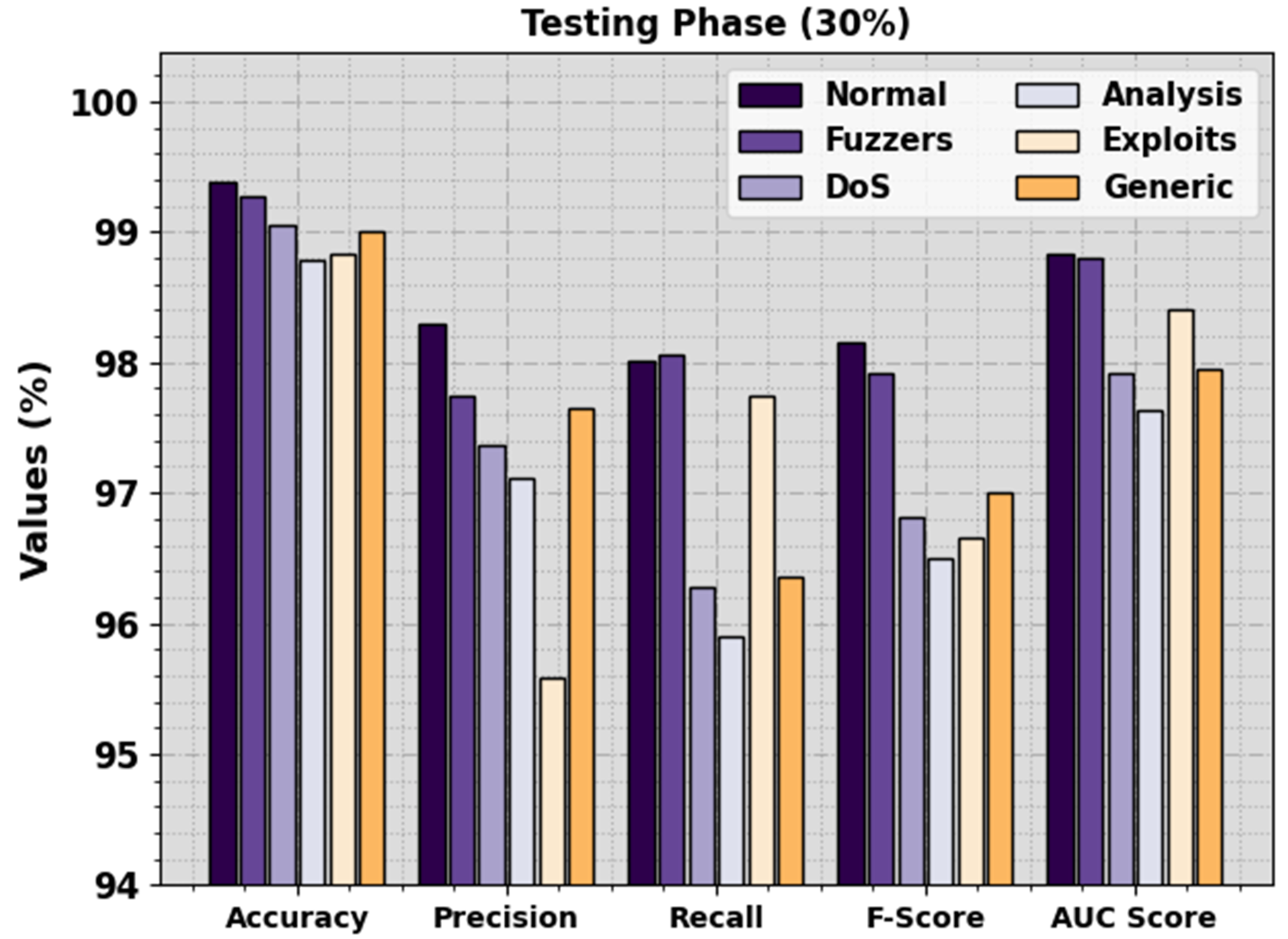
| Testing Phase (30%) | |||||
| Normal | 99.61 | 98.31 | 99.32 | 98.81 | 99.49 |
| Fuzzers | 99.28 | 97.75 | 98.06 | 97.91 | 98.80 |
| DoS | 99.06 | 97.37 | 96.28 | 96.82 | 97.91 |
| Analysis | 98.78 | 97.12 | 95.89 | 96.50 | 97.64 |
| Exploits | 98.83 | 95.58 | 97.74 | 96.65 | 98.40 |
| Generic | 99.00 | 97.65 | 96.36 | 97.00 | 97.95 |
| Average | 99.09 | 97.30 | 97.28 | 97.28 | 98.36 |
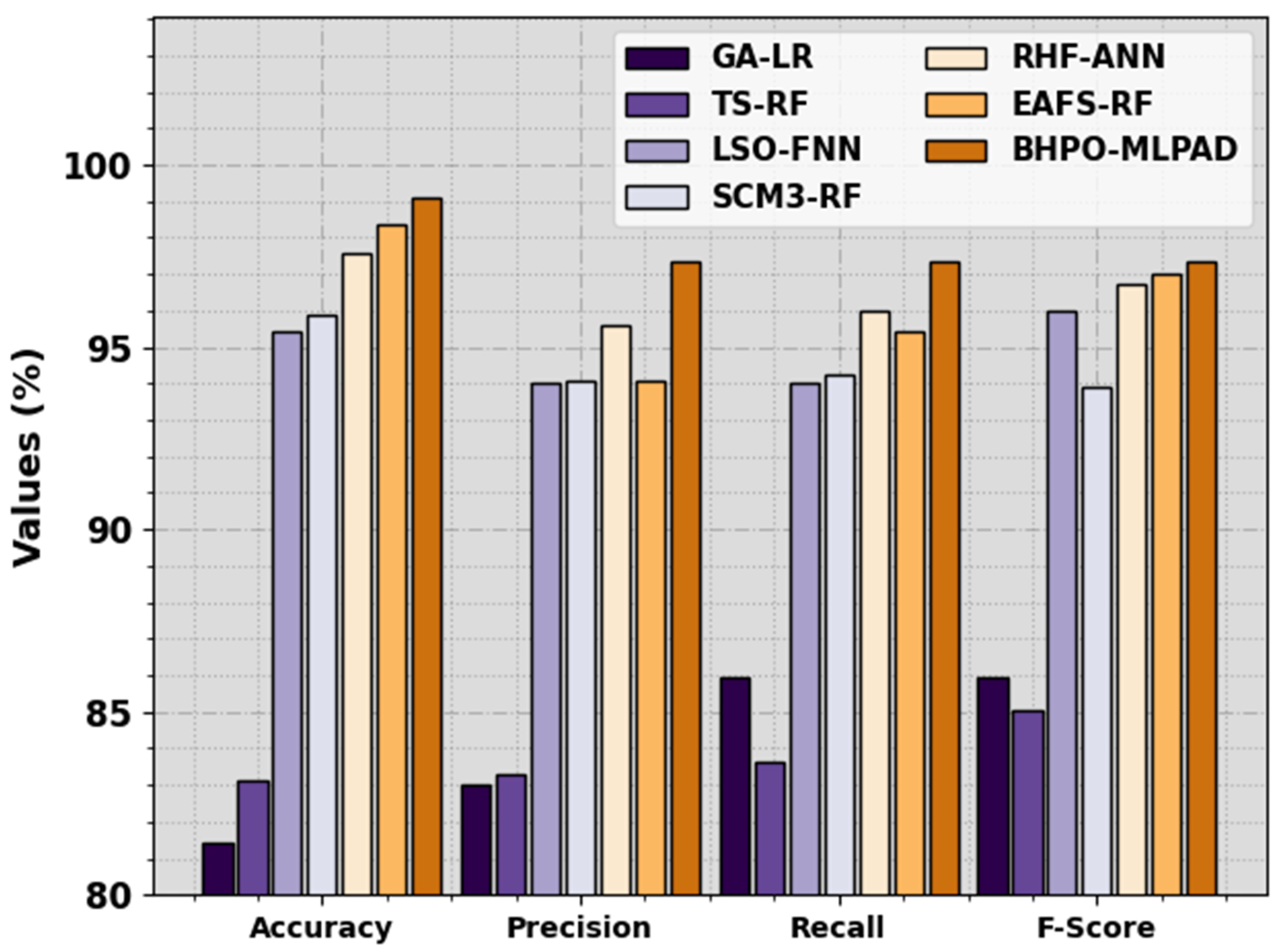
| Technology | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA-LR | 81.42 | 83.03 | 85.93 | 85.95 |
| TS-RF | 83.12 | 83.28 | 83.63 | 85.06 |
| LSO-FNN | 95.42 | 94.03 | 94 | 95.98 |
| SCM3-RF | 95.87 | 94.08 | 94.22 | 93.89 |
| RHF-ANN | 97.60 | 95.62 | 95.98 | 96.71 |
| EAFS-RF | 98.36 | 94.08 | 95.41 | 97.01 |
| BHPO-MLPAD | 99.11 | 97.35 | 97.33 | 97.33 |
| Technology | Computational Time (s) |
|---|---|
| GA-LR | 0.30 |
| TS-RF | 0.28 |
| LSO-FNN | 0.25 |
| SCM3-RF | 0.30 |
| RHF-ANN | 0.27 |
| EAFS-RF | 0.28 |
| BHPO-MLPAD | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khadidos, A.O.; AlKubaisy, Z.M.; Khadidos, A.O.; Alyoubi, K.H.; Alshareef, A.M.; Ragab, M. Binary Hunter–Prey Optimization with Machine Learning—Based Cybersecurity Solution on Internet of Things Environment. Sensors 2023, 23, 7207. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167207
Khadidos AO, AlKubaisy ZM, Khadidos AO, Alyoubi KH, Alshareef AM, Ragab M. Binary Hunter–Prey Optimization with Machine Learning—Based Cybersecurity Solution on Internet of Things Environment. Sensors. 2023; 23(16):7207. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167207
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhadidos, Adil O., Zenah Mahmoud AlKubaisy, Alaa O. Khadidos, Khaled H. Alyoubi, Abdulrhman M. Alshareef, and Mahmoud Ragab. 2023. "Binary Hunter–Prey Optimization with Machine Learning—Based Cybersecurity Solution on Internet of Things Environment" Sensors 23, no. 16: 7207. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167207
APA StyleKhadidos, A. O., AlKubaisy, Z. M., Khadidos, A. O., Alyoubi, K. H., Alshareef, A. M., & Ragab, M. (2023). Binary Hunter–Prey Optimization with Machine Learning—Based Cybersecurity Solution on Internet of Things Environment. Sensors, 23(16), 7207. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167207






