Abstract
2,4,6-trichloroanisole (TCA) is mainly responsible for cork taint in wine, which causes significant economic losses; therefore, the wine and cork industries demand an immediate, economic, noninvasive and on-the-spot solution. In this work, we present a novel prototype of an electronic nose (e-nose) using an array of digital and analog metal-oxide gas sensors with a total of 31 signals, capable of detecting TCA, and classifying cork samples with low TCA concentrations (≤15.1 ng/L). The results show that the device responds to low concentrations of TCA in laboratory conditions. It also differentiates among the inner and outer layers of cork bark (81.5% success) and distinguishes among six different samples of granulated cork (83.3% success). Finally, the device can predict the concentration of a new sample within a ±10% error margin.
1. Introduction
Artificial olfactory systems, commonly known as electronic noses (e-noses), are devices that try to mimic the biological sense of smell but eliminate its subjective component and exhaustion. The parallels between the two are enormous, as an artificial olfactory system reproduces all the stages of a biological one [1]. The first block of an e-nose is the sensing system, which consists of an array of gas sensors, each of which is sensitive in different ways to different aromas. The signals generated by these sensors pass to the learning stage, where the signals are first pre-processed and then pass through a pattern recognition system. Finally, these patterns are identified in the classification stage.
There are several types of gas sensors commonly used in electronic noses, such as electrochemical [2,3,4], digital Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) [5,6], analog MOS [7,8,9,10], conducting polymer (CP) [11], surface acoustic wave (SAW) [12] and quartz crystal microbalances (QMB) sensors [13]. Some of these sensors, like digital MOS, have integrated their own microprocessor, analog/digital converter and a digital interface communication, such as I2C or SPI, all in a very small package of a few millimetres. This makes it easier for e-noses to become smaller and more portable.
E-noses have been used in a wide variety of applications and industries, with a current trend of using low-cost, low-consumption and low-size sensors. The application and the sensors used usually determine the portability of the e-nose. For example, devices have been developed to monitor urban pollution in fixed locations [14] and portable devices for monitoring indoor air quality [15]. Among other applications, they are also used in medicine to measure the air exhaled by patients for the early diagnosis of different diseases, such as lung cancer [16] or gastrointestinal disorders [17]. Electronic noses have even been used for exotic applications such as the detection of explosives [18] or drugs [19]. They have also gained popularity in determining the quality properties of food and drinks, where the applications are innumerable [20,21]. Within the field of beverages, special attention is paid to determining the quality of wine. In this respect, one of the materials most closely related to wine is the cork.
Cork is the material par excellence used to manufacture wine bottle stoppers, mainly due to its elastic, insulating, impermeable and durable properties [22]. However, natural cork can be contaminated with different substances produced by bacteria that, in contact with the wine, cause it to lose its organoleptic characteristics, leading to irreversible defects and consequent rejection by the consumer, as well as losses for wine producers. Some of these substances are 2,3,4,6-tetrachloroanisole (TeCA), 2,4,6-tribromoanisole (TBA) and 2-methylisoborneol (2-MIB), with 2,4,6-trichloroanisole (TCA) being the most common and important of all [23], and the target of this study.
As TCA is produced by bacteria, this substance can appear in localized points or areas of the cork planks, which means that contaminated and non-contaminated corks can come out of the same cork plank, making it difficult to detect and monitor the contaminant in the cork. Although there are non-destructive TCA detection techniques [24], one of the most widely used chemical analysis methods for its detection in the cork industry is gas chromatography [25,26,27]. This technique requires the destruction of the sample, considerable time to be carried out and it is conducted by specialised technicians. This means that in the industry, this technique is performed on random and representative samples of the batch produced, rather than on the whole batch, so that some TCA-contaminated closures may be put on the market. As an alternative to the use of these chemical analyses, the use of electronic noses is proposed. As an advantage, the e-nose can provide a non-destructive, faster and cheaper method of analysis compared to traditional methods.
Data processing of the signals obtained by an e-nose is of great importance to obtain an output that could be understood by non-technicians and to integrate e-noses into an online classification system. Among the most common techniques are Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [28], Support Vector Machines (SVM) [29], Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) [30] and Fuzzy Logic [31]. For this study, PCA and ANN techniques were used. PCA is a technique that reduces the dimensionality of a dataset into new uncorrelated variables (components) [32], which is quite useful for electronic noses due to the large number of sensors and, therefore, signals obtained. The ANN is a powerful classifier based on machine learning, consisting of interconnected layers of artificial neurons that are trained by adjusting the weight between neuron connections [33]. For the validation of the data obtained, the Leave One Out Cross-Validation (LOOCV) technique has been used, which is a procedure used to estimate the performance of machine learning algorithms when they are used to make predictions on data that are not used to train the model.
This article will describe the e-nose developed, its communication protocol with a smartphone, the measurements carried out, and the results and conclusions obtained.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the MultisensorNOSE
The electronic nose, called multisensorNOSE, because of its number of sensors, is a home-designed and home-developed portable prototype with 14 sensors returning a total of 31 different signals. This device consists of a power supply that converts alternating current from 220 VAC to 5 VDC, a 75 mm × 84.9 mm printed circuit board (PCB) that contains all the electronic circuitry of the e-nose, a pneumatic pump with fixed flow and a solenoid valve. All these components are housed inside a 3D printed case, which contains a switch to turn the device on-off and three-wall bushing that functions as inlets and outlets for the gases to be measured. The final size of the whole device is 150.76 mm × 147.40 mm × 35.20 mm, with a total weight of 450 g, which makes it a very easy and comfortable device to carry. The multisensorNOSE is shown in Figure 1.
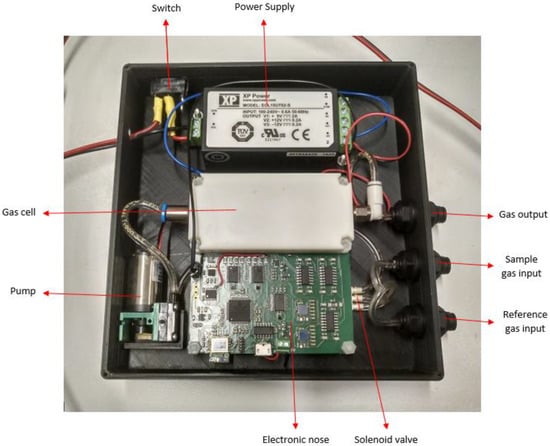
Figure 1.
MultisensorNOSE top view.
The PCB is represented in the block diagram in Figure 2. The e-nose is governed by a PIC32MM0256GPM064 microcontroller from Microchip Technology Inc. (Chandler, AZ, USA), which has 32 KB of data memory, 256 KB of programme memory, a frequency of 24 MHz, several I2C, SPI and UART modules, and an analog/digital converter of up to 24 channels and 12 bits of resolution, characteristics that make it an ideal microcontroller for this application. For external communication, a Bluetooth Low Energy module, Microchip’s RN4871, has been included, which allows communication via transparent UART.
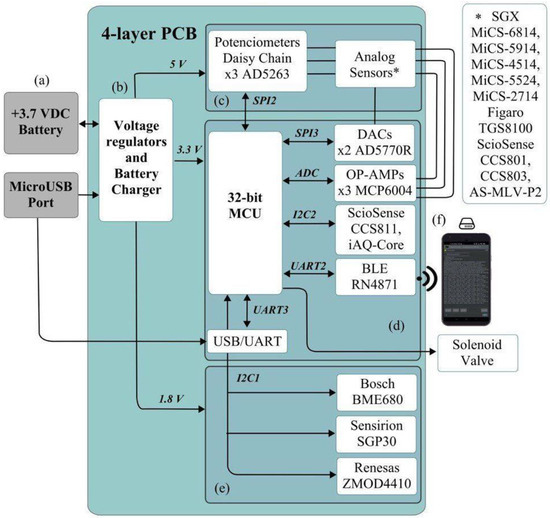
Figure 2.
MultisensorNOSE block diagram. External battery (a); Voltage regulators and Battery Charger (b); 5 VDC components (c); 3.3 VDC components (d); 1.8 VDC components (e); Smartphone connected via Bluetooth (f).
As for the sensors, both digital and analog sensors were used (Table 1). Both types are based on MOS technology and have two types of resistors: the chemiresistive sensing element, which provides the signal, and the heater, whose function is to heat the sensor resistor to be able to operate. The digital sensors communicate via the I2C bus with the microcontroller and return the processed data in digital format. The signals from the analog resistors have to be amplified using some operational amplifiers, the Microchip’s MCP6004, and then converted to digital format in the microcontroller itself. Several AD5263 digital potentiometers from Analog Devices (Norwood, MA, USA) are included to vary the closed-loop gain of the operational amplifiers, communicating via I2C bus with the microcontroller. Moreover, two digital/analog current converters, Analog Devices’ AD5770R, have been used to inject current into the heaters of the analog sensors.

Table 1.
Sensors used in multisensorNOSE and output signals.
The e-nose circuitry also integrates voltage regulators that provide voltages of 1.8 VDC, 3.3 VDC and 5 VDC, a connection to a solenoid valve controlled by the microcontroller, LEDs to indicate the status of the nose (on/off, measurements on/off) and a micro USB-B port connected to a battery charger, which allows using the device with an external 5 V power source. It can also communicate to an external device via a UART interface using the micro USB-B connector.
Regarding the pneumatic connections, the housing has two gas inlets, one dedicated to clean or reference air and one for the sample to be sniffed. These two inlets communicate with the two inlets of the solenoid valve, whose output is connected to the pump inlet. The gas is directed towards the sensors from the pump outlet, which are encapsulated in a cell made by 3D resin printing. The output of this cell is connected directly to the output of the housing.
2.2. Communication Protocol
We developed an application for Android smartphones for data collection and configuration, using an ASCII code-based protocol for communication with the e-nose. In this way, we can quickly configure different parameters from the multisensorNOSE, such as adsorption time (reference air measurement time), desorption time (sample measurement time) and sampling period. In this application, there are four sections:
- Experiment: This section is where data are collected and stored with an easy user interface. Users can add smartphone GPS coordinates to the data and select the type of experiment. Buttons for starting and stopping the experiment and saving the data are available.
- Configuration: In this section, the user can change the adsorption and desorption times and the sampling period in an easy user interface.
- Graphics: In this section, the user can select one signal and see how it changes in real time using a graphic.
- Raw data: The application works like a UART terminal and shows all the data sent by the e-nose in this section.
The application, called eNoseLab, is shown in Figure 3.
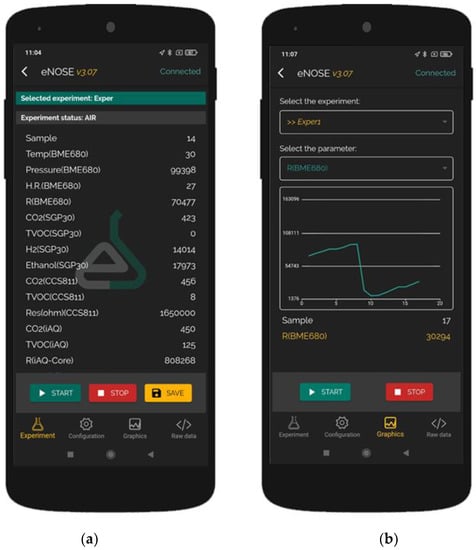
Figure 3.
Developed application screenshots. (a) Data from the sensors; (b) Graphic with the time evolution from one of the signals.
The different types of experiments that the nose is capable of performing are shown in Table 2, which explains the name of the command, its ASCII code and a description. The experiment used for this study is one that contains all the sensors, EXP_MAIN.

Table 2.
ASCII codes for multisensorNOSE experiments commands.
2.3. Measurement Set-Up
To study the detection and discrimination capabilities of the device, several experiments have been carried out. Specifically, we measured TCA concentrations using permeation tubes in the lab and real cork samples (bark slab and granulated cork). With the first experiment, our goal is to assess whether the device can detect the compound at low concentrations. In the second, the aim is to test the ability to differentiate between the different layers of a cork slab. However, the third one was intended to evaluate the ability of the device to detect and quantify small changes in TCA concentration.
The first experiment consisted of detecting small concentrations of TCA in a gas flow, simulating real conditions to assess the performance of the device. To generate controlled gas properties mixed with water vapour, a gas generator and a humidity generator (models OVG-4 and OHG-4 from Owlstone, Westport, CT, USA) were used. Additionally, we used a commercial TCA permeation tube (KIN-TEK Analytical, Inc., La Marque, TX, USA) to produce a constant TCA concentration. Permeation tubes are plastic tubes with a semi-permeable membrane filled with a solid or liquid compound that releases this compound into the ambient air in gaseous form, depending on the temperature and the airflow. Then, knowing the characteristics of the compound and controlling the airflow and the temperature, it is possible to control the concentration of the compound that is being released.
Figure 4 shows the experimental setup of the first experiment. The gas generator takes dry air from a bottle. This air flows through the cavity where the permeation tube is stored and through the humidity generator, thus producing two gas lines that are then mixed in a single line with known TCA concentration and humidity. This generated flows through the sensors and its responses are stored. The TCA permeation tube used was supplied by the manufacturer KIN-TEK Analytical (La Marque, TX, USA). This is a 10 cm tube with a permeation rate of 547 ng/min at 80 °C.
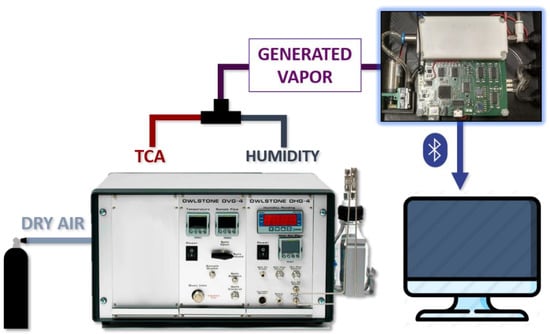
Figure 4.
Experimental setup.
For the second experiment, samples from three different layers of tree bark were measured. The TCA usually concentrates in the outer zone of the bark. The sample of layer 1 corresponds to the outer zone, layer 2 corresponds to the intermediate zone, and layer 3 corresponds to the inner zone of the bark. To carry out the measurements, 2 pieces of 4 grams (±0.5) were cut for each layer. These samples were placed in glass vials, and then the static headspace was transferred by active sampling with a pump to the gas cell (flow rate approximately 170 mL/m). Eighteen measurement cycles were performed for each sample. Each measurement cycle (2 min) is composed of two phases with a 1-min duration: the filtered air phase and the sample phase. In this way, the solenoid valve switches the air inlet between filtered air (used as a reference) and the corresponding sample headspace.
In the last experiment, granulated cork samples were measured at 6 different TCA concentrations: 4.1 ng/L, 6.5 ng/L, 8.3 ng/L, 10.7 ng/L, 12.4 ng/L and 15.1 ng/L. These samples were provided by a cork stopper factory, DIAM Corchos S.A. (Badajoz, Spain), and the concentrations were calculated following the UNE 56930:2017 standard. The samples will be named A, B, C, D, E and F, respectively, in the results section. For this test, 2 g of a sample were placed in the vials. The rest of the measurement protocol was the same as the one described above for the experiment with cork slabs. A picture of the samples that were used in experiments one, two and three are shown in Figure 5.
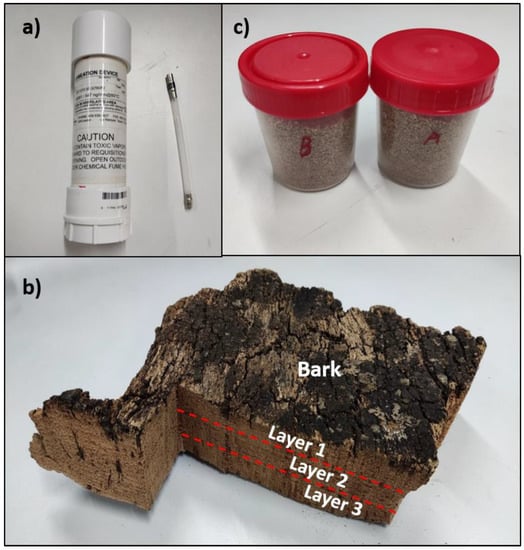

Figure 5.
Samples. (a) Permeation tube with TCA; (b) Layers of bark slab; (c) Granulated cork samples.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gas Generator
With the previous setup, two different approaches were considered. First, a single concentration step was generated (Figure 6, top). In this case, the TCA concentration ranged from 1.4 ng/L, which is the minimum that the system could generate, to 3.0 ng/L. This first step allowed us to confirm that the e-nose detected small concentration variations. Second, we presented the sensors to a wider range of TCA concentrations (Figure 6 bottom), from 1.4 to 110 ng/L, to confirm the recovery of the sensors after being exposed to high concentrations. During this process, relative humidity was set to a constant value so we could assess that the changes in the sensors’ response were only due to variations in TCA concentration and not by the effect of humidity.
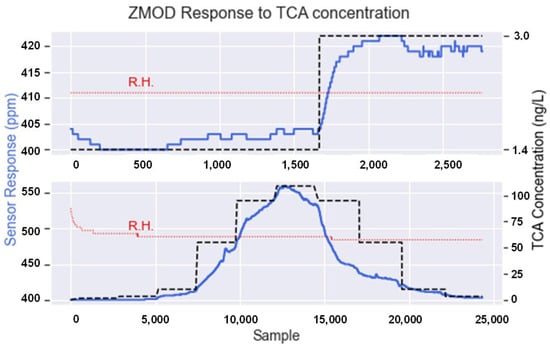
Figure 6.
ZMOD4410 response to different TCA concentrations. The black dashed line represents the TCA concentration, the blue line represents the sensor response, and the red dotted lines show that the relative humidity remained constant during the experiment (33% R.H. approx.).
3.2. Cork Slab
The concentration of TCA is known to be higher in the outermost part of the tree bark [34]. Therefore, first, a test was carried out to study whether the system can differentiate between different layers of the tree bark. Once all the measurements were obtained, baseline manipulation pre-processing was performed following Equation (1).
where Characteristic Value is the pre-processed value, Reference is an average of the last 5 values reached during the clean air measurement phase and Sample is an average of the last 5 values reached during the analyte measurement phase. A neural network was then trained using Rectified Linear Unit activation function and 4 hidden layers. Using a Leave One Out Cross-Validation (LOOCV), a success rate of 81.5% is achieved. Figure 7 shows the resulting confusion matrix, where it is observed that 7 of the errors are made in the classification of samples from layer 2 as layer 1. This interference may be due to the similarity in the TCA concentration between these two outermost layers. However, the device can differentiate very successfully between the innermost layer (L3) and the outermost layer (L1).
Characteristic Value = (Reference/Sample) · 100,
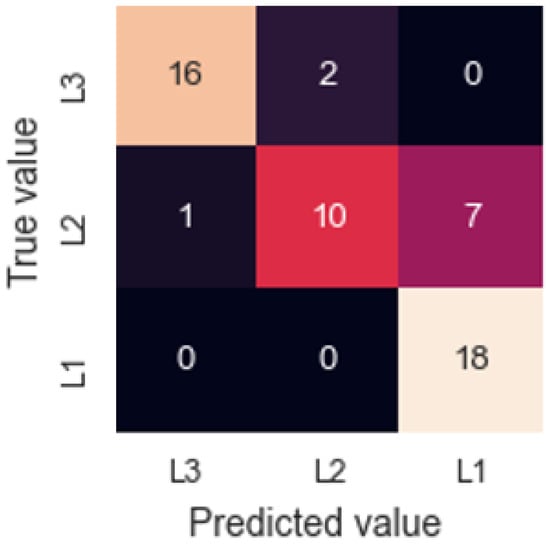
Figure 7.
Confusion matrix for cork slab results.
3.3. Granulated Cork
The procedure followed for the pre-processing of these data is the same as described in the previous section. In this case, the first repetition or cycle of each sample was discarded. Principal component analysis (PCA) of the pre-processed data was then performed. By selecting the first three components, 86.6% of the variance in the data was explained. Short-term drift through PC3 can be seen in Figure 8. This effect was attributed to the experimental procedure; the recipient was opened and cleaned after each measurement. Long-term drift was not considered given the length of our experiments, but it should be addressed in future works.
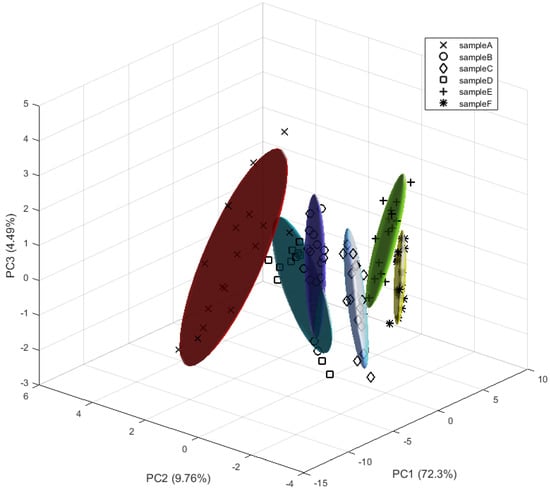
Figure 8.
PCA plot for measurements with granulated corks at different concentrations.
Figure 8 shows that the clusters can be broadly differentiated, but there is an overlap between samples B and D.
In addition, to study the classification capacity, a neural network with the same programming characteristics was trained. However, in this case, it was trained and validated (LOOCV) with 14 repetitions per sample and re-validated with the remaining three. The model achieved a 94.0% success rate in the model validation step and an 83.3% rate when classifying three new repetitions. The confusion matrices obtained in both cases are shown in Figure 9. Once the new three samples were presented, the model successfully classified all of them but sample C, which was classified as sample B and C, meaning the model underestimated the concentration of sample C, which could be caused by the ageing or heterogeneity of the samples.
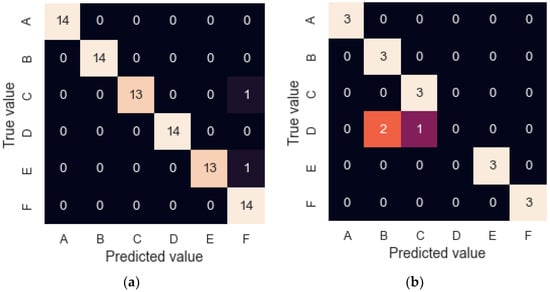
Figure 9.
Confusion matrices for granulated cork results. (a) LOOCV with 14 cycles; (b) CV with the remaining three cycles.
Since the classification success rate was adequate, we decided to programme a predictor to determine if it was possible to predict the estimated concentration of TCA present in the sample. The programmed features were the same as for the classifier. The results can be seen in Table 3 and Figure 10, where the predicted vs. actual concentration values are plotted. The grey dotted line represents the 1:1 line, whereas the grey solid lines represent a ±10% error margin of the real concentration.

Table 3.
Real concentration and predicted concentration in ng/L.
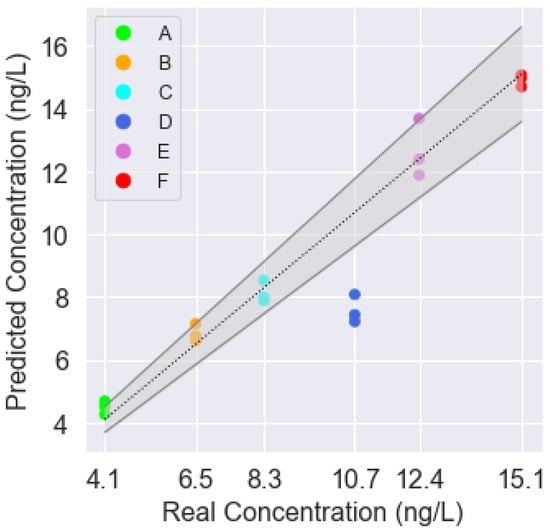
Figure 10.
Results of the prediction model.
It was observed that, once again, errors appeared with sample D since the system detects a lower TCA concentration than the expected one (23–25% lower). For every other sample, the predicted concentration was very close to or within the ±10% error margin. The concentration of sample A was 12-2% higher. For sample B, the concentration was 9-2% above the real concentration. In the case of sample C, the model predicted a TCA concentration 2% higher or 6% lower than the real concentration. The concentration of sample E was within the range 95–109%. Finally, sample F had the lowest deviation from the real concentration, only 1–3% lower. If all 18 samples were considered, the performance of the device could be estimated with error rates of R2 = 0.87, MAE = 0.84 ng/L and RMSE = 1.36 ng/L.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we designed and built an electronic olfaction system based on an array of 14 digital and analog sensors (31 signals) with the aim of detecting 2,4,6-trichloroanisole in cork. Three different experiments were conducted. First, generating known TCA concentrations in a gas generator; second, using a bark slab sample; and third, using granulated cork.
We confirmed that the device detects low variations in the concentration of the compound (1.4–3.0 ng/L). The performance of the e-nose when higher concentrations (up to 110 ng/L) were presented was also evaluated.
The e-nose differentiated between the different layers of the bark slab with an 81.5% success rate, thus detecting those parts with higher TCA concentrations.
With the use of granulated cork, six different samples (A–F) with TCA concentrations ranging from 4.1 to 15.1 ng/L were presented to the device. The principal component analysis showed that the device could identify the samples. To quantify this, we used a classifier neural network model, which, after training, achieved an 83.3% success rate. A prediction model was also built demonstrating that the system could predict the TCA concentration within a ±10% concentration range (R2 = 0.87, MAE = 0.84 and RMSE = 1.36).
The overall performance of the device was satisfactory. The work presented in this paper is intended to be a further step in our goal of detecting TCA, helping the cork industry to develop an online, immediate and low-cost system for detecting faulty cork stoppers. Future work will focus on improving the design of the device and carrying out experiments with real cork stoppers to differentiate clean stoppers from those with high TCA concentrations. In addition, a comparison of sensitivity and accuracy will be made with other TCA detection techniques, such as spectroscopy and gas chromatography.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and J.I.S.; methodology, P.A.; software, J.G.-S.; validation, J.G.-S. and S.P.-M.; investigation, F.M.; data curation, J.G.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M.; writing—review and editing, P.A.; visualization, S.P.-M.; supervision, J.L.; project administration, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Junta de Extremadura and the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation for supporting IB18049 and PID2019-107697RB-C44 projects, respectively.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the Instituto del Corcho y la Madera Vegetal of CICYTEX and the company DIAM for providing the cork and granulated cork samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Keller, P.E. Mimicking Biology: Applications of Cognitive Systems to Electronic Noses. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control Intelligent Systems and Semiotics (Cat. No.99CH37014), Cambridge, MA, USA, 17 September 1999; pp. 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo, P.; Gómez-Suárez, J.; Suárez, J.I.; Lozano, J. Low-Cost Air Quality Measurement System Based on Electrochemical and PM Sensors with Cloud Connection. Sensors 2021, 21, 6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Suárez, J.; Arroyo, P.; Alfonso, R.; Suárez, J.I.; Pinilla-Gil, E.; Lozano, J. A Novel Bike-Mounted Sensing Device with Cloud Connectivity for Dynamic Air-Quality Monitoring by Urban Cyclists. Sensors 2022, 22, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnowski, W.; Majchrzak, T.; Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Portable Electronic Nose Based on Electrochemical Sensors for Food Quality Assessment. Sensors 2017, 17, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arroyo, P.; Meléndez, F.; Suárez, J.I.; Herrero, J.L.; Rodríguez, S.; Lozano, J. Electronic Nose with Digital Gas Sensors Connected via Bluetooth to a Smartphone for Air Quality Measurements. Sensors 2020, 20, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiele, A.; Wicaksono, A.; Ayyala, S.K.; Covington, J.A. Development of a Compact, IoT-Enabled Electronic Nose for Breath Analysis. Electronics 2020, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suárez, J.I.; Arroyo, P.; Lozano, J.; Herrero, J.L.; Padilla, M. Bluetooth Gas Sensing Module Combined with Smartphones for Air Quality Monitoring. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.C.; Morgera, S.D.; Saddow, S.E.; Takshi, A.; Palm, M. Electronic Nose with Detection Method for Alcohol, Acetone, and Carbon Monoxide in Coronavirus Disease 2019 Breath Simulation Model. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 15935–15943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancarz, M.; Malaga-Toboła, U.; Oniszczuk, A.; Tabor, S.; Oniszczuk, T.; Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Rusinek, R. Detection and Measurement of Aroma Compounds with the Electronic Nose and a Novel Method for MOS Sensor Signal Analysis during the Wheat Bread Making Process. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 127, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatli, S.; Mirzaee-Ghaleh, E.; Rabbani, H.; Karami, H.; Wilson, A.D. Rapid Detection of Urea Fertilizer Effects on VOC Emissions from Cucumber Fruits Using a MOS E-Nose Sensor Array. Agronomy 2021, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Oberle, C.; Oberle, D. Detection of Off-Flavor in Catfish Using a Conducting Polymer Electronic-Nose Technology. Sensors 2013, 13, 15968–15984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, J.; Fernández, M.J.; Fontecha, J.L.; Aleixandre, M.; Santos, J.P.; Sayago, I.; Arroyo, T.; Cabellos, J.M.; Gutiérrez, F.J.; Horrillo, M.C. Wine Classification with a Zinc Oxide SAW Sensor Array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 120, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lerma, N.L.; Moreno, J.; Peinado, R.A. Determination of the Optimum Sun-Drying Time for Vitis Vinifera L. Cv. Tempranillo Grapes by E-Nose Analysis and Characterization of Their Volatile Composition. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir Shaban, K.; Kadri, A.; Rezk, E. Urban Air Pollution Monitoring System with Forecasting Models. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, T.; Ling, S.; Szymanski, J.; Zhang, W.; Su, S. Air Quality Monitoring for Vulnerable Groups in Residential Environments Using a Multiple Hazard Gas Detector. Sensors 2019, 19, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binson, V.A.; Subramoniam, M.; Mathew, L. Discrimination of COPD and Lung Cancer from Controls through Breath Analysis Using a Self-Developed e-Nose. J. Breath Res. 2021, 15, 046003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A. Application of Electronic-Nose Technologies and VOC-Biomarkers for the Noninvasive Early Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Sensors 2018, 18, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palaparthy, V.S.; Doddapujar, S.N.; Gupta, G.; Das, P.; Chandorkar, S.A.; Mukherji, S.; Baghini, M.S.; Rao, V.R. E-Nose: Multichannel Analog Signal Conditioning Circuit with Pattern Recognition for Explosive Sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, L.S.; Visani, V.; Marques, P.C.F.; Seabra, M.A.B.L.; Oliveira, N.C.L.; Gubert, P.; de Medeiros, V.W.C.; de Albuquerque, J.O.; de Lima Filho, J.L. Design and Implementation of an Electronic Nose System for Real-Time Detection of Marijuana. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portalo-Calero, F.; Lozano, J.; Meléndez, F.; Arroyo, P.; Suárez, J.I. Identification of Poisonous Mushrooms by Means of a Hand-Held Electronic Nose. Proceedings 2019, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Xu, J. Applications of Electronic Nose (e-Nose) and Electronic Tongue (e-Tongue) in Food Quality-Related Properties Determination: A Review. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Lambri, M.; De Faveri, M.D. Evaluation of the Performances of Synthetic and Cork Stoppers up to 24 Months Post-Bottling. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2003, 216, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravero, M.C. Musty and Moldy Taint in Wines: A Review. Beverages 2020, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, C.; Zalacain, A.; Alonso, G.L.; Salinas, M.R. Non-Destructive Method to Determine Halophenols and Haloanisoles in Cork Stoppers by Headspace Sorptive Extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1114, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Rodríguez, M.L.; Recio, E.; Coque, J.J.R. The Analysis of Natural Cork Stoppers in Transversal Sections as an Effective Tool to Determine the Origin of the Taint by 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 230, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, C.; Trias, R.; Culleré, L.; Escudero, A.; Anticó, E.; Bañeras, L. Off-Odor Compounds Produced in Cork by Isolated Bacteria and Fungi: A Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry and Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7473–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jové, P.; Pareras, A.; De Nadal, R.; Verdum, M. Development and Optimization of a Quantitative Analysis of Main Odorants Causing off Flavours in Cork Stoppers Using Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Gas Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhao, Y. A Feature Selection Strategy of E-Nose Data Based on PCA Coupled with Wilks Λ-Statistic for Discrimination of Vinegar Samples. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2406–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laref, R.; Losson, E.; Sava, A.; Adjallah, K.; Siadat, M. A Comparison between SVM and PLS for E-Nose Based Gas Concentration Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Lyon, France, 20–22 February 2018; pp. 1335–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Sanaeifar, A.; ZakiDizaji, H.; Jafari, A.; de la Guardia, M. Early Detection of Contamination and Defect in Foodstuffs by Electronic Nose: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Mishra, G.; Mishra, H.N. Fuzzy Controller Based E-Nose Classification of Sitophilus Oryzae Infestation in Stored Rice Grain. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Balzano, L.; Fessler, J.A. Asymptotic Performance of PCA for High-Dimensional Heteroscedastic Data. J. Multivar. Anal. 2018, 167, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, M.W.; Dorling, S.R. Artificial Neural Networks (the Multilayer Perceptron)-A Review of Applications in the Atmospheric Sciences. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanola, R.; Subirà, D.; Salvadó, V.; Garcia Regueiro, J.; Anticó, E. Evaluation of an Extraction Method in the Determination of the 2,4,6-Trichloroanisole Content of Tainted Cork. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 953, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).