pH Measurement at Elevated Temperature with Vessel Gate and Oxygen-Terminated Diamond Solution Gate Field Effect Transistors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
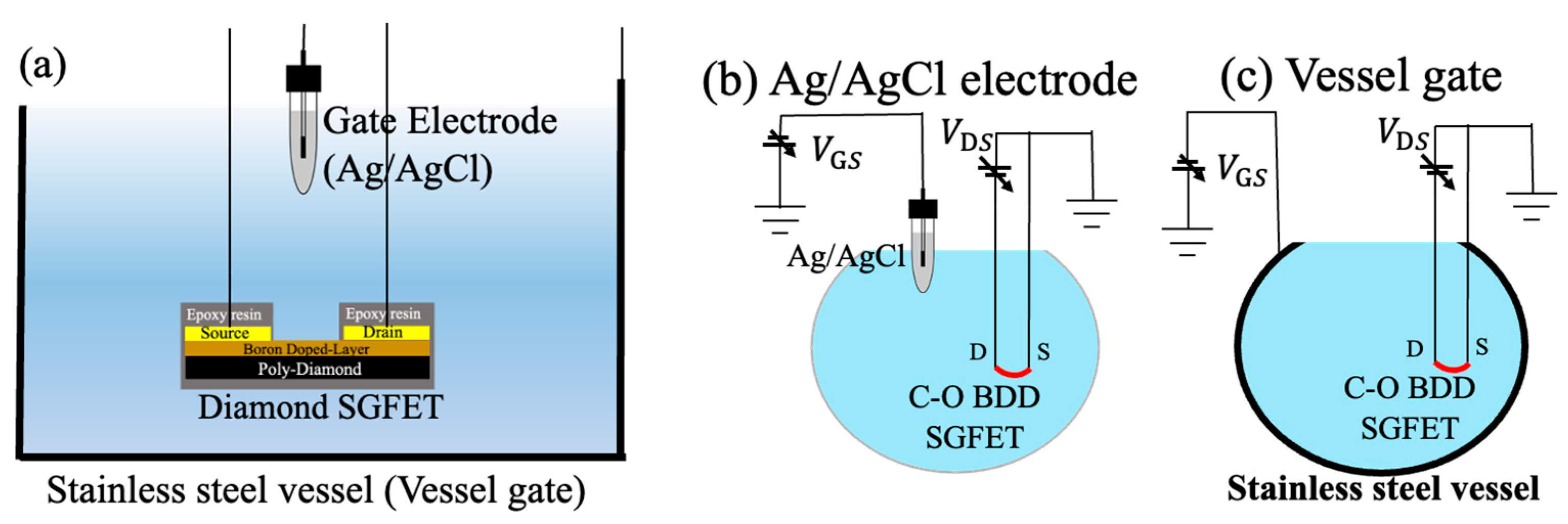
2.1. Fabrication Process and pH Measurement Systems
2.2. How to Measure pH Sensitivity
3. Results and Discussion
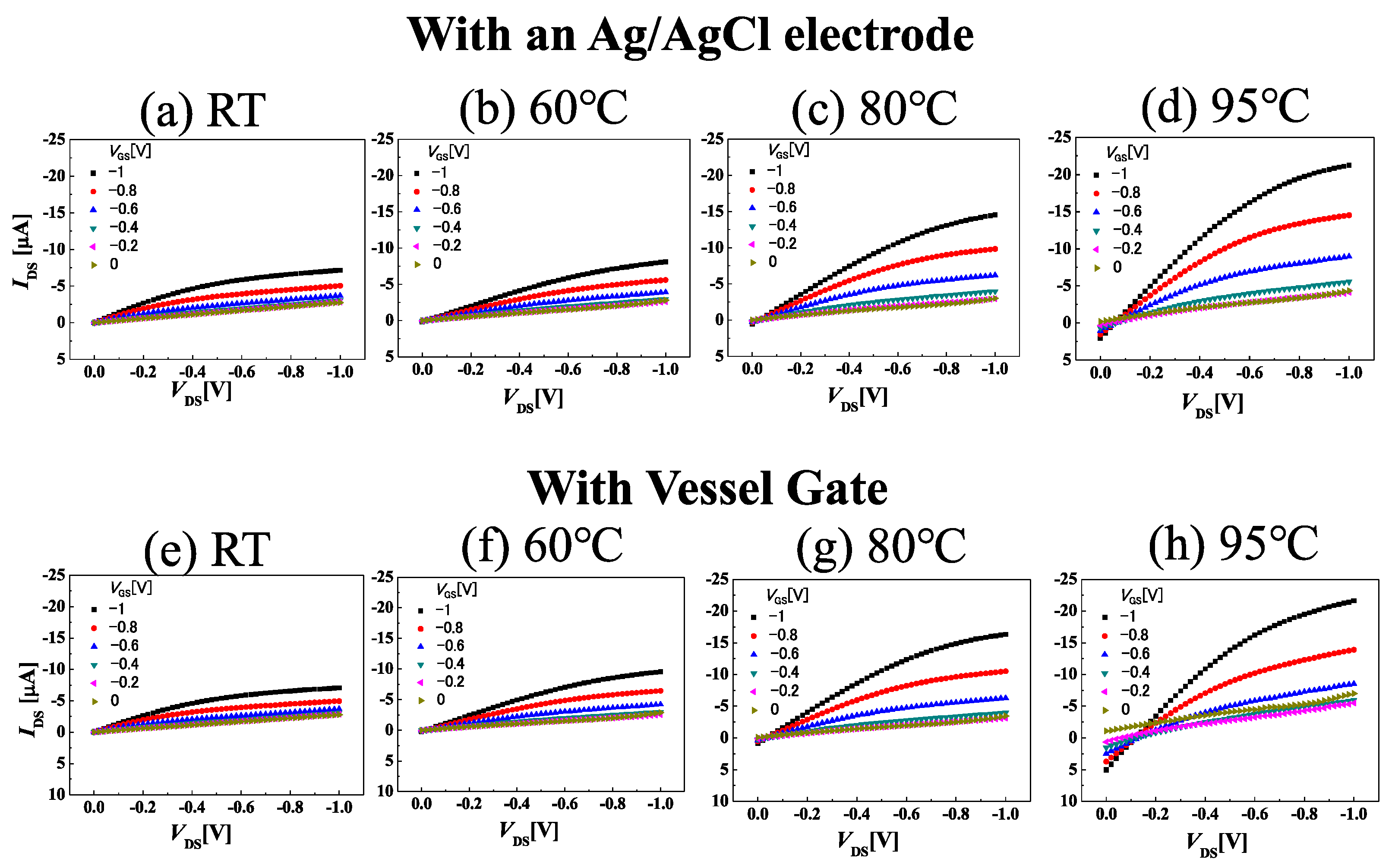
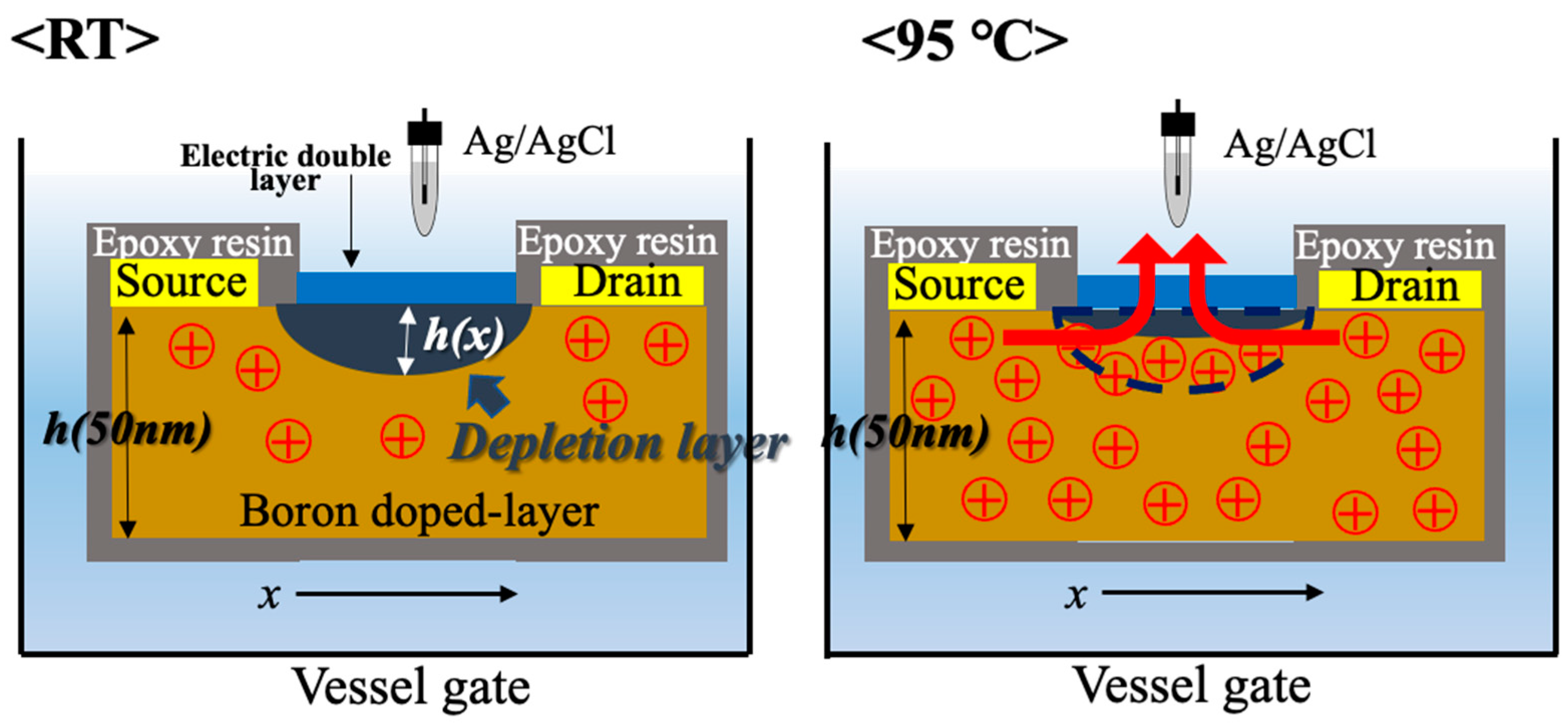
3.1. Temperature Dependence of IDS-VDS Characteristics of C-O BDD SGFET
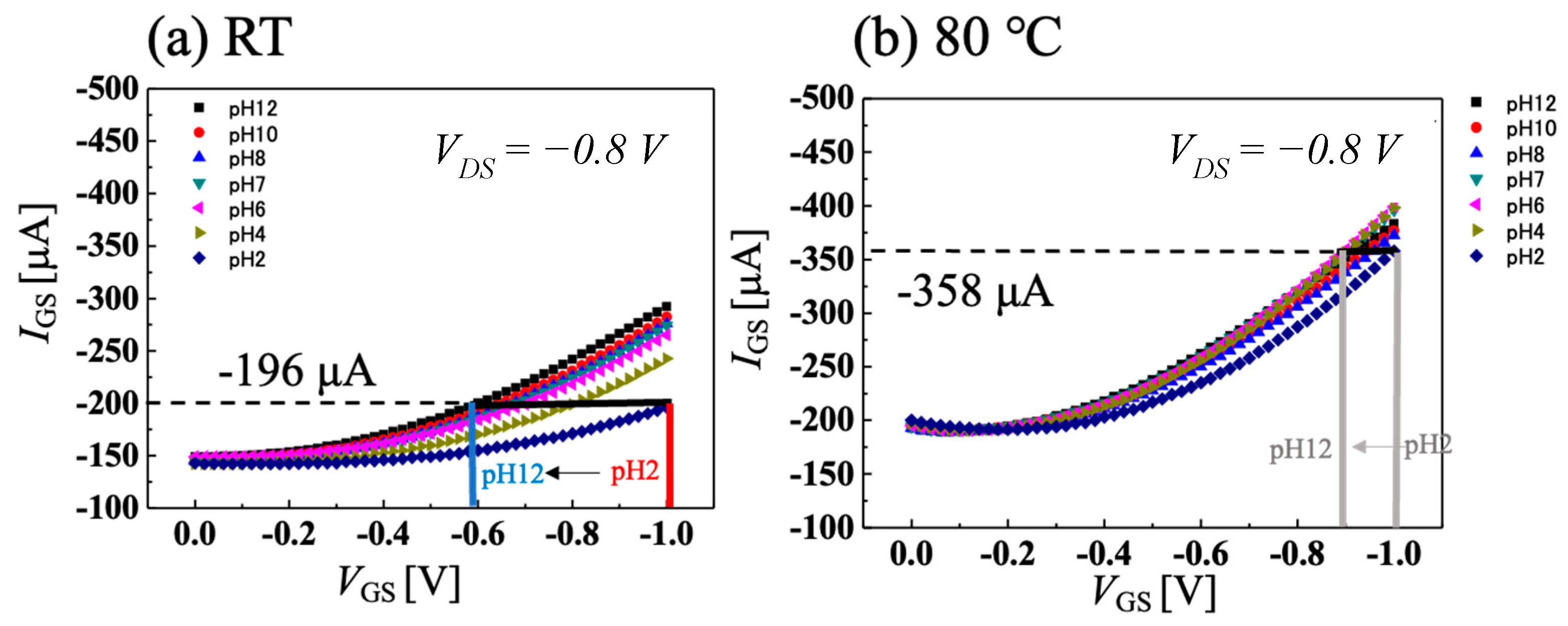
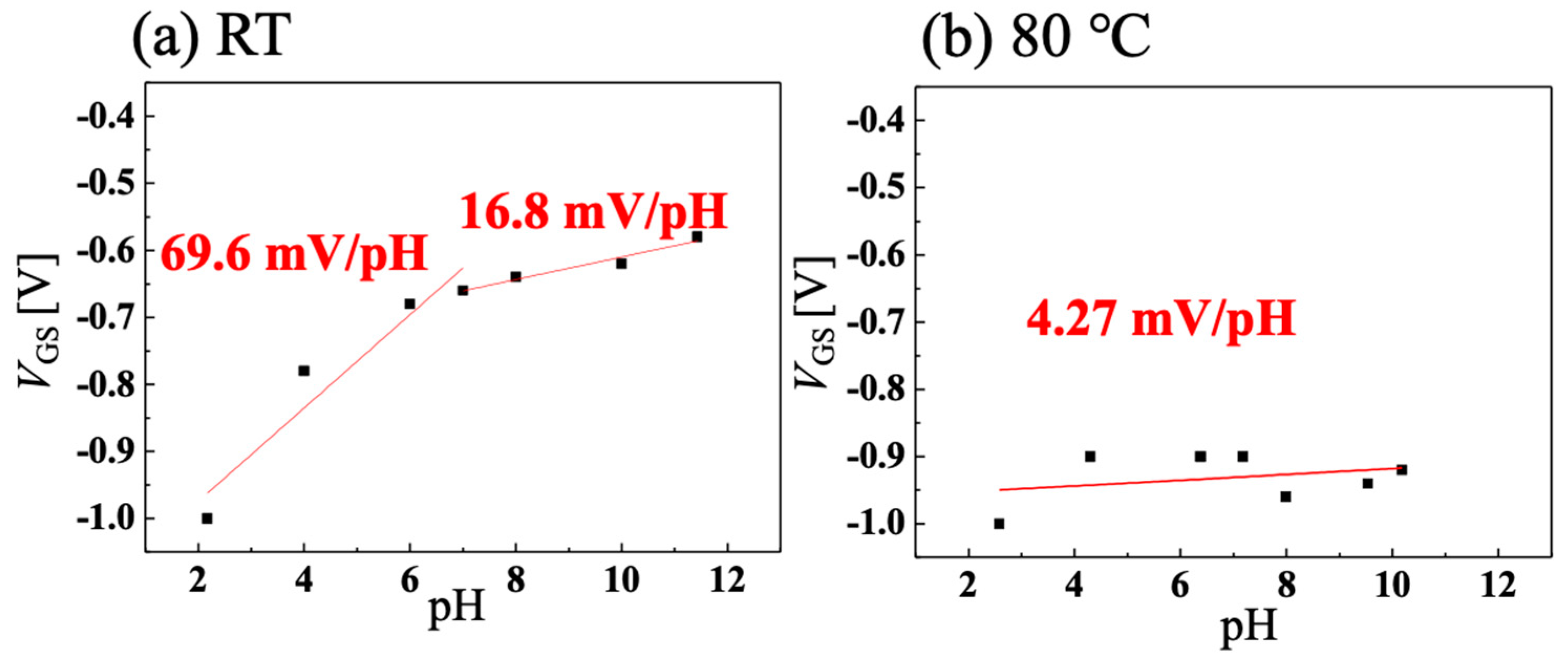
3.2. Temperature Dependence of pH Sensitivity of C-O BDD SGFET
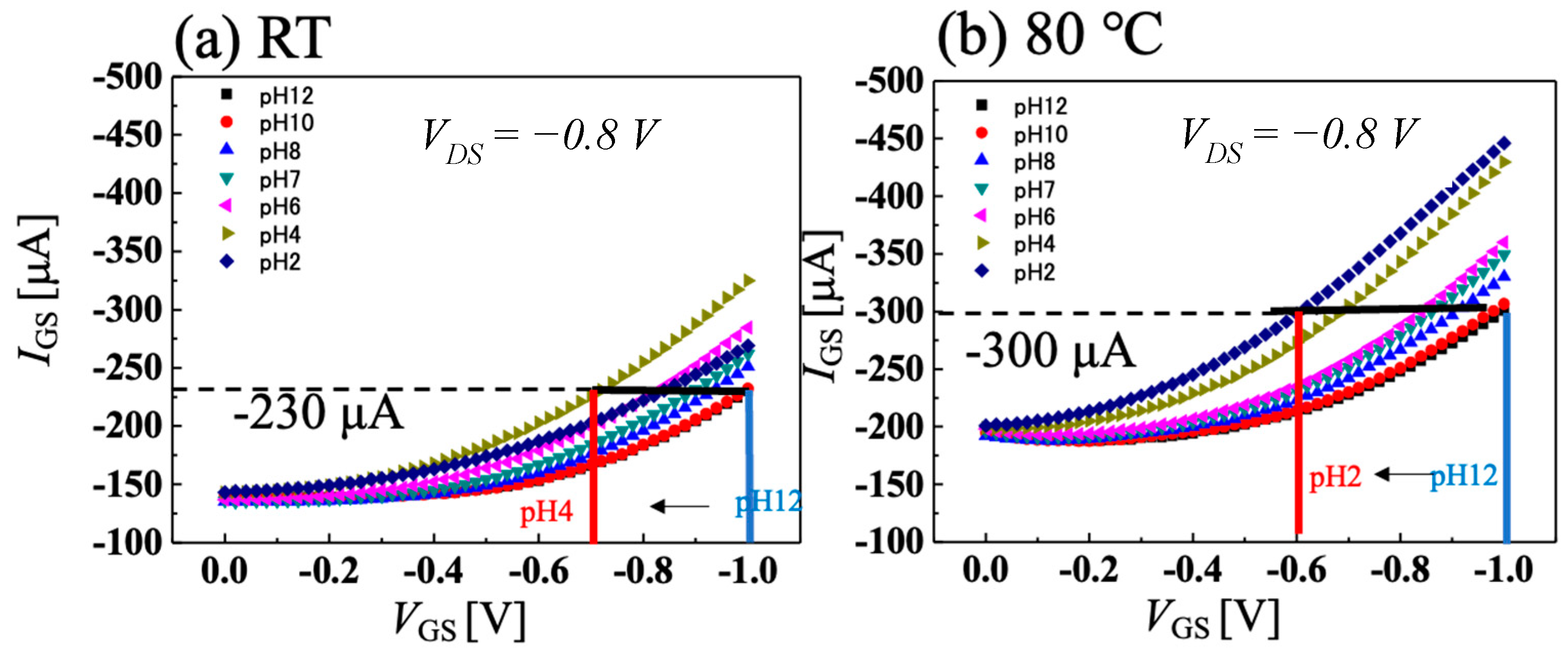
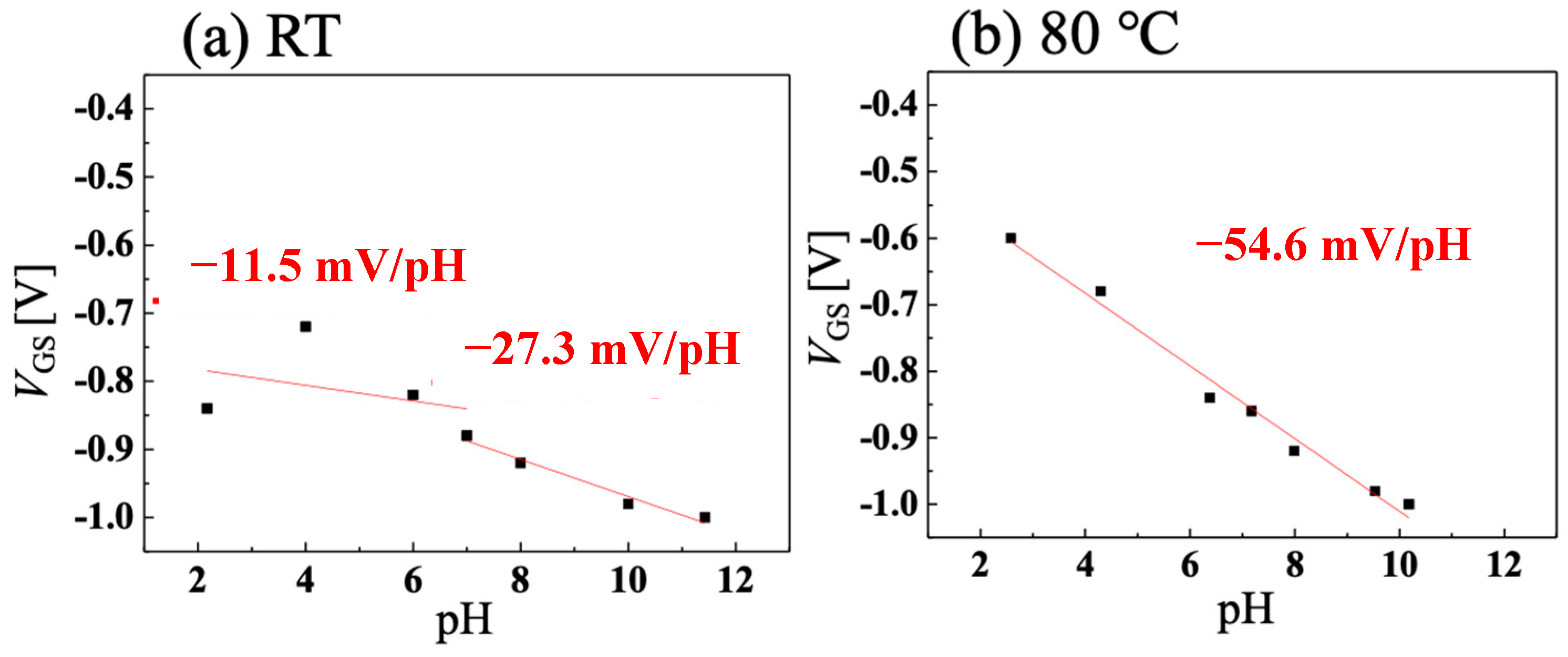
3.3. pH Sensing System at High Temperature with C-O BDD SGFET and Vessel Gate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergveld, P. Development of an ion-sensitive solid-state device for neurophysiological measurements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1970, 1, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergveld, P. Development, Operation, and Application of the Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor as a Tool for Electrophysiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1972, BME-19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, T.; Wise, K.D. An Integrated Field-Effect Electrode for Biopotential Recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1974, BME-21, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausells, J.; Carrabina, J.; Errachid, A.; Merlos, A. Ion-sensitive field-effect transistors fabricated in a commercial CMOS technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 57, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, T.; Nakajima, H. Characteristics of reference electrodes using a polymer gate ISFET. Sens. Actuators 1984, 5, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarada, H.; Araki, Y.; Sakai, T.; Ogawa, T.; Umezawa, H. Electrolyte-Solution-Gate FETs Using Diamond Surface for Biocompatible Ion Sensors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2001, 185, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarada, H.; Ruslinda, A.R. Diamond electrolyte solution gate FETs for DNA and protein sensors using DNA/RNA aptamers. Phys. Status Solidi A 2011, 208, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellgren, N.; Berlind, T.; Gueorguiev, G.K.; Johansson, M.P.; Stafström, S.; Hultman, L. Fullerene-like BCN thin films: A computational and experimental study. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2004, 113, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, P.V.; Gueorguiev, G.K.; Stafström, S. Bonding, charge rearrangement and interface dipoles of benzene, graphene, and PAH molecules on Au (1 1 1) and Cu (1 1 1). Carbon 2015, 81, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Degawa, M.; Yang, J.; Kawarada, H. pH-sensitive diamond field-effect transistors (FETs) with directly aminated channel surface. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 573–574, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salm, E.; Zhong, Y.; Reddy, B., Jr.; Duarte-Guevara, C.; Swaminathan, V.; Liu, Y.; Bashir, R. Electrical detection of nucleic acid amplification using an on-chip quasi-reference electrode and a PVC REFET. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6968–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Chang, C.; Chao, K.; Chen, J. Development of FET-type reference electrodes for pH-ISFET applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, J143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergveld, P.; Van Den Berg, A.; Van Der Wal, P.D.; Skowronska-Ptasinska, M.; Sudhölter, E.; Reinhoudt, D.N. How electrical and chemical requirements for REFETs may coincide. Sens. Actuators 1989, 18, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, T.; Nakade, K.; Ishihara, A.; Nishio, Y. Development of Ag and Ag alloys-precipitated Ag2O-TeO2 glass and Ag2O-TeO2 glass/stainless steel reference electrodes for pH sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Kitabayashi, H.; Ito, K.; Nasu, H.; Ishihara, A.; Nishio, Y. Effect of heat-treatment on the pH sensitivity of stainless-steel electrodes as pH sensors. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nomura, K.; Ujihira, Y. Analysis of oxide layers on stainless steel (304, and 316) by conversion electron Mössbauer spectrometry. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Ujihira, Y. Response of oxide films on stainless steel as a pH sensor. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 2564–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niigata, K.; Narano, K.; Maeda, Y.; Ao, J. Temperature dependence of sensing characteristics of a pH sensor fabricated on AlGaN/GaN heterostructure. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 11RD01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Szwagierczak, D.; Dahiya, R. Metal oxides based electrochemical pH sensors: Current progress and future perspectives. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinlen, P.J.; Heider, J.E.; Hubbard, D.E. A solid-state pH sensor based on a Nafion-coated iridium oxide indicator electrode and a polymer-based silver chloride reference electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark Westcott, C. pH Measurements, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1973; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, R.G. Determination of pH. In Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1973; p. 386. [Google Scholar]
- Syamsul, M.; Kitabayashi, Y.; Matsumura, D.; Saito, T.; Shintani, Y.; Kawarada, H. High voltage breakdown (1.8 kV) of hydrogenated black diamond field effect transistor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 203504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, O.A.; Jackman, R.B.; Nebel, C.; Foord, J.S. Black diamond: A new material for active electronic devices. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2002, 11, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Iyama, Y.; Tadenuma, K.; Kawaguchi, S.; Takarada, T.; Falina, S.; Syamsul, M.; Kawarada, H. Over 59 mV pH− 1 Sensitivity with Fluorocarbon Thin Film via Fluorine Termination for pH Sensing Using Boron-Doped Diamond Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2021, 218, 2000278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjon, J.; Chikoidze, E.; Jomard, F.; Dumont, Y.; Pinault-Thaury, M.; Issaoui, R.; Brinza, O.; Achard, J.; Silva, F. Homoepitaxial boron-doped diamond with very low compensation. Phys. Status Solidi A 2012, 209, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrange, J.; Deneuville, A.; Gheeraert, E. Activation energy in low compensated homoepitaxial boron-doped diamond films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1998, 7, 1390–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, H. Momose, H. Miniaturization and performance limits of silicon devices. Appl. Phys. 1995, 64, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.H. New All-solid-state pH Sensing System Utilizing Diamond Solution Gate Field-Effect Transistors and Stainless Steel Vessel Gate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021; submitted. [Google Scholar]
|
Activation energy of boron [eV] | 298 [K] | 368 [K] | 368 [K]/298 [K] |
| 0.15 | 0.0029 | 0.0088 | 3.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawaguchi, S.; Nomoto, R.; Sato, H.; Takarada, T.; Chang, Y.H.; Kawarada, H. pH Measurement at Elevated Temperature with Vessel Gate and Oxygen-Terminated Diamond Solution Gate Field Effect Transistors. Sensors 2022, 22, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051807
Kawaguchi S, Nomoto R, Sato H, Takarada T, Chang YH, Kawarada H. pH Measurement at Elevated Temperature with Vessel Gate and Oxygen-Terminated Diamond Solution Gate Field Effect Transistors. Sensors. 2022; 22(5):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051807
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawaguchi, Shuto, Reona Nomoto, Hirotaka Sato, Teruaki Takarada, Yu Hao Chang, and Hiroshi Kawarada. 2022. "pH Measurement at Elevated Temperature with Vessel Gate and Oxygen-Terminated Diamond Solution Gate Field Effect Transistors" Sensors 22, no. 5: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051807
APA StyleKawaguchi, S., Nomoto, R., Sato, H., Takarada, T., Chang, Y. H., & Kawarada, H. (2022). pH Measurement at Elevated Temperature with Vessel Gate and Oxygen-Terminated Diamond Solution Gate Field Effect Transistors. Sensors, 22(5), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051807





