Characterizing and Removing Artifacts Using Dual-Layer EEG during Table Tennis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
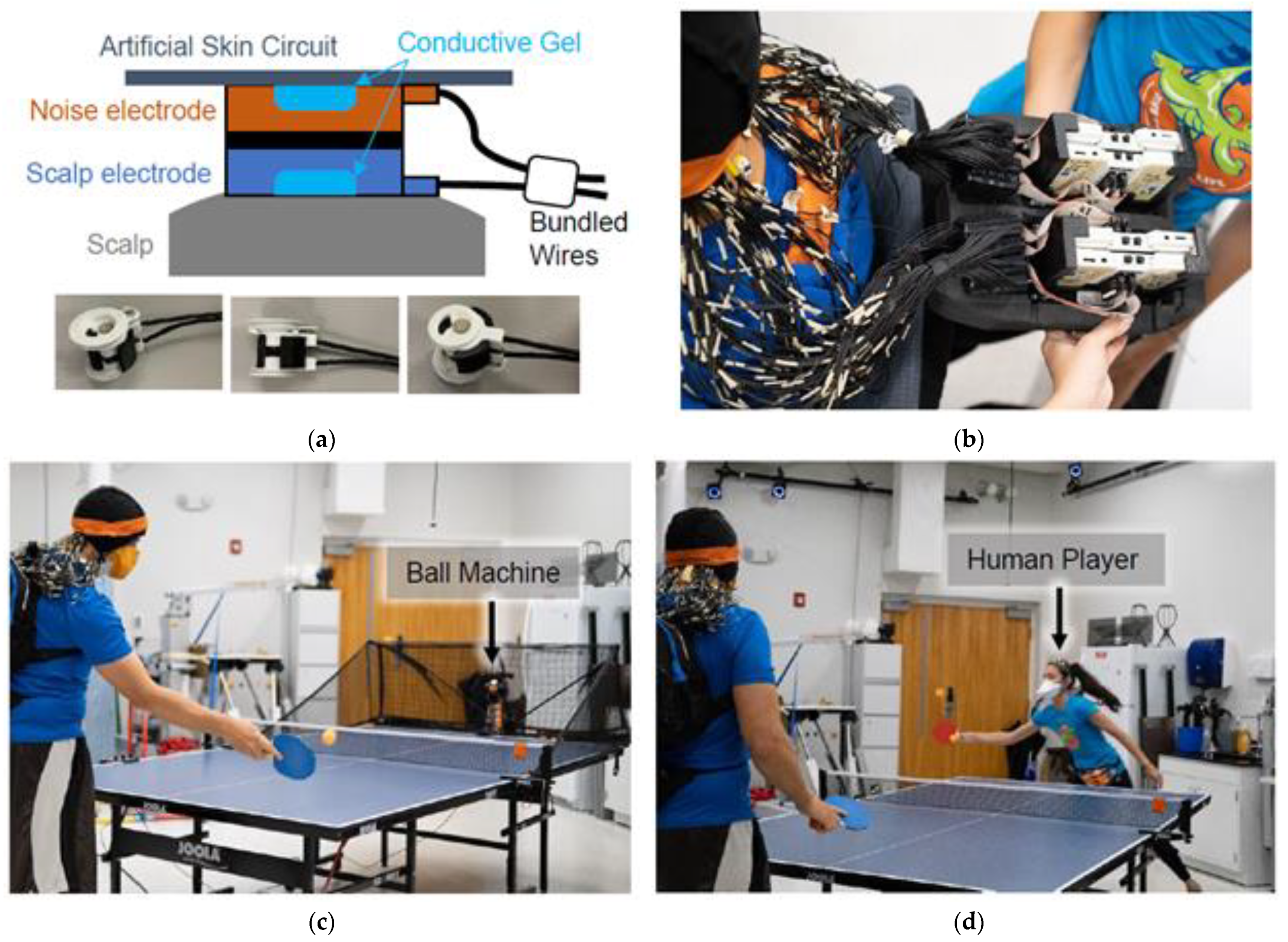
2.2. Dual-Layer Approach
2.3. Inertial Measurement Units
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.5. Artifact Characterization
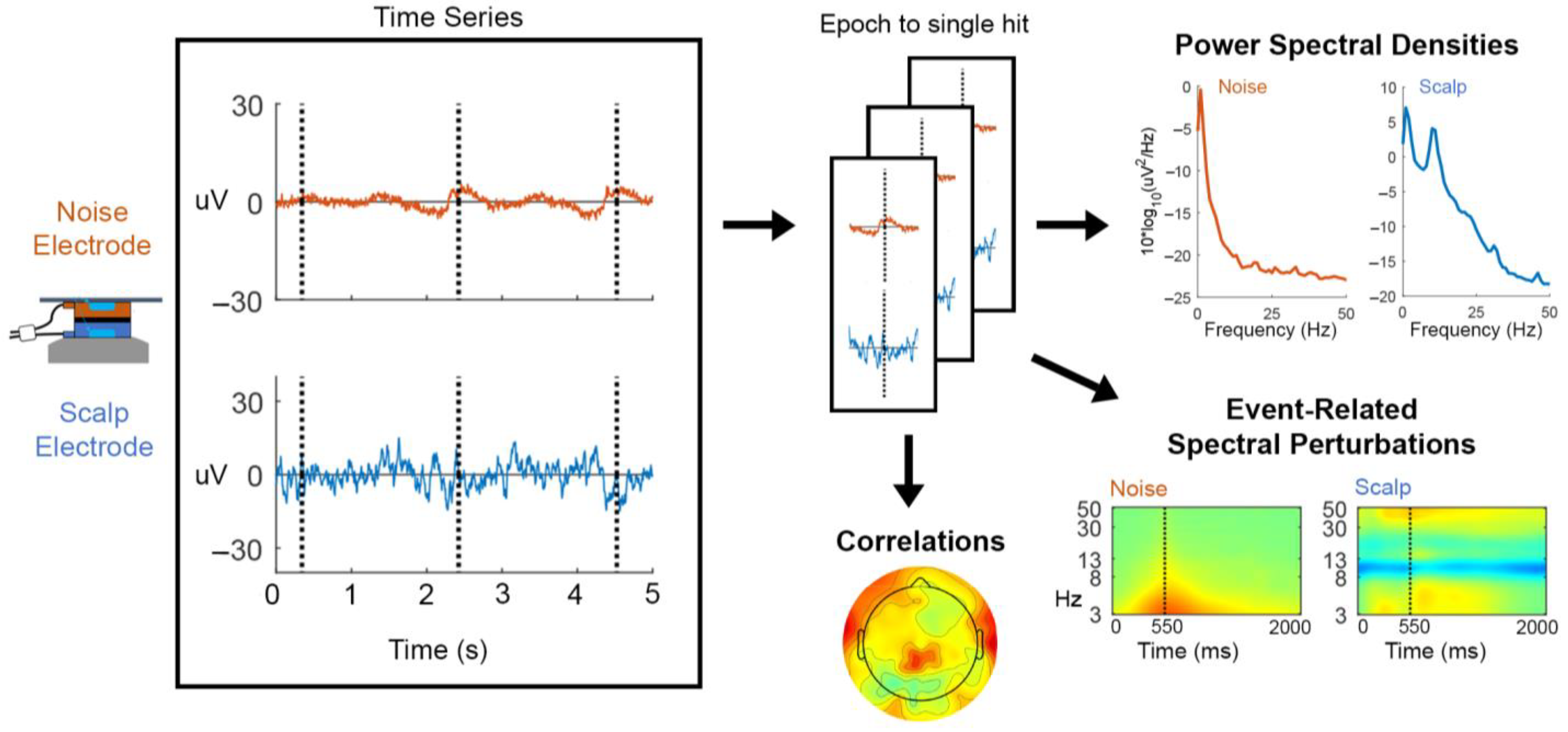
2.5.1. Preprocessing
2.5.2. Power Spectral Density
2.5.3. Event-Related Spectral Perturbation
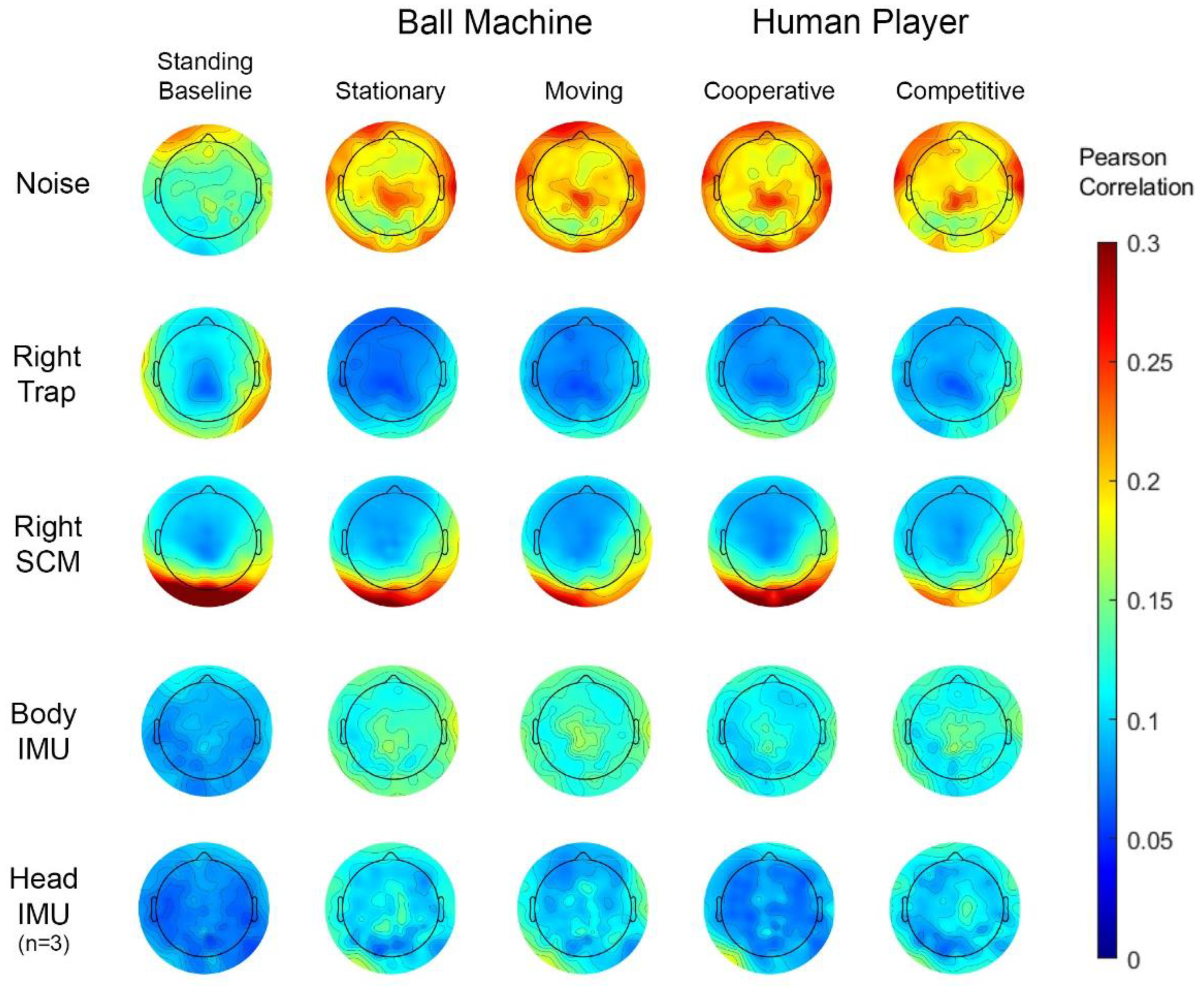
2.5.4. Correlation Analyses
2.6. Artifact Removal
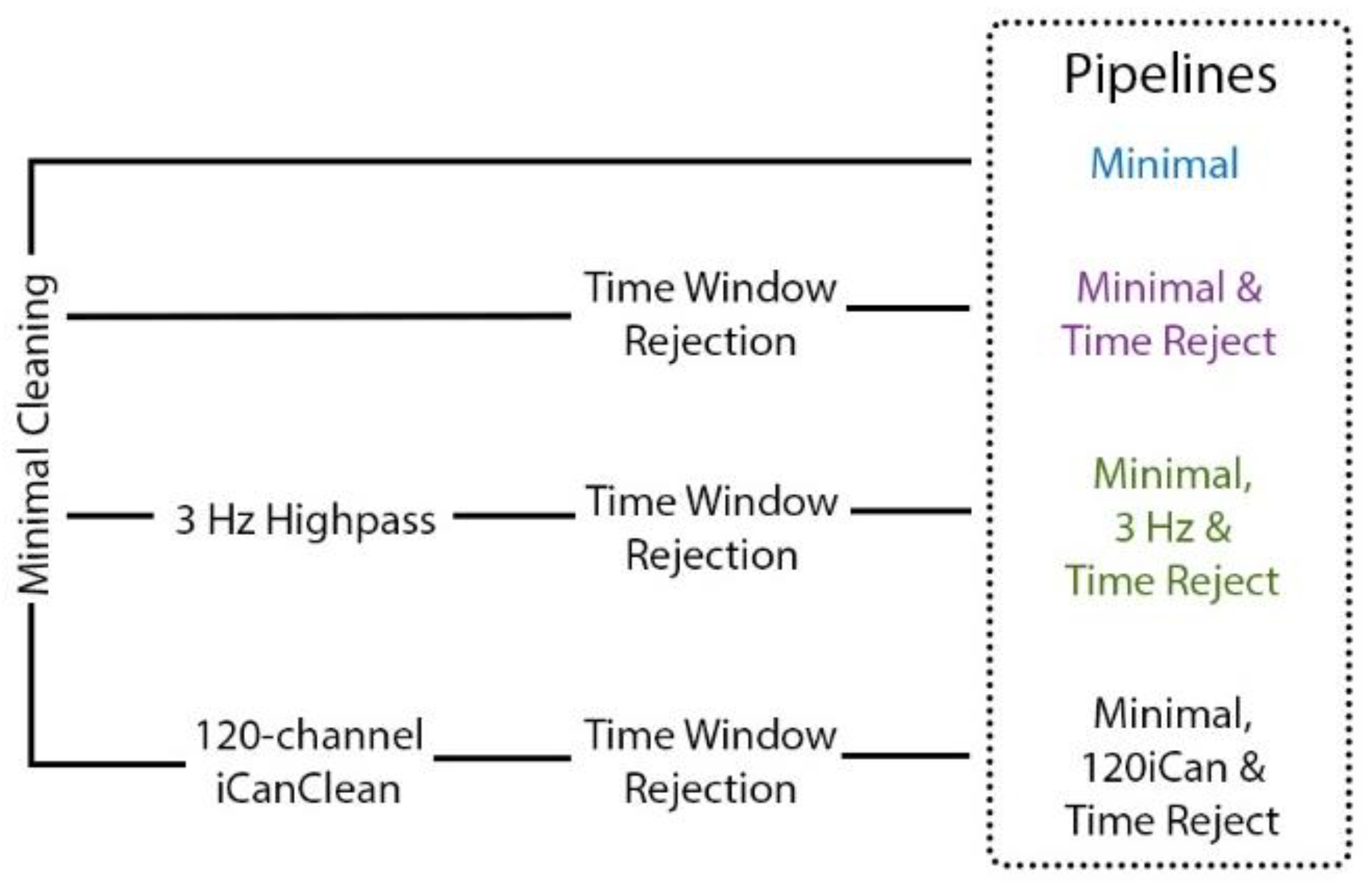
2.6.1. Artifact Removal Strategies
2.6.2. Pipeline Comparison
3. Results
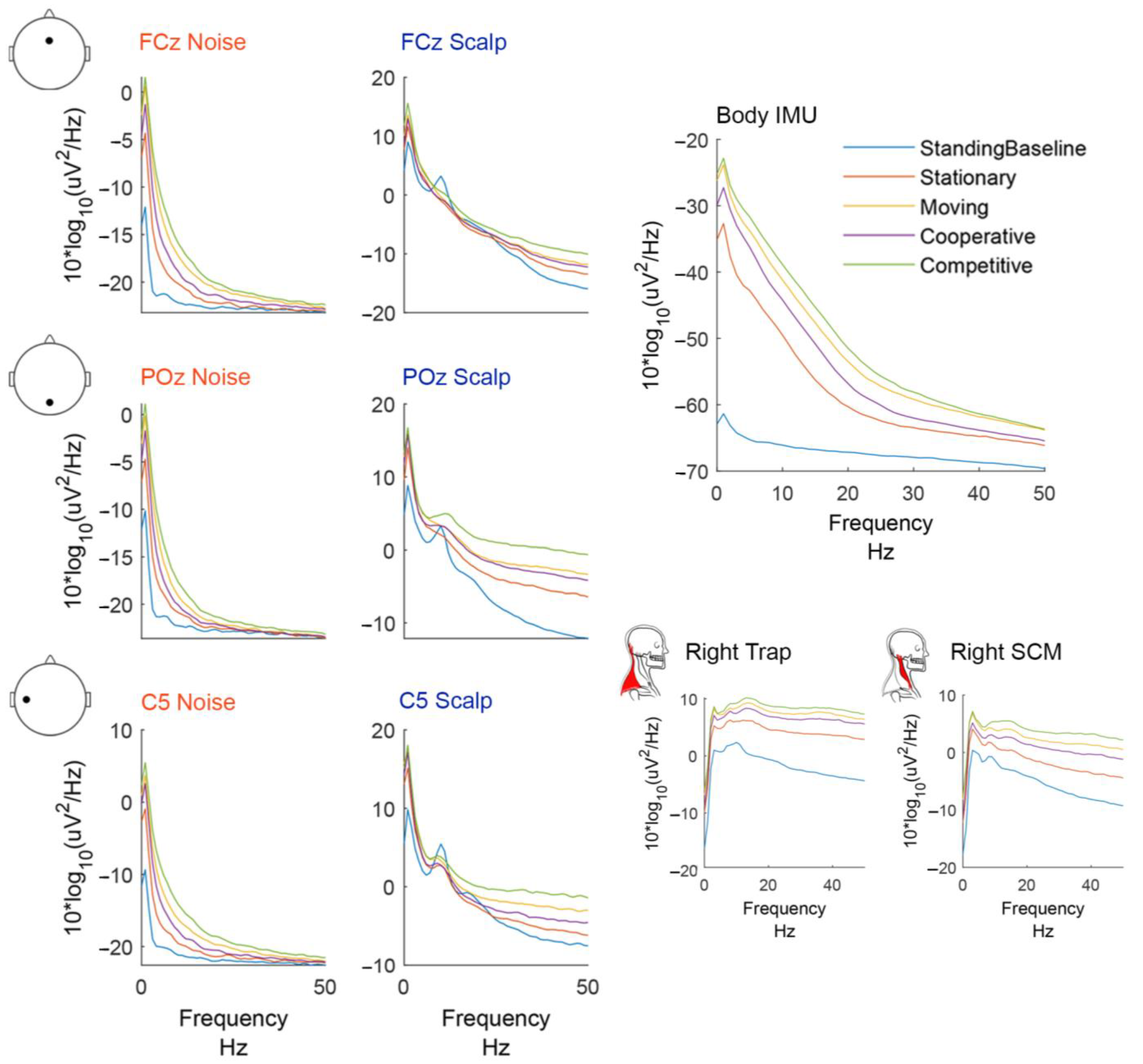
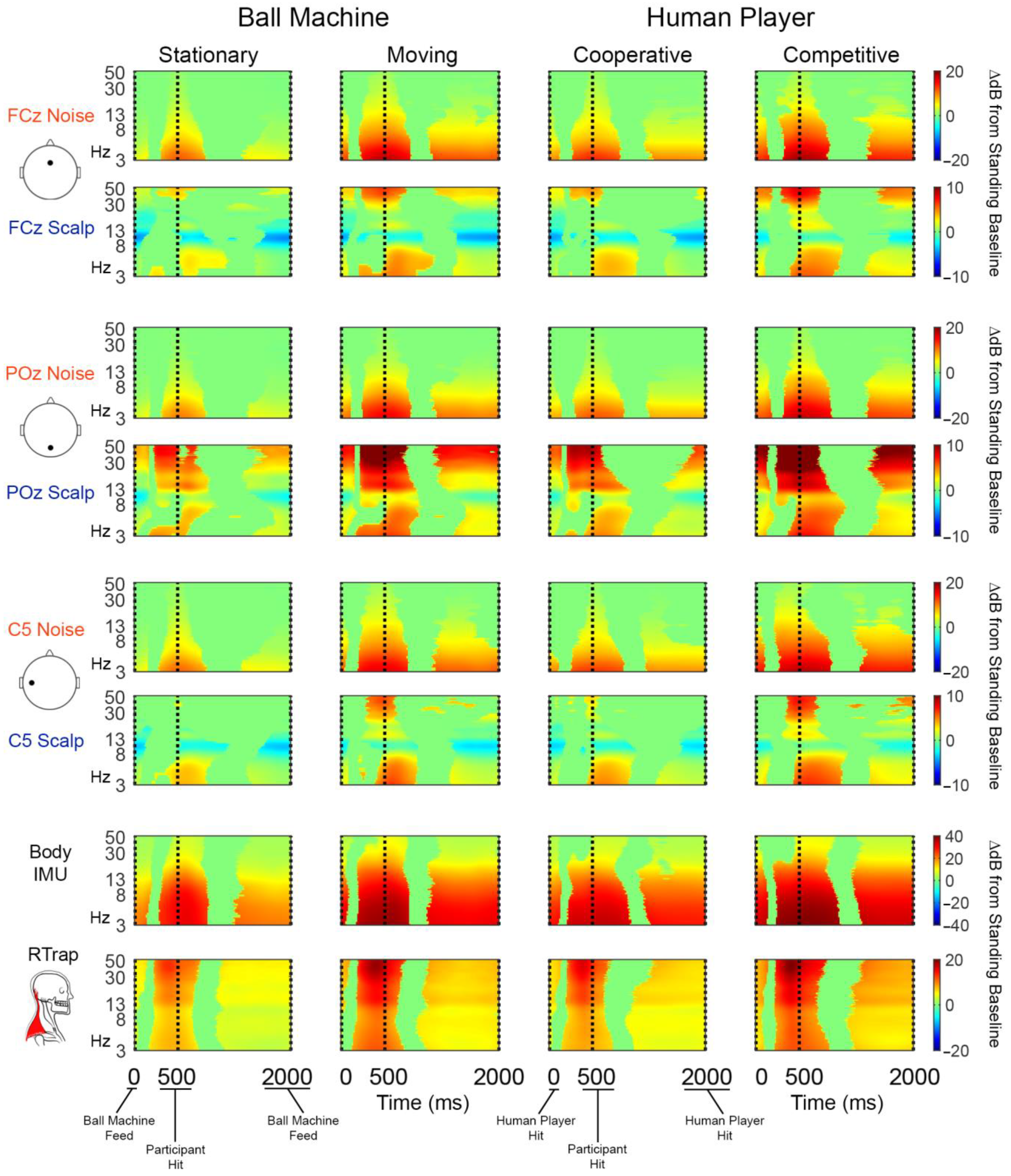
3.1. Artifact Characterization
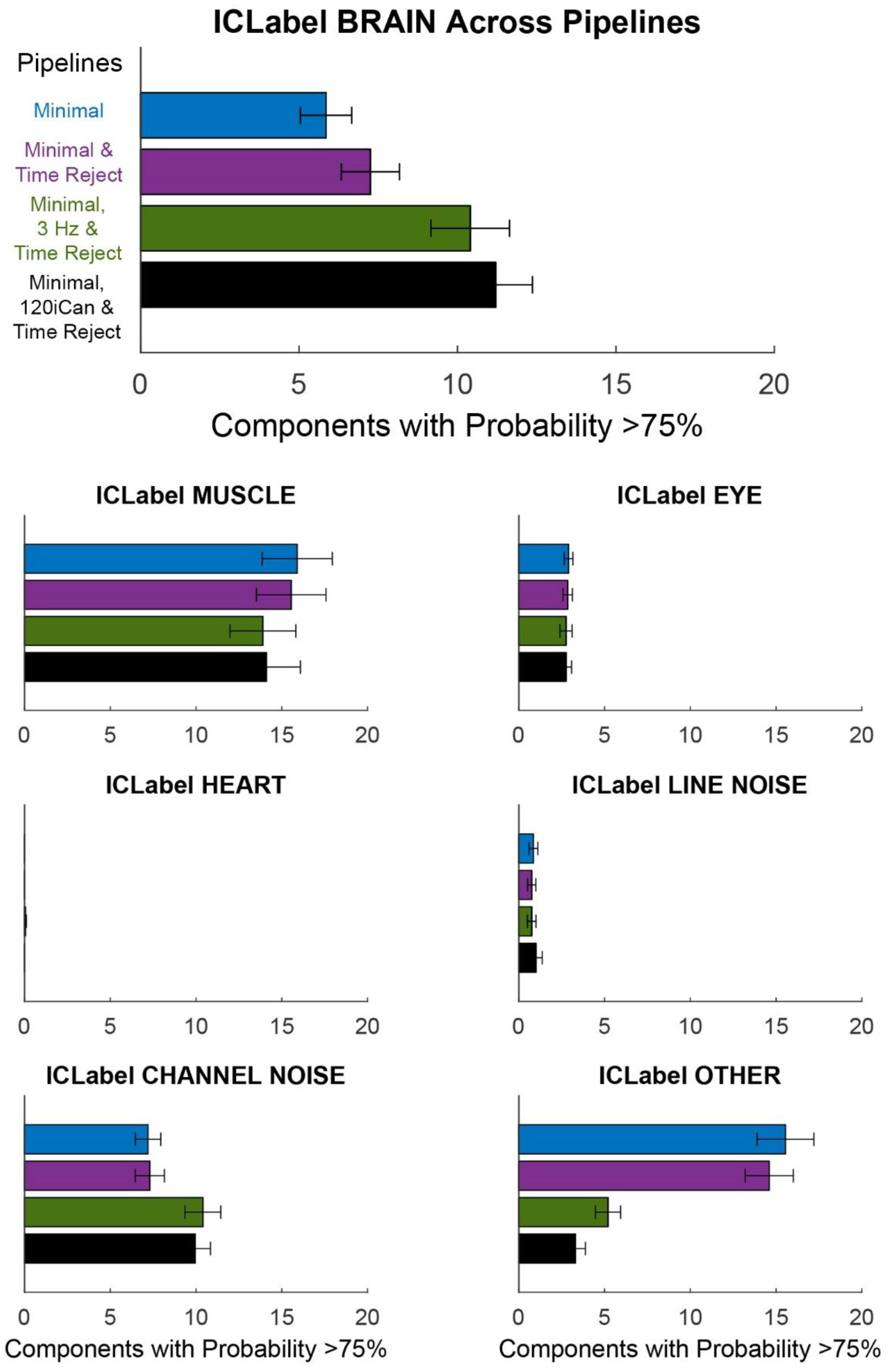
3.2. Pipeline Comparison
4. Discussion
4.1. Artifact Characterization
4.2. Pipeline Comparison
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luu, T.P.; He, Y.; Brown, S.; Nakagame, S.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Gait adaptation to visual kinematic perturbations using a real-time closed-loop brain-computer interface to a virtual reality avatar. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 036006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungnickel, E.; Gehrke, L.; Klug, M.; Gramann, K. MoBI—Mobile Brain/Body Imaging. Neuroergon. Brain Work Everyday Life 2019, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onton, J.; Westerfield, M.; Townsend, J.; Makeig, S. Imaging human EEG dynamics using independent component analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Sejnowski, T.; Makeig, S. Enhanced detection of artifacts in EEG data using higher-order statistics and independent component analysis. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makeig, S.; Jung, T.-P.; Bell, A.J.; Sejnowski, T.J. Independent Component Analysis of Electroencephalographic Data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1995, 8, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Mullen, T.; Kothe, C.; Chi, Y.M.; Ojeda, A.; Kerth, T.; Makeig, S.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Jung, T.P. Real-time modeling and 3D visualization of source dynamics and connectivity using wearable EEG. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 2013, 2184–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Urigüen, J.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. EEG artifact removal—State-of-the-art and guidelines. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Mitra, S.; Van Hoof, C.; Yazicioglu, R.F.; Makinwa, K.A.A. Active Electrodes for Wearable EEG Acquisition: Review and Electronics Design Methodology. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 10, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeonidou, E.R.; Nordin, A.D.; Hairston, W.D.; Ferris, D.P. Effects of Cable Sway, Electrode Surface Area, and Electrode Mass on Electroencephalography Signal Quality during Motion. Sensors 2018, 18, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, J.A.; Luu, T.P.; Nakagome, S.; Zhu, F.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Full body mobile brain-body imaging data during unconstrained locomotion on stairs, ramps, and level ground. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.M.; Ferris, D.P. Differentiation in Theta and Beta Electrocortical Activity between Visual and Physical Perturbations to Walking and Standing Balance. eNeuro 2018, 5, ENEURO.0207-18.2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castermans, T.; Duvinage, M.; Cheron, G.; Dutoit, T. About the cortical origin of the low-delta and high-gamma rhythms observed in EEG signals during treadmill walking. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 561, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, K.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Negligible motion artifacts in scalp electroencephalography (EEG) during treadmill walking. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, J.E.; Huang, H.J.; Snyder, K.L.; Ferris, D.P. Isolating gait-related movement artifacts in electroencephalography during human walking. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 046022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Arumuganathan, R.; Sivakumar, K.; Vimal, C. Removal of artifacts from EEG signals using adaptive filter through wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2008 9th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 26–29 October 2008; pp. 2138–2141. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; Wilson, G.; Russell, C. Removal of ocular artifacts from electro-encephalogram by adaptive filtering. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2004, 42, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilicarslan, A.; Grossman, R.G.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. A robust adaptive denoising framework for real-time artifact removal in scalp EEG measurements. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 026013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucarquer, J.A.; Prado, P.; Escobar, M.J.; El-Deredy, W.; Zanartu, M. Improving EEG Muscle Artifact Removal with an EMG Array. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, I.; Billinger, M.; Scherer, R.; Müller-Putz, G. On the automated removal of artifacts related to head movement from the EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 21, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onikura, K.; Iramina, K. Evaluation of a head movement artifact removal method for EEG considering real-time prosessing. In Proceedings of the 2015 8th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–27 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kilicarslan, A.; Contreras Vidal, J.L. Characterization and real-time removal of motion artifacts from EEG signals. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 056027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richer, N.; Downey, R.J.; Hairston, W.D.; Ferris, D.P.; Nordin, A.D. Motion and Muscle Artifact Removal Validation Using an Electrical Head Phantom, Robotic Motion Platform, and Dual Layer Mobile EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, A.D.; Hairston, W.D.; Ferris, D.P. Human electrocortical dynamics while stepping over obstacles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, A.D.; Hairston, W.D.; Ferris, D.P. Dual-electrode motion artifact cancellation for mobile electroencephalography. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, A.D.; Hairston, W.D.; Ferris, D.P. Faster Gait Speeds Reduce Alpha and Beta EEG Spectral Power from Human Sensorimotor Cortex. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwin, J.T.; Gramann, K.; Makeig, S.; Ferris, D.P. Removal of movement artifact from high-density EEG recorded during walking and running. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 3526–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, N.S.J.; Blum, S.; Witt, K.; Debener, S. A walk in the park? Characterizing gait-related artifacts in mobile EEG recordings. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 54, 8421–8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramann, K.; Hohlefeld, F.U.; Gehrke, L.; Klug, M. Human cortical dynamics during full-body heading changes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, S.; di Fronso, S.; Bertollo, M.; Werthner, P. Individual alpha peak frequency in ice hockey shooting performance. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wong, D.W.C.; Lee, W.C.C.; Lam, W.K. Biomechanics of Table Tennis: A Systematic Scoping Review of Playing Levels and Maneuvers. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombini, M.; Zappasodi, F.; Zollo, L.; Pellegrino, G.; Cavallo, G.; Tecchio, F.; Guglielmelli, E.; Rossini, P.M. Brain activity preceding a 2D manual catching task. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 1735–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, H.; Sommer, W.; Takasawa, N.; Yamazaki, K. Neural mechanisms of timing control in a coincident timing task. Exp. Brain Res. 2012, 218, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazmir, B.; Reiner, M. Monitoring brain potentials to guide neurorehabilitation of tracking impairments. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 983–988. [Google Scholar]
- Denis, D.; Rowe, R.; Williams, A.M.; Milne, E. The role of cortical sensorimotor oscillations in action anticipation. Neuroimage 2017, 146, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wriessnegger, S.C.; Brunner, C.; Müller-Putz, G.R. Frequency specific cortical dynamics during motor imagery are influenced by prior physical activity. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramann, K.; Ferris, D.P.; Gwin, J.; Makeig, S. Imaging natural cognition in action. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 91, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makeig, S.; Gramann, K.; Jung, T.P.; Sejnowski, T.J.; Poizner, H. Linking brain, mind and behavior. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2009, 73, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramann, K.; Gwin, J.T.; Ferris, D.P.; Oie, K.; Jung, T.P.; Lin, C.T.; Liao, L.-D.; Makeig, S. Cognition in action: Imaging brain/body dynamics in mobile humans. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 22, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladouce, S.; Donaldson, D.I.; Dudchenko, P.A.; Ietswaart, M. Understanding minds in real-world environments: Toward a mobile cognition approach. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada, F.J. Understanding Natural Cognition in Everyday Settings: 3 Pressing Challenges. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuckler, M.A. What Is Ecological Validity? A Dimensional Analysis. Infancy 2001, 2, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsalou, L.W. Grounded Cognition. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 617–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiel, H.J.; Beer, R.D. The brain has a body: Adaptive behavior emerges from interactions of nervous system, body and environment. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, R.J.; Ferris, D.P.; Crayton Pruitt, J. The iCanClean Algorithm: How to Remove Artifacts using Reference Noise Recordings. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.11798. [Google Scholar]
- LiveAmp Series. Available online: https://www.brainproducts.com/solutions/liveamp/ (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- O’Regan, S.; Faul, S.; Marnane, W. Automatic detection of EEG artefacts arising from head movements using EEG and gyroscope signals. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihajlovic, V.; Patki, S.; Grundlehner, B. The impact of head movements on EEG and contact impedance: An adaptive filtering solution for motion artifact reduction. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 5064–5067. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, N.C.; Dunlap, W.P. Averaging Correlation Coefficients: Should Fisher’s z Transformation Be Used? J. Appl. Psychol. 1987, 72, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoto’s Preprocessing Pipeline (n.d.). Available online: https://sccn.ucsd.edu/wiki/Makoto’s_preprocessing_pipeline (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Mullen, T.R.; Kothe, C.A.E.; Chi, Y.M.; Ojeda, A.; Kerth, T.; Makeig, S.; Jung, T.P.; Cauwenberghs, G. Real-time neuroimaging and cognitive monitoring using wearable dry EEG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2553–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Hsu, S.H.; Pion-Tonachini, L.; Jung, T.P. Evaluation of Artifact Subspace Reconstruction for Automatic Artifact Components Removal in Multi-Channel EEG Recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.A.; Kreutz-Delgado, K.; Makeig, S. Super-Gaussian Mixture Source Model for ICA. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 3889, pp. 854–861. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.A.; Makeig, S.; Kreutz-Delgado, K.; Rao, B.D. Newton method for the ica mixture model. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March 2008–4 April 2008; pp. 1805–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Palmer, J.; Onton, J.; Oostenveld, R.; Makeig, S. Independent EEG Sources Are Dipolar. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenveld, R.; Oostendorp, T.F. Validating the boundary element method for forward and inverse EEG computations in the presence of a hole in the skull. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pion-Tonachini, L.; Kreutz-Delgado, K.; Makeig, S. ICLabel: An automated electroencephalographic independent component classifier, dataset, and website. Neuroimage 2019, 198, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. Source J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, M.; Gramann, K. Identifying key factors for improving ICA-based decomposition of EEG data in mobile and stationary experiments. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 54, 8406–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carius, D.; Kenville, R.; Maudrich, D.; Riechel, J.; Lenz, H.; Ragert, P. Cortical processing during table tennis—An fNIRS study in experts and novices. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2021, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Studnicki, A.; Downey, R.J.; Ferris, D.P. Characterizing and Removing Artifacts Using Dual-Layer EEG during Table Tennis. Sensors 2022, 22, 5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155867
Studnicki A, Downey RJ, Ferris DP. Characterizing and Removing Artifacts Using Dual-Layer EEG during Table Tennis. Sensors. 2022; 22(15):5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155867
Chicago/Turabian StyleStudnicki, Amanda, Ryan J. Downey, and Daniel P. Ferris. 2022. "Characterizing and Removing Artifacts Using Dual-Layer EEG during Table Tennis" Sensors 22, no. 15: 5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155867
APA StyleStudnicki, A., Downey, R. J., & Ferris, D. P. (2022). Characterizing and Removing Artifacts Using Dual-Layer EEG during Table Tennis. Sensors, 22(15), 5867. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155867





