Abstract
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are defined as crystalline organic polymers with programmable topological architectures using properly predesigned building blocks precursors. Since the development of the first COF in 2005, many works are emerging using this kind of material for different applications, such as the development of electrochemical sensors and biosensors. COF shows superb characteristics, such as tuneable pore size and structure, permanent porosity, high surface area, thermal stability, and low density. Apart from these special properties, COF’s electrochemical behaviour can be modulated using electroactive building blocks. Furthermore, the great variety of functional groups that can be inserted in their structures makes them interesting materials to be conjugated with biological recognition elements, such as antibodies, enzymes, DNA probe, aptamer, etc. Moreover, the possibility of linking them with other special nanomaterials opens a wide range of possibilities to develop new electrochemical sensors and biosensors.
1. Introduction
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a type of polymer, which connect organic molecules in two (2D) or three dimensions (3D) via covalent bonds [1,2]. Their most noteworthy feature is their intrinsic order, which is predetermined by the monomers or linkers, employed in the polymerization, building crystalline structures with pre-designable architectures [3,4,5]. The design of the network’s topology lies in the control of the direction of covalent bond formation during the polymerization [1]. To ensure the directionality of growth, the monomers must be formed by relatively rigid bonds and present the functionalities in specific positions [6,7]. To do this, the design is approached from a simplified block model, where each monomer is represented with a specific geometric shape that symbolizes the relative positions of the reactive points [6,7,8]. In this way, as depicted in Figure 1A, a linear monomer could generate hexagonal networks by cyclotrimerization (for example boroxine formation) or produce square COFs if it is combined with a C4 linker. Following the pioneering work of Yaghi and the co-workers of Yaghi [9], several structural motifs have been described, including hexagonal [10,11], kagome [12,13,14] or square [15,16] two-dimensional networks (2D-COFs), and diamonoid [17,18], Cubic [19], or PtS [20] three-dimensional architectures (3D-COFs). It is worth pointing out that the dimensionality of the COF network is also determined by the linkers employed in the polymerization. The aforementioned 2D-COFs are generally built from flat molecules, while 3D-COFs are usually based on linkers endowed with sp3 centres [18] or a geometry significantly distorted from planarity via steric tuning [20].
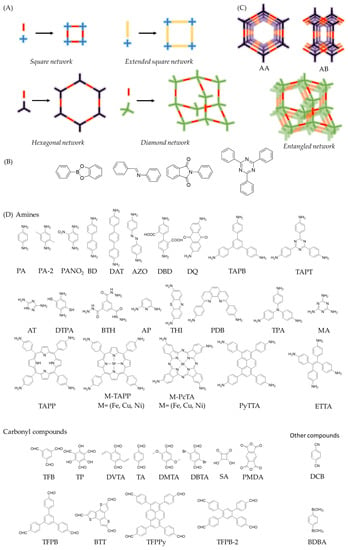
Figure 1.
(A) Examples of COFs topology diagrams. (B) Examples of linkages commonly used for the synthesis of COFs (from left to right: boronate ester, imine, imide, and triazine. (C) Examples of arrangements of COF’s networks. (D) List of linkers named in this review.
The type of bond used to connect the building blocks, commonly known as linkage, is crucial during the formation of the framework as multiple covalent structures with different degrees of crystallinity can be produced during the polymerization reactions [6,7]. In fact, the main difference between COFs and porous organic polymers (POPs) is the crystalline order. The generally most widespread strategy to prevent the formation of amorphous products and favour the COF’s crystallization is the use of reversible reactions [6,7]. In this way, the balance between reactants and products allows curing and error correction of the amorphous network, usually associated to kinetic control products, until the COF crystallizes as the thermodynamically more stable product [7]. These are the characteristic features of dynamic covalent chemistry (DCC) [21,22]. In simple terms, in a system where DCC operates, it is the stability of the products that decides the final distributions [2]. Thus, several linkages have been used for the formation of COFs, such as boroxine, boronate esterification, imine, azine, imide, or triazine (Figure 1B) [6]. Other approaches to enhance the crystallinity of the systems includes the addition of monofunctional modulators [18], competitors [23], and protected monomers [24] as strategies to control the nucleation and growth of the crystalline phases [25,26]. Unfortunately, the crystallization conditions to obtain the more thermodynamically stable products are not known a priori, and the COF crystallization is usually achieved via iterative screening methodology. Nevertheless, a plethora of methodologies have been reported in the last years to enhance the crystallinity of COFs, including the solvothermal synthesis [10], microwave-assisted methods [27], ionothermal synthesis [28], interfacial synthesis [29], repolymerization methods [30], or on-surface synthesis [31]. Furthermore, the screening of experimental conditions and structure–property relationships are being accelerated through computational calculations and automated machine learning [32,33,34], which are emerging as powerful tools to obtain tailor-made materials in record times.
Another distinctive characteristic of COFs is their inherent porosity [35,36,37]. On the one hand, the overlap of the 2D-COFs layers can build up a three-dimensional structure, traversed by unidirectional cavities also known as pores, which can mainly present as two isomers. The first one is an eclipsed structure (AA), composed by adjacent layers, which are located in the same position. The second one, is a staggered structure (AB or ABC), where every COF layer is shifted with respect to the previous one. It is worth pointing out that the staggered structure in 2D-COFs also presents pores traversing the three-dimensional structure. However, in terms of porosity, the structure that presents the highest surface area is the eclipsed isomer network [1,2]. On the other hand, network entanglements can be produced in 3D-COFs, thus lowering the theoretical surface area (Figure 1C) [18].
COFs presents high thermal, mechanical, and chemical stabilities, with differences depending on the linkage and/or the monomers used in the polymerization reaction [6]. The above-mentioned characteristics, together with their inherent insolubility [1], place COFs as ideal materials to explore their applicability in heterogeneous phases. In this way, COFs have already been used in different applications, such as catalysis [38,39,40], solar cells [41], batteries [42,43], gas storage and separation [44,45], water remediation [39,46], and sensing [47].
Concerning the integration in devices, COFs must face the doble edged sword of one of their main attributes, their inherent insolubility. In this way, the most common procedure to achieve tailor-made devices are two depending on the followed path: (i) Top-down protocol involves the destruction of the granular COF structure, achieving the sheet separation in a process known as exfoliation producing covalent organic nanosheets (CONs) [48]. To address this end, several methods have been developed. The most common procedure is liquid phase exfoliation, which consists in the use of different solvents to produce layer slipping and the subsequent delamination in an ultrasonic bath [49]. Another method is the mechanical delamination, which produces the exfoliation by using an external force over the bulk COF [50]. Chemical or acid spontaneous exfoliations are receiving a great deal of attention because they cause the COF delamination using chemical energy, reducing the costs for obtaining CONs [49]. Finally, nitrogen delamination consists in the gentle heating of the bulk COF and subsequent addition of liquid nitrogen, which intercalates between the COF layers and produces exfoliation by the thermal expansion in the liquid-to-gas phase transition [51]. (ii) The use of bottom-up methods involves the formation of the CONs or the tailor-made COF directly from the monomers. On the one hand, for the synthesis of nanosheets it usually requires the use of additives, such as tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride (TBAF) micelles or surfactants mediators producing monomodal distribution of CONs by the restriction of the growth dimensions. Thus, mi-cellar synthesis allows the growing of large few-layered COFs in the interphase between two immiscible solvents [29,52]. On the other hand, tailor-shaped COFs are obtained by using either the 3D-printing technique, which involves the preparation of a COF “ink” and the subsequent printing following a layer-by-layer protocol [53,54] or the formation of monolithic COF aerogels by crystallization in moulds to produce tailor-made macroscopic objects [55,56].
Concerning sensing applications, between all the COF-based sensor assemblies, electrochemical sensors present important advantages, such as their high porosity, which results in increased sensibility, and the high specificity and fantastic biocompatibility that improves the stability of the electrochemical sensors [57]. The most common procedure followed to achieve these devices is the use of COFs as supports to anchor the active species (or guests) towards the recognition [58,59]. In this way, the COF enhances the electrochemically active surface area of the electrode by preventing the agglomeration of the active species [59,60]. There are three main methods to anchor the active species into COFs. The first one involves the coordination of the metallic species in Lewis acid or basic positions of the COF [61]. The second one involves the active specie anchorage by other non-covalent interactions, such as π-interactions [59]. Finally, covalent immobilization can also be achieved by chemical reactions involving backbone modification or pendant groups reactions, highlighting Hüisgen’s azide–alkyne cycloaddition as the most prominent example of these guests’ immobilization methods [5].
To achieve electrochemical sensing, great conductivity is desired. However, despite COFs presenting an ordered and columnar π-skeleton, the electrochemical sensing is still limited due to the polygranular COF’s morphology, leading to insignificant hopping-type electrical conductivity in most of the examples [62]. In the past few years, several strategies have been developed to address this problem. To avoid this problem, conductive additives can be added during the sensor assembly. The most common example is the in situ reduction of metallic precursors to produce metallic nanoparticles (MNPs), which can be anchored to the COF pore walls by coordinative interactions preventing the NPs agglomeration [63,64]. Other common conductive additives are carbonaceous compounds, such as carbon black (CB) [65], pyrolyzed three-dimensional kenaf stem (3D-KSC) [66,67,68], or multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) [69].
Sensor assemblies are usually achieved by different strategies. One of them involves the mixing of the COF with the conductive additives in a hollow glass tube [70,71]. A second strategy involves the electrode modification with Covalent Organic Nanosheets (also known as CONs [72,73]), produced by delamination of COFs usually by liquid phase exfoliation (LPE) and subsequent drop casting of CONs colloids [74,75,76]. Finally, the sensor’s design can be based on simple electrodes [58,61] of dual systems, highlighting the sandwich-type electrodes [77,78].
Different examples of electrochemical sensors and biosensors are exposed in this review, showing the great versatility of functions and capabilities of materials based on COFs, resulting in interesting approaches that can enhance the sensibility and selectivity of the final devices.
2. Electrochemical Sensors
COFs have been widely used in the development of the electrochemical sensor. We have classified COFs in three different groups attending to their main role in electrochemical sensors.
2.1. COFs Acting as Electrocatalysts
The easiest configuration for the use of COFs in the development of electrochemical sensors involves the direct deposition of the COF as the modifier on top of a working electrode surface. The high porosity of the COFs-based materials and their crystalline structure make them interesting materials for that purpose, as shown in the work developed by Y.-H. Pang et al. [79]. The COF synthesis is based on the functionalization of 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol (Tp) with chiral (+)-diacetyl-L-tartaric anhydride to produce the reactive monomer CTp. The subsequent condensation of CTp with the other reactive monomer, 2,5-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine (Pa-2) generates the chiral COF CTpPa-2. The COF is suspended in an ethanol/Nafion solution, and the suspension is drop-casted on top of a GC electrode. In this example, the COF improves the electrocatalytic performance through the electrooxidation of bisphenol A and bisphenol S. A similar example is presented by the same research group [80], but in this case using a pencil graphite as working electrode, which is modified by drop casting with β-ketoenamine-linked COF DQTP. This COF is synthesized by 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol (TP) and 2,6-diaminoanthraquinone (DQ) by using the solvothermal method. The developed electrochemical sensor exhibited high electrical conductivity and catalytic activity. It has been applied for simultaneous determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol S in food packages with a good linearity range (from 0.5 to 30 μM) for two bisphenols and a detection limit of 0.15 μM (S/N = 3). Another example for the use of a COF material directly deposited on top of the working electrode is reported by P. Arul, et al. [81]. In this case, the COF used is the 3,5-diamino-1,2,4-triazole-COF (DAT-COF). The DAT-COF is dissolved in 0.1 M H2SO4 and a film of DAT-COF on GC electrode is generated by potential cycling between −0.40 to +1.70 V at a scan rate of 50 mV s−1 for 20 cycles. DAT-COF film/GCE not only determines simultaneously dihydroxybenzene isomers with detection limits lower than 0.12, (S/N = 3), but also selectively determines one isomer in the presence of the other two isomers.
2.1.1. COFs Combined with Carbon Materials
The main drawback of using COFs as electrode modifiers is their usual insulating character. To avoid this inconvenience, they are usually employed together with carbon conducting materials. In this sense, the easiest way of improving the electron/hole transport is mixing COFs with conductive carbon and fabricating traditional paste carbon electrodes. This strategy has been followed by Hou et al. [71]. TpBD-COF was synthesized using 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol and benzidine as the precursors. The main advantages of TpBD-COF are its high chemical stability, the abundance of functional groups, and its large surface area. This sensor presents the rapid quantitative determination of hydroquinone and catechol by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Another approach of the use of COF with conductive carbon materials is described by Zhang et al. [65]. Thus, a triphenylamine-based covalent-organic framework (TPA-COF) is composited with carbon black (CB) using a one-pot solvothermal method. A GC electrode can be modified by drop casting the CB-doped TPA-COF, suspended in a solution of water: ethanol (50:50) and Nafion. The modified electrode has been successfully applied to the detection of dopamine in real samples.
COFs have also been used in combination with carbon nanomaterials to avoid the lack of electron conductivity. One example is described by Yang et al. [82]. The COF used in this case (TAPT-TFP-COF) is prepared by Schiff base condensation reaction between 1,3,5-tris-(4-aminophenyl)triazine (TAPT) and 1,3,5-triformyl phloroglucinol (TFP). The composite material based on TAPT-TFP-COF and carboxyl-functionalized multi-wall carbon nanotubes (COOH-MWCNTs) are drop casted on the GC electrode. The modified electrode can be used as an electrochemical sensor for the simultaneous determination of paracetamol and dopamine with detection limits (LOD) of 0.14 μM and 0.19 μM, respectively. COOH-MWCNTs interconnect TAPT-TFP-COF domains and act as bridges between the COF particles, showing a good synergistic effect and accelerating electron transfer. Another similar approach is described by Y. Sun, et al. [83]. The COF used in this example is synthesized using 1,3,5-tris-(4-aminophenyl)benzene (TAPB) and terephthaldicarboxaldehyde (TPA) in the presence of NH2-CNT. The obtained COF@NH2-CNT possesses good conductivity and high specific surface area, when it is deposited on a GC electrode. The COF@NH2-CNT/GCE sensor showed great analytical performance for the determination of furazolidone (nitrofuran antibacterial agent). It offered a wide range furazolidone quantification range from 0.2 μM to 100 μM, with a low detection limit of 7.75 × 10−8 M.
2.1.2. COFs Combined with Conducting Polymers
Some innovative approaches to improve the conductivity of COFs involves the development of composite materials that combine COFs with conducting polymers [84]. A core–shell material made of TAPB-DMTP-COF (TAPB, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene; DMTP, 2,5-dimethoxyterephaldehyde) core and a polyanyline-conducting polymer as shell, TAPB-DMTP-COF@PANI, is solvothermally synthesized. A GC electrode is modified by drop casting from a water suspension of the TAPB-DMTP-COF@PANI. The modified electrode has been successfully applied for the detection of acetaminophen in commercial tablets, human blood, and urine. The composite material facilitated the interaction of acetaminophen with absorption positions by π–π stacking and hydrogen bonding at the time that improves the COF conductivity. Under the optimal conditions, a detection limit of 0.032 μmol/L and a wide linear range of 0.10–500 μmol/L acetaminophen were obtained. The electrochemical platform was almost unaffected by other interfering substances.
2.1.3. COFs Combined with Metal Oxide Particles
An excellent alternative is the modification of magnetic nanomaterials with COFs instead of directly modifying the working electrode surface. This alternative has been described by Q. Wang, et al. [85] (see Figure 2). The Fe3O4@AT-COF is prepared via a one-pot ambient temperature solution phase method by adjusting the amount of reaction solvent. A mixture of 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl) benzene (TAPB) and 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxaldehyde (TFB) with Fe3O4 particles is employed during the synthesis. The obtained Fe3O4@AT-COF exhibits high surface area, good water dispersion, long-term stability, excellent electrical conductivity, and pre-concentration effect. Once the modified magnetic beads are retained in the working electrode surface by a magnet, the electrochemical platform has been used for the simultaneous detection of p-nitrophenol (PNP) and o-nitrophenol (ONP) with a wide linear range from 10 to 3000 μM and the low detection limits of 0.2361 μM and 0.6568 μM, respectively. It can be applied in lake and tap water for monitoring PNP and ONP with outstanding sensitivity and reliability.
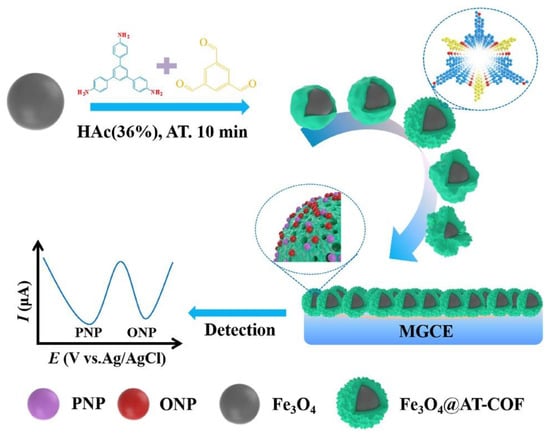
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of a glassy carbon electrode modified with a magnetic Fe3O4@AT-COF nanocomposite used for the simultaneous detection of PNP and ONP. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [85]. Copyright 2019 Elsevier.
2.1.4. CODs with Electroactive Moieties
The great versatility in the syntheses of COFs allows the introduction of electroactive moieties in their structures. Some examples of COFs endowed with electroactive units have been reported, which originates the appearance of redox processes confined on the electrode surface as a consequence of reductions/oxidations within the COF structure itself. The first example reporting an electrochemical sensor using an electroactive COF was described by Y. Song et al. [69]. The COF used was obtained by dehydration condensation reaction between 1,3,5-tris(p-formylphenyl)benzene (TFPB) and thionine (Thi) mixed with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to prepare COF-Thi−TFPB−CNT composites. The GC electrode modification is carried out by drop casting a water suspension prepared with COF-Thi−TFPB−CNT. The modified electrode was efficiently used for the determination of ascorbic acid (AA) and pH sensing. The three-dimensional porous carbon from kenaf stem (3D-KSC) has been also combined with COF-Thi-TFPB [66] to prepare a composite material to be used as a carbon paste electrode. The composite 3D-KSC/COF-Thi-TFPB electrocatalyzes the reduction of riboflavin. Double signals allow measurement correction with the aim to make them more accurate and reliable. As a consequence, the selectivity and reproducibility of the sensor is greatly improved. Another example of an electroactive COF is described by P. Zhu et al. [86]. These authors managed to synthetize a reduced-GO-COF-based composite by in situ polymerization. First, 3D graphene aerogel was prepared by hydrazine reduction of freeze-dried GO. Afterwards, the solvothermal synthesis of the COF was carried out by reaction between 5,10,15,20-tetrakis[(4-aminophenyl) porphinato]-iron [Fe (TAPP)] and terephthalaldehyde, using 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene, ethanol and aqueous acetic acid as solvents in the presence of the prepared graphene aerogel (GA) generating the three-dimensional COF-366-Fe/GA composite. The composite was suspended in a mixture of ethanol, water, and Nafion and drop casted on top of the GC electrode. The COF-366-Fe/GA-based sensing platform benefits from the remarkable synergy effect between COF-366-Fe and 3D GA, presenting ultrasensitive response to NO in the wide range from 0.18 to 400 μM with a lower detection limit (30 nM) and higher sensitivity (8.8 μA·μM−1·cm−2). It has been applied for the real-time identification of NO secreted from complex biological systems.
On the other hand, Yonghai Song and col. [87] managed to synthetize a porphyrin-based COF by the Schiff base condensation reaction between 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxaldehyde and 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)-21H,23H-porphyrin to yield COFp-por NH2-BTA. Subsequent Iron coordination afforded the metalated COFp-Fepor NH2-BTA. Finally, drop casting was used to produce COF-p-FePor NH2-BTA/GC electrodes. The modified electrodes were successfully used as H2O2 and pH electrochemical sensor.
2.2. COFs Acting as Support of Electrocatalyst and/or Recognition Elements
One of the main functions of COFs in this context is their role as a recognition element in the sensor. The high porosity of COFs together with the possibility of the delamination of 2D-COFs allow the production of 2D-nanomaterials with enhanced surface–volume ratio, which allows an increment of the sensor recognition element or the electroactive centre exposition to the measuring solution media.
2.2.1. COFs with Metal Nanoparticles and/or Carbon Materials
Simple examples of the joint use of COFs and metal nanoparticles have been also reported. Among them, it is worth highlighting the new squarine-linked COF (TS-COF) obtained by reaction between tris-(4-aminophenyl)-s-triazine (TAPT) and squaric acid (SA) under solvothermal conditions [88]. In order to increase the electrochemical performance, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were loaded by the in situ reduction of chloroauric acid and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) to enhance the electrical conductivity. The AuNPs@TS-COF/RGO nanocomposite thus obtained was used as a sensor with an enhanced sensibility due to the synergic properties of AuNPs, TS-COF, and RGO. It has been successfully used for the simultaneous recognition of uric acid, dopamine, and ascorbic acid.
A similar strategy was followed by Guan et al. [64]. They designed a pyrene-based TF-Py-COF, which could be obtained by the solvothermal reaction between 1,3,6,8-tetrakis(4-formyl phenyl)-pyrene (TFPPy) and 1,3,6,8-tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)-pyrene (PyTTA). The electrochemical sensing platform was developed by the physical mixture of TF-Py-COF and a 3D carbon material containing nitrogen and AuNPs. It was used for the simultaneous detection of acetaminophen and 4-aminophenol. Good electrochemical performance was a consequence of the synergetic effect of the porous structure of the COF, the great conductivity of 3D carbon material containing nitrogen, and the excellent electrocatalytic activity of AuNPs.
Other carbon-based materials with high conductivity, such as multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), have also been used to improve the low conductivity of COFs together with AuNPs, to enhance the electrocatalytic activity of the electrochemical platform [89]. The research group of Wu Yang synthetized a pyrene-based COF by the Schiff base condensation reaction between 1,3,6,8-Tetra (4-formyl phenyl) pyrene (TFPPY) and 1,4-phenylenediamine under solvothermal reaction conditions to afford IL COF-1. In a second-step, electrode modification was achieved by a first liquid phase exfoliation of the IL COF-1 in the presence of MWCNT-NH2 and AuNPs synthetized in situ, followed by the subsequent drop casting over a GC electrode of the colloid to prepare the COF-NH2-MWCNT/Au/GC. The porous IL COF-1 with pyrene groups effectively increases the number of binding sites available on the surface of the electrode. The resulting modified electrode provided excellent electrochemical activity for the simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid. Another example of the combination of COF and AuNPs is described by Yang et al. [90]. In this work, the condensation between 1,3,6,8-tetra(4-formyl phenyl) pyrene (TFPPy) and 2,6-diaminopyridine yield the new DP-Py COF with an unusual wavy topology. This COF presents multiple chelation points for metal nanoparticles, such as the imine linkages or the pyridine moieties. Thus, the prepared DP-Py COF was modified with AuNPs and drop casted in a GCE to fabricate a novel electrochemical sensor DP-Py-COF/AuNPs/GCE for sensitive and rapid determination of theophylline and caffeine.
Other research groups use the strong electrostatic interaction of AuNPs and the unsaturated amine group present on TAPB-DMTP-COFs (TAPB, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene; DMTP, 2,5-dimethoxyterephaldehyde) to successfully immobilize AuNPs in the COF-porous nanostructure [91]. GC electrodes modified by a drop casting deposition of the nanocomposite material show high electrocatalytic activity toward the oxidation of chlorogenic acid. These electrochemical sensors show a wide linear range of 1.0 × 10−8–4.0 × 10−5 M and a low detection limit of 9.5 × 10−9 M, as well as a good repeatability of 4.1% in 2.0 × 10−5 M chlorogenic acid.
There also some examples of electrochemical sensors that use silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) together with COFs as support materials. Thus, Shankar and co-workers [92] reported the synthesis of a COF by reaction between p-phenylenediamine and terephthalaldehyde under reflux (DMF; 150 °C; 12 h). AgNPs can be subsequently embedded in the COF from aqueous solutions of AgNO3 and NaBH4. Finally, GC electrodes drop casted with the obtained suspension were used to electrocatalyze DNA bases oxidation at different potentials, allowing the simultaneous determination of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV).
Platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) have also been employed in electrode configurations similar to that described above [63]. In a representative contribution, Yang and co-workers reported the Schiff base condensation reaction between 1,3,5-tris-(4-formylphenyl) benzene (TFPB) and benzidine (BD) to yield the TFPB-BD-COF. For the sensor assembly, the authors reacted to the aldehyde terminal groups with NH2—MWCNTs and assembled PtNPs by in situ reduction. In this way, the TFPB-BD-COF/PtNPs/NH2-MWCNTs offers a large surface area platform thanks to the presence of TFPB-BD-COF, with highly dispersed PtNPs, which enhance electrocatalytic activity, and high conductivity contributed by the MWCNTs. The novel electrochemical sensor is successfully used for the simultaneous detection of catechol, hydroquinone, and resorcinol. Li Wang’s research team described another example of the use of PtNPs [67]. Three-dimensional porous carbon (3D-KSC) is used during the synthesis of TAPB-PDA-COF generating a hybrid material 3D-KSC/COF-TAPB-PDA. The obtained material is used to prepare a carbon paste electrode, which displays a large specific active surface area. In a second step, NPs loading was achieved by in situ electro-deposition of CuCl2 and H2PtCl6 to produce CuNPs and PtNPs. The 3D-KSC/COFTAPB-PDA/CuNPs and 3D-KSC/COFTAPB-PDA/PtNPs showed good analytical parameters for glucose and H2O2 determination, respectively.
2.2.2. COFs with Metal Oxide Nanomaterials
Metal oxide nanomaterials have also been combined with COFs to provide materials for the development of electrochemical sensors as recently reported by Yang and co-workers [93]. In this work, the reaction between 2,5-dibromobenzene-1,4-dicarbaldehyde (DBTA) and 2,4,6-tris(4-aminophenyl)-s-triazine (TAPT) under solvothermal conditions was used to obtain Br-COF. For the sensor assembly, a mixed of Br-COF, electrocatalytic La2O3, and high conducting MWCNTs were drop casted over GC electrode. The developed electrochemical platform was applied for the sensitive and selective detection of dopamine and uric acid with low detection limits (0.039 μM and 0.024 μM for dopamine and uric acid, respectively) and wide linear ranges (2–450 μM for dopamine and 0.4–450 μM for uric acid). Hence, it could be employed to detect simultaneously the contents of these analytes in biological and medicine samples.
Other examples of the combination of COF with a metal oxide nanomaterial is reported by Y. Chen et al. [94]. A monomer-mediated in situ growth strategy is followed for the controllable construction of the core–shell Co3O4@TAPB-DMTP−COF composite using TAPB (1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene) and DMTP, (2,5-dimethoxyterephaldehyde) as precursors. A suspension of Co3O4@TAPB-DMTP−COF in water is drop casted on top of a GC electrode. The modified electrode is successfully used for tert-butylhydroquinone detection at a detection limit as low as 0.02 μM (S/N = 3). Little to no interference effects from other co-existing ions allows the sensor to detect low-abundance TBHQ from complicated real samples. The role of TAPB-DMTP-COF is essential to improve the electrochemical stability and to ensure a longer operational time of the Co3O4 electrocatalyst.
2.2.3. COFs with 2D-Nanomaterials
2D-nanomaterials have been combined with COFs in some sensor developments. In the first simpler example, a COF was combined with graphene oxide (GO) [95]. The GO@COF is obtained using benzene-1,4-diboronic acid as monomer, and it is commercially available by Baiyin COFs Chemistry Technology Co., Ltd. (Baiyin, China). GC electrode is modified by drop casting a water suspension of the COF, after which a molecularly imprinted polypirrole (MIP) is electrodeposited on the modified electrode. The developed electrochemical sensor is capable of simultaneously determining sulfadiazine and acetaminophen thanks to the selectivity granted by the MIP and the great conductivity and high porosity awarded by the GO and COF, respectively. Under optimal testing conditions, linear calibration curves were obtained over the concentration range of 0.5–200 μM sulfadiazine and 0.05–20 μM acetaminophen, with limits of detection being 0.16 μM and 0.032 μM, respectively.
The next example showed the combination of COF with two 2D-nanomaterials, reduced graphene oxide, and layer molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) nanosheets [96]. The COF (TFPB-PDA-COF) is synthesized by Schiff reaction between 1,3,5-tris(4-formylphenyl)-benzene (TFPB) and 1,4-diaminobenzene (PDA). The COF is mixed with amino functionalized graphene (NH2-rG) to form COF/NH2-rG. After that, the assembly of MoS2 and COFs/NH2-rG on GCE results in a novel COF/NH2-rG/MoS2/GCE electrochemical sensor. The use of MoS2 and NH2-rGO enhances conductivity and electrocatalysis. This methodology has been successfully used to determine the concentration of the purine bases (adenine and guanine) in thermally denatured herring sperm DNA samples with excellent results. MoS2 has been also used in other configuration combined with amino-functionalized carbon nanotubes@covalent organic frameworks (NH2-MWCNT@COF) [97]. NH2-MWCNT@COF nanocomposite materials enhance the electrode sensibility for sulfamerazine determination. Once NH2-MWCNT@COF is deposited by drop casting over a GC electrode, a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) membrane was anchored on the surface of this modified GC by electrochemical polymerization to achieve selective recognition for sulfamerazine. The measurements are carried out in the presence of a redox probe (ferricyanide).
2.2.4. COFs with Porphyrins Derivatives
Porphyrins and metalloporphyrins have been widely used for the development of electrochemical sensors [98]. Porphyrins have many applications due to their large surface area, redox mediators, regular porosity and tuneable structures, making them suitable for detecting small molecules. The combination of porphyrins and COFs has been reported for the development of electrochemical sensors, as recently shown by Hu and co-workers [74]. The TAPB-DMTA-COF was used as the basic structure for the assembly of an electrochemical sensor by a one-pot method. First, they functionalized polyvinylpyrrolidone with hemin and they were able to one-pot encapsulate these particles during the COF crystallization at room temperature. Secondly, hierarchically AuNPs loading was accomplished by chloroauric reduction. Finally, the electrode modification was achieved by drop casting from water containing the previously dispersed hemin/TAPB-DMTP-COF/AuNPs. The prepared electrode is used for the sensitive and selective bisphenol A detection. The satisfactory signal amplification is based on the abundant Fe3+ sites of Fe-porphyrin, the high conductivity of AuNPs and the large specific surface area of the TAPB-DMTP-COF. The other example is reported by the research group of Wu Yang [99]. The synthetized COF (CuP-SQ) is obtained by the condensation of squaric acid (SA) and Copper (II) 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-aminophenyl) porphyrin (TAP-CuP) under solvothermal conditions. Drop casting of COOH-MWCNT colloids over a GC electrode and controlled electrodeposition of CuP-SQ colloids allows the building of the modified electrode named as MWCNTs-COOH/CuP-SQ COF/GC. Finally, electrodeposition of CoNPs is used to afford the modified MWCNTs-COOH/CuP-SQ COF/CoNPs/GC electrode. The resulting modified electrode is used for the simultaneous detection of guanine and adenine by DPV. Wide concentration ranges from 0.04 to 130 μM for guanine and 0.06 to 130 μM for adenine for simultaneous quantitative analysis were found. The lower detection limits were 5.5 nM and 7.2 nM (S/N = 3), respectively.
2.2.5. COFs with Macrocycles
COFs can be used together with macrocyclic cationic pillar[6]arene (CP6) for the development of host–guest recognition sensors. In the example reported by Tan et al. [100], 2,4,6-triformylphloroglucinol (Tp) and 4,4′-azobisbenzenamin (Azo) were used as the precursors for the synthesis of a COF by following a hydrothermal synthesis process. After the synthesis of the COF, Co(II) cations are incorporated into the structure of the COF to yield COF-Co through a hydrothermal reaction. CP6 can be easily adsorbed onto the surface of the COF by π−π interactions and hydrogen bond interactions to produce CP6-COF-Co. The composite material is drop casted on top of a GC electrode. The developed sensor is used for the determination of ascorbic acid in solutions. The Co(II) ion exhibits excellent electrocatalytic activity when CP6 is used as the recognition element. The porous structure of the COF allows the diffusion of the species involved in the sensing process, at the time that increases the surface–volume ratio of the electrode surface, enhancing the sensor sensibility.
Some examples have demonstrated the use of COFs as supports for metal nanoparticles, which contain the specific element for the host–guest recognition (Figure 3). This is the case of the research reported by Tan et al. [58]. In this example Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) are modified with pillar[6]arene, which act as recognition element of herbicide paraquat. The modified AgNPs are loaded in the COF. In this case the synthesis of the COFs was achieved by reaction between 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol (TP) and 2,4,6-tris(4-aminophenyl)-s-triazine (TAPT) to yield a hexagonal β-ketoamine linked network. The researchers managed to load the AgNPs through a two-step sequence to enhance the COF’s conductivity in the assembly of the electrochemical sensor. First, they introduced acid functionalities in the COF by post-carboxylation to grant hydrophilicity to the pore walls. Secondly, the loading of COF with silver nanoparticles was accomplished by the in situ reduction of AgNO3. It should be mentioned that an abundant number of Lewis’ bases (such as N and O) introduced in the pore walls during the COF crystallization facilitated the anchoring of AgNPs via coordination interactions. In this way, they achieved the synthesis of a conductive composite enriched in hydrogen bonding donor/acceptor functionalities that allowed the simultaneous detection of gallic acid and uric acid. Glassy carbon (GC) electrodes are modified with the obtained composite material. Paraquat establishes host−guest interactions with pillar[6]arene adsorbed on the AgNPs. The Ag nanoparticles play an electrocatalytic role in sensing paraquat showing two redox processes corresponding to its reduction, being successfully quantified by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Other similar examples have been reported based on COFs modified with gold nanoparticles containing dihydroxylatopillar[6]arene (2HP6@Au) as a recognition element [101]. The COF used for this purpose is synthesized by condensation between 1,4-diaminobenzene and triformylphloroglucinol under hydrothermal reaction conditions. The COF can be functionalized with cationic pillar[6]arene (CP6@COF) and both composite materials are assembled by adsorption to generate a 2D heterogeneous composite (2HP6@Au@CP6@COF), which is subsequently drop casted on top of GC electrodes. The prepared modified electrode has been successfully used for the detection of the explosive sodium picrate (SP) with a detection limit of 1.7 nM. The aforementioned 2HP6@Au is responsible for the electrocatalytic response in sensing SP while CP6@COF acts as a prominent material for gathering and recognizing sodium picrate onto the electrode surface. The picrate can settle inside the cavity of CP6, showing excellent host–guest interactions.
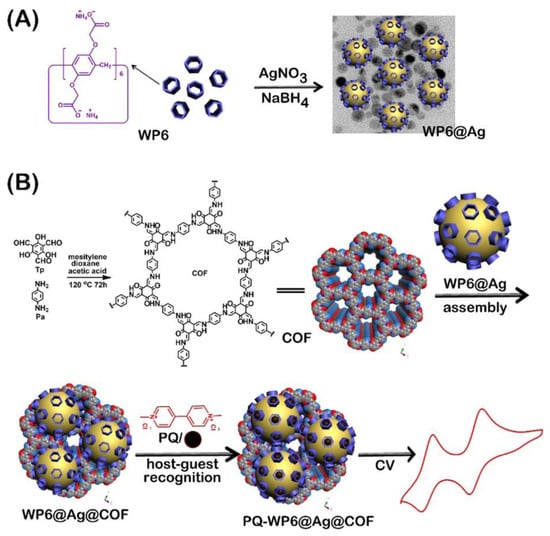
Figure 3.
Schematic representation for the production of WP6@Ag (A); synthetic route to produce the COF and assembly of WP6-modified Ag nanoparticles on the surface of COF and its application for electrochemical sensing of PQ (B). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [58]. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.
2.2.6. COFs with Molecular Imprinted Polymers
Other strategies using different host–guest receptors have also been used. Instead of using macrocycles, new set-ups are using molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP) as recognition elements together with the use of COFs and metal nanoparticles. A good example for the determination of sulfathiazole was described by Sun et al. [84,102] using a molecularly imprinted polypyrrole film. AuNPs@COF with good electrical conductivity was introduced on the electrode surface for signal amplification and facilitation of the electron transfer processes of the redox probe employed, CuS. The sensor exhibited excellent selectivity, due to the MIP, sensitivity, reproducibility, and repeatability.
2.2.7. COF Templates
COFs have also been used to enhance electron transfer efficiency in electrochemical sensors for enantiomer recognition. One recent example has been reported by L. Wang et al. [103] that prepared a COF surrounded by Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4@COF). As a working electrode, a 3D-printed nanocarbon was used. The working electrode was modified by drop casting an Fe3O4@COF and a bovine serum albumin (BSA) suspension. The BSA is the protein responsible for chiral sensing, while Fe3O4@COF increases the electron transfer in the L-tryptophan electrooxidation. The prepared Fe3O4@COF@BSA/3DE presented excellent selectivity to L-Trp compared with its isomer D-Trp, which can be explained by the favourable formation of H-bonds between BSA and L-Trp.
Sometimes COFs have been used as templates to obtain high porous heteroatom doped carbon materials. In these examples, COF are synthesized but the obtained material is used after a calcination treatment. The advantages of these strategies are the obtaining of a high conductive carbon material with high porosity that can incorporate homogeneous heteroatom doping the graphitic carbon structure, improving the electrocatalytic activity of the material. An example reported by Yonghai Song et al. [104] starts with the solvothermal reaction between (1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyl)trianiline (TZT) and benzo [1,2-b:3,4-b’:5,6-b’’]trithiophene-2,5,8-tricarbaldehyde (BTT) to yield COF-BTT-TZT, which presents numerous coordinative points in its structure (S and N atoms). In a second step, Pd nanorods were synthetized by in situ reduction of Pd(OAc)2 in a tubular atmosphere furnace under a H2/Ar current. The obtained material was then drop casted on top of a GC electrode in order to obtain N,S-doped C@Pd nanorods/GC. This electrochemical platform was successfully used as a paracetamol sensor, showing a low detection limit of 11 nM and wide linear range of 33 nM–120 μM, as well as good stability, reproducibility, and selectivity.
2.3. COFs Chelating Properties for Anodic Stripping Analysis
The capability of COFs to include multiple functional groups in their structures allows the development of COFs endowed with chelating groups. There are several examples in the literature showing the use of COFs as chelating agents to promote the pre-concentration of metal cations for differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. This strategy was used by Wenzhi Li and col. [105] who developed a type of COF based in the imide condensation reaction between pyromellitic dianhydride and tris-(4-aminofenil)benzene (PMDA-TAPB-COF) by the solvothermal method. A carbon paste electrode was subsequently prepared by using the PMDA-TAPB-COF. This COF showed an excellent Pb2+ chelating ability, which was used to assist the pre-concentration step of differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry for the analysis of lead. Furthermore, PMDA-TAPB-COF selectively chelates Pb2+ cations, showing only a slight influence by the presence of other cations, such as Ni2+, Ag+, Cd2+, Fe3+, Co2+, Sr2+, Ca2+, Mn2+, Cr3+, and Zn2+.
T. Zhang et al. [70] reported another example of a COF carbon paste electrode for lead detection based on the synthesized TAPB-DMTA-COF (TAPB, 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene; DMTP, 2,5-dimethoxyterephaldehyde). The carbon paste electrode modification was accomplished by physically mixing the COF with graphite powder and paraffin in a mortar and the paste was packed into a glass tube. The electrode was used for voltametric determination of lead with high sensitivity, low detection limit, reproducibility, good stability, and broad linear range. All these excellent properties are a consequence of the high number of active sites, and high surface area of TAPB-DMTA-COF. Yongmei Zhu and colleagues [106] synthetized another example of β-Ketoamine-linked COF by condensation reaction between 2,4,6-triformylphloroglucinol and melamine (COF-TDBA-TPA). This COF was efficiently used for the electrochemical sensing of metallic species without the need of other additives. The modification of the glassy carbon (GC) electrode with the COF was accomplished by simple liquid phase exfoliation (LPE) followed by drop casting. The COF-TDBA-TPA-based electrochemical sensor was used to simultaneously detect Cd2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, Hg2+, and Zn2+ in drinking water.
Other example of a COF-based material with chelating properties has been reported by F. Pan et al. [107]. For the synthesis of COF-V, 2,5-Divinylterephthalaldehyde and 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene were used as precursors. This COF was mixed with 2,2′-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) and trithiocyanuric acid in a post synthetic modification step, generating a COF endowed with hydrosulphonyl groups (COF-SH). This COF was mixed with graphene followed by the addition of Nafion and water to generate a uniform suspension after sonication. The prepared suspension was drop casted on top of the GC electrode. The presence of numerous adsorption sites (18 sulphur atoms and 30 nitrogen atoms per pore) in COF-SH, was beneficial for the accumulation of heavy metals, while graphene enhanced the electrical conductivity. Under the optimal conditions, the sensor simultaneously detects the presence of heavy metal ions in coastal water samples at concentrations ranging from 1 to 1000 μg L−1. The detection limits of Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+ were 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, and 1.1 μg L−1, respectively. Furthermore, the sensor exhibited good stability after multiple uses keeping 95% of the response.
COF is also combined with a carbon nanomaterial to generate a composite material with chelating properties has been reported by J. Han et al. [108]. In this work, the COF-BTLP-1 was prepared by condensation reaction between 1,4-benzenedithiol-2,5-diamino-hydrochloride and 1,3,5-triformylbenzene in the presence of a kenaf stem-derived macroporous carbon (3D-KSC). Each unit of COF-BTLP-1 has 12 adsorption sites (6 sulphur atoms and 6 nitrogen atoms) for heavy metal ions and regular holes to facilitate their transfer. The high amount of adsorption sites for heavy metal ions generated allows the identification and capture of them selectively. As result, Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+ can be detected simultaneously. Soil and sewage samples have been successfully analysed using this modified electrode.
COFs can also be used to pre-concentrate organic compounds due to the high amounts of adsorption sites present in their structures (Figure 4). A recent example has been described by Li Wang and colleagues [109] who synthetized a COF from 2,4,6-triformylphloroglucinol (TFP) and benzene-1,3,5-tricarbohydrazide (BTH) in the presence of NH2-MWCNTs to afford a NH2-MWCNTs@COF-TFP-BTH. The composite was subsequently dispersed and drop casted to afford NH2-MWCNTs@COF-TFP-BTH/GC. Nitrofural is an antimicrobial drug, which was widely used in aquaculture in the past several years. The prepared composite material NH2-MWCNTs@COF-TFP-BTH can be employed to concentrate nitrofural. Therefore, the NH2-MWCNTs@COF-TFP-BTH/GC electrode was efficiently used as a nitrofural electrochemical sensor, showing a wide linear range (9.6 nM–100 μM), good reproducibility, and stability.
Figure 4.
Schematic illustration of MWCNTs@COF-TFP-BTH showing possible adsorption sites for Hg2+ and nitrofural. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [109]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier.
3. Electrochemical Biosensors
COF skeletons are superior scaffolds to allow charge migration and improve the signal amplification in electrochemical sensors. The large specific surface area and tuneable pore structure of COFs makes them good candidates for the development of functional biosensors.
3.1. Enzymatic Biosensors
The structure tunability, porosity, crystallinity, and stability of COFs are promising characteristics for their use envisaged as host arrays for the immobilization of enzymes, among them tunability [110]. Their customizable composition through the proper choosing of their precursor, which also determines the functional groups on their surfaces, can be tailored to favour some specific interactions between them and enzymes. Furthermore, the regular distribution of nanopores in the COFs is beneficial to provide a high surface area interface for the adsorption and desegregation of enzymes and to allow a rapid movement of reagents. Moreover, the structural robustness of COFs represents an important attribute to stabilize enzymes during the biosensor manufacture process.
In the first example of a COF-based electrochemical enzymatic biosensor, a COF is able to serve as a matrix for co-immobilizing the electron mediator (1,10-dimethylferrocene, DMFc) and enzymes (glucose oxidase, GOD) onto a carbon fibre microelectrode [111]. The COF was synthesized using 1,3,5-Triformylbenzene (TFB) and 1,4-diaminobenzene in the presence of the carbon fibres (CFs) in the reaction medium as a result producing the composite material COF-LZU1. After that, the microelectrode is immersed in a saturated DMFc solution for 10 h. Finally, once the electrode is clean and dried, the microelectrode is immersed in a GOD solution. The resulting biosensor (GOD/DMFc/COF-LZU1/CFMEs) has been used for glucose detection in rats’ brains, being implanted on the animals’ heads. The methodology demonstrated in this study should be applicable to generalise in vivo measurements. Another enzymatic biosensor was reported by Y. Liu et al. [68]. They obtained three-dimensional kenaf stem composites (3D-KSC) by pyrolytic carbonization of kenaf stem (KS). Secondly, they synthetized COF-LZU-1 by Schiff base condensation reaction between 1,3,5-Triformylbenzene and 1,4-diaminobenzene in the presence of the 3D-KSC in order to obtain the LZU-1-COF/3D-KSC composite. Finally, acetylcholinesterase (AChE), graphite powder, and paraffin were mixed with the COF-LZU-1/3D-KSC to obtain the AChE/COF-LZU1/3D-KSC electrode (AChE/COF-LZU1/3D-KSCE) for identifying trichlorfon organophosphorus (OP) pesticide. The measurements were carried out in the presence of acetylthiocholine chloride, and the signal followed during the measurements is the irreversible oxidation peak of the thiocholine generated through enzymatic (AChe) catalysis. The presence of trichlorfon produces the inhibition of AChe, avoiding the generation of thiocholine, and, as a consequence, a decrease in the intensity of the oxidation wave. The enzymatic biosensor shows a wide linear range of 0.2–19 ng/mL and a low detection limit of 0.067 ng/mL.
Other reported works have used COFs to encapsulate multiple enzymes simultaneously (Figure 5). A representative example was reported by L. Wang et al. [112] that assembled microperoxidase-11 (MP-11) and GOD into the pores of the COF. The condensation between 4, 4, 4′′,4′′′-(ethene-1,1,2,2-tetrayl)-tetraaniline (ETTA) and terephthalaldehyde (TPAL) was used to obtain COF-ETTA-TA with a Kagome type lattice. The electrode modification was achieved by drop casting COF colloids on top of a GC electrode followed by the subsequent s deposition of MP-11 and GOD to afford GOD-MP-11/COF-ETTA-TPAL/GC composite. Hydrogen bonds are formed between the N atoms of COF-ETTA-TPAL and the carboxylic groups of GOD and MP-11 thus enhancing the immobilization of both enzymes. The biocompatibility of COF-ETTA-TPAL was good due to the lack of metal ions in the COF nanostructure. Furthermore, COF-ETTA-TPAL presents a 2D nanosheet structure with ordered conjugated moieties and nano-sized pores. This structure promotes fast electron transfer and enhances the mass transfer, resulting in a large specific surface area nanocomposite, with great benefits for electrochemical sensors. Regarding the biosensor detection mechanism, the O2 is usually used as a marker to quantify glucose given that the GOD modified electrode and MP-11 can catalyse the O2 reduction. In this way, the intensity of the reduction peak ascribed to the O2 reduction decreases as the glucose concentration increases because of the high consumption of GOD during the transformation of glucose into gluconolactone. The developed glucose biosensor presented great performances and high selectivity for glucose determination. The reported linear range and LOD were 0.017–3 mM and 4.97 μM, respectively. Another example of multienzyme microcapsules constructed from a covalent-organic framework is reported by H. Liang et al. [75] (Figure 5). In this work, the authors synthesized a core–shell structure enzyme@ZIF-8@COF by the Schiff base condensation reaction. To address the synthesis of the core–shell structure, the reaction between 1,3,5-tris(p-formylphenyl) benzene (TFPB) and 4,4′-diaminobiphenyl-2,2′-dicarboxylic acid (DBD) was carried out in the presence of enzyme@ZIF-8, thus allowing the production of a composite based on a COF covalently linked to different enzymes. By using this strategy, the physical encapsulation of enzymes, such as GOD, horseradish peroxidase (HRP), and acetylcholinesterase (AChE), was accomplished. Finally, the modified nanoparticles were drop-casted on top of GC electrodes yield the modified electrodes. The COF’s shell with good chemical stability protects encapsulated enzymes against the external harsh environments to ultimately boost enzymatic activities. The biosensors based on the enzymes@COF microcapsules have been successfully used for glucose, H2O2, and malathion determination.
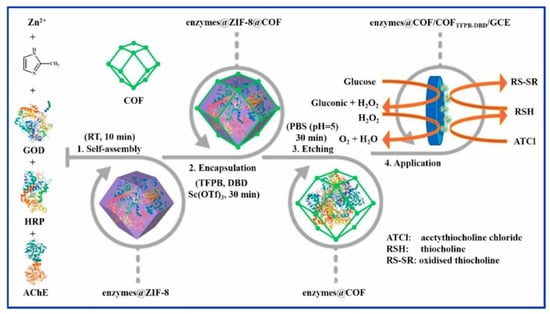
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of preparation and application of enzymes@COF microcapsule. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [75]. Copyright 2021 Elsevier.
3.2. Immunosensors
COFs have also been used as a support material for the development of immunosensors. For example, a kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) immunosensor has been recently developed [113]. A COF based on 3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene (TAB) and p-phthalaldehyde (PTA) was modified with AuNPs (COFs-AuNPs). The composite material was drop casted on top of a GC electrode and the capture antibody was immobilized on the AuNPs due to efficient amino–gold interactions. The sandwich immunosensor was completed with the addition of a secondary antibody conjugated to NiCo2S4@CeO2 microspheres through electrostatic interactions. The NiCo2S4@CeO2 microspheres provide signal amplification in differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), enhancing the signal for the H2O2 oxidation. The developed immunosensor showed high selectivity and sensitivity for KIM-1 determination in a short analysis time.
COFs can be also used to develop electroactive labels linked with secondary antibodies. The high porosity together with the high amount of adsorption sites along the COFs nanostructure make them excellent candidates to guest electroactive molecules, which can be reduced or oxidized during the measuring step, obtaining an electrochemical signal proportional to the concentration of the antigen being analysed. The first example is a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) immunosensor developed by H. Liang et al. [114]. In a first step, as immunosensing platform, black phosphorene (BPene) was prepared via water-phase exfoliation. BPene nanocomposite (Au@BPene) was subsequently prepared by depositing Au nanoparticles (Au NPs) onto BPene. This nanocomposite was used as an immunosensing platform to bind primary antibodies and improve electron transfer. Regarding the labelling composite nanomaterial, they synthetized a magnetic β-ketoamine linked COF by reaction between 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol and 4,4′-bifenildiamine in a two-step sequence (Figure 6). First, the amorphous product was synthetized in the presence of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles, which were isolated and subdued to the thermodynamic conditions to produce the reticulation processes and yield the crystalline COF. Finally, the encapsulation of Au NPS, methylene blue, and Ab2 yielded the active bioconjugate. Once the sandwich-based immunosensor was completed, the electrochemical measurements were carried out by the DPV sensing of the electrochemical reduction of methylene blue adsorbed in the labelled nanocomposite material. The fabricated sensor exhibited linear range from 0.0001 ng/mL to 10 ng/mL, with an LOD of 30 fg/mL for the detection of PSA.
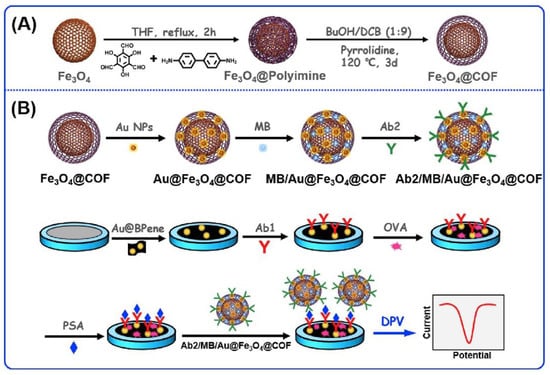
Figure 6.
Synthesis of the Fe3O4@COF nanohybrid by H. Liang et al. [114] (A) and assembly of the immunosensor for the PSA and signal conversion strategy (B). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [114]. Copyright 2019 Elsevier.
A similar example for PSA determination has been reported by J. Zheng et al. [115]. Polydopamine-coated boron-doped carbon nitride (Au@PDA@BCN) was used as sensing platform to attach AuNPs and immobilize primary antibodies. AuPt metallic nanoparticles and manganese dioxide (MnO2) were used as labelling agents to functionalize covalent organic frameworks (AuPt@MnO2@COF). The COF used was obtained by using the solvothermal method in the reaction between 1,2,4,5-tetrakis-(4-formylphenyl) benzene (TFPB) and 1,4-diaminobenzene (PPDA). Then, methylene blue was incubated with AuPt@MnO2@COF, and then the PSA affinity peptide was added, being adsorbed over the nanocomposite material. The whole material serves as a nano-catalyst and the ordered nano-pore structure allows the enrichment and amplification of the methylene blue signal molecules. DPV measurements of methylene blue reduction are carried out, showing a logarithmic relation between current intensity and PSA concentration. A linear range from 5 × 10−5 ng/mL to 10 ng/mL and a limit of the detection of 16.7 fg/mL were determined. Similar examples have been reported using COFs labelled with other electroactive molecules, such as toluidine blue (TB). A representative example is the development of an immunosensor for cytokeratin fragment antigen 21-1 (CYFRA21-1), which can be used as an important indicator for predicting non–small cell lung cancer [116]. In this work, the authors synthetized the TpPa-NO2-COF by Schiff base condensation reaction between triformylphloroglucinol and 2-nitrobenzene-1,4-diamine, loaded with AuNPs by the in situ reduction of chloroauric acid and loaded with CYFRA21-1 antibodies (Ab2) and TB. This platform offers the possibility of dispersing numerous Au-Ab2 assemblies and provides a large number of signal TB units and secondary antibodies. In this way, a sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor was developed with AuTi3C2Tx/GC loaded with the CYFRA21-1 antibodies (Ab1) for the detection of CYFRA21-1. The electrochemical oxidation of TB is followed by DPV, relating the peak current with the logarithm concentration of CYFRA21-1. The potential of this immunosensor for practical use has been proven by using it for determining CYFRA 21-1 in normal human serum. To verify the accuracy and reliability of the method, five serum samples of lung cancer patients were analysed, and the results were confirmed by magnetic particle chemiluminescence assay (MPCA). On the other hand, an immunosensor for human chorionic gonadotropin (a biomarker of bowel cancer, lung cancer, or ovarian adenocarcinoma) in human serum was developed using TB adsorbed on COFs in the labelling agent preparation [78]. Pa-Tp-COF was synthesized by Schiff-base reaction between 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol (Tp) with p-phenylenediamine (Pa). Before the COF synthesis, they were able to incorporate MnO2 nanosheets by the room temperature reduction of KMnO4 in the presence of calix[6]arene (SCX6). Interestingly, the SCX6-functionalized MnO2 displayed great water dispersity and can be generated in the presence of the COF structure without affecting the crystallinity of the network. The COF/MnO2 composite was impregnated with AuNPs by simple dispersion, centrifugation, and freeze-drying yielding Au/COF/MnO2. Following, toluidine blue (TB) was incorporated via impregnation as a signal molecule for the electrochemical sensing. Finally, the specific binding bio-site was added also by mixing the TB/Au/Pa-Tp-COF/MnO2 with anti-HCG (Ab2) to obtain the bioconjugate solution of Ab2/TB/Au/Pa-Tp-COF/MnO2. In parallel to this, a GC electrode was modified with AuNPs and halloysite nanotubes (HNTs). Following, to block non-specific binding, ovalbumin solution was incubated to yield a Ab1/Au/eHNT modified electrode. Finally, HCG and Ab2 bioconjugate solutions were incubated to yield HCG/OVA/Ab1/Au/eHNT-modified electrode. Following this green and facile method, the authors construct a sandwich-type COF-based carrier–analyte–electrode selective sensor, taking advantage of the hierarchical structure of the COF to incorporate both electroactive and bio-site moieties. Measurements were carried out in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, which oxidises TB. DPV measurements were used to correlate the peak current for the reduction of TBox with the logarithm concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin.
A different strategy to obtain a labelling agent is the use of COFs together with peroxidase enzymes, which are adsorbed by the COFs nanostructures. This strategy has been followed by S. Feng et al. [117] during the development of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) immunosensor. They managed to crystallize the HRP-Ab2-Au-COF nanocomposite material in a three step-method. First, the COF crystallization was performed by the Schiff base condensation reaction between the 1,3,5-Tris-(4-aminofenil)benzene (TAPB) and the 2,5-dimethoxyterephaldehyde (DMTA) at room temperature in acetonitrile, to afford the TAPB-DMTA-COF as a spherulite polymorph with an average diameter centred at 256 nm. In a second step, AuNPs loading was achieved by suspending COF in water followed by the subsequent chloroauric acid reduction with sodium borohydride similar to that described by Shirong Hu and col. [118]. It is worth pointing out that the generation of AuNPs did not affect the COF morphology as revealed by the microscopy analysis. Finally, the electrochemical immunosensor was assembled through a Au-NH2 reaction between AuNPs and secondary antibody (Ab2) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The synergistic effect between the high AuNPs conductivity and the high dispersion due to the COF’s intrinsic porosity makes this composite an ideal platform for selective target recognition and signalling. The gold-working electrode was modified by adsorbing the specific capture antibody (Ab1) and the subsequent block of the surface with BSA. DPV measurements were carried out in a solution containing hydroquinone as redox mediator and H2O2, which is employed as substrate by the HRP enzyme to oxidized hydroquinone. The electrochemical immunosensor showed a wide linear range from 5 pg/mL to 10 ng/mL for the detection of cardiac troponin levels (cTnI), with a detection limit of 1.7 pg/mL, demonstrating good selectivity and reproducibility.
3.3. Genosensors
COFs can be used as structural materials to adsorb oligonucleotides and their further use as DNA probes for the development of genosensors. A hybrid MOF/COF nanocomposite material was developed by Miao Du’s research group [119] (Figure 7). The developed nanocomposite material has been used on a label free genosensor for HIV-1 DNA probe. They developed the synthesis of a phtalocyanine-based COF by the Schiff base condensation reaction of copper-phthalocyaninetetra-amine (CoPc-TA) and 2,9-bis[p-(formyl)phenyl]-1,10-phenanthroline in the presence of a Cu-MOF, yielding the Cu-MOF@CuPc-TA-COF dual-structure. Electrode modification was performed at variable percentages of the Cu-MOF@CuPc-TA-COF colloids by drop casting onto a GC electrode to obtain a Cu-MOF@CuPc-TA-COF/GC electrode. Cu-MOF@CuPc-TA-COF acts as the sensitive platform for anchoring the HIV-1 DNA probe strands and can be used as the signal transducers for EC biosensors. The electrochemical detection is carried out by DPV, using ferrocyanide as redox probe. The current intensity decreases when increasing amounts of HIV-1 DNA target sequence is retained by hybridization with the DNA probe immobilized on the Cu-MOF@CuPc-TA-COF. The genosensor has been successfully used for the detection of HIV-1 DNA in human serum, demonstrating good agreement with real concentrations. Another example of genosensor using COF in the electrochemical platform has been reported by L. Guo et al. [120]. The novel biosensor was applied for the non-small cell lung cancer of circulating tumour DNA (NSCLC ctDNA) detection with acceptable stability, reproducibility, and specificity. COF-TAPB-TFPB was synthesized 1,3,5-tris(p-formylphenyl) benzene (TFPB) and 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl) benzene (TAPB). After that, nitrogen-doped graphene (NG) is suspended together with polyethyleneimine (PEI), and then is mixed with COF-TAPB-TFPB, generating a NG-PEI-COFTAPB-TFPB composite material. GC electrode is modified by drop casting a suspension of NG-PEI-COFTAPB-TFPB. Secondly, AuNPs are drop casted on top of the modified electrode, and the specific DNA capture probe is incubated, being immobilized due to the formation of Au–N bonds. As a label element, Fe-MOF with amine groups was synthesized according to [121]. AuNPs were bound to the surface of Fe-MOF through Au–N bonds (Fe-MOF@AuNPs). Fe-MOF@AuNPs was incubated with the probe for DNA detection. The DNA target probe is incubated over a capture Probe-NG-PEI-COF-TAPB-TFPB/GC electrode, and after that, the label element is incubated. Finally, after the typical sandwich hybridization, the electrochemical detection is carried out in the presence of K4[Fe(CN)6], which is transformed into Prussian blue (PB) on the surface of the electrode due to the Fe3+ provided by the label element. The signal obtained by DPV for the electrochemical oxidation of PB was finally related with the concentration of the DNA target probe.
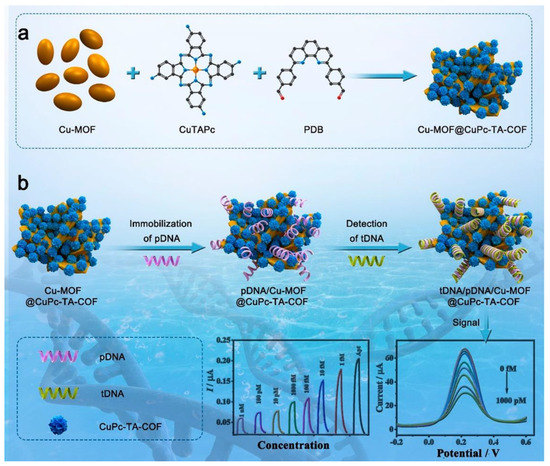
Figure 7.
(a) Preparation of the Cu-MOF@CuPc-TA-COF Hybrid Material by the Miao Du’s research group [119] and (b) Construction Procedure of the HIV-1 DNA Biosensor Based on the Cu-MOF@CuPc-TA-COF Hybrid. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [119]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society.
3.4. Aptasensors
Similar to that shown above for genosensors, COFs can be also used as supports to adsorb oligonucleotides, which are capable of recognizing target proteins with an affinity and specificity rivalling that of antibodies [122].
Zhongyi Liuc and col. [123] obtained a porphyrin-based COF (pCOF) by Schiff base condensation reaction between 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-aminophenyl) porphyrin (TAPP) and terephthaldehyde (TA). Gold electrodes were modified by drop casting a suspension of pCOF. The authors used pCOF as platform to immobilize the label-free epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeting aptamer stands (Apt) by non-covalent interactions. The porous structure of the pCOF allowed the functionalization of the aptamer beyond the particle outside surface, allowing an increase to the surface area of the accessible binding sites with living cells. Furthermore, the pCOF displayed high charge carrier mobility and good electrochemical activity even after functionalization. The pCOF-based aptasensor benefits from the C=N- and secondary-NH2 groups, as well as from the macromolecular structure of pCOF. It possesses a π-conjugated network, and its electrons are expected to migrate quickly into the pCOF layers. The developed aptasensor has been used to directly determine an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) protein, as well as living Michigan cancer foundation-7 (MCF-7) cells. The measurements were carried out by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and DPV using [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− as a redox probe showing low LOD of 5.64 fg/mL and 7.54 fg/mL, respectively. The determined linear range was 0.05–100 pg/mL. For the detection of living MCF-7 cells, the aptasensor showed an LOD of 61 cell/mL and a linear range of 500 × 105 cell/mL. Another example of a cancer biomarker aptasensor was developed by Jiangnan Li et al. [124] from melem and hexaketocyclohexane octahydrate. The M-HO-COF was suspended and then drop casted on top of a gold electrode (AuE). Then, the M-HO-COF/AuE was incubated with the aptamer solution. The M-HO-COF network is composed of C=N and highly conjugated aromatic moieties and presents large pore size, high surface area, and excellent bio-affinity toward aptamer strands. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165)-targeted aptamer is anchored to M-HO-COF through intermolecular forces. EIS was used during the measurements using ferricyanide as redox probe. A bi-functional aptasensor for the detection VEGF165 and K7M2 cells has been developed. The aptasensor showed appropriate selectivity toward other biomarkers or normal cells, good stability, acceptable reproducibility, and applicability.
Antibiotics have also been the target of aptasensors based on COFs, as shown in a recent study reported by M. Wang et al. [125]. To address the synthesis of the COF network, 1,3,6,8-tetrakis(4-formylphenyl)pyrene was reacted with melamine in DMSO as a solvent to afford the Py-M-COF as a powder (Figure 8). Liquid phase exfoliation of Py-M-COF in water allowed the modification of Au-electrodes via drop casting. Finally, the modified electrodes were immersed in aptamer-saturated solutions of enrofloxacin (ENR) and ampicillin (AMP) separately and dried under a N2 flow affording the Apt/Py-M-COF/AuE. Because of the high amounts of the functional groups, the high specific surface areas, and the pore cavities of the COF porous frameworks, important amounts of aptamer strands can be immobilized on the Py-M-COF. EIS measurements showed that Py-M-COF-based aptasensors presented good sensing performances and low LOD of 6.07 and 0.04 fg/mL for detecting ENR and AMP, respectively.
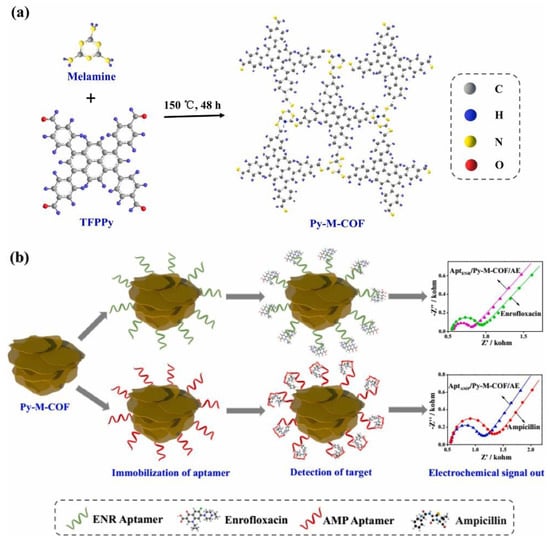
Figure 8.
(a) Scheme of the synthesis of Py-M-COF. (b) Scheme of electrochemical detection of ENR and AMP using the Py-M-COF-based aptasensors. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [125]. Copyright 2019 Elsevier.
The combination of COFs with carbon nanomaterials has been also used for the development of aptasensors as recently reported by He and co-workers [126]. For this purpose, a COF was synthesized using 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene and 2,5-dimethoxyterephthalaldehyde as precursors in the presence of amino carbon nanotubes. The composite material suspension was drop casted on top of a Au electrode. The modified AuE was incubated in an aptamer phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution. The sensing performance was mainly attributed to the mass of aptamers immobilized on the COF through π–π stacking and hydrogen bond interactions and the great electrical conductivity of the CNTs. Atrazine, an extensively used artificial herbicide, has been detected using EIS, showing an LOD of 0.67 pg/mL. Real water samples from rivers and taps were also successfully analysed. Another example of the combination of COFs with carbon nanomaterials was described by M. Sarabaegi et al. [127]. In this example, the COF is obtained from the reaction between 2,4,6-triamino-1,3,5-triazine and trimesic acid. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) was mixed with the COF using DMF as a solvent. After that, an electrospinning device was used to generate a composite nanomaterial made of nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers and the COF (COFCNF). COFCNF was dispersed in DMF and drop casted on top of the GC electrode. The COFCNF was functionalized with mercaptopropionic acid (MPA), and then used to impregnate the fibres. EDC/NHS was employed to activate the carboxylic groups. The aptamer probe was attached to the COFCNF through the formation of covalent bonds given that amide bonds stimulate amine aptamer groups to COFCNF/GCE carboxyl groups. The proposed aptasensor was used for tyrosinamide determination. Quantifying tyrosinamide in the blood serum as a risk factor for diabetes can be very helpful in treating and preventing this issue. The measurements were carried out using EIS. The aptasensor present an LOD of 0.53 pM, linearity from 0.0016–0.08 nM, and 0.08–9 nM.
COFs have also been used in combination with metal nanoparticles for the development of aptasensors. Metal nanoparticles can supply the limited electrical conductivity of COFs. T. Zhang et al. [128] reported an aptasensor for the target cancer biomarker thrombin (TB) detection. The cyclotrimerization of benzene-1,4-diboronicacid (BDBA) yielded a hexagonal boroxine-linked COF. Subsequent liquid phase exfoliation and drop casting of the COF-colloids over a GCE yielded a COF/GCE modified electrode, which was loaded with AuNPs by in situ reduction of chloroauric acid and anchored to the capture probe (TBA 1). Finally, BSA incubation yielded the BSA/TBA 1/Au-COFs/GCE modified electrode. The authors used a sandwich-type sensor by the incorporation of Thrombin binding aptamers (TBA 2) to the Au@ZIF-8-(NiPd) composite. The amount of TB was determined by measuring the peroxidase activity of TBA 2–Au@ZIF-8-(NiPd) using TMB, ABTS, and OPD as the chromogenics in the presence of H2O2. The synthetized BSA/TBA 1/Au-COFs/GCE and TBA 2–Au@ZIF-8-(NiPd) bioconjugates were used for TB determination in real serum samples.
COFs have been also combined with MOFs for the development of aptasensors. A recent study reported by Zhihong Zhang and col [59] started with the synthesis of a triazine based COF through nitrile cyclotrimerization reaction of 1,4-dicyanobenzene in melt ZnCl2 al 300 °C. The subsequent in situ formation of Co-MOF yielded a Co-MOF@TPN-COF nano-architecture. Drop casting a dispersion of Co-MOF@TPN-COF on top of a Au electrode yielded the modified gold electrode (AuE). Finally, the immersion of AuE into the aptamer solution afforded the final electrode with the DNA-strand anchored to the nanostructure walls. The multi-layered Co-MOF@TPN-COF nanosheets exhibit a high specific surface area, nitrogen-rich groups, and excellent electrochemical activity. As a result, large amounts of aptamer strands are retained on the Co-MOF@TPN-COF nanosheets due to the strong π–π stacking and hydrogen bonds. The developed aptasensor uses EIS to obtain the signal response, which is specific to ampicillin (AMP). The LOD of 0.217 fg/mL of AMP and a linear range between 1.0 fg/mL to 2.0 ng/mL were obtained. Siyu Lu’s research group developed an alternative strategy that involved the incorporation of Ce-MOF by in situ formed MCA-COF nanosheets at different weight ratios [76].
These nano-layers were synthetized according to a bottom-up method, which involves the reaction between melamine and cyanuric acid. Finally, for the fabrication of the Ce-MOF@COF based aptasensor, a dispersion of the composite in deionized water was drop casted on top of an electrode, dried, and immersed in aptamer solutions. Oxytetracycline has been successfully determined by EIS, showing an LOD of 17.4 fg/mL and a linear range between 0.1 and 0.5 ng/mL. Another example showed the use of (4-aminophenyl)benzene (TAPB) and 2,5-imethoxyterephaldehyde (DMTP) to generate a COF-based material coating a microporous MOF (UiO-66-NH2) [129]. The obtained material (UiO-66-NH2@COF) was dispersed into ethanol and drop casted on top of a gold electrode. This strategy to prepare MOF@COF core–shell composites is based on the Schiff base reaction between aldehyde group of monomers and the amine groups present on the MOF. The UiO-66-NH2@COF core–shell composite can be rationally designed and prepared using microporous UiO-66-NH2 as core and mesoporous TAPB-DMTP-COF as shell. The modified electrode UiO-66-NH2@COF/AuE was incubated with the aptamer oligonucleotide sequence. The proposed strategy was used for two different aptamer sensors, using different specific oligonucleotides sequences for adenosine triphosphate (ATP), important physiological energy source for human body, and chloramphenicol (CAP), widely used in the therapeutic field and that can cause several health problems in human beings. EIS was used to obtain the signal response after the modified electrodes were incubated with the corresponding analyte.
In the last example, a COF-based material was used in the preparation of a label agent. The aforementioned 2,6-diaminoanthraquinone (DA) and 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol (Tp) were used together with Fe3O4 nanoparticles to generate [Fe3O4@COF(TpDA)] to provide WP5A@Au@COF@Fe3O4. After that, the oligonucleotide used as aptamer was incubated with the nanocomposite material. Finally, methylene blue (MB) was accommodated into WP5A, giving a result of MB@Apt@WP5A@Au@COF@Fe3O4. The biosensor construction was carried out using GC electrodes. AuNps were electrodeposited on the electrodes (Au@GCE), then the electrode was incubated with peptides, and finally blocked using 1-hexanethiol (HT). The immobilized peptide is specific for human norovirus (HuNoV). The amount of HuNoV was correlated with the DPV oxidation peak of MB retained on the label agent MB@Apt@WP5A@Au@COF@Fe3O4. The described biosensor detects unprocessed specimens without nucleoid acid extraction and amplification. Accordingly, this biosensor has the potential application in HuNoV detection in real samples and point of care testing (POCT). The fabricated biosensors were used for HuNoV detection in spiked oyster, strawberry, and faecal samples to explore their practical application in real samples.
Table 1 contain examples of COFs application in different real samples including sensors and biosensors.

Table 1.
Examples of COFs application in different samples.
4. Conclusions
COFs are new and emerging materials with multiple application fields. Among them, sensor and biosensor development is a wide area of the application of these materials, as a consequence of their extraordinary properties. In particular, it is worth highlighting their high porosity, appropriate pore sizes for the immobilization of specific recognition elements, and post-modification capacity. In addition, the possibility of predesigning chemical structures according to the correct selection of their precursors is opening the door to interesting sensors and biosensors developments. COF can be used in the sensor platforms in order to improve specific area, serving as a supportive material for electrocatalysts, enzymes, antibodies, oligonucleotides, etc. COF can also have a specific function related to their structure, acting as an electrocatalyst, recognizing elements, and offering the functional groups needed for specific adsorption or the chelating process. Innovative strategies are using COFs as label agent developments, linking them with specific antibodies, aptamer, enzymes, oligonucleotides, etc. The great variety of COFs structures and the enormous amount of new COF designs would have a starring role in the next generation of electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Finally, the prospects of sensor assemblies should address the problems produced from the inherent insolubility of the COFs. Thus, the use of dynamic covalent chemistry to produce CONs with monomodal distributions through bottom-up strategies may improve the sensor quality, since the top-down strategies may be very destructive, yielding the uncontrolled distribution of nanosheets sizes. Furthermore, to ensure a sustainable future, the inclusion of metallic additives on the sensor composition should be avoided. In addition, other additives could produce pore blockage limiting the analyte diffusion to the active sites. Furthermore, the characteristic electrical insulator behaviour of COFs must be addressed by either developing conductive COFs or by using few-layer COFs, ensuring close contact between COFs and electrodes. Finally, the new trends on tailor-made COFs by 3D-printing techniques and shapable monolithic aerogels will pave the way for the production of tailor-made sensors based on COFs to ensure proper device integrations and scalability.
Author Contributions
E.M.-P.: Conceptualization, Resources and Writing. M.M.-F.: Conceptualization, Resources and Writing. J.L.S.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing Abstract, Conclusions, Review, and Editing. E.L.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing Abstract, Conclusions, Review, and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been supported by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (PID2020-116728RB-I00; RED2018-102412-T), Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (PID2019-106268GB-C33) and Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid (SI3/PJI/2021-00341, P2018/NMT-4349 TRANSNANOAVANSENS Program).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Geng, K.; He, T.; Liu, R.; Dalapati, S.; Tan, K.T.; Li, Z.; Tao, S.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, D. Covalent Organic Frameworks: Design, Synthesis, and Functions. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 8814–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Gupta, S.K.; Ozdemir, J.; Beyzavi, H. Applications of Dynamic Covalent Chemistry Concept toward Tailored Covalent Organic Framework Nanomaterials: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 6239–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Kirlikovali, K.O.; Varma, R.S.; Jin, Z.; Jang, H.W.; Farha, O.K.; Shokouhimehr, M. Covalent Organic Frameworks: Emerging Organic Solid Materials for Energy and Electrochemical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27821–27852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.S.; Bein, T. Covalent Organic Frameworks: Structures, Synthesis, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segura, J.L.; Royuela, S.; Ramos, M.M. Post-synthetic modification of covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3903–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, H.; Mathe, S.D.R.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Covalent Organic Frameworks: From Materials Design to Biomedical Application. Nanomaterials 2017, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, C.; Sun, B.; Cai, S.; Chen, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Expeditious synthesis of covalent organic frameworks: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16045–16060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourda, L.; Krishnaraj, C.; Van Der Voort, P.; Van Hecke, K. Conquering the crystallinity conundrum: Efforts to increase quality of covalent organic frameworks. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2811–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diercks, C.S.; Yaghi, O.M. The atom, the molecule, and the covalent organic framework. Science 2017, 355, eaal1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, M.; Gavara, R.; Royuela, S.; Fernández-Ecija, L.; Martínez, J.I.; Zamora, F.; Segura, J.L. Following the light: 3D-printed COF@poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) dual emissive composite with response to polarity and acidity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 4634–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández, M.; Martínez-Periñán, E.; Royuela, S.; Martínez, J.I.; Zamora, F.; Lorenzo, E.; Segura, J.L. Covalent organic frameworks based on electroactive naphthalenediimide as active electrocatalysts toward oxygen reduction reaction. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, S.-Q.; Liang, R.-R.; Qian, C.; Jiang, G.-F.; Zhao, X. Construction of two heteropore covalent organic frameworks with Kagome lattices. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2017, 19, 4877–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzeid, H.R.; El-Mahdy, A.F.M.; Kuo, S.-W. Hydrogen bonding induces dual porous types with microporous and mesoporous covalent organic frameworks based on bicarbazole units. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2020, 300, 110151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Zheng, W.; Gao, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Fu, S.; Song, X.; Zhao, Z.; Osella, S.; Martínez-Abadía, M.; et al. Nonplanar Rhombus and Kagome 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks from Distorted Aromatics for Electrical Conduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5042–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitler, E.L.; Colson, J.W.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Woll, A.R.; Giovino, M.R.; Saldivar, A.; Dichtel, W.R. Lattice Expansion of Highly Oriented 2D Phthalocyanine Covalent Organic Framework Films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2623–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royuela, S.; Almarza, J.; Mancheño, M.J.; Flores, J.C.P.; Michel, E.G.; Ramos, M.M.; Zamora, F.; Ocón, P.; Segura, J.L. Synergistic Effect of Covalent Bonding and Physical Encapsulation of Sulfur in the Pores of a Microporous COF to Improve Cycling Performance in Li-S Batteries. Chem. A Eur. J. 2019, 25, 12394–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Gu, S.; Kaspar, R.B.; Zhuang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Guo, H.; Qiu, S.; Yan, Y. 3D Porous Crystalline Polyimide Covalent Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8352–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-B.; Su, J.; Furukawa, H.; Yun, Y.; Gándara, F.; Duong, A.; Zou, X.; Yaghi, O.M. Single-Crystal Structure of a Covalent Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16336–16339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bahri, M.; Fu, Z.; Little, M.A.; Liu, L.; Niu, H.; Browning, N.D.; Chong, S.Y.; Chen, L.; Ward, J.W.; et al. A Cubic 3D Covalent Organic Framework with nbo Topology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 15011–15016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; He, M.; Sun, J.; Wang, C. Tailoring the Pore Surface of 3D Covalent Organic Frameworks via Post-Synthetic Click Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 61, e202113852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, S.J.; Cantrill, S.J.; Cousins, G.R.L.; Sanders, J.K.M.; Stoddart, J.F. Dynamic Covalent Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 898–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yu, C.; Denman, R.J.; Zhang, W. Recent advances in dynamic covalent chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6634–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.J.; Dichtel, W.R. Mechanistic Studies of Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks Rapidly Polymerized from Initially Homogenous Conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8783–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chen, W.; Xing, G.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L. An Upgraded “Two-in-One” Strategy toward Highly Crystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, D.M.; Rhoades, G.; Espy, C.; Goldberg, F.; Smith, B.J. Controlling the crystalline structure of imine-linked 3D covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 3594–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.L.; Flanders, N.C.; Evans, A.M.; Ji, W.; Castano, I.; Chen, L.X.; Gianneschi, N.C.; Dichtel, W.R. Controlled growth of imine-linked two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanoparticles. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 3796–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, L.K.; Trewin, A.; Reguera-Galan, A.; Hasell, T.; Cooper, A.I. Synthesis of COF-5 using microwave irradiation and conventional solvothermal routes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 132, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschita, J.; Banerjee, T.; Savasci, G.; Haase, F.; Ochsenfeld, C.; Lotsch, B.V. Ionothermal Synthesis of Imide-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15750–15758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qi, H.; Dong, R.; Shivhare, R.; Addicoat, M.; Zhang, T.; Sahabudeen, H.; Heine, T.; Mannsfeld, S.; Kaiser, U.; et al. On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Guo, Q.; Kang, H.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D. Self-Controlled Growth of Covalent Organic Frameworks by Repolymerization. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 5634–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-H.; Guan, C.-Z.; Ding, S.-Y.; Wang, W.; Yan, H.-J.; Wang, D.; Wan, L.-J. On-Surface Synthesis of Single-Layered Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks via Solid–Vapor Interface Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10470–10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Gándara, F.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, C.; Lyu, H.; Trickett, C.A.; Kapustin, E.A.; Terasaki, O.; et al. A Synthetic Route for Crystals of Woven Structures, Uniform Nanocrystals, and Thin Films of Imine Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13166–13172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, P.; Nguyen, T.C.; Saxena, A.; Aluru, N.R. Machine Learning Assisted Screening of Two-Dimensional Materials for Water Desalination. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, H.; Lai, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, Q.; Yu, D. Accelerating the Selection of Covalent Organic Frameworks with Automated Machine Learning. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17149–17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschita, J.; Banerjee, T.; Lotsch, B.V. Direct and Linker-Exchange Alcohol-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Imide-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, T.; Rotter, J.M.; Reuter, S.; Kandambeth, S.; Bach, N.N.; Döblinger, M.; Merz, J.; Clark, T.; Marder, T.B.; Bein, T.; et al. Switching on and off Interlayer Correlations and Porosity in 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 12570–12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Hunt, J.R.; Furukawa, H.; Klöck, C.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. A Crystalline Imine-Linked 3-D Porous Covalent Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4570–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arroyo, P.; Martínez-Periñán, E.; Cabrera-Trujillo, J.J.; Salagre, E.; Michel, E.G.; Martínez, J.I.; Lorenzo, E.; Segura, J.L. Pyrenetetraone-based covalent organic framework as an effective electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3907–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Navarro, M.J.; Barrio, J.; Royuela, S.; Karjule, N.; Ramos, M.M.; Martínez, J.I.; Shalom, M.; Segura, J.L. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants through conjugated poly(azomethine) networks based on terthiophene–naphthalimide assemblies. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2701–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, J.; Jiang, D. Stable, crystalline, porous, covalent organic frameworks as a platform for chiral organocatalysts. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Duan, C.; Pan, Q.; Zhu, J.; Hu, F.; Ma, X.; Jiu, T.; Li, Z.; et al. Highly Conjugated Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks Based on Spirobifluorene for Perovskite Solar Cell Enhancement. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10016–10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Jagt, R.; Vasileiadis, A.; Veldhuizen, H.; Shao, P.; Feng, X.; Ganapathy, S.; Habisreutinger, N.C.; van der Veen, M.A.; Wang, C.; Wagemaker, M.; et al. Synthesis and Structure–Property Relationships of Polyimide Covalent Organic Frameworks for Carbon Dioxide Capture and (Aqueous) Sodium-Ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Luo, B.; Chen, Y. Crystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks from Triazine Nodes as Porous Adsorbents for Dye Pollutants. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22504–22513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, M.; Ota, R.; Endo, T.; Yanase, T.; Nagahama, T.; Shimada, T. Free-Standing Nanometer-Thick Covalent Organic Framework Films for Separating CO2 and N2. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 2367–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tian, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, H.; Zou, X.; Ma, Y.; Meihaus, K.R.; Long, J.R.; Zhu, G. A Crystalline Polyimide Porous Organic Framework for Selective Adsorption of Acetylene over Ethylene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15724–15730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royuela, S.; Millán, R.G.-S.; Mancheño, M.J.; Ramos, M.M.; Segura, J.L.; Navarro, J.A.R.; Zamora, F. Catalytically Active Imine-based Covalent Organic Frameworks for Detoxification of Nerve Agent Simulants in Aqueous Media. Materials 2019, 12, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Qin, L.; Wang, H.; Yi, H.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; et al. Recent advances in covalent organic frameworks (COFs) as a smart sensing material. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5266–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-San-Miguel, D.; Montoro, C.; Zamora, F. Covalent organic framework nanosheets: Preparation, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2291–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ji, W.; Ding, X.; Han, B.-H. Exfoliated covalent organic framework nanosheets. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 7336–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Kandambeth, S.; Biswal, B.P.; Lukose, B.; Kunjir, S.M.; Chaudhary, M.; Babarao, R.; Heine, T.; Banerjee, R. Chemically Stable Multilayered Covalent Organic Nanosheets from Covalent Organic Frameworks via Mechanical Delamination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17853–17861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Fang, L.; He, Z.; Xie, H.; Liu, B.; Guo, B.; Yao, Y. Surfactant-Modulated a Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Probe of Fully Conjugated Covalent Organic Nanosheets for Detecting Copper Ions in Aqueous Solution. Small 2022, 18, 2200388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mow, R.E.; Lipton, A.S.; Shulda, S.; Gaulding, E.A.; Gennett, T.; Braunecker, W.A. Colloidal three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks and their application as porous liquids. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 23455–23462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lim, G.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mullangi, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Ding, J.; Cheetham, A.K.; Wang, J. Binder-free 3D printing of covalent organic framework (COF) monoliths for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 403, 126333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Lin, Q.; Tang, M.; Wu, Y.; Ke, C. Hierarchical-Coassembly-Enabled 3D-Printing of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5154–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karak, S.; Dey, K.; Torris, A.; Halder, A.; Bera, S.; Kanheerampockil, F.; Banerjee, R. Inducing Disorder in Order: Hierarchically Porous Covalent Organic Framework Nanostructures for Rapid Removal of Persistent Organic Pollutants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7572–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Illán, J.; Rodríguez-San-Miguel, D.; Castillo, O.; Beobide, G.; Perez-Carvajal, J.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D.; Zamora, F. Macroscopic Ultralight Aerogel Monoliths of Imine-based Covalent Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13969–13977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yuan, B.; Liu, G.; Zhang, D. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Covalent Organic Frameworks: A Critical Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 601044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, T.; Zeng, W.; Huang, T.; Zhao, G. Control Assembly of Pillar[6]arene-Modified Ag Nanoparticles on Covalent Organic Framework Surface for Enhanced Sensing Performance toward Paraquat. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 20051–20059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, M.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Zhou, N.; He, L.; Zhang, Z. Novel nanoarchitecture of Co-MOF-on-TPN-COF hybrid: Ultralowly sensitive bioplatform of electrochemical aptasensor toward ampicillin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 123, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kou, B.; Yuan, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Porous Fe3O4@COF-Immobilized gold nanoparticles with excellent catalytic performance for sensitive electrochemical detection of ATP. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 197, 113758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Pang, C.; Li, S.; Xiong, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of Zr-coordinated amide porphyrin-based two-dimensional covalent organic framework at liquid-liquid interface for electrochemical sensing of tetracycline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.; Yin, J.; Zhu, J. Recent Advances on Conductive 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks. Small 2021, 17, 2006043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, H.; Pan, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, T.; Yang, M.; Wu, N.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, W. In-situ reducing platinum nanoparticles on covalent organic framework as a sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of catechol, hydroquinone and resorcinol. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 635, 128114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Guo, H.; Wu, N.; Cao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W. Highly sensitive determination of acetaminophen and 4-aminophenol based on COF/3D NCNF-T/Au NPs composite electrochemical sensing platform. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 630, 127624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.-H.; Zhu, X.-G.; Xie, A.-D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.-E. Facile fabrication of carbon-loaded covalent-organic framework composites with enhanced electrochemical performance for dopamine determination. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 323, 111186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Du, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, L. Double signal ratiometric electrochemical riboflavin sensor based on macroporous carbon/electroactive thionine-contained covalent organic framework. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 608, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, L. Three-dimensional porous carbon/covalent-organic framework films integrated electrode for electrochemical sensors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 855, 113590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Jin, C.; Zeng, J.; Huang, C.; Song, Q.; Song, Y. Preparation of a Sensor Based on Biomass Porous Carbon/Covalent-Organic Frame Composites for Pesticide Residues Detection. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. Electroactive Covalent Organic Frameworks/Carbon Nanotubes Composites for Electrochemical Sensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gao, C.; Huang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Covalent organic framework as a novel electrochemical platform for highly sensitive and stable detection of lead. Talanta 2018, 188, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.; Gao, W.; Chen, M.; Liu, N.; Duan, J.; Hou, B. Electrochemical detection of hydroquinone and catechol with covalent organic framework modified carbon paste electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 877, 114530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, M.; Phan, H.; Wang, D.; Herng, T.S.; Ding, J.; Lu, Z.-G.; Wu, J. Toward Two-Dimensional π-Conjugated Covalent Organic Radical Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8007–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.M.; Parent, L.R.; Flanders, N.C.; Bisbey, R.P.; Vitaku, E.; Kirschner, M.S.; Schaller, R.D.; Chen, L.X.; Gianneschi, N.C.; Dichtel, W.R. Seeded growth of single-crystal two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Science 2018, 361, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, N.; Sun, X.; Chu, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Triple-signaling amplification strategy based electrochemical sensor design: Boosting synergistic catalysis in metal–metalloporphyrin–covalent organic frameworks for sensitive bisphenol A detection. Analyst 2021, 146, 4585–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, L. A novel biosensor based on multienzyme microcapsules constructed from covalent-organic framework. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Ma, Y.; Hu, B.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S. Construction of Ce-MOF@COF hybrid nanostructure: Label-free aptasensor for the ultrasensitive detection of oxytetracycline residues in aqueous solution environments. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 127, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Song, W. Liposomal Controlled Release Ag-Activated DNAzyme Cycle Amplification on a 2D Pyrene COF-Based Photocathode for α-Synuclein Immunosensing. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 8647–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Ning, G.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, C.-P. Covalent Framework Particles Modified with MnO2 Nanosheets and Au Nanoparticles as Electrochemical Immunosensors for Human Chorionic Gonadotropin. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4593–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Wang, L.; Shen, X.-F.; Wang, Y.-Y. Determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol S by a covalent organic framework electrochemical sensor. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Pang, Y.-H.; Shen, X.-F.; Jiang, R.; Wang, Y.-Y. Covalent organic framework DQTP modified pencil graphite electrode for simultaneous determination of bisphenol A and bisphenol S. Talanta 2021, 236, 122859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, P.; Narayanamoorthi, E.; John, S.A. Covalent organic framework film as an effective electrocatalyst for the simultaneous determination of dihydroxybenzene isomers in water samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 313, 128033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, M.; Wu, N.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, W. A novel electrochemical sensor based on TAPT-TFP-COF/COOH-MWCNT for simultaneous detection of dopamine and paracetamol. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4994–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suna, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Xua, L.; Qiaoa, X.; Xua, Z. Three-dimensional electrochemical sensor with covalent organic framework decorated carbon nanotubes signal amplification for the detection of furazolidone. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Conducting polymer engineered covalent organic framework as a novel electrochemical amplifier for ultrasensitive detection of acetaminophen. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 32, 2061–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhe, T.; Bu, T.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Hu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, X.; et al. Surface morphology-controllable magnetic covalent organic frameworks: A novel electrocatalyst for simultaneously high-performance detection of p-nitrophenol and o-nitrophenol. Talanta 2020, 219, 121255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Ren, N.; Ge, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J. In situ grown COFs on 3D strutted graphene aerogel for electrochemical detection of NO released from living cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 420, 127559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Liang, H.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. Iron-porphyrin-based covalent-organic frameworks for electrochemical sensing H2O2 and pH. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, H.; Wu, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, B.; Pan, Z.; Peng, L.; Yang, W. A novel triazine-based covalent organic framework combined with AuNPs and reduced graphene oxide as an electrochemical sensing platform for the simultaneous detection of uric acid, dopamine and ascorbic acid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 634, 127928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Guo, H.; Xue, R.; Wang, M.; Zhao, X.; Fan, T.; Yang, W.; Xu, M.; Yang, W. Electrochemical sensor based on covalent organic frameworks-MWCNT-NH2/AuNPs for simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 880, 114932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Guo, H.; Xue, R.; Wang, M.; Wu, N.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, W. Electrochemical sensing platform based on covalent organic framework materials and gold nanoparticles for high sensitivity determination of theophylline and caffeine. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. A novel AuNPs-doped COFs composite as electrochemical probe for chlorogenic acid detection with enhanced sensitivity and stability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, P.; Huang, S.-T.; Gowthaman, N.S.K.; Shankar, S. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of DNA nucleobases using AgNPs embedded covalent organic framework. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; Guo, H.; Sun, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Peng, L.; Yang, W. A novel electrochemical platform based on COF/La2O3/MWCNTS for simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 635, 128083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chena, Y.; Xiea, Y.; Suna, X.; Wanga, Y.; Wangb, Y. Tunable construction of crystalline and shape-tailored Co3O4@TAPB-DMTP-COF composites for the enhancement of tert-butylhydroquinone electrocatalysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 331, 129438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suna, Y.; Hea, J.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Xua, L.; Zhangc, H.; Qiaoa, X.; Xua, Z. A selective molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor with GO@COF signal amplification for the simultaneous determination of sulfadiazine and acetaminophen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 300, 126993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, H.; Xue, R.; Wang, M.; Guan, Q.; Fan, T.; Yang, W.; Yang, W. Electrochemical sensing and simultaneous determination of guanine and adenine based on covalent organic frameworks/NH2-rG/MoS2 modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchem. J. 2020, 160, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Wang, M.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. Novel three-dimensional electrochemical sensor with dual signal amplification based on MoS2 nanosheets and high-conductive NH2-MWCNT@COF for sulfamerazine determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 281, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negut, C.C.; van Staden, R.-I.S.; van Staden, J.F. Porphyrins-as Active Materials in the Design of Sensors. An Overview. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 051005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, H.; Xue, R.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Yang, W. A novel electrochemical sensor based on MWCNTs-COOH/metal-covalent organic frameworks (MCOFs)/Co NPs for highly sensitive determination of DNA base. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Gou, Q.; Yu, Z.; Pu, Y.; Huang, J.; Huang, H.; Dai, S.; Zhao, G. Nanocomposite Based on Organic Framework-Loading Transition-Metal Co Ion and Cationic Pillar[6]arene and Its Application for Electrochemical Sensing of l-Ascorbic Acid. Langmuir 2020, 36, 14676–14685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.-P.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Shi, W.; Huang, T.; Zhao, G. Ultrasensitive and highly selective electrochemical sensing of sodium picrate by Dihydroxylatopillar[6]arene-Modified gold nanoparticles and cationic Pillar[6]arene functionalized covalent organic framework. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 335, 135706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, H.; Xu, L.; Waterhouse, G.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. Ultrasensitive determination of sulfathiazole using a molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor with CuS microflowers as an electron transfer probe and Au@COF for signal amplification. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Ng, S.; Pumera, M. Chiral Protein–Covalent Organic Framework 3D-Printed Structures as Chiral Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 5277–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Liang, H.; Wu, N.; Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. A novel N,S-rich COF and its derived hollow N,S-doped carbon@Pd nanorods for electrochemical detection of Hg2+ and paracetamol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 409, 124528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ni, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ge, B.; Zhao, H.; Li, W. Multifunctional triphenylbenzene-based polyimide covalent organic framework with absolute eclipsed stacking models for fluorescence detecting of Fe2+ and electrochemical detecting of Pb2+. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pei, L.; Du, Y.; Zhu, Y. Tripolycyanamide-2,4,6-triformyl pyrogallol covalent organic frameworks with many coordination sites for detection and removal of heavy metal ions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 107, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Tong, C.; Wang, Z.; Han, H.; Liu, P.; Pan, D.; Zhu, R. Nanocomposite based on graphene and intercalated covalent organic frameworks with hydrosulphonyl groups for electrochemical determination of heavy metal ions. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Y. COFBTLP-1/three-dimensional macroporous carbon electrode for simultaneous electrochemical detection of Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ and Hg2+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, L. A novel covalent organic framework with multiple adsorption sites for removal of Hg2+ and sensitive detection of nitrofural. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 106, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Fu, C.-W.; Aguila, B.; Perman, J.A.; Wang, S.; Huang, H.-Y.; Xiao, F.-S.; Ma, S. Pore Environment Control and Enhanced Performance of Enzymes Infiltrated in Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Feng, B.; Xu, P.; Zeng, Q.; Shan, B.; Song, Y. Covalent organic frameworks and electron mediator-based open circuit potential biosensor for in vivo electrochemical measurements. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4320–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Song, Y. Ratiometric electrochemical biosensing based on double-enzymes loaded on two-dimensional dual-pore COFETTA-TPAL. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacıoğlu, H.; Yola, B.B.; Karaman, C.; Karaman, O.; Atar, N.; Yola, M.L. A novel electrochemical kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) immunosensor based covalent organic frameworks-gold nanoparticles composite and porous NiCo2S4@CeO2 microspheres: The monitoring of acute kidney injury. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 578, 152093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhaoa, Y.; Zhenga, J.; Zhaob, H.; Lic, G.; Lia, C.P. Ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for prostate specific antigen detection with a phosphorene platform and magnetic covalent organic framework signal amplifier. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 144, 111691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, H.; Ning, G.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Liang, H.; Xu, H.; He, C.; Li, C.-P. A novel affinity peptide–antibody sandwich electrochemical biosensor for PSA based on the signal amplification of MnO2-functionalized covalent organic framework. Talanta 2021, 233, 122520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Hu, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Kong, J. Electrochemical ultrasensitive detection of CYFRA21-1 using Ti3C2Tx-MXene as enhancer and covalent organic frameworks as labels. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2543–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Yan, M.; Xue, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, X. Electrochemical Immunosensor for Cardiac Troponin I Detection Based on Covalent Organic Framework and Enzyme-Catalyzed Signal Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13572–13579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Deng, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, S. Construction of hydrophilic N, O-rich carboxylated triazine-covalent organic frameworks for the application in selective simultaneous electrochemical detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 545, 149047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, K.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M. MOF@COF Heterostructure Hybrid for Dual-Mode Photoelectrochemical–Electrochemical HIV-1 DNA Sensing. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13479–13492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Mu, Z.; Yan, B.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Bai, L. A novel electrochemical biosensor for sensitive detection of non-small cell lung cancer ctDNA using NG-PEI-COFTAPB-TFPB as sensing platform and Fe-MOF for signal enhancement. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 350, 130874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhao, X.J.; Yang, X.X.; Li, Y.F. A nanosized metal–organic framework of Fe-MIL-88NH2 as a novel peroxidase mimic used for colorimetric detection of glucose. Analyst 2013, 138, 4526–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, A.D.; Pai, S.; Ellington, A. Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, C.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z. Two-dimensional porphyrin-based covalent organic framework: A novel platform for sensitive epidermal growth factor receptor and living cancer cell detection. Biosens. Bioelecatron. 2018, 126, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Z. Determination of VEGF165 using impedimetric aptasensor based on cyclohexanehexone-melem covalent-organic framework. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hu, M.; Liu, J.; Guo, C.; Peng, D.; Jia, Q.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M. Covalent organic framework-based electrochemical aptasensors for the ultrasensitive detection of antibiotics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-Q.; Li, H.-K.; Sun, X.-L.; Han, Z.-Y.; Sun, J.; He, H. Rational incorporation of covalent organic framework/carbon nanotube (COF/CNT) composites for electrochemical aptasensing of ultra-trace atrazine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 8043–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabaegi, M.; Roushani, M.; Hosseini, H.; Hoseini, S.J.; Bahrami, M. Facile synthesis of a covalent organic framework (COF) based on the reaction of melamine and trimesic acid incorporated electrospun nanofiber and its application as an electrochemical tyrosinamide aptasensor. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 14922–14927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Song, Y.; Xing, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, N.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; et al. The synergistic effect of Au-COF nanosheets and artificial peroxidase Au@ZIF-8(NiPd) rhombic dodecahedra for signal amplification for biomarker detection. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 20221–20227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-W.; Zhu, Q.-Q.; Yuan, R.; He, H. Crystal engineering of MOF@COF core-shell composites for ultra-sensitively electrochemical detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 329, 129144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).