Real-Time Identification of Time-Varying Cable Force Using an Improved Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Governing Equation of the Stay Cable Motion
2.2. Cable Force Identification by IAEKF
2.2.1. Update of the Error Covariance Matrices
2.2.2. Update of the Fading-Factor Matrix
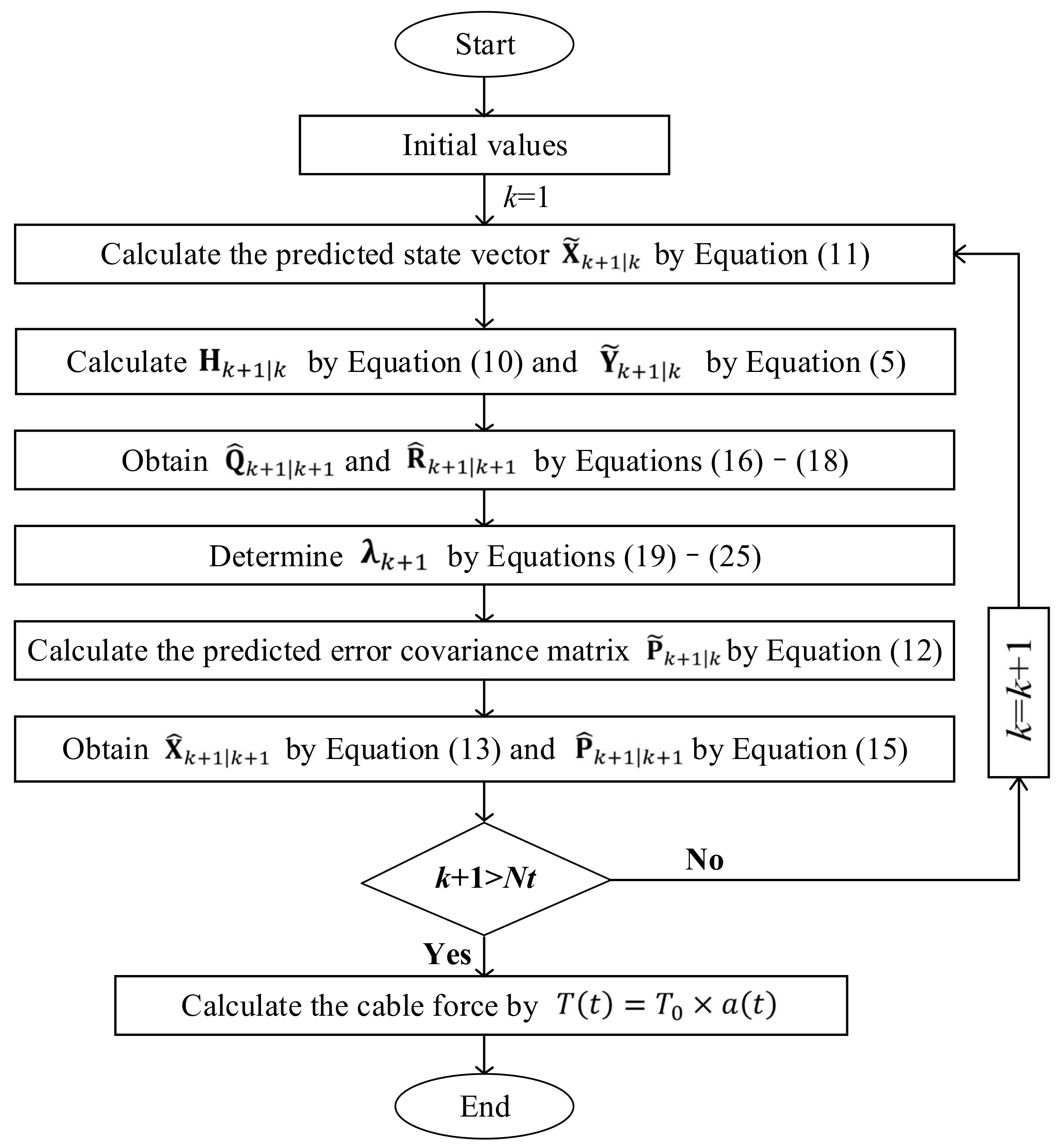
2.3. Flowchart of the Proposed Method
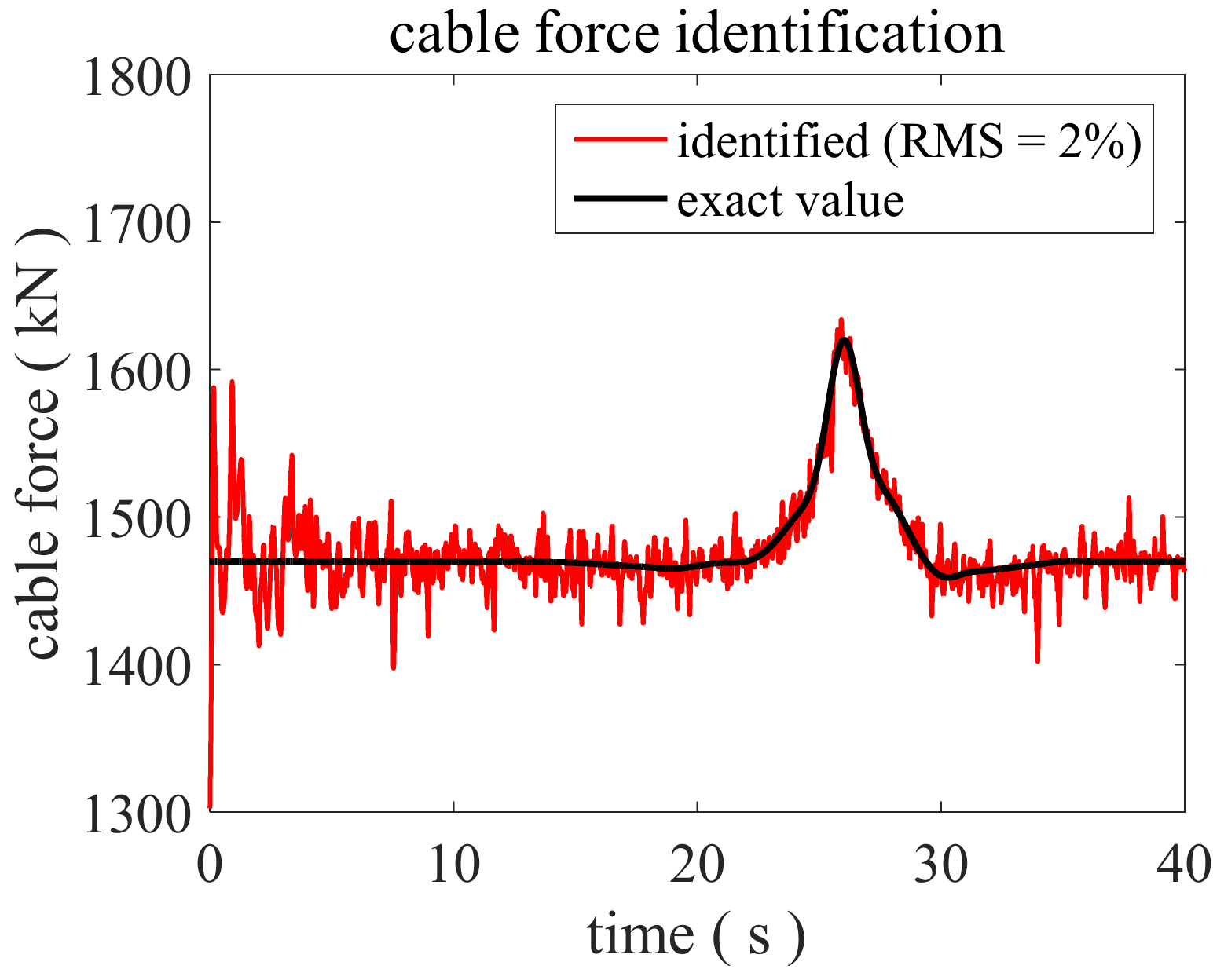
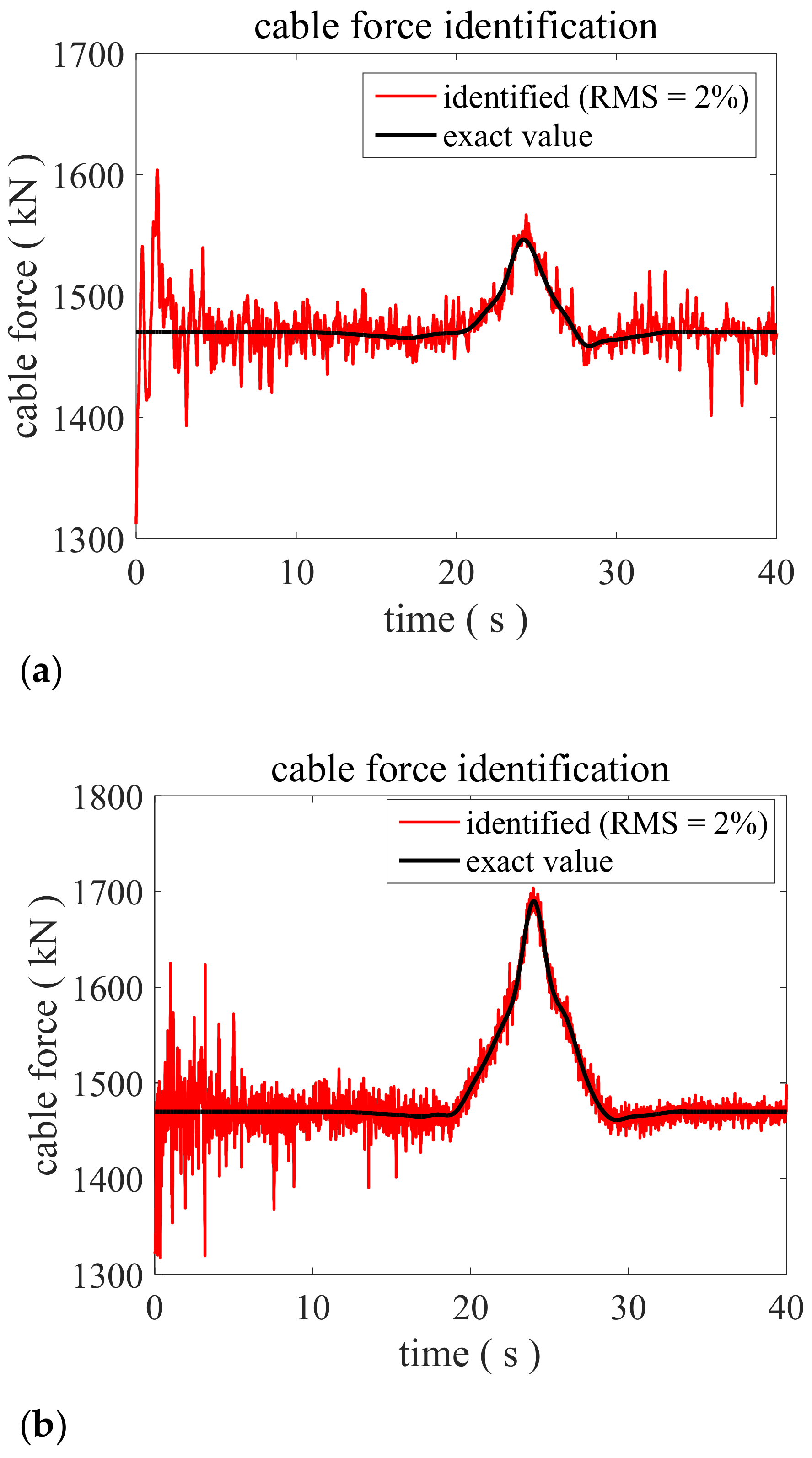
3. Numerical Validation
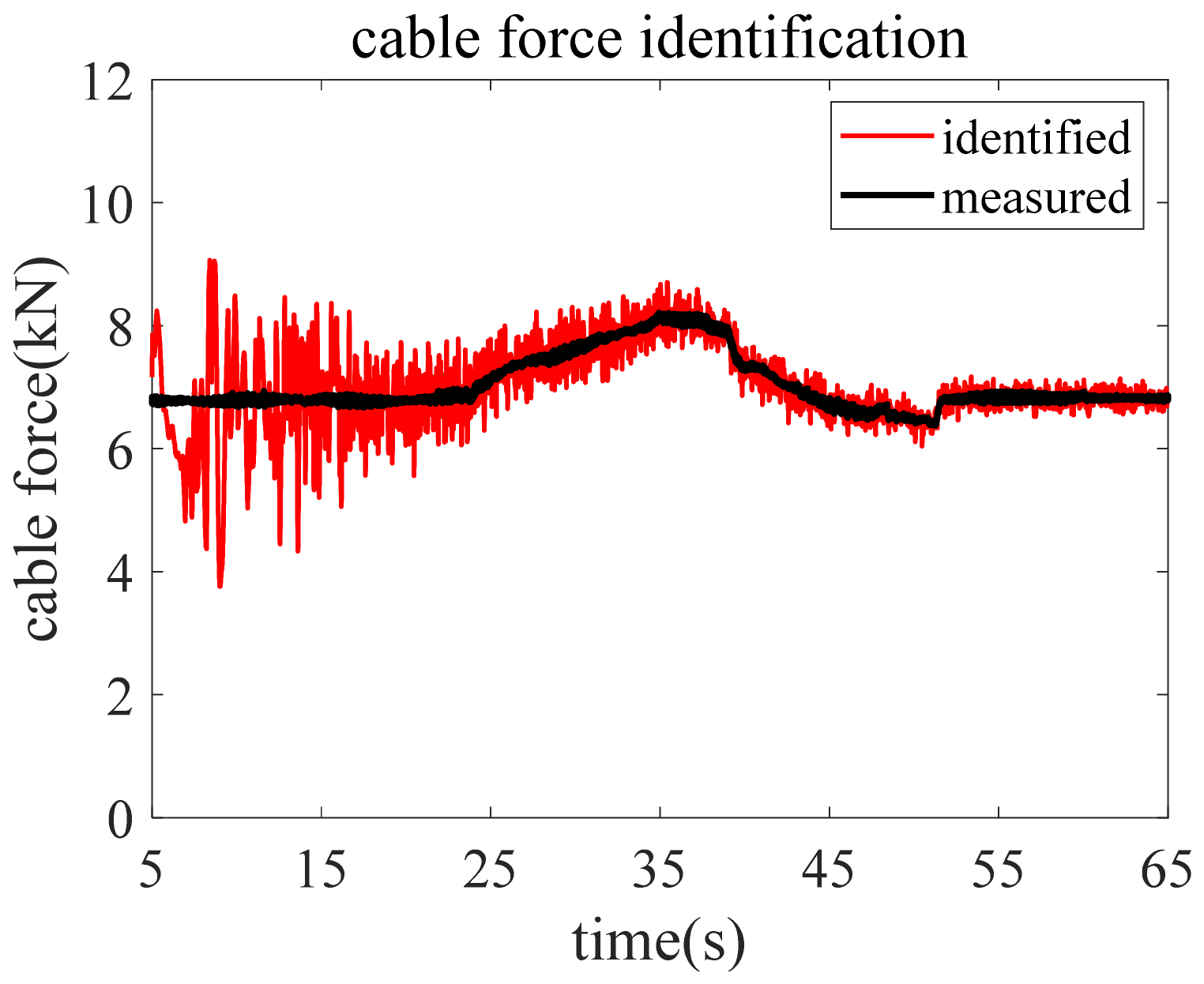
4. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alamdari, M.M.; Khoa, N.L.D.; Wang, Y.; Samali, B.; Zhu, X.Q. A multi-way data analysis approach for structural health monitoring of a cable-stayed bridge. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Wei, S.Y.; Bao, Y.Q.; Li, H. Condition assessment of cables by pattern recognition of vehicle-induced cable tension ratio. Eng. Struct. 2018, 155, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Au, F.T.K.; Yang, D. Finite element model updating of long-span cable-stayed bridge by kriging surrogate model. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2020, 74, 157–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, J.Y.; Cao, M.S.; Damjanovic, D.; Ostachowicz, W. Identification of instantaneous tension of bridge cables from dynamic responses: STRICT algorithm and applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 142, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ou, J.P. The state of the art in structural health monitoring of cable-stayed bridges. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 6, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Q.; Li, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Yang, N.; Hao, H. Damage detection of wind turbine blades by Bayesian multivariate cointegration. Ocean Eng. 2022, 258, 111603. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Xu, M.Q. Modal strain energy-based structural damage identification: A review and comparative study. Struct. Eng. Int. 2019, 29, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Li, J.; Hao, H. Structural damage identification with limited modal measurements and ultra-sparse Bayesian regression. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbaf, S.E.H.A.M.Z.; Norouzi, M.; Allemang, R.; Hunt, V.; Helmicki, A.; Venkatesh, C. Vibration-based cable condition assessment: A novel application of neural networks. Eng. Struct. 2018, 177, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, S.H. Damaged cable identification in cable-stayed bridge from bridge deck strain measurements using support vector machine. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2022, 25, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.L.; Li, C.; Jankowski, L.; Shi, Y.K.; Su, L.; Yu, S.; Geng, T.S. Damage identification of suspender cables by adding virtual supports with the substructure isolation method. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2020, 28, e2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Q.; Shi, Z.Q.; Beck, J.L.; Li, H.; Hou, T.Y. Identification of time-varying cable tension forces based on adaptive sparse time-frequency analysis of cable vibrations. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2016, 24, e1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Q.; Guo, Y.B.; Li, H. A machine learning-based approach for adaptive sparse time frequency analysis used in structural health monitoring. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 19, 1963–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wei, X.J.; Ren, W.X.; Laory, I. A combined method for instantaneous frequency identification in low frequency structures. Eng. Struct. 2019, 194, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Ren, W.X.; Wang, Z.C.; Hu, Y.D. Instantaneous frequency identification based on synchrosqueezing wavelet transformation. J. Vib. Shock 2013, 32, 37–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wei, X.J.; Liao, F.Y.; Luo, Y.P. A new instantaneous frequency extraction method for nonstationary response signals in civil engineering structures. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 2018, 37, 146134841879053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ren, W.X.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhu, H.P. Instantaneous frequency identification of time-varying structures by continuous wavelet transform. Eng. Struct. 2013, 52, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.P. A combined method for time-varying parameter identification based on variational mode decomposition and generalized Morse wavelet. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2020, 10, 2050077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.T.; Dong, B.; Fan, J.H.; Wu, G.; Wang, H.C.; Han, Y.T.; Zhao, X.J. Variational mode decomposition based time-varying force identification of stay cables. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.L.; Shen, R.L. Real time cable force identification by short time sparse time domain algorithm with half wave. Measurement 2020, 152, 107355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Li, S.L.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Li, H.; Zhou, P. Real-time output-only identification of time varying cable tension from accelerations via complexity pursuit. J. Struct. Eng. 2016, 142, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, F.J.; Jin, Y.Z. Real-time identification of time-varying tension in stay cables by monitoring cable transversal acceleration. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2014, 21, 1100–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.J.; Li, H.; Mao, C.X. Identification of time-variant stay cable tension force using a wavelet method in combination with extended Kalman filter. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2013, 30, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, N. Simultaneous identification of structural time-varying physical parameters and unknown excitations using partial measurements. Eng. Struct. 2020, 214, 110672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, J.; Lei, Y.; Hao, H. Identification of time-varying nonlinear structural physical parameters by integrated WMA and UKF/UKF-UI. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 681–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshiya, M.; Saito, E. Structural identification by extended Kalman filter. J. Eng. Mech. (ASCE) 1984, 110, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhou, H. An algorithm based on two-step Kalman filter for intelligent structural damage detection. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2014, 22, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, C.; Fritzen, C.P.; Kraemer, P.; Ntotsios, E. Fatigue predictions in entire body of metallic structures from a limited number of vibration sensors using Kalman filtering. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2011, 18, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, K.V.; Kuok, S.C. Online updating and uncertainty quantification using nonstationary output-only measurement. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 66–67, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.N.; Lin, S.L.; Huang, H.W.; Zhou, L. An adaptive extended Kalman filter for structural damage identification. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2006, 13, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Xu, Y.L.; Liu, H.J. An efficient algorithm for simultaneous identification of time-varying structural parameters and unknown excitations of a building structure. Eng. Struct. 2015, 98, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Nagayama, T.; Xue, K. Structure system estimation under seismic excitation with an adaptive extended Kalman filter. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 489, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.Q.; Kuok, S.C.; Yuen, K.V. Stable robust extended Kalman filter. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2016, 30, B4016010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhar Azam, S.; Mariani, S. Online damage detection in structural systems via dynamic inverse analysis: A recursive Bayesian approach. Eng. Struct. 2018, 159, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafei, A.; Shafei, H. A systematic method for the hybrid dynamic modeling of open kinematic chains confined in a closed environment. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2016, 38, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.W.; Samali, B.; Gu, X.Y. Real-time tracking of structural stiffness reduction with unknown inputs, using self-adaptive recursive least-square and curvature-change techniques. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2019, 19, 1950123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Lei, Y.; Li, J.; Hao, H.; Huang, J.S. A substructural and wavelet multiresolution approach for identifying time-varying physical parameters by partial measurements. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 523, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.H.; Frank, P.M. Strong tracking filtering of nonlinear time-varying stochastic systems with coloured noise: Application to parameter estimation and empirical robustness analysis. Int. J. Control 1996, 65, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, N.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, S. Real-Time Identification of Time-Varying Cable Force Using an Improved Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter. Sensors 2022, 22, 4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114212
Yang N, Li J, Xu M, Wang S. Real-Time Identification of Time-Varying Cable Force Using an Improved Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter. Sensors. 2022; 22(11):4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114212
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ning, Jun Li, Mingqiang Xu, and Shuqing Wang. 2022. "Real-Time Identification of Time-Varying Cable Force Using an Improved Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter" Sensors 22, no. 11: 4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114212
APA StyleYang, N., Li, J., Xu, M., & Wang, S. (2022). Real-Time Identification of Time-Varying Cable Force Using an Improved Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter. Sensors, 22(11), 4212. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114212






