Detrending Technique for Denoising in CW Radar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Detrending Technique
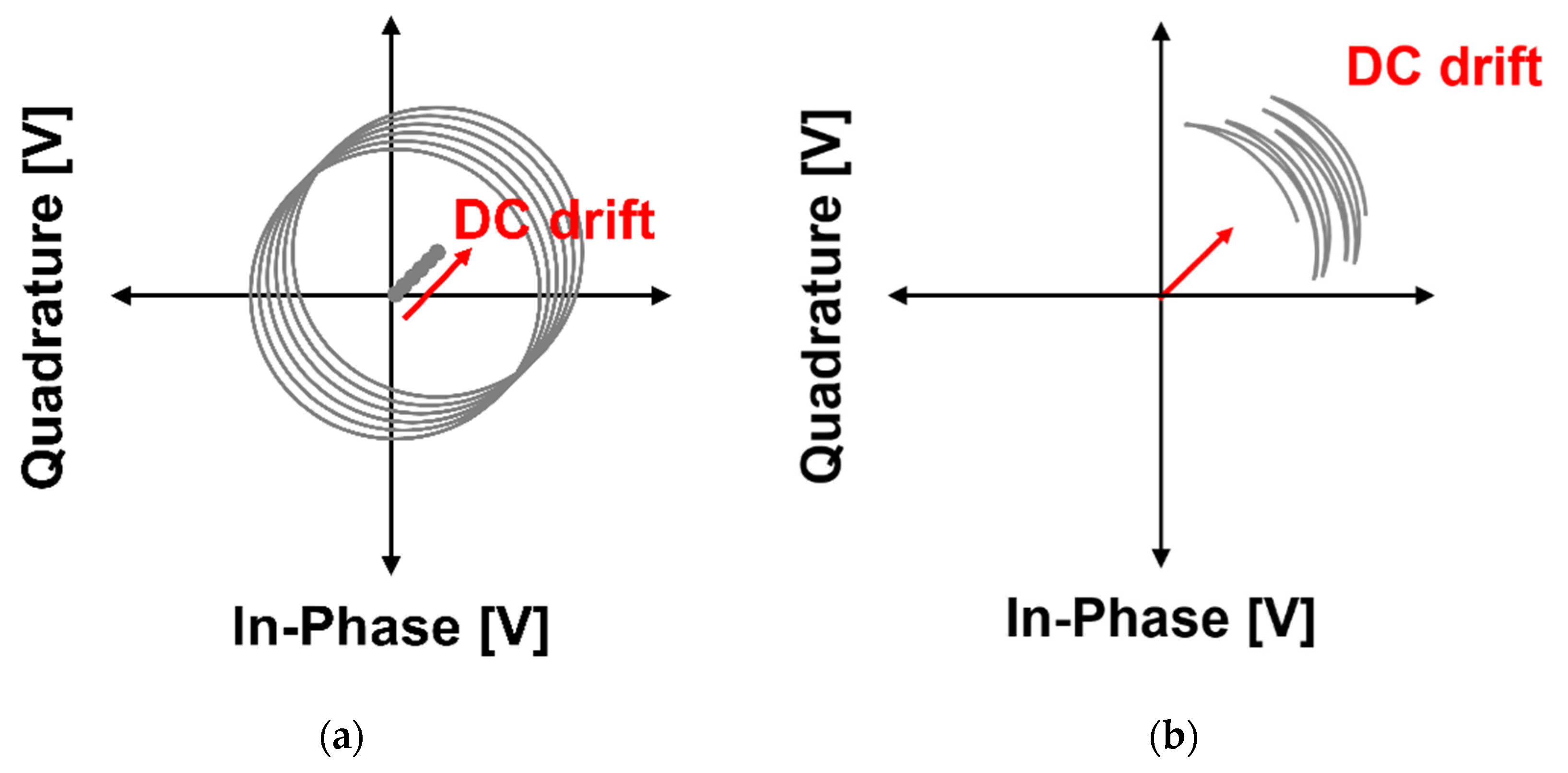
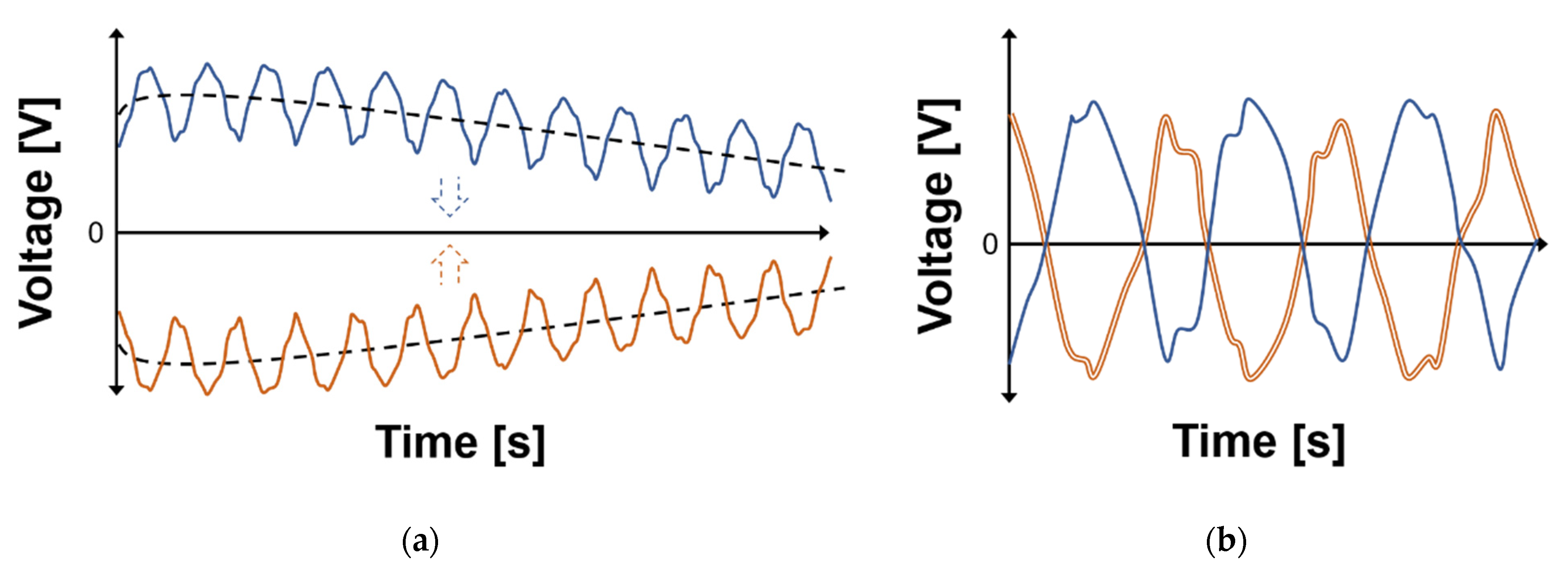
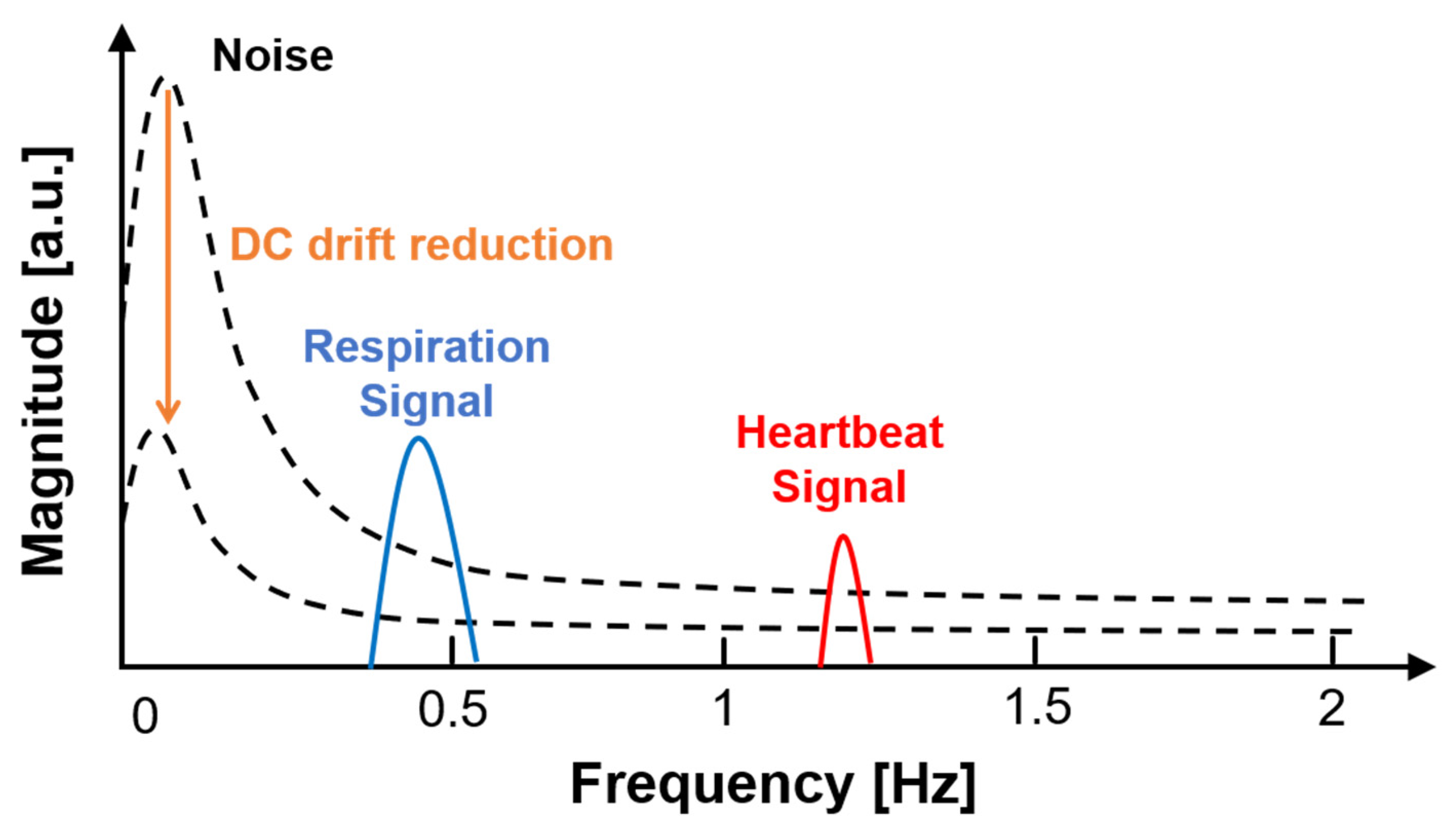
2.1. DC Offset and Drift in the CW Radar
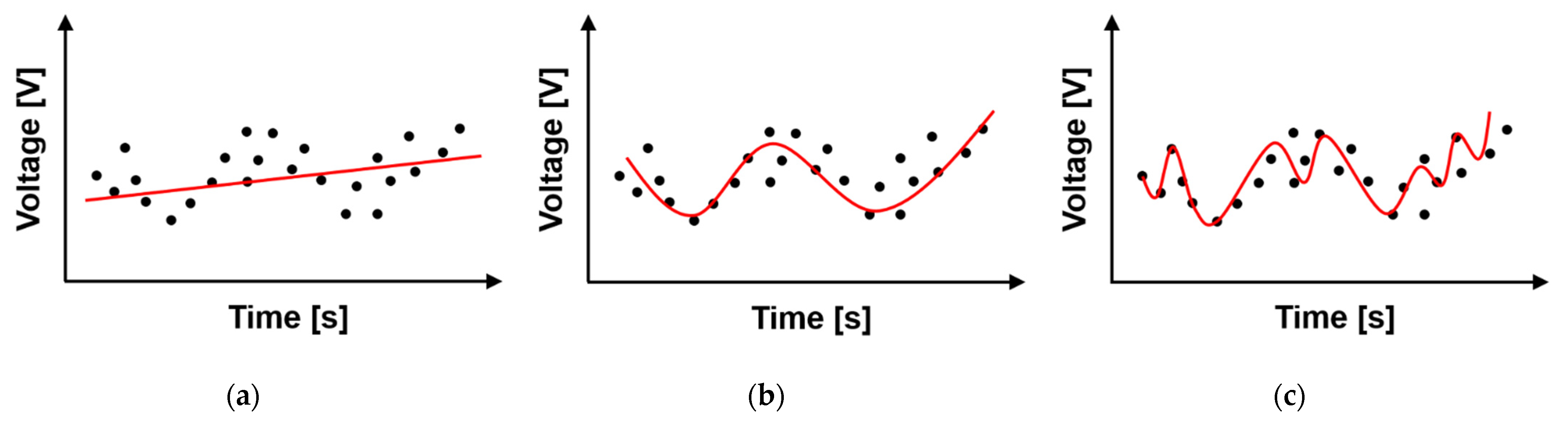
2.2. Detrending Technique Based on Polynomial Fitting in Time Domain
2.3. Signal Processing of the CW Radar, including the Proposed Technique
3. Simulation Results
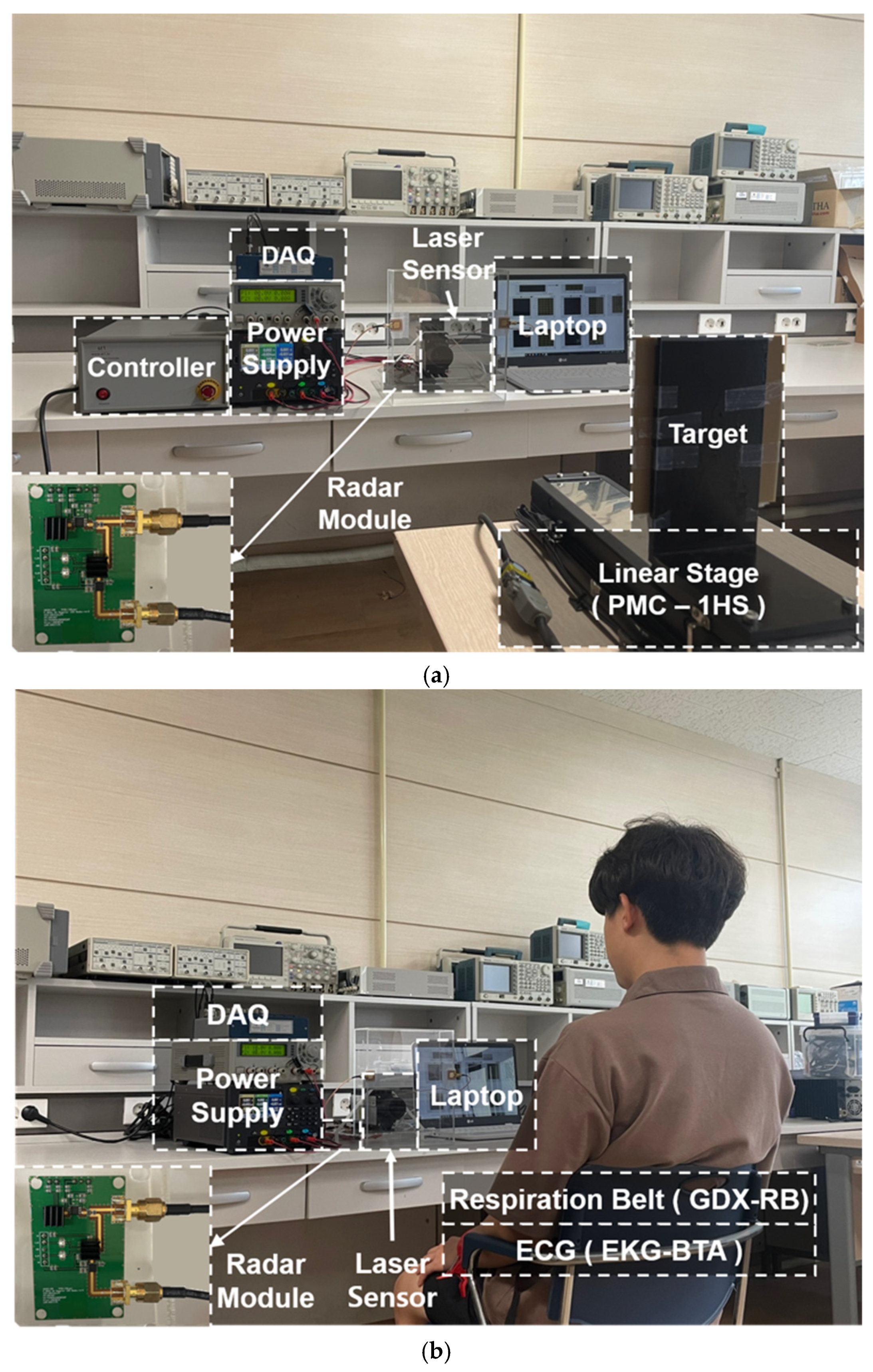
4. Experiment Setup
4.1. CW Radar Sensor Module
4.2. Data Acquisition from the Radar and Reference Sensors
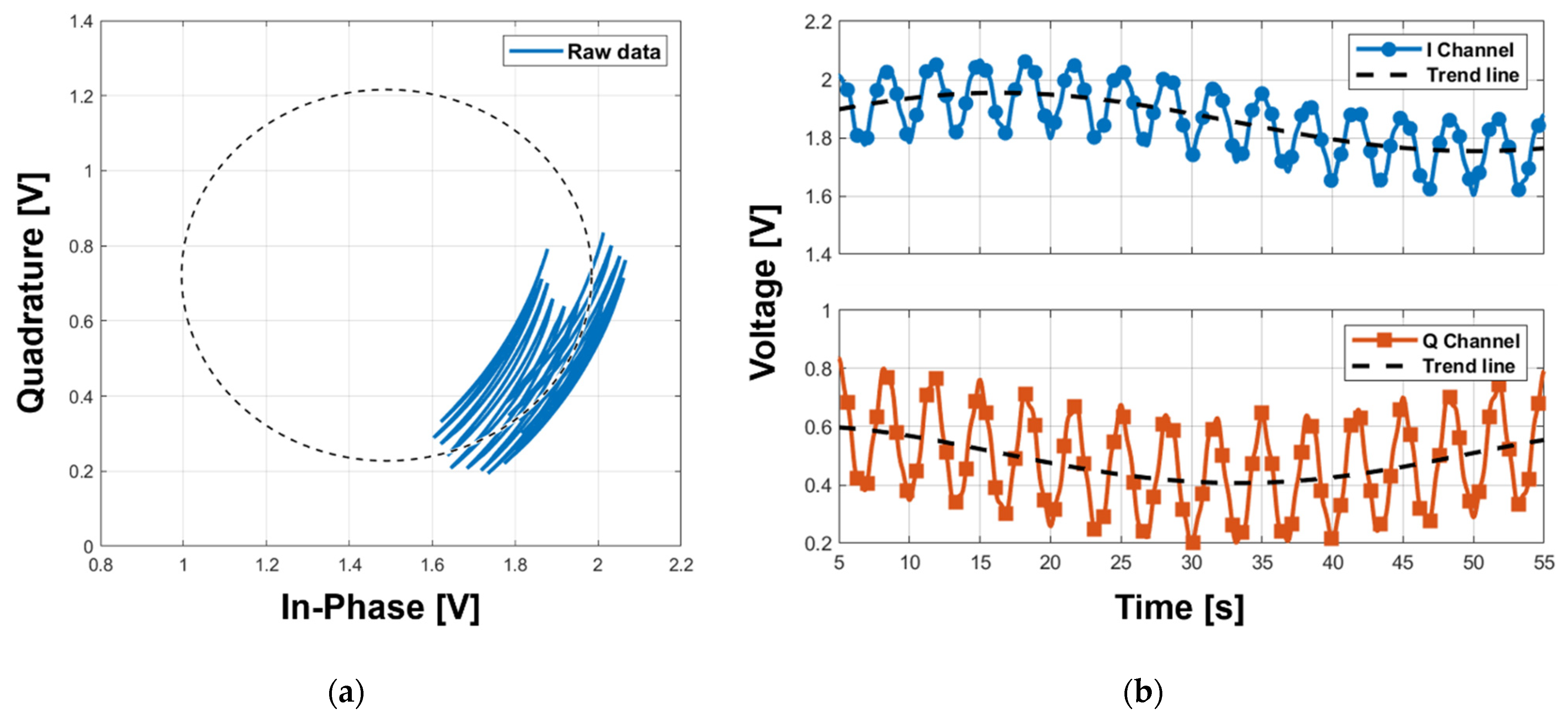
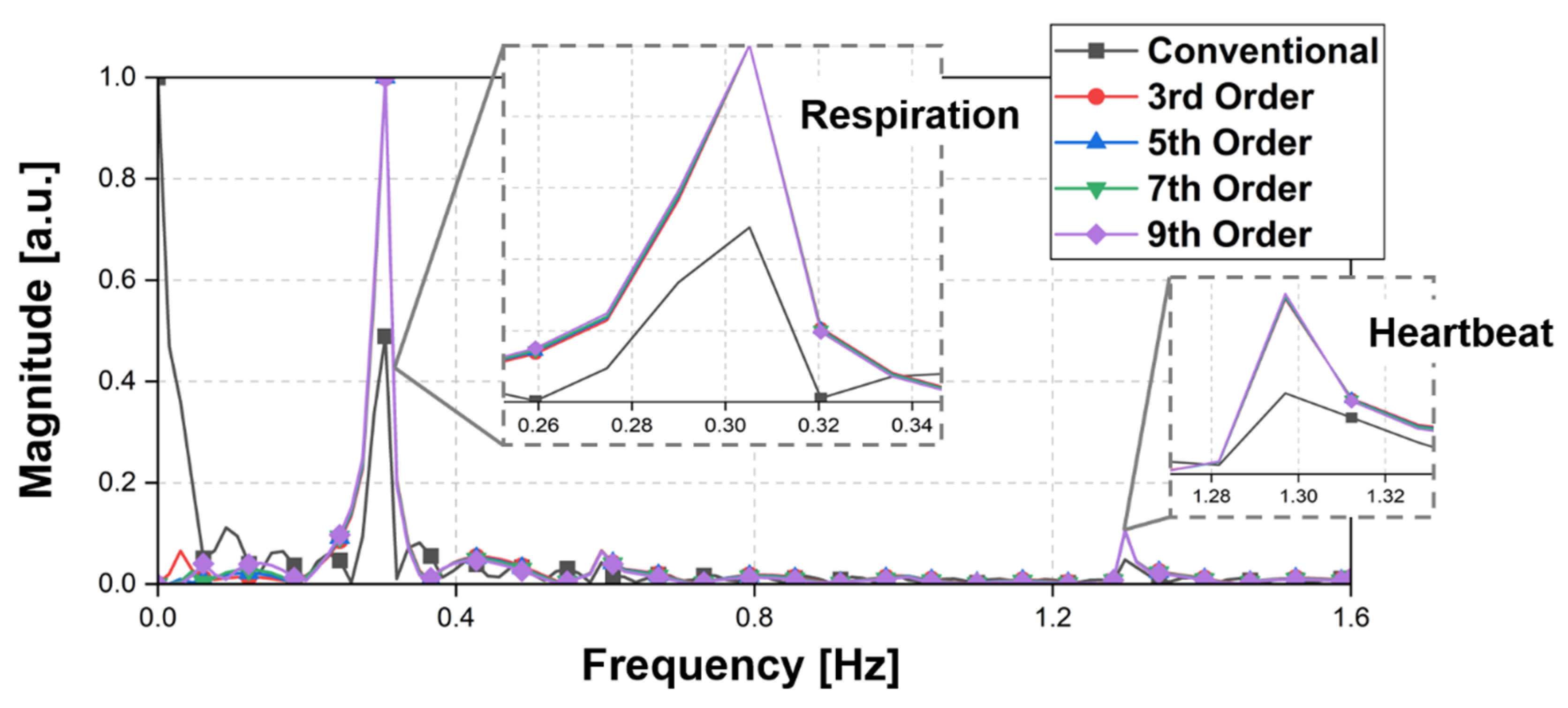
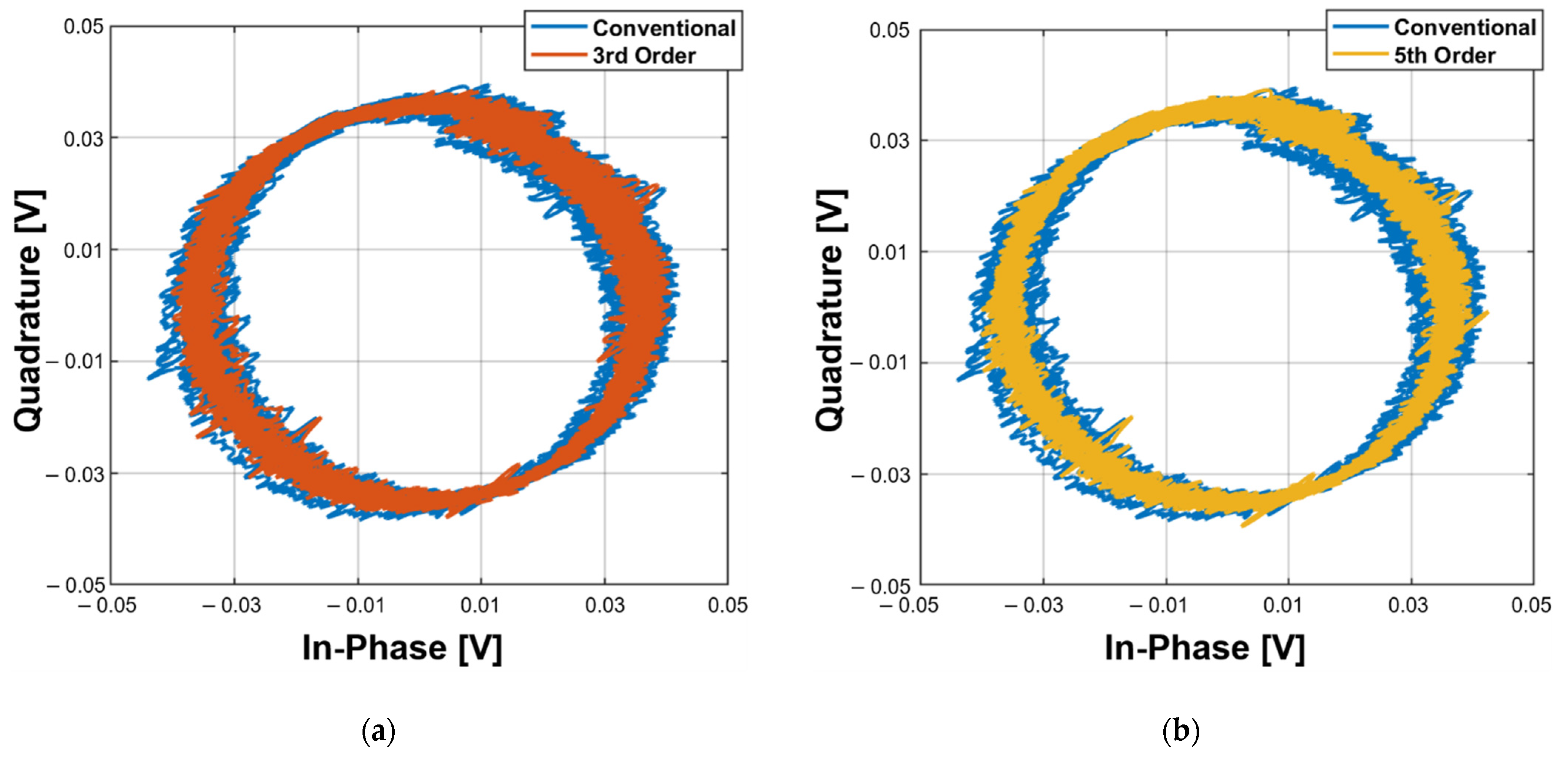
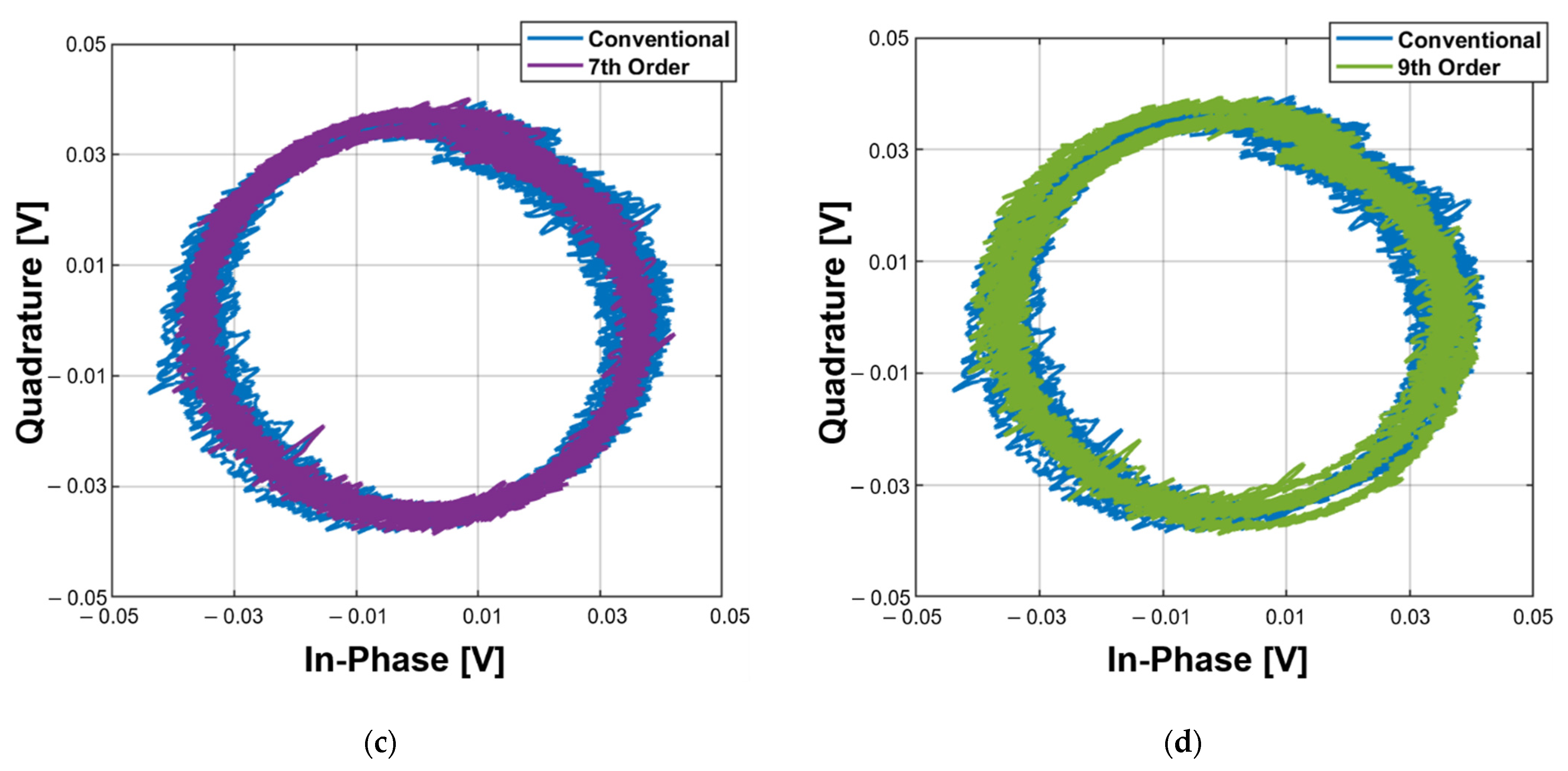
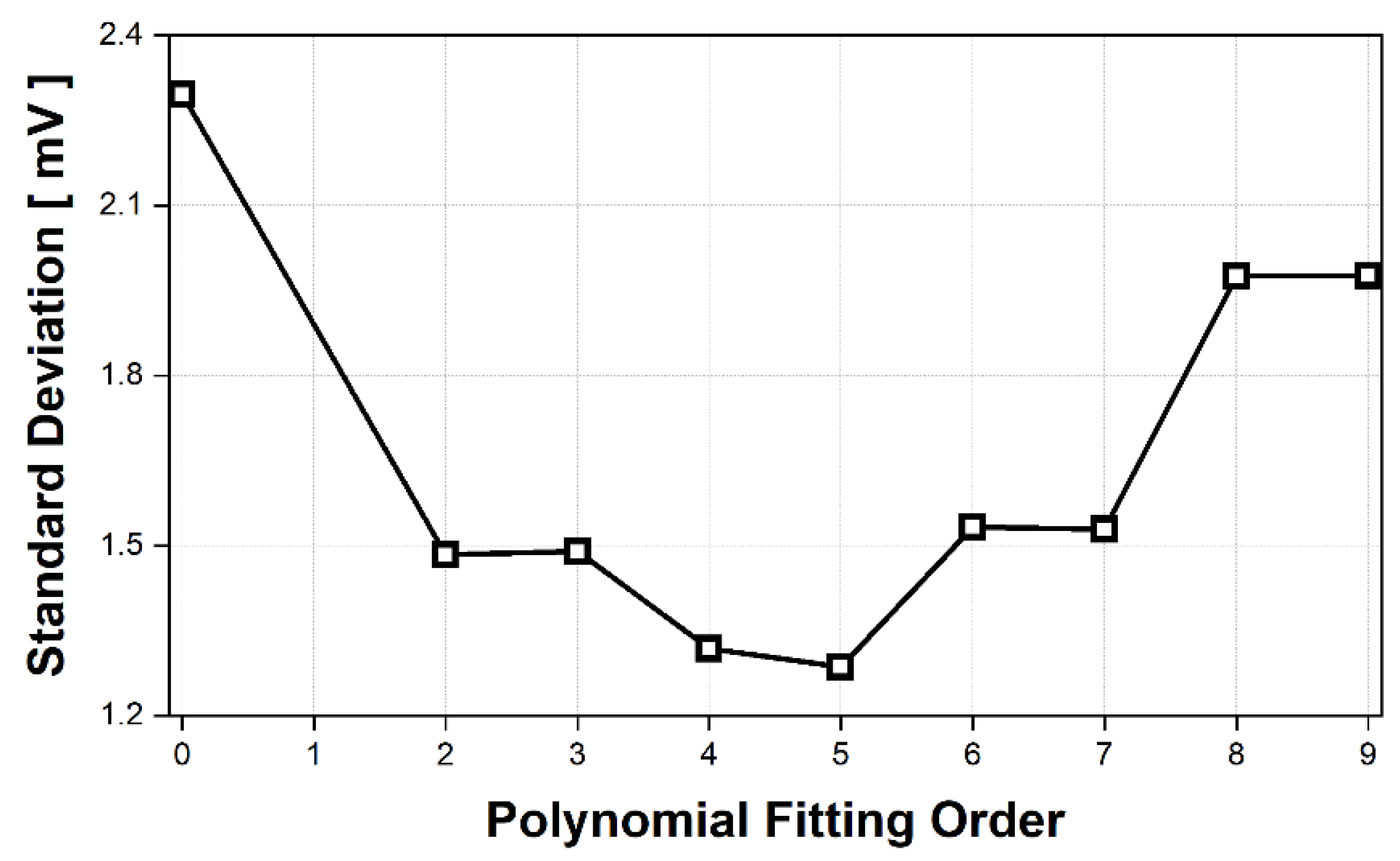
5. Measurement Results and Discussions
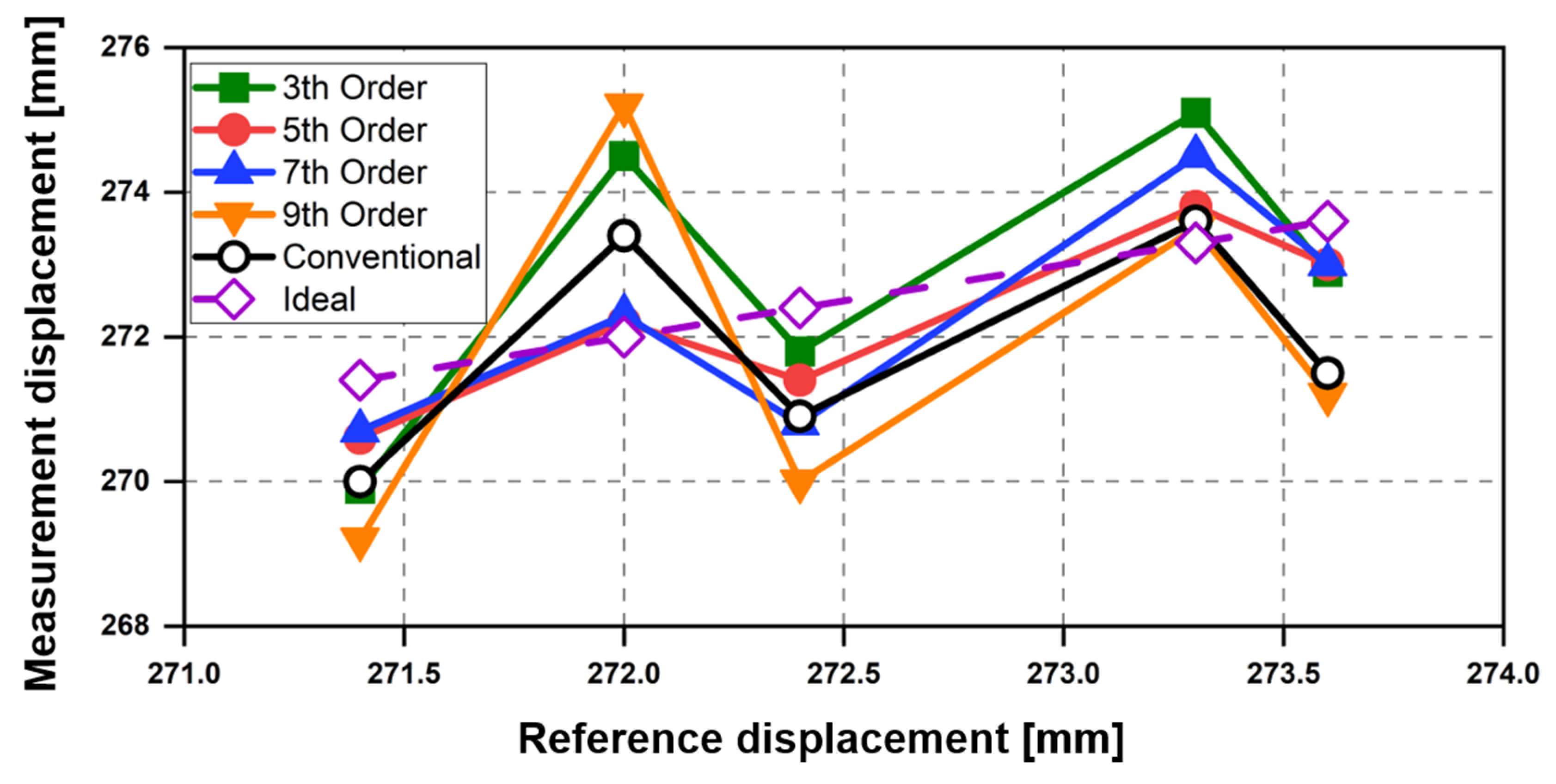
5.1. Displacement Measurement
5.2. Vital Signal Detection
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwata, Y.; Thanh, H.T.; Sun, G.; Ishibashi, K. High accuracy heartbeat detection from CW-Doppler radar using singular value decomposition and matched filter. Sensors 2021, 21, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constanzo, S. Software-defined Doppler radar sensor for human breathing detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Jeong, J. Non-contact measurement of human respiration and heartbeat using W-band Doppler radar sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Jang, S.-Y.; Yang, J.-R. Peak detection algorithm for vital sign detection using Doppler radar sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, G.; Oh, J.; Yang, J. 915-MHz Continuous-wave Doppler radar sensor for detection of vital signs. Electronics 2019, 8, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyun, E.; Jin, Y.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Yang, J.-R. Machine learning-based human recognition scheme using a Doppler radar sensor for in-vehicle applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lin, J. A Review on recent advances in Doppler radar sensors for noncontact healthcare monitoring. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 2046–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennarelli, G.; Ludeno, G.; Soldovieri, F. Real-time through-wall situation awareness using a microwave Doppler radar sensor. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, H.; Zhang, L.; Gu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, X. Noncontact sleep stage estimation using a CW Doppler radar. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2018, 8, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.Y.; Park, J.-H.; Yang, J.-R. Vital-signs detector based on frequency-shift keying radar. Sensors 2020, 20, 5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Karp, T.; Muňoz-Ferreras, J.-M.; Gómez-García, R.; Li, C. A spectrum-efficient FSK radar technology for range tracking of both moving and stationary human subjects. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 5406–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Yang, J.-R. Two-tone continuous-wave Doppler radar based on envelope detection method. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 3146–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuutti, J.; Paukkunen, M.; Aalto, M.; Eskelinen, P.; Sepponen, R.E. Evaluation of a Doppler radar sensor system for vital signs detection and activity monitoring in a radio-frequency shielded room. Measurement 2015, 68, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-R.; Kim, D.-W.; Hong, S. A calibration method of a range finder with a six-port network. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2007, 17, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gao, X.; Yavari, E.; Zakrzewski, M.; Cao, X.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Data-based quadrature imbalance compensation for a CW Doppler radar system. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, Y. Quadrature frequency-group radar and its center estimation algorithms for small vibration displacement. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Yang, J.-R. Multiphase continuous-wave Doppler radar with multiarc circle fitting algorithm for small periodic displacement measurement. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewski, M.; Raittinen, H.; Vanhala, J. Comparison of center estimation algorithms for heart and respiration monitoring with microwave Doppler radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Radius correction technique for Doppler radar noncontact periodic displacement measurement. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Singh, A.; Yavari, E.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O. Non-contact displacement estimation using Doppler radar. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 1602–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V. Arctangent demodulation with DC offset compensation in quadrature Doppler radar receiver systems. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, A.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Lubecke, V. DC information preservation for cardiopulmonary monitor utilizing CW Doppler radar. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008; pp. 1246–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xiong, Y.; Ren, Z.; Gu, C.; Peng, Z. Ultra-micro vibration measurement method using CW Doppler radar. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sensing, Measurement & Data Analytics in the era of Artificial Intelligence (ICSMD), Xi’an, China, 15–17 October 2020; pp. 235–237. [Google Scholar]
- Svitek, R.; Raman, S. DC offsets in direct-conversion receivers: Characterization and implications. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2005, 6, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, D. Experimental characterization process of DC-offset performance for multiple CW Doppler radar. In Proceedings of the International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers and Communications (ITC-CSCC), Jeju, Korea, 23–26 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, H.; Chou, C.; Lin, C.; Yu, C.; Huang, T.; Chuang, H. A 60-Ghz CMOS direct-conversion doppler radar RF sensor with clutter canceller for single-antenna noncontact human vital-signs detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–19 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Wang, Z.; Tang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Huangfu, J.; Ran, L. DC offset and low frequency noise compensation for direct-conversion receiver in pulse compression radar. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Antenna Technology (iWAT), Hong Kong, China, 7–9 March 2011; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Q.; Chen, L.; An, K.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Ye, D.; Huangfu, J.; Li, C.; Ran, L. Doppler vital signs detection in the presence of large-scale random body movements. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 4261–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, D. Control the value of I/Q DC-bias and gain from the experimental result of 24GHz Doppler radar. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 1368–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.; Lubecke, V.; Boric-Lubecke, O.; Host-Madsen, A. Center tracking quadrature demodulation for a Doppler radar motion detector. In Proceedings of the IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–8 June 2007; pp. 1323–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.; Yamada, S.; Lubecke, V. Measurement method for imbalance factors in direct-conversion quadrature radar systems. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2007, 17, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, B.; Knill, C.; Schindler, D.; Waldschmidt, C. IQ-imbalance compensation for wideband OFDM-radar. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Copenhagen, Denmark, 15–20 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.; Ma, C.; Gu, Z.; Lv, Q.; Chen, J.; Ye, D.; Huangfu, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Ran, L. Wireless hand gesture recognition based on continuous-wave Doppler radar sensors. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 4012–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-I.; Yang, J.-R. 5.8-GHz patch antenna with enhanced defected ground structure for size reduction and increased bandwidth. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2021. [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, I.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Yang, J.-R. Detrending Technique for Denoising in CW Radar. Sensors 2021, 21, 6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196376
Lee I-S, Park J-H, Yang J-R. Detrending Technique for Denoising in CW Radar. Sensors. 2021; 21(19):6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196376
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, In-Seong, Jae-Hyun Park, and Jong-Ryul Yang. 2021. "Detrending Technique for Denoising in CW Radar" Sensors 21, no. 19: 6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196376
APA StyleLee, I.-S., Park, J.-H., & Yang, J.-R. (2021). Detrending Technique for Denoising in CW Radar. Sensors, 21(19), 6376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21196376






