Design and Calibration of an Instrumented Seat Post to Measure Sitting Loads While Cycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
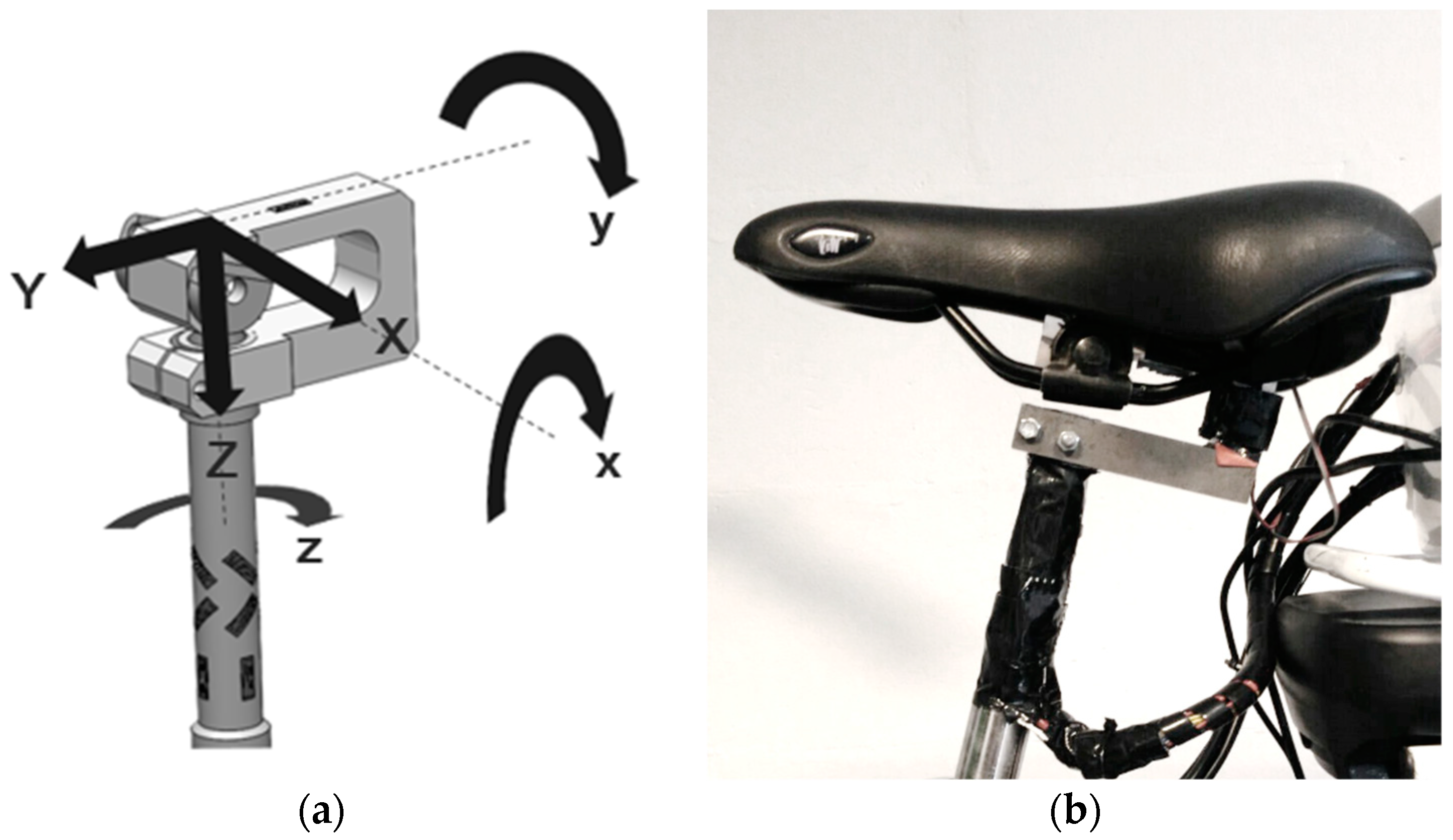
2.1. Seat Post Design

2.2. Data Processing
2.3. Testing
3. Results
3.1. Output Accuracy
3.2. Output Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Output Accuracy
4.2. Output Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanwalleghem, J.; Mortier, F.; De Baere, I.; Loccufier, M.; Van Peapegem, W. Instrumentation of a racing bicycle for outdoor field testing and evalutation of the cyclist’s comfort perception. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Experimental Mechanics (ICEM15), Porto, Portugal, 22–27 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lepine, J.; Champoux, Y.; Drouet, J.M. Road bike comfort: On the measurement of vibrations induced to cyclist. Sports Eng. 2014, 17, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelland-Leblanc, J.P.; Lépine, J.; Champoux, Y.; Drouet, J.M. Using power as a metric to quantify vibration transmitted to the cyclist. Procedia Eng. 2014, 72, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.D. Clinical syndromes associated with bicycle seats. Clin. Sports Med. 1994, 13, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mellion, M.B. Bicycling injuries: Prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. In Office Sports Medicine; Hanley & Belfus: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, K.V.; Bovim, G. Impotence and nerve entrapment in long distance amateur cyclists. Acta Nuerol. Scand. 1997, 95, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennet, L.; Kavner, D.; Lee, B.K.; Trainor, F.A. Shear vs. pressure as causative factors in skin blood flow occlusion. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1979, 60, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, D.A. Comparative effects of posture on pressure and shear at the body-seat interface. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1992, 29, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edsberg, L.E.; Mates, R.E.; Baier, R.E.; Lauren, M. Mechanical characteristics of human skin subjected to static versus cyclic normal pressures. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1999, 36, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hug, F.; Bendahan, D.; Le Fur, Y.; Cozzone, P.J.; Grelot, L. Heterogeneity of muscle recruitment pattern during pedaling in professional road cyclists: A magnetic resonance imaging and electromyography study. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 93, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jammes, Y.; Arbogast, S.; Faucher, M.; Montmayeur, A.; Tagliarinin, F.; Robinet, C. Interindividual variability of surface EMG changes during cycling exercise in healthy humans. Clin. Physiol. 2001, 21, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolourchi, F.; Hull, M.L. Measurement of Rider Induced Loads during Simulated Bicycling. Int. J. Sport Biomech. 1985, 1, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, C.; Hull, M.L. The effect of rider weight on rider-induced loads during common cycling situations. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoux, Y.; Vanwallenghem, J.; Drouet, J.M. Dynamic calibration of an instrumented bike brake hood in measuring power absorbed by the hands. Procedia Eng. 2015, 112, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilson, C.; Bush, T.R. Interface forces on the seat during a cycling activity. Clin. Biomech. 2007, 22, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newmiller, J.; Hull, M.L.; Zajac, F.E. A mechanical decoupled two force component bicycle pedal dynamometer. J. Biomech. 1988, 21, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mornieux, G.; Zameziati, K.; Mutter, E.; Bonnefoy, R.; Belli, A. A cycle ergometer mounted on a standard force platform for three-dimensional pedal forces measurement during cycling. J. Biomech. 2005, 39, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandford, A. Calibration for the Sensitivity Matrix of the Collins Strain Gauge Balance. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.1019.5683&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Nouri, N.M.; Mostafapour, K.; Kamran, M.; Bohadori, R. Design methodolgy of a six-component balance for measuring forces in water tunnel tests. Measurement 2014, 58, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.; Fairlie, B.D. A wind tunnel strain gauge balance calibration system. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Australian Fluid Mechanics Conference, Sydney, Australia, 10–15 December 1995. [Google Scholar]





| Lateral (X) | Anterior (Y) | Normal (Z) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of body weight applied to the seat post | 4–5% | 11–12% | 49–52% |
| Seat post loading for a cyclist of 100 kg | 40–50 N | 110–120 N | 490–520 N |
| Load | Std. Error Percentage Full Scale (FS) | Max. Error Percentage FS |
|---|---|---|
| Anterior force | 0.15 | 0.37 |
| Normal force | 0.34 | 1.55 |
| Lateral force | 1.14 | 0.46 |
| Frontal torque | 3.02 | 1.43 |
| Transversal torque | 0.58 | 0.25 |
| Sagittal torque | 0.28 | 0.51 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sien, D.; Jordi, D.; Juwet, M.; Shariatmadar, K.; Versteyhe, M. Design and Calibration of an Instrumented Seat Post to Measure Sitting Loads While Cycling. Sensors 2020, 20, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051384
Sien D, Jordi D, Juwet M, Shariatmadar K, Versteyhe M. Design and Calibration of an Instrumented Seat Post to Measure Sitting Loads While Cycling. Sensors. 2020; 20(5):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051384
Chicago/Turabian StyleSien, Dieltiens, D’hondt Jordi, Marc Juwet, Keivan Shariatmadar, and Mark Versteyhe. 2020. "Design and Calibration of an Instrumented Seat Post to Measure Sitting Loads While Cycling" Sensors 20, no. 5: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051384
APA StyleSien, D., Jordi, D., Juwet, M., Shariatmadar, K., & Versteyhe, M. (2020). Design and Calibration of an Instrumented Seat Post to Measure Sitting Loads While Cycling. Sensors, 20(5), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051384






