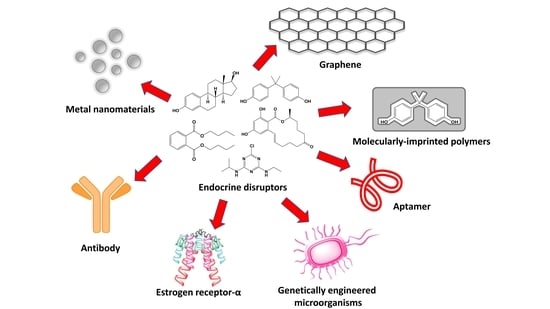
Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Detection of Endocrine Disruptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Analyte | IUPAC Name | Chemical Structure | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Source | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17β-estradiol (E2) | (8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-Methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol | 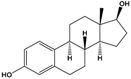 | 272.388 | endogenous hormone, medication | [13] |
| Acetamiprid (AAP) | N-[(6-chloro-3-pyridyl)methyl]-N′-cyano-N-methyl-acetamidine | 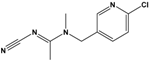 | 222.678 | insecticide | [14] |
| Atrazine (ATZ) | 6-chloro-N2-ethyl-N4-(propan-2-yl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine | 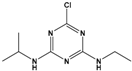 | 215.69 | herbicide for grassy weeds in crops | [15] |
| Pentabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) | 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether | 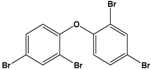 | 485.79 | flame retardant | [16] |
| Bisphenol A (BPA) | 4,4′-(propane-2,2-diyl)diphenol | 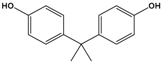 | 228.291 | precursor to polycarbonates, plastic and epoxy resins | [17] |
| Carbendazim (CBZ) | methyl 1H-benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate | 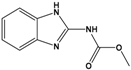 | 191.187 | fungicide | [18] |
| Cortisol | 11β,17α,21-Trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione | 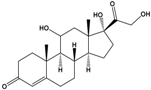 | 362.46 | endogenous hormone, medication | [19] |
| Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) | Dibutyl benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate | 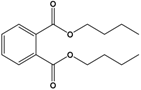 | 278.348 | plasticizer | [20] |
| Dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT) | 1-chloro-4-[2,2,2-trichloro-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethyl]benzene | 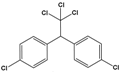 | 354.48 | pesticide | [21] |
| Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate | 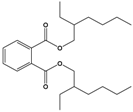 | 390.564 | plasticizer | [22] |
| Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) | (5R,8S,11R,12S,15S,18S,19S,22R)-15-[3-(diaminomethylideneamino)propyl]-18-[(1E,3E,5S,6S)-6-Methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-7-phenylhepta-1,3-dienyl]-1,5,12,19-tetramethyl-2-methylidene-8-(2-methylpropyl)-3,6,9,13,16,20,25-heptaoxo-1,4,7,10,14,17,21-heptazacyclopentacosane-11,22-dicarboxylic acid | 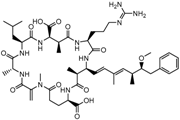 | 995.189 | cyanobacteria toxin | [23] |
| Norfluoxetine (NorFLX) | (S)-3-Phenyl-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propan-1-amine | 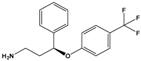 | 295.305 | antidepressant | [24] |
| 3,3’,4,4’-tetrachlorobiphenyl (PCB-77) | 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachloro-1,1′-biphenyl | 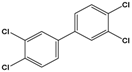 | 291.99 | flame retardants, plasticizers, dielectric and heat transfer fluids | [25] |
| Testosterone | (8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-Hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one | 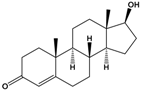 | 288.431 | endogenous hormone, anabolic steroid | [26] |
| Tributyltin hydride | tributylstannane | 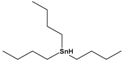 | 291.06 | precursor in organic synthesis | [27] |
| Zearalenone (ZEN) | (3S,11E)-14,16-Dihydroxy-3-methyl-3,4,5,6,9,10-hexahydro-1H-2-benzoxacyclotetradecine-1,7(8H)-dione | 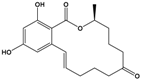 | 318.369 | mycotoxin | [28] |
2. Basic Elements of EIS-Based Sensors
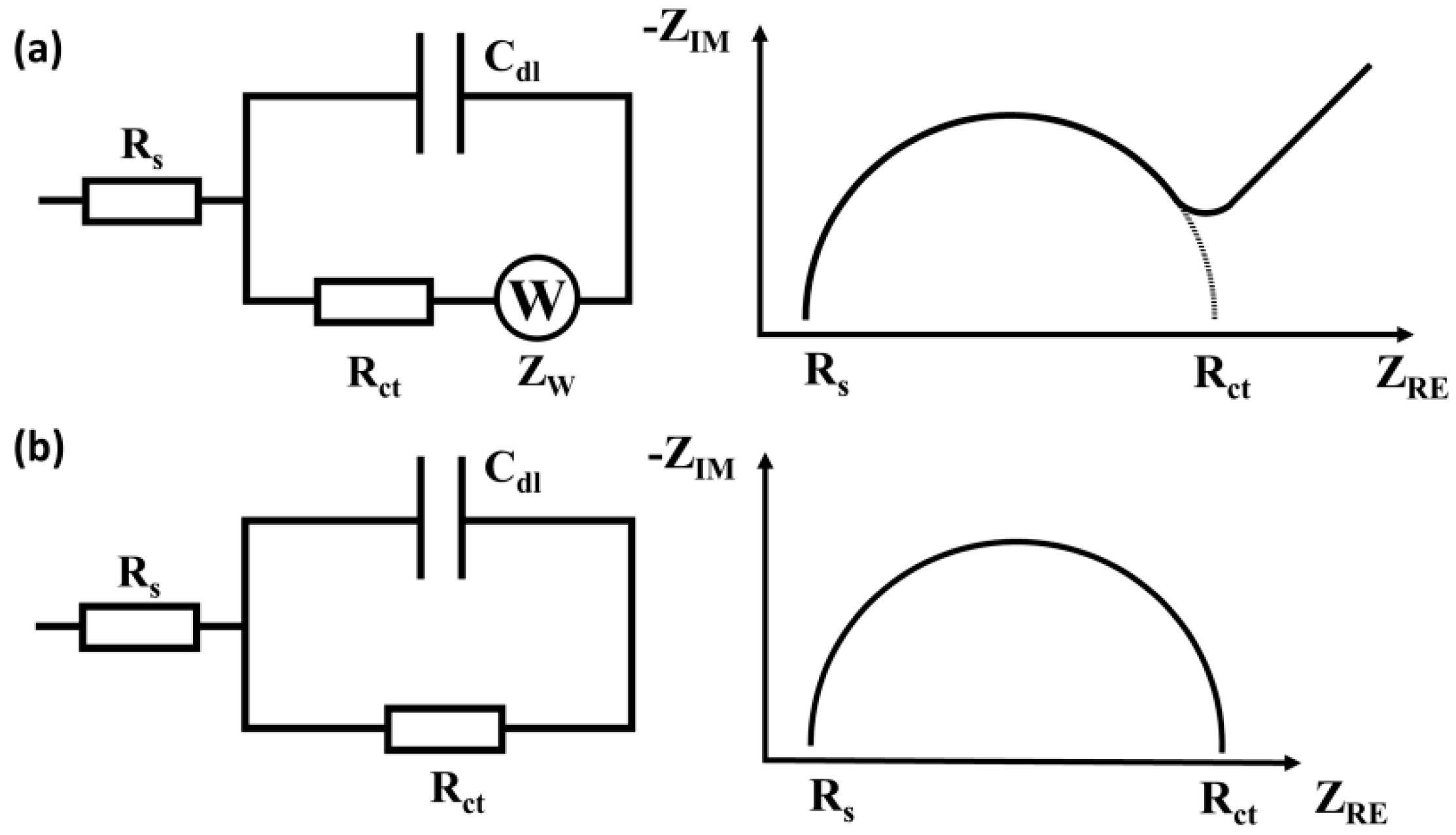
2.1. Principle of EIS Detection
2.2. Types of Impedance Sensors
2.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy for Biosensing Applications
3. EIS Sensors for EDs Detection
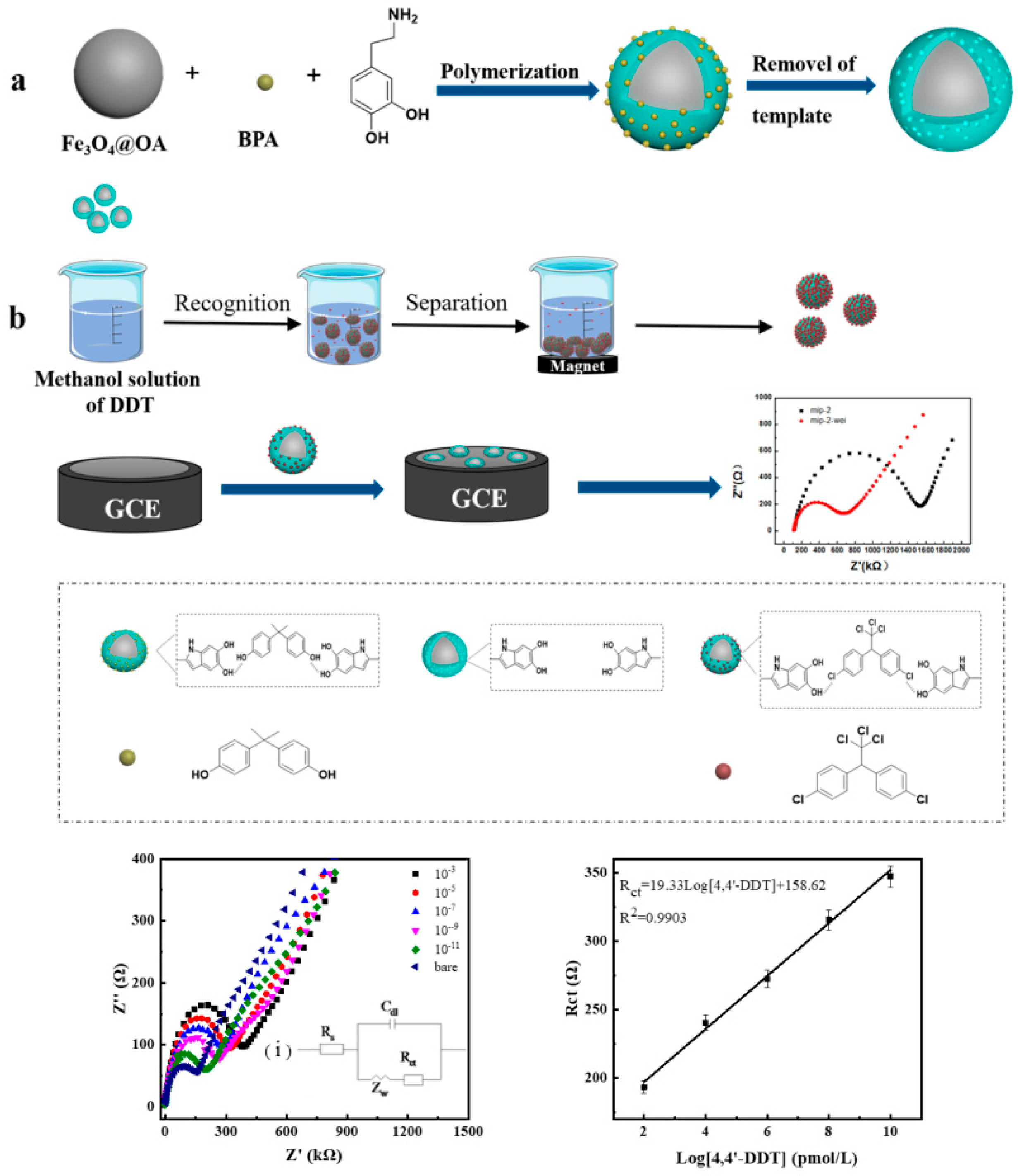
3.1. Molecular-Imprinted Polymer Sensors
3.2. Metal Composite-Based Sensors
3.3. Graphene, Carbon-Nanotubes and Cyclodextrins Based Sensors
4. EIS Biosensors for the Detection of EDs
4.1. Immunosensors
4.2. Aptamer-Based Biosensors
| Analyte | Platform | Linear Range | LOD | Real Sample | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | mAb/11-MUA/Ag wire electrode | 1–200 pg/mL | 1 pg/mL | water | Fast response time; Label-free; Low sample volume; High sensitivity | Low stability compared to MIP and aptamer-based systems; Risk of cross-reactivity | [61] |
| E2 | Ag-ZnONRs-16-PHA-mAb-E2 | 0.1–200 pg/mL | 0.1 pg/mL | tap and packaged water | Label-free; Low sample volume; High sensitivity; Fast response time | Multiple preparation and optimization steps | [67] |
| ATZ | GCE/MNF/MPA/EDC-NHS/Ab | 1 zg/mL–1 μg/mL | 0.22 zg/mL | water | Label-free; High sensitivity; Simple protocol; Wide linear range | Requires blocking of non-specific sites | [68] |
| ATZ | Ab-SPA-MWCNT-ZnO/GCE | 10 zM–1 µM | 5.368 zM | - | Label-free; Low detection limit; Wide linear range | Multiple preparation steps; Requires blocking of non-specific sites | [62] |
| BDE-47 | Ab/11-MUA/Au electrode | 0.01–0.40 μg/mL | 1.3 ng/mL | - | Facile antibody regeneration | Narrow linear ranges; Risk of non-specific binding | [69] |
| NorFLX | 0.02–0.32 μg/mL | 8.5 ng/mL | - | [69] | |||
| BPA | Ab-nano-CP/GCE | 1–100 ng/mL | 0.3 ± 0.07 ng/mL | human serum | Label-free | Narrow linear ranges | [70] |
| Cortisol | Ab/β-MnO2 CNs/GCE | 0.1 pM–1500 pM | 0.023 pM | human sweat and saliva | High stability; Wide linear range | Requires blocking of non-specific sites; Requires sample deoxygenation | [71] |
| DBP | antigen/CS/MWCNTs@GONRs/GCE; Ab2-AuNP conjugate | 5–500 ng/L | 7 ng/mL | pure, tap, pond and river water | Low detection limit; Low sample volume | Risk of non-specific binding | [72] |
| MC-LR | Ab/MC-LR/3D GF electrode | 0.05–20 μg/L | 0.05 μg/L | tap water | High sensitivity; Low detection limit | Additional preparation steps for the electrode materials; Low stability of bound antibodies | [73] |
| ZEN | Ab2@ssCo3O4/ZEN/Ab1/HA-TiO2 MC/GCE | 0.1 fg/mL–10 pg/mL | 33 ag/mL | beer | Low detection limit; Use of enzyme mimic | Low resolution of sensing system; Requires redox label | [74] |
| ZEN | peptide@Tyr-RMC, Ab/poly(Gly)/AuNCs/CNHs/GCE | 10−6–10 ng/mL | 10−6 ng/mL | soybean sauce | Fast response time; Wide linear range | Multiple preparation and optimization steps; Requires blocking of non-specific sites; Requires redox label | [63] |
| Analyte | Platform | Linear Range | LOD | Real Samples | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | Apt/dendritic Au/BDD electrode | 1 × 10−14–1 × 10−9 M | 5 × 10−15 M | river water | High sensitivity; High specificity | - | [75] |
| E2 | Apt/CDs/SPCE | 1.0 × 10−7–1.0 × 10−12 M | 0.5 × 10−12 M | river water | High selectivity; High stability | Additional preparation steps for the electrode materials | [76] |
| AAP | MCH/Apt/AuNPs/Au electrode | 5–600 nM | 1 nM | wastewater, tomatoes | Simple modification protocol | Relatively low sensitivity; Relatively narrow linear range | [77] |
| AAP | MCH/Apt/Au/MWCNT-rGONR/GCE | 5 × 10−14–1 × 10−5 M | 1.7 × 10−14 M | - | Wide linear range | Long preparation procedure | [78] |
| AAP | MCH/Apt/GOPTS/PtNPs/PMMA/IDE | 10 pM–100 nM | 1 pM | tap and bottled mineral water | High sensitivity | Long incubation time (60min) due to large custom-made electrochemical cell | [79] |
| ATZ | 100 pM–1 μM | 10 pM | [79] | ||||
| BPA | Apt-Au/AOO, capacitive biosensor | 1 × 10−9–1 × 10−7 M | 100 pM | - | High sensitivity; Microfluidic system | Requires custom-made electrodes; Single-use device | [64] |
| BPA | Apt/Cu2+/PPY-NTA/GCE | 10−11–10−6 M | 1.24 × 10−12 M | - | Simple modification protocol; Wide linear range | - | [80] |
| BPA | MCH/Apt/Au-NPs/BDD | 1 × 10−14–1 × 10−9 M | 7.2 × 10−15 M | spiked milk | Low detection limit; Simple modification protocol | [81] | |
| BPA | Apt/interdigitated aluminum microelectrode, capacitive biosensor | 1 fM–1 pM | 10 fM | human serum | Fast response time (20s); High sensitivity; Low sample volume | - | [65] |
| BPA | PPY/BPA@p-63/AuNP/GCE | 0.5 fM–5 pM | 80 aM | fresh milk, milkpowder, tap and pretreated water in baby glass | Low detection limit; Short assay time | - | [52] |
| BPA | Apt/IDE, capacitive biosensor | 1 fM–10 pM | 152.93 aM | - | Fast response time (20s); Low detection limit | - | [66] |
| BPA | MB-DNA/MWCNTs-CS/PdNPs/C60/GCE | 0.5–25 μM | 0.35 μM | - | Detection of DNA damage induced by ED | Relatively low sensitivity; Narrow linear range | [82] |
| CBZ | MCH/Apt/Au electrode | 10 pg/mL–10 ng/mL | 8.2 pg/mL | mango juice, soya milk, tomato, plum | Simple modification protocol | Long preparation time | [83] |
| CBZ | MCH/Apt/AuNPs/1-AP-CNHs/GCE | 1–1000 pg/mL | 0.5 pg/mL | lettuce andorange juice | High selectivity | Long preparation time | [84] |
| DEHP | Apt/AuNPs/MCH/Au | 7.629 pg/mL–2 µg/mL | 0.103 pg/mL | tap water | High sensitivity; Low detection limit | - | [85] |
4.3. Estrogen Receptor-Based Biosensors
4.4. Enzyme-Based Biosensors
4.5. Peptide-Based Biosensors
4.6. Microbial Biosensors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Environmental causes of cancer: Endocrine disruptors as carcinogens. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedia, C.; Dalmau, N.; Jaumot, J.; Tauler, R. Phenotypic malignant changes and untargeted lipidomic analysis of long-term exposed prostate cancer cells to endocrine disruptors. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, R.; Hatch, E.E.; Palmer, J.R.; Titus, L.; Sampson, J.N.; Xu, X.; Hoover, R.N. Estrogen Metabolism in Postmenopausal Women Exposed In Utero to Diethylstilbestrol. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giulivo, M.; Lopez de Alda, M.; Capri, E.; Barcelo, D. Human exposure to endocrine disrupting compounds: Their role in reproductive systems, metabolic syndrome and breast cancer. A review. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohore, O.E.; Zhang, S. Endocrine disrupting effects of bisphenol A exposure and recent advances on its removal by water treatment systems. A review. Sci. Afr. 2019, 5, e00135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.S.; Fenton, S.E.; Hines, E.P. Endocrine disrupting properties of perfluorooctanoic acid. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, M.; Pfeiffer, E. Chemistry of Natural and Anthropogenic Endocrine Active Compounds. In Endocrine Disruptors—Part I; Metzler, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- Benigni, P.; Thompson, C.J.; Ridgeway, M.E.; Park, M.A.; Fernandez-Lima, F. Targeted High-Resolution Ion Mobility Separation Coupled to Ultrahigh-Resolution Mass Spectrometry of Endocrine Disruptors in Complex Mixtures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintado-Herrera, M.G.; González-Mazo, E.; Lara-Martín, P.A. In-cell clean-up pressurized liquid extraction and gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry determination of hydrophobic persistent and emerging organic pollutants in coastal sediments. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1429, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, R.L.; Escandar, G.M. Multivariate calibration-assisted high-performance liquid chromatography with dual UV and fluorimetric detection for the analysis of natural and synthetic sex hormones in environmental waters and sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, S.; Busetto, M.; Colzani, L.; Clerici, L.; Daverio, D.; Dellavedova, P.; Balzamo, S.; Calabretta, E.; Ubaldi, V. Determination of estrogenic endocrine disruptors in water at sub-ng L−1 levels in compliance with Decision 2015/495/EU using offline-online solid phase extraction concentration coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myridakis, A.; Balaska, E.; Gkaitatzi, C.; Kouvarakis, A.; Stephanou, E.G. Determination and separation of bisphenol A, phthalate metabolites and structural isomers of parabens in human urine with conventional high-pressure liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanczyk, F.Z.; Archer, D.F.; Bhavnani, B.R. Ethinyl estradiol and 17β-estradiol in combined oral contraceptives: Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and risk assessment. Contraception 2013, 87, 706–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Zhang, S.; Tan, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Zeng, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Acetamiprid inhibits testosterone synthesis by affecting the mitochondrial function and cytoplasmic adenosine triphosphate production in rat Leydig cells†. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 96, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveyra, G.R.; Canosa, I.S.; Zanitti, M.; Rodríguez, E.M.; Medesani, D.A. Interference of an atrazine commercial formulation with the endocrine control of ovarian growth exerted by the eyestalks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, I.A. Endocrine-disrupting potential of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) on androgen receptor signaling: A structural insight. Struct. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, L.F.; Coden, M.E.; Berdnikovs, S. Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A (BPA) Triggers Systemic Para-Inflammation and is Sufficient to Induce Airway Allergic Sensitization in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, M.; Zha, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Luo, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Carbamazepine Caused Endocrine-Disrupting Effects on Nontarget Organisms, Chinese Rare Minnows (Gobiocypris rarus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oray, M.; Abu Samra, K.; Ebrahimiadib, N.; Meese, H.; Foster, C.S. Long-term side effects of glucocorticoids. Expert Opin. Drug. Saf. 2016, 15, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Chen, X.; Weng, S.; Xia, T.; Sun, X.; Luo, T.; Li, P. Effects of two environmental endocrine disruptors di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) and mono-n-butyl phthalate (MBP) on human sperm functions in vitro. Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 83, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, A.M.; Sonnenschein, C. Endocrine disruptors: DDT, endocrine disruption and breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 507–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowdhwal, S.S.S.; Chen, J. Toxic Effects of Di-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate: An Overview. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1750368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallia, V.; Ivanova, L.; Eriksen, G.S.; Harper, E.; Connolly, L.; Uhlig, S. Investigation of In Vitro Endocrine Activities of Microcystis and Planktothrix Cyanobacterial Strains. Toxins 2020, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudon Thibeault, A.-A.; Laurent, L.; Vo Duy, S.; Sauvé, S.; Caron, P.; Guillemette, C.; Sanderson, J.T.; Vaillancourt, C. Fluoxetine and its active metabolite norfluoxetine disrupt estrogen synthesis in a co-culture model of the feto-placental unit. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 442, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.R. Endocrine-disrupting actions of PCBs on brain development and social and reproductive behaviors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 19, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, E.M.; Rodriguez, K.M.; Pastuszak, A.W.; Khera, M. Alternatives to Testosterone Therapy: A Review. Sex. Med. Rev. 2018, 6, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Srivastava, A.; Khandelwal, S. Long term impact of the endocrine disruptor tributyltin on male fertility following a single acute exposure. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Habrowska-Górczyńska, D.E.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Zearalenone as an endocrine disruptor in humans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasia, A. Definition of Impedance and Impedance of Electrical Circuits. In Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Its Applications; Lasia, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 7–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. A review on impedimetric biosensors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrattenecker, J.D.; Heer, R.; Melnik, E.; Maier, T.; Fafilek, G.; Hainberger, R. Hexaammineruthenium (II)/(III) as alternative redox-probe to Hexacyanoferrat (II)/(III) for stable impedimetric biosensing with gold electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Capacitive Biosensors and Molecularly Imprinted Electrodes. Sensors 2017, 17, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Kou, J.; Tan, D.; Guo, Z. New trends in the electrochemical detection of endocrine disruptors in complex media. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5913–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
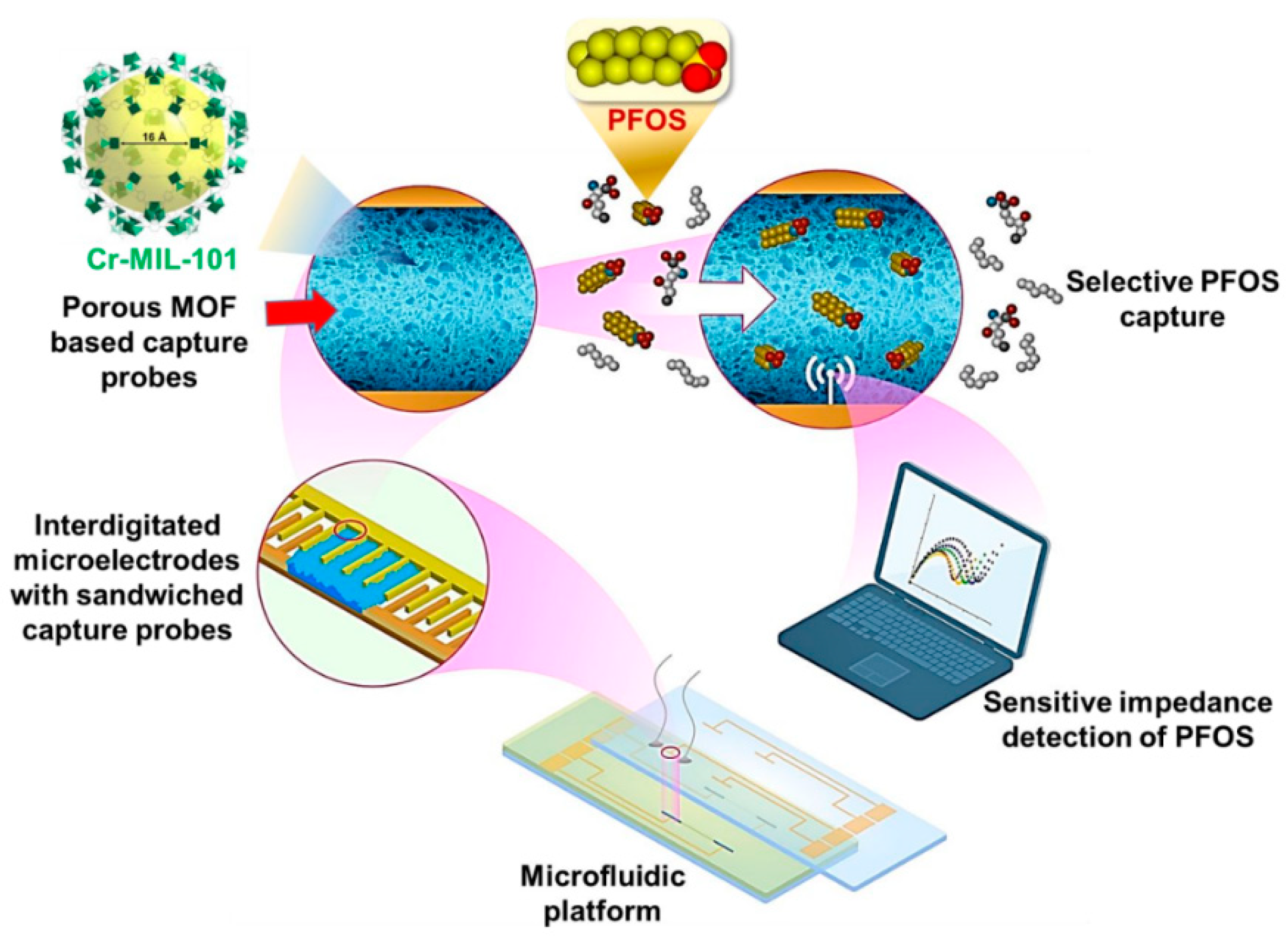
- Luka, G.; Ahmadi, A.; Najjaran, H.; Alocilja, E.; DeRosa, M.; Wolthers, K.; Malki, A.; Aziz, H.; Althani, A.; Hoorfar, M. Microfluidics Integrated Biosensors: A Leading Technology towards Lab-on-a-Chip and Sensing Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 30011–30031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, M.; Roy, S.; Kumar, R.; Wadhwa, S.; Mathur, A.; Dubey, A.K. MnO2 Based Bisphenol-A Electrochemical Sensor Using Micro-Fluidic Platform. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Barpaga, D.; Soltis, J.A.; Shutthanandan, V.; Kargupta, R.; Han, K.S.; McGrail, B.P.; Motkuri, R.K.; Basuray, S.; Chatterjee, S. Metal–Organic Framework-Based Microfluidic Impedance Sensor Platform for Ultrasensitive Detection of Perfluorooctanesulfonate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 10503–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Noir, M.; Lepeuple, A.-S.; Guieysse, B.; Mattiasson, B. Selective removal of 17β-estradiol at trace concentration using a molecularly imprinted polymer. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2825–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Hudson, A.; Foster, C.W.; Eersels, K.; Grinsven, B.V.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Recent Advances in Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensing Platforms for Bioanalyte Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Medical Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; You, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Water-compatible temperature and magnetic dual-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers for recognition and extraction of bisphenol A. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1435, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Liu, A.; Wu, L.; Yu, M.; Wei, W.; Liu, S. Magnetic ferroferric oxide and polydopamine molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposites based electrochemical impedance sensor for the selective separation and sensitive determination of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1095, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, A.; Eissa, A.; Wahdan, T. Molecularly Imprinted Impedimetric Sensor for Determination of Mycotoxin Zearalenone. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Niu, L.; Li, G. Poly(3,6-diamino-9-ethylcarbazole) based molecularly imprinted polymer sensor for ultra-sensitive and selective detection of 17-β-estradiol in biological fluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 104, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che Lah, N.F.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C.; Shoparwe, N.F. The role of porogen-polymer complexation in atrazine imprinted polymer to work as an electrochemical sensor in water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apodaca, D.C.; Pernites, R.B.; Ponnapati, R.; Del Mundo, F.R.; Advincula, R.C. Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film: EIS Sensing of Bisphenol A. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6669–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, G.; Yaman, Y.T.; Abaci, S. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical impedance sensor for sensitive dibutyl phthalate (DBP) determination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 299, 127000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, A.I.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Yu, P.-L.; Al-Bahadly, I.H.; Gooneratne, C.P.; Kosel, J. Rapid and molecular selective electrochemical sensing of phthalates in aqueous solution. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, A.I.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Al-Bahadly, I.H.; Yu, P.L.; Gooneratne, C.P.; Kosel, J. Introducing molecular selectivity in rapid impedimetric sensing of phthalates. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Montevideo, Uruguay, 12–15 May 2014; pp. 838–843. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, S.; Deng, J.; Wei, H. Molecularly imprinted polymers on graphene oxide surface for EIS sensing of testosterone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Gálvez, A.; Mayorga-Matinez, C.C.; Parolo, C.; Pons, J.; Merkoçi, A. Magnetic nanoparticle-molecular imprinted polymer: A new impedimetric sensor for tributyltin detection. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 82, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Amini, M.; Rezaei, B. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical aptasensor for the attomolar detection of bisphenol A. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Deep, A.; Kim, K.-H. Metal organic frameworks for sensing applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 73, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sireesha, M.; Jagadeesh Babu, V.; Kranthi Kiran, A.S.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on carbon nanotubes in biosensor devices and their applications in medicine. Nanocomposites 2018, 4, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Kong, L.-T.; Yang, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.-H.; Huang, X.-J. Electrochemical impedance determination of polychlorinated biphenyl using a pyrenecyclodextrin-decorated single-walled carbon nanotube hybrid. Chem. Comm. 2011, 47, 5340–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsine, Z.; Bizid, S.; Zahou, I.; Ben Haj Hassen, L.; Nasri, H.; Mlika, R. A highly sensitive impedimetric sensor based on iron (III) porphyrin and thermally reduced graphene oxide for detection of Bisphenol A. Synth. Met. 2018, 244, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Cheng, J.; He, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. Detection of di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate through graphene–β-cyclodextrin composites by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Cheng, J.; He, L.; Cai, D.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin/graphene/1,10-diaminodecane composite on glassy carbon electrode and impedimetric method for Di(2-ethyl hexyl) phthalate determination. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 743, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, G.F.; Moore, E.J. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Food Analysis: A Review of Recent Developments. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, C. A label-free electrochemical bisphenol A immunosensor based on chlorogenic acid as a redox probe. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.C.; Bacher, G.; Bhand, S. A label free immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of 17β-Estradiol in water. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, P.; Singh, V.; Vanjari, S.R.K.; Govind Singh, S. Electrospun CNT embedded ZnO nanofiber based biosensor for electrochemical detection of Atrazine: A step closure to single molecule detection. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hong, Z.; Lin, Y.; Dai, H. A mimotope peptide-based dual-signal readout competitive enzyme-linked immunoassay for non-toxic detection of zearalenone. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6972–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Yoo, K.-H. Aptamer-modified anodized aluminum oxide-based capacitive sensor for the detection of bisphenol A. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 073703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wu, J.; Eda, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Zheng, L. Rapid capacitive detection of femtomolar levels of bisphenol A using an aptamer-modified disposable microelectrode array. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzajani, H.; Cheng, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Eda, S.; Najafi Aghdam, E.; Badri Ghavifekr, H. A highly sensitive and specific capacitive aptasensor for rapid and label-free trace analysis of Bisphenol A (BPA) in canned foods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.C.; Asif, M.H.; Bacher, G.; Danielsson, B.; Willander, M.; Bhand, S. Nanoimmunosensor based on ZnO nanorods for ultrasensitive detection of 17β-Estradiol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supraja, P.; Tripathy, S.; Krishna Vanjari, S.R.; Singh, V.; Singh, S.G. Label free, electrochemical detection of atrazine using electrospun Mn2O3 nanofibers: Towards ultrasensitive small molecule detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R.; Suni, I.I.; Bever, C.S.; Hammock, B.D. Impedance Biosensors: Applications to Sustainability and Remaining Technical Challenges. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Park, J.-S.; Shim, Y.-B. An impedimetric immunosensor for the label-free detection of bisphenol A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Kannan, P.; Natarajan, B.; Maiyalagan, T.; Subramanian, P.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, S. MnO2 cacti-like nanostructured platform powers the enhanced electrochemical immunobiosensing of cortisol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 317, 128134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-R.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Liu, Z.-J.; Wang, K.; Wu, X.-Y.; Zeng, K.; Meng, H.; Zhang, Z. A highly sensitive signal-amplified gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor for dibutyl phthalate detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Han, C.; Jia, B.; Saint, C.; Nadagouda, M.; Falaras, P.; Sygellou, L.; Vogiazi, V.; Dionysiou, D.D. A 3D graphene-based biosensor as an early microcystin-LR screening tool in sources of drinking water supply. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 236, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dai, H.; Lin, Y. Strip-shaped Co3O4 as a peroxidase mimic in a signal-amplified impedimetric zearalenone immunoassay. Microchim. Acta 2019, 187, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, H.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, L.; Li, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhao, G. A Fetomolar Level 17β-estradiol Electrochemical Aptasensor Constructed On Hierachical Dendritic Gold Modified Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 137, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Zaid, M.H.; Abdullah, J.; Rozi, N.; Mohamad Rozlan, A.A.; Abu Hanifah, S. A Sensitive Impedimetric Aptasensor Based on Carbon Nanodots Modified Electrode for Detection of 17ß-Estradiol. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, G.; Shi, H.; Liu, M.; Li, Z. A highly selective electrochemical impedance spectroscopy-based aptasensor for sensitive detection of acetamiprid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, A.; Liu, Q.; Huan, J.; Qian, J.; Dong, X.; Qiu, B.; Mao, H.; Wang, K. Label-free impedimetric aptasensor for detection of femtomole level acetamiprid using gold nanoparticles decorated multiwalled carbon nanotube-reduced graphene oxide nanoribbon composites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madianos, L.; Tsekenis, G.; Skotadis, E.; Patsiouras, L.; Tsoukalas, D. A highly sensitive impedimetric aptasensor for the selective detection of acetamiprid and atrazine based on microwires formed by platinum nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 101, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazane, I.; Gorgy, K.; Gondran, C.; Spinelli, N.; Zazoua, A.; Defrancq, E.; Cosnier, S. Highly Sensitive Bisphenol-A Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Poly(Pyrrole-Nitrilotriacetic Acid)-Aptamer Film. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7268–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Diamond-based electrochemical aptasensor realizing a femtomolar detection limit of bisphenol A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalvand, A.R.; Haseli, A.; Farzadfar, F.; Goicoechea, H.C. Fabrication of a novel biosensor for biosensing of bisphenol A and detection of its damage to DNA. Talanta 2019, 201, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Zourob, M. Selection and Characterization of DNA Aptamers for Electrochemical Biosensing of Carbendazim. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3138–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; You, T. An ultra-sensitive aptasensor based on carbon nanohorns/gold nanoparticles composites for impedimetric detection of carbendazim at picogram levels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 546, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Hou, J.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, S. Selection of Aptamers Specific for DEHP Based on ssDNA Library Immobilized SELEX and Development of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Aptasensor. Molecules 2020, 25, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Spina, R.; Ferrero, V.E.V.; Aiello, V.; Pedotti, M.; Varani, L.; Lettieri, T.; Calzolai, L.; Haasnoot, W.; Colpo, P. Label-Free Biosensor Detection of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds Using Engineered Estrogen Receptors. Biosensors 2017, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Chen, T.; Wei, J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, S. Electrochemical biosensor for estrogenic substance using lipid bilayers modified by Au nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, J.-E.; Han, J.-A.; Kim, B.K.; Han, J.H.; Park, T.S.; Hwang, S.; In Cho, S.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kim, Y.-R. Electrochemical detection of estrogen hormone by immobilized estrogen receptor on Au electrode. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, S275–S278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Li, J.; Im, J.-E.; Ahn, K.-S.; Park, T.S.; Cho, S.I.; Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, W.-Y. Impedometric estrogen biosensor based on estrogen receptor alpha-immobilized gold electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 671, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kim, B.K.; Wang, K.-K.; Im, J.-E.; Choi, H.N.; Kim, D.-H.; Cho, S.I.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kim, Y.-R. Sensing Estrogen with Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 9081375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, S.; Vinoth Kumar, V. Recent developments in the use of tyrosinase and laccase in environmental applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadgol, Z.; Forootanfar, H.; Rezaei, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Faramarzi, M.A. Removal of phenol and bisphenol-A catalyzed by laccase in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Reza, K.K.; Ali, M.A.; Agrawal, V.V.; Biradar, A.M. Self assembled DC sputtered nanostructured rutile TiO2 platform for bisphenol A detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.M.V.; Campiña, J.M.; Silva, A.F. A layered nanocomposite of laccase, chitosan, and Fe3O4 nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide for the nanomolar electrochemical detection of bisphenol A. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Boyd, B.J. Peptide-based biosensors. Talanta 2015, 136, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, S.; Berti, F. Short peptides as biosensor transducers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3055–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutés, A.; Lee, B.-Y.; Carraro, C.; Mickelson, W.; Lee, S.-W.; Mabouduan, R. Impedimetric graphene-based biosensors for the detection of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6048–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, S.; Elad, T.; Belkin, S. Microbial sensor cell arrays. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawrys, M.D.; Hartman, I.; Landweber, L.F.; Wood, D.W. Use of engineered Escherichia coli cells to detect estrogenicity in everyday consumer products. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2009, 84, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, A.L.; Hoepker, A.C.; Francis, M.B. Quantifying Hormone Disruptors with an Engineered Bacterial Biosensor. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, B.L.; Santos, A.; Bueno, P.R. Perspectives on and Precautions for the Uses of Electric Spectroscopic Methods in Label-free Biosensing Applications. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2216–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.; Montes, R.; Baeza, M. Trends in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy involving nanocomposite transducers: Characterization, architecture surface and bio-sensing. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
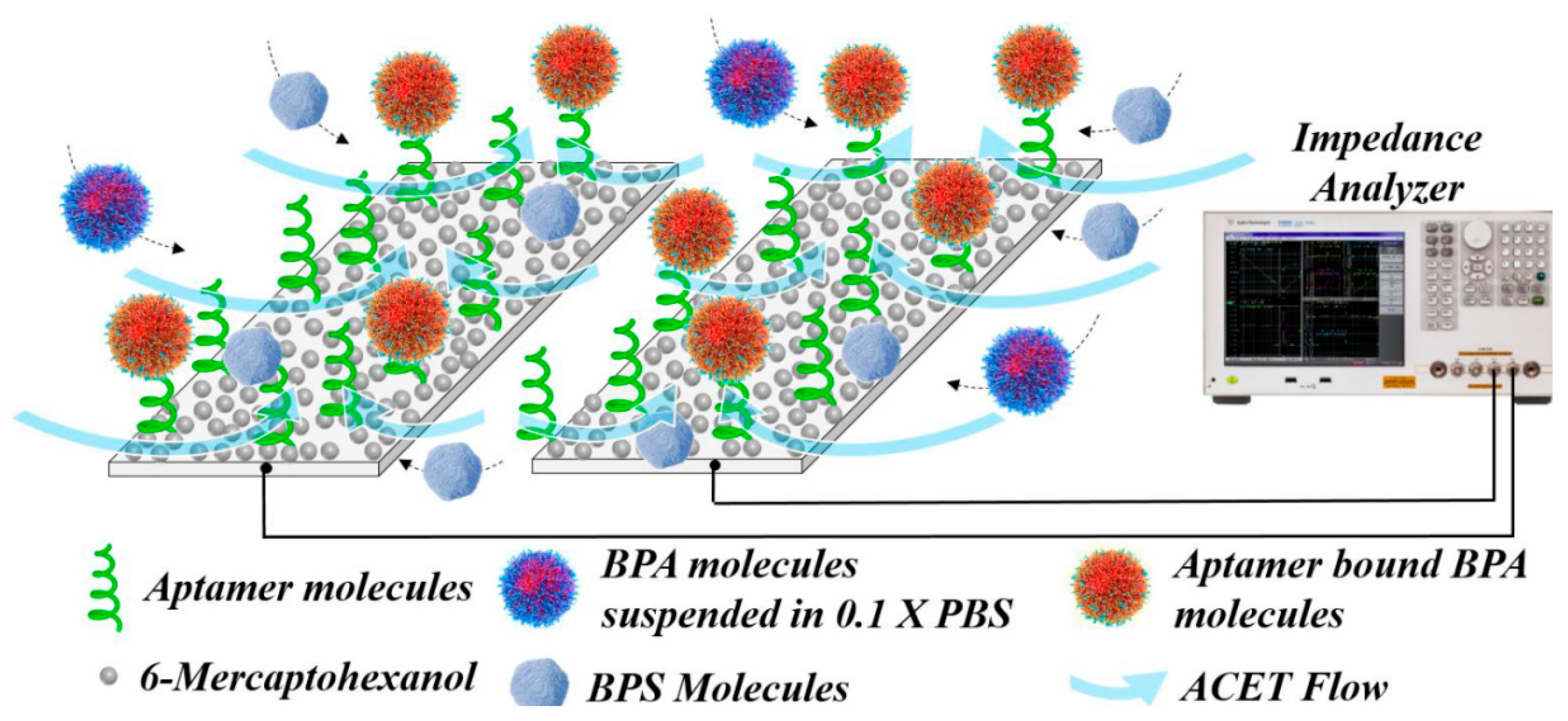
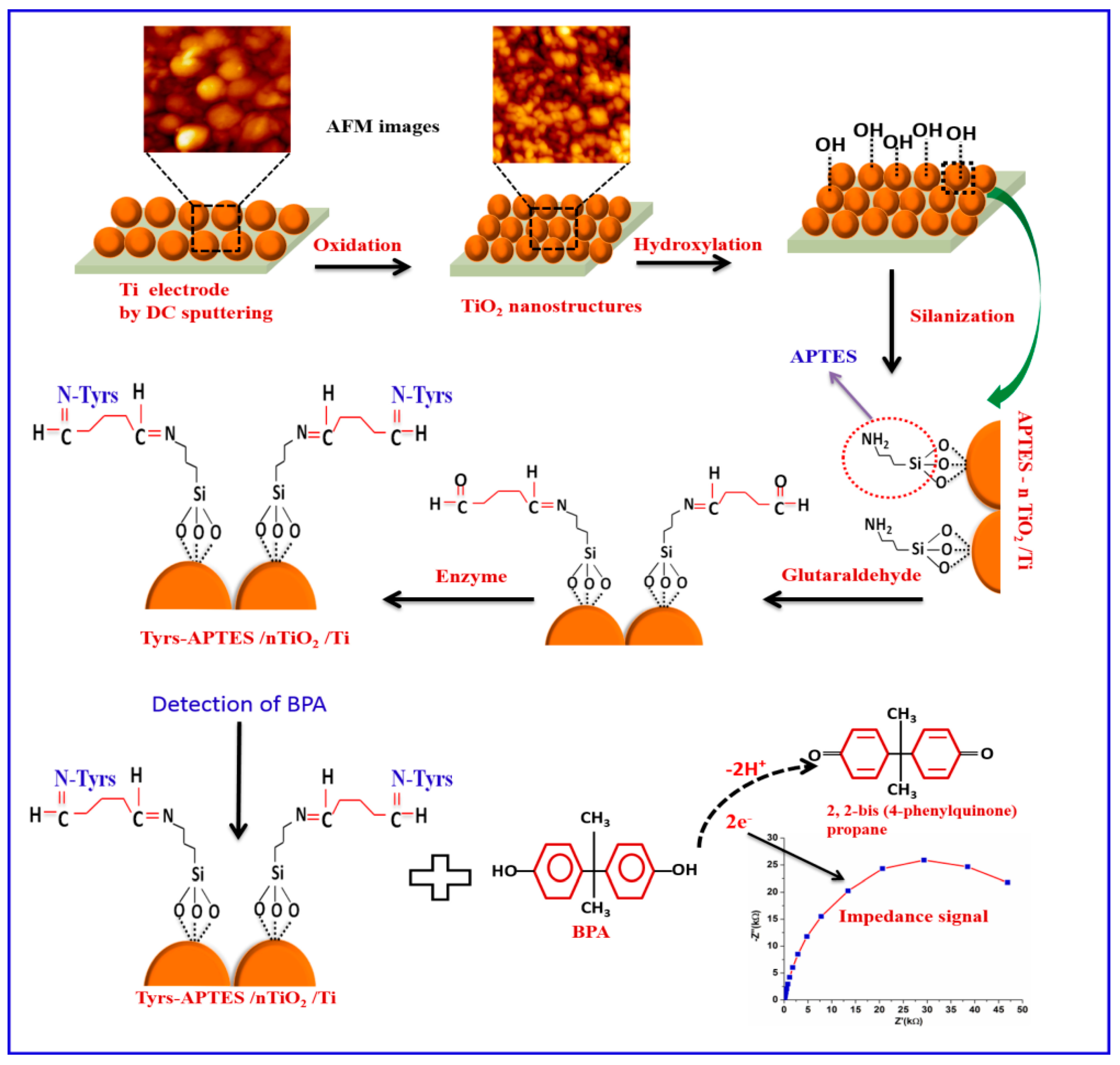
| Analyte | Platform | Linear Range | LOD | Real Sample | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | MIP/GCE | 1 aM–1 μM | 0.36 aM | human serum | Low detection limit; High stability | Multiple preparation and optimization steps | [44] |
| ATZ | MIP/GFE | 5–20 ppm | - | - | High selectivity; Simple modification protocol | Narrow linear range | [45] |
| BPA | E-MIP/ITO | 1–12 mM | 0.42 mM | - | Selectivity | Low sensitivity; High detection limit; Narrow linear range | [46] |
| DBP | MIP-PPY/PGE | 0.01–1 μM | 4.5 nM | - | Simple modification protocol | Relatively high detection limit | [47] |
| DDT | PDA@Fe3O4-MIP MNPs in solution, EIS measurements on GCE | 1 × 10−11–1 × 10−3 M | 6 × 10−12 M | radish | Reusability; Wide linear range | Long assay time; Multiple preparation and separation steps; Requires a magnet | [42] |
| DEHP | MIP-APTES SAM/AuIDE | 10–100 ppm | - | - | Low sample volume | Narrow linear range; Requires electrode fabrication | [48] |
| DEHP | MIP/AuIDE, capacitive sensor | 10–200 ppm | - | - | Simple modification protocol | Limited sensor reusability; Narrow linear range | [49] |
| Testosterone | poly(o-PD) MIP/GO/GCE | 1 fM–1 μM | 0.4 fM | human serum | Fast response time; Low detection limit; High stability | - | [50] |
| Tributyltin | MIP-Fe3O4NPs/SPE | 5 pM–5 μM | 5.37 pM | sea water | Large active surface area; High sensitivity; Wide linear range | Multiple separation and washing steps; Requires a magnet | [51] |
| ZEN | poly(o-PD) MIP/SPGE | 2.5–200 ng/mL | 2.5 ng/mL | corn flakes | High selectivity; Simple modification protocol; Short incubation time | Narrow linear range | [43] |
| Analyte | Platform | Linear Range | LOD | Real Samples | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | Fe(III)TMPP/TRGO/Au | 1 × 10−12–1 × 10−8 M | 2.1 × 10−13 M | fresh milk | High selectivity; Wide linear range | Additional preparation steps for the electrode materials | [56] |
| DEHP | β-CD–GO/ GCE | 2–18 μM | 0.12 μM | wastewater from plastics factory | High selectivity | Narrow linear range; Requires sample deoxygenation | [57] |
| DEHP | DEHP/β-CD/G/DAD/ GCE | 0.2–1.2 μM | 0.01 μM | river water | Good stability | Multiple preparation and optimization steps; Narrow linear range | [58] |
| PCB-77 | PyCD/SWCNT/GCE | 2–10 μM | 1 nM | - | High selectivity | Long preconcentration time (3h); Narrow linear range | [55] |
| Analyte | Platform | Linear Range | LOD | Real Samples | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2 | ER-α/AuNPs/s-BLM/Pt | 5–150 ng/L | 1 ng/L | river water | Does not require blocking of non-specific sites; Label-free; Simple modification protocol | Low stability; Narrow linear range; Only detects total estrogenic activity | [87] |
| E2 | ER-α/3-MPA/Au | - | - | - | Label-free; Simple modification protocol | Only detects total estrogenic activity; Requires blocking of non-specific sites | [88] |
| E2 | ER-α/3-MPA/Au | 1 × 10−13–1 × 10−9 M | 1 × 10−13 M | human urine | Label-free; Simple modification protocol; Wide linear range | Longer incubation time (90 min); Only detects total estrogenic activity; Requires blocking of non-specific sites | [89] |
| E2 | ER-α/3-MPA/Au | 3.7 × 10−4–3.7 ng/L | 3.7 × 10−4 ng/L | - | Label-free; Simple modification protocol | Only detects total estrogenic activity; Requires blocking of non-specific sites | [90] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamfir, L.-G.; Puiu, M.; Bala, C. Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Detection of Endocrine Disruptors. Sensors 2020, 20, 6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226443
Zamfir L-G, Puiu M, Bala C. Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Detection of Endocrine Disruptors. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226443
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamfir, Lucian-Gabriel, Mihaela Puiu, and Camelia Bala. 2020. "Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Detection of Endocrine Disruptors" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226443
APA StyleZamfir, L.-G., Puiu, M., & Bala, C. (2020). Advances in Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Detection of Endocrine Disruptors. Sensors, 20(22), 6443. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226443