Feasibility of Smartphone-Based Badminton Footwork Performance Assessment System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. App Development
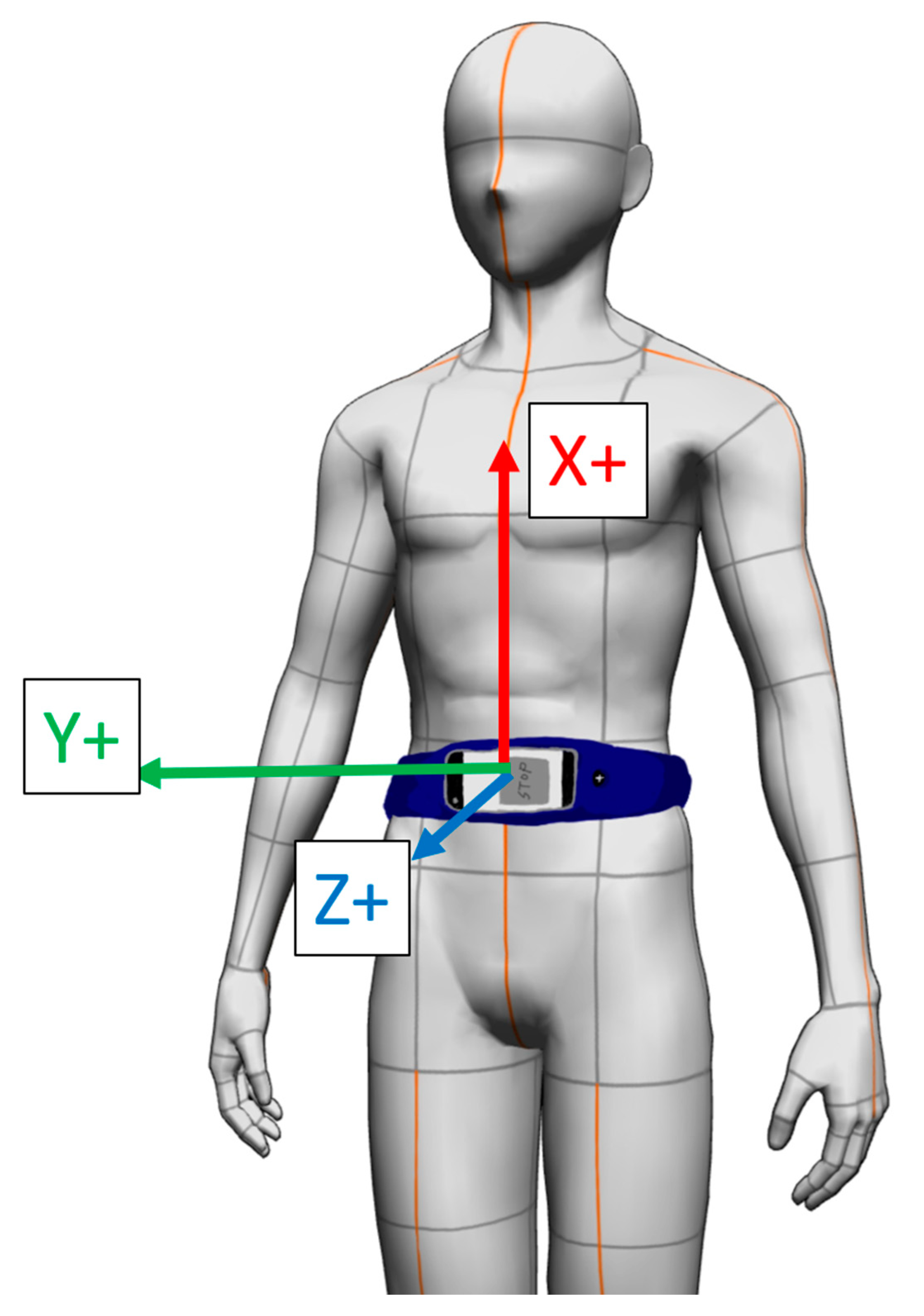
2.3. Instrument
2.4. Data Process
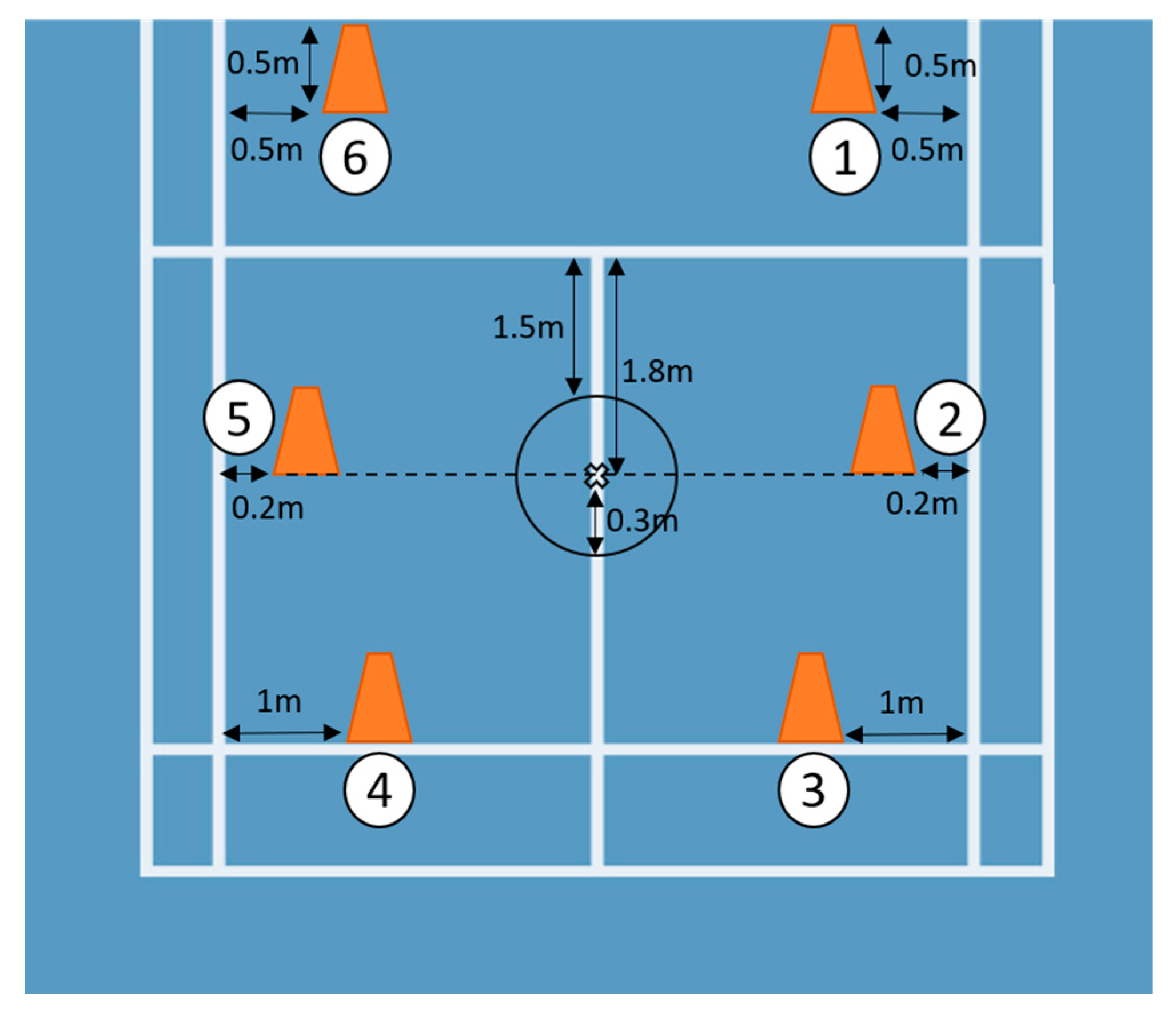
2.5. Procedures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statements
References
- Lees, A. Science and the major racket sports: A review. J. Sports Sci. 2003, 21, 707–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, D.C.; Gonzalez-Badillo, J. Analysis of the characteristics of competitive badminton. Br. J. Sports Med. 2003, 37, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, L.; Rai, V.; Srinet, S. Relationship of selected motor fitness components with the performance of badminton player. Asian J. Phys. Educ. Comput. Sci. Sports 2011, 5, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kuntze, G.; Mansfield, N.; Sellers, W. A biomechanical analysis of common lunge tasks in badminton. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Raza, S.; Mohammad, A. Physical characteristics and level of performance in badminton: A relationship study. J. Educ. Pract. 2011, 2, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Grice, T. Badminton: Steps to Success; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1996; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis, R.S.; Cain, S.M.; Davidson, S.P.; Vitali, R.V.; McLean, S.G.; Perkins, N.C. Inertial sensor and cluster analysis for discriminating agility run technique and quantifying changes across load. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 32, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, M.S.; Lim, H.N.; Salim, M.S.M.; Baharuddin, M.Y. Motion Analysis of Arm Movement during Badminton Smash. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 30 November–2 December 2010; pp. 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Wang, Z. Analysis on Smashing Motion in Badminton. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Engineering and Applications (IEA), Chongqing, China, 26–28 October 2012; pp. 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Ren, F.; Baker, J.S. Comparison of joint loading in badminton lunging between professional and amateur badminton players. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2017, 2017, 5397656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Zakaria, W.N.W.; Tomari, M.R.B.M. Implementation of IMU sensor for elbow movement measurement of badminton players. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd IEEE International Symposium on Robotics and Manufacturing Automation (ROMA), Ipoh, Malaysia, 25–27 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Camomilla, V.; Bergamini, E.; Fantozzi, S.; Vannozzi, G. Trends supporting the in-field use of wearable inertial sensors for sport performance evaluation: A systematic review. Sensors 2018, 18, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-F.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, D.-Y. Analysis of movement effectiveness in badminton strokes with accelerometers. In Genetic and Evolutionary Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, C.Z.; Ming, E.S.L.; Rahman, H.A.; Fai, Y.C. Investigation of upper limb movement during badminton smash. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 31 May–3 June 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jaitner, T.; Gawin, W. A mobile measure device for the analysis of highly dynamic movement techniques. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 3005–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, R.S.; Cain, S.M.; Davidson, S.P.; Vitali, R.V.; Perkins, N.C.; McLean, S.G. Quantifying the effects of load carriage and fatigue under load on sacral kinematics during countermovement vertical jump with IMU-based method. Sports Eng. 2016, 19, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaferiou, A.M.; Ojeda, L.; Cain, S.M.; Vitali, R.V.; Davidson, S.P.; Stirling, L.; Perkins, N.C. Quantifying performance on an outdoor agility drill using foot-mounted inertial measurement units. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, C.U.; Cain, S.M.; Stirling, L.A. Strategy quantification using body worn inertial sensors in a reactive agility task. J. Biomech. 2017, 64, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.-L.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Hou, Y.-R.; Sung, W.-H. Evaluation of a smartphone-based assessment system in subjects with chronic ankle instability. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 139, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogh, J.W.L.; Cox, A.; Anderson, S.; Liew, B.; Olsen, A.; Schram, B.; Furness, J. Reliability and validity of clinically accessible smartphone applications to measure joint range of motion: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wundersitz, D.W.T.; Gastin, P.B.; Richter, C.; Robertson, S.J.; Netto, K.J. Validity of a trunk-mounted accelerometer to assess peak accelerations during walking, jogging and running. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2015, 15, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silsupadol, P.; Teja, K.; Lugade, V. Reliability and validity of a smartphone-based assessment of gait parameters across walking speed and smartphone locations: Body, bag, belt, hand, and pocket. Gait Posture 2017, 58, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartphone Market Share. Available online: https://www.idc.com/promo/smartphone-market-share/os (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Hou, Y.-R.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Chiang, S.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Sung, W.-H. Feasibility of a smartphone-based balance assessment system for subjects with chronic stroke. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobsar, D.; Osis, S.T.; Hettinga, B.A.; Ferber, R. Classification accuracy of a single tri-axial accelerometer for training background and experience level in runners. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 2508–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bris, R.; Billat, V.; Auvinet, B.; Chaleil, D.; Hamard, L.; Barrey, E. Effect of fatigue on stride pattern continuously measured by an accelerometric gait recorder in middle distance runners. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2006, 46, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Stetter, B.J.; Buckeridge, E.; Nigg, S.R.; Sell, S.; Stein, T. Towards a wearable monitoring tool for in-field ice hockey skating performance analysis. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, H.; Sagawa, K.; Kuroshima, K.; Tsukamoto, T.; Urita, K.; Ishibashi, Y. 3D measurement of forearm and upper arm during throwing motion using body mounted sensor. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 2010, 4, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Sutter, K.J.; Askew, C.D.; Burkett, B.J. Identifying symmetry in running gait using a single inertial sensor. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 30) | Fast Group (n = 15) | Slow Group (n = 15) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (M:F) | 22:8 | 12:3 | 10:5 | 0.409 |
| Age (years) | 20.7 ± 1.6 | 20.1 ± 1.6 | 21.3 ± 1.5 | 0.051 |
| Height (m) | 1.70 ± 0.07 | 1.73 ± 0.06 | 1.68 ± 0.08 | 0.086 |
| Weight (kg) | 62.1 ± 7.6 | 62.2 ± 7.2 | 62.0 ± 8.3 | 0.950 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.3 ± 1.8 | 20.8 ± 2.1 | 21.8 ± 1.4 | 0.112 |
| Training time (hours/week) | 4.4 ± 2.5 | 5.3 ± 2.4 | 3.5 ± 2.5 | 0.062 |
| Experience of badminton (years) | 6.6 ± 4.5 | 6.7 ± 4.1 | 6.6 ± 5.0 | 0.937 |
| Finished time (s) | 14.8 ± 2.5 | 13.4 ± 2.43 | 16.3 ± 2.81 | <0.001 * |
| Footwork | Fast Group (n = 15) | Slow Group (n = 15) | p Value | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
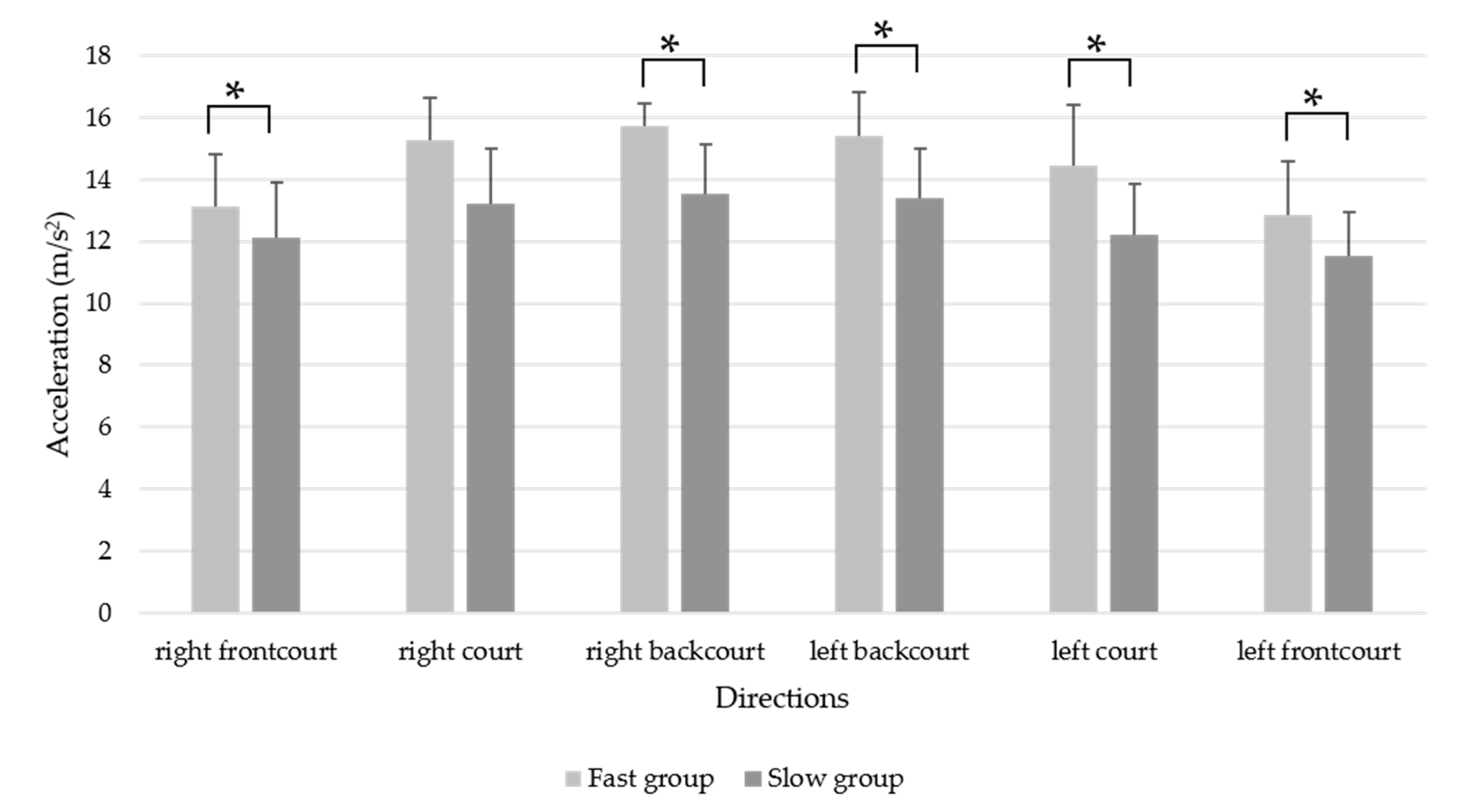
| Total | 14.45 ± 1.00 | 12.69 ± 1.38 | <0.001 * | 1.48 | 0.86–2.66 |
| Right frontcourt | 13.13 ± 1.66 | 12.13 ± 1.78 | 0.124 | 0.57 | −0.29–2.29 |
| Right court | 15.25 ± 1.41 | 13.20 ± 1.77 | 0.002 * | 1.30 | 0.86–3.25 |
| Right backcourt | 15.71 ± 0.74 | 13.55 ± 1.60 | <0.001 * | 1.70 | 1.23–3.10 |
| Left backcourt | 15.39 ± 1.41 | 13.41 ± 1.59 | 0.001 * | 1.33 | 0.85–3.10 |
| Left court | 14.43 ± 1.97 | 12.20 ± 1.67 | 0.002 * | 1.19 | 0.87–3.60 |
| Left frontcourt | 12.83 ± 1.97 | 11.54 ± 1.41 | 0.035 * | 0.75 | 0.10–2.48 |
| Footwork | Fast Group (n = 15) | Slow Group (n = 15) | p Value | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
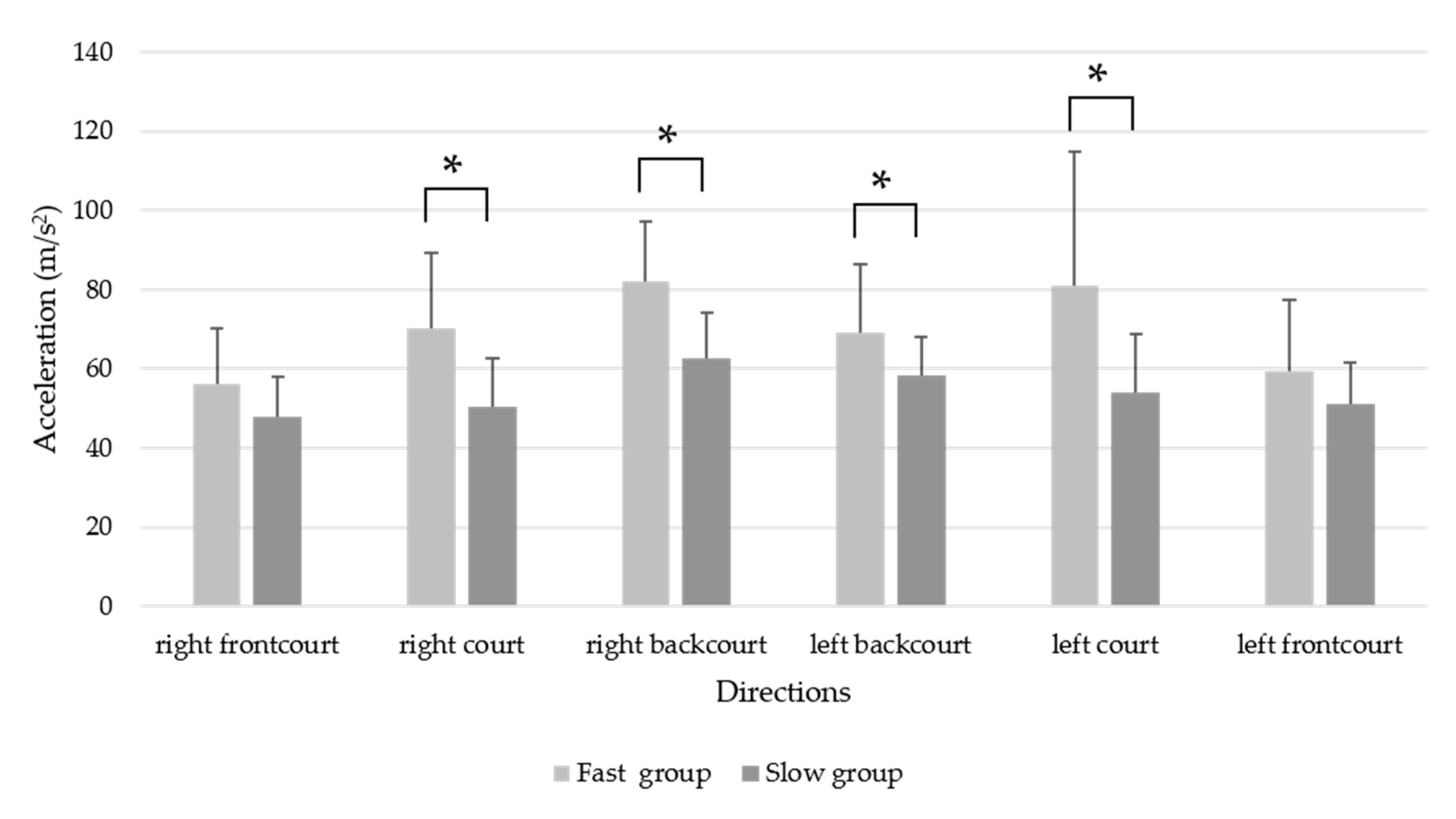
| Total | 101.55 ± 19.10 | 72.32 ± 10.37 | <0.001 * | 1.91 | 17.57–40.87 |
| Right frontcourt | 56.33 ± 14.05 | 47.88 ± 9.94 | 0.068 | 0.69 | −0.65–17.55 |
| Right court | 70.29 ± 19.08 | 50.57 ± 12.14 | 0.002 * | 1.51 | 7.66–31.78 |
| Right backcourt | 82.20 ± 14.95 | 62.80 ± 11.32 | <0.001 * | 1.46 | 9.48–29.32 |
| Left backcourt | 69.10 ± 17.18 | 58.29 ± 9.72 | 0.043 * | 0.77 | 0.37–21.25 |
| Left court | 81.03 ± 33.71 | 53.94 ± 14.82 | 0.010 * | 1.04 | 7.21–46.98 |
| Left frontcourt | 59.47 ± 18.00 | 51.11 ± 10.61 | 0.132 | 0.56 | −2.69–19.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, Y.-L.; Tsai, C.-L.; Sung, W.-H.; Tsai, Y.-J. Feasibility of Smartphone-Based Badminton Footwork Performance Assessment System. Sensors 2020, 20, 6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216035
Chiu Y-L, Tsai C-L, Sung W-H, Tsai Y-J. Feasibility of Smartphone-Based Badminton Footwork Performance Assessment System. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216035
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Ya-Lan, Chia-Liang Tsai, Wen-Hsu Sung, and Yi-Ju Tsai. 2020. "Feasibility of Smartphone-Based Badminton Footwork Performance Assessment System" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216035
APA StyleChiu, Y.-L., Tsai, C.-L., Sung, W.-H., & Tsai, Y.-J. (2020). Feasibility of Smartphone-Based Badminton Footwork Performance Assessment System. Sensors, 20(21), 6035. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216035







