Influence of Data Sampling Frequency on Household Consumption Load Profile Features: A Case Study in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To dynamically adjust electricity tariffs as fine temporal resolutions make it possible to quickly adapt to changes in consumption and thus reduce the electricity bill.
- To improve energy efficiency, comfort, and safety in households with an intelligent automation system.
- To recognize activities (i.e., analysis of energy consumption through observation) that are potentially more meaningful to users.
- To optimally size renewable generation system and storage systems.
- To forecast household load profiles with different time horizons, from a short-term load forecast (hourly and daily) to long-term forecast-based planning studies.
- To perform studies of angle stability, transient analysis, and frequency control in electrical energy systems.
- To characterize household consumption load profile features.
- To perform load forecasting by applying probabilistic techniques.
2. Methodology
2.1. Time-Series Theory
2.1.1. Stationary
2.1.2. Metrics for Statistics and Probability Analysis
2.1.3. Autocorrelation and Spectrum
2.2. Temporal Granularity and Time Slices
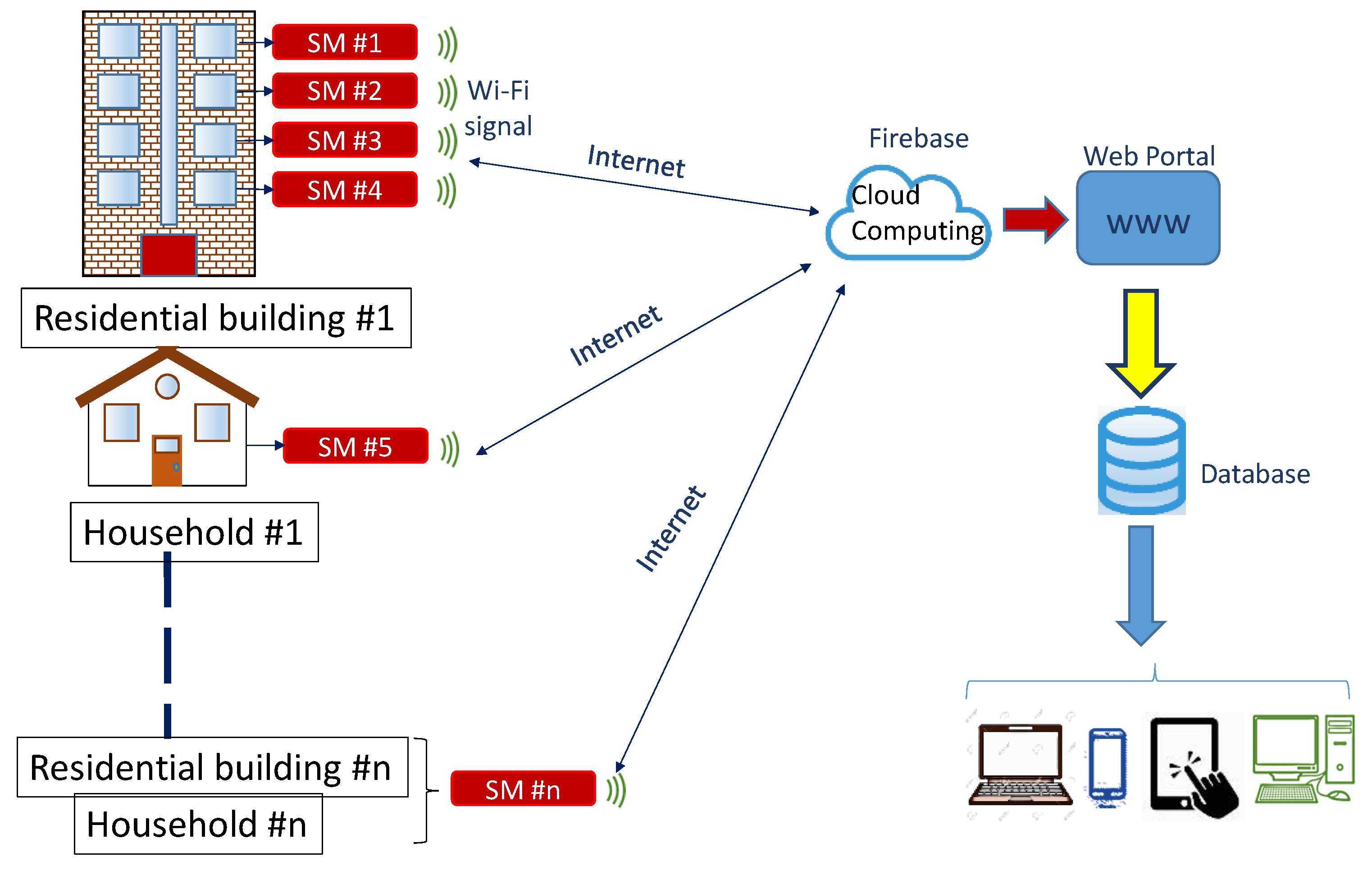
2.3. Planned Framework for Consumption Data Collection in Households
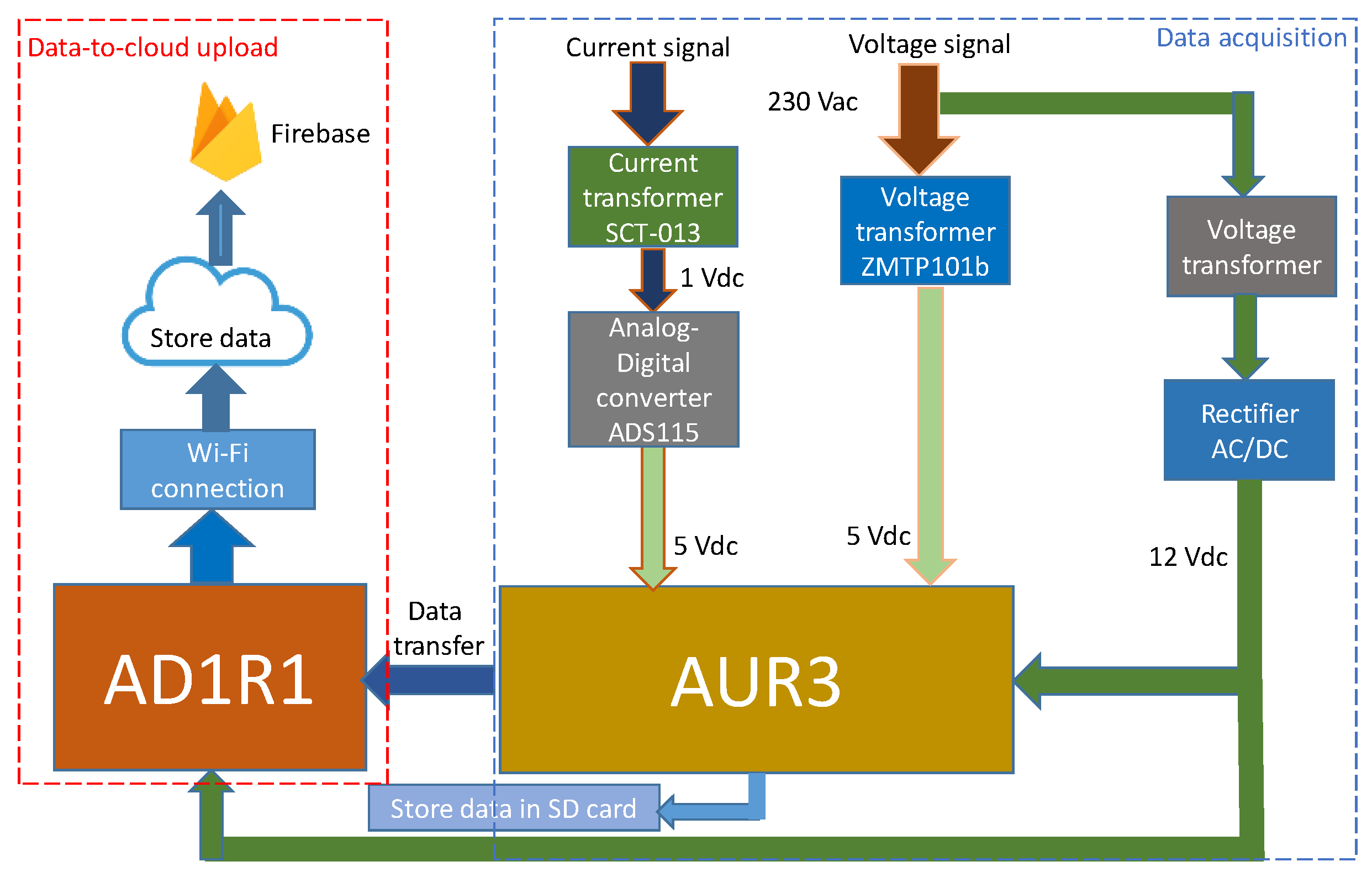
2.3.1. SM
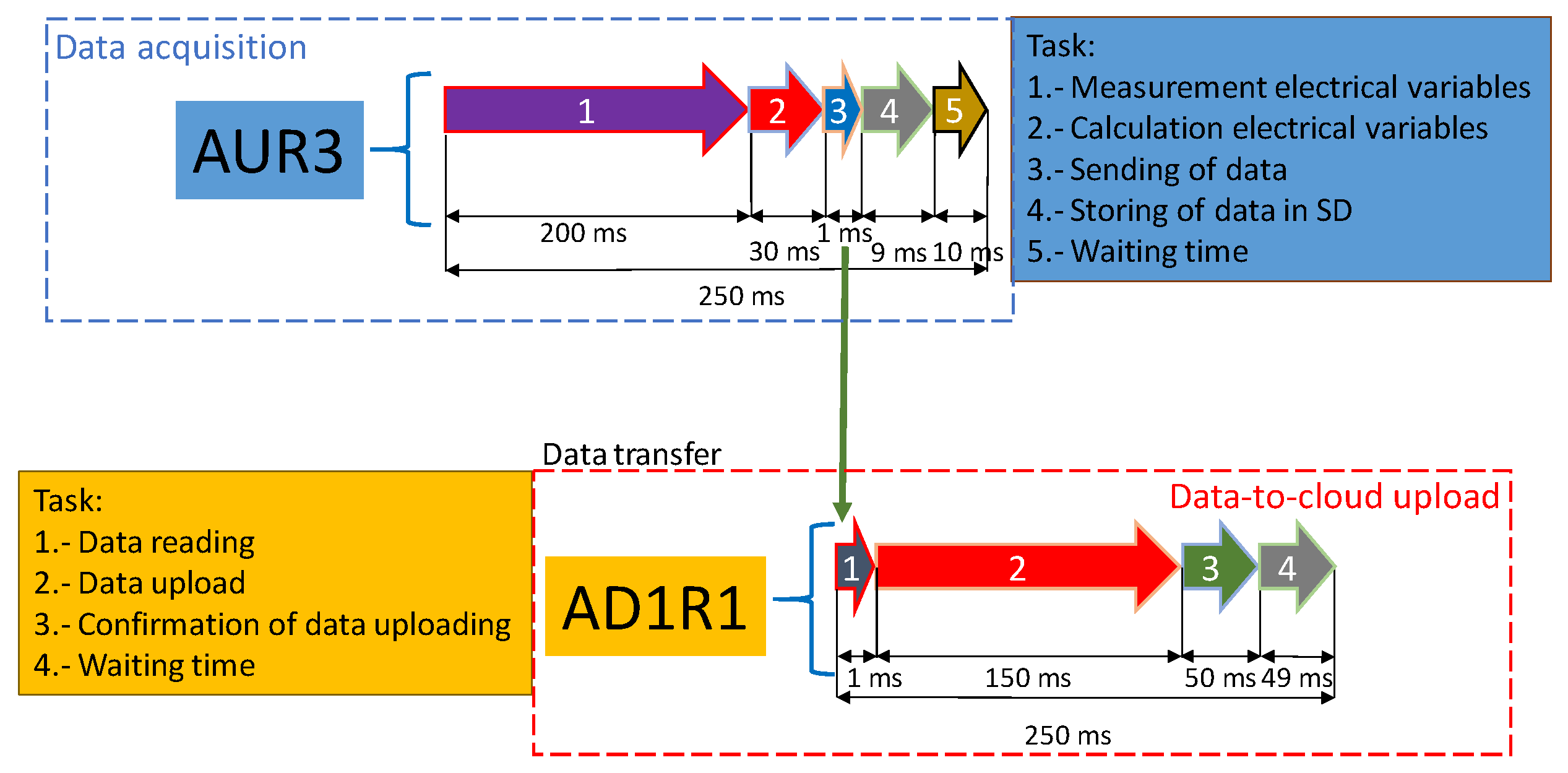
Data Acquisition
Data-To-Cloud Upload
Local Data Storage
2.4. Data Post-Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Case Study
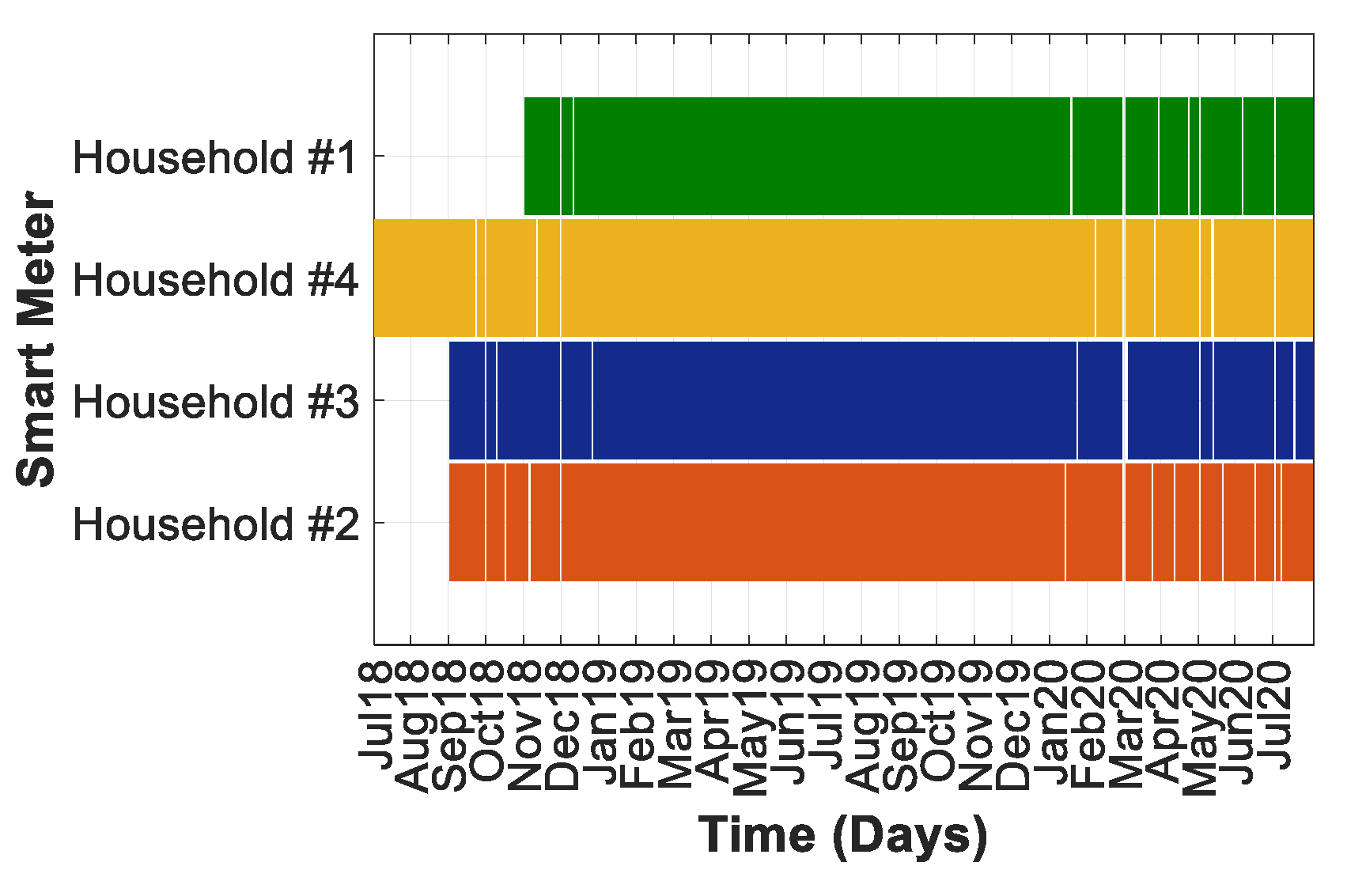
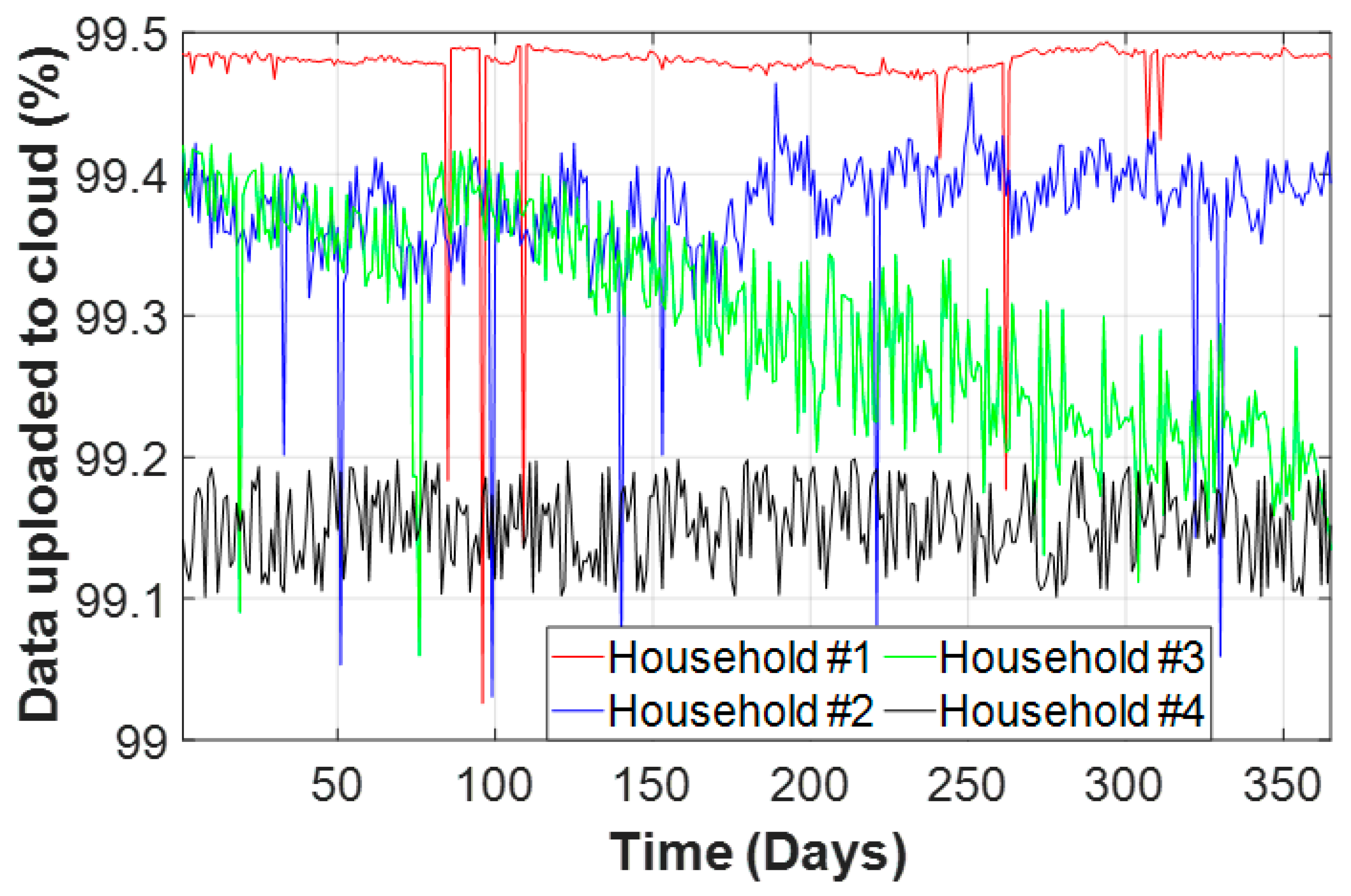
3.2. Reliability of the Planned Framework to Provide Data
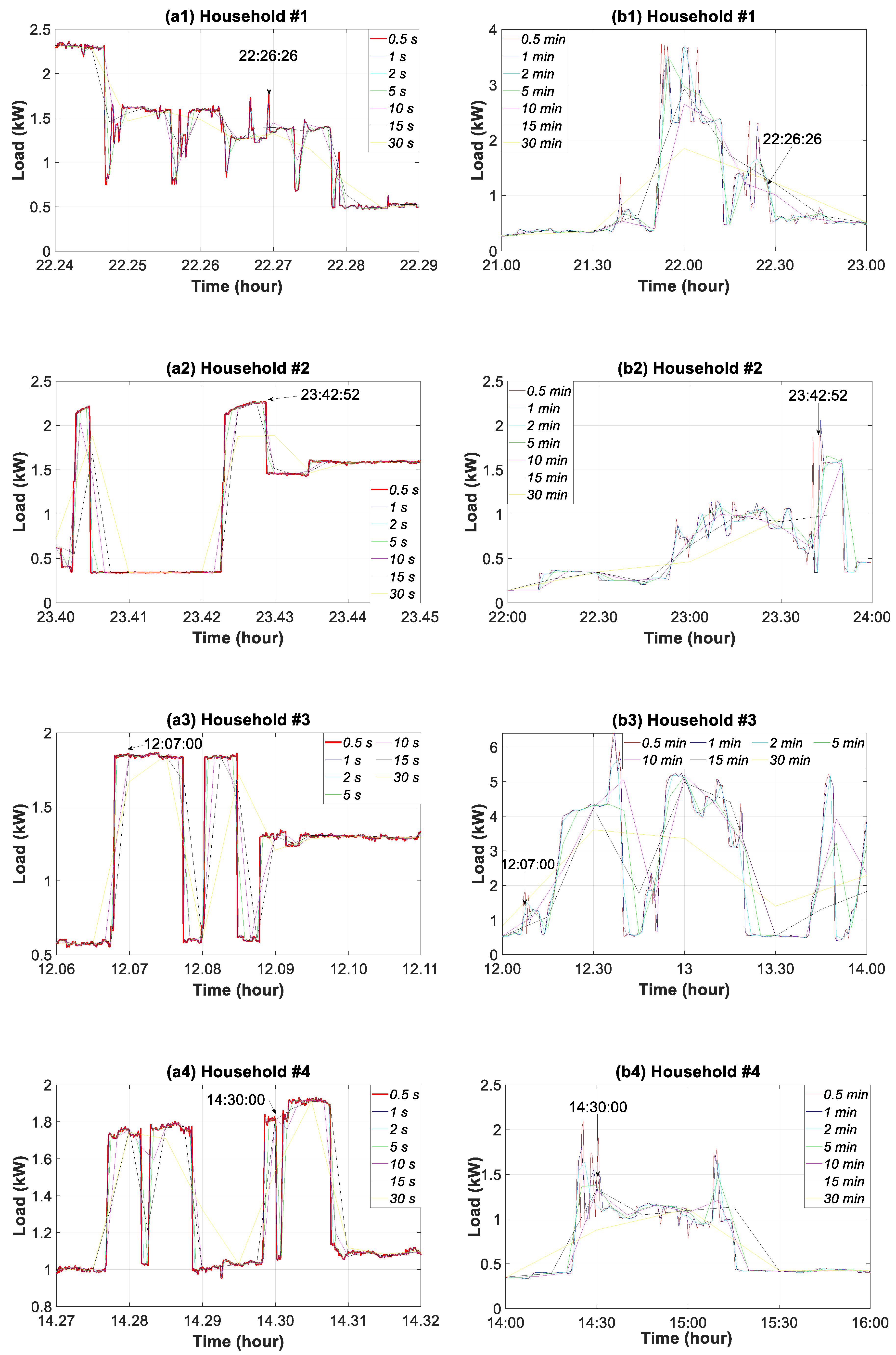
3.3. Sub-Hourly Time Slice Analysis
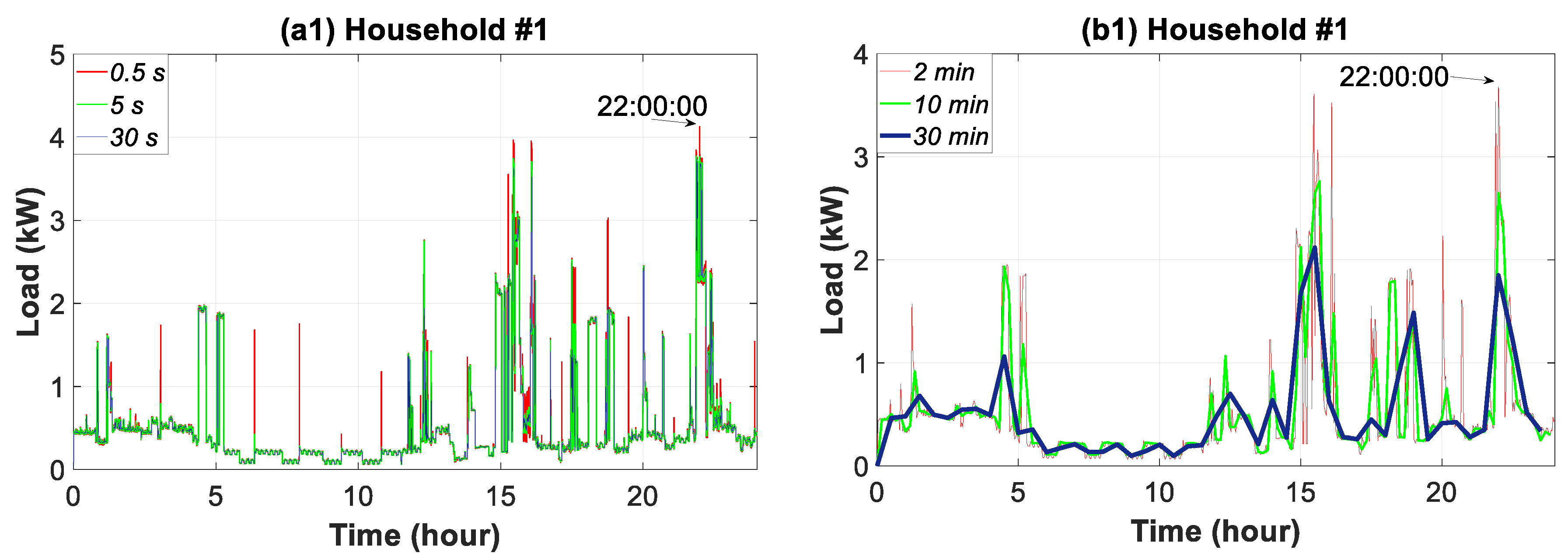
3.4. Daily Time Slice Analysis
3.5. Weekly Time Slice Analysis
3.6. Monthly Time Slice Analysis
3.7. Yearly Time Slice Analysis
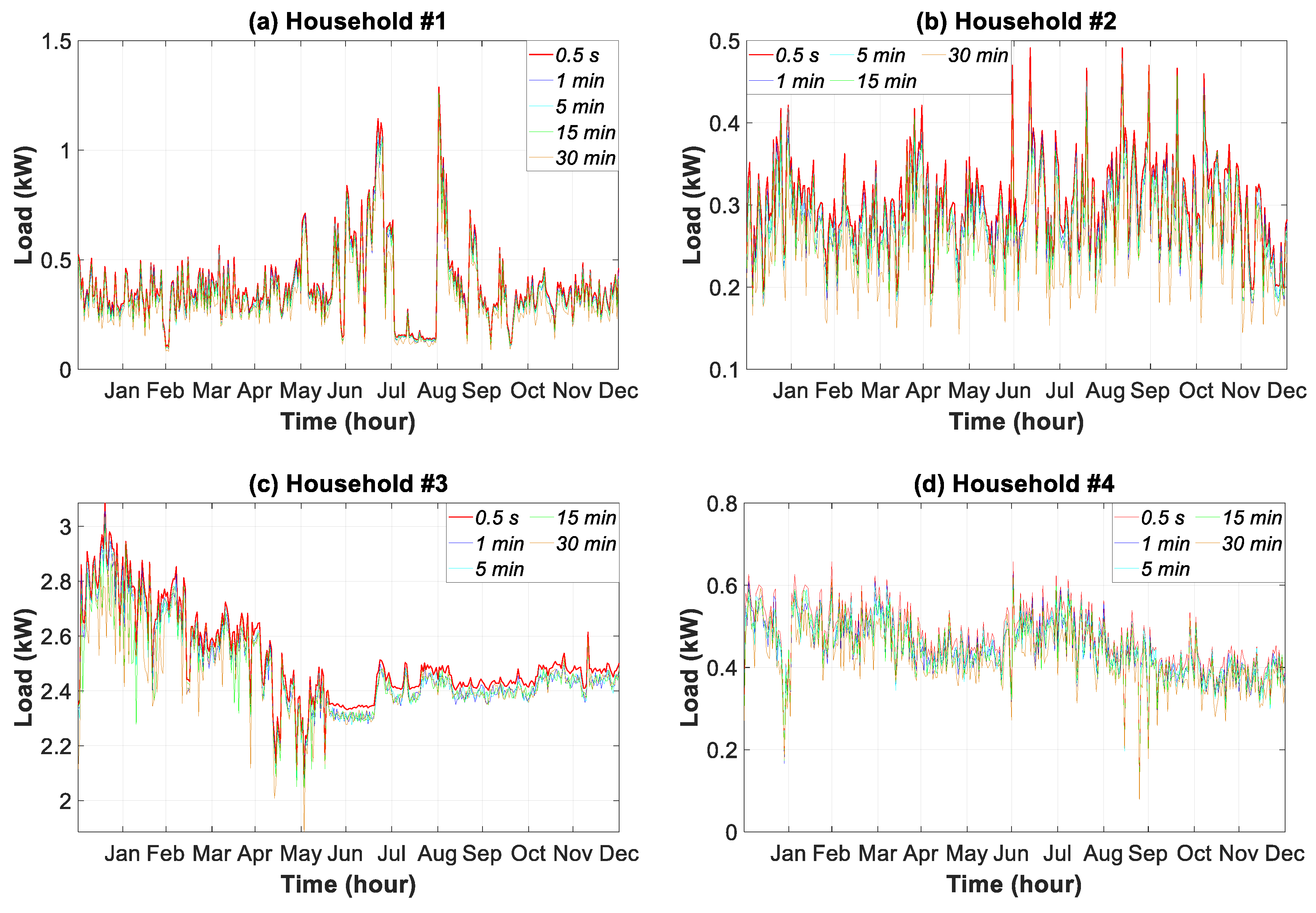
3.7.1. Temporal Consumption Pattern
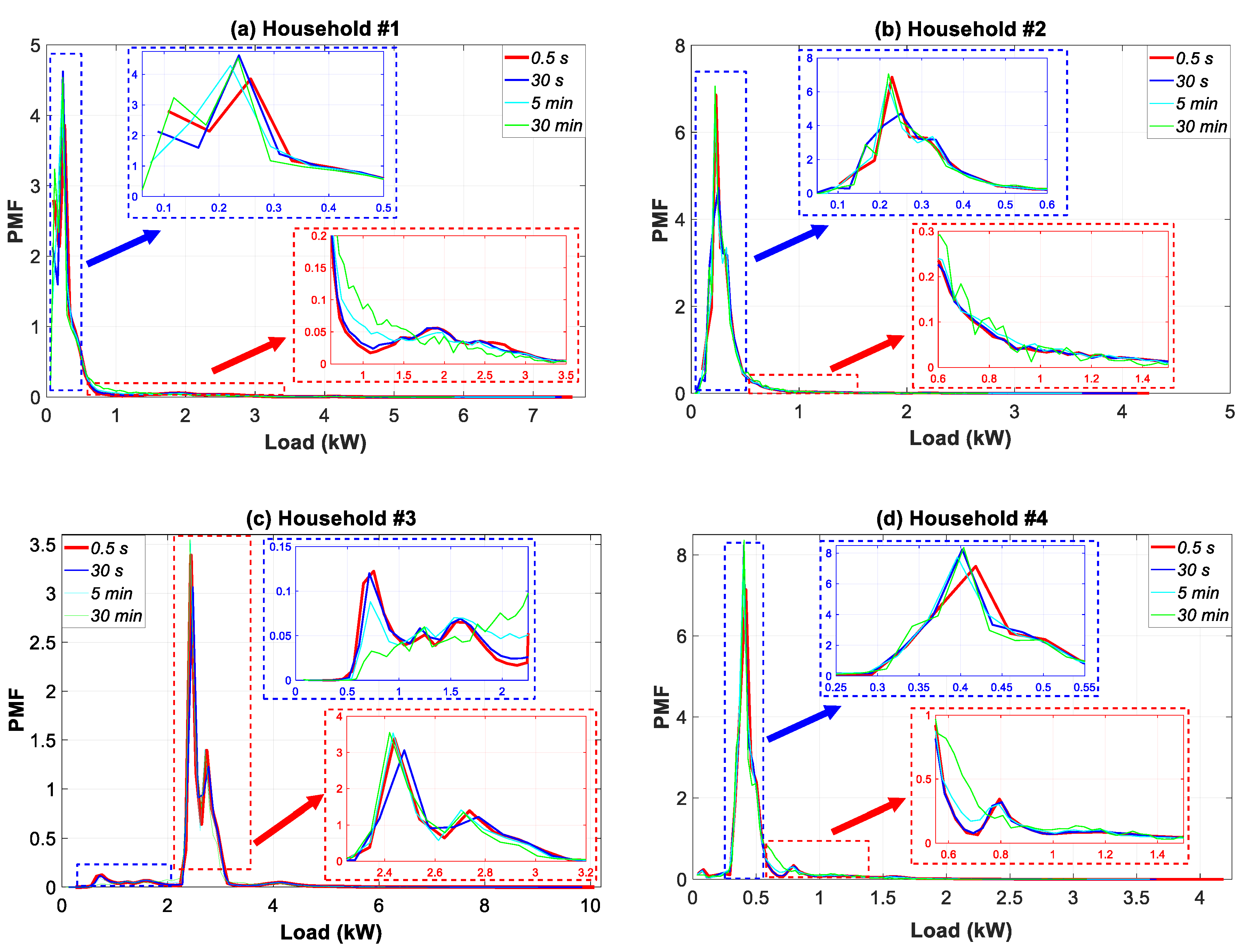
3.7.2. Statistical Analysis
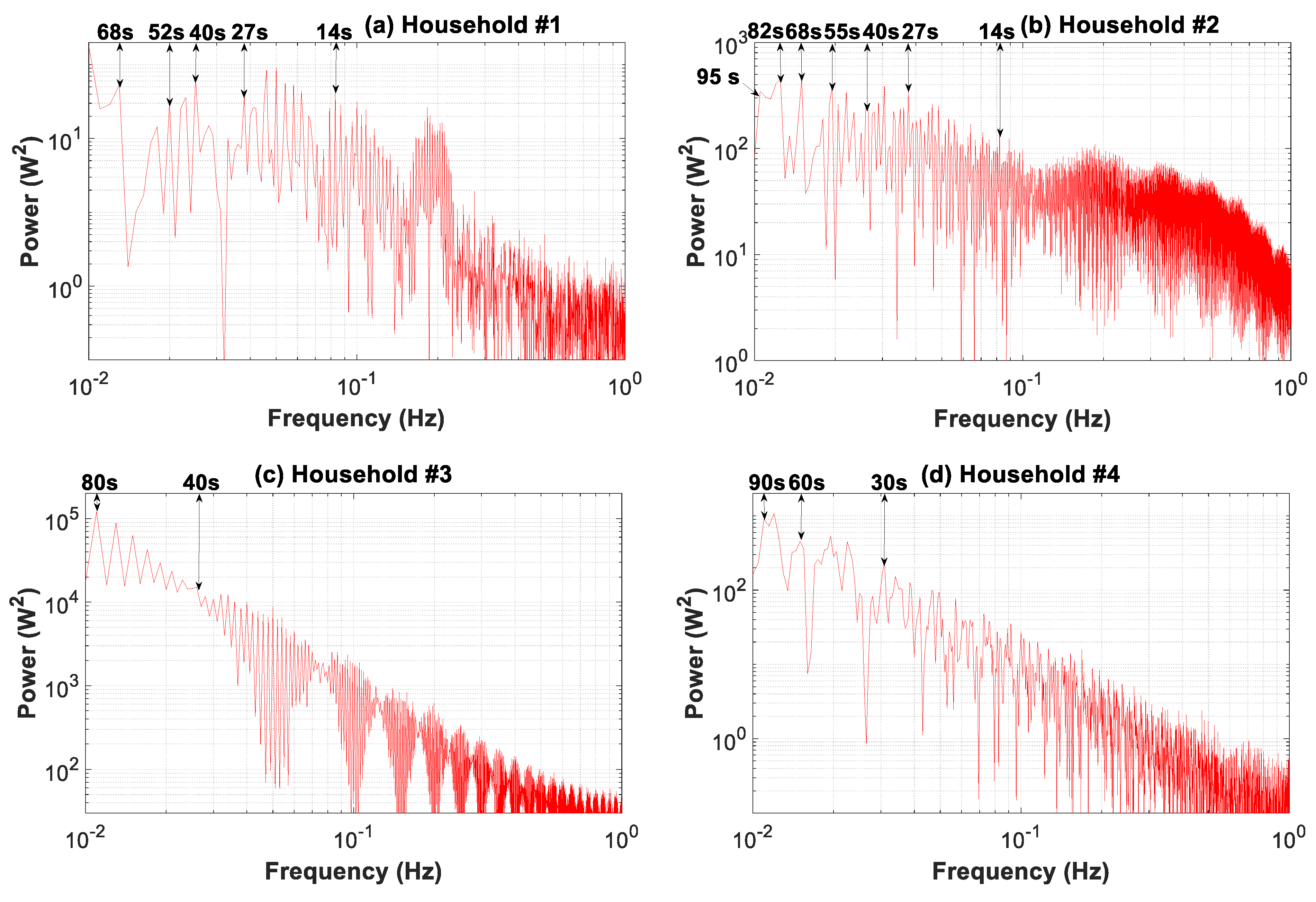
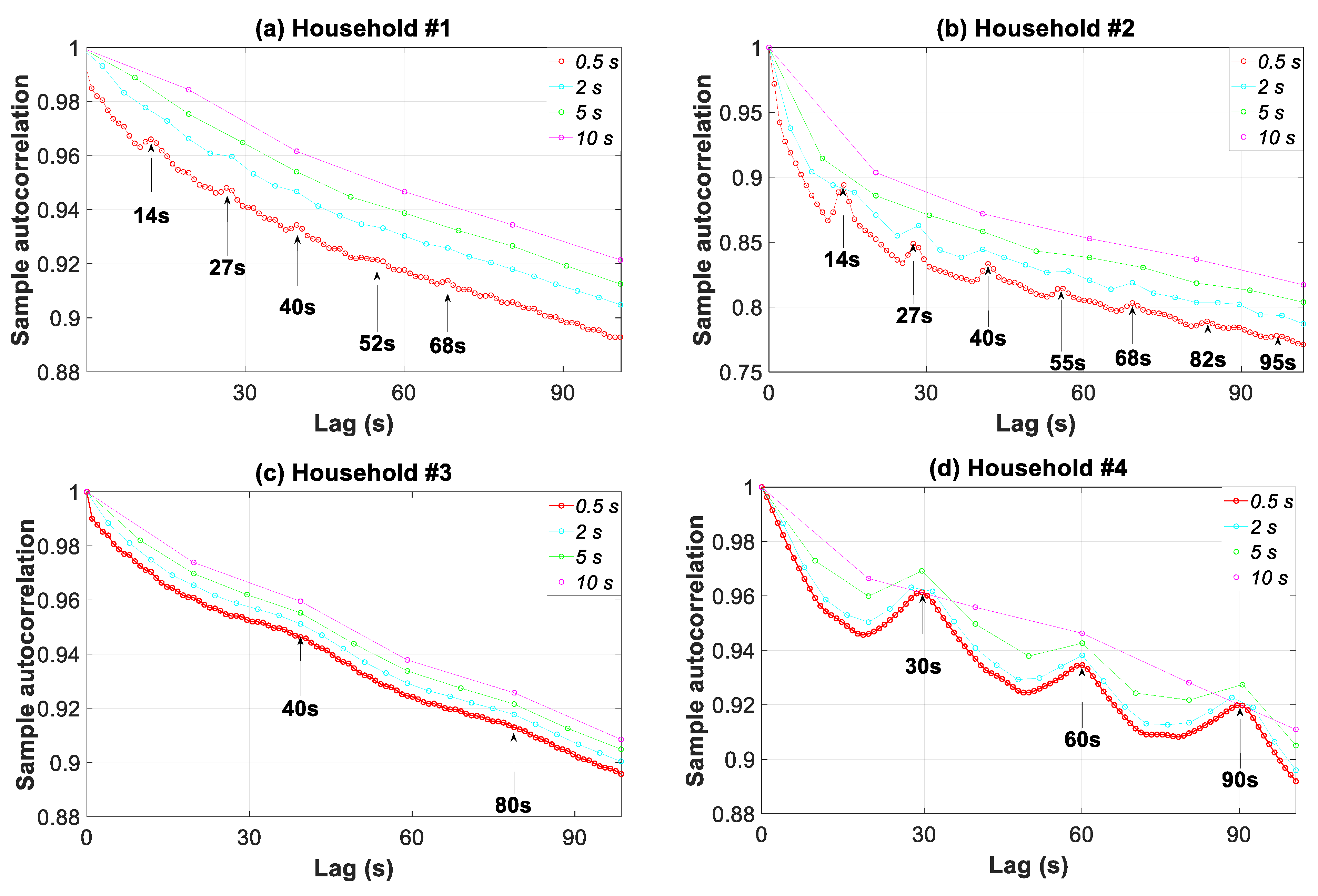
3.7.3. Periodogram, Autocorrelation, and Partial Autocorrelation Analyses
3.8. Comparative Study of Granularity Impact in the Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, K.; Fu, C.; Yang, S. Big data driven smart energy management: From big data to big insights. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Understanding household energy consumption behavior: The contribution of energy big data analytics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torriti, J. A review of time use models of residential electricity demand. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.; Stephen, B.; Infield, D.; Melero, J.J. Using high-frequency SCADA data for wind turbine performance monitoring: A sensitivity study. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakova, S.; Jankin Mikhaylov, S. Big data to the rescue? Challenges in analysing granular household electricity consumption in the United Kingdom. Energy Res. Social Sci. 2020, 64, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Swan, L.G. A method for distinguishing appliance, lighting and plug load profiles from electricity ‘SM’ datasets. Energy Build. 2017, 134, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Branchini, L.; Ferrari, C.; Melino, F. Optimal sizing of grid-independent hybrid photovoltaic–battery power systems for household sector. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Knottenbelt, W. The UK-DALE dataset, domestic appliance-level electricity demand and whole-house demand from five UK homes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipattanasomporn, M.; Kuzlu, M.; Rahman, S.; Teklu, Y. Load profiles of selected major household appliances and their demand response opportunities. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.; Mishra, A.; Irwin, D.; Cecchet, E.; Shenoy, P. Smart: An open data set and tools for enabling research in sustainable homes. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Beijing, China, 12–16 August 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cano-Ortega, A.; Sánchez-Sutil, F. Performance optimization LoRa network by artificial bee colony algorithm to determination of the load profiles in dwellings. Energies 2020, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tascikaraoglu, A.; Sanandaji, B.M. Short-term residential electric load forecasting: A compressive spati-temporal approach. Energy Build 2016, 111, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdowsi, F.; Mehraeen, S.; Upton, G.B. Integration of behind-the-meter solar into distribution feeders: The importance of time resolution on model results. In Proceedings of the IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech), Lafayette, LA, USA, 3–6 April 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridgen, G.; Kahlen, M.; Ketter, W.; Rieger, A.; Thimmel, M. One rate does not fit all: An empirical analysis of electricity tariffs for residential microgrids. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elma, O.; Tascıkaraoglu, A.; Tahir Ince, A.; Selamogullar, U.S. Implementation of a dynamic energy management system using real, time pricing and local renewable energy generation forecasts. Energy 2017, 134, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xiao, F.; Jorgensen Bagterp, J.; Wang, S. Frequency control of air conditioners in response to real-time dynamic electricity prices in smart grids. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Huanxin, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H. Smart energy forecasting strategy with four machine learning models for climate-sensitive and non-climate sensitive conditions. Energy 2020, 198, 117283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassamzadeh, N.; Ghanem, R. Multiscale stochastic prediction of electricity demand in smart grids using Bayesian networks. Appl. Energy 2017, 193, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Fan, S. A university of probabilistic electric load forecasting: A tutorial review. Int. J. Forecast. 2016, 32, 914–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, M.; Alessandri, A.; Catalano, F. Seasonal climate forecasts for medium-term electricity demand forecasting. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, F.M.; Larsen, H.V.; Gaardestrup, R.B. Long term forecasting of hourly electricity consumption in local areas in Denmark. Appl. Energy 2013, 110, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteinaki, K.; Li, R.; Rode, C.; Korsholm, R. Andersen Modelling household electricity load profiles based on Danish time-use survey data. Energy Build. 2019, 202, 109355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünewald, P.; Diakonova, M. The specific contributions of activities to household electricity demand. Energy Build. 2019, 204, 109498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, S.; Vergara, C.; Astolfi, M.; Li, V.; Perez-Arriaga, I.; Macchi, E. Assessing the value of forecast-based dispatch in the operation of off-grid rural microgrids. Renew. Energy 2017, 108, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kools, L.; Phillipson, F. Data granularity and the optimal planning of distributed generation. Energy 2016, 112, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, N.; Zhang, L.; Navarro-Espinosa, A.; Mancarella, P. High resolution modelling of multi-energy domestic demand profiles. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.; Firth, S. The nature of domestic electricity-loads and effects of time averaging on statistics and on-site generation calculations. Appl. Energy 2007, 84, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widen, J.; Molin, A.; Ellegard, K. Models of domestic occupancy, activity and energy use based on time use data: Deterministic and stochastic approaches with application to building-related simulations. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2011, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, H.; Luo, X. A Kalman filter-based bottom-up approach for household short-term load forecast. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wan, J.; Yang, S. Short-term power load probability density forecasting based on quantile regression neural network and triangle kernel function. Energy 2016, 114, 498–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causonea, F.; Carlucci, S.; Ferrando, M.; Marchenko, A.; Erba, S. A data-driven procedure to model occupancy and occupant-related electric load profiles in residential buildings for energy simulation. Energy Build. 2019, 202, 109342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, J.P.; Seixas, J. Unraveling electricity consumption profiles in households through clusters: Combining smart meters and door-to-door surveys. Energy Build. 2016, 116, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Ruiz, J.P. Stochastic unit commitment with sub-hourly dispatch constraints. Appl. Energy 2013, 105, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusis, P.; Rajab Khalilpour, K.; Andrew, L.; Liebman, A. Short-term residential load forecasting: Impact of calendar effects and forecast granularity. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.W. An evaluation of methods for very short-term load forecasting using minute-by-minute British data. Int. J. Forecast. 2008, 24, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K.; Smith, K.M.; Culligan, P.J.; Taylor, J.E. Forecasting energy consumption of multi-family residential buildings using support vector regression: Investigating the impact of temporal and spatial monitoring granularity on performance accuracy. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Noh, J.; Kim, H. Deep neural network based demand side short term load forecasting. Energies 2017, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.; Stankovic, L.; Stankovic, V. An electrical load measurements dataset of United Kingdom households from a two-year longitudinal study. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naspolini, H.F.; Rüther, R. The effect of measurement time resolution on the peak time power demand reduction potential of domestic solar hot water systems. Renew. Energy 2016, 88, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, C.; Betcke, J.; Andersson, G. Effects of variation of temporal resolution on domestic power and solar irradiance measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE Grenoble Conference, Grenoble, France, 16–20 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ming, H.; Shakkottai, S.; Xie, L.; Yao, J. Nonintrusive load monitoring in residential households with low-resolution data. Appl. Energy 2019, 252, 113283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, D.W.; Munkhammar, J.; Widén, J. Probabilistic forecasting of solar power, electricity consumption and net load: Investigating the effect of seasons, aggregation and penetration on prediction intervals. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, S. Dealing with multiple decades of hourly wind and PV time series in energy models: A comparison of methods to reduce time resolution and the planning implications of inter-annual variability. Appl. Energy 2017, 197, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sutil, F.; Cano-Ortega, A.; Hernandez, J.C.; Rus-Casas, C. Development and calibration of an open source, low-cost power smart meter prototype for PV household-prosumers. Electronics 2019, 8, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Siren, K. Impact of simulation time-resolution on the matching of PV production and household electric demand. Appl. Energy 2014, 128, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracale, A.; Carpinelli, G.; De Falco, P. A Bayesian-based approach for the short-term forecasting of electrical loads in smart grids. Part I: Theoretical aspects. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Anacapri, Italy, 22–24 June 2016; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracale, A.; Carpinelli, G.; De Falco, P. A Bayesian-based approach for the short-term forecasting of electrical loads in smart grids. Part II: Numerical application. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Anacapri, Italy, 22–24 June 2016; pp. 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widen, J.; Wackelgard, E.; Paatero, J.; Lund, P. Impacts of different data averaging times on statistical analysis of distributed domestic photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy 2010, 84, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.C.; Sanchez-Sutil, F.; Muñoz-Rodriguez, F.J. Design criteria for the optimal sizing of a hybrid energy storage system in PV household-prosumers to maximize self-consumption and self-sufficiency. Energy 2019, 186, 115827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Rodríguez, L.; Brennenstuhl, M.; Yadack, M.; Boch, P.; Eicker, U. Heuristic optimization of clusters of heat pumps: A simulation and case study of residential frequency reserve. Appl. Energy 2019, 233, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavasiliou, A.; Mou, Y.; Cambier, L.; Scieur, D. Application of stochastic dual dynamic programming to the real-time dispatch of storage under renewable supply uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 9, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC. IEC Standard 61000-4-30. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Testing and Measurement Techniques—Power Quality Measurement Methods. In Proceedings of the International Electrotechnical Commission, Geneva, Switzerland, May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, T.; Jin, N.; Flach, P.; Thumim, J. A Big Data platform for SM data analytics. Comput. Ind. 2019, 105, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Wu, L.; Wang, J. A novel smart meter data compression method via stacked convolutional sparse auto-encoder. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 118, 105761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecan Street. Available online: https://www.pecanstreet.org (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Mack, B.; Tampe-Mai, K. An action theory-based electricity saving web portal for households with an interface to SMs. Util. Policy 2016, 42, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J. UK-DALE. Available online: https://jack-kelly.com/data (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- ACS. Available online: https://icosys.ch/acs-f2 (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- DRED. Available online: http://www.st.ewi.tudelft.nl/akshay/dred (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- ECO. Available online: http://vs.inf.ethz.ch/res/show.html?what=eco-data (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- GREEN. Available online: https://sourceforge.net/projects/greend (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- SMART. Available online: http://traces.cs.umass.edu/index.php/smart/smart (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- NZERlF. Available online: https://catalog.data.gov/dataset/the-net-zero-energy-residential-test-facility-nzertf-42ce6 (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Hoevenaars, E.J.; Crawford Curran, A. Implications of temporal resolution for modeling renewables-based power systems. Renew. Energy 2012, 41, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, S.A.; Razavi, A.A.; Haghighi, A.; Ghader, S. AGP-based approach for improving wind-wavesimulations over the persian gulf. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Coasts, Ports and Marine Structures (Icopmas) Ports & Maritime Organization, Tehran, Iran, 31 October–2 November 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Broersen, P.M.T. Automatic Autocorrelation and Spectral Analysis; Springer: Delft, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C. Time Series Analysis, 4th ed.; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bartos, S. Prediction of Energy Load Profiles. Master’s Thesis, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arvamtis, S. A note on the limit theory of a Dickey—Fuller unit root test with heavy tailed innovations. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2017, 126, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, D.; Phillips, P.C.; Schmidt, P.; Shin, Y. Testing the null hypothesis of stationarity against the alternative of a unit root: How sure are we that economic time series have a unit root? J. Econom. 1992, 54, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Schmidt, P. The KPSS stationarity test as a unit root test. Econ. Lett. 1992, 38, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, B.A. Wavelet variance ratio cointegration test and wavestrapping. J. Multivar. Anal. 2019, 171, 298–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caner, M.; Kilian, L. Size distortions of tests of the null hypothesis of stationarity: Evidence and implications for the PPP debate. J. Int. Money Finance 2001, 28, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobari, D.; García, S.; Mellado, C. Identifying bubbles in Latin American equity markets: Phillips-Perron-based tests and linkages. Emerg. Mark. Rev. 2017, 33, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullagh, P. Tensor Methods in Statistics; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G.; Stuart, A. The Advanced Theory of Statistics; Charles Grin and Company Limited: London, UK, 1963; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Strickland, J. Predictive Modeling and Analytics; lulu.com: Morrisville, NC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis, Forecasting and Control, 5th ed.; Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khintchine, A. Korrelationstheorie der Stationären Stochastischen Prozessen. Math. Ann. 1934, 109, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, N. Generalised harmonic analysis. Acta Math. 1930, 35, 117–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, M.B. Spectral Analysis and Time Series; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Mathur, J.; Bhakar, R.; Amit Kanudi, A. Implications of short-term renewable energy resource intermittency in long-term power system planning. Energy Strategy Rev. 2018, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Ogayar, B.; Hernandez, J.C.; Sutil, F.S. Survey and assessment of technical and economic features for the provision of frequency control services by household-prosumers. Energy Policy 2020, 146, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.C.; Sanchez-Sutil, F.; Muñoz-Rodríguez, F.J.; Baier, C.R. Optimal sizing and management strategy for PV household-prosumers with self-consumption/sufficiency enhancement and provision of frequency containment reserve. Appl. Energy 2020, 277, 115529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino Uno Rev3. Available online: https://store.arduino.cc/arduino-uno-rev3 (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- WEMOS Electronics. Available online: https://wiki.wemos.cc/products:d1:d1 (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- STC013 Dechang Electronics Co. Ltd. Available online: http://en.yhdc.com/product/SCT013-401.html (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Texas Instruments. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/ads1114.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Interplus Industry Co. Ltd. Available online: http://www.interplus-industry.fr/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=52&Itemid=173&lang=en (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Firebase. Available online: https://firebase.google.com/?hl=es (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- Najim, K.; Ikonen, E.; Daoud, A.-K. Stochastic Processes: Estimation, Optimisation and Analysis, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
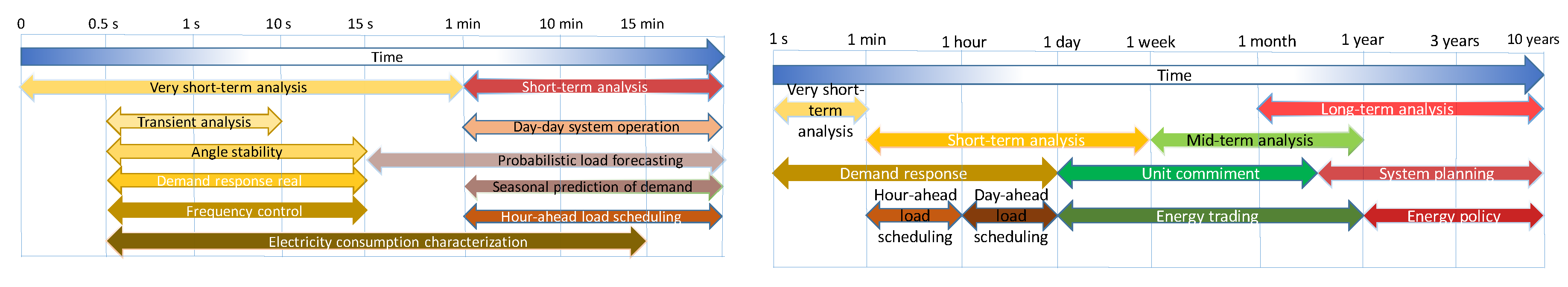
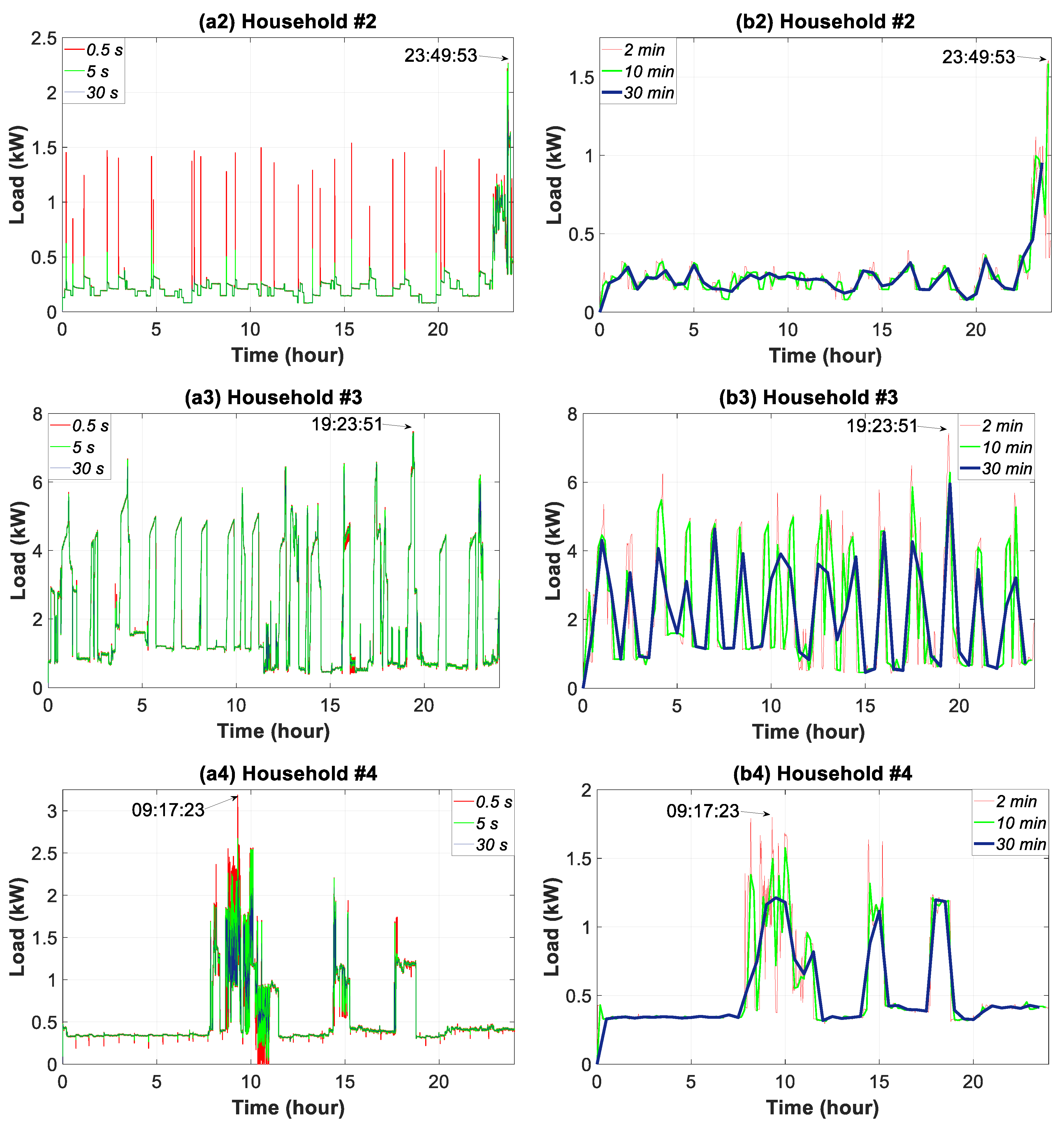
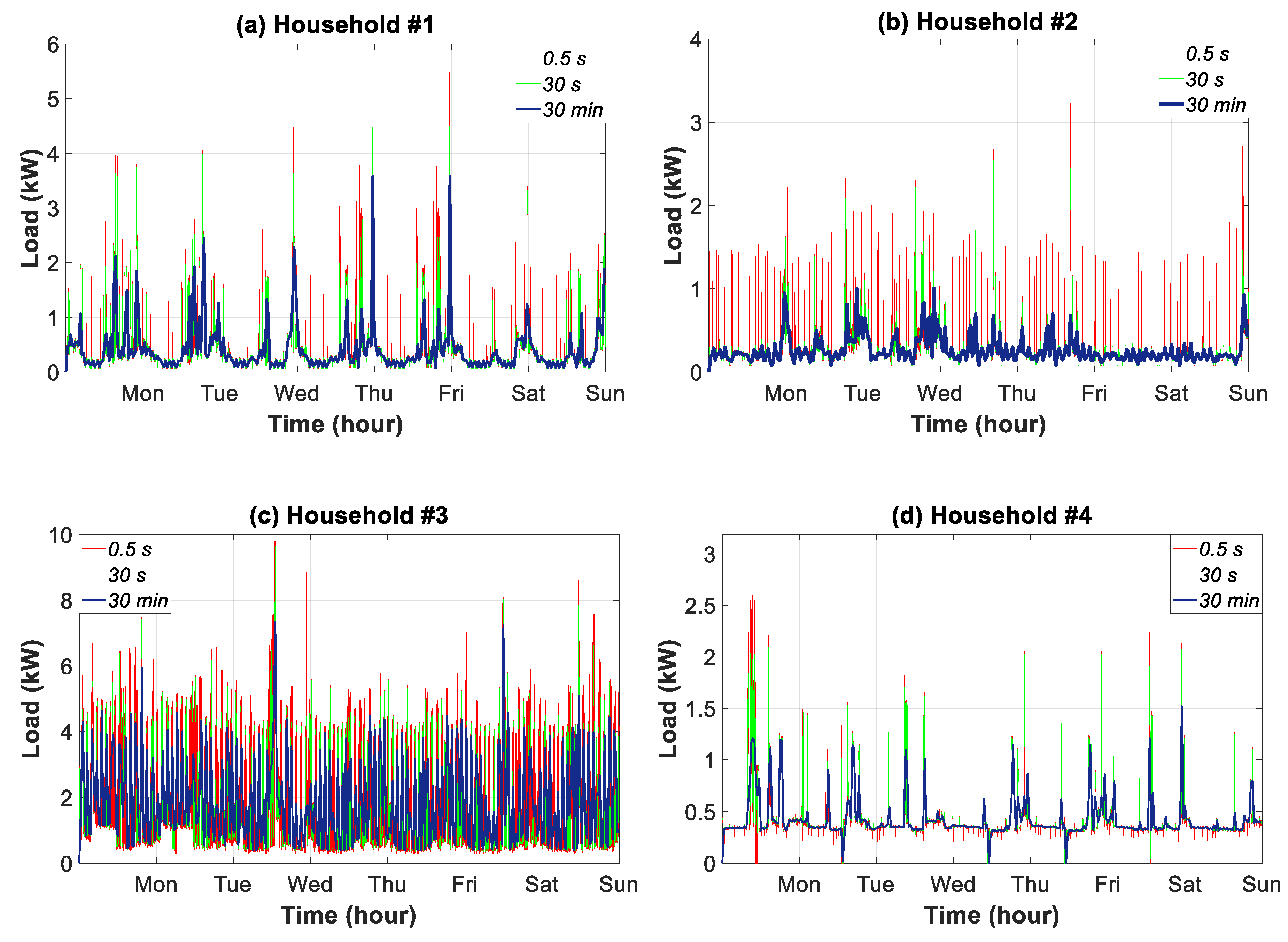
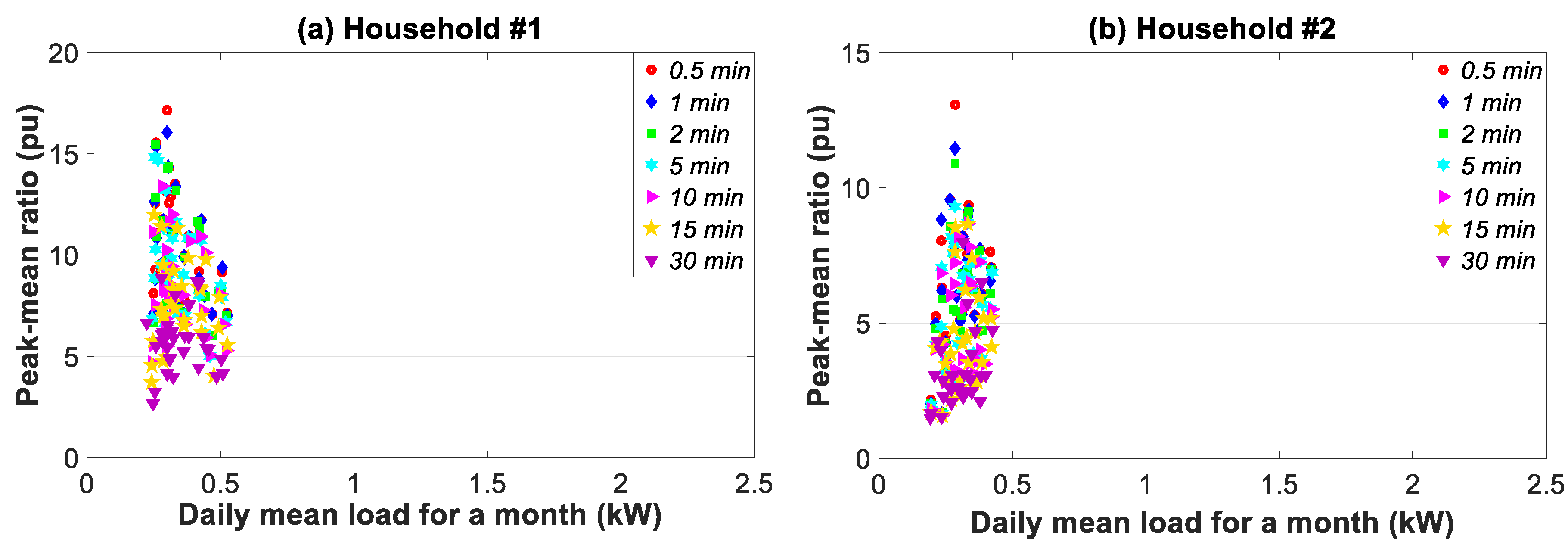
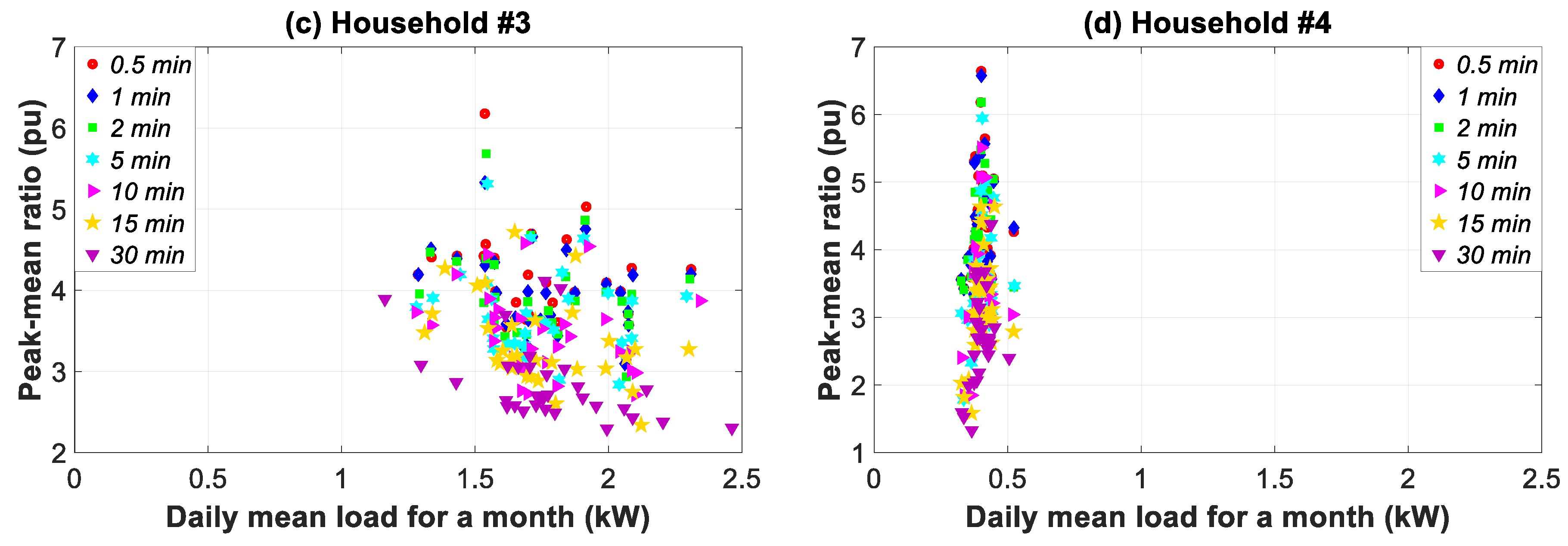
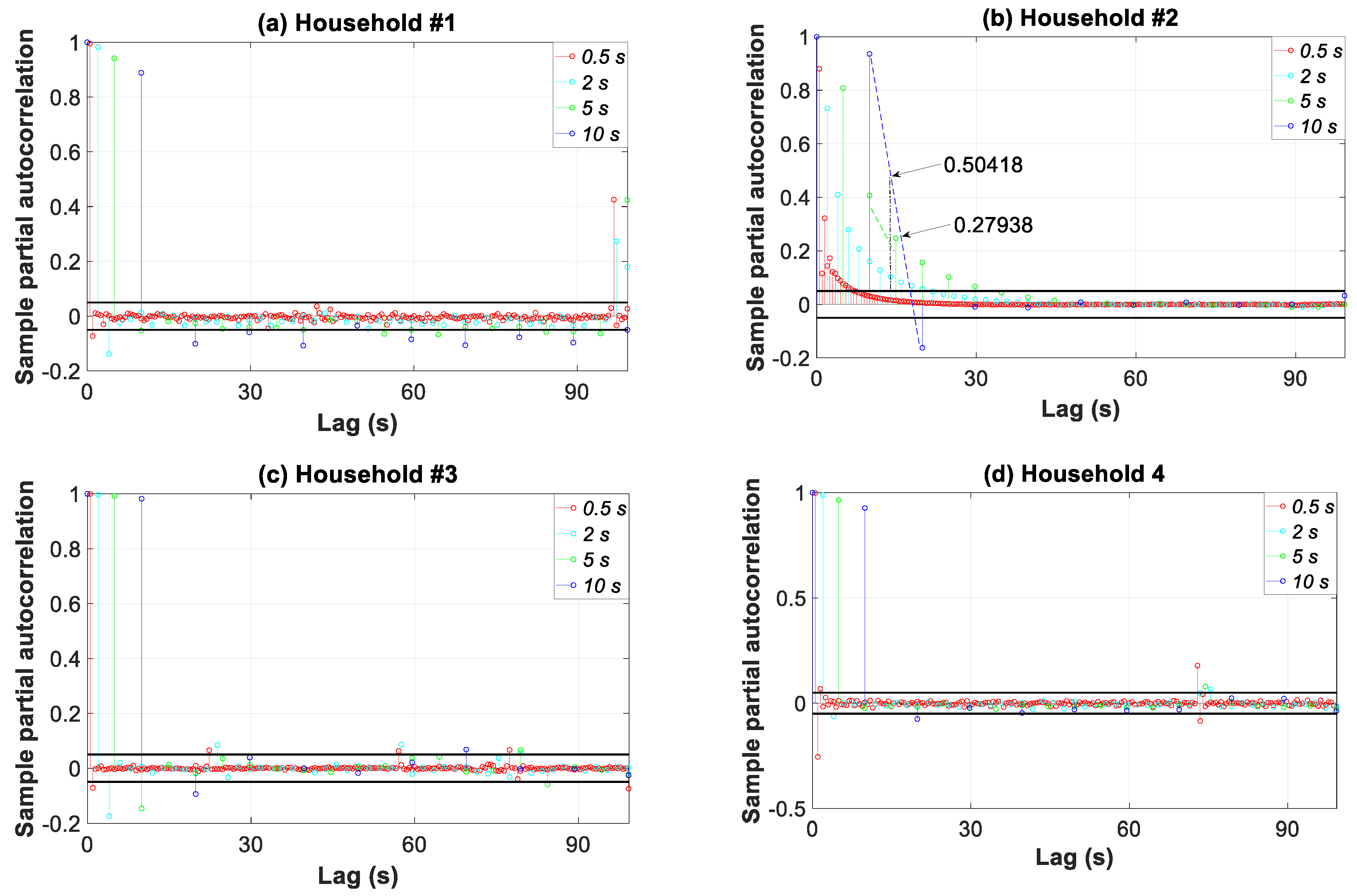
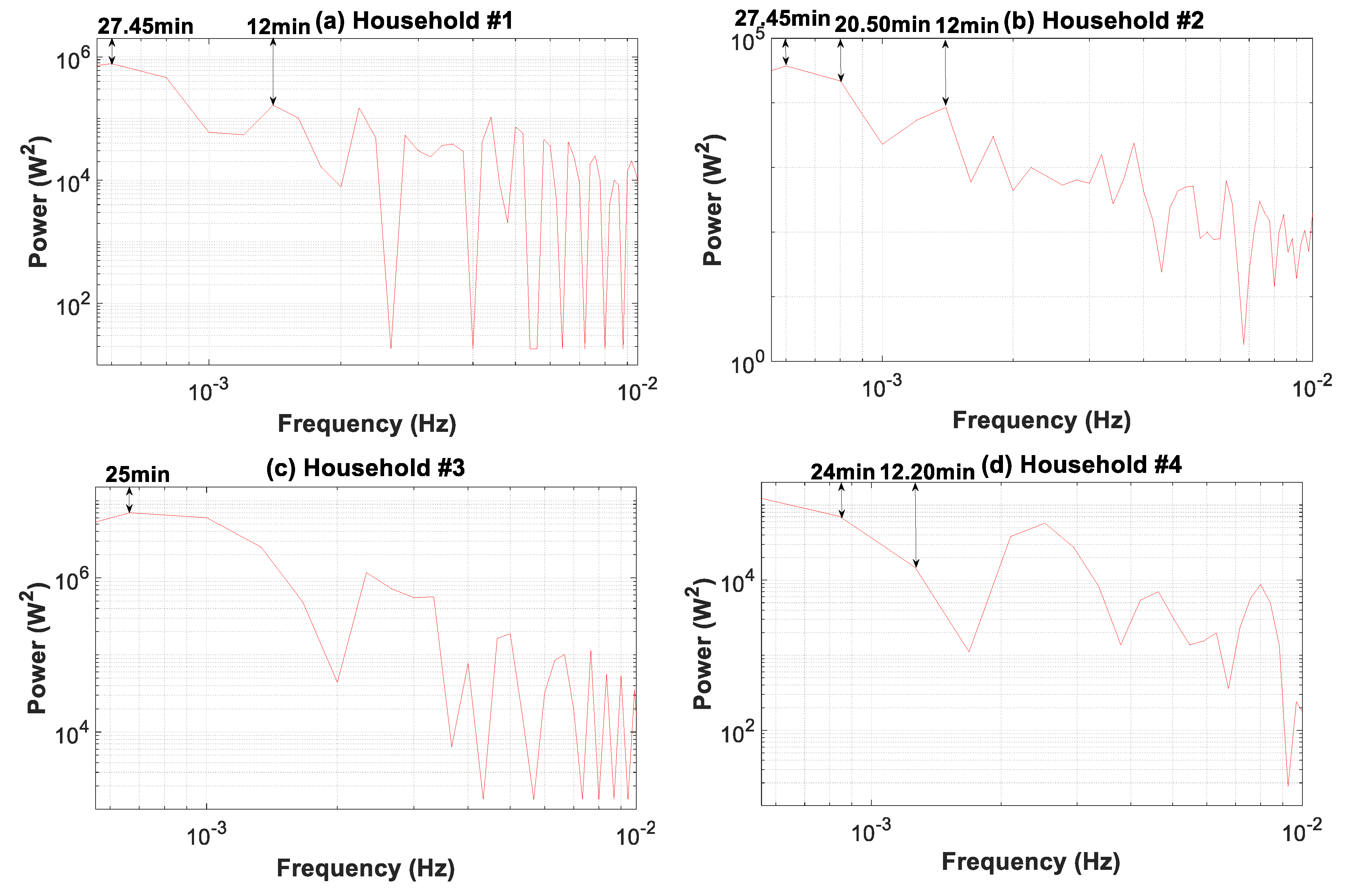
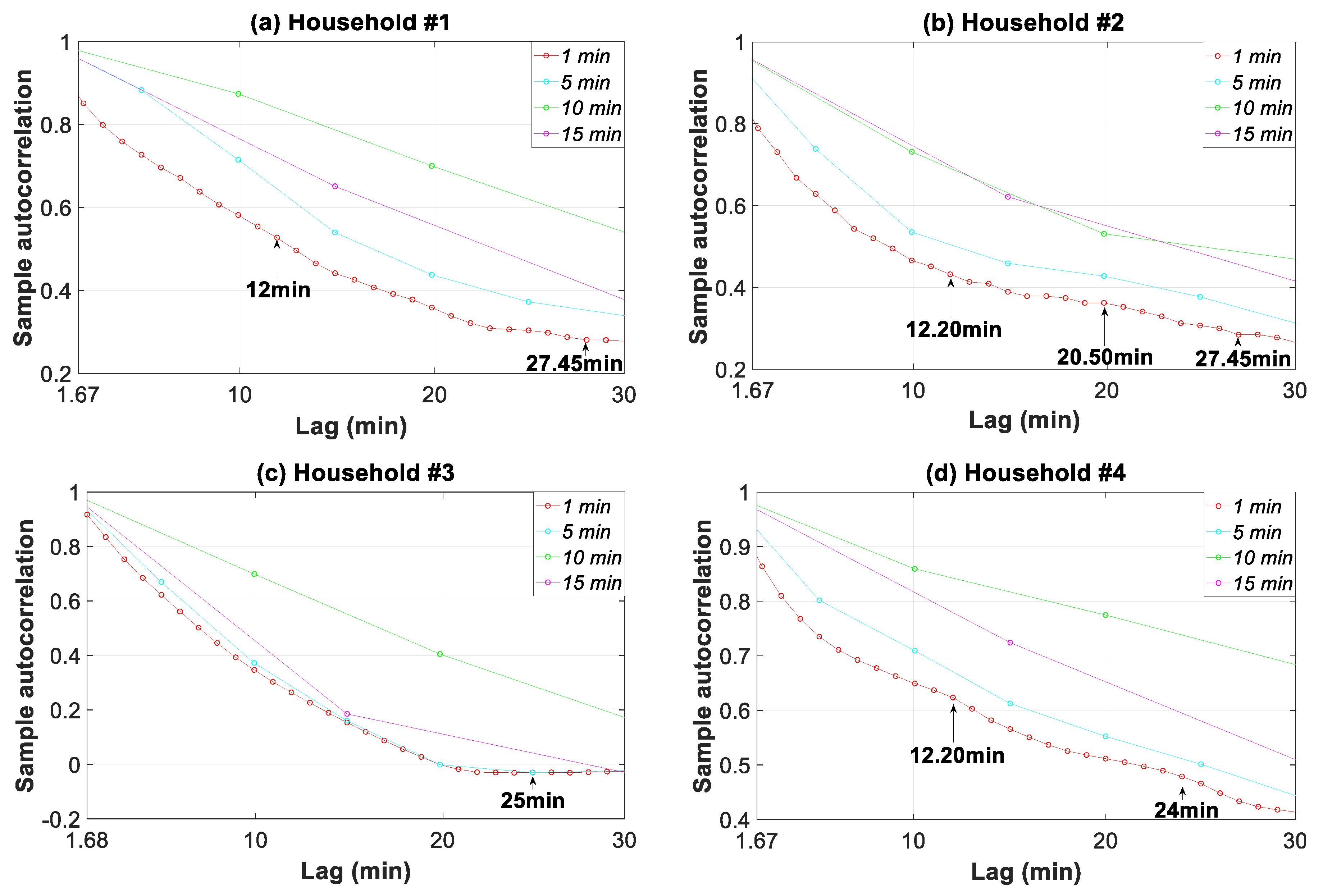
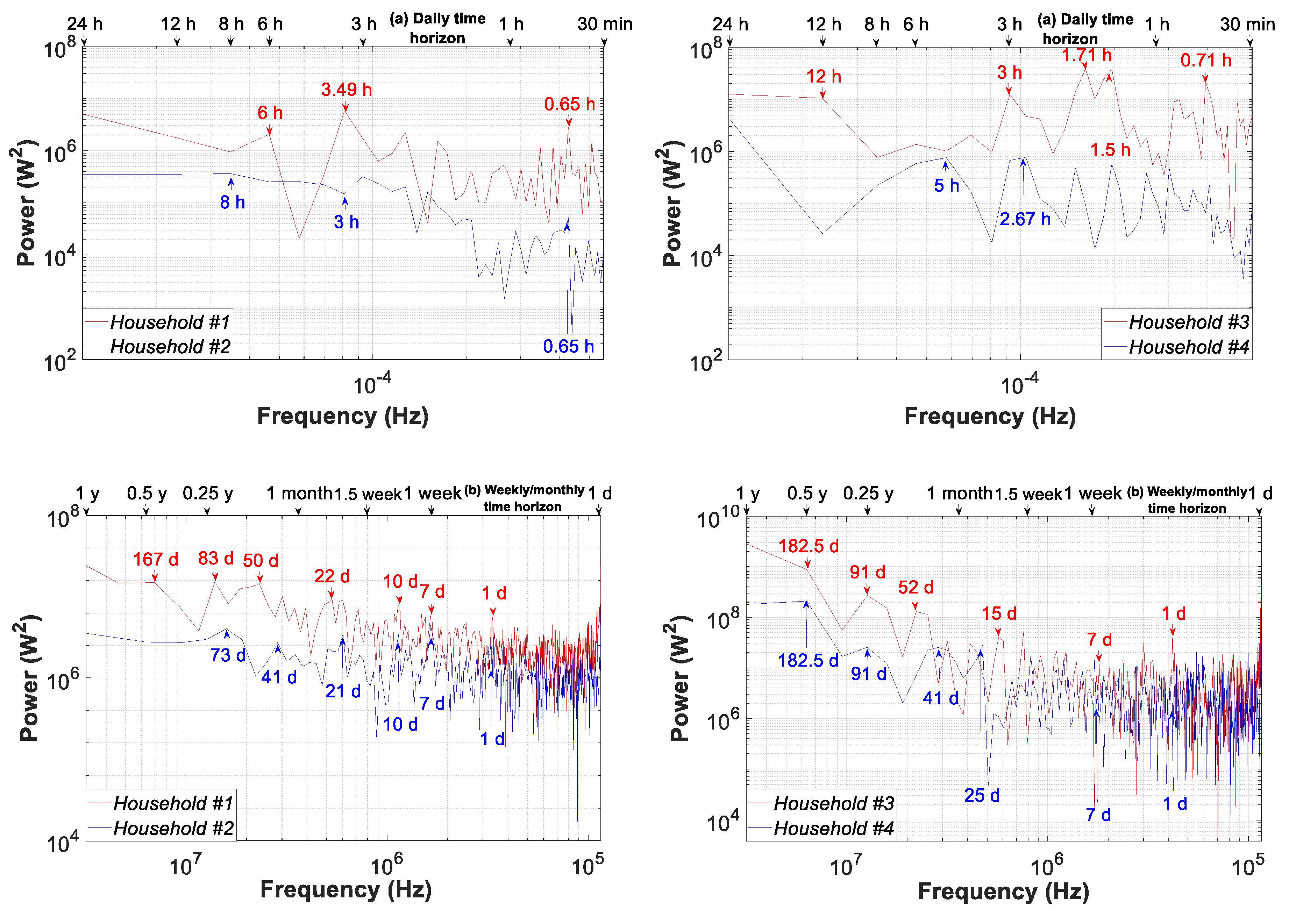
| Time Resolutions (Data Granularity -Sampling Frequency) | Actions or Assessments | Time Horizon (Time Slice) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjust Tariff Electrics | Energy Efficiency & Comfort | Recognize Activities | Optimization Size Renewable Generation | Electrical Load Forecasting | Power Consumption Characterization | Applying Probabilistic Techniques | A Few Minutes | A Few Hours | A Few Days | |
| <0.5 s | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | [8] | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 1 s | -- | [8,9,12] | [23] | [13,42] | [12] | [7,8,9,11] | -- | [7,13] | [9,23] | [13] |
| >1 s and <10 s | -- | [8,38] | -- | [13] | -- | [8,38,41] | -- | [13] | -- | [13] |
| 15 s | -- | -- | -- | [13,14] | [14] | -- | -- | [13] | -- | [13] |
| 1 min | -- | [9,12] | [6,12,26] | [13,45] | [12,24,25,26,27,29] | [6,9,27] | -- | [19,26,27] | [6,9] | -- |
| 5 min | [15] | [15,17] | [26] | [7,16] | [17,18,26,27] | [7,27] | [18] | [15,16,17,18,26,27] | [17] | [17] |
| 15 min | [16] | -- | [6,22,26] | [16] | [22,25,26,30,34,37,47] | [6,11,32] | -- | [16,26] | [6,33,34,47] | [22] |
| 30 min | -- | -- | [26] | [42,45] | [22,27,30,33,34,35,42] | [35] | [42] | [26,27,35,42] | [33,34] | [22,35,42] |
| 1 h | -- | -- | [26,28,36] | [45,48] | [25,26,30,34,36] | [28] | -- | [26] | [34,36] | [22] |
| 1 day | -- | -- | [36] | [43] | [36,37,43] | [37] | -- | [37] | [36] | [43] |
| No available information | [14] | -- | [4,40,49] | [19,20,21,29] | [7] | [19,20] | [20] | [19,21] | ||
| Household #1 | Household #2 | Household #3 | Household #4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total annual consumption (kWh/year) | 3033 | 2626 | 22,058 | 4139 |
| Total surface (m2) | 100 | 125 | 210 | 140 |
| Number of family members | 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Is there at least an adult during the morning at home? | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Electric heating | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Electric air conditioned | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Building type | Flat | Semi-Detached house | Detached house | Terraced house |
| Contracted power from the electric mains (kW) | 3.45 | 2.3 | 5.75 | 4.6 |
| Number of phases | 1-phase | 1-phase | 3-phase | 1-phase |
| Item | Power (W) | Household #1 | Household #2 | Household #3 | Household #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oven | 1200–2200 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Electric cooker | 900–2000 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Extractor hood | 70–200 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Microwave oven | 900–2500 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Dishwasher | 1500–2200 | √ | ---- | √ | √ |
| Refrigerator | 250–350 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Washing machine | 1500–2200 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Electric water heater | 1500–5500 | ---- | ---- | √ | ---- |
| Vacuum cleaner | 1100–2000 | √ | ---- | √ | ---- |
| Dryer | 1000–2500 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Clothes dryer | 1500–3000 | √ | ---- | √ | ---- |
| Desktop computer | 150–300 | √ | ---- | √ | ---- |
| Laptop | 100–250 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Smart phone | 15–25 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Tablet | 20–30 | √ | ---- | √ | --- |
| LED TV | 150–550 | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| BlueRay-DVD player | 50–75 | ---- | √ | ---- | ---- |
| Stereo system | 100–150 | √ | √ | ---- | √ |
| Video games console | 25–150 | √ | ---- | √ | √ |
| Low energy bulbs | 5–20 | √ | √ | √ | ---- |
| Florescent lamps | 18–58 | √ | √ | ---- | √ |
| LED lamps | 4–12 | √ | ---- | √ | √ |
| Halogen lamps | 25–60 | ---- | ---- | ---- | √ |
| Data Granularity | Household #1 | Household #2 | Household #3 | Household #4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Peak-Mean | Minimum Trough-Mean | Maximum Peak-Mean | Minimum Trough-Mean | Maximum Peak-Mean | Minimum Trough-Mean | Maximum Peak-Mean | Minimum Trough-Mean | |
| 0.5 s | 17.7714 | 7.4346 | 13.2673 | 6.1029 | 6.3413 | 3.1745 | 6.9320 | 3.2970 |
| 1 s | 17.4875 | 7.4233 | 13.2562 | 5.4252 | 6.3114 | 3.1726 | 6.9318 | 3.2951 |
| 2 s | 17.5749 | 7.2256 | 13.2559 | 4.7885 | 6.2524 | 3.1693 | 6.8127 | 3.2876 |
| 5 s | 17.4989 | 7.0880 | 13.1816 | 3.6465 | 6.2348 | 3.1668 | 6.7546 | 3.2712 |
| 10 s | 17.3746 | 6.8418 | 13.1445 | 2.3266 | 6.2191 | 3.1642 | 6.7268 | 3.2671 |
| 15 s | 17.1912 | 6.5573 | 13.0965 | 2.0043 | 6.2258 | 3.1601 | 6.6947 | 3.2524 |
| 30 s | 17.1558 | 6.5692 | 13.0793 | 1.6689 | 6.1782 | 3.1554 | 6.6404 | 3.2491 |
| 1 min | 16.0662 | 6.5542 | 11.4579 | 1.6763 | 5.3288 | 3.0967 | 6.5740 | 3.2495 |
| 2 min | 15.4650 | 6.0329 | 10.8880 | 1.7029 | 5.6834 | 2.9352 | 6.1811 | 3.0951 |
| 5 min | 14.8479 | 5.0117 | 9.3116 | 1.6465 | 5.3142 | 2.8401 | 5.9447 | 1.7821 |
| 10 min | 13.4116 | 4.7214 | 8.6840 | 1.6023 | 4.5818 | 2.7117 | 5.5095 | 1.8488 |
| 15 min | 12.0069 | 3.7204 | 8.6675 | 1.5882 | 4.7191 | 2.3409 | 4.6373 | 1.5840 |
| 30 min | 8.8820 | 2.6709 | 8.0044 | 1.5119 | 4.1170 | 2.2958 | 4.3747 | 1.3305 |
| Household | Data Granularity | Sample Mean (kW) | Maximum Value (W) | Minimum Value (kW) | Sample Variance (kW2) | Sample Skewness (kW3) | Sample Kurtosis (kW4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 0.5 s | 0.3771 | 1.2884 | 0.1021 | 0.0326 | 1.7935 | 7.8044 |
| 1 s | 0.3752 | 1.2821 | 0.1016 | 0.0323 | 1.7932 | 7.8035 | |
| 2 s | 0.3733 | 1.2756 | 0.1011 | 0.0320 | 1.7938 | 7.8060 | |
| 5 s | 0.3658 | 1.2497 | 0.0991 | 0.0307 | 1.7930 | 7.8024 | |
| 10 s | 0.3628 | 1.2397 | 0.0982 | 0.0302 | 1.7931 | 7.8048 | |
| 15 s | 0.3619 | 1.2369 | 0.0980 | 0.0301 | 1.7959 | 7.8179 | |
| 30 s | 0.3582 | 1.2247 | 0.0971 | 0.0295 | 1.7940 | 7.8073 | |
| 1 min | 0.3545 | 1.2112 | 0.0960 | 0.0288 | 1.7950 | 7.8130 | |
| 2 min | 0.3506 | 1.1994 | 0.0950 | 0.0283 | 1.7988 | 7.8334 | |
| 5 min | 0.3430 | 1.1722 | 0.0918 | 0.0270 | 1.7963 | 7.8290 | |
| 10 min | 0.3388 | 1.1616 | 0.0926 | 0.0264 | 1.8027 | 7.8813 | |
| 15 min | 0.3285 | 1.1191 | 0.0884 | 0.0248 | 1.7985 | 7.8953 | |
| 30 min | 0.3106 | 1.0882 | 0.0801 | 0.0224 | 1.8782 | 8.5657 | |
| #2 | 0.5 s | 0.2998 | 0.4912 | 0.1922 | 0.0030 | 0.4923 | 3.6786 |
| 1 s | 0.2983 | 0.4888 | 0.1912 | 0.0028 | 0.4920 | 3.6774 | |
| 2 s | 0.2968 | 0.4863 | 0.1903 | 0.0029 | 0.4934 | 3.6812 | |
| 5 s | 0.2908 | 0.4764 | 0.1864 | 0.0028 | 0.4927 | 3.6803 | |
| 10 s | 0.2884 | 0.4725 | 0.1849 | 0.0028 | 0.4930 | 3.6810 | |
| 15 s | 0.2878 | 0.4715 | 0.1845 | 0.0028 | 0.4906 | 3.6731 | |
| 30 s | 0.2848 | 0.4668 | 0.1827 | 0.0027 | 0.4913 | 3.6795 | |
| 1 min | 0.2818 | 0.4622 | 0.1809 | 0.0027 | 0.4947 | 3.6930 | |
| 2 min | 0.2788 | 0.4573 | 0.1790 | 0.0026 | 0.4876 | 3.6675 | |
| 5 min | 0.2728 | 0.4488 | 0.1748 | 0.0025 | 0.4886 | 3.6615 | |
| 10 min | 0.2701 | 0.4417 | 0.1732 | 0.0025 | 0.4827 | 3.6079 | |
| 15 min | 0.2606 | 0.4229 | 0.1683 | 0.0023 | 0.4702 | 3.5331 | |
| 30 min | 0.2469 | 0.4014 | 0.1539 | 0.0021 | 0.3548 | 3.3360 | |
| #3 | 0.5 s | 2.5180 | 3.0848 | 2.0955 | 0.0276 | 0.8327 | 3.4692 |
| 1 s | 2.5054 | 3.0690 | 2.0844 | 0.0273 | 0.8323 | 3.4684 | |
| 2 s | 2.4928 | 3.0545 | 2.0745 | 0.0270 | 0.8332 | 3.4696 | |
| 5 s | 2.4425 | 2.9928 | 2.0321 | 0.0260 | 0.8329 | 3.4723 | |
| 10 s | 2.4224 | 2.9683 | 2.0174 | 0.0255 | 0.8328 | 3.4685 | |
| 15 s | 2.4173 | 2.9608 | 2.0108 | 0.0254 | 0.8317 | 3.4663 | |
| 30 s | 2.3922 | 2.9311 | 1.9906 | 0.0249 | 0.8312 | 3.4660 | |
| 1 min | 2.3670 | 2.9016 | 1.9720 | 0.0244 | 0.8309 | 3.4660 | |
| 2 min | 2.3420 | 2.8627 | 1.9485 | 0.0239 | 0.8324 | 3.4470 | |
| 5 min | 2.2913 | 2.7917 | 1.9029 | 0.0229 | 0.8126 | 3.4436 | |
| 10 min | 2.2669 | 2.8123 | 1.8726 | 0.0225 | 0.8498 | 3.5525 | |
| 15 min | 2.1899 | 2.6639 | 1.8024 | 0.0211 | 0.7854 | 3.5506 | |
| 30 min | 2.0736 | 2.6612 | 1.7269 | 0.0200 | 1.0132 | 4.1224 | |
| #4 | 0.5 s | 0.4726 | 0.6576 | 0.0880 | 0.0059 | −0.5149 | 4.8532 |
| 1 s | 0.4702 | 0.6544 | 0.0876 | 0.0058 | −0.5147 | 4.8532 | |
| 2 s | 0.4678 | 0.6510 | 0.0871 | 0.0057 | −0.5154 | 4.8545 | |
| 5 s | 0.4584 | 0.6379 | 0.0854 | 0.0055 | −0.5152 | 4.8533 | |
| 10 s | 0.4546 | 0.6323 | 0.0847 | 0.0054 | −0.5175 | 4.8579 | |
| 15 s | 0.4537 | 0.6314 | 0.0845 | 0.0054 | −0.5147 | 4.8602 | |
| 30 s | 0.4489 | 0.6251 | 0.0836 | 0.0053 | −0.5129 | 4.8537 | |
| 1 min | 0.4442 | 0.6179 | 0.0828 | 0.0052 | −0.5167 | 4.8618 | |
| 2 min | 0.4396 | 0.6133 | 0.0819 | 0.0051 | −0.5198 | 4.8590 | |
| 5 min | 0.4302 | 0.5983 | 0.0803 | 0.0049 | −0.5133 | 4.8487 | |
| 10 min | 0.4248 | 0.5972 | 0.0797 | 0.0048 | −0.5042 | 4.8242 | |
| 15 min | 0.4111 | 0.5617 | 0.0773 | 0.0044 | −0.5558 | 4.9013 | |
| 30 min | 0.3888 | 0.5360 | 0.0739 | 0.0041 | −0.4903 | 4.7124 |
| Household | Data Granularity | ADF Test | KPSS Test | Variance Ratio Test | LMC Test | PP Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null Hypothesis (H) | p-Value | Null Hypothesis (H) | p-Value | Null Hypothesis (H) | p-Value | Null Hypothesis (H) | p-Value | Null Hypothesis (H) | p-Value | ||
| #1 | 0.5 s | 0 | 0.0374 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 1.5166 × 10−9 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0374 |
| 1 s | 0 | 0.0363 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 6.8206 × 10−8 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0363 | |
| 2 s | 0 | 0.0472 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 5.6420 × 10−7 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0472 | |
| 5 s | 0 | 0.0455 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 6.2874 × 10−11 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0455 | |
| 10 s | 0 | 0.0436 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 1.4630 × 10−7 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0436 | |
| 15 s | 0 | 0.0433 | 1 | 0.0174 | 0 | 7.1719 × 10−6 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0433 | |
| 30 s | 0 | 0.0499 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 2.6792 × 10−40 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0399 | |
| 1 min | 0 | 0.0399 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 4.9340 × 10−10 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0399 | |
| 2 min | 0 | 0.0379 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0001 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0379 | |
| 5 min | 0 | 0.0279 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0458 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0279 | |
| 10 min | 0 | 0.0456 | 1 | 0.0478 | 0 | 0.0215 | 0 | 0.0181 | 0 | 0.0456 | |
| 15 min | 0 | 0.0158 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0036 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0158 | |
| 30 min | 0 | 0.0183 | 1 | 0.0213 | 0 | 0.0184 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0183 | |
| #2 | 0.5 s | 0 | 0.0010 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0410 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0010 |
| 1 s | 0 | 0.0224 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0328 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0224 | |
| 2 s | 0 | 0.0010 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0321 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0010 | |
| 5 s | 0 | 0.0152 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0320 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0152 | |
| 10 s | 0 | 0.0446 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0306 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0446 | |
| 15 s | 0 | 0.0470 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0341 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0470 | |
| 30 s | 0 | 0.0387 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0412 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0387 | |
| 1 min | 0 | 0.0401 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0152 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0401 | |
| 2 min | 0 | 0.0408 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0117 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0408 | |
| 5 min | 0 | 0.0434 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0399 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0434 | |
| 10 min | 0 | 0.0446 | 1 | 0.0310 | 0 | 0.0324 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0446 | |
| 15 min | 0 | 0.0475 | 1 | 0.0386 | 0 | 0.0320 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0475 | |
| 30 min | 0 | 0.0470 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0483 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0470 | |
| #3 | 0.5 s | 0 | 0.0302 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0223 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0302 |
| 1 s | 0 | 0.0299 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0332 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0299 | |
| 2 s | 0 | 0.0361 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0135 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0361 | |
| 5 s | 0 | 0.0357 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0442 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0357 | |
| 10 s | 0 | 0.0331 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0443 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0331 | |
| 15 s | 0 | 0.0330 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0447 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0330 | |
| 30 s | 0 | 0.0329 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0477 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0329 | |
| 1 min | 0 | 0.0314 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0206 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0314 | |
| 2 min | 0 | 0.0338 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0379 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0338 | |
| 5 min | 0 | 0.0417 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0464 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0417 | |
| 10 min | 0 | 0.0265 | 1 | 0.0333 | 0 | 0.0426 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0265 | |
| 15 min | 0 | 0.0151 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0150 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0151 | |
| 30 min | 0 | 0.0415 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0408 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0415 | |
| #4 | 0.5 s | 0 | 0.0298 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 1.6278 × 10−30 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0298 |
| 1 s | 0 | 0.0263 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 7.7177 × 10−20 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0263 | |
| 2 s | 0 | 0.0429 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 5.5778 × 10−219 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0429 | |
| 5 s | 0 | 0.0491 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 1.9919 × 10−52 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0391 | |
| 10 s | 0 | 0.0459 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0459 | |
| 15 s | 0 | 0.0444 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 4.1505 × 10−150 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0447 | |
| 30 s | 0 | 0.0436 | 1 | 0.0229 | 0 | 4.8221 × 10−9 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0364 | |
| 1 min | 0 | 0.0451 | 1 | 0.0719 | 0 | 4.3992 × 10−22 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0418 | |
| 2 min | 0 | 0.0449 | 1 | 0.0450 | 0 | 2.2699 × 10−7 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0498 | |
| 5 min | 0 | 0.0458 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 6.6692 × 10−18 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0482 | |
| 10 min | 0 | 0.0451 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0155 | 0 | 0.0238 | 0 | 0.0413 | |
| 15 min | 0 | 0.0482 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0051 | 0 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0421 | |
| 30 min | 0 | 0.0389 | 1 | 0.0100 | 0 | 0.0384 | 0 | 0.1000 | 0 | 0.0399 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez, J.C.; Sanchez-Sutil, F.; Cano-Ortega, A.; Baier, C.R. Influence of Data Sampling Frequency on Household Consumption Load Profile Features: A Case Study in Spain. Sensors 2020, 20, 6034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216034
Hernandez JC, Sanchez-Sutil F, Cano-Ortega A, Baier CR. Influence of Data Sampling Frequency on Household Consumption Load Profile Features: A Case Study in Spain. Sensors. 2020; 20(21):6034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216034
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez, J. C., F. Sanchez-Sutil, A. Cano-Ortega, and C. R. Baier. 2020. "Influence of Data Sampling Frequency on Household Consumption Load Profile Features: A Case Study in Spain" Sensors 20, no. 21: 6034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216034
APA StyleHernandez, J. C., Sanchez-Sutil, F., Cano-Ortega, A., & Baier, C. R. (2020). Influence of Data Sampling Frequency on Household Consumption Load Profile Features: A Case Study in Spain. Sensors, 20(21), 6034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20216034








