Evaluation of a Novel Ear Pulse Oximeter: Towards Automated Oxygen Titration in Eyeglass Frames
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
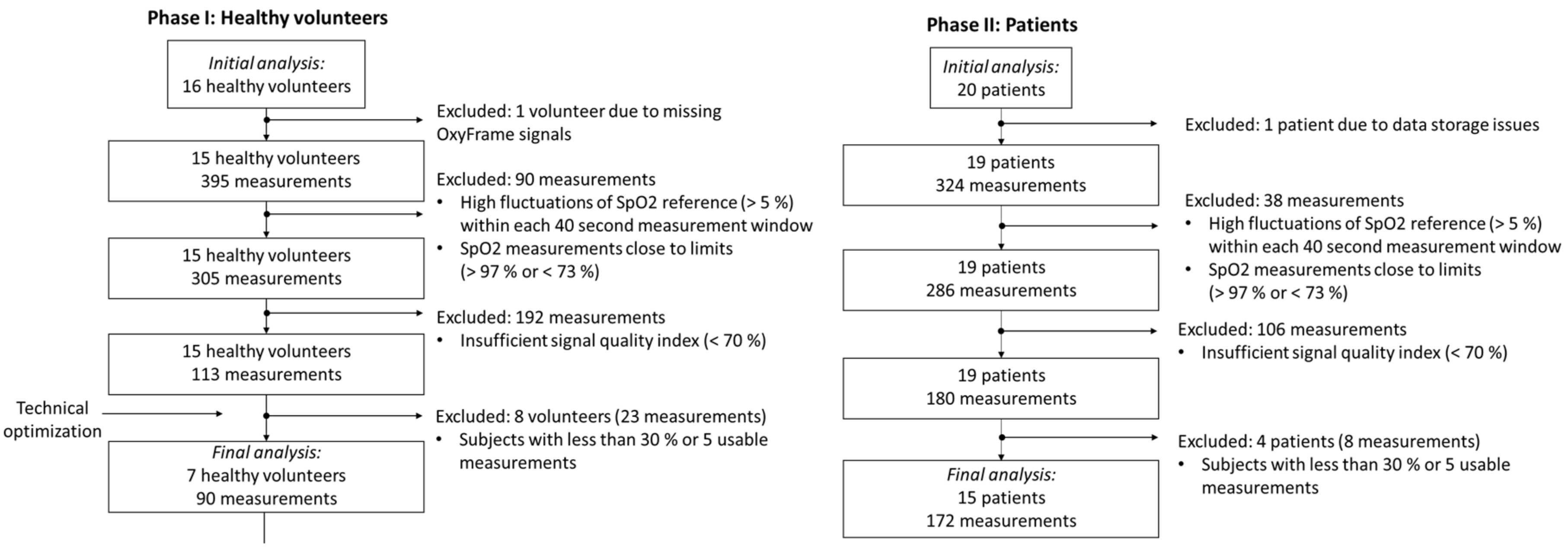
2.1. Study Participants and Protocol
2.1.1. Healthy Volunteers
2.1.2. Patients
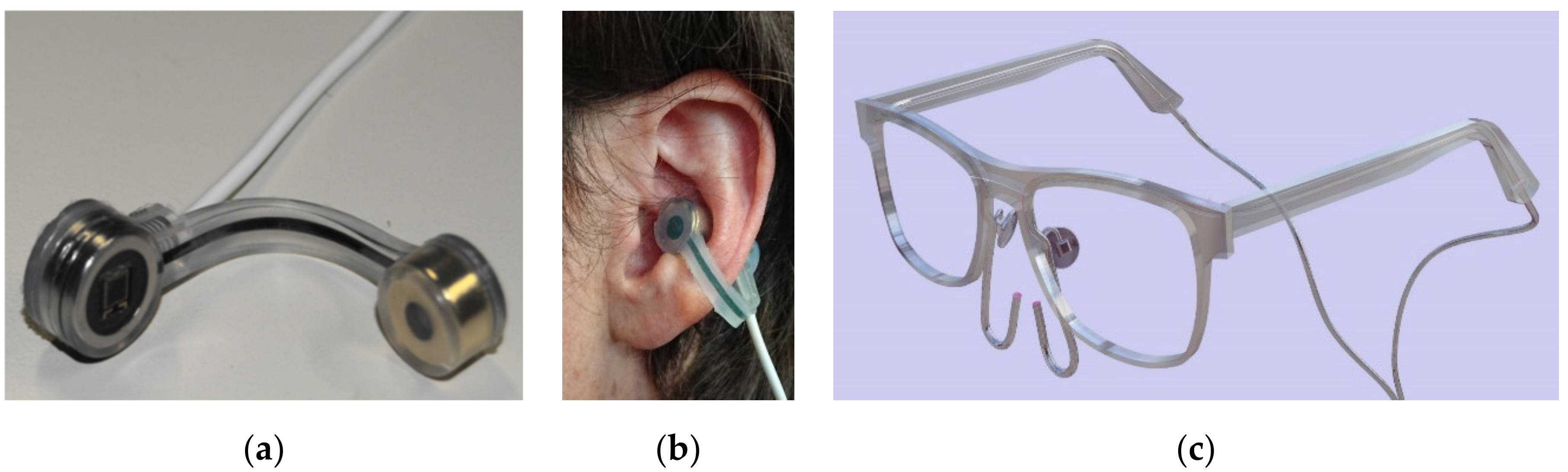
2.2. Sensor Electronics and Data Processing
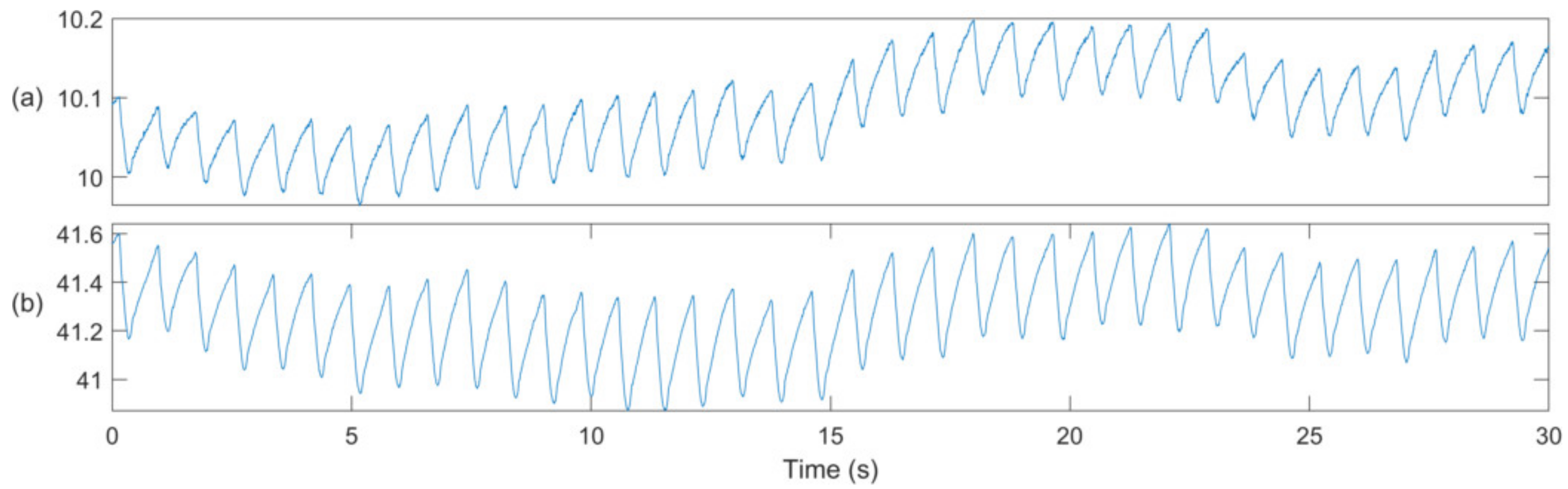
2.3. OxyFrame SpO2 Performance Evaluation
3. Results
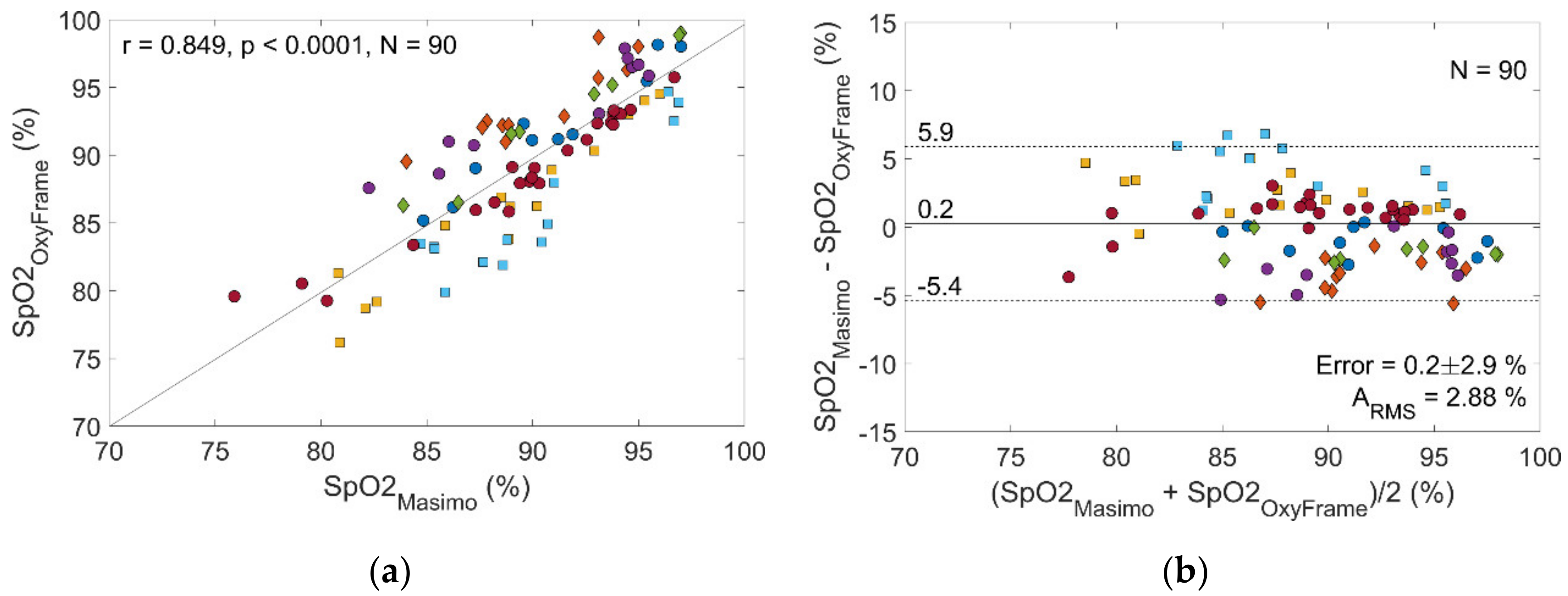
3.1. Healthy Volunteers
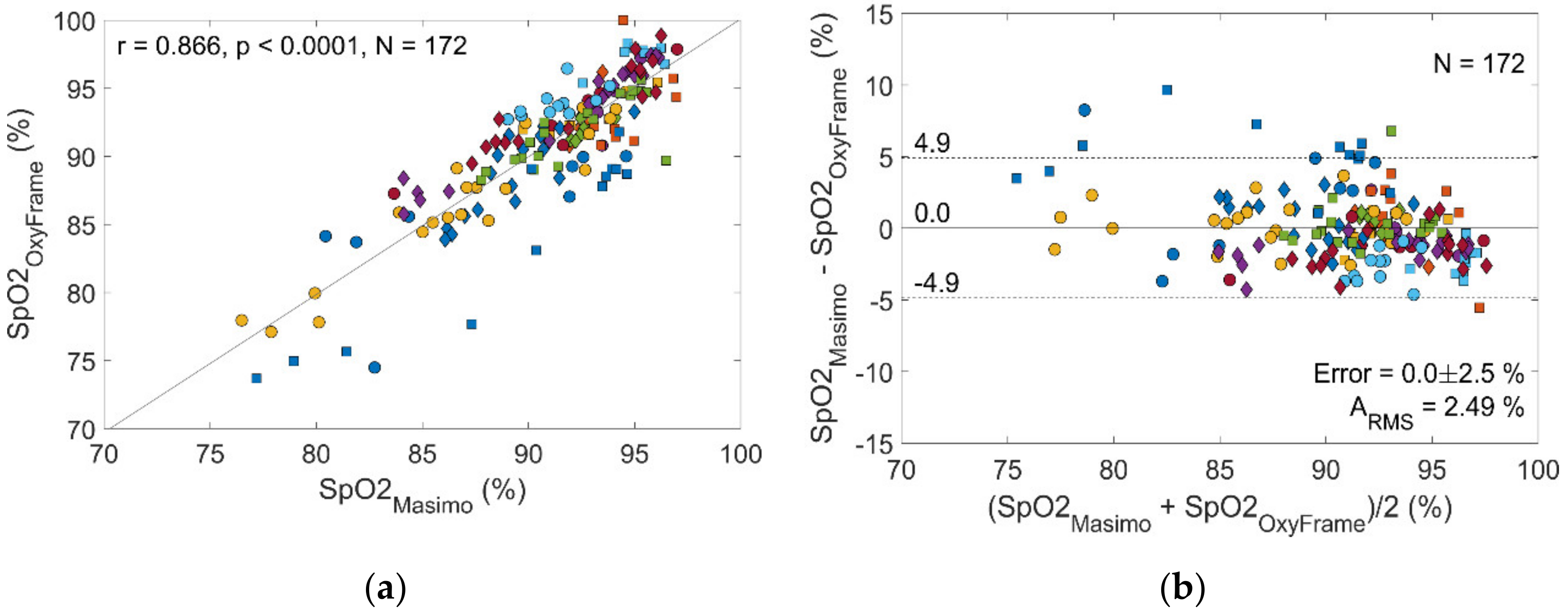
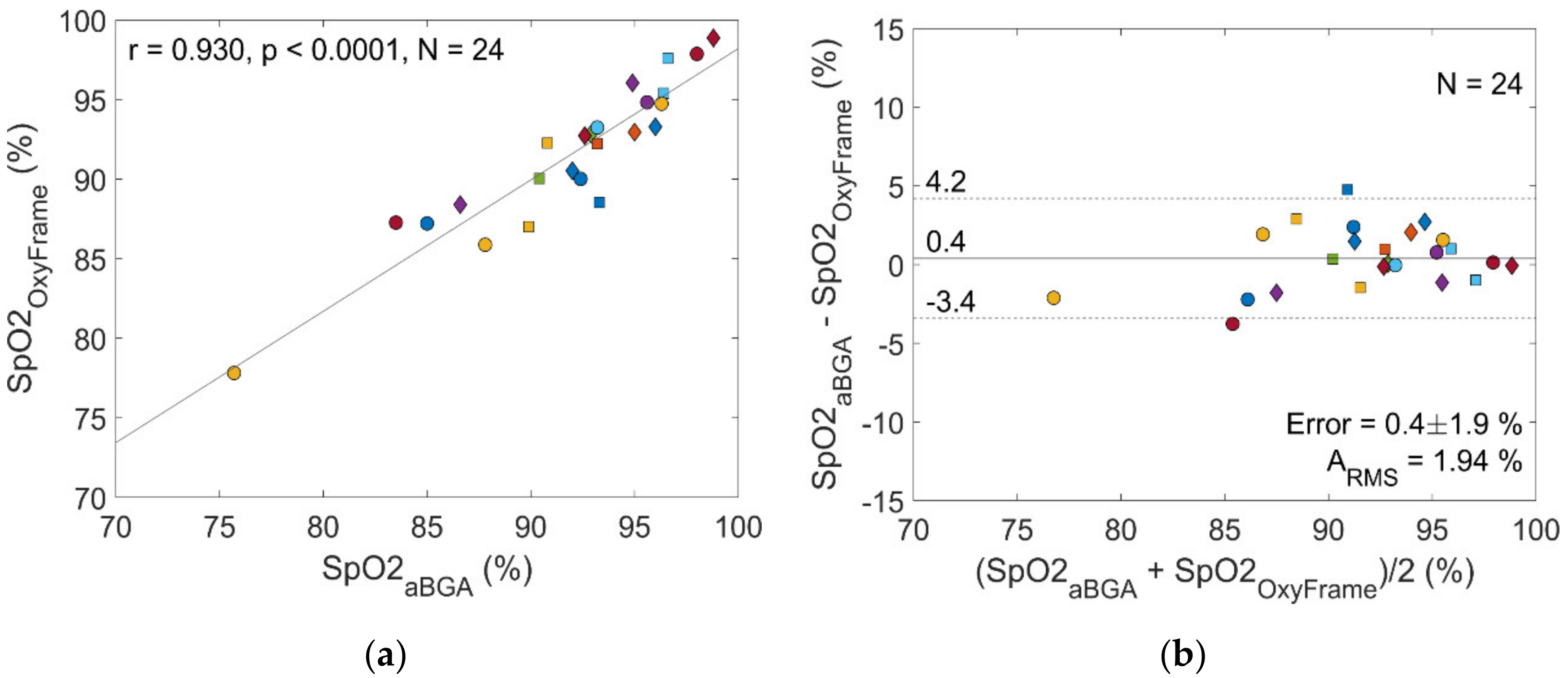
3.2. Patients
4. Discussion
4.1. Low Signal Quality and High Rejection Rates
4.2. Issues and Potential Solutions Related to the OxyFrame Sensor
4.3. Clinical Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, D.; Agusti, A.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Bourbeau, J.; Celli, B.R.; Criner, G.J.; Frith, P.; Halpin, D.M.G.; Han, M.; et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: The GOLD science committee report 2019. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1900164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, T.; Garrett, J.E.; Young, P.; Fergusson, W.; Kolbe, J.; Rudkin, S.; Whyte, K. Ambulatory oxygen improves quality of life of COPD patients: A randomised controlled study. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Funke-Chambour, M.; Azzola, A.; Adler, D.; Barazzone-Argiroffo, C.; Benden, C.; Boehler, A.; Bridevaux, P.-O.; Brutsche, M.; Clarenbach, C.F.; Hostettler, K.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Switzerland: Diagnosis and Treatment. Respiration 2017, 93, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, M.R.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ramsook, A.H.; Molgat-Seon, Y.; Wilkie, S.S.; Dhillon, S.S.; Mitchell, R.A.; Sheel, A.W.; Khalil, N.; Camp, P.G.; et al. Effects of hyperoxia on dyspnoea and exercise endurance in fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Camp, P.G.; Eves, N.D.; Schaeffer, M.; Syed, N.; Dhillon, S.; Jensen, D.; Maltais, F.; O’Donnell, D.E.; Raghavan, N.; et al. High Oxygen Delivery to Preserve Exercise Capacity in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treated with Nintedanib. Methodology of the HOPE-IPF Study. Annals ATS 2016, 13, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitzan, M.; Romem, A.; Koppel, R. Pulse oximetry: Fundamentals and technology update. MDER 2014, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengelkoch, L.J.; Martin, D.; Lawler, J. A Review of the Principles of Pulse Oximetry and Accuracy of Pulse Oximeter Estimates During Exercise. Phys. Ther. 1994, 74, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.; Cecins, N.; Jenkins, S.; Melang, M.; Singh, B.; Hill, K. Comparing finger and forehead sensors to measure oxygen saturation in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Comparing pulse oximetry sensors in COPD. Respirology 2013, 18, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schallom, L.; Sona, C.; McSweeney, M.; Mazuski, J. Comparison of forehead and digit oximetry in surgical/trauma patients at risk for decreased peripheral perfusion. Heart Lung 2007, 36, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wei, W. Esophageal pulse oximetry is more accurate and detects hypoxemia earlier than conventional pulse oximetry during general anesthesia. Front. Med. 2012, 6, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimacombe, J.; Keller, C. Successful pharyngeal pulse oximetry in low perfusion states. Can. J. Anesth. 2000, 47, 907–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brimacombe, J.; Keller, C.; Margreiter, J. A Pilot Study of Left Tracheal Pulse Oximetry. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 91, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey, T.E.; Rice, M.J.; Vasilopoulos, T.; Dennis, D.M.; Melker, R.J. Feasibility and accuracy of nasal alar pulse oximetry. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 112, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Budidha, K.; Kyriacou, P.A. Devepopment of an optical probe to investigate the suitability of measuring photoplethysmographs and blood oxygen saturation from the human auditory canal. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1736–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Budidha, K.; Kyriacou, P.A. Investigation of photoplethysmography and arterial blood oxygen saturation from the ear-canal and the finger under conditions of artificially induced hypothermia. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 7954–7957. [Google Scholar]
- Venema, B.; Gehring, H.; Michelsen, I.; Blanik, N.; Blazek, V.; Leonhardt, S. Robustness, Specificity, and Reliability of an In-Ear Pulse Oximetric Sensor in Surgical Patients. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchelder, P.B.; Raley, D.M. Maximizing the Laboratory Setting for Testing Devices and Understanding Statistical Output in Pulse Oximetry. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 105, S85–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelmeier, C.F.; Criner, G.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Bourbeau, J.; Celli, B.R.; Chen, R.; Decramer, M.; Fabbri, L.M.; et al. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2017 Report. GOLD Executive Summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2017, 195, 557–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proença, M.; Grossenbacher, O.; Dasen, S.; Moser, V.; Ostojic, D.; Lemkaddem, A.; Ferrario, D.; Lemay, M.; Wolf, M.; Fauchére, J.; et al. Performance Assessment of a Dedicated Reflectance Pulse Oximeter in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. In Proceedings of the EMBC 2018, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 1502–1505. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Non-Invasive Sphygmomanometers—Part 2: Clinical Investigation of Intermittent Automated Measurement Type; ISO 81060-2:2018; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, F.; Theurillat, P.; Proenca, M.; Lemkaddem, A.; Ferrario, D.; Jaegere, K.D.; Horvath, C.M.; Roth, C.; Brill, A.-K.; Lemay, M.; et al. Pulse Oximetry at the Wrist During Sleep: Performance, Challenges and Perspectives. In Proceedings of the EMBC 2020, Montréal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020. (In press). [Google Scholar]
- Long term domiciliary oxygen therapy in chronic hypoxic cor pulmonale complicating chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Report of the Medical Research Council Working Party. The Lancet 1981, 317, 681–686. [CrossRef]
- Continuous or Nocturnal Oxygen Therapy in Hypoxemic Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: A Clinical Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1980, 93, 391. [CrossRef]
- The Long-Term Oxygen Treatment Trial Research Group A Randomized Trial of Long-Term Oxygen for COPD with Moderate Desaturation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1617–1627. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, R.C.; Hicks, S.; Duck, A.M.; Spencer, L.; Leonard, C.T.; Barnett, E. Ambulatory oxygen in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Of what benefit? Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visca, D.; Montgomery, A.; de Lauretis, A.; Sestini, P.; Soteriou, H.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Renzoni, E.A. Ambulatory oxygen in interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soguel Schenkel, N.; Burdet, L.; de Muralt, B.; Fitting, J.W. Oxygen saturation during daily activities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 1996, 9, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.F.; Nelson, S.B.; Hubmayr, R.D. Oxygen-induced Hypercarbia in Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 144, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassoon, C.S.H.; Hassell, K.T.; Mahutte, C.K. Hyperoxic-Induced Hypercapnia in Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 135, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Greenberg, J.; Grodman, R.; Gunawardena, R.; Naidu, A. Effect of oxygen on breath markers of oxidative stress. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rice, K.L.; Schmidt, M.F.; Buan, J.S.; Lebahn, F.; Schwarzock, T.K. AccuO2 Oximetry-Driven Oxygen-Conserving Device Versus Fixed-Dose Oxygen Devices in Stable COPD Patients. Respir. Care 2011, 56, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cirio, S.; Nava, S. Pilot Study of a New Device to Titrate Oxygen Flow in Hypoxic Patients on Long-Term Oxygen Therapy. Respir. Care 2011, 56, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lellouche, F.; L’Her, E. Automated Oxygen Flow Titration to Maintain Constant Oxygenation. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Claure, N.; Bancalari, E. Automated Closed Loop Control of Inspired Oxygen Concentration. Respir. Care 2013, 58, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, A.B.; Rissmiller, R.W.; Meade, K.; Paladenech, C.; Conforti, J.; Adair, N.E.; Haponik, E.F.; Chin, R., Jr. Reproducibility of the 6-Minute Walk Test for Ambulatory Oxygen Prescription. Respiration 2010, 79, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, T.; Young, P.; Milne, D.; Wells, A.U. Six-Minute Walk, Maximal Exercise Tests: Reproducibility in Fibrotic Interstitial Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, Y.H.; Goh, N.S.L.; McDonald, C.F.; Holland, A.E. Oxygen Therapy for Interstitial Lung Disease. A Mismatch between Patient Expectations and Experiences. Annals ATS 2017, 14, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Volunteers | Patients | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Walking | Stationary | Overall | Walking | Stationary | |
| Error (%) | 0.2 (2.9) | 1.5 (2.8) | 0.1 (2.9) | 0.0 (2.5) | 1.6 (3.4) | 0.3 (2.2) |
| r | 0.849 * | 0.901 † | 0.845 * | 0.866 * | 0.829 * | 0.804 * |
| ARMS (%) | 2.88 | 2.99 | 2.87 | 2.49 | 3.65 | 2.17 |
| Rejection Rate (%) | 77.2 | 92.4 | 72.6 | 46.9 | 71.3 | 35.9 |
| All (n = 20) | COPD (n = 9) | ILD (n = 11) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age, years | 65.9 (55–72) | 66.6 (59–72) | 65.4 (55–72) |
| Male/female | 15/5 | 7/2 | 8/3 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.1 (5.9) | 23.8 (7.0) | 28.1 (3.8) |
| Smoked pack-years | 46 (36) | 75 (31.6) | 20 (11.9) |
| Pulmonary Function Test | |||
| TLC, % predicted | 85.5 (31.6) | 123.3 (15.4) | 64.8 (14.2) |
| FEV1/FVC, % | 62.2 (21.4) | 40.9 (10.9) | 79.6 (7.7) |
| FVC, % predicted | 64.1 (17.6) | 66.1 (17.6) | 62.5 (17.4) |
| FEV1, % predicted | 51.5 (24.3) | 34.9 (15.3) | 65.0 (21.8) |
| DLCO, % predicted | 41.0 (14.7) | 37.6 (9.4) | 43.8 (17.3) |
| 6-min Walking Test | |||
| 6MWD, meters | 366 (119) | 327 (126) | 387 (108) |
| 6MWD, % predicted | 69 (20.7) | 65.2 (23.6) | 73.9 (16.6) |
| SpO2 at rest | 91.8 (3.7) | 92.8 (3.7) | 90.9 (3.5) |
| SpO2 nadir | 84 (5.6) | 87.1 (3.5) | 82 (6.1) |
| O2 for 6MWT, yes/no | 12/8 | 6/3 | 6/5 |
| O2, l/min | 3.7 (1.5–6) | 3.6 (1.5–6) | 3.8 (2–6) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braun, F.; Verjus, C.; Solà, J.; Marienfeld, M.; Funke-Chambour, M.; Krauss, J.; Geiser, T.; Guler, S.A. Evaluation of a Novel Ear Pulse Oximeter: Towards Automated Oxygen Titration in Eyeglass Frames. Sensors 2020, 20, 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113301
Braun F, Verjus C, Solà J, Marienfeld M, Funke-Chambour M, Krauss J, Geiser T, Guler SA. Evaluation of a Novel Ear Pulse Oximeter: Towards Automated Oxygen Titration in Eyeglass Frames. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113301
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraun, Fabian, Christophe Verjus, Josep Solà, Marcus Marienfeld, Manuela Funke-Chambour, Jens Krauss, Thomas Geiser, and Sabina A. Guler. 2020. "Evaluation of a Novel Ear Pulse Oximeter: Towards Automated Oxygen Titration in Eyeglass Frames" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113301
APA StyleBraun, F., Verjus, C., Solà, J., Marienfeld, M., Funke-Chambour, M., Krauss, J., Geiser, T., & Guler, S. A. (2020). Evaluation of a Novel Ear Pulse Oximeter: Towards Automated Oxygen Titration in Eyeglass Frames. Sensors, 20(11), 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113301





