Spatial-Temporal Signals and Clinical Indices in Electrocardiographic Imaging (II): Electrogram Clustering and T-Wave Alternans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. EGM Clustering
- Assign each observation to one cluster. For each observation () choose the index of the centroid closest to :where is the index of the cluster assigned to .
- Recalculate the centroid of the k-th cluster by averaging the points assigned to it.
2.2. T-Wave Alternans Algorithms
3. Experiments and Results
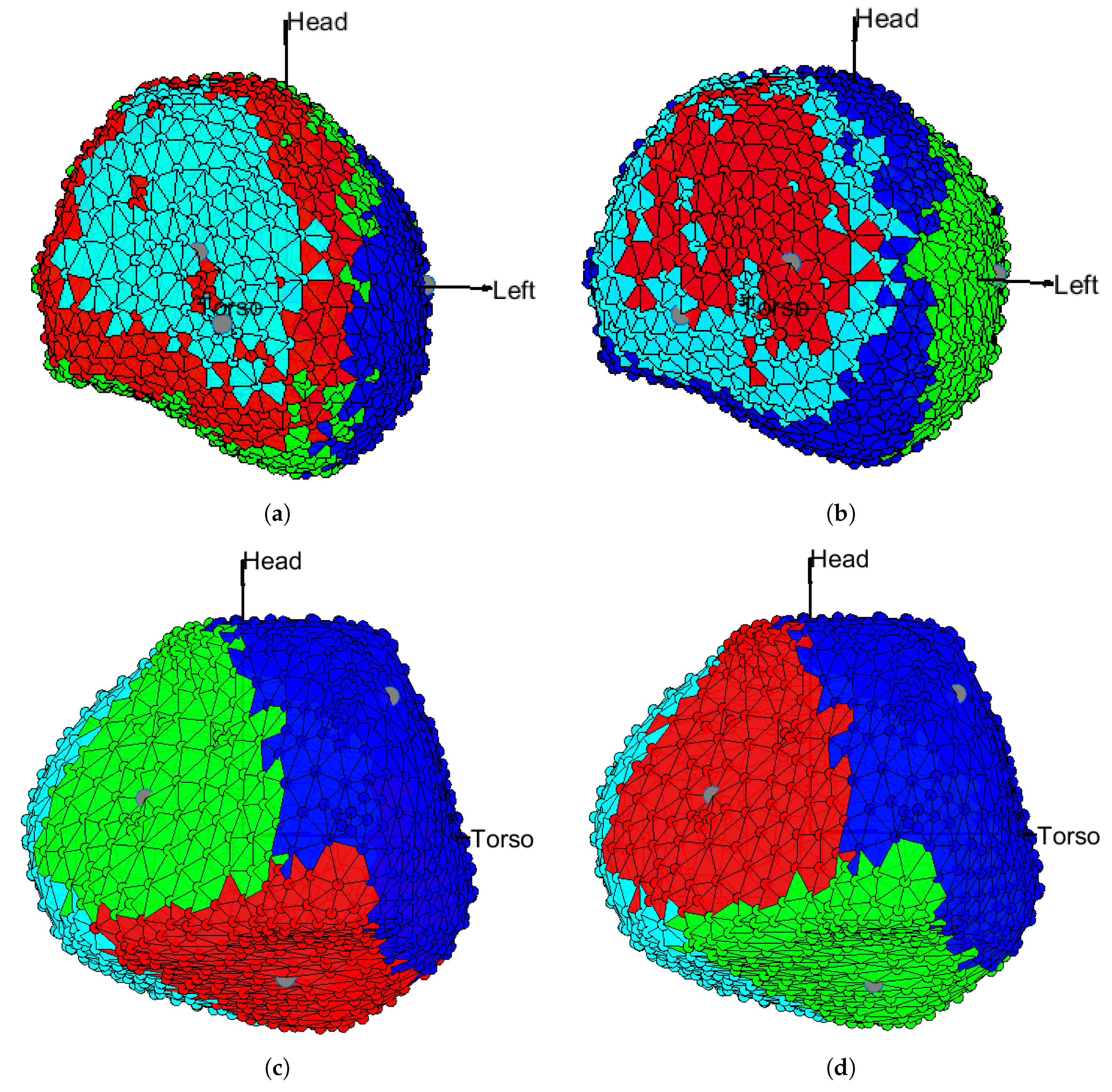
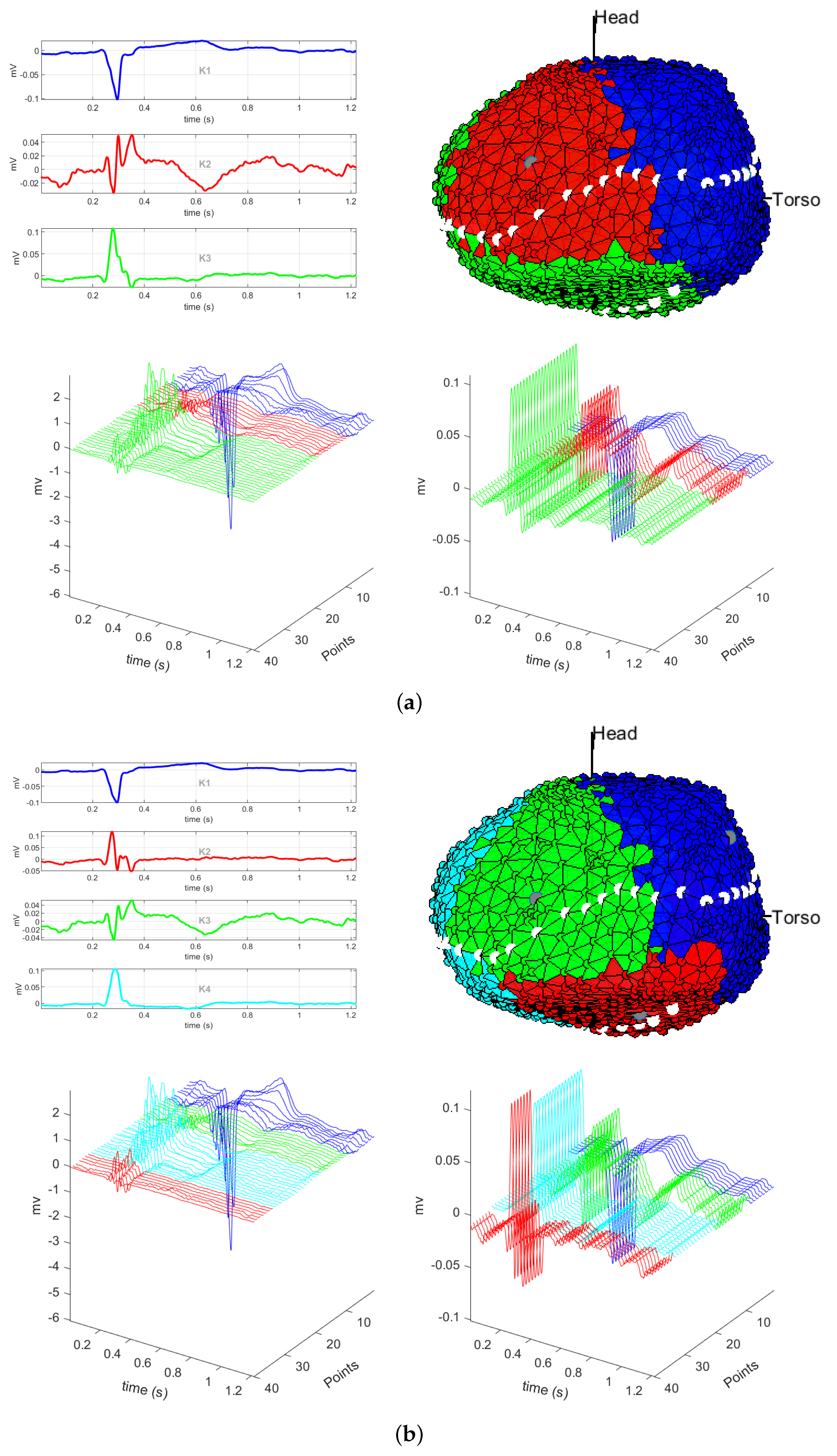
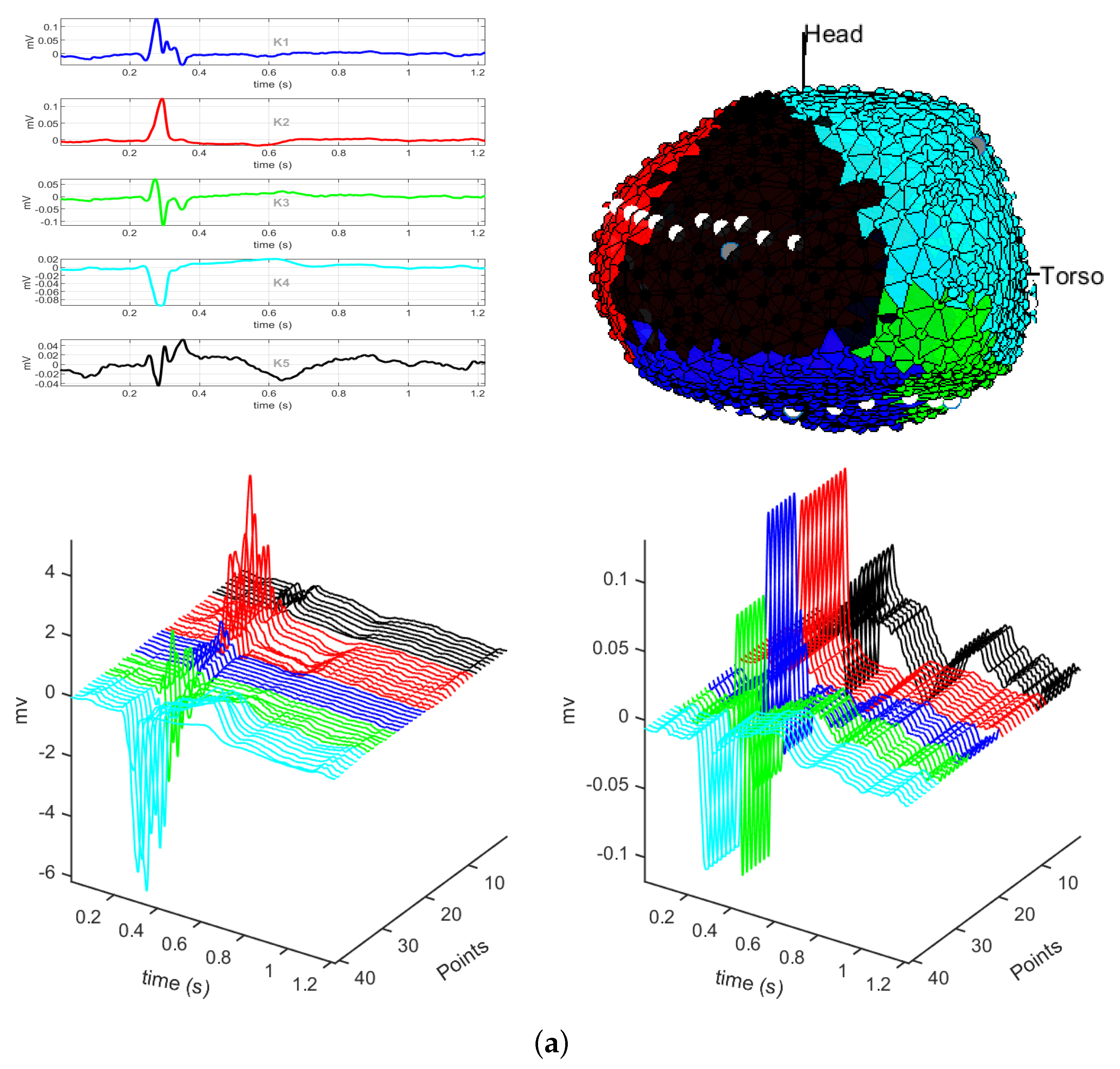
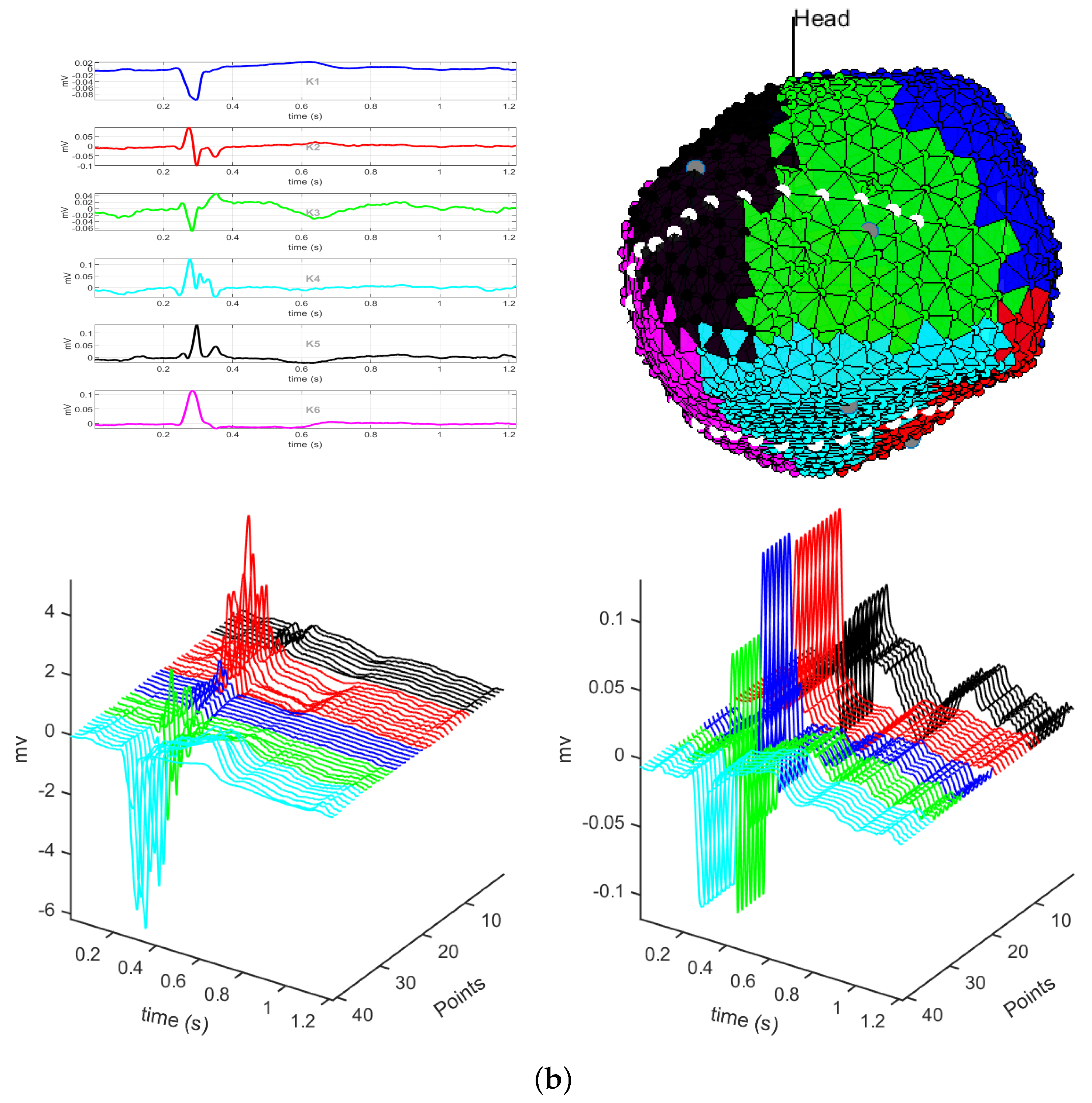
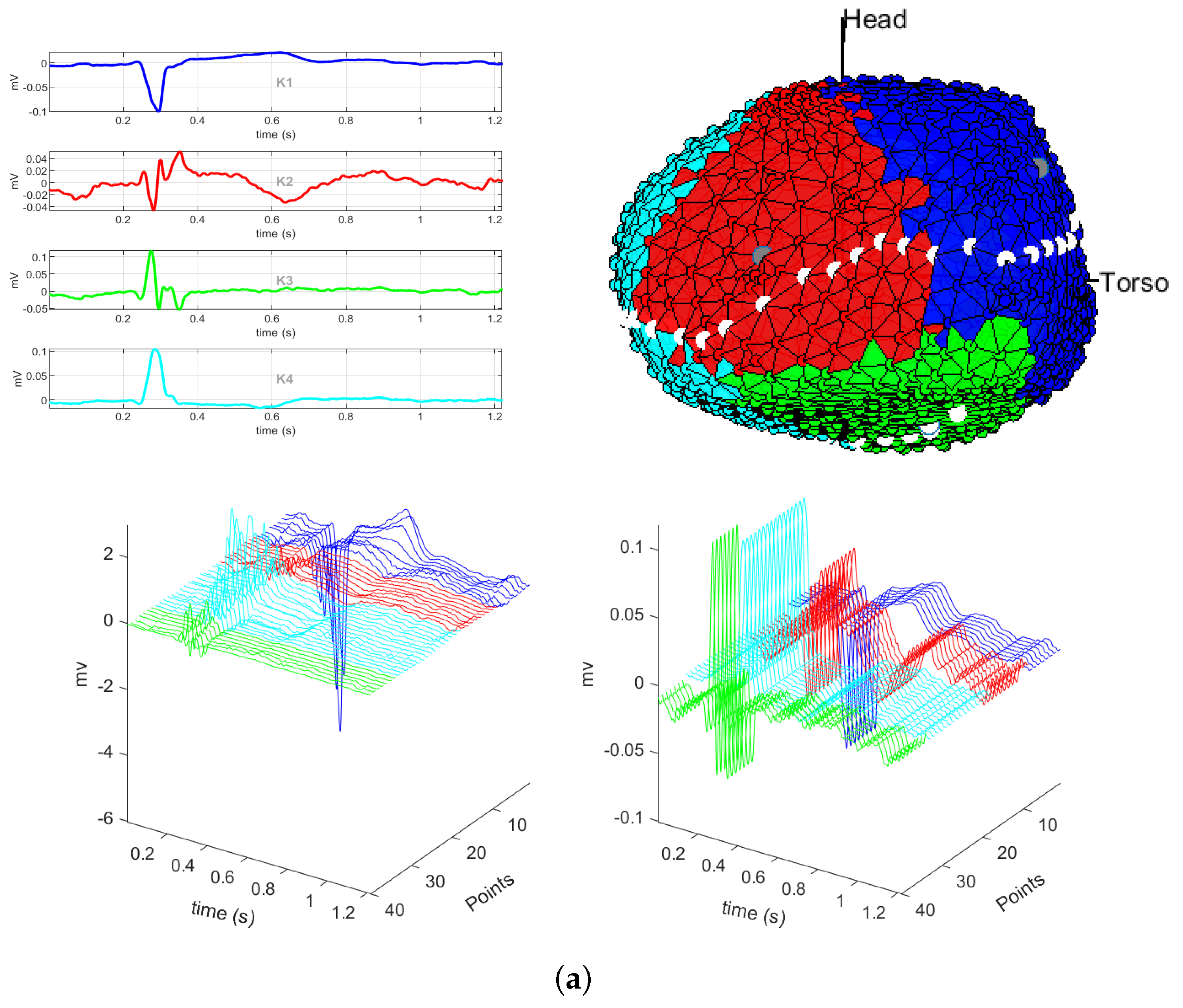
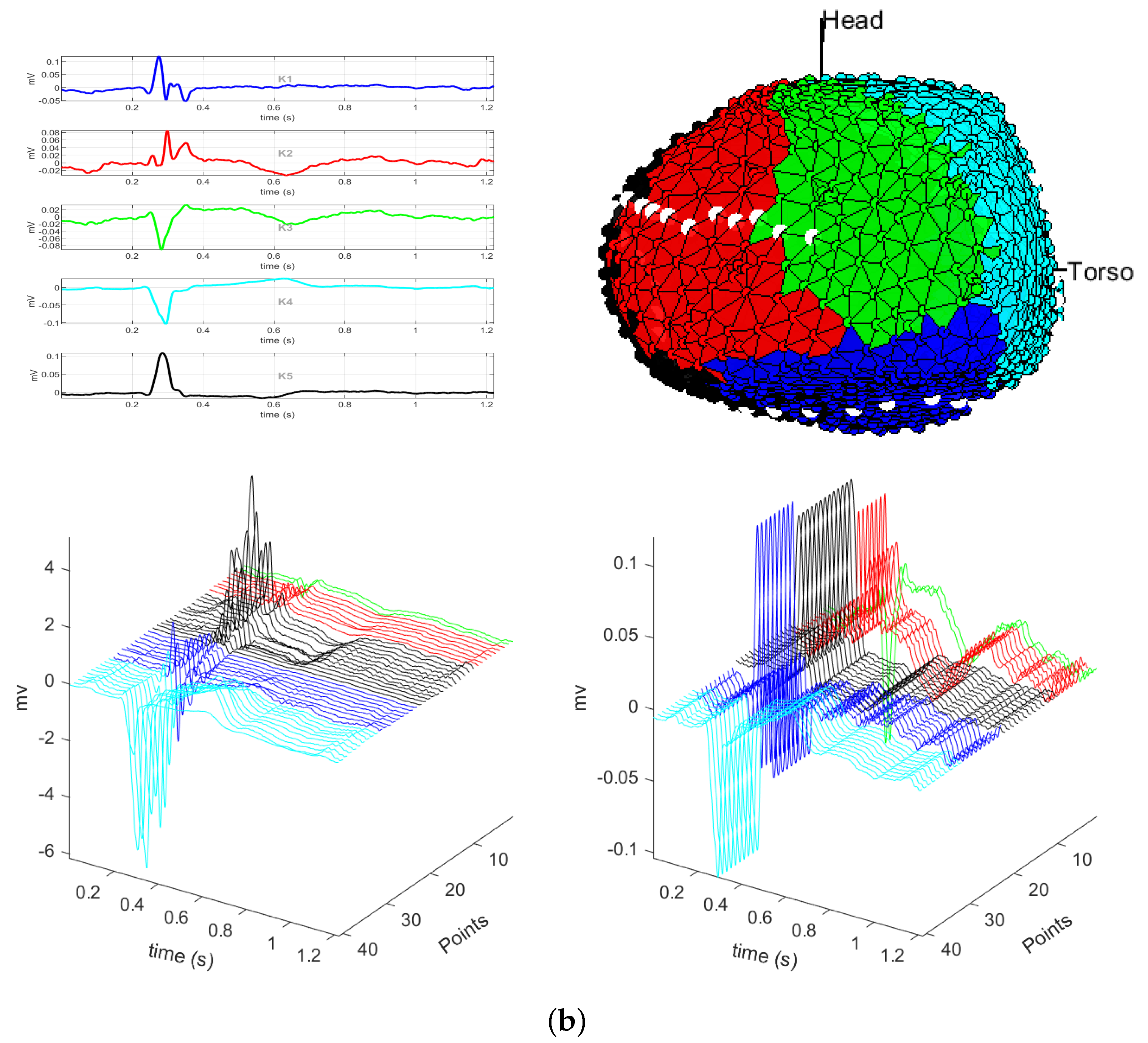
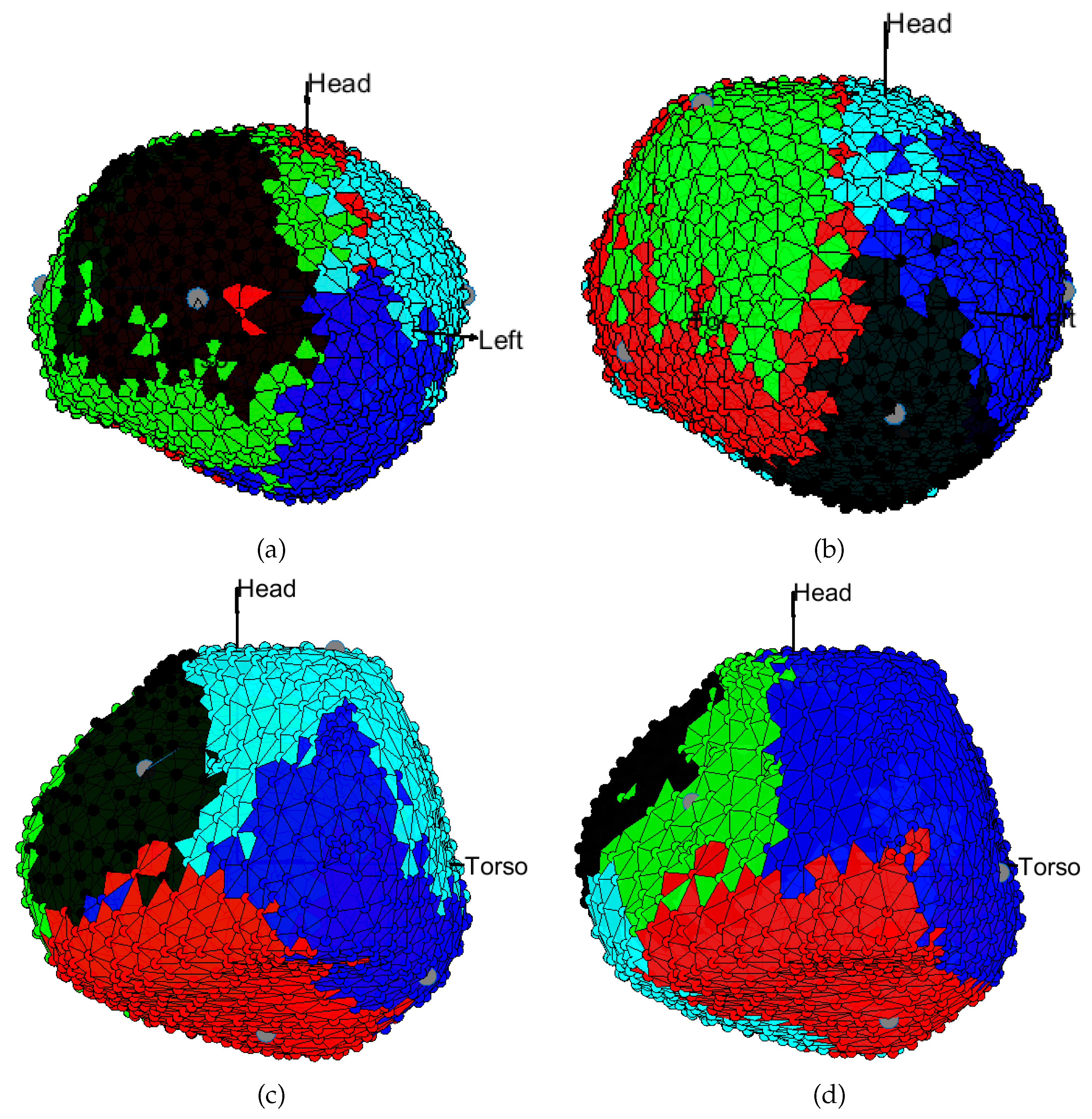
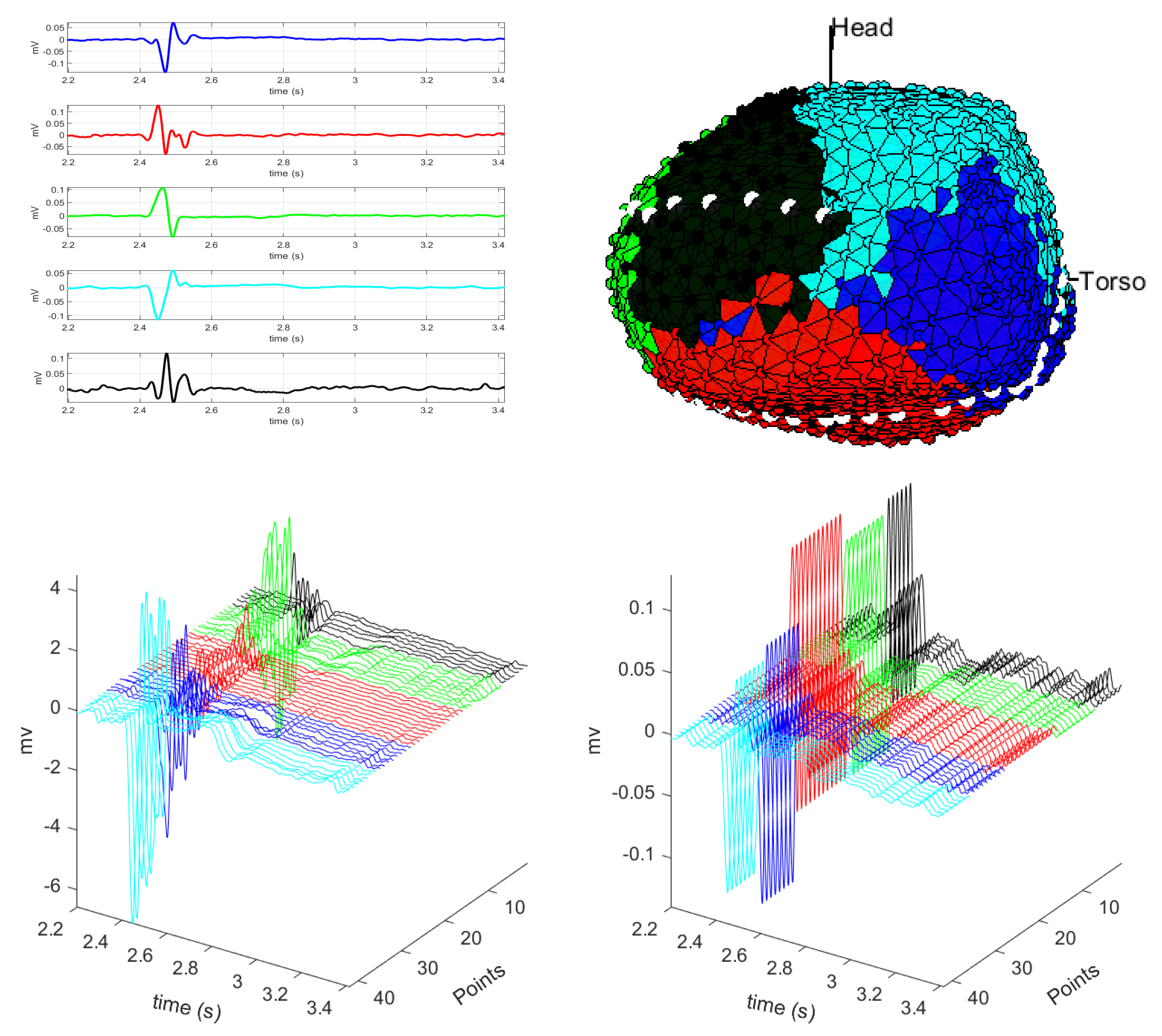
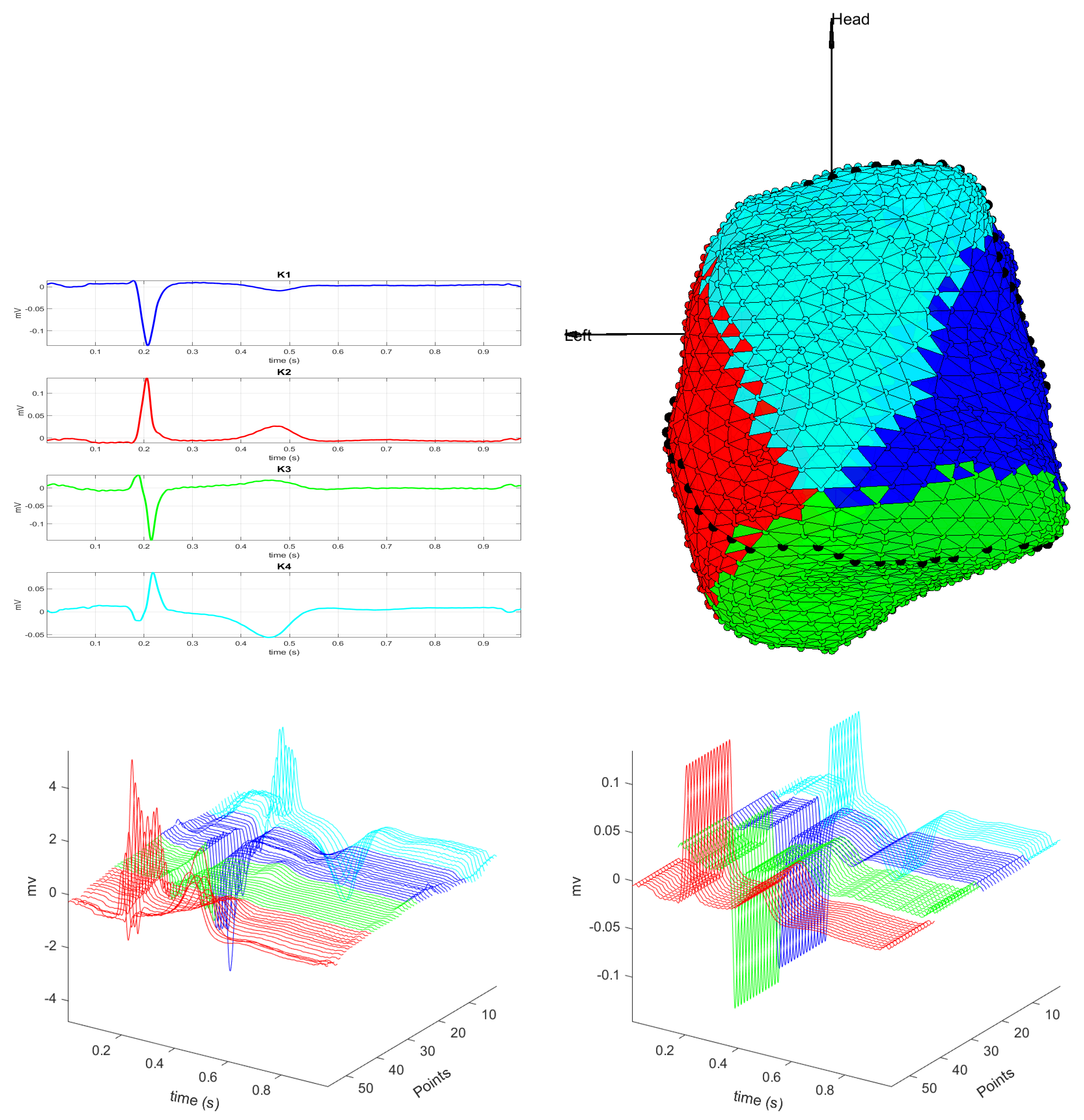
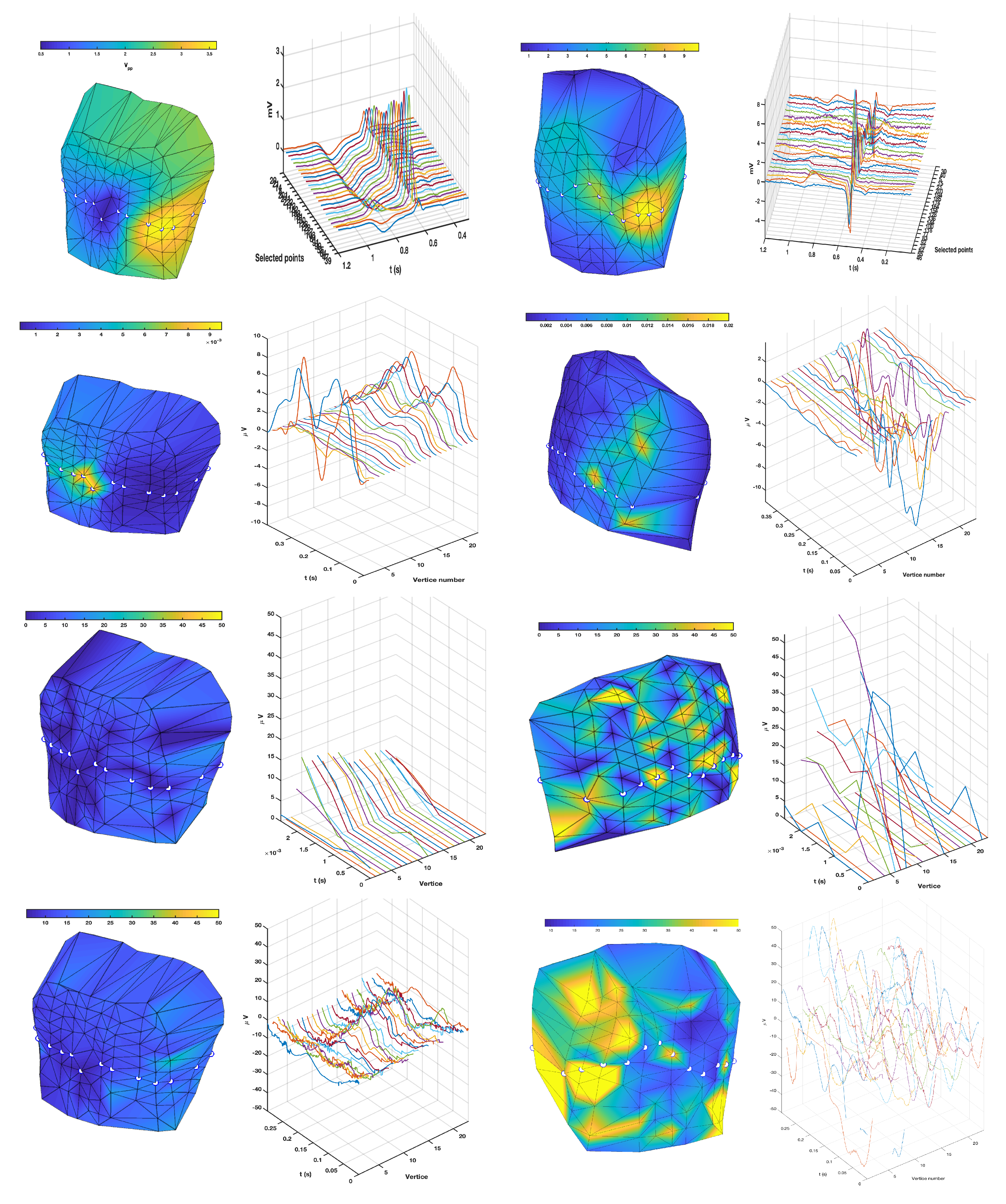
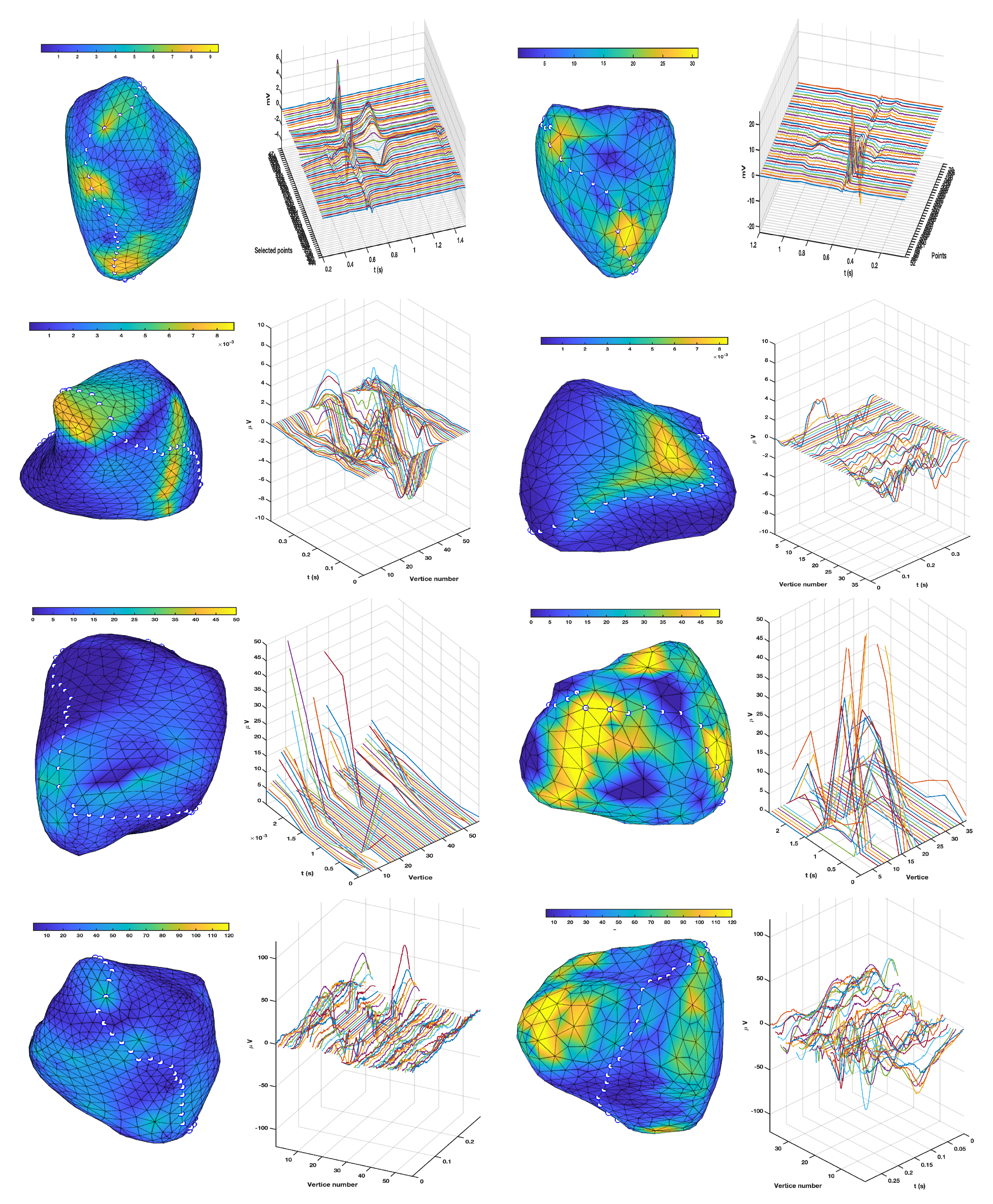
3.1. EGM Clustering in the Presence of Infarction
3.2. Comparison of TWA Algorithms
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Cuculich, P.S.; Zhang, J.; Desouza, K.A.; Vijayakumar, R.; Chen, J.; Faddis, M.N.; Lindsay, B.D.; Smith, T.W.; Rudy, Y. Noninvasive electroanatomic mapping of human ventricular arrhythmias with electrocardiographic imaging. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 98ra84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, C.; Srinivasan, N.; Rosmini, S.; Bulluck, H.; Orini, M.; Jenkins, S.; Pantazis, A.; McKenna, W.; Moon, J.; Lambiase, P.; et al. Electrical and Structural Substrate of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Determined Using Noninvasive Electrocardiographic Imaging and Late Gadolinium Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e005105. [Google Scholar]
- Cheniti, G.; Puyo, S.; Martin, C.A.; Frontera, A.; Vlachos, K.; Takigawa, M.; Bourier, F.; Kitamura, T.; Lam, A.; Dumas-Pommier, C.; et al. Noninvasive mapping and electrocardiographic imaging in atrial and ventricular arrhythmias (CardioInsight). Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2019, 11, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudy, Y. Noninvasive ECG imaging (ECGI): Mapping the arrhythmic substrate of the human heart. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 237, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rudy, Y. Role for electrocardiographic imaging in cardiac resynchronization therapy? Heart Rhythm 2018, 15, 1070–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, L.; Groeneveld, S.; Wulterkens, B.; van Rees, B.; Nguyen, U.; Roudijk, R.; Cluitmans, M.; Volders, P.; Hassink, R. Novel use of repolarization parameters in electrocardiographic imaging to uncover arrhythmogenic substrate. J. Electrocardiol. 2020, 59, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudy, Y. Electrophysiology of heart failure: Non-invasive mapping of substrate and guidance of cardiac resynchronization therapy with Electrocardiographic imaging. In Cardiac Mapping, 5th ed.; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 220–235. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oosterom, A. Closed-form analytical expressions for the potential fields generated by triangular monolayers with linearly distributed source strength. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2012, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Aryana, A.; Bowers, M.; O’Neill, P. Outcomes Of Cryoballoon Ablation Of Atrial Fibrillation: A Comprehensive Review. J. Atr. Fibrillation 2015, 8, 1231. [Google Scholar]
- Duchateau, J.; Sacher, F.; Pambrun, T.; Derval, N.; Chamorro-Servent, J.; Denis, A.; Ploux, S.; Hocini, M.; Jaïs, P.; Bernus, O.; et al. Performance and limitations of noninvasive cardiac activation mapping. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azpilicueta, J.; Chmelevsky, M.; Potyagaylo, D. ECGI in atrial fibrillation: A clinician’s wish list. J. Electrocardiol. 2018, 51, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CollFont, J.; Dhamala, J.; Potyagaylo, D.; Schulze, W.; Tate, J.; Guillem, M.; van Dam, P.; Dossel, O.; Brooks, D.; Macleod, R. The Consortium for Electrocardiographic Imaging. Comput. Cardiol. 2016, 43, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Caulier-Cisterna, R.; Sanromán-Junquera, M.; Muñoz-Romero, S.; Blanco-Velasco, M.; Goya-Esteban, R.; García-Alberola, A.; Rojo-Álvarez, J. Spatial-temporal Signals and Clinical Indices in Electrocardiographic Imaging (I): Preprocessing and Bipolar Potentials. Sensors 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.; Albrecht, P.; Cohen, R. Predicting Sudden Cardiac Death From T Wave Alternans of the Surface Electrocardiogram. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1996, 7, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.L.; Rosenbaum, D.S. Repolarization alternans: Implications for the mechanism and prevention of sudden cardiac death. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 57, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno-Blanes, F.; Blanco-Velasco, M.; Barquero-Pérez, O.; García-Alberola, A.; Rojo-Álvarez, J. Sudden Cardiac Risk Stratification with Electrocardiographic Indices—A Review on Computational Processing, Technology Transfer, and Scientific Evidence. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andrews, C.; Cupps, B.; Pasque, M.; Rudy, Y. Electromechanics of the Normal Human Heart In Situ. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e007484. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, R.; Silva, J.N.; Desouza, K.A.; Abraham, R.L.; Strom, M.; Sacher, F.; Van Hare, G.F.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Roden, D.M.; Rudy, Y. Electrophysiologic substrate in congenital long QT syndrome: Noninvasive mapping with electrocardiographic imaging (ECGI). Circulation 2014, 130, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hocini, M.; Strom, M.; Cuculich, P.S.; Cooper, D.H.; Sacher, F.; Haïssaguerre, M.; Rudy, Y. The Electrophysiological Substrate of Early Repolarization Syndrome: Noninvasive Mapping in Patients. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ding, Y.; Hao, K. A novel automatic detection system for ECG arrhythmias using maximum margin clustering with immune evolutionary algorithm. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 453402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Duque, A.; Duque, S.; Ugarte, J.; Tobon, C.; Novak, D.; Kremen, V.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G.; Saiz, J.; Bustamante, J. Fractionated electrograms and rotors detection in chronic atrial fibrillation using model-based clustering. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; pp. 1579–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Haldar, N.; Khan, F.; Ali, A.; Abbas, H. Arrhythmia classification using Mahalanobis distance based improved Fuzzy C-Means clustering for mobile health monitoring systems. Neurocomputing 2017, 220, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tan, Y. Automatic pattern recognition of ECG signals using entropy-based adaptive dimensionality reduction and clustering. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 55, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Hao, D.; Chen, Y.; Parmar, M.; Li, K. GDPC: Gravitation-based Density Peaks Clustering algorithm. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 502, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesanto, J.; Alhoniemi, E. Clustering of the self-organizing map. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 2000, 11, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Qiu, J. A novel divisive hierarchical clustering algorithm for geospatial analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.; Belo, D.; Gamboa, H. Noise detection on ECG based on agglomerative clustering of morphological features. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 87, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Nataliani, Y. Robust-learning Fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm with unknown number of clusters. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 71, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Rosario, A.; Adeli, H.; Buford, J. MUSIC-Expected maximization gaussian mixture methodology for clustering and detection of task-related neuronal firing rates. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 317, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S. Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1982, 28, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goya-Esteban, R.; Barquero-Pérez, O.; Blanco-Velasco, M.; Caamaño-Fernández, A.; García-Alberola, A.; Rojo-Álvarez, J. Nonparametric Signal Processing Validation in T-Wave Alternans Detection and Estimation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Olmos, S. Methodological principles of T wave alternans analysis: A unified framework. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Velasco, M.; Goya-Esteban, R.; Cruz-Roldán, F.; García-Alberola, A.; Rojo-Alvarez, J. Benchmarking of a T-wave alternans detection method based on empirical mode decomposition. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 145, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.P.; Olmos, S.; Laguna, P. T wave alternans detection: A simulation study and analysis of the European ST-T database. In Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 24–27 September 2000; Volume 27, pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nearing, B.; Verrier, R. Modified moving average analysis of T-wave alternans to predict ventricular fibrillation with high accuracy. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchlinski, F.; Callans, D.; Gottlieb, C.; Zado, E. Linear ablation lesions for control of unmappable ventricular tachycardia in patients with ischemic and nonischemic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2000, 101, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, B.; Crawford, T.; Good, E.; Oral, H.; Chugh, A.; Pelosi, F.; Morady, F.; Bogun, F. Infarct architecture and characteristics on delayed enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and electroanatomic mapping in patients with postinfarction ventricular arrhythmia. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, E.M.; Bogun, F.; Maury, P.; Peichl, P.; Chen, M.; Namboodiri, N.; Aguinaga, L.; Leite, L.; Al-Khatib, S.; Anter, E.; et al. 2019 HRS/EHRA/APHRS/LAHRS expert consensus statement on catheter ablation of ventricular arrhythmias. Europace 2019, 21, 1143–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sroubek, J.; Rottmann, M.; Barkagan, M.; Leshem, E.; Shapira-Daniels, A.; Brem, E.; Fuentes-Ortega, C.; Malinaric, J.; Basu, S.; Bar-Tal, M.; et al. A novel octaray multielectrode catheter for high-resolution atrial mapping: Electrogram characterization and utility for mapping ablation gaps. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019, 30, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlich, M.; Iden, L.; Kuhnhardt, K.; Paetsch, I.; Hindricks, G.; Sommer, P. 3D mapping for PVI-geometry, image integration and incorporation of contact force into work flow. J. Atr Fibrillation 2018, 10, 1795. [Google Scholar]
- Cluitmans, M.; Peeters, R.; Westra, R.; Volders, P. Noninvasive reconstruction of cardiac electrical activity: Update on current methods, applications and challenges. Neth. Heart J. 2015, 23, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluitmans, M.; Brooks, D.; MacLeod, R.; Dössel, O.; Guillem, M.; van Dam, P.M.; Svehlikova, J.; He, B.; Sapp, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Validation and Opportunities of Electrocardiographic Imaging: From Technical Achievements to Clinical Applications. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenasa, M.; Razavi, S.; Shenasa, H.; Al-Ahmad, A. The ideal cardiac mapping system. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2019, 11, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, L.; Dogrusoz, Y.; Svehlikova, J.; Coll-Font, J.; Good, W.; van Dam, E.; Macleod, R.; Abell, E.; Walton, R.; Coronel, R.; et al. Effects of ECG Signal Processing on the Inverse Problem of Electrocardiography. Comput Cardiol 2018, 45, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Orozco-Duque, A.; Bustamante, J.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G. Semi-supervised clustering of fractionated electrograms for electroanatomical atrial mapping. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2016, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coll-Font, J.; Erem, B.; Brooks, D. A Potential-Based Inverse Spectral Method to Non-Invasively Localize Discordant Distributions of Alternans on the Heart from the ECG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rudy, Y. Noninvasive Electrocardiographic Imaging ECGI of Arrhythmogenic Substrates in Humans. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caulier-Cisterna, R.; Blanco-Velasco, M.; Goya-Esteban, R.; Muñoz-Romero, S.; Sanromán-Junquera, M.; García-Alberola, A.; Rojo-Álvarez, J.L. Spatial-Temporal Signals and Clinical Indices in Electrocardiographic Imaging (II): Electrogram Clustering and T-Wave Alternans. Sensors 2020, 20, 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113070
Caulier-Cisterna R, Blanco-Velasco M, Goya-Esteban R, Muñoz-Romero S, Sanromán-Junquera M, García-Alberola A, Rojo-Álvarez JL. Spatial-Temporal Signals and Clinical Indices in Electrocardiographic Imaging (II): Electrogram Clustering and T-Wave Alternans. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113070
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaulier-Cisterna, Raúl, Manuel Blanco-Velasco, Rebeca Goya-Esteban, Sergio Muñoz-Romero, Margarita Sanromán-Junquera, Arcadi García-Alberola, and José Luis Rojo-Álvarez. 2020. "Spatial-Temporal Signals and Clinical Indices in Electrocardiographic Imaging (II): Electrogram Clustering and T-Wave Alternans" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113070
APA StyleCaulier-Cisterna, R., Blanco-Velasco, M., Goya-Esteban, R., Muñoz-Romero, S., Sanromán-Junquera, M., García-Alberola, A., & Rojo-Álvarez, J. L. (2020). Spatial-Temporal Signals and Clinical Indices in Electrocardiographic Imaging (II): Electrogram Clustering and T-Wave Alternans. Sensors, 20(11), 3070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113070






